Novel Single-Phase Short-Stroke Tubular Permanent Magnet Oscillating Machines with Partitioned Stator
Abstract
1. Introduction
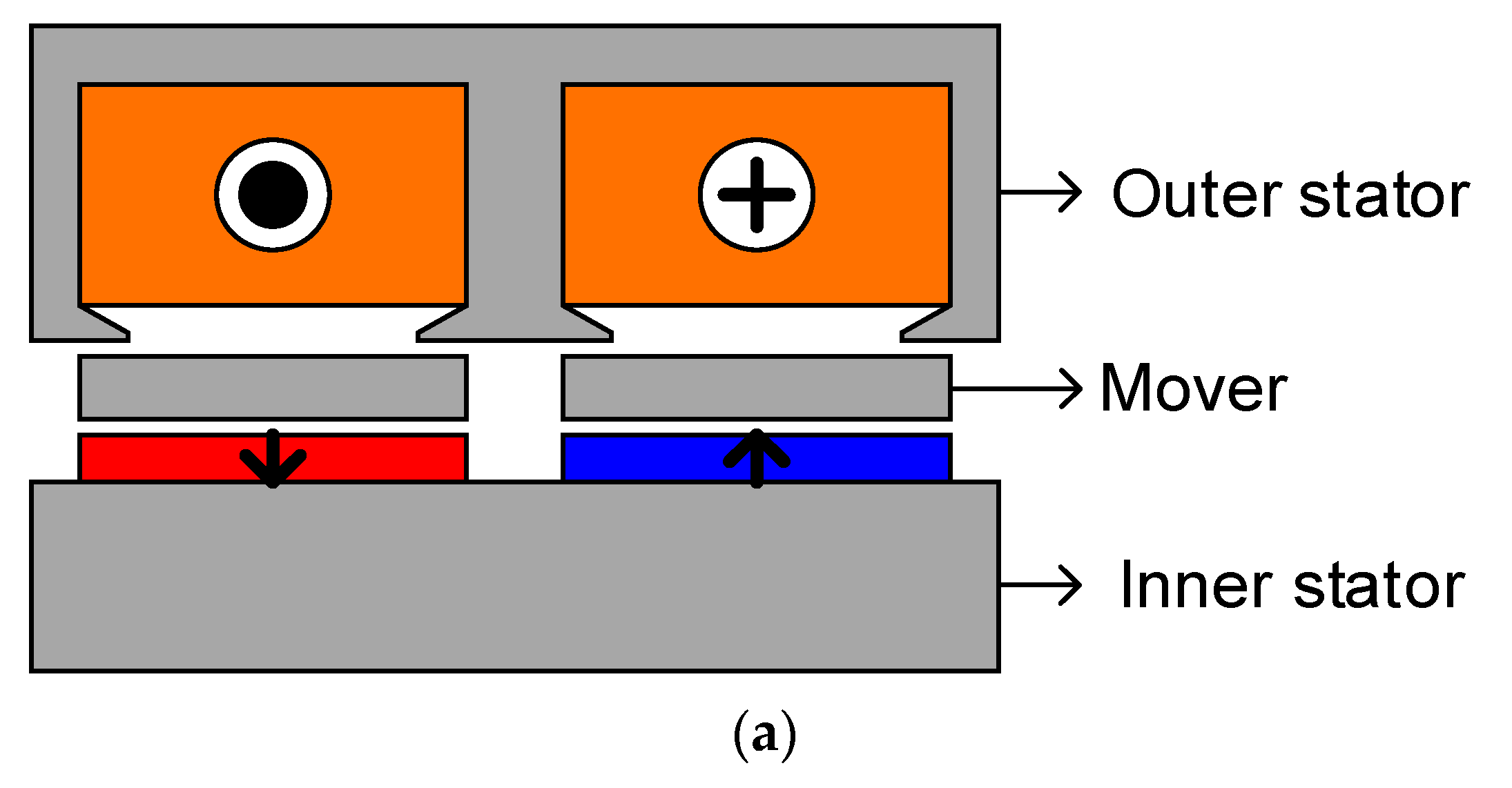
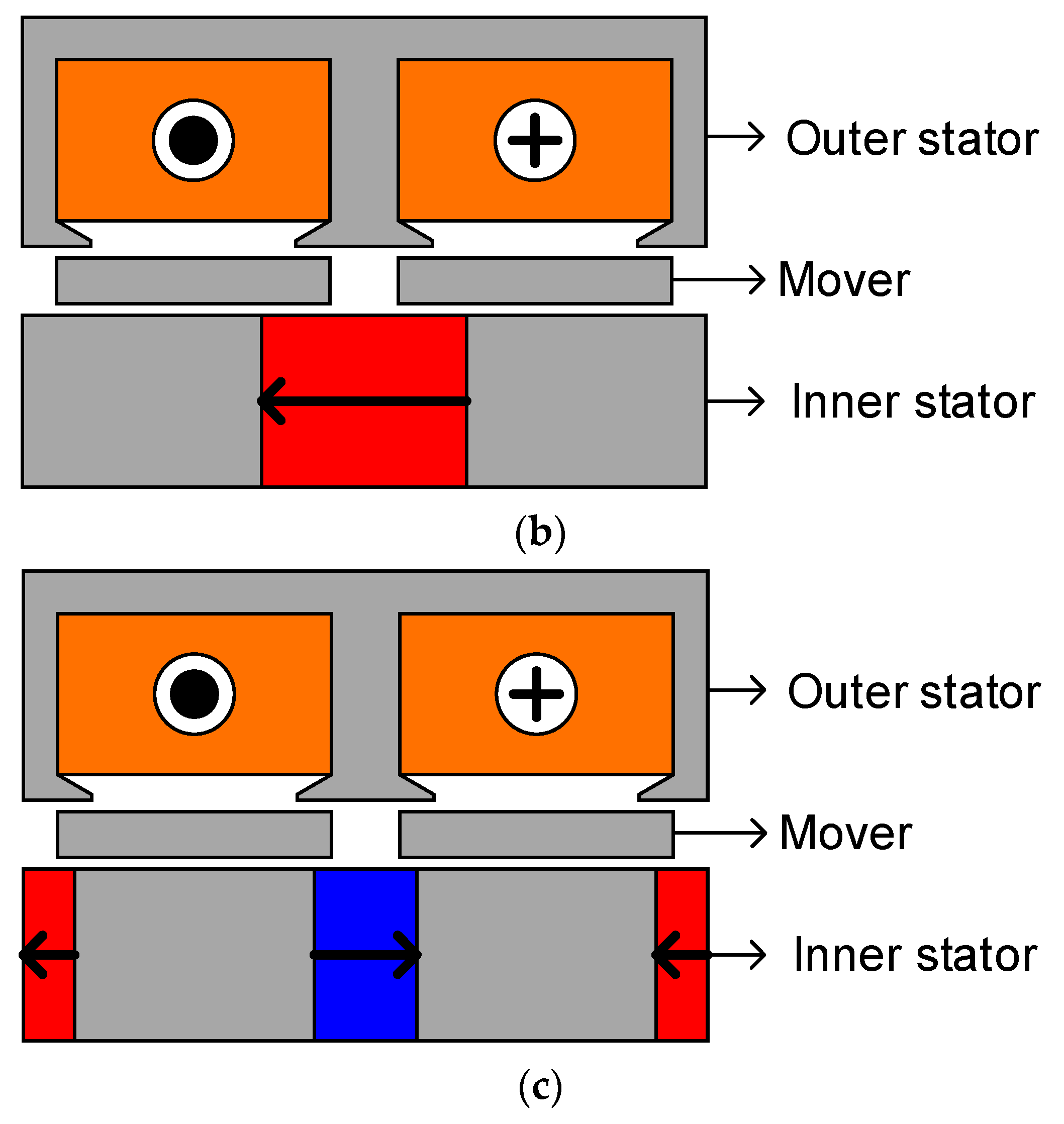
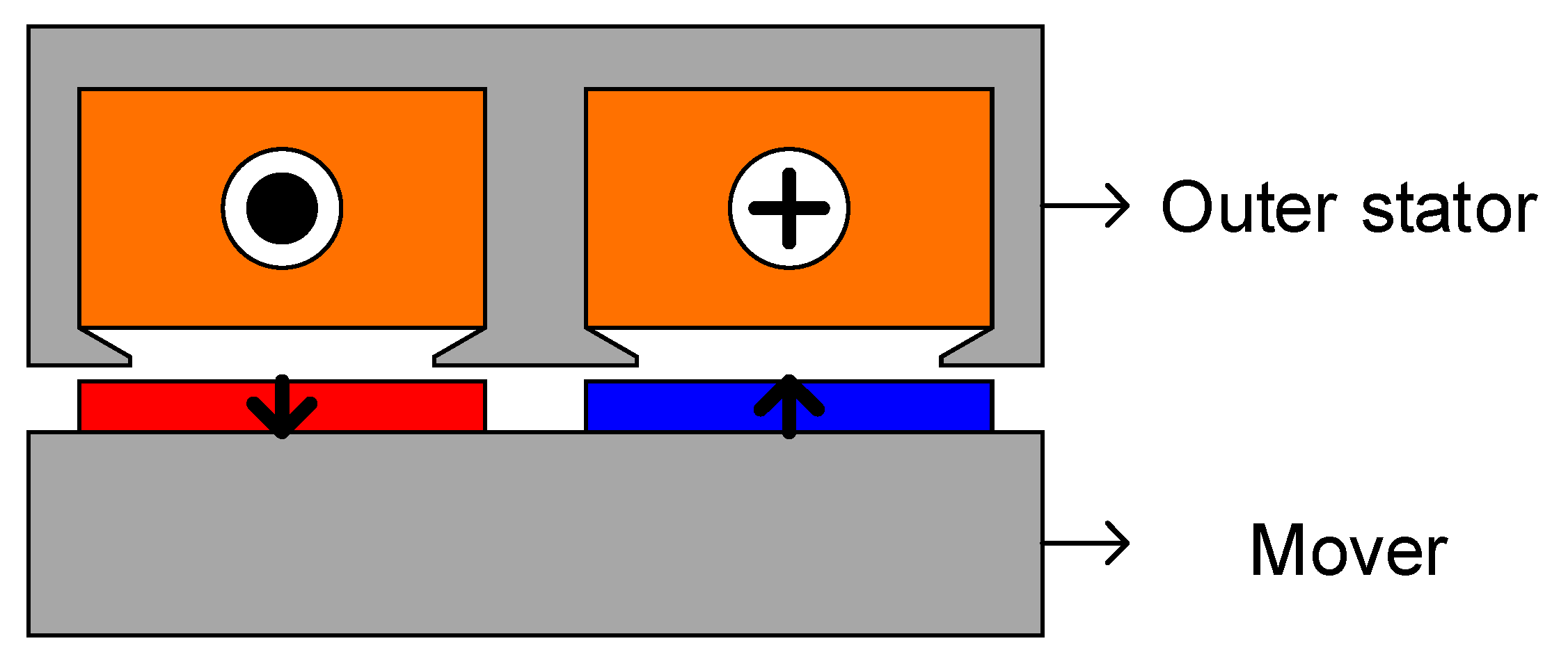
2. Machine Configurations
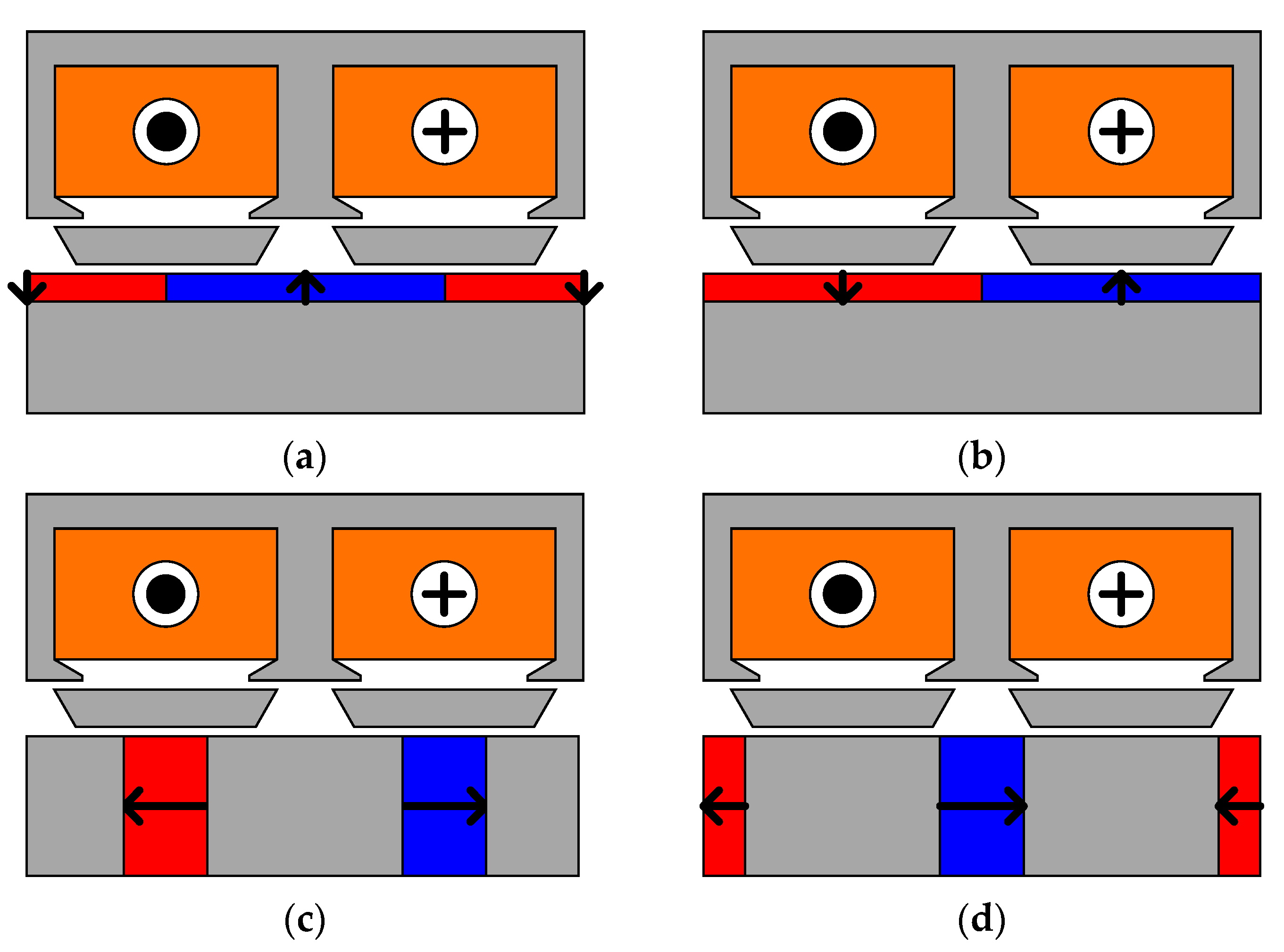
3. Influence of Permanent Magnet Alignment
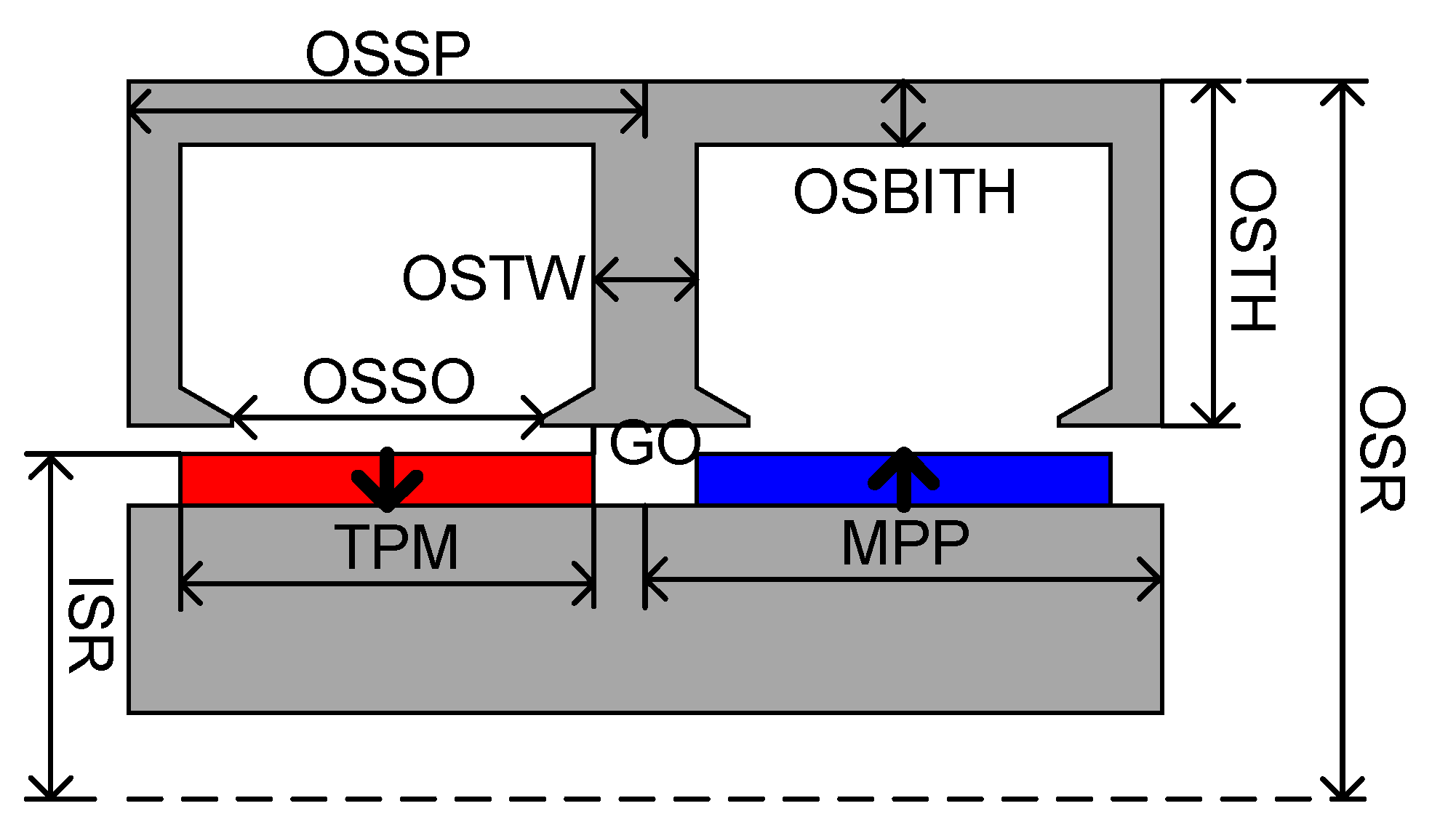
4. Machine Optimization
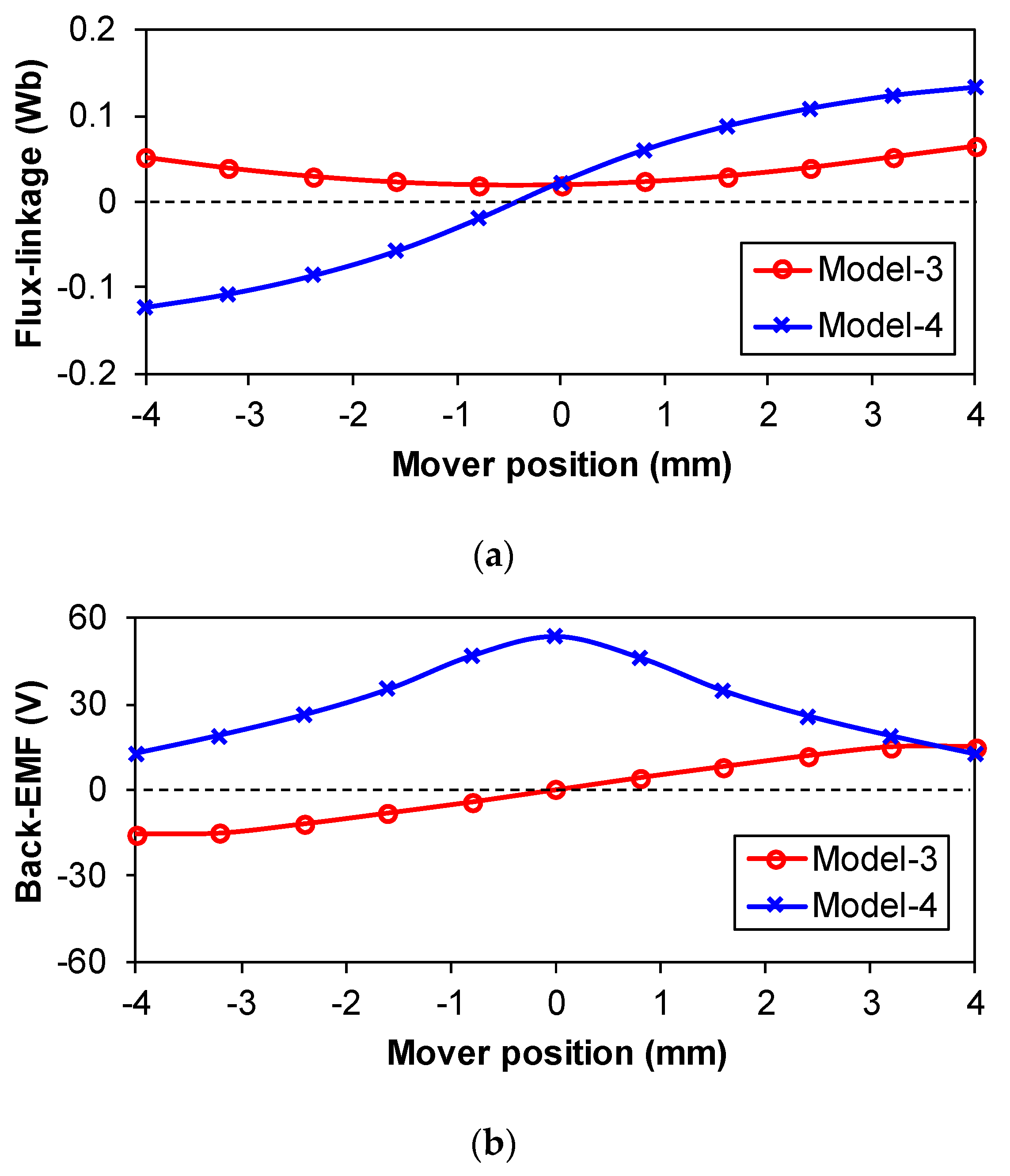
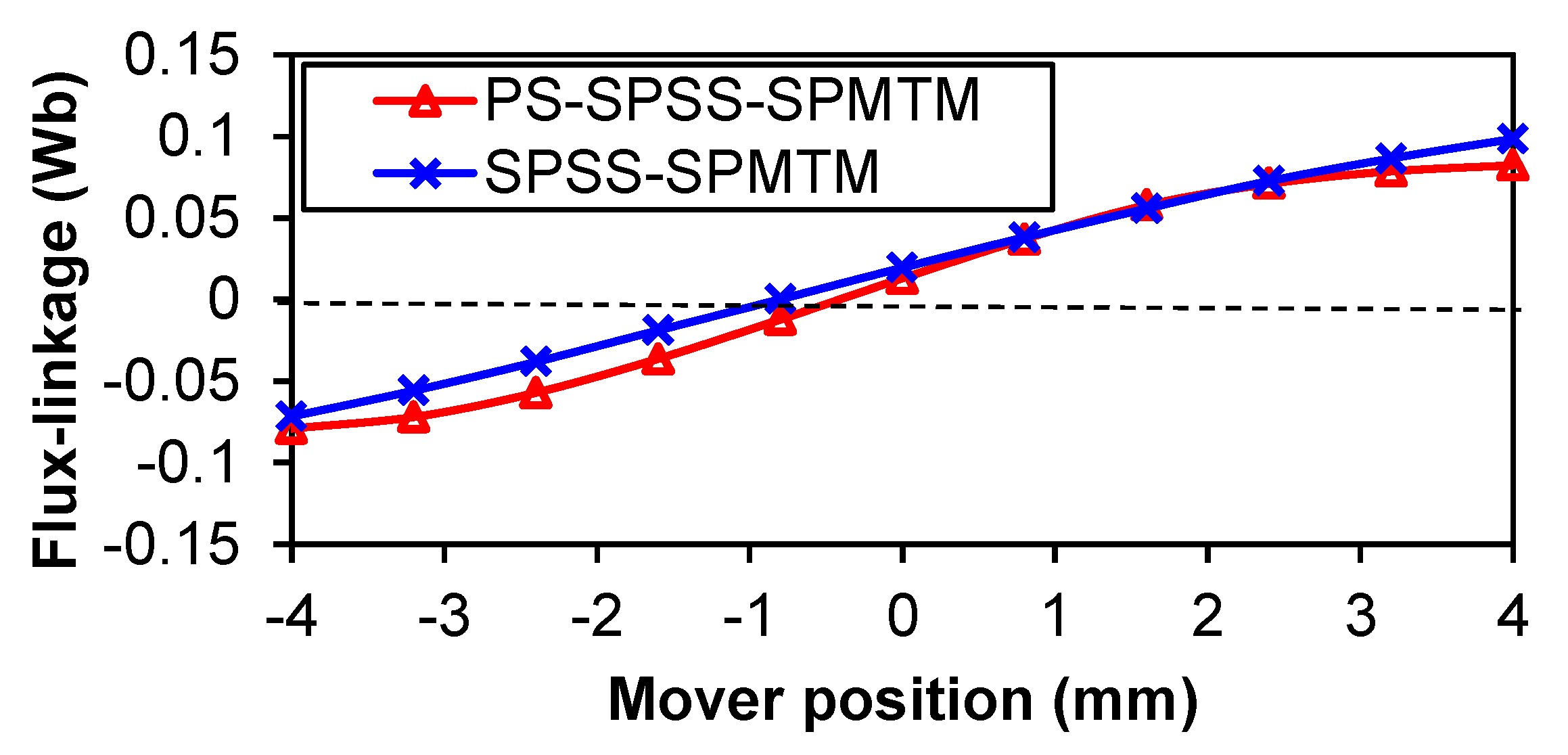
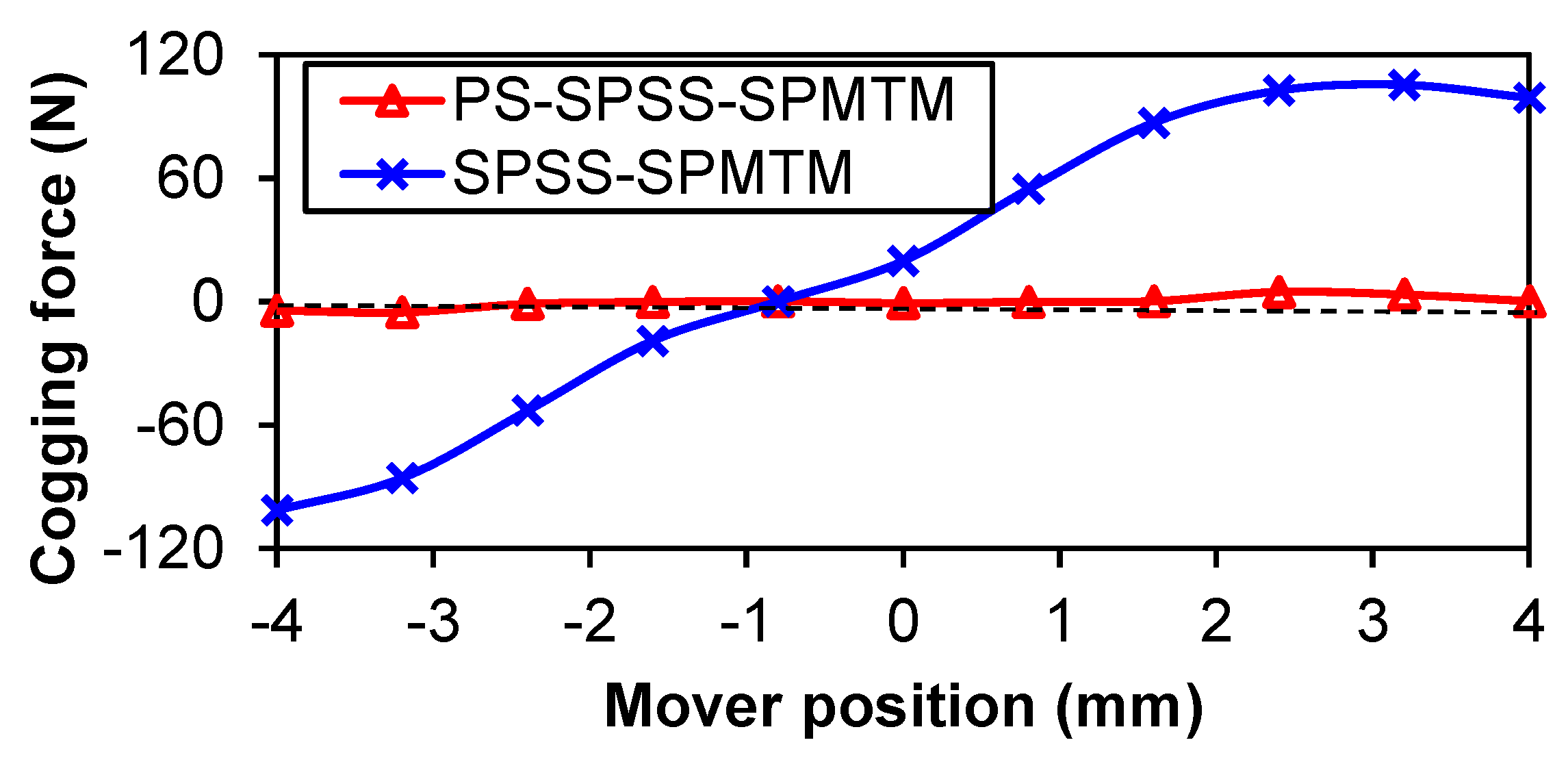
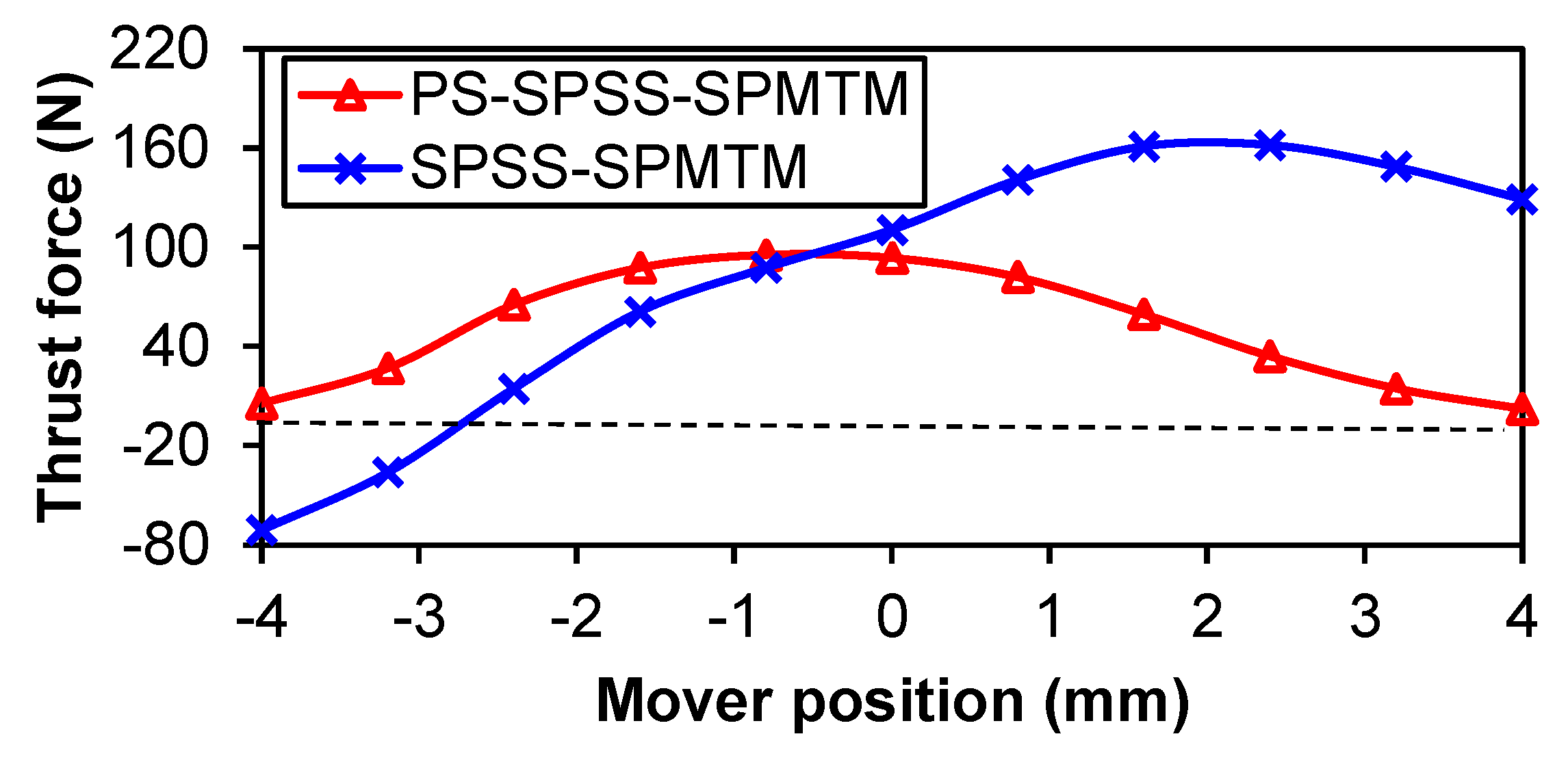
5. No-Load and Load Performance
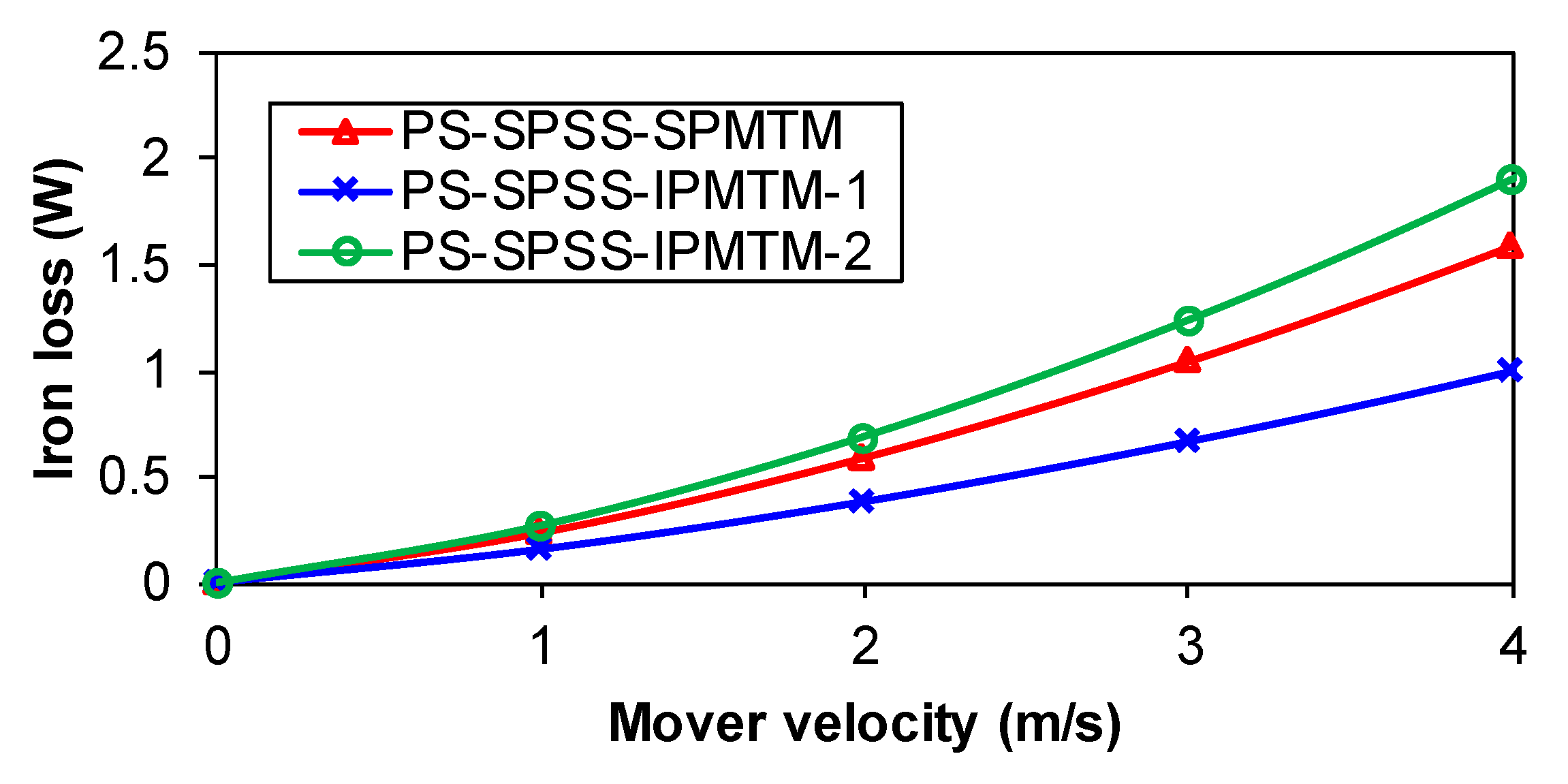
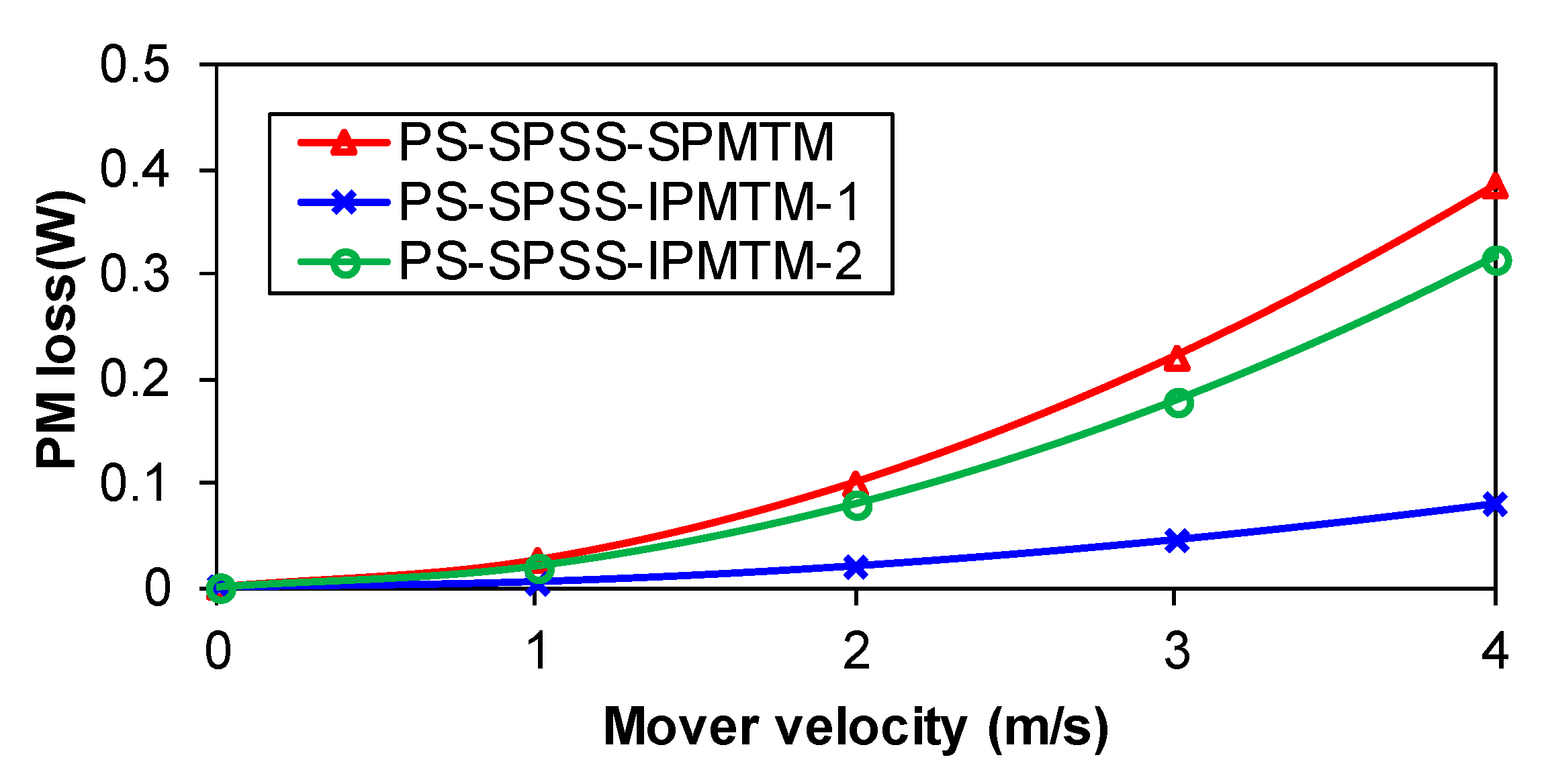
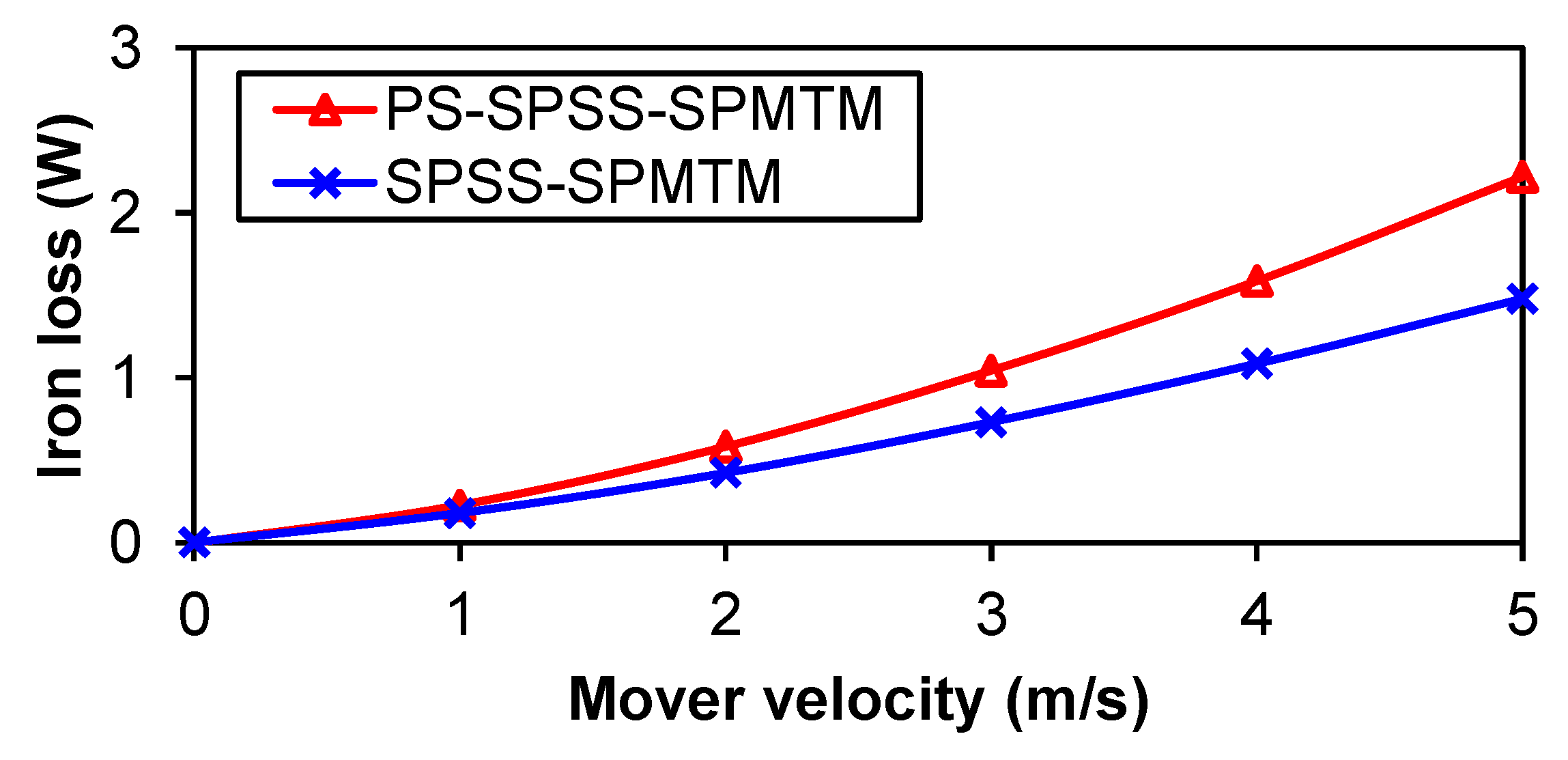
6. Comparison of Losses
7. Comparison of PS-SPSS-SPMTM with a Conventional Single-Phase Short-Stroke Surface-Mounted Permanent Magnet Tubular Machine
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lv, G.; Zhou, T.; Zeng, D.; Liu, Z. Design of ladder-slit secondaries and performance improvement of linear induction motors for urban rail transit. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 65, 1187–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, R.; Jin, Y.; Lu, M.; Zhang, Z. Quantitative comparison of linear flux-switching permanent magnet motor with linear induction motor for electromagnetic launch system. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 65, 7569–7578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, R.; Lu, M.; Jiang, N.; Cheng, M. Comparison between linear induction motor and linear flux-switching permanent-magnet motor for railway transportation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 66, 9394–9405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobo, N.S.; Lim, H.S.; Krishnan, R. Comparison of linear switched reluctance machines for vertical propulsion application: Analysis, design, and experimental correlation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2008, 44, 1134–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vatani, M.; Mirsalim, M. Comprehensive research on a modular-stator linear switched reluctance motor with a toroidally wound mover for elevator applications. In Proceedings of the International Power Electronics, Drive Systems and Technologies Conference (PEDSTC), Shiraz, Iran, 12–14 February 2019; pp. 61–66. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Du, X.; Zhang, D.; Wang, X. Design, optimization, and prototyping of segmental-type linear switched-reluctance motor with a toroidally wound mover for vertical propulsion application. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 65, 1865–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, Y.-S.; Kim, W.-J. Detent-force minimization of double-sided interior permanent-magnet flat linear brushless motor. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2016, 52, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Li, J.; Qu, R.; Lai, J.; Huang, H.; Liu, H. Study on high efficiency permanent magnet linear synchronous motor for maglev. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 2018, 28, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.Z.; Yu, H.C.; Zhou, B.; Li, L.Y.; Gerada, D.; Gerada, C.; Qian, Z.Y. Detent-force minimization of double-sided permanent magnet linear synchronous motor by shifting one of the primary components. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020, 67, 180–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.Z.; Li, J.; Zhang, C.; Qian, Z.Y.; Li, L.; Gerada, D. Electromagnetic and thrust characteristics of double-sided permanent magnet linear synchronous motor adopting staggering primaries structure. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 66, 4826–4836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.B.; Howe, D. Analysis of an axially magnetized iron-cored tubular PM machine. IET Proc. Electr. Power Appl. 2004, 151, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Refaie, A.M. Fractional-slot concentrated-windings synchronous permanent magnet machines: Opportunities and challenges. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020, 57, 107–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Howe, D.; Jewell, G.W. Analysis and design optimization of an improved axially magnetized tubular permanent-magnet machine. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2004, 19, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, Y.; Zheng, P.; Yu, B.; Cheng, L.; Liu, Z. Research on a tubular yokeless linear PM machine. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2015, 51, 8204904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Jewell, G.; Howe, D. Design optimization and comparison of tubular permanent magnet machine topologies. IET Proc. Electr. Power Appl. 2001, 148, 456–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, J.; Yan, S.; Zhao, W.; Liu, G.; Zhu, X. Minimization of cogging force in a novel linear permanent-magnet motor for artificial hearts. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2013, 49, 3901–3904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andriollo, M.; Dall’Ora, L.; Tortella, A. Electromagnetic parameter characterization of a short-stroke linear PM generator for renewable energy application. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Clean Electrical Power (ICCEP), Alghero, Italy, 11–13 June 2013; pp. 383–390. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Howe, D.; Lin, Z. Analysis of a short-stroke, single-phase, quasi-Halbach magnetized tubular permanent magnet motor for linear compressor applications. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2008, 2, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Fu, Z.; Yu, B.; Sui, Y.; Zhu, S.; Zheng, P. Design and optimization of a single-phase oscillating PM alternator used for free-piston stirling engines. In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (ICEMS), Hangzhou, China, 22–25 October 2014; pp. 1738–1742. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, C.-W.; Jang, G.-H.; Seo, S.-W.; Yoon, I.-J.; Lee, S.-H.; Jeong, S.-S.; Choi, J.-Y. Comparison of electromagnetic and dynamic characteristics of linear oscillating actuators with rare-earth and ferrite magnets. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2019, 55, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, N.; Bolognani, S.; Corte, D.D.; Tonel, F. Tubular linear permanent magnet motors: An overall comparison. IEEE Trans. Ind. Applicat. 2003, 39, 466–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, S.G.; Sarlioglu, B. A comparative study of coreless-type PM linear synchronous machines with non-overlapping windings. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2019, 55, 2481–2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Howe, D.; Lin, Z. Comparative study of winding configurations of short-stroke, single phase tubular permanent magnet motor for refrigeration applications. In Proceedings of the IEEE Industry Applications Annual Meeting, New Orleans, LA, USA, 23–27 September 2007; pp. 311–318. [Google Scholar]
- Abdalla, I.; Ibrahim, T.; Nor, N. Comparative study of permanent magnet configurations of short-stroke linear motor for reciprocating compressor in household refrigerator application. Inf. Technol. Electr. Eng. 2013, 2, 16–24. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, S.L.; Wang, Q.; Niu, S.; Fu, W.N. A novel magnetic-geared tubular linear machine with Halbach permanent-magnet arrays for tidal energy conversion. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2015, 51, 8113604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhu, Z.Q.; Howe, D.; Dai, J. Comparative study of alternative permanent magnet linear oscillating actuators. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems, Wuhan, China, 17–20 October 2008; pp. 2826–2831. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Xu, W.; Ye, C.; Zhu, J. Novel hybrid-flux-path moving-iron linear oscillatory machine with magnets on stator. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2017, 53, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuheng, Q.; Jie, Z.; Chi, Z. Effects of Halbach and non-Halbach arrays on thrust characteristics of ironless permanent magnet linear motors: A simulation and optimization. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems, Hamamatsu, Japan, 24–27 November 2020; pp. 1659–1662. [Google Scholar]
- Souissi, A.; Abdennadher, I.; Masmoudi, A. Comparison of the no-load features of IPM and consequent pole tubular-linear PM synchronous machines. In Proceedings of the Fourteenth International Conference on Ecological Vehicles and Renewable Energies (EVER), Monte-Carlo, Monaco, 8–10 May 2019; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, R.; Cheng, M.; Mi, C.C.; Hua, W. Influence of leading design parameters on the force performance of a complementary and modular linear flux-switching permanent-magnet motor. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 61, 2165–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Cheng, M.; Hua, W.; Jia, H.; Cao, R. Back-EMF harmonic analysis and fault-tolerant control of flux-switching permanent-magnet machine with redundancy. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2011, 58, 1926–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, R.; Cheng, M.; Hua, W. Investigation and general design principle of a new series of complementary and modular linear FSPM motors. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2013, 60, 5436–5446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Cheng, M.; Chau, K.T.; Cao, R.; Ji, J. Remedial injected harmonic current operation of redundant flux-switching permanent magnet motor drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2013, 60, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.; Hua, W.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, W. Overview of stator permanent magnet brushless machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2011, 58, 5087–5101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, P.; Sui, Y.; Tong, C.; Bai, J.; Yu, B.; Lin, F. A novel single-phase flux-switching permanent magnet linear generator used for free-piston stirling engine. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 115, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, P.; Sui, Y.; Yu, B.; Cheng, L.; Wang, W. A tubular single-phase dual-stator flux-switching PM oscillating generator with series magnetic circuit. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Magnetics Conference, Beijing, China, 11–15 May 2015; p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Zhu, Z. Modelling and evaluation of linear oscillating actuators. J. Int. Conf. Electr. Mach. Syst. 2012, 1, 517–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wang, M.; Li, L.; Pan, D. Detent force compensation for pmlsm systems based on structural design and control method combination. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 62, 6845–6854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sano, H.; Narita, K.; Asanuma, T.; Yamada, T. An accurate iron loss evaluation method based on finite element analysis for permanent magnet motors. In Proceedings of the 2016 XXII International Conference on Electrical Machines (ICEM), Lausanne, Switzerland, 4–7 September 2016; pp. 1284–1289. [Google Scholar]
- Hor, P.J.; Zhu, Z.Q.; Howe, D.; Rees-Jones, J. Eddy-current loss in a moving-coil linear tubular permanent magnet brushless motor. IEEE Trans. Magn. 1999, 35, 3601–3603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Howe, D. Influence of soft magnetic materials on the design and performance of tubular permanent magnet machines. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2005, 41, 4057–4059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


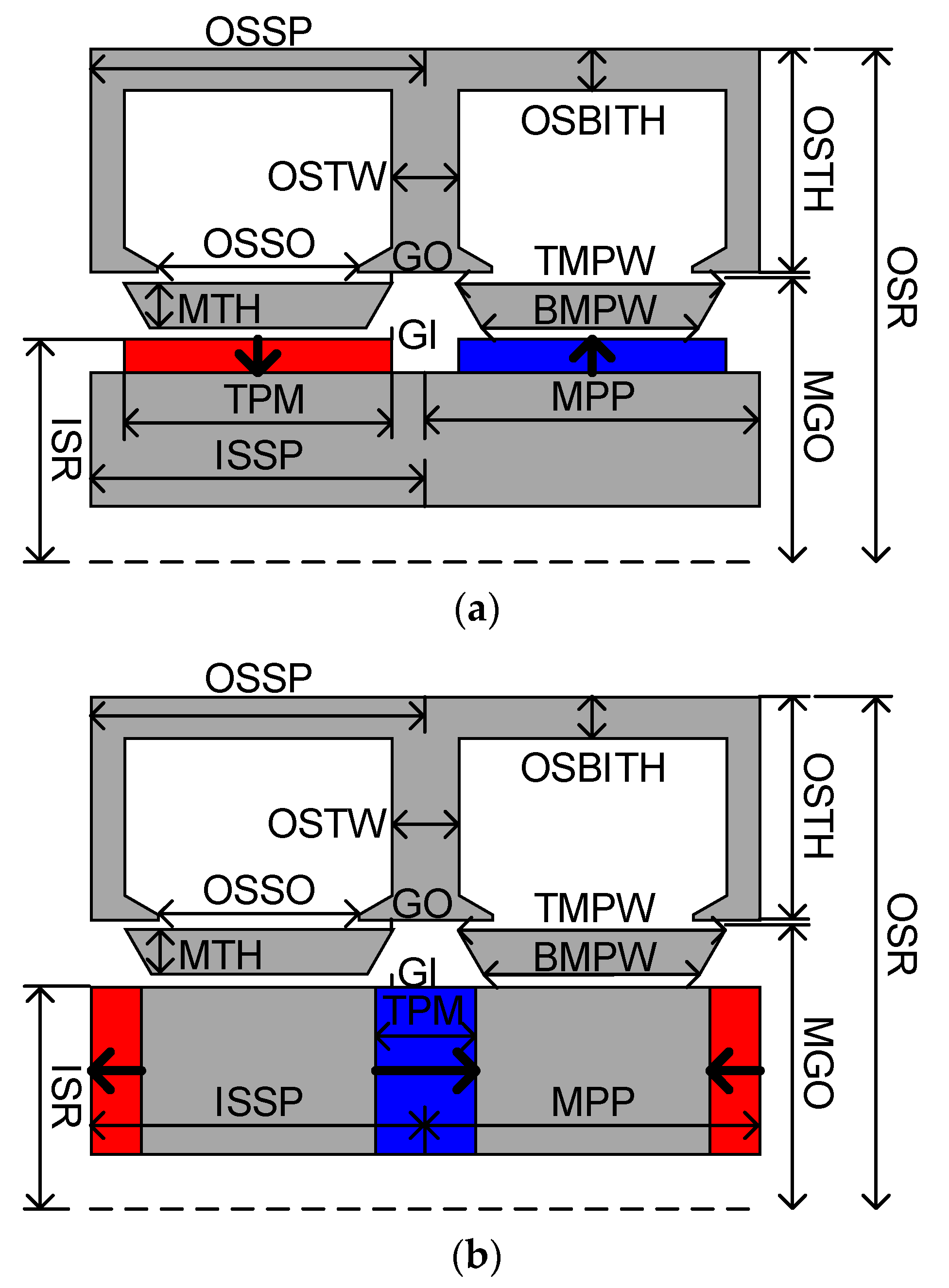
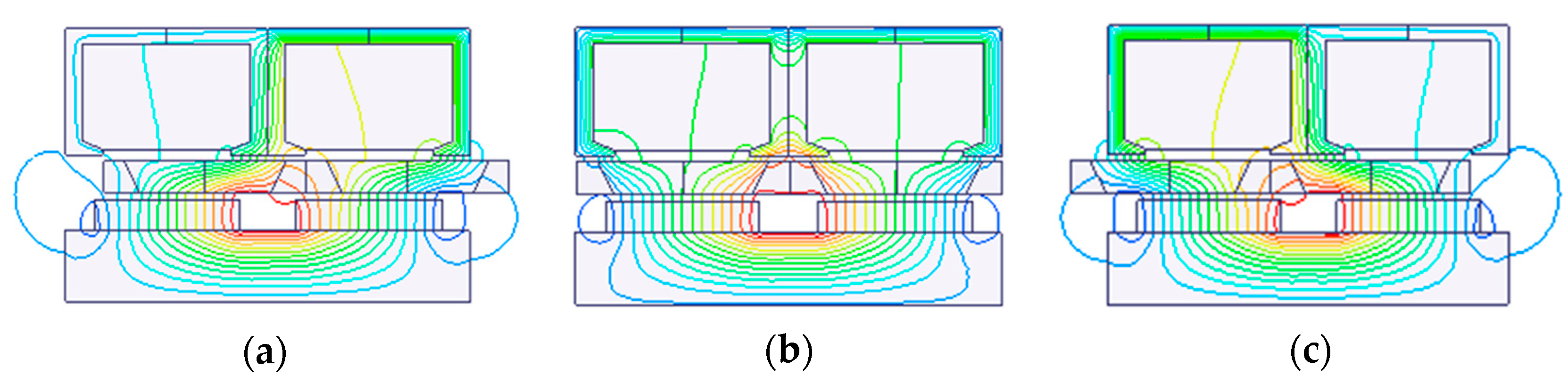
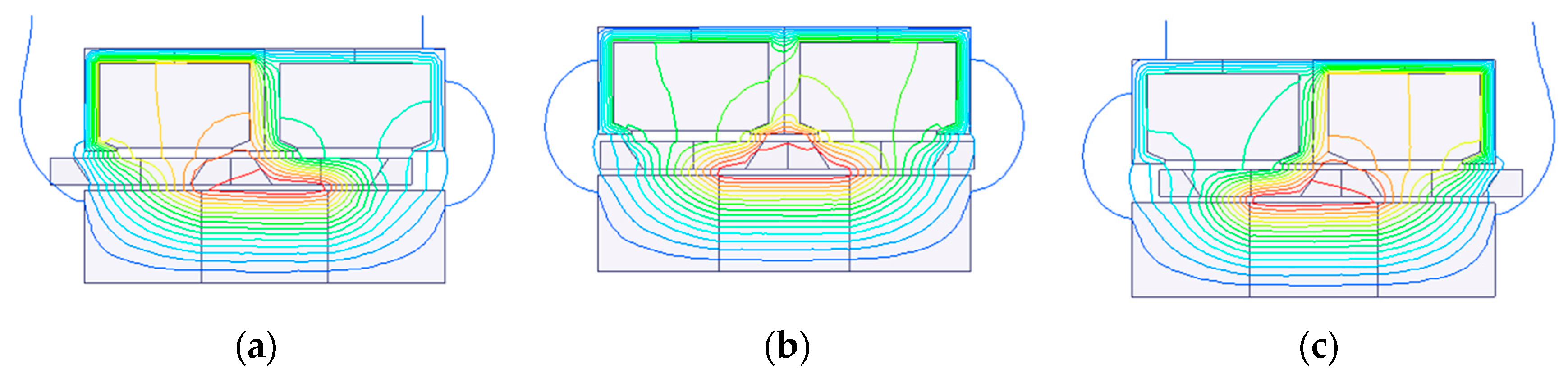
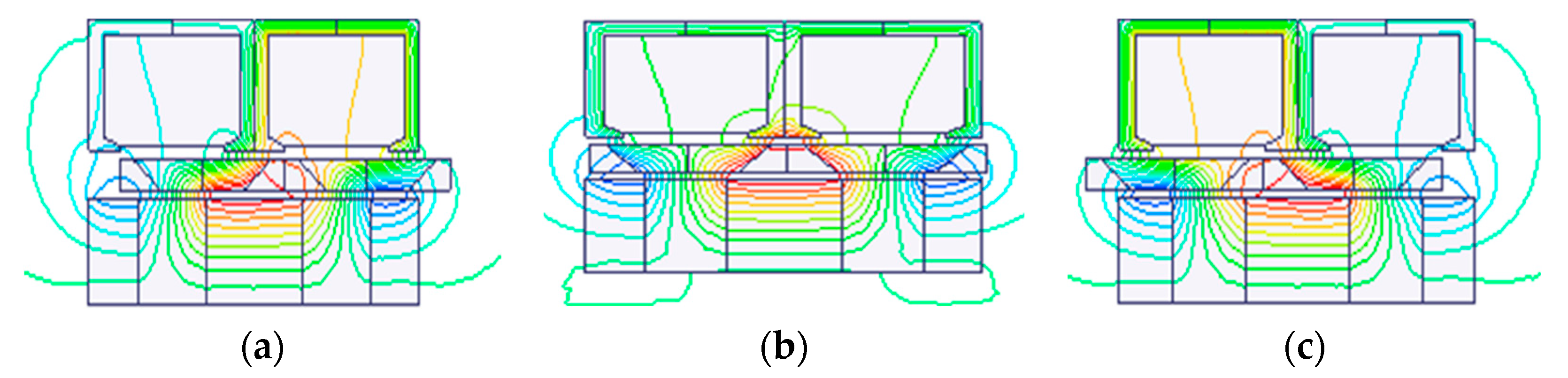
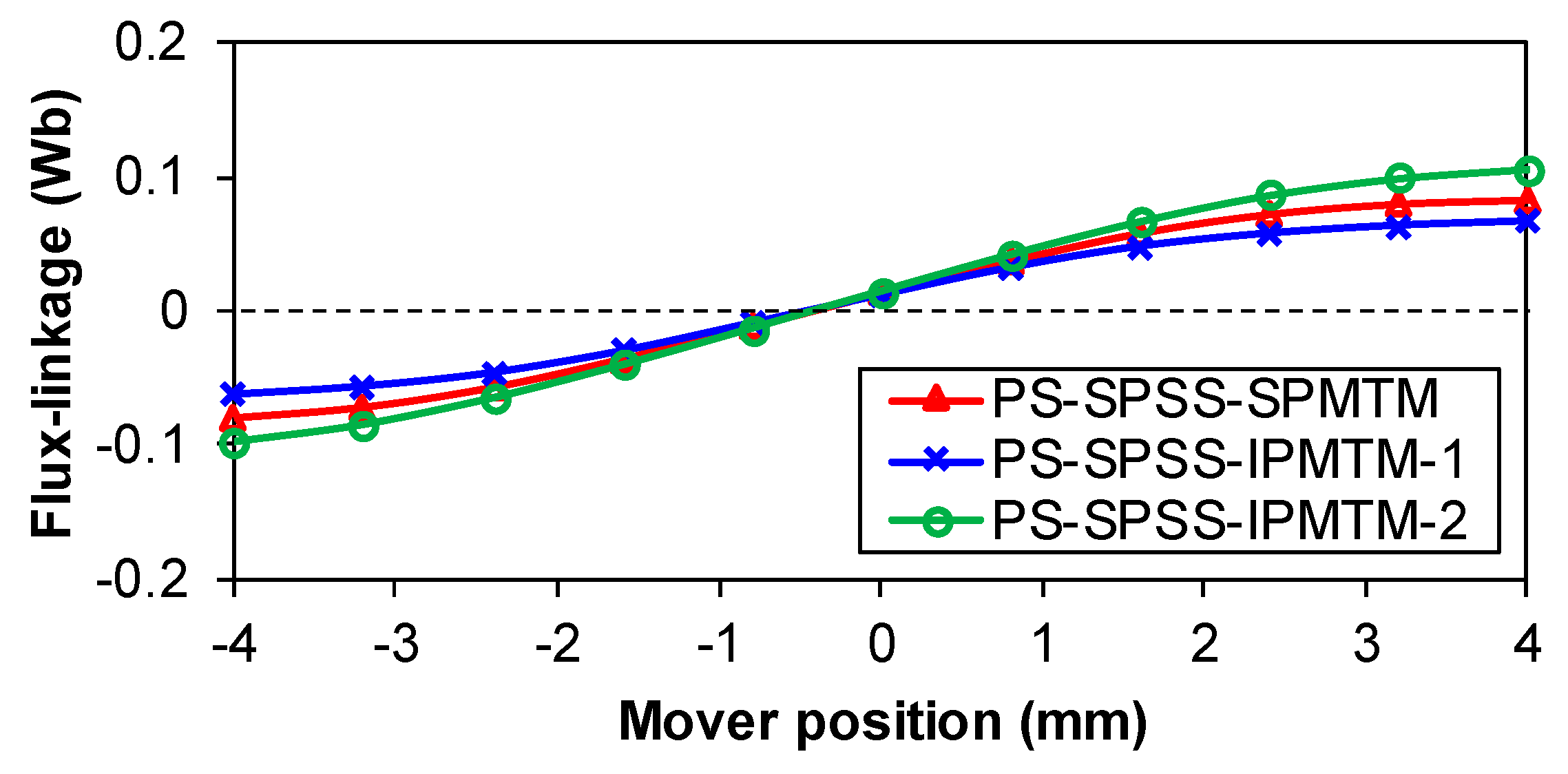
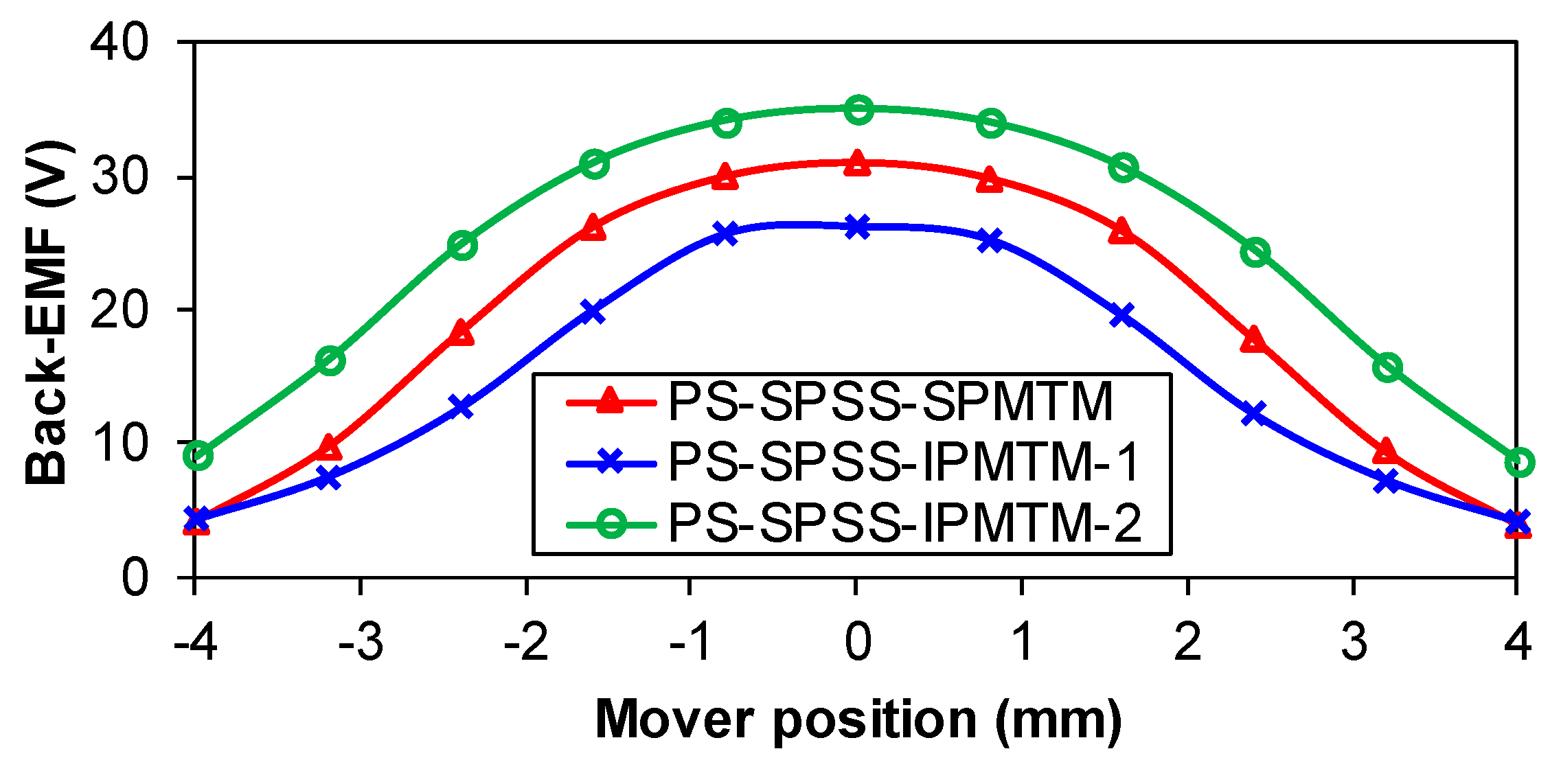
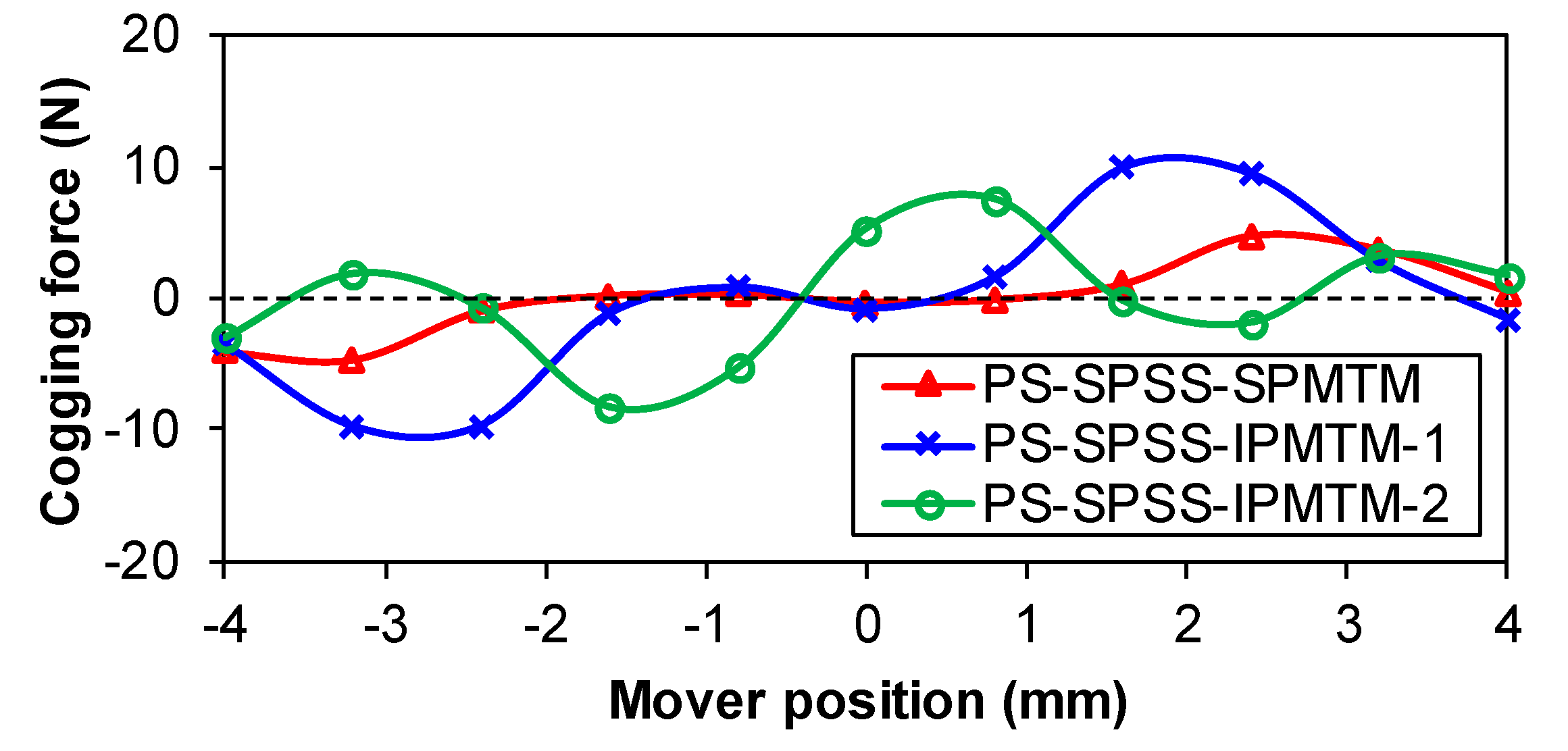

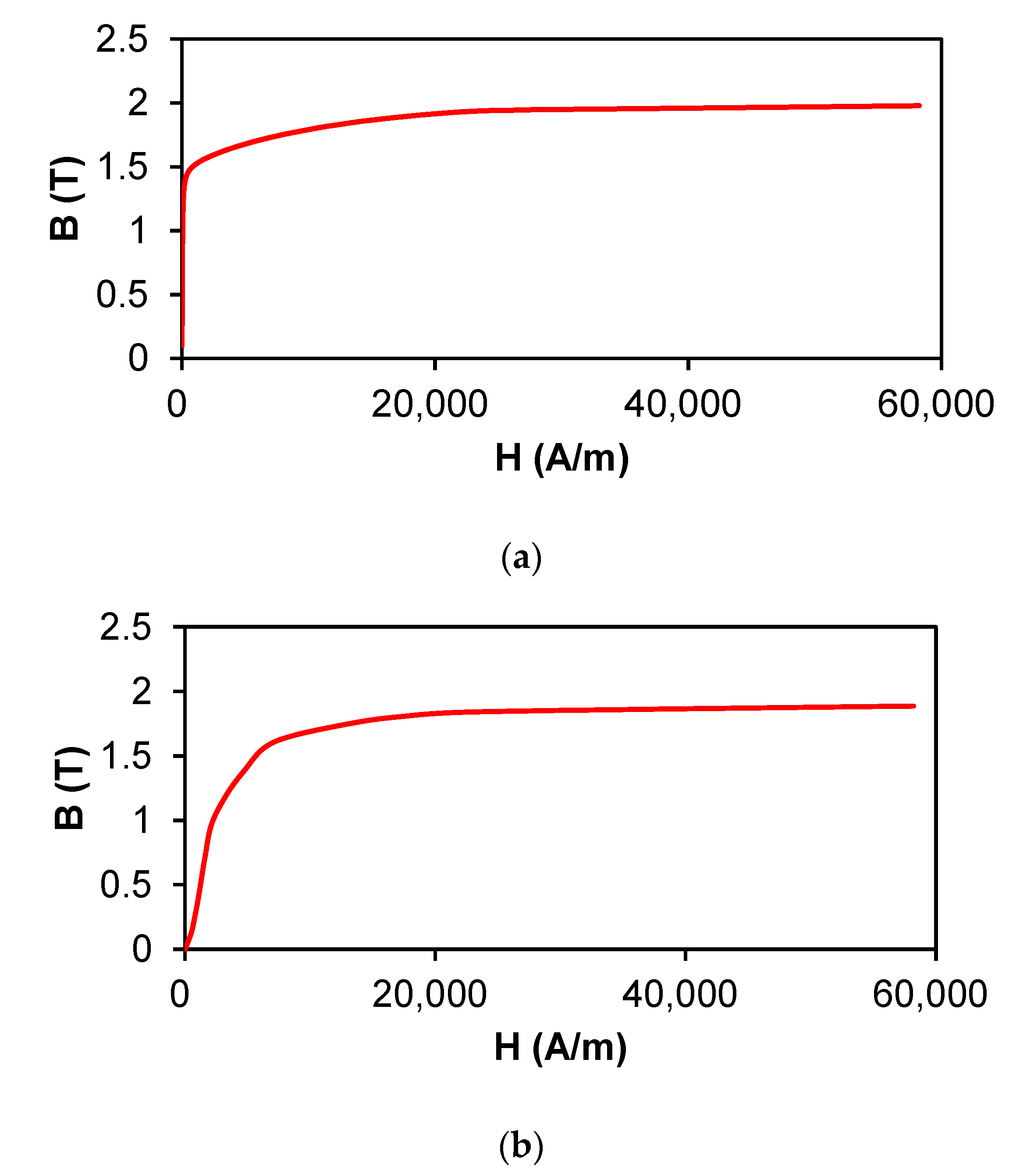



| Items | Values |
|---|---|
| Outer radius (mm) | 35 |
| Machine active length (mm) | 47.2 |
| Inner air gap length (mm) | 0.8 |
| Outer air gap length (mm) | 0.8 |
| Slot number | 2 |
| Pole number | 2 |
| Current density (A/mm2) | 4 |
| Turns per coil | 350 |
| Remanence of magnet (T) | 1.2 |
| Recoil permeability of magnet | 1.05 |
| Symbols | Definitions | Expressions |
|---|---|---|
| SR | Split ratio | MGO */OSR |
| TMPWR | Top mover pole pitch width ratio | TMPW/MPP |
| BMPWR | Bottom mover pole pitch width ratio | BMPW/MPP |
| OSTWR | Outer stator tooth width ratio | OSTW/OSSP |
| OSSOR | Outer stator slot opening ratio | OSSO/OSSP |
| OSBITHR | Outer stator back iron thickness ratio | OSBITH/OSTH |
| TPMR | PM pole ratio | TPM/ISPP |
| Symbols | Initials | Restrictions | Optimal | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PS-SPSS-SPMTM | PS-SPSS-IPMTM-1 | PS-SPSS-IPMTM-2 | |||
| SR | 0.5 | [0.3, 0.75] | 0.58 | 0.6 | 0.58 |
| TMPWR | 0.8 | [0.3, 0.9] | 0.73 | 0.75 | 0.85 |
| BMPWR | 0.6 | [0.3, 0.9] | 0.796 | 0.55 | 0.5 |
| OSTWR | 0.15 | [0.1, 0.35] | 0.17 | 0.167 | 0.17 |
| OSSOR | 0.5 | [0.18, 0.7] | 0.628 | 0.633 | 0.627 |
| OSBITHR | 0.15 | [0.1, 0.3] | 0.12 | 0.14 | 0.12 |
| TPMR | 0.5 | [0.4, 0.9] | 0.86 | 0.7 | 0.59 |
| MTH (mm) | 4 | [3, 5.5] | 3.5 | 3.5 | 3.5 |
| Symbols | Initials | Restrictions | Optimal |
|---|---|---|---|
| SR | 0.5 | [0.3, 0.75] | 0.52 |
| OSTWR | 0.2 | [0.1, 0.3] | 0.185 |
| OSSOR | 0.5 | [0.3, 0.9] | 0.58 |
| OSBITHR | 0.15 | [0.1, 0.3] | 0.133 |
| TPMR | 1 | [0.6, 1] | 0.85 |
| Machines | SPSS-SPMTM | PS-SPSS-SPMTM | PS-SPSS-IPMTM-1 | PS-SPSS-IPMTM-2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total machine volume (cm3) | 181.64 | 181.64 | 181.64 | 181.64 |
| PM volume (cm3) | 9.26 | 10.58 | 12.95 | 19.88 |
| Mover mass (g) | 609.9 | 146.87 | 146.87 | 146.87 |
| Thrust force (Nm) | 161.57 | 95.28 | 81.27 | 117.51 |
| Force per PM volume (Nm/cm3) | 17.45 | 9.01 | 6.28 | 5.91 |
| Force to mass ratio (Nm/g) | 0.26 | 0.65 | 0.55 | 0.80 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, Z.-Q.; Shuraiji, A.L.; Lu, Q.; Li, Y.; Qu, H. Novel Single-Phase Short-Stroke Tubular Permanent Magnet Oscillating Machines with Partitioned Stator. Energies 2021, 14, 1863. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14071863
Zhu Z-Q, Shuraiji AL, Lu Q, Li Y, Qu H. Novel Single-Phase Short-Stroke Tubular Permanent Magnet Oscillating Machines with Partitioned Stator. Energies. 2021; 14(7):1863. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14071863
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Zi-Qiang, Ahlam Luaibi Shuraiji, Qinfen Lu, Yanxin Li, and Huan Qu. 2021. "Novel Single-Phase Short-Stroke Tubular Permanent Magnet Oscillating Machines with Partitioned Stator" Energies 14, no. 7: 1863. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14071863
APA StyleZhu, Z.-Q., Shuraiji, A. L., Lu, Q., Li, Y., & Qu, H. (2021). Novel Single-Phase Short-Stroke Tubular Permanent Magnet Oscillating Machines with Partitioned Stator. Energies, 14(7), 1863. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14071863







