Full-Scale Investigation of Dry Sorbent Injection for NOx Emission Control and Mercury Retention
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (1)
- The influence of dry urea–halloysite blend on NOx emission;
- (2)
- The influence of dry urea–halloysite blend on ammonia slip in flue gas and fly ash;
- (3)
- The influence of dry urea–halloysite on mercury sorption.
2. Materials and Methods
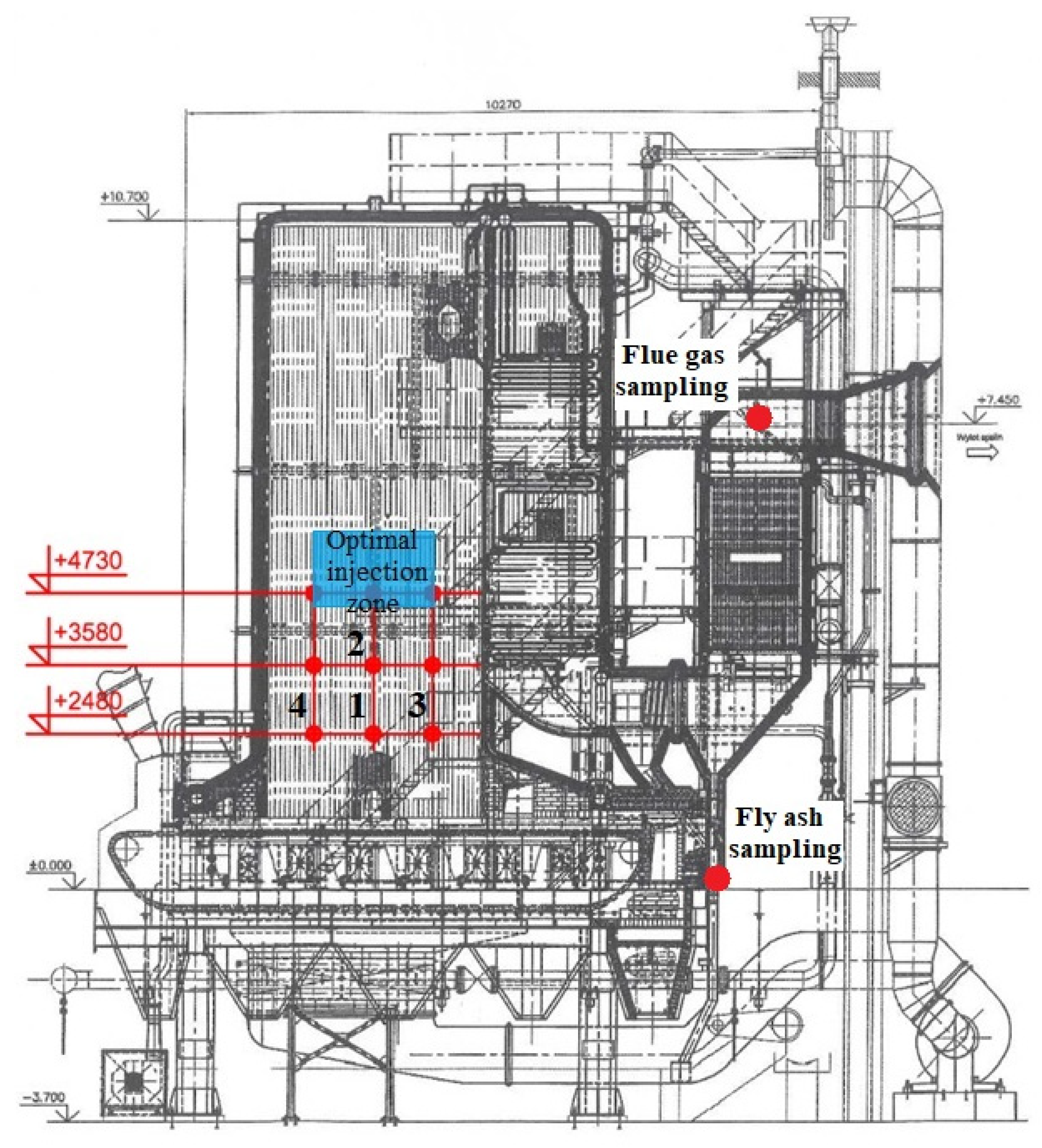
2.1. Stoker Boiler and In-Furnace Temperature Measurement
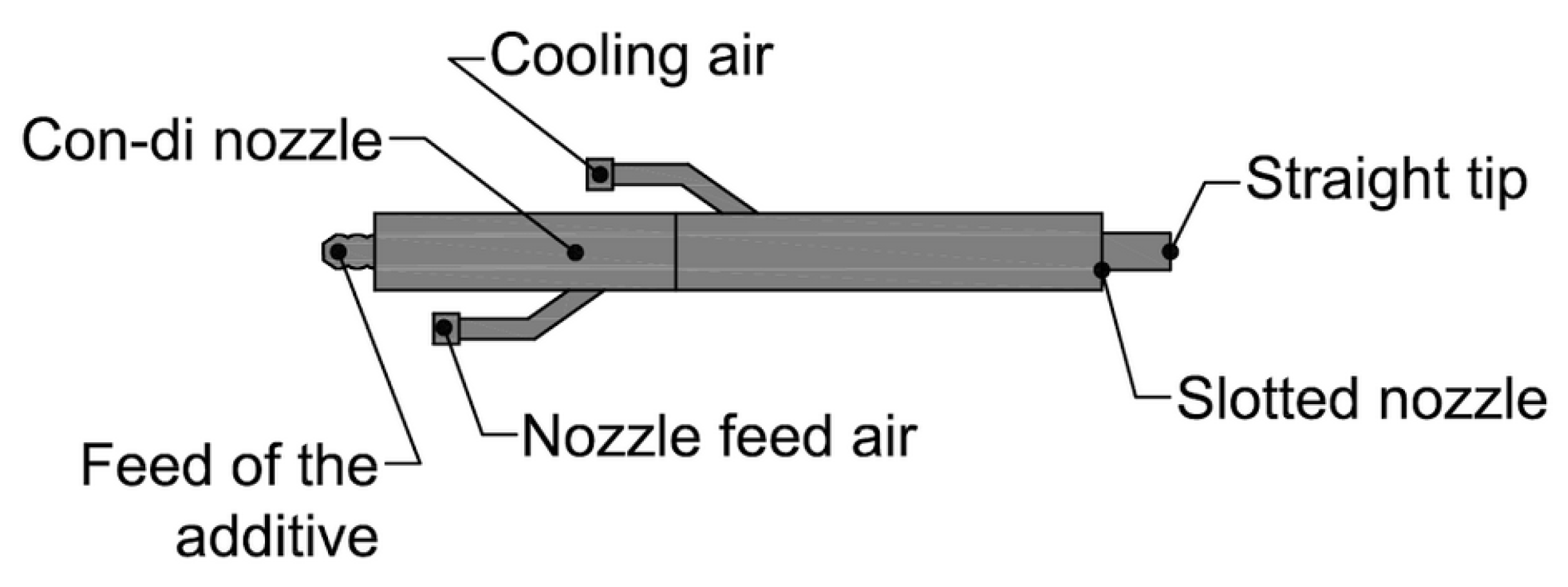
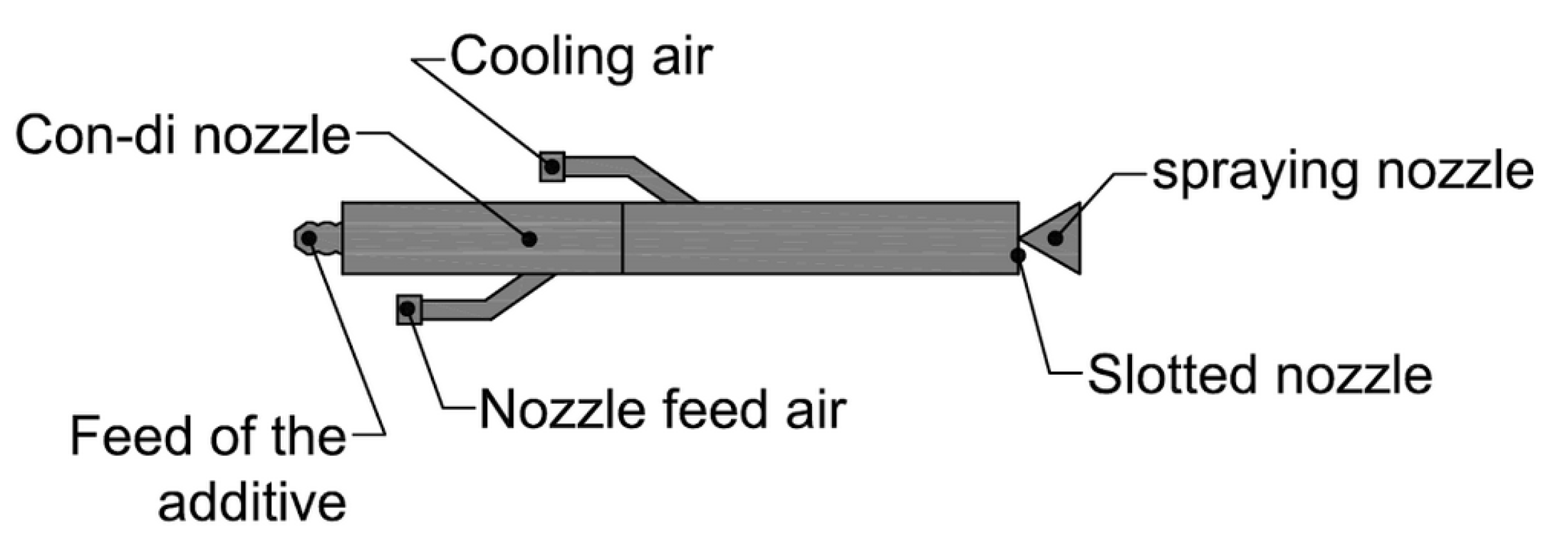
2.2. Sorbent Injection System
2.3. Fly Ash and Fuel Sampling and Chemical Analysis
2.4. Flue Gas Sampling and Analysis
3. Results
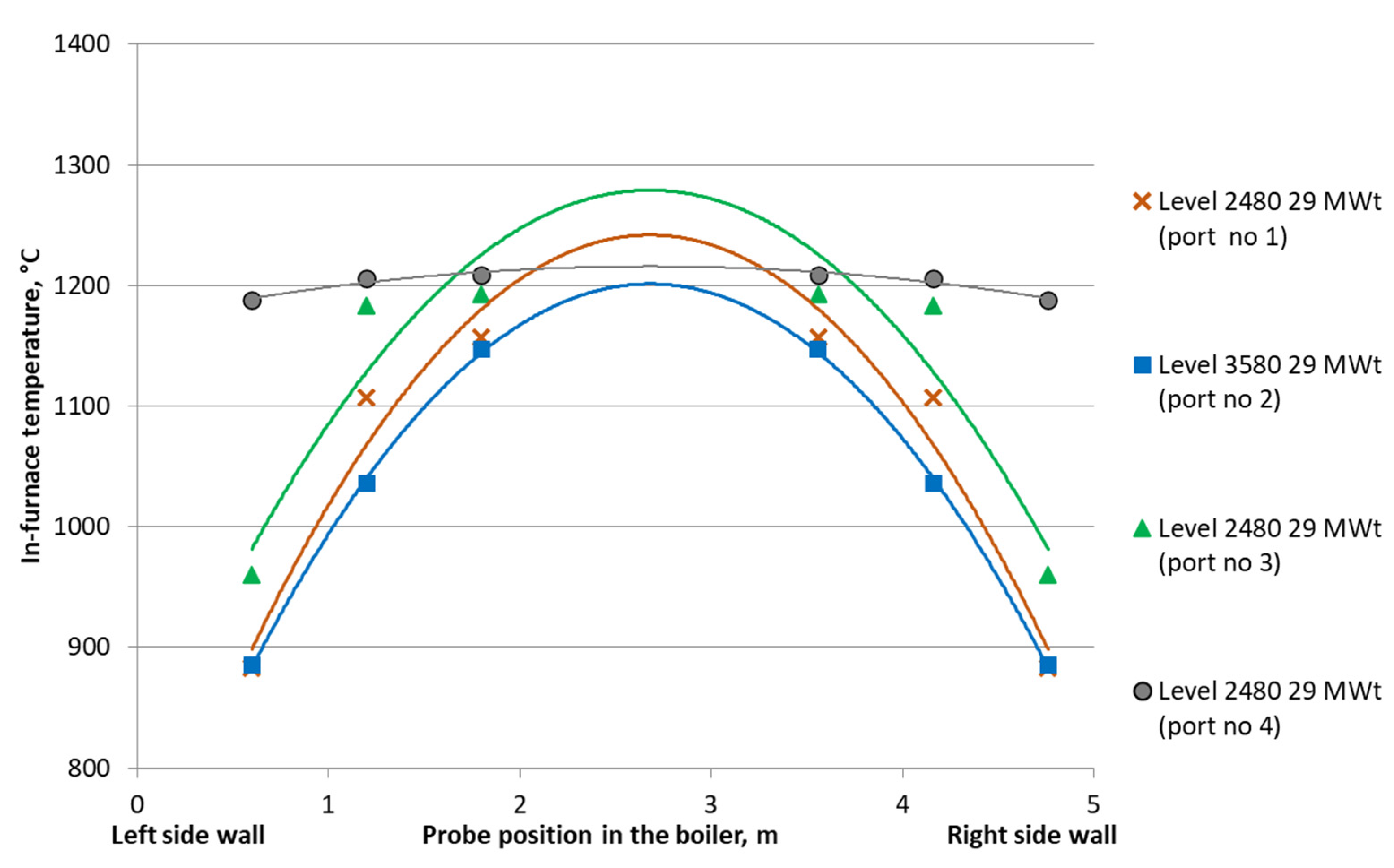
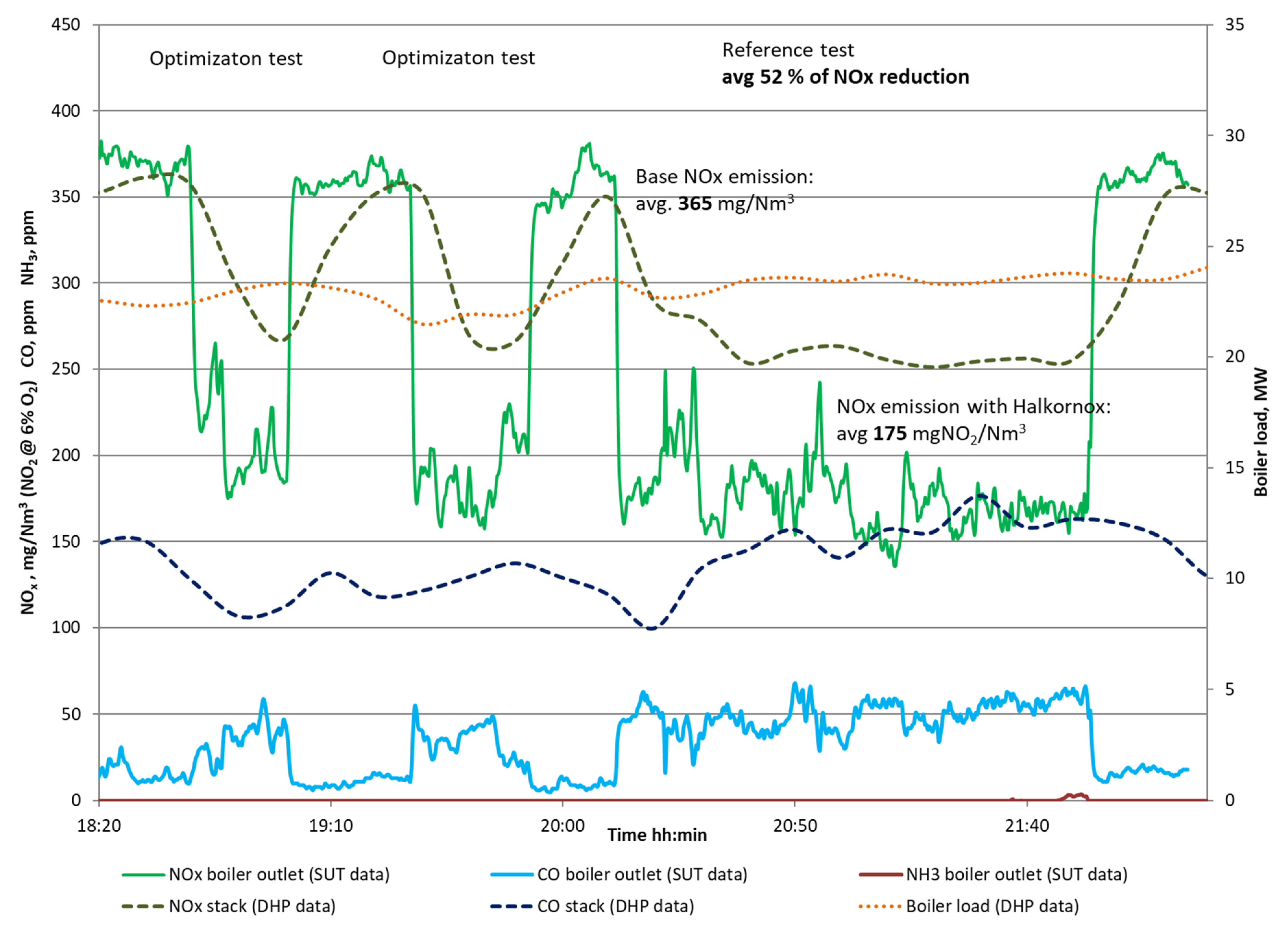
- Optimization tests at 27.5 MWth; sorbent distribution at level +4730 mm.
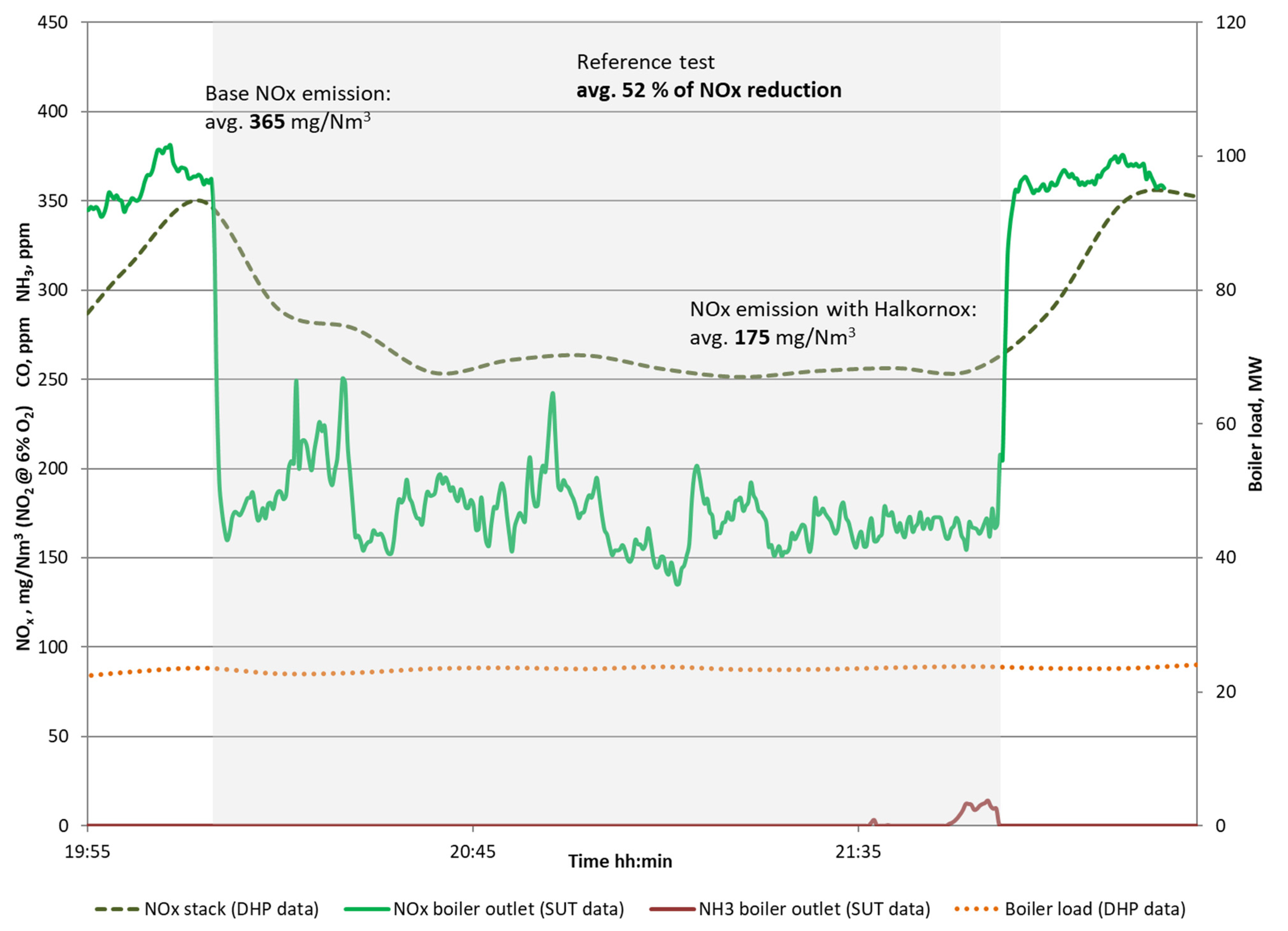
- Reference test at 23.5 MWth; sorbent distribution at level +4730 mm.
- Low load—the level of 4730 mm—nozzles tilted down −20°.
- Average load—the level of 4730 mm—nozzle leveled +0°.
- High load—the level of 4730 mm—nozzle tilted up +20°.
4. Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wasielewski, R.; Głód, K.; Telenga-Kopyczyńska, J. Energy and Emission Aspects of Co-Combustion Solid Recovered Fuel with Coal in a Stoker Boiler. E3S Web Conf. 2018, 28, 01037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sefidari, H.; Razmjoo, N.; Strand, M. An Experimental Study of Combustion and Emissions of Two Types of Woody Biomass in a 12-MW Reciprocating-Grate Boiler. Fuel 2014, 135, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Sun, R.; Fei, J.; Wu, S.; Liu, X.; Dai, K.; Yao, N. Experimental Study on Effects of Moisture Content on Combustion Characteristics of Simulated Municipal Solid Wastes in a Fixed Bed. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 7238–7246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krawczyk, P. The Designing Method of NOx Reduction Installation for Coal Stocker-Fired Boilers Using SNCR Technology; Oficyna Wydawnicza Politechniki Warszawskiej: Warsaw, Poland, 2019. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Krawczyk, P. Experimental Investigation of N2O Formation in Selective Non-Catalytic NOx Reduction Processes Performed in Stoker Boiler. Pol. J. Chem. Technol. 2016, 18, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Więckowski, Ł.; Krawczyk, P.; Badyda, K. Numerical Investigation of Temperature Distribution in the Furnace of a Coal Fired Grate Boiler in Part Load Conditions. J. Power Technol. 2018, 97, 359–365. [Google Scholar]
- Houshfar, E.; Skreiberg, Ø.; Todorović, D.; Skreiberg, A.; Løvås, T.; Jovović, A.; Sørum, L. NOx Emission Reduction by Staged Combustion in Grate Combustion of Biomass Fuels and Fuel Mixtures. Fuel 2012, 98, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staiger, B. Development of an Air Staging Technology to Reduce NOx Emissions in Grate Fired Boilers. Energy 2005, 30, 1429–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houshfar, E.; Skreiberg, Ø.; Løvås, T.; Todorović, D.; Sørum, L. Effect of Excess Air Ratio and Temperature on NOx Emission from Grate Combustion of Biomass in the Staged Air Combustion Scenario. Energy Fuels 2011, 25, 4643–4654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuropka, J. Denitrogenation of Flue Gases from Power and Heat Generation/Odazotowanie Spalin z Elektrociepłowni. Ochr. Środowiska 1999, 72, 23–24. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Kuropka, J.; Gostomaczyk, M.A. Badania Selektywnej Redukcji Niekatalitycznej Tlenków Azotu. Ochr. Sr. 1996, 4, 10–17. [Google Scholar]
- Punjak, W.A.; Shadman, F. Aluminosilicate Sorbents for Control of Alkali Vapors during Coal Combustion and Gasification. Energy Fuels 1988, 2, 702–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, T.; Kordylewski, W.; Mościcki, K. Use of Aluminosilicate Sorbents for Control of KCl Vapors in Biomass Combustion Gases. J. Power Technol. 2013, 93, 37–43. [Google Scholar]
- Kalisz, S.; Ciukaj, S.; Tymoszuk, M.; Kubiczek, H. Fouling and Its Mitigation in PC Boilers Co-Firing Forestry and Agricultural Biomass. Heat Transf. Eng. 2015, 36, 763–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalisz, S.; Ciukaj, S.; Mroczek, K.; Tymoszuk, M.; Wejkowski, R.; Pronobis, M.; Kubiczek, H. Full-Scale Study on Halloysite Fireside Additive in 230 t/h Pulverized Coal Utility Boiler. Energy 2015, 92, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mroczek, K.; Kalisz, S.; Pronobis, M.; Sołtys, J. The Effect of Halloysite Additive on Operation of Boilers Firing Agricultural Biomass. Fuel Process. Technol. 2011, 92, 845–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szul, M.; Iluk, T.; Sobolewski, A. High-Temperature, Dry Scrubbing of Syngas with Use of Mineral Sorbents and Ceramic Rigid Filters. Energies 2020, 13, 1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, P.; Zhang, B.; Zeng, X.; Luo, G.; Li, X.; Yao, H.; Zheng, C. Deep Study on Effects of Activated Carbon’s Oxygen Functional Groups for Elemental Mercury Adsorption Using Temperature Programmed Desorption Method. Fuel 2017, 200, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granite, E.J.; Pennline, H.W.; Senior, C. Mercury Control: For Coal-Derived Gas Streams; Somerset, D.E., Ed.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ghose, M.K. Complete Physico-Chemical Treatment for Coke Plant Effluents. Water Res. 2002, 36, 1127–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazda-Grzywacz, M.; Winconek, Ł.; Burmistrz, P. Carbon Footprint for Mercury Capture from Coal-Fired Boiler Flue Gas. Energies 2021, 14, 3844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charpenteau, C.; Seneviratne, R.; George, A.; Millan, M.; Dugwell, D.R.; Kandiyoti, R. Screening of Low Cost Sorbents for Arsenic and Mercury Capture in Gasification Systems. Energy Fuels 2007, 21, 2746–2750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, D.; Zhao, B.; Feng, L.; Ni, M.; Jin, J. Mercury Removal Based on Adsorption and Oxidation by Fly Ash: A Review. Energy Fuels 2020, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Wang, H.; Zhu, T.; Kuang, J.; Jing, P. Mercury Removal from Coal Combustion Flue Gas by Modified Fly Ash. J. Environ. Sci. 2013, 25, 393–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, S.; Liu, H.; Chang, L.; Ma, S.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, C. Mercury Removal from Flue Gas by Magnetospheres Present in Fly Ash: Role of Iron Species and Modification by HF. Fuel Process. Technol. 2017, 167, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Chen, H.; Han, X.; Ding, S.; Shan, Y.; Liu, Y. Preparation of Magnetic Co-Fe Modified Porous Carbon from Agricultural Wastes by Microwave and Steam Activation for Mercury Removal. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 381, 120981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Union. Regulation (EC) No 1272/2008 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 16 December 2008 on Classification, Labelling and Packaging of Substances and Mixtures. 2008; Volume 51, pp. 1–1355. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/reg/2008/1272/oj (accessed on 15 November 2021).
- Lee, S.J.; Yun, J.G.; Lee, H.M.; Kim, J.Y.; Yun, J.H.; Hong, J.G. Dependence of N2O/NO Decomposition and Formation on Temperature and Residence Time in Thermal Reactor. Energies 2021, 14, 1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daood, S.S.; Javed, M.T.; Gibbs, B.M.; Nimmo, W. NOx Control in Coal Combustion by Combining Biomass Co-Firing, Oxygen Enrichment and SNCR. Fuel 2013, 105, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pronobis, M. Environmentally Oriented Modernization of Power Boilers; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; ISBN 9780128199213. [Google Scholar]
- Blevins, L.G. Behavior of Bare and Aspirated Thermocouples in Compartment Fires. In Proceedings of the 33rd National Heat Transfer Conference, Albuquerque, NM, USA, 15–17 August 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Muzio, L.; Bogseth, S.; Himes, R.; Chien, Y.-C.; Dunn-Rankin, D. Ammonium Bisulfate Formation and Reduced Load SCR Operation. Fuel 2017, 206, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.W.; Kilgore, J.D.; Ghorishi, S.B. Mercury Control Research: Effects of Fly Ash and Flue Gas Parameters on Mercury Speciation; United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Ghorishi, S.B.; Lee, C.W.; Kilgroe, J.D. Mercury speciation in combustion systems: Studies with simulated flue gases and model fly ashes. In Proceedings of the AWMA Annual Meeting, St. Louis, MO, USA, 20–24 June 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, Y.; Tan, H.; Hui, S. Ash-Related Issues during Biomass Combustion: Alkali-Induced Slagging, Silicate Melt-Induced Slagging (Ash Fusion), Agglomeration, Corrosion, Ash Utilization, and Related Countermeasures. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2016, 52, 1–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Parameter | Basis | Unit | Fuel |
|---|---|---|---|
| Moisture | a.r. | % | 3.10 |
| Ash | d.b. | % | 19.80 |
| Volatile matter | a.r. | % | 26.10 |
| HHV | a.r | J/g | 26,307 |
| LHV | a.r. | J/g | 25,403 |
| C | a.r. | % | 64.28 |
| H | a.r. | % | 4.03 |
| N | a.r. | % | 1.09 |
| S | a.r. | % | 0.72 |
| Ammonium compounds as NH3 | d.b. | mg/kg | 9.10 |
| Hg | d.b. | mg/kg | 0.138 |
| Parameter | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Boiler load | 23.5 | MWth |
| Test duration | 100 | min. |
| Avg. NO2 concentration at the inlet (at 6% O2) | 365 | mg//Nm3 |
| Avg. NO2 concentration at the exit (at 6% O2) | 175 | mg//Nm3 |
| NOx conversion (max) | 52 | % |
| The percentage of urea in the sorbent | 25 | % |
| The stoichiometric excess ratio | 2 | - |
| Urea mass flow | 7.5 | kg of urea/h |
| Halloysite mass flow | 22.5 | kg of halloysite/h |
| Sorbent total mass flow | 30.0 | kg/h |
| NH3 slip in flue gas | <2.0 | ppm |
| NH3 slip in fly ash (avg.) | 279 | mg/kg |
| No | Sample | Sulfur as SO3 (%) | Mercury as Hg (mg/kg) | Ammonia as NH3 (mg/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Reference coal ash sample | - | 0.138 | 9.1 |
| 2 | Fly ash 14:10 (27 MWth) | 1.25 | 2.14 | 59.6 |
| 3 | Fly ash 21:10 (23.5 MWth) | 0.96 | 1.40 | 325 |
| 4 | Fly ash 22:10 (23.5 MWth) | 0.9 | 1.64 | 279 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wejkowski, R.; Kalisz, S.; Tymoszuk, M.; Ciukaj, S.; Maj, I. Full-Scale Investigation of Dry Sorbent Injection for NOx Emission Control and Mercury Retention. Energies 2021, 14, 7787. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14227787
Wejkowski R, Kalisz S, Tymoszuk M, Ciukaj S, Maj I. Full-Scale Investigation of Dry Sorbent Injection for NOx Emission Control and Mercury Retention. Energies. 2021; 14(22):7787. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14227787
Chicago/Turabian StyleWejkowski, Robert, Sylwester Kalisz, Mateusz Tymoszuk, Szymon Ciukaj, and Izabella Maj. 2021. "Full-Scale Investigation of Dry Sorbent Injection for NOx Emission Control and Mercury Retention" Energies 14, no. 22: 7787. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14227787
APA StyleWejkowski, R., Kalisz, S., Tymoszuk, M., Ciukaj, S., & Maj, I. (2021). Full-Scale Investigation of Dry Sorbent Injection for NOx Emission Control and Mercury Retention. Energies, 14(22), 7787. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14227787








