Misalignment-Tolerant Series Hybrid with Active Adjustable Constant Current and Constant Voltage Output Wireless Charging System
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Analysis
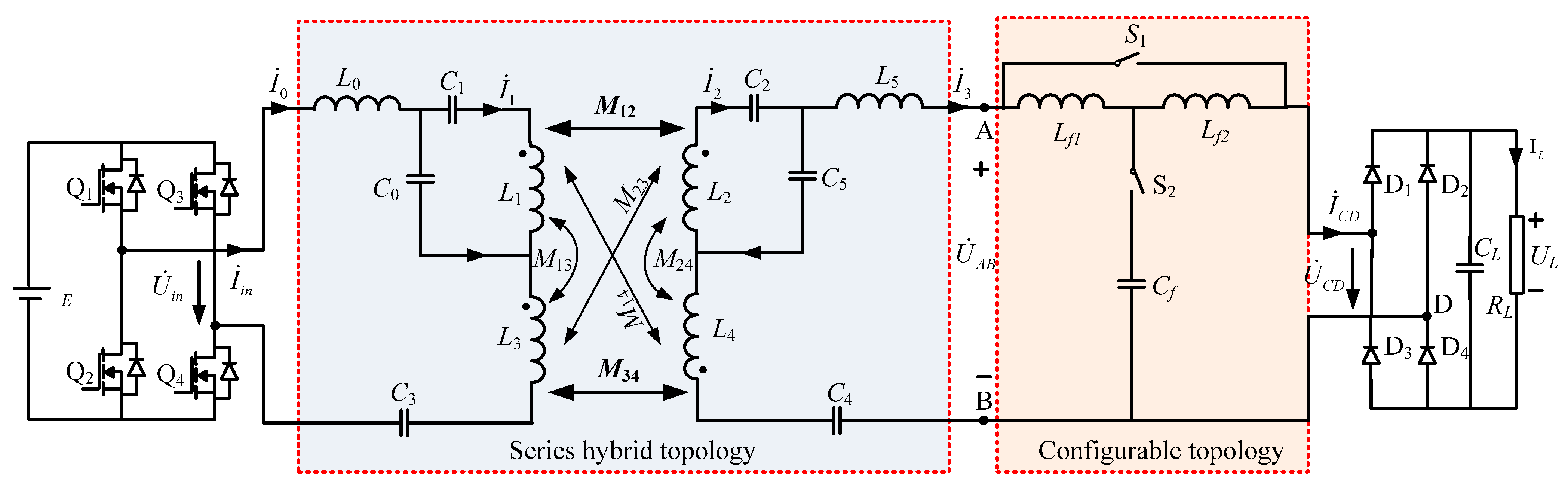
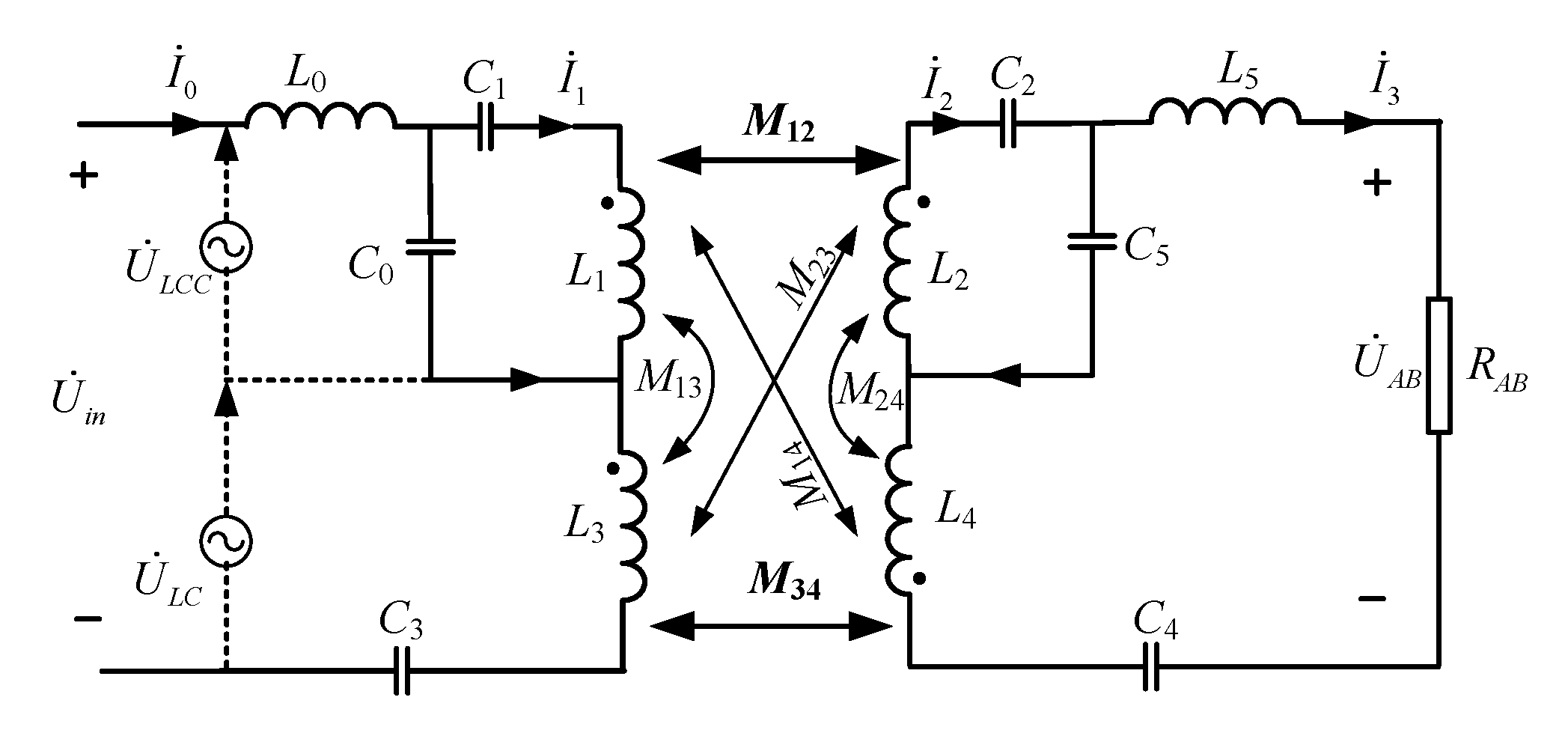
2.1. Analysis of the Series Hybrid Topology
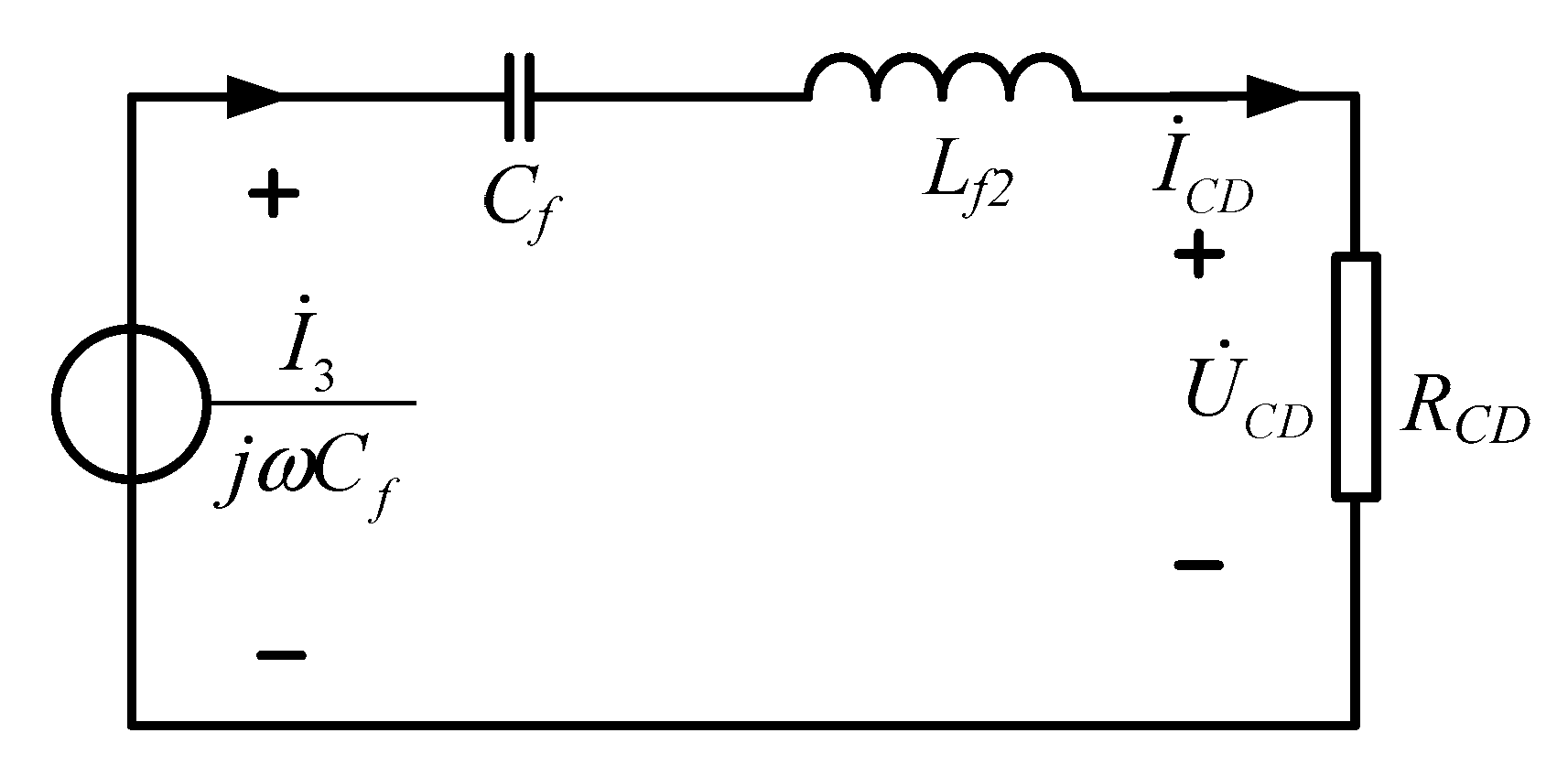
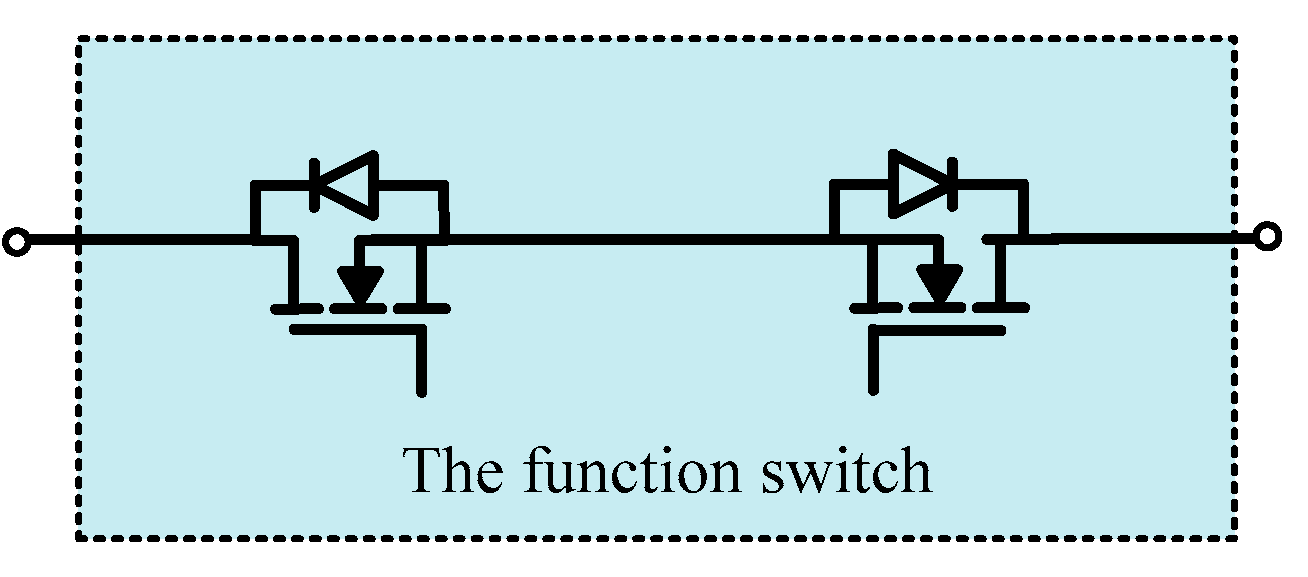
2.2. Analysis of the Configurable Topology
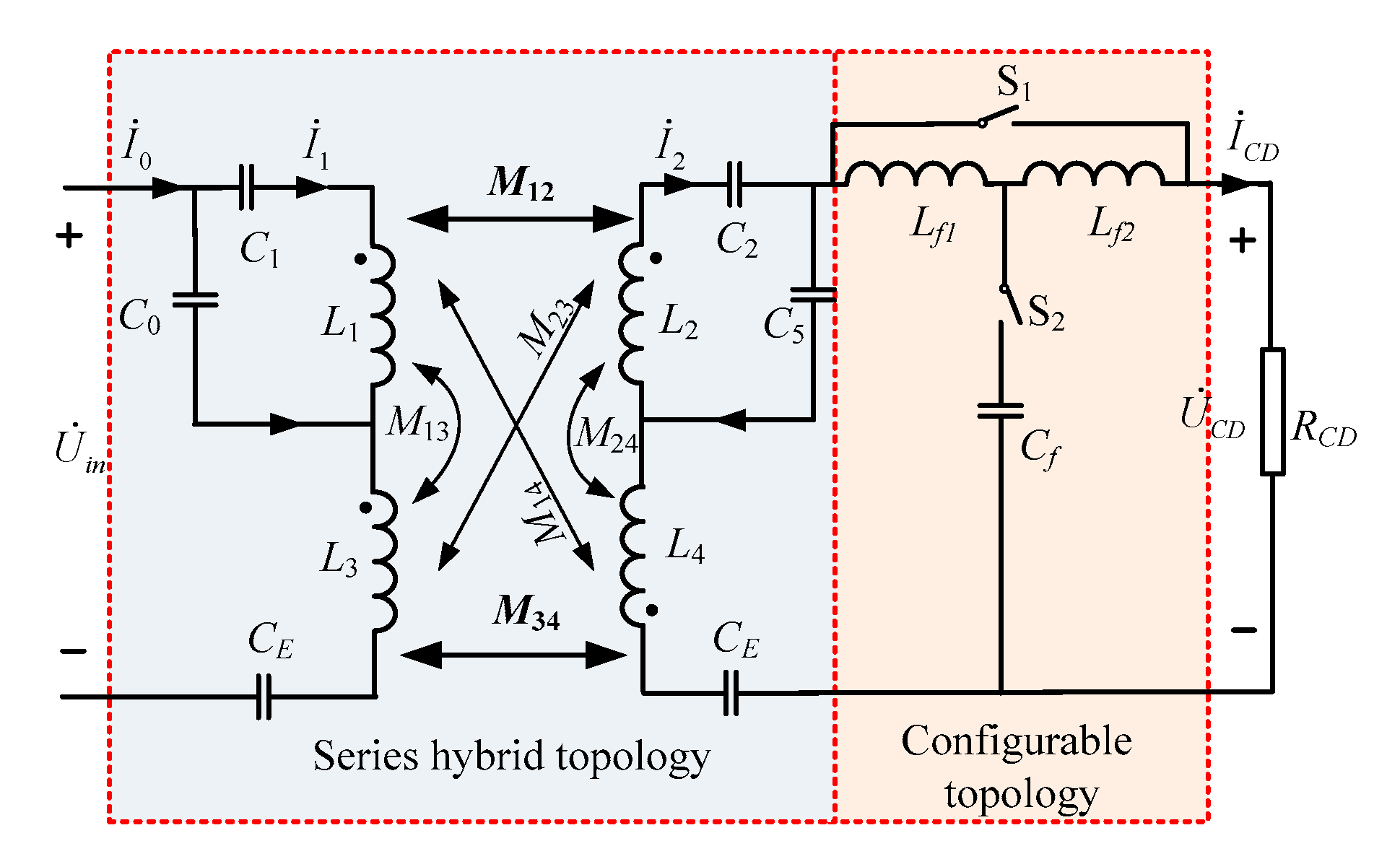
2.3. The Proposed Combination of Series Hybrid and Configurable Topology
3. Design and Implementation of the Hybrid and Configurable Topology
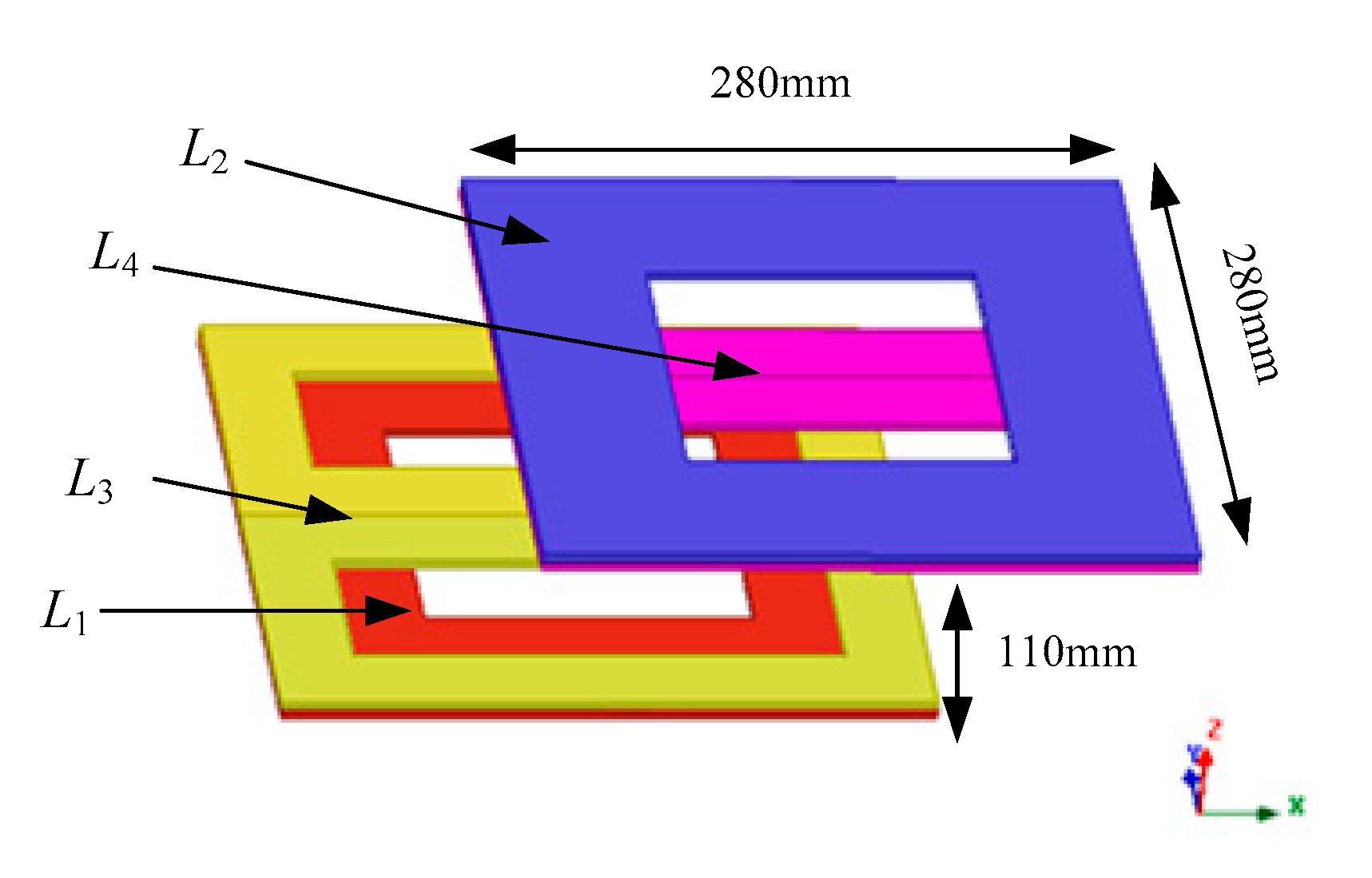
3.1. Coupler Design
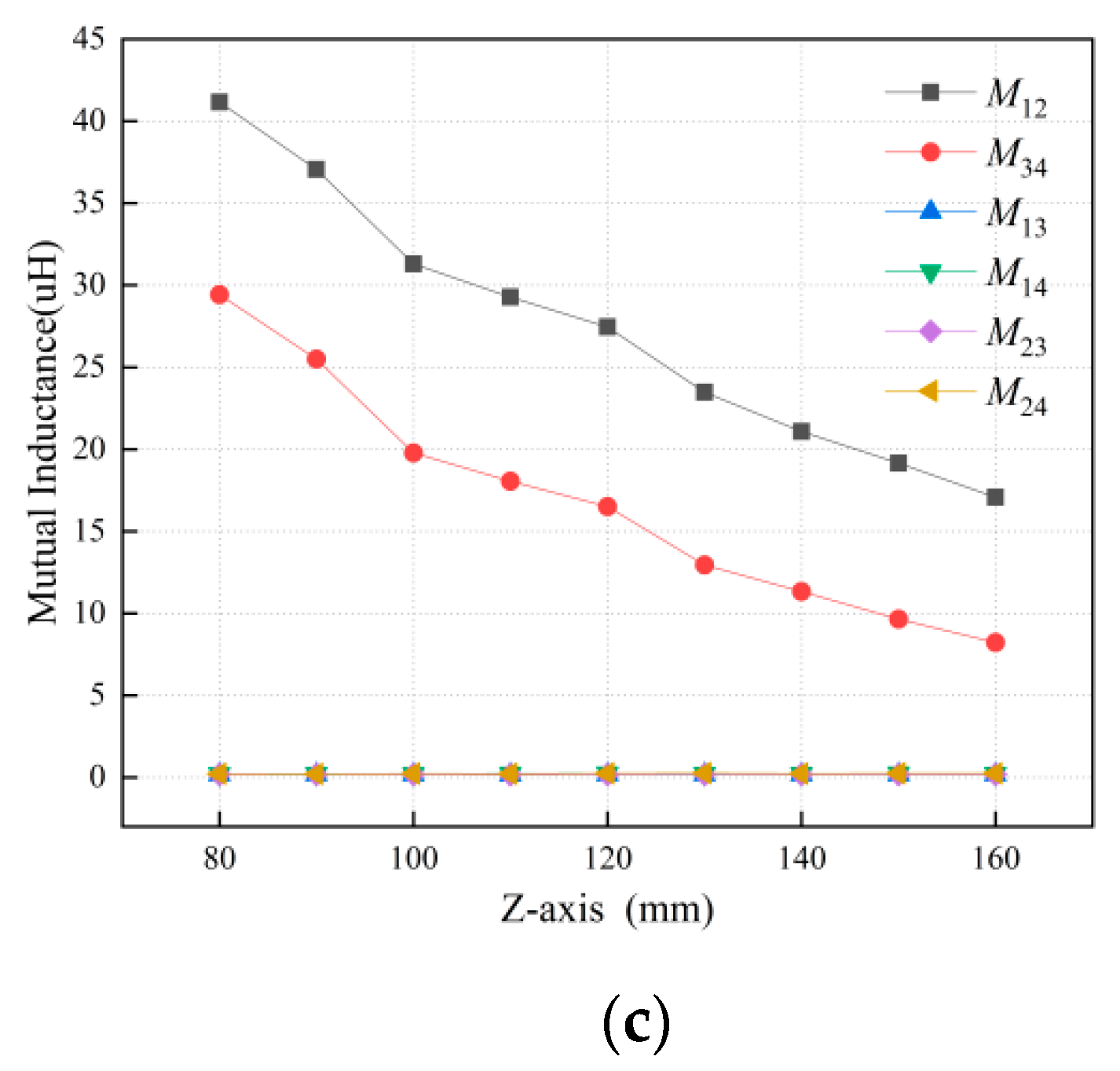
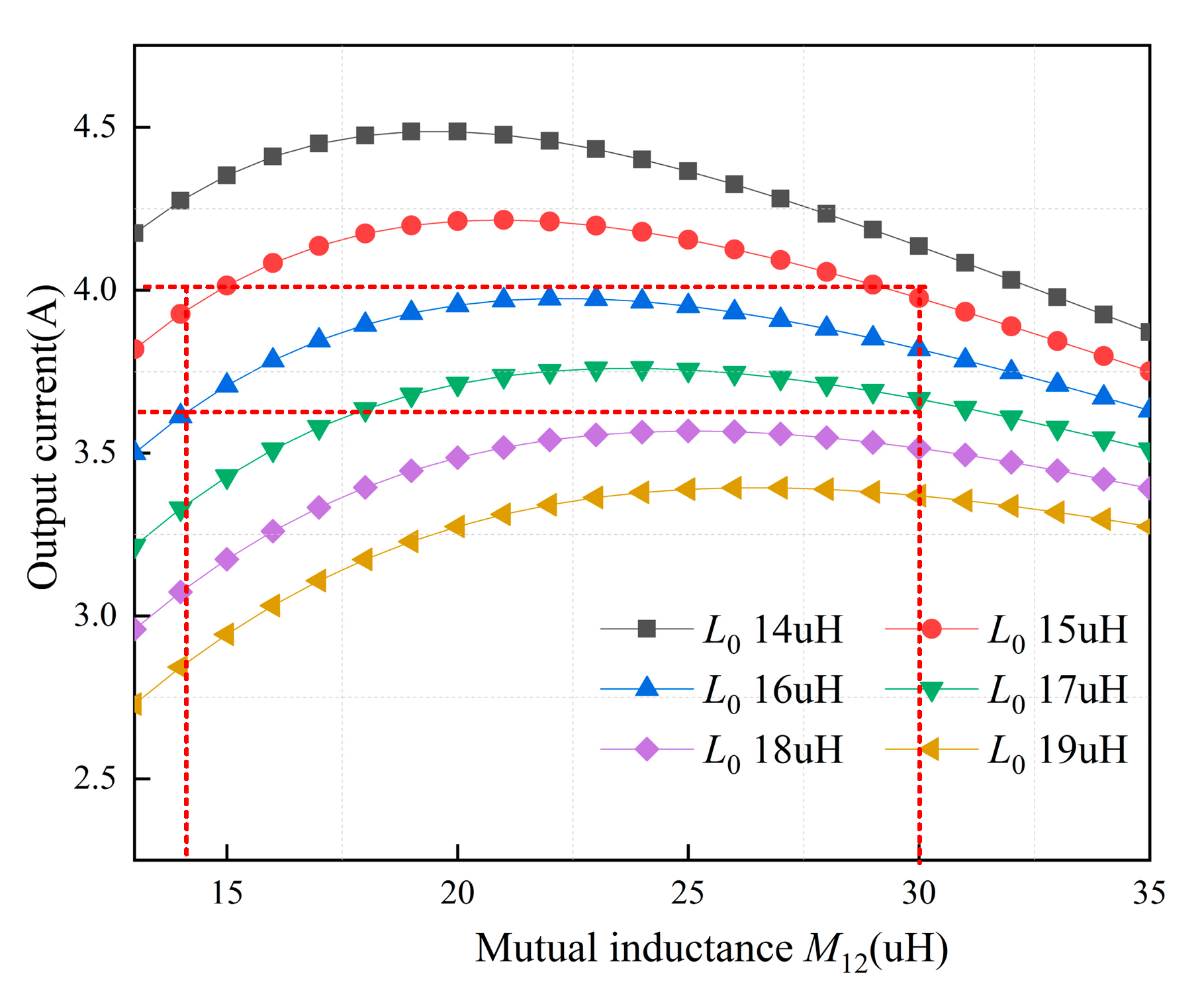
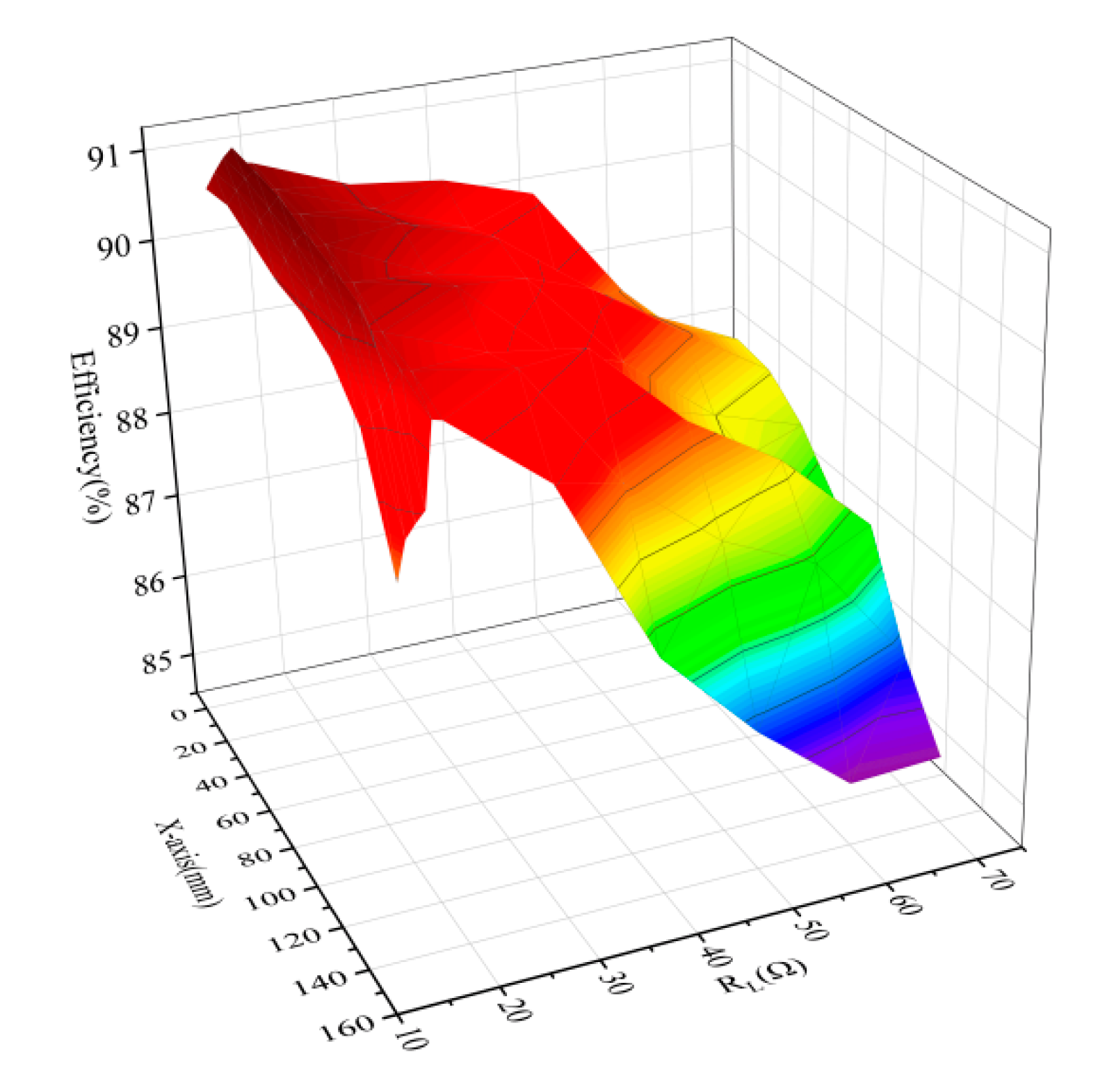
3.2. Parameter Optimization Design
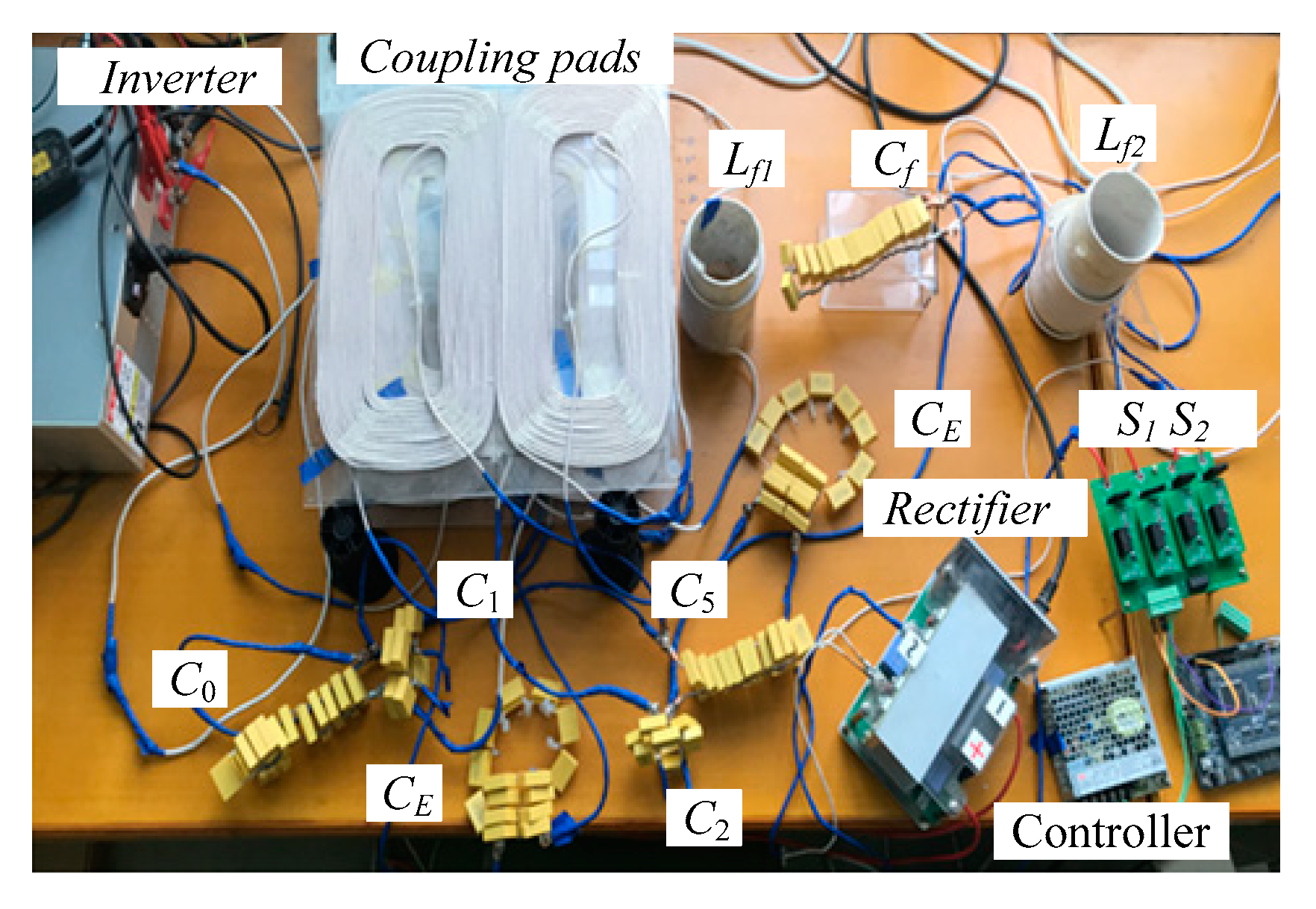
4. Experimental Results and Discussion
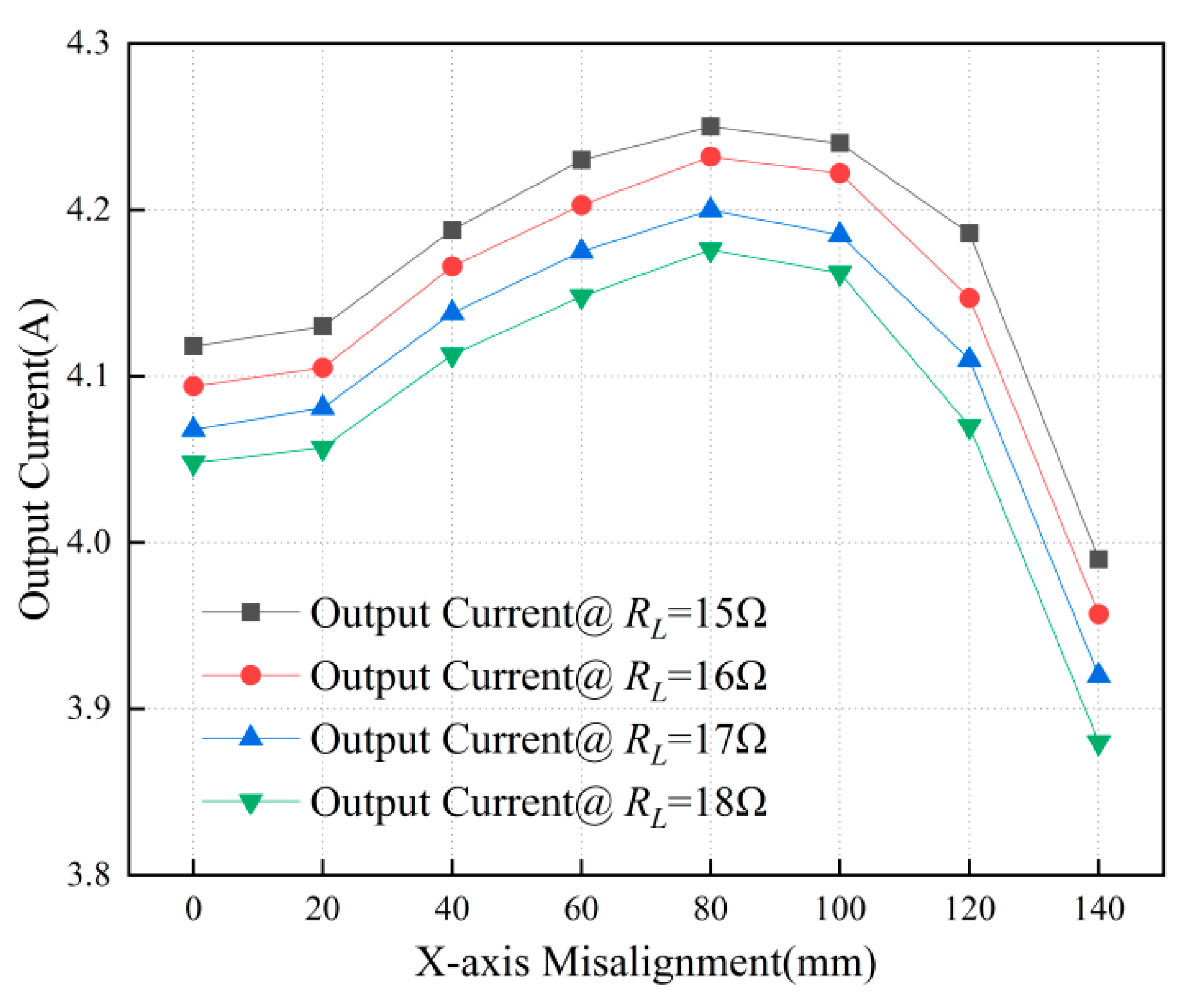
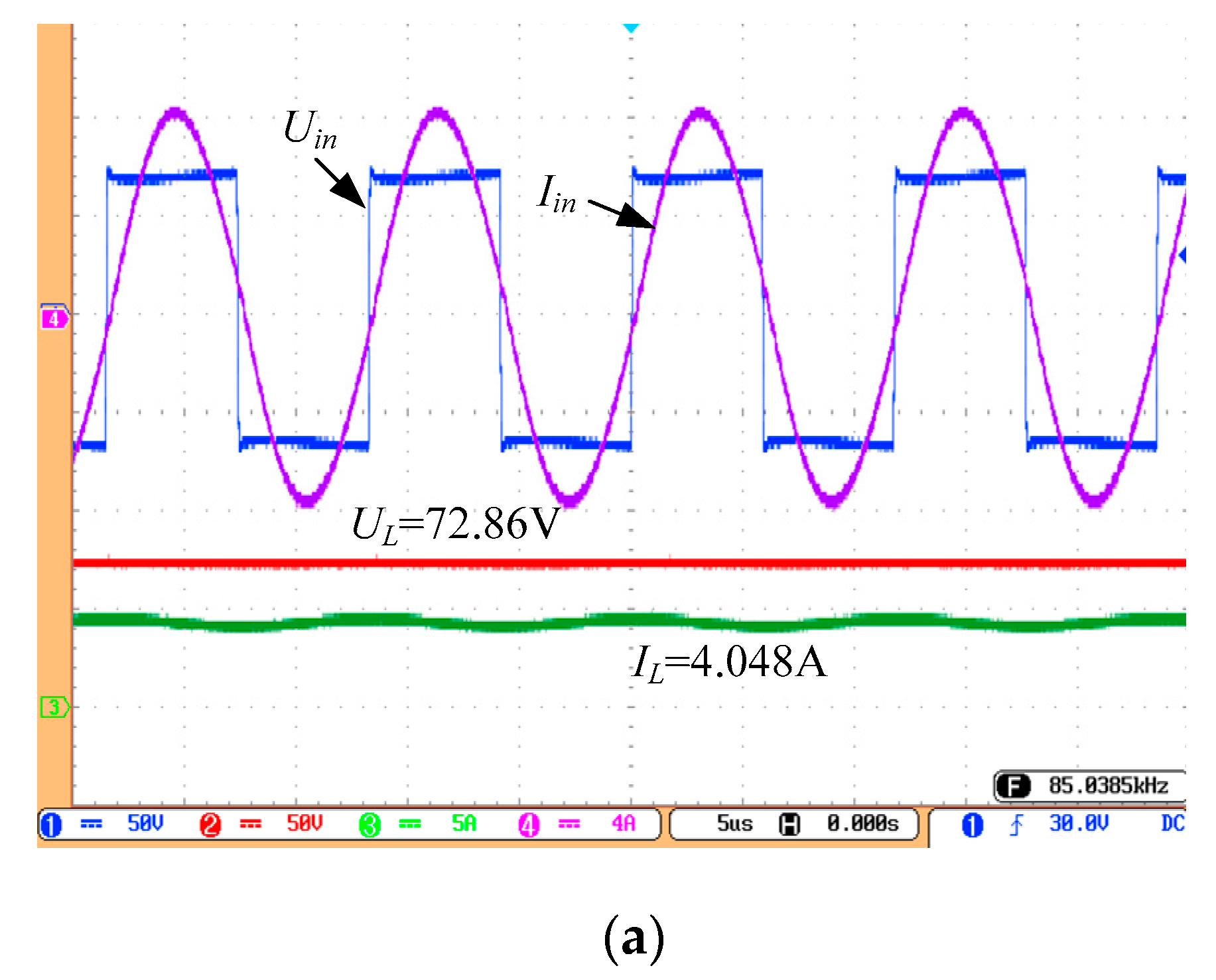
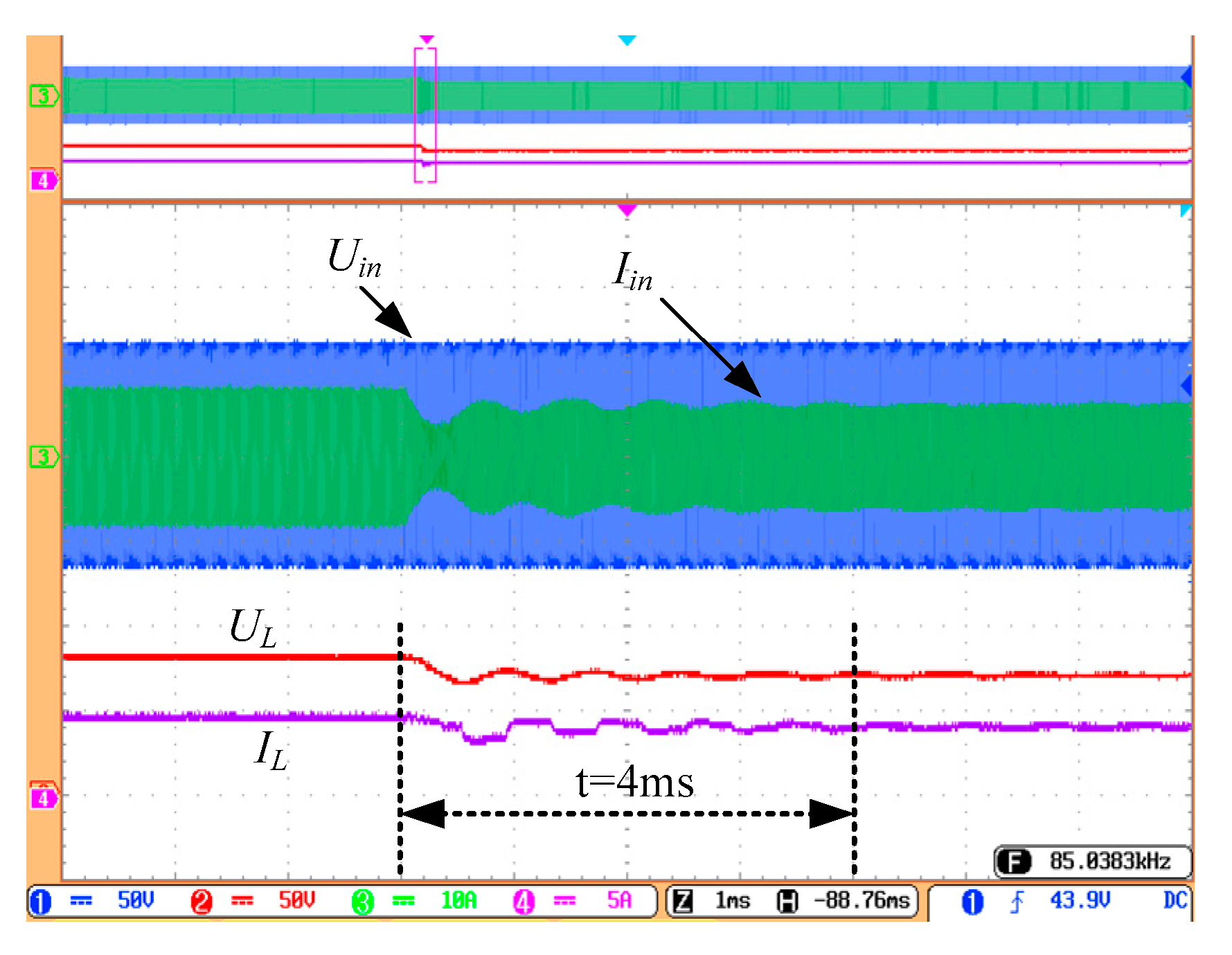
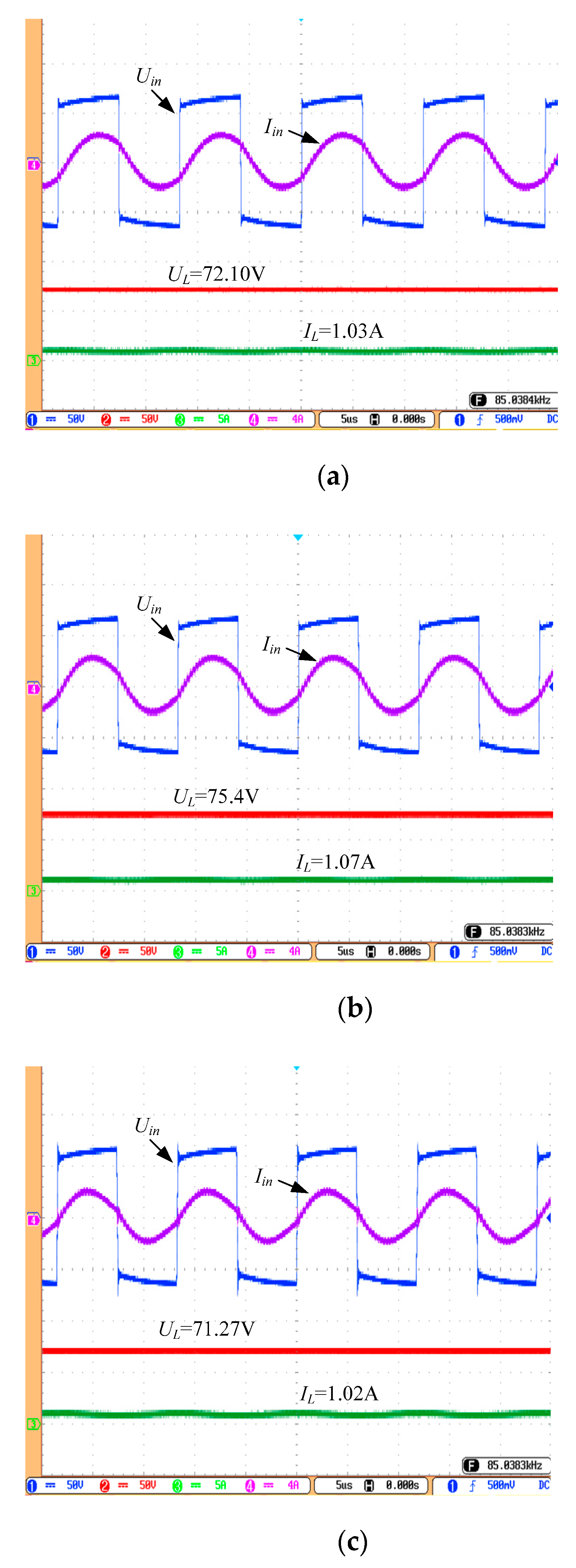
4.1. CC Output Performance of the System
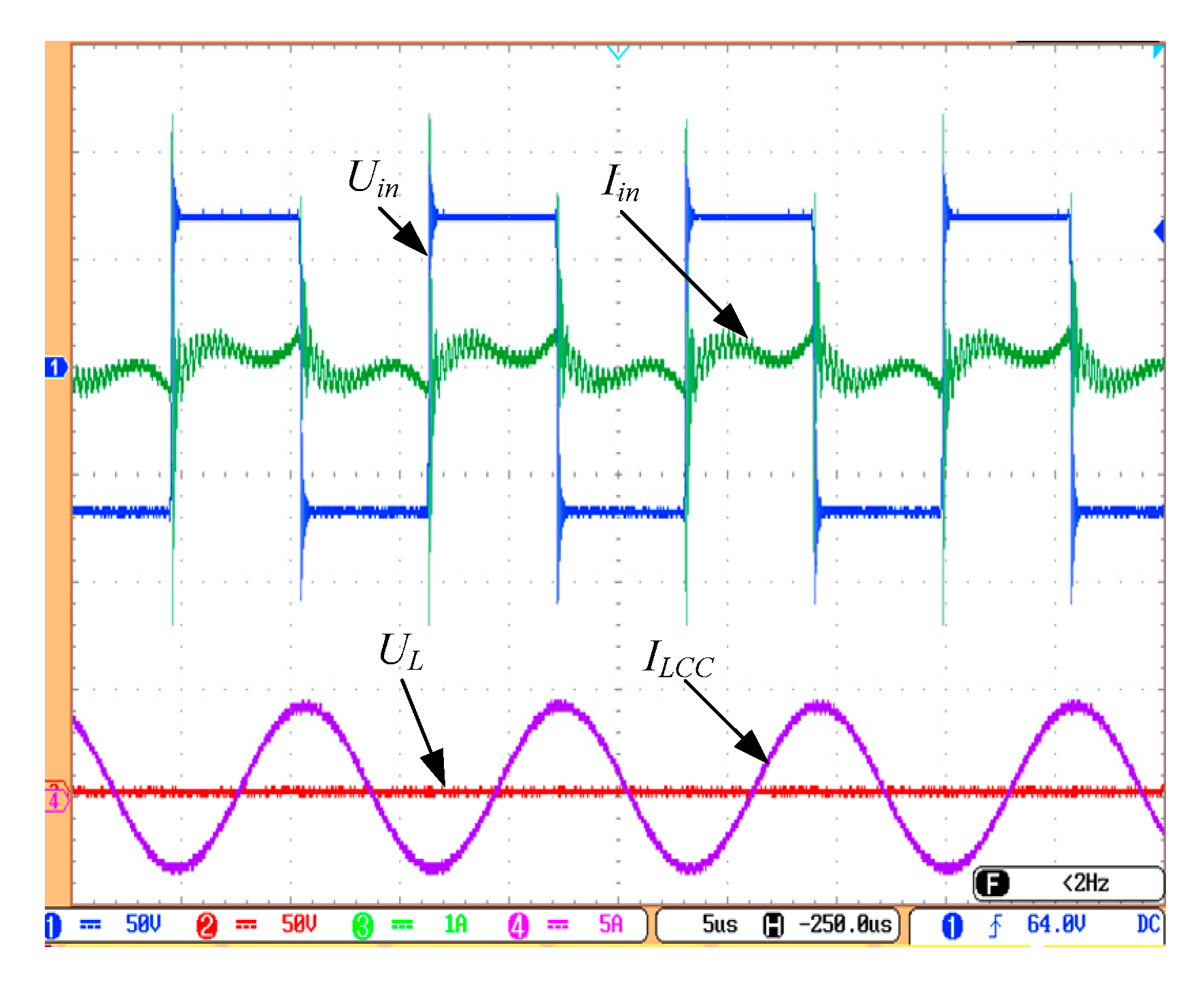
4.2. CV Output Performance of the System
4.3. Comparison with Other Methods
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ke, G.; Chen, Q.; Gao, W. Research on IPT Resonant Converters with High Misalignment Tolerance Using Multicoil Receiver Set. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2020, 35, 3697–3712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, T.; Mai, R.; Mercier, P.-P.; Mi, C.-C. Design and Analysis of a Three-Phase Wireless Charging System for Lightweight Autonomous. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2018, 33, 6622–6632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xu, J.; Leng, M. Individually Regulated Dual—Output IPT System Based on Current—Mode Switching Cells. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2021, 68, 12930–12934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Li, X.; Hu, A.-P. Maximum Efficiency Tracking for Wireless Power Transfer Systems with Dynamic Coupling Coefficient Estimation. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2018, 33, 5005–5015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.-Y.; Gu, B.-W.; Jeong, S.Y. Advances in Wireless Power Transfer Systems for Roadway-Powered Electric Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2015, 3, 18–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Zhu, G.; Member, S.; Lin, D. Load-Independent Voltage and Current Transfer Characteristics of High-Order Resonant Network in IPT System. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2019, 7, 422–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madawala, U.-K.; Thrimawithana, D.-J. A Bidirectional Inductive Power Interface for Electric Vehicles in V2G Systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2011, 58, 4789–4796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, C.; Buja, G.; Choi, S.; Su, Y. Modern Advances in Wireless Power Transfer Systems for Roadway Powered Electric Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 6533–6545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Chen, L.; Wu, X. Load and Mutual Inductance Identification from the Primary Side of Inductive Power Transfer System with Parallel-Tuned Secondary Power Pickup. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2018, 33, 9952–9962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thrimawithana, D.-J.; Madawala, U.-K.; Neath, M. A Synchronization Technique for Bidirectional IPT Systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2013, 60, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, V.-B.; Phan, V.-T.; Dahidah, M. Multiple Output Inductive Charger for Electric Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2019, 34, 7350–7368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weerasinghe, S.; Madawala, U.-K.; Thrimawithana, D.-J. A Matrix Converter-Based Bidirectional Contactless Grid Interface. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2017, 32, 1755–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Hu, A.-P. Impedance-Matching Range Extension Method for Maximum Power Transfer Tracking in IPT System. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2018, 33, 4419–4428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhu, C.; Jiang, J.; Song, K.; Wei, G. A 3-kW Wireless Power Transfer System for Sightseeing Car Supercapacitor Charge. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2017, 32, 3301–3316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X. Analysis Design and Optimization of LC/S Compensation Topology with Excellent Load-Independent Voltage Output for Inductive Power Transfer. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2018, 4, 767–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.; Li, Z.; Jiang, J. Constant Current/Voltage Charging Operation for Series—Series and Series—Parallel Compensated Wireless Power Transfer Systems Employing Primary-Side Controller. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2018, 33, 8065–8080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Song, K.; Jiang, J.; Zhu, C. Constant Current Charging and Maximum Efficiency Tracking Control Scheme for Supercapacitor. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2018, 33, 9088–9100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Covic, G.-A.; Stielau, O.-H. Power Transfer Capability and Bifurcation Phenomena of Loosely Coupled Inductive Power Transfer Systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2004, 51, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Hu, J.; Chen, F.; Liu, S.; Yan, Z.; He, Z. A New-Variable-Coil-Structure-Based IPT System with Load-Independent Constant Output Current or Voltage for Charging Electric Bicycles. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2018, 33, 8226–8230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, M.; Yang, B.; Chen, S.; Li, Q. Variable-Parameter T-Circuit Based IPT System Charging Battery with Constant Current or Constant Voltage Output. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2020, 35, 1672–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, R.; Chen, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y. Inductive Power Transfer for Massive Electric Bicycles Charging Based on Hybrid Topology Switching with a Single Inverter. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2017, 32, 5897–5906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Qu, X.; Yao, Y.; Yang, P. Hybrid Inductive-Power-Transfer Battery Chargers for Electric Vehicle Onboard Charging with Configurable Charging Profile. IEEE Trans. Intell Transp. 2021, 22, 592–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Mai, R.; Yue, P.; Li, Y.; He, Z. Efficiency Optimization for Wireless Dynamic Charging System with Overlapped DD Coil Arrays. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2018, 33, 2832–2846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.-M.; Onar, O.-C.; Chinthavali, M. Primary-Side Power Flow Control of Wireless Power Transfer for Electric Vehicle Charging. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2015, 3, 147–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.; Lee, S.; Jeong, S.-Y.; Cho, G.; Rim, C.-T. Uniform Power I-Type Inductive Power Transfer System with DQ -Power Supply Rails for On-Line Electric Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2015, 30, 6446–6455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.-I.; Zhang, N.-J.; Zhu, Y. A Flexible Wireless Power Transfer System with Switch Controlled Capacitor. IEEE Access. 2019, 7, 106873–106881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, B. Angular-Misalignment Insensitive Omnidirectional Wireless Power Transfer. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020, 67, 2755–2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Covic, G.-A.; Boys, J.-T. Tripolar Pad for Inductive Power Transfer Systems for EV Charging. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2017, 32, 5045–5057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yang, B.; Zhou, X.; Li, Q.; He, Z. A Hybrid Inductive Power Transfer System with Misalignment Tolerance Using Quadruple-D Quadrature Pads. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020, 35, 6039–6049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Pei, Y. A Novel Unsymmetrical Coupling Structure Based on Concentrated Magnetic Flux for. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2019, 34, 3110–3123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Thrimawithana, D.-J.; Madawala, U.-K. Hybrid Bidirectional Wireless EV Charging System Tolerant to Pad Misalignment. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 7079–7086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Member, S.; Thrimawithana, D.-J.; Member, S.; Madawala, U.-K.; Hu, A.-P.; Member, S.; Mi, C.-C. A Misalignment-Tolerant Series-Hybrid Wireless EV Charging System with Integrated Magnetics. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2019, 34, 1276–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.; Yao, Y.; Wang, D.; Wong, S.; Tse, C.-K. A Family of Hybrid IPT Topologies with Near Load-Independent Output and High Tolerance to Pad Misalignment. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020, 35, 6867–6877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yang, B.; Kou, Z.; He, Z. Hybrid and Reconfigurable IPT Systems with High-Misalignment Tolerance for Constant-Current and Constant-Voltage Battery Charging. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2018, 33, 8259–8269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Parameter | Value | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| f | 85 kHz | C1 | 26.6 nF |
| L1 | 150.1 uH | C2 | 220.1 nF |
| L2 | 149.8 uH | C3 | 22.5 nF |
| L3 | 156.1 uH | C4 | 22.5 nF |
| L4 | 156.0 uH | C5 | 26.5 nF |
| CE | 25.0 nF | E | 70 V |
| C0 | 220.2 nF |
| Proposed in | Ref. [14] | Ref. [16] | Ref. [17] | Ref. [19] | Ref. [20] | Ref. [31] | Ref. [32] | Ref. [33] | Ref. [34] | This Work |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control scheme | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | No | No | No | No | No |
| Number of Component | 2 + dc-dc converter | 2 | 2 + semi-active rectifier | 4 | 5 | 8 | 6 | 8 | 12 | 11 |
| k | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.15 | 0.22 | 0.17 | 0.18–0.30 | 0.15–0.35 | 0.08–0.16 | 0.1–0.2 | 0.1–0.2 |
| Max. power | 3 kW | 103 W | 66 W | 105 W | 400 W | 3.3 kW | 3.3 kW | 3.5 kW | 1 kW | 280 W |
| CC or CV | CC | CC-CV | CC | CC-CV | CC-CV | CC | CC | CV | CC-CV | CC-CV |
| Peak efficiency | 88% | 75% | 86% | 91% | 94% | 91% | 94% | 93% | 94% | 91% |
| Frequency (kHz) | 85.5 | 85.5 | 85.5 | 500 | 85 | 85 | 85 | 85 | 85 | 85 |
| Misalignment tolerance | No | No | No | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Wireless communication | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes | No | No | No | No | No |
| Operate without pickup pad | \ | \ | \ | \ | \ | No | Yes | Yes | No | Yes |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gong, Z.-W.; Li, J.-G.; Tong, X.-Q. Misalignment-Tolerant Series Hybrid with Active Adjustable Constant Current and Constant Voltage Output Wireless Charging System. Energies 2021, 14, 7594. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14227594
Gong Z-W, Li J-G, Tong X-Q. Misalignment-Tolerant Series Hybrid with Active Adjustable Constant Current and Constant Voltage Output Wireless Charging System. Energies. 2021; 14(22):7594. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14227594
Chicago/Turabian StyleGong, Zhao-Wei, Jin-Gang Li, and Xiang-Qian Tong. 2021. "Misalignment-Tolerant Series Hybrid with Active Adjustable Constant Current and Constant Voltage Output Wireless Charging System" Energies 14, no. 22: 7594. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14227594
APA StyleGong, Z.-W., Li, J.-G., & Tong, X.-Q. (2021). Misalignment-Tolerant Series Hybrid with Active Adjustable Constant Current and Constant Voltage Output Wireless Charging System. Energies, 14(22), 7594. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14227594





