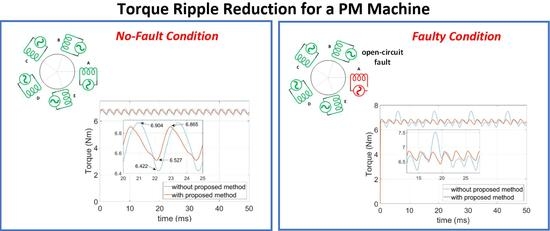
Torque Ripple Reduction Method in a Multiphase PM Machine for No-Fault and Open-Circuit Fault-Tolerant Conditions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
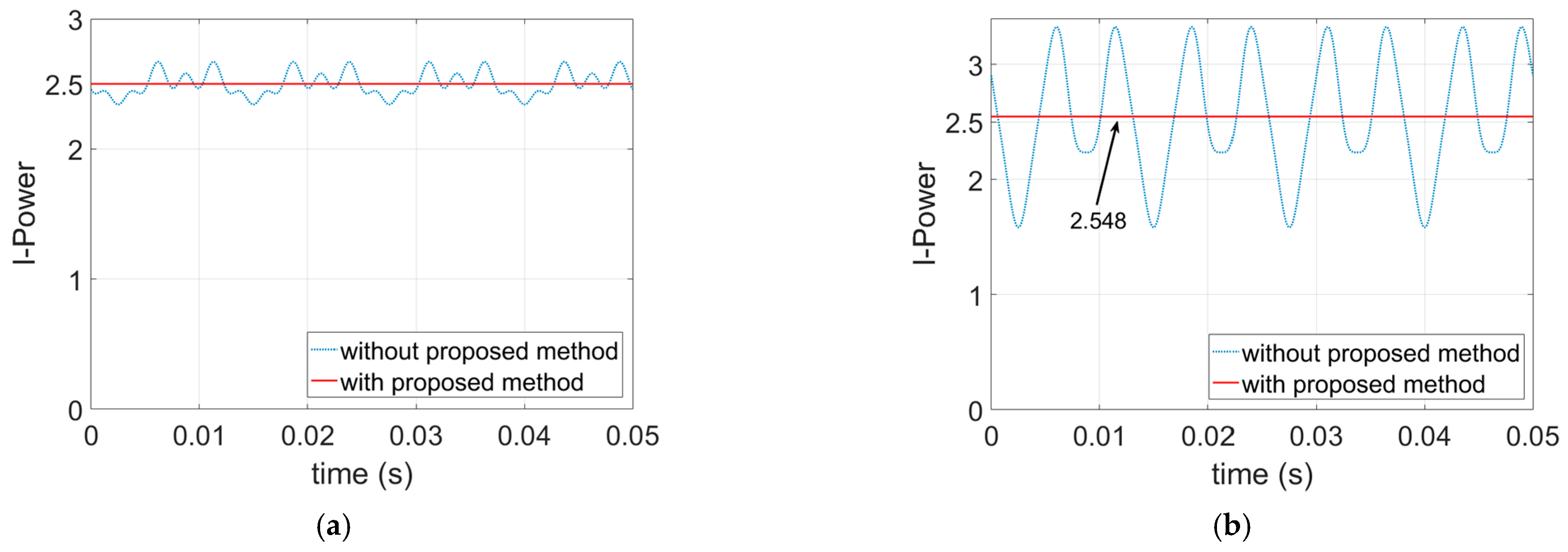
2. Instantaneous Power Approach
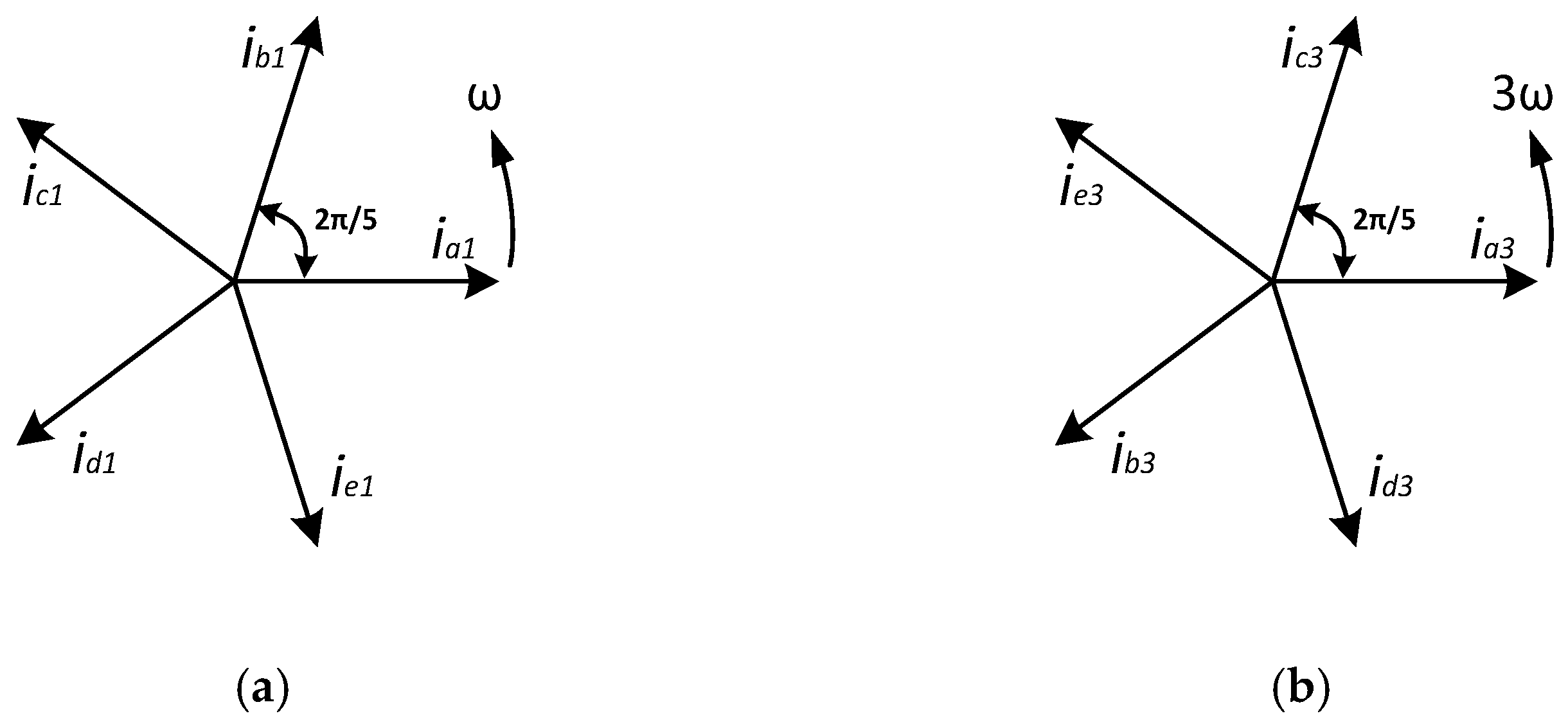
3. Methodology of Proposed Torque Ripple Reduction Method
4. Torque Ripple Reduction Method for the No-Fault Condition
5. Torque Ripple Reduction for the Open-Circuit Fault-Tolerant Conditions
5.1. Single Phase Open-Circuit Fault-Tolerant Currents
5.2. Adjacent Double Phase Open-Circuit Fault-Tolerant Currents
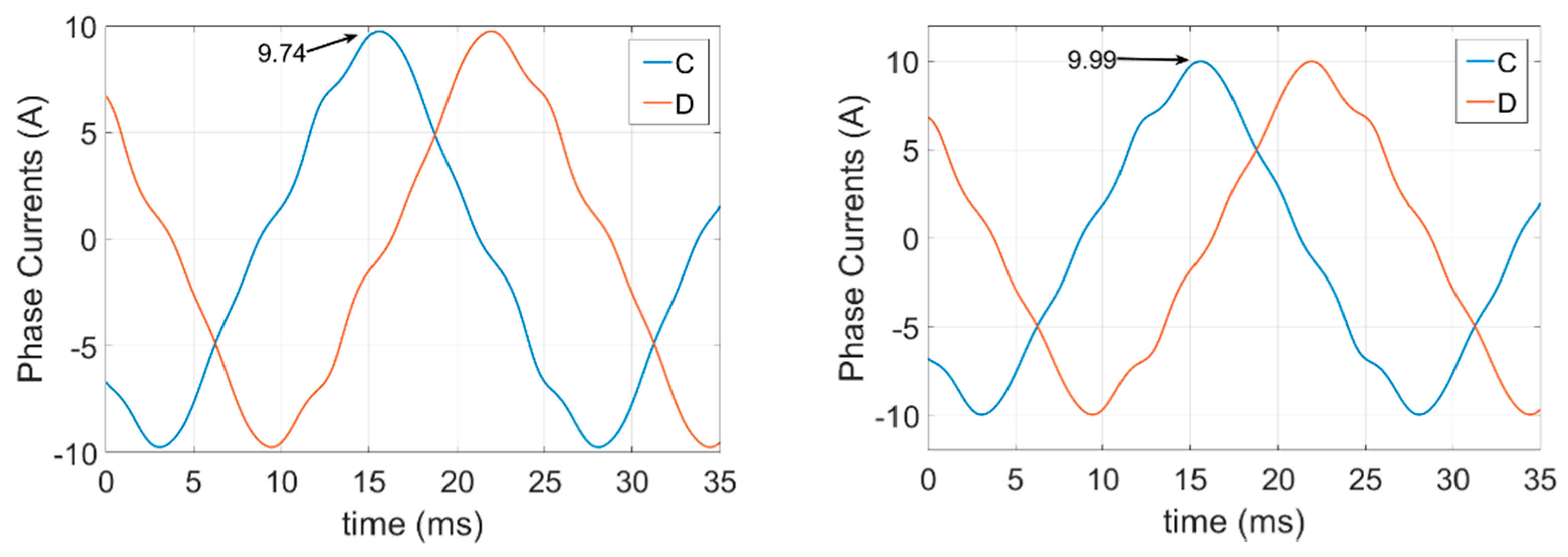
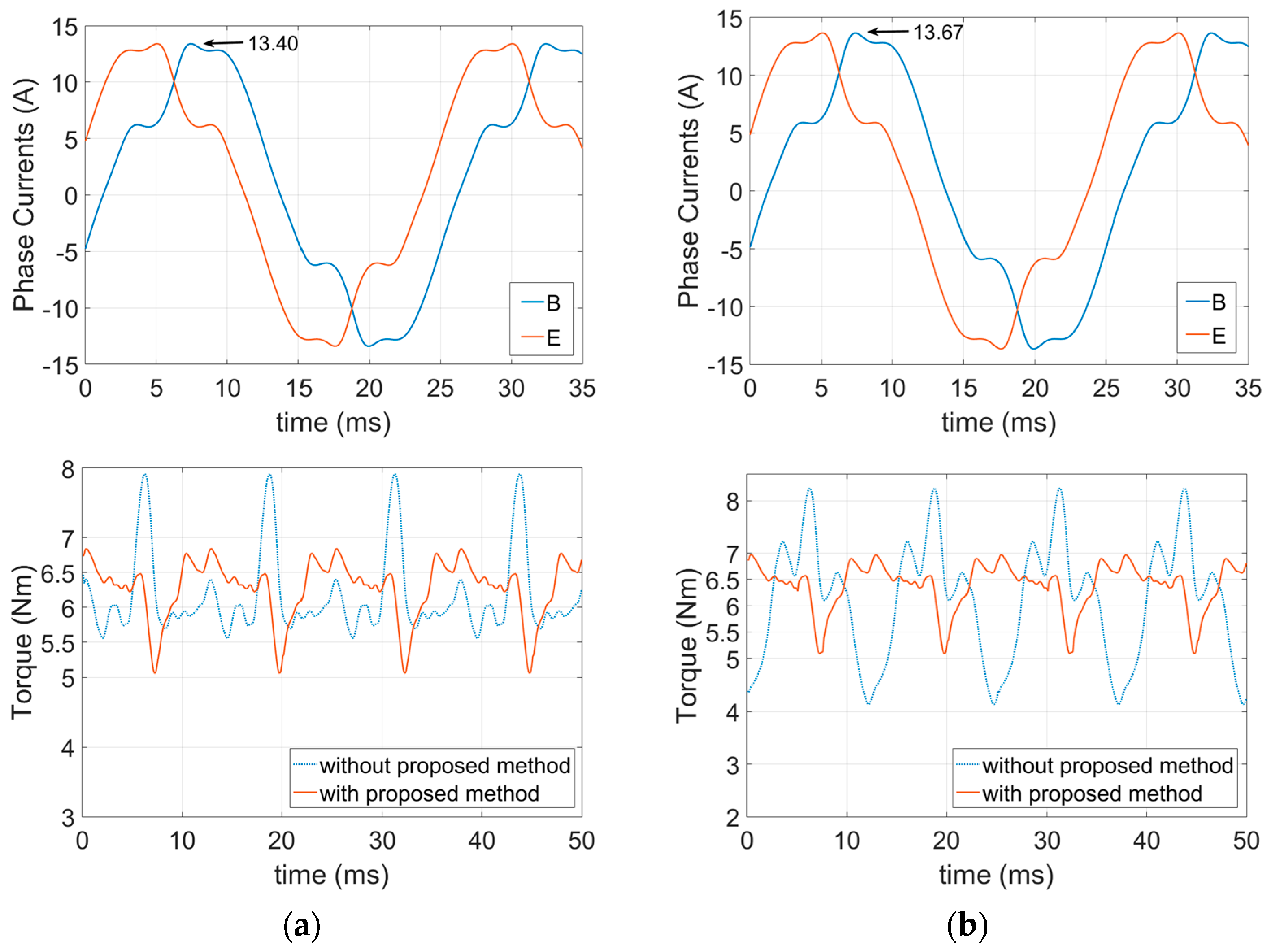
5.3. Nonadjacent Double Phase Open-Circuit Fault-Tolerant Currents
5.4. Adjacent Three-Phase Open-Circuit Fault-Tolerant Currents
5.5. Nonadjacent Three-Phase Open-Circuit Fault-Tolerant Currents
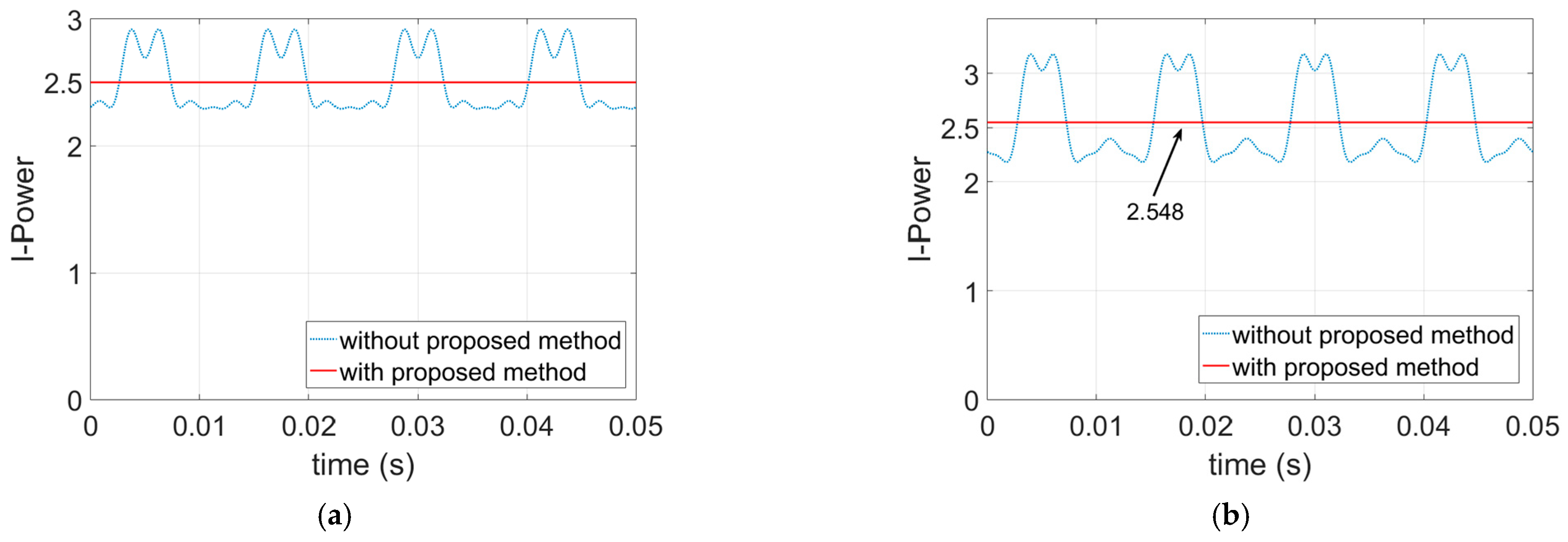
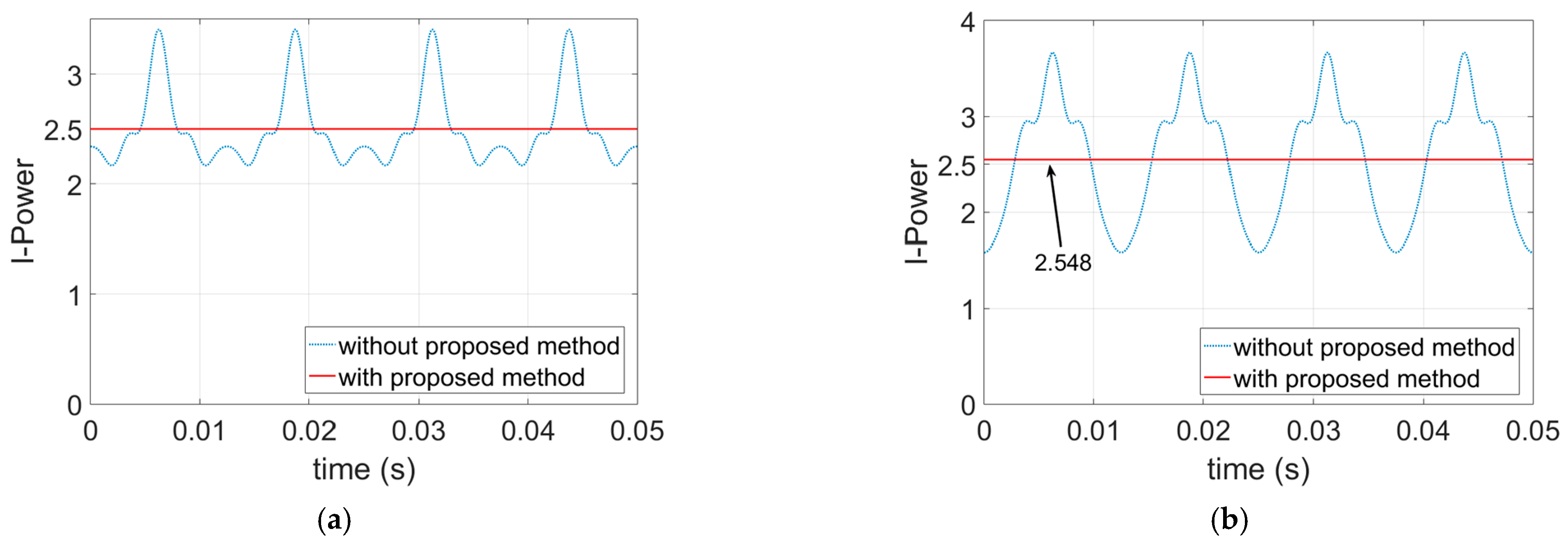
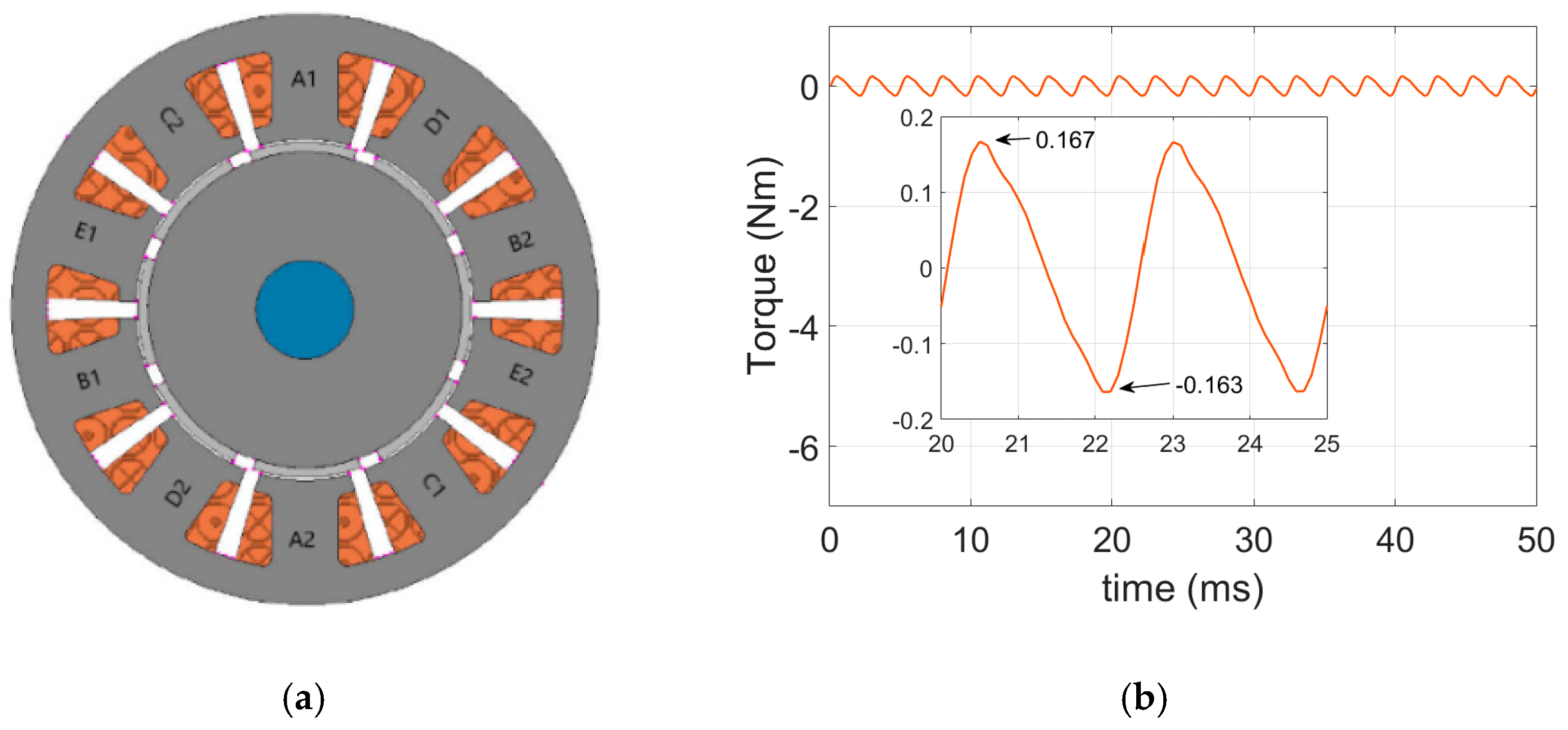
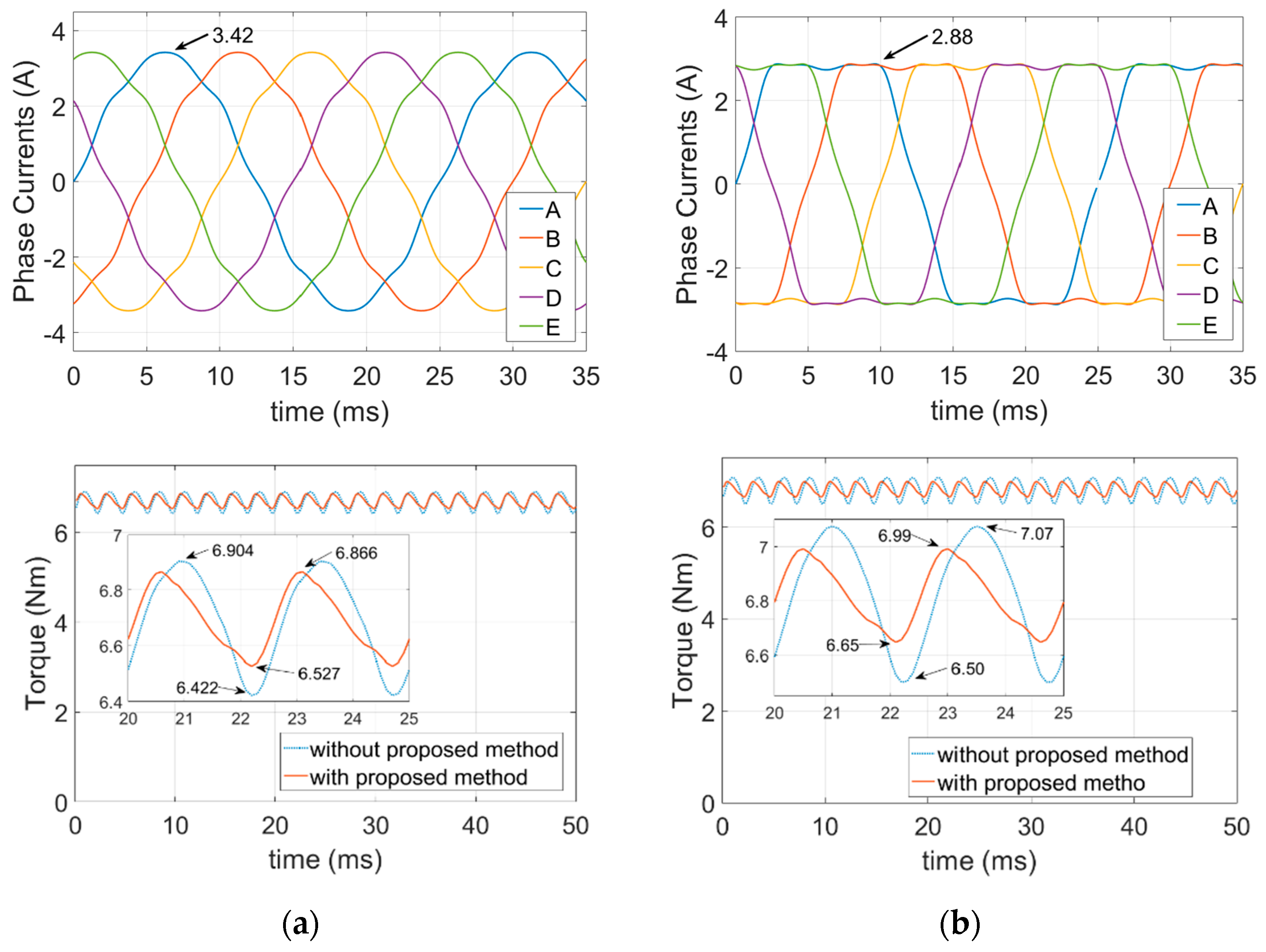
6. FEA Simulation Results of the Proposed Method
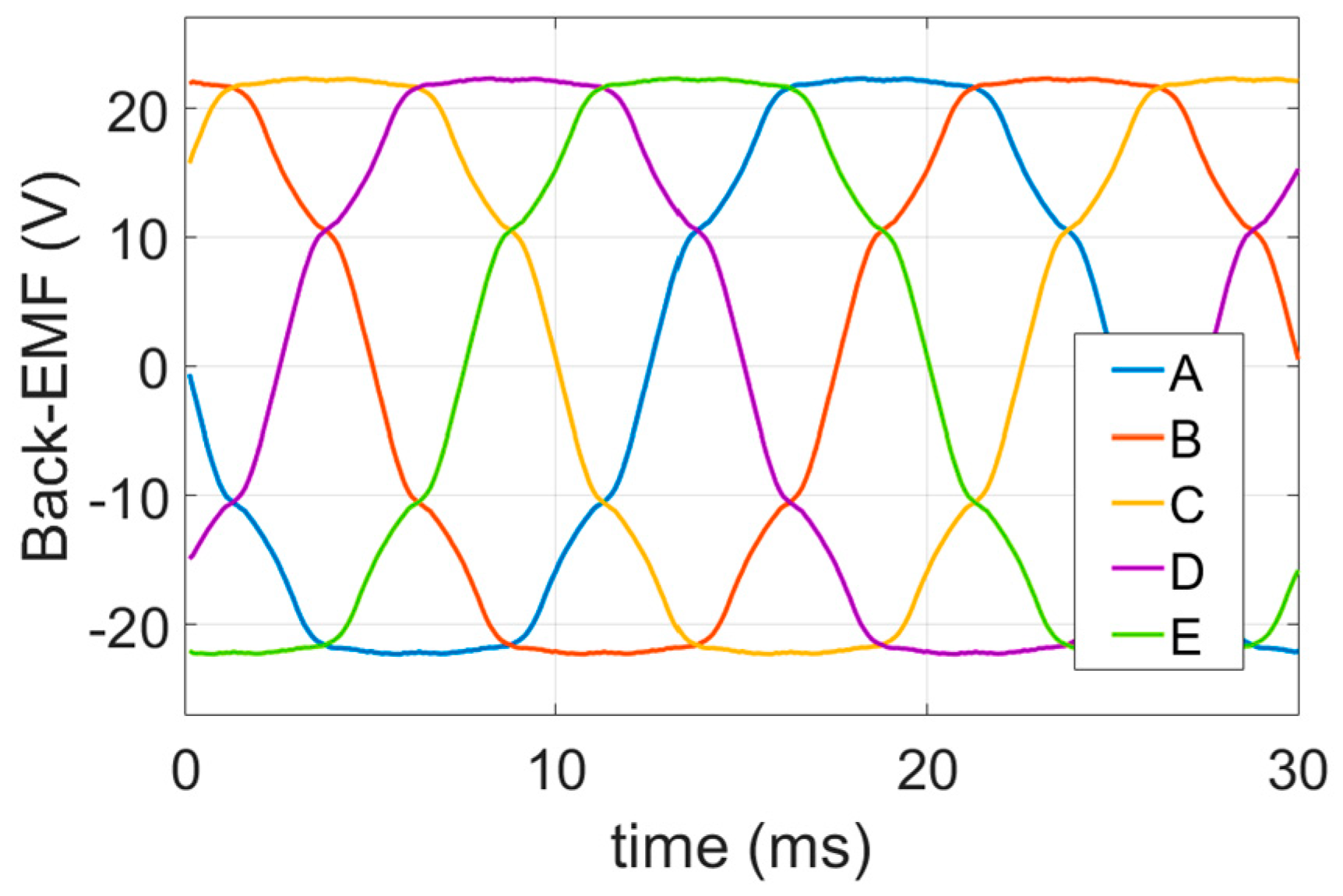
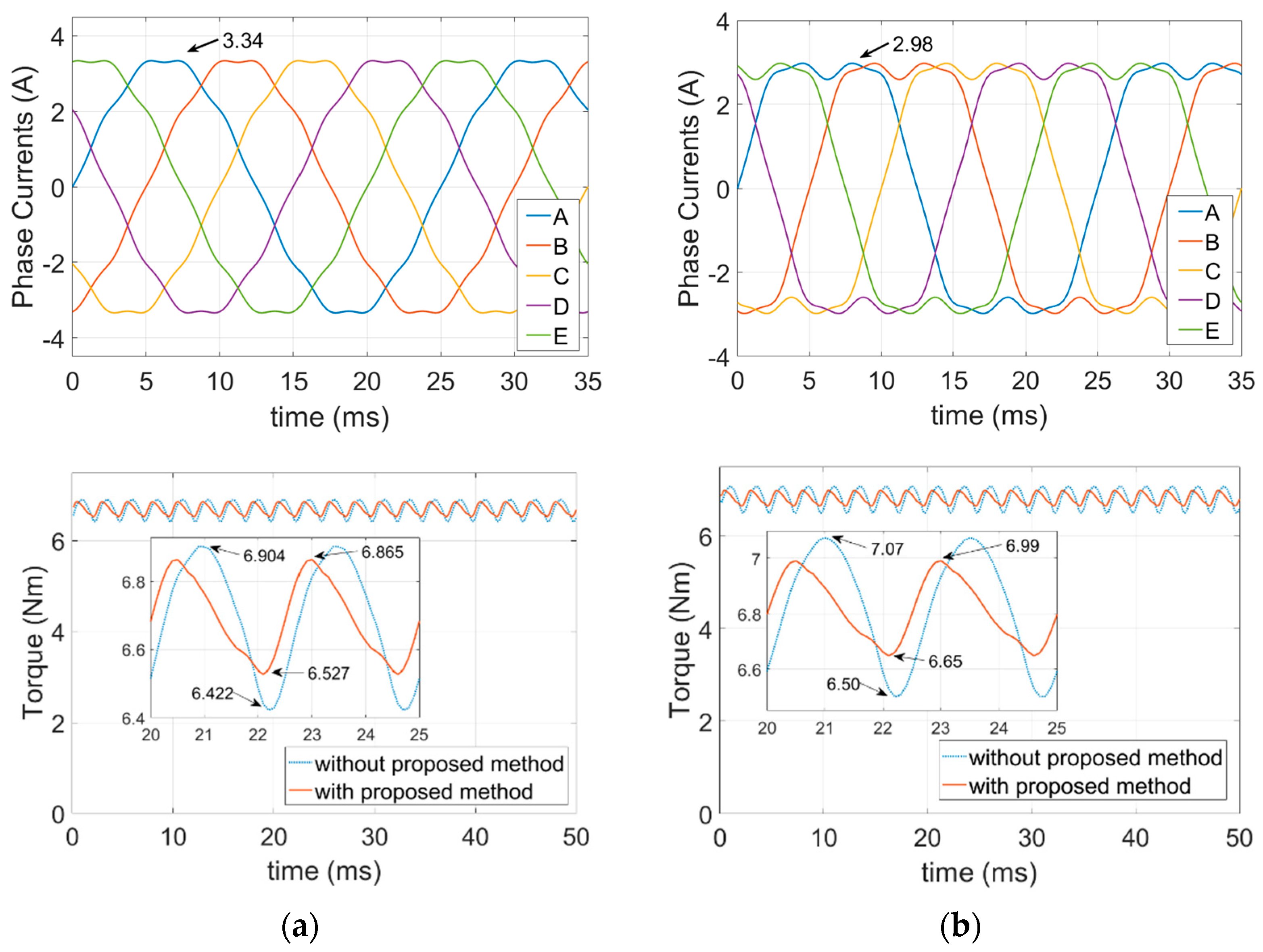
6.1. FEA Simulations of the Healthy Condition
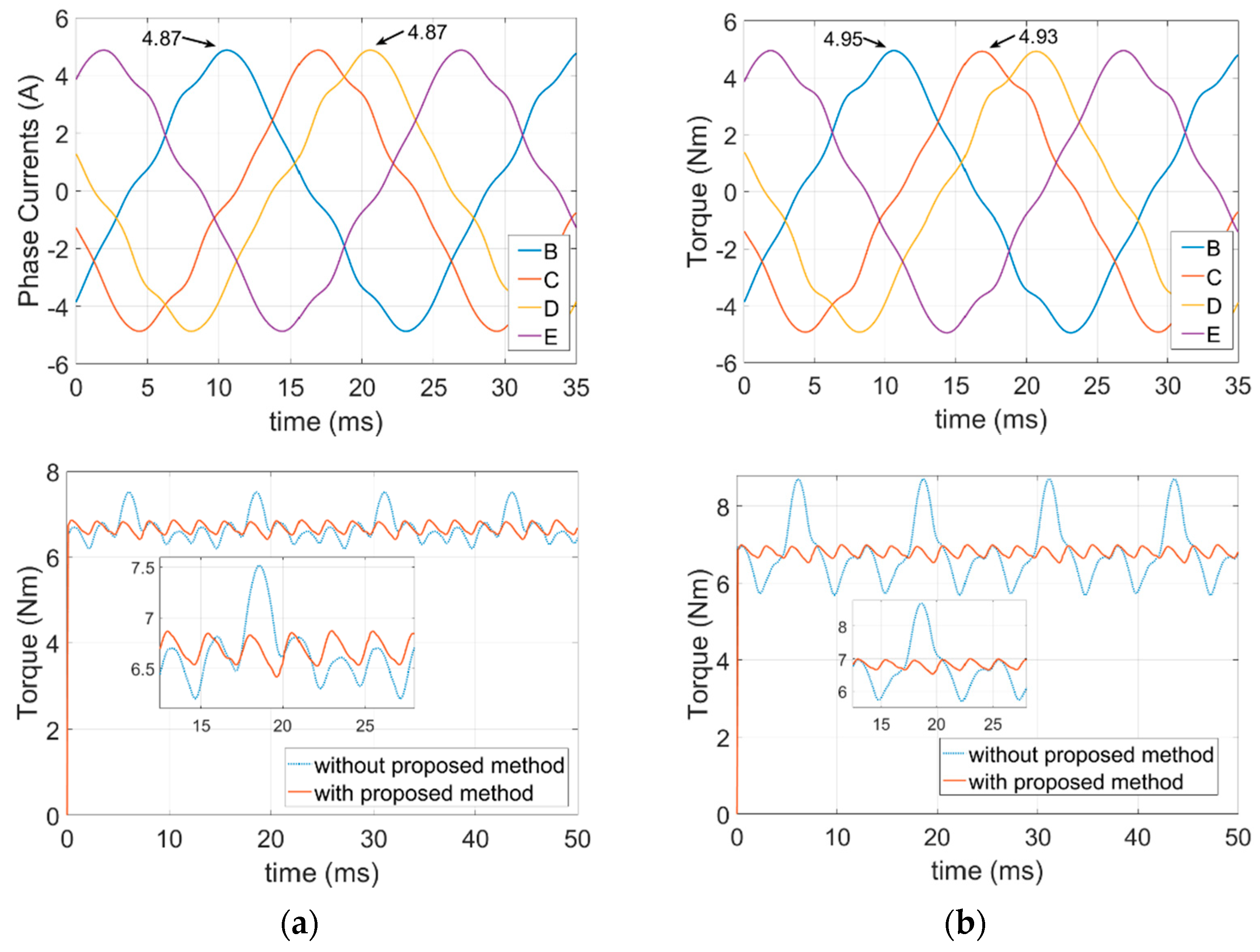
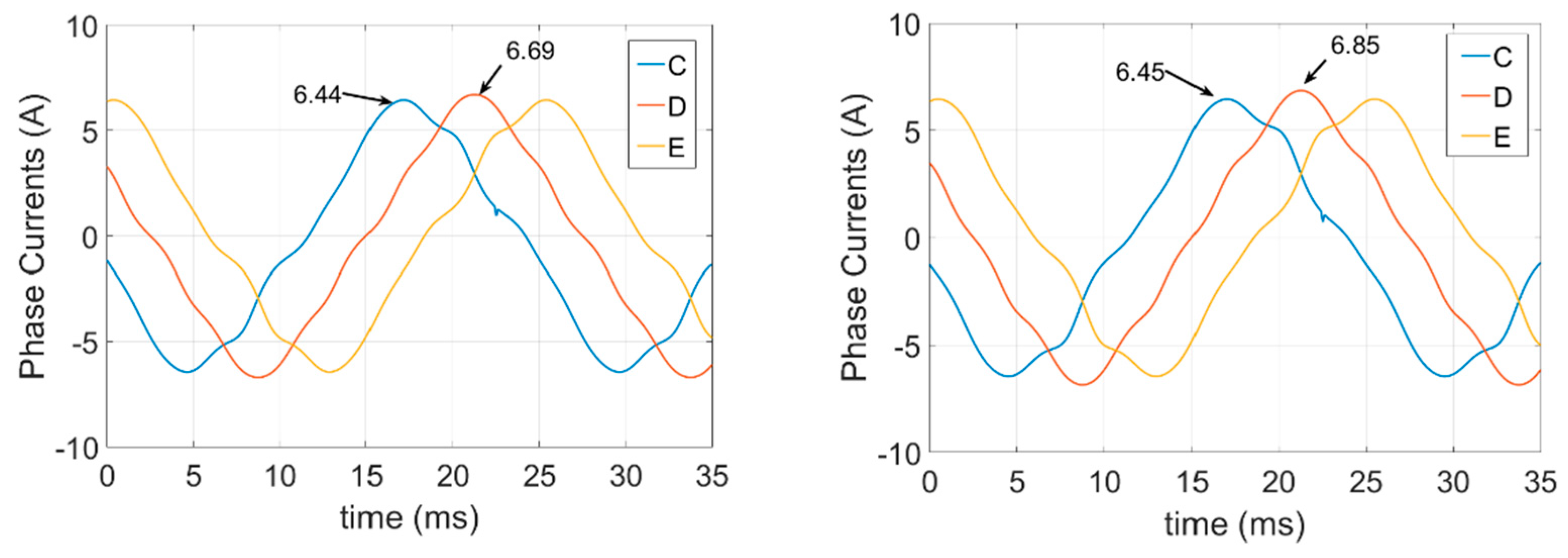
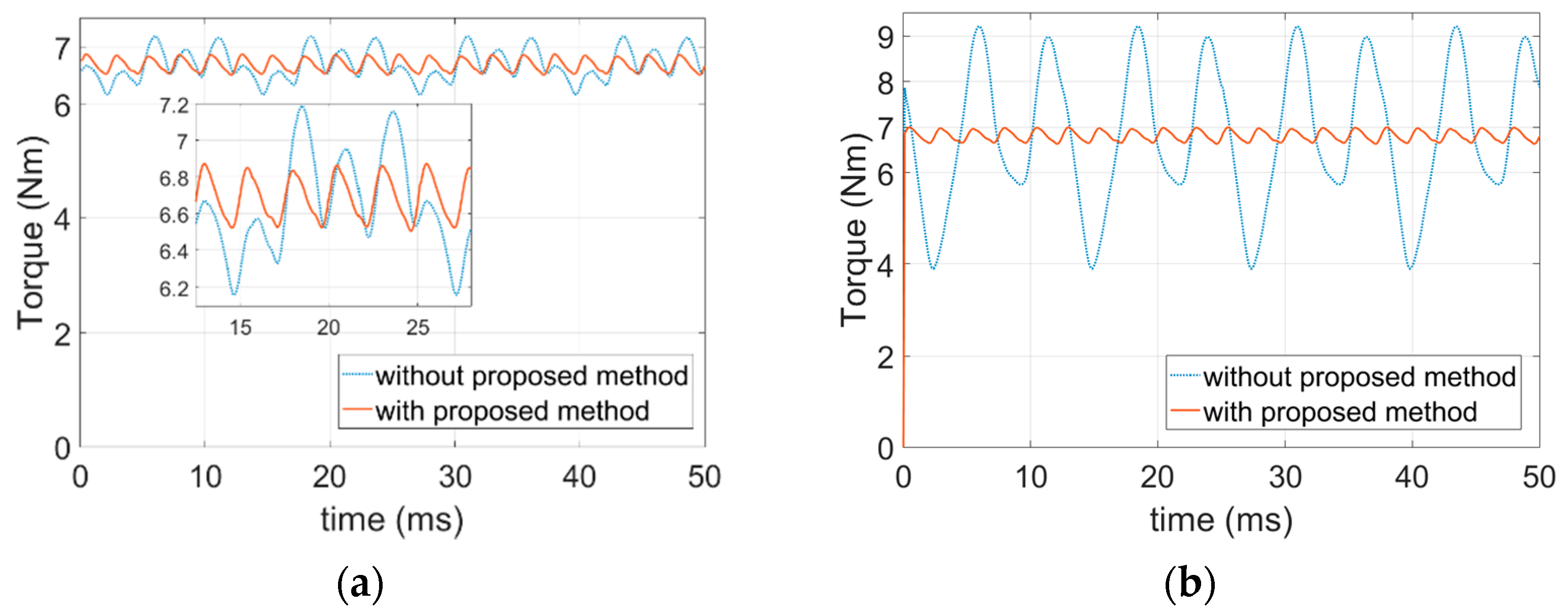
6.2. FEA Simulations of the Open-Circuit Fault-Tolerant Conditions
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Levi, E. Multiphase electric machines for variable-speed applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2008, 55, 1893–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levi, E. Advances in converter control and innovative exploitation of additional degrees of freedom for multiphase machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 63, 433–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parsa, L. On advantages of multi-phase machines. In Proceedings of the IECON 2005—31st Annual Conference of IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Raleigh, NC, USA, 6–10 November 2005; p. 6. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Zheng, P.; Sui, Y.; Zheng, J.; Yin, Z.; Cheng, L. Third Harmonic Current Injection in Different Operating Stages of Five-Phase PMSM With Hybrid Single/Double Layer Fractional-Slot Concentrated Winding. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 15670–15685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervone, A.; Slunjski, M.; Levi, E.; Brando, G. Optimal Third-Harmonic Current Injection for Asymmetrical Multiphase Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2021, 68, 2772–2783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Slunjski, M.; Jones, M.; Levi, E. Control of a symmetrical nine-phase PMSM with highly non-sinusoidal back-electromotive force using third harmonic current injection. In Proceedings of the IECON 2019—45th Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Lisbon, Portugal, 14–17 October 2019; Volume 1, pp. 969–974. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, K.; Sun, H.; Zhu, S. Multiphase PM machines with Halbach array considering third harmonic flux density. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 66, 9184–9193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Zhang, J.; Gu, Z.; Sun, H.; Zhu, Z. Torque improvement of dual three-phase permanent magnet machine using zero sequence components. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2017, 53, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, Y.; Zheng, P.; Fan, Y.; Zhao, J. Research on the vector control strategy of five-phase permanent-magnet synchronous machine based on third-harmonic current injection. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Electric Machines and Drives Conference (IEMDC), Miami, FL, USA, 21–24 May 2017; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, M.; Centner, M.; Stiebler, M. Five-phase permanent magnet synchronous machine under consideration of the third current harmonic. In Proceedings of the 2016 XXII International Conference on Electrical Machines (ICEM), Lausanne, Switzerland, 4–7 September 2016; pp. 2784–2788. [Google Scholar]
- Scuiller, F.; Zahr, H.; Semail, E. Maximum reachable torque, power and speed for five-phase SPM machine with low armature reaction. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2016, 31, 959–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scuiller, F. Magnet shape optimization to reduce pulsating torque for a five-phase permanent-magnet low-speed machine. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2013, 50, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parsa, L.; Toliyat, H.A. Five-phase permanent-magnet motor drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2005, 41, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toliyat, H.A.; Rahimian, M.M.; Lipo, T. dq modeling of five phase synchronous reluctance machines including third harmonic of air-gap MMF. In Proceedings of the Conference Record of the 1991 IEEE Industry Applications Society Annual Meeting, Dearborn, MI, USA, 28 September–4 October 1991; pp. 231–237. [Google Scholar]
- Levi, E.; Barrero, F.; Duran, M.J. Multiphase machines and drives—Revisited. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 429–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jones, M.; Levi, E.; Vukosavic, S.; Toliyat, H. Independent vector control of a seven-phase three-motor drive system supplied from a single voltage source inverter. In Proceedings of the PESC’03—IEEE 34th Annual Conference on Power Electronics Specialist, Acapulco, Mexico, 15–19 June 2003; Volume 4, pp. 1865–1870. [Google Scholar]
- Levi, E.; Iqbal, A.; Vukosavic, S.; Toliyat, H. Modeling and control of a five-phase series-connected two-motor drive. In Proceedings of the IECON’03—29th Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society (IEEE Cat. No. 03CH37468), Roanoke, VA, USA, 2–6 November 2003; Volume 1, pp. 208–213. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, M.; Vukosavic, S.N.; Levi, E.; Iqbal, A. A novel six-phase series-connected two-motor drive with decoupled dynamic control. In Proceedings of the Conference Record of the 2004 IEEE Industry Applications Conference—39th IAS Annual Meeting, Seattle, WA, USA, 3–7 October 2004; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Levi, E.; Jones, M.; Vukosavic, S.N.; Toliyat, H.A. A novel concept of a multiphase, multimotor vector controlled drive system supplied from a single voltage source inverter. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2004, 19, 320–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, M.; Vukosavic, S.; Levi, E. Combining induction and permanent magnet synchronous machines in a series-connected six-phase vector-controlled two-motor drive. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE 36th Power Electronics Specialists Conference, Dresden, Germany, 16 June 2005; pp. 2691–2697. [Google Scholar]
- Levi, E.; Jones, M.; Vukosavic, S.N. A series-connected two-motor six-phase drive with induction and permanent magnet machines. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2006, 21, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levi, E.; Jones, M.; Vukosavic, S.N.; Iqbal, A.; Toliyat, H.A. Modeling, control, and experimental investigation of a five-phase series-connected two-motor drive with single inverter supply. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2007, 54, 1504–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsa, L.; Toliyat, H.A. Fault-tolerant five-phase permanent magnet motor drives. In Proceedings of the Conference Record of the 2004 IEEE Industry Applications Conference—39th IAS Annual Meeting, Seattle, WA, USA, 3–7 October 2004; Volume 2, pp. 1048–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwari, S.; Parsa, L. An Optimal Control Technique for Multiphase PM Machines Under Open-Circuit Faults. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2008, 55, 1988–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwari, S.; Parsa, L. Fault-Tolerant Control of Five-Phase Permanent-Magnet Motors With Trapezoidal Back EMF. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2011, 58, 476–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadpour, A.; Sadeghi, S.; Parsa, L. A generalized fault-tolerant control strategy for five-phase PM motor drives considering star, pentagon, and pentacle connections of stator windings. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2013, 61, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadpour, A.; Parsa, L. Global fault-tolerant control technique for multiphase permanent-magnet machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2014, 51, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Gao, X.; Li, B.; Liu, X.; Guan, X. Open-phase fault tolerance techniques of five-phase dual-rotor permanent magnet synchronous motor. Energies 2015, 8, 12810–12838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, Y.; Zheng, P.; Yin, Z.; Wang, M.; Wang, C. Open-circuit fault-tolerant control of five-phase PM machine based on reconfiguring maximum round magnetomotive force. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 66, 48–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, R.; Husain, I.; Fardoun, A.; McLaughlin, K. Permanent-Magnet Synchronous Motor Magnet Designs With Skewing for Torque Ripple and Cogging Torque Reduction. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2009, 45, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flieller, D.; Nguyen, N.K.; Wira, P.; Sturtzer, G.; Abdeslam, D.O.; Mercklé, J. A self-learning solution for torque ripple reduction for nonsinusoidal permanent-magnet motor drives based on artificial neural networks. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2013, 61, 655–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gómez-Espinosa, A.; Hernández-Guzmán, V.M.; Bandala-Sánchez, M.; Jiménez-Hernández, H.; Rivas-Araiza, E.A.; Rodríguez-Reséndiz, J.; Herrera-Ruíz, G. A new adaptive self-tuning Fourier coefficients algorithm for periodic torque ripple minimization in permanent magnet synchronous motors (PMSM). Sensors 2013, 13, 3831–3847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Z.; Sun, D.; Zhu, J. Torque ripple suppression of open-winding PMSMs by current injection considering magnetic saturation. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Vehicle Power and Propulsion Conference (VPPC), Hangzhou, China, 17–20 October 2016; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhu, W.; Xu, L. Research on Torque Ripple Suppression of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2018, 170, 042129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Gui, X. Torque Ripple Suppression Based Fast Harmonics Decomposition. In Proceedings of the 2019 22nd International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (ICEMS), Harbin, China, 11–14 August 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Q.; Wei, F.; Li, Z.; Deng, Y.; Wang, Y. Torque Ripple Suppression of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Based On Robust Current Injection. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 782, 032082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, K.; Gu, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Wu, Z. Optimum injected harmonics into magnet shape in multiphase surface-mounted PM machine for maximum output torque. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 4434–4443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, N.; Bolognani, S. Design techniques for reducing the cogging torque in surface-mounted PM motors. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2002, 38, 1259–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsa, L.; Hao, L. Interior Permanent Magnet Motors With Reduced Torque Pulsation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2008, 55, 602–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Liao, Y.; Lin, H.; Sun, J. Torque ripple suppression of permanent magnet synchronous machines by minimal harmonic current injection. IET Power Electron. 2019, 12, 1368–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jędryczka, C.; Danielczyk, D.; Szeląg, W. Torque Ripple Minimization of the Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machine by Modulation of the Phase Currents. Sensors 2020, 20, 2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arafat, A.; Choi, S. Active current harmonic suppression for torque ripple minimization at open-phase faults in a five-phase PMa-SynRM. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 66, 922–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Wu, L.; Huang, X.; Fang, Y.; Liu, J. Adaptive Torque Ripple Suppression Methods of Three-Phase PMSM During Single-Phase Open-Circuit Fault-Tolerant Operation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2020, 56, 4955–4965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akay, A.; Lefley, P. Research on torque ripple under healthy and open-circuit fault-tolerant conditions in a PM multiphase machine. CES Trans. Electr. Mach. Syst. 2020, 4, 349–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Rated Power (kW) | 1 |
| Rated Speed (rpm) | 2000 |
| Rated Current (Amps)(Peak) | 3.39 |
| Rated Torque (Nm) | 6.6966 |
| Number of Poles | 8 |
| Number of slots | 10 |
| Only Fundamental Current | Fundamental + Third Harmonic Current | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| without Proposed Method | with Proposed Method | without Proposed Method | with Proposed Method | |||||
| Average | Ripple (%) | Average | Ripple (%) | Average | Ripple (%) | Average | Ripple (%) | |
| Healthy1 | 6.6964 | 7.1934 | 6.6943 | 5.0640 | 6.8233 | 8.4299 | 6.8179 | 5.0705 |
| Healthy2 | 6.6964 | 7.1934 | 6.6942 | 5.0417 | 6.8233 | 8.4299 | 6.8189 | 5.0399 |
| A Open | 6.6721 | 19.7249 | 6.6753 | 6.7930 | 6.7772 | 44.5119 | 6.8009 | 6.9170 |
| A and B Open | 6.6889 | 15.3699 | 6.6869 | 5.5672 | 6.8075 | 78.0180 | 6.8142 | 5.4545 |
| A and C Open | 6.5032 | 23.4750 | 6.5515 | 13.5374 | 6.5829 | 34.5335 | 6.6689 | 13.7595 |
| A, B and E Open | 6.5042 | 22.4154 | 6.5481 | 13.3304 | 6.5873 | 108.1307 | 6.6616 | 13.8070 |
| A, C and D Open | 6.1680 | 38.2906 | 6.2744 | 28.5654 | 6.1080 | 67.1371 | 6.3800 | 29.5695 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Akay, A.; Lefley, P. Torque Ripple Reduction Method in a Multiphase PM Machine for No-Fault and Open-Circuit Fault-Tolerant Conditions. Energies 2021, 14, 2615. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14092615
Akay A, Lefley P. Torque Ripple Reduction Method in a Multiphase PM Machine for No-Fault and Open-Circuit Fault-Tolerant Conditions. Energies. 2021; 14(9):2615. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14092615
Chicago/Turabian StyleAkay, Ali, and Paul Lefley. 2021. "Torque Ripple Reduction Method in a Multiphase PM Machine for No-Fault and Open-Circuit Fault-Tolerant Conditions" Energies 14, no. 9: 2615. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14092615
APA StyleAkay, A., & Lefley, P. (2021). Torque Ripple Reduction Method in a Multiphase PM Machine for No-Fault and Open-Circuit Fault-Tolerant Conditions. Energies, 14(9), 2615. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14092615