Designing for the Environment: An Example of Multi-Criteria Analysis Used for Solar Hot Water System Selection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Solar Hot Water Systems: Economic Evaluation
3.2. Solar Hot Water Systems: Energy Balance
3.3. Solar Hot Water Systems: Environmental Impact Indicators
3.4. Solar Hot Water Systems: Multi-Criteria Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Van Ruijven, B.J.; De Cian, E.; Wing, I.S. Amplification of future energy demand growth due to climate change. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jackson, R.B.; Le Quéré, C.; Andrew, R.M.; Canadell, J.G.; Korsbakken, J.I.; Liu, Z.; Peters, G.P.; Zheng, B. Global energy growth is outpacing decarbonization. Environ. Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 120401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Żelazna, A.; Gołębiowska, J.; Zdyb, A.; Pawłowski, A. A Hybrid vs. On-Grid Photovoltaic System: Multicriteria Analysis of Environmental, Economic, and Technical Aspects in Life Cycle Perspective. Energies 2020, 13, 3978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asdrubali, F.; Baldinelli, G.; D’Alessandro, F.; Scrucca, F. Life cycle assessment of electricity production from renewable energies: Review and results harmonization. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 42, 1113–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Żelazna, A.; Zdyb, A.; Pawłowski, A. The influence of selected factors on PV systems environmental indicators. Annu. Set Environ. Prot. 2016, 18, 722–732. [Google Scholar]
- Olczak, P.; Matuszewska, D.; Zabagło, J. The Comparison of Solar Energy Gaining Effectiveness between Flat Plate Collectors and Evacuated Tube Collectors with Heat Pipe: Case Study. Energies 2020, 13, 1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mularczyk, A.; Husa, B. Rozwój i perspektywy energii solarnej w Polsce i Województwie Śląskim. Zesz. Naukowe. Organ. Zarządzanie Politech. Śląska 2015, 86, 361–377. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Olczak, P. The comparison of solar installation heat gains and SHW simulation results–case study. Polityka Energetyczna 2020, 23, 41–54. (In Polish) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hang, Y.; Qu, M.; Zhao, F. Economic and environmental life cycle analysis of solar hot water systems in the United States. Energy Build. 2012, 45, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souliotis, M.; Arnaoutakis, N.; Panaras, G.; Kavga, A.; Papaefthimiou, S. Experimental study and Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) of Hybrid Photovoltaic/Thermal (PV/T) solar systems for domestic applications. Renew. Energy 2018, 126, 708–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saint, R.M.; Pomponi, F.; Currie, J.I. A method for a cradle-to-cradle life cycle assessment of integrated collector-storage solar water heaters. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 556, 012061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kalogirou, S. Thermal performance, economic and environmental life cycle analysis of thermosiphon solar water heaters. Sol. Energy 2009, 83, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Żelazna, A. The influence of collector type on emission indicators in solar systems life cycle assessment. Annu. Set Environ. Prot. 2013, 15, 258–271. [Google Scholar]
- Głuszek, A.; Magiera, J.; Neupauer, K. Analiza cyklu życia (LCA) cieczowego kolektora słonecznego. Inżynieria Apar. Chem. 2010, 49, 35–36. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Koroneos, C.J.; Nanaki, E.A. Life cycle environmental impact assessment of solar water heater. J. Clean. Prod. 2012, 37, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altun-Ciftcioglu, G.A.; Gokulu, O.; Kardigan, F.; Kardigan, M.A.N. Life cycle (LCA) of solar selective surface produced by continuous process and solar flat collectors. Sol. Energy 2016, 135, 284–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comodi, G.; Bevilacqua, M.; Caresana, F.; Paciarotti, C.; Pelagalli, L.; Venella, P. Life cycle assessment and energy-CO2-economic payback analyses of renewable domestic hot water systems with unglazed and glazed solar thermal panels. Appl. Energy 2016, 164, 944–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milousi, M.; Souliotis, M.; Arampatzis, G.; Papaefthimiou, S. Evaluating the Environmental Performance of Solar Energy Systems Through a Combined Life Cycle Assessment and Cost Analysis. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mahmud, M.A.P.; Huda, N.; Farjana, S.H.; Lang, C. Environmental Impacts of Solar-Photovoltaic and Solar-Thermal Systems with Life-Cycle Assessment. Energies 2018, 11, 2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Laborderie, A.; Puech, C.; Adra, N.; Blanc, I.; Beloin-Saint-Pierre, D.; Padey, P.; Payet, J.; Sie, M.; Jacquin, P. Environmental Impacts of Solar Thermal Systems with Life Cycle Assessment. In The World Renewable Energy Congress; Linköping University Electronic Press: Linkoping, Sweden, 2011; pp. 8–13. Available online: https://hal-mines-paristech.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-00668172/document (accessed on 10 May 2021).
- Barbir, F. Fuel Cell Applications. In PEM Fuel Cells, Theory and Practice, 2nd ed.; Barbir, F., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2013; pp. 373–434. [Google Scholar]
- Astudillo-Flores, M.; Zalamea-Leon, E.; Pelaez-Samaniego, A.B.E.M.; Calle-Siguencia, J. Modelling of solar thermal energy for household use in equatorial latitude by using the F-Chart model. Renew. Energy Power Qual. J. 2021, 19, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolliet, O.; Margni, M.; Charles, R.; Humbert, S.; Payet, J.; Rebitzer, G.; Rosenbaum, R. IMPACT 2002+: A New Life Cycle Impact Assessment Methodology. Int. J. LCA 2003, 8, 324–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frischknecht, R.; Wyss, F.; Knöpfel, S.B.; Lützkendorf, T.; Balouktsi, M. Cumulative energy demand in LCA: The energy harvested approach. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2015, 20, 957–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Energy Regulatory Office. Available online: https://www.ure.gov.pl/en (accessed on 4 May 2021).
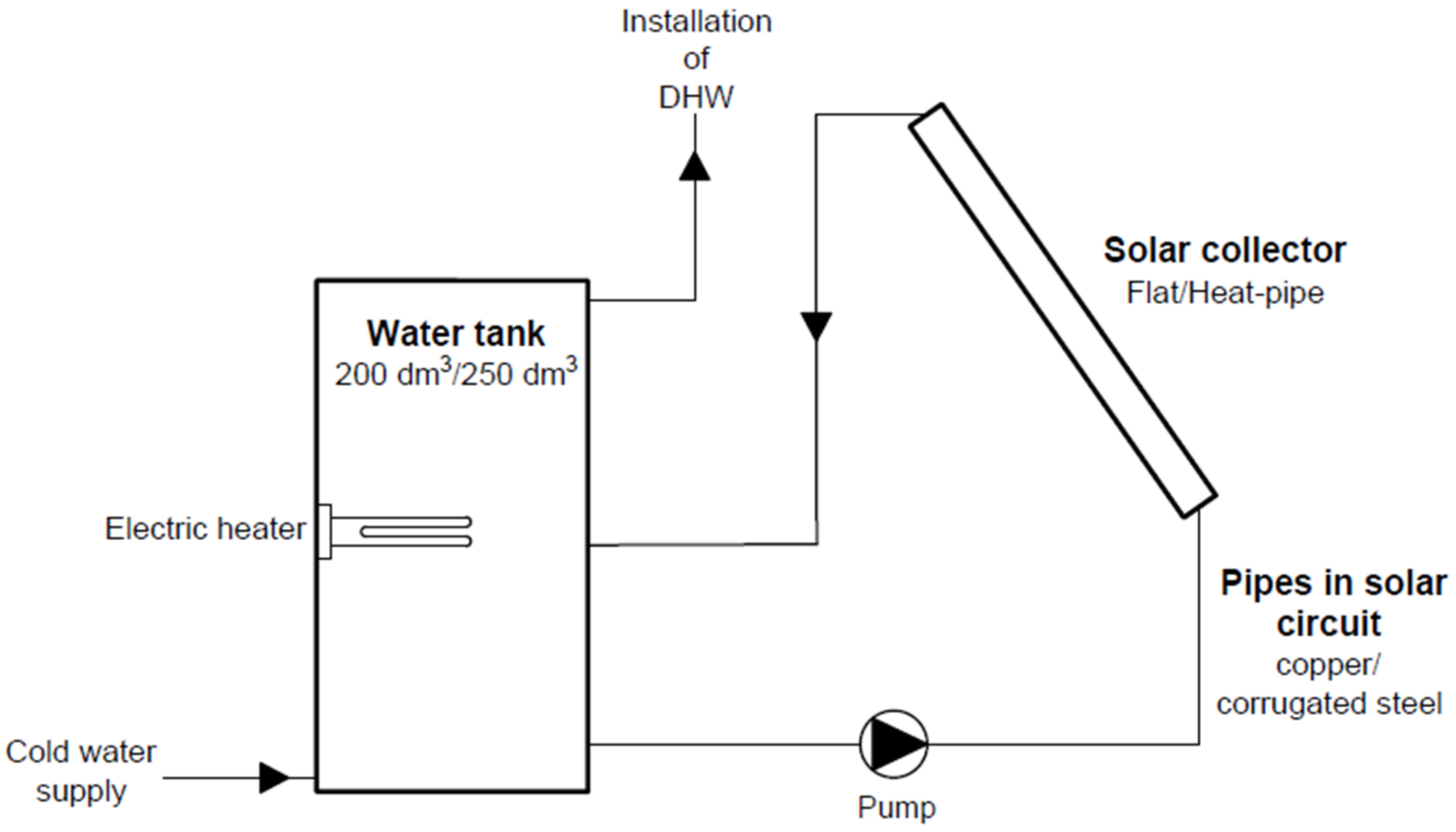



| Variant of Installation | Solar Collector | Absorber Area | Pipes | Water Tank | Solar Energy | Annual Efficiency |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| - | - | m2 | - | dm3 | kWh/yr | % |
| Variant I | Flat-plate, CU absorber | 4.66 | Copper | 200 | 1602 | 30 |
| Variant II | Flat-plate, CU absorber | 4.66 | Copper | 250 | 1627 | 30.5 |
| Variant III | Flat-plate, CU absorber | 4.66 | Steel (corrugated) | 200 | 1576 | 29.5 |
| Variant IV | Flat-plate, CU absorber | 4.66 | Steel (corrugated) | 250 | 1600 | 30 |
| Variant V | Heat pipe | 4.29 | Copper | 200 | 1842 | 37.5 |
| Variant VI | Heat pipe | 4.29 | Copper | 250 | 1865 | 37.9 |
| Variant VII | Heat pipe | 4.29 | Steel (corrugated) | 200 | 1810 | 36.8 |
| Variant VIII | Heat pipe | 4.29 | Steel (corrugated) | 250 | 1834 | 37.3 |
| Variant of Installation | Investment Cost | Pump Operation Cost | Servicing/Utilization Cost | Savings | SPBT * | SPBT ** | SPBT *** |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| - | Euro | Euro/yr | Euro | Euro/yr | Years | Years | Years |
| Variant I | 1795.43 | 13.56 | 220.26 | 164.8 | 12.2 | 9.8 | 4.6 |
| Variant II | 1998.07 | 13.77 | 220.26 | 167.4 | 13.3 | 10.5 | 4.9 |
| Variant III | 1759.91 | 13.34 | 220.26 | 162.1 | 12.2 | 9.8 | 4.6 |
| Variant IV | 1962.56 | 13.54 | 220.26 | 164.6 | 13.3 | 10.6 | 4.9 |
| Variant V | 1871.53 | 15.59 | 220.26 | 189.5 | 11.0 | 8.8 | 4.1 |
| Variant VI | 2074.17 | 15.78 | 220.26 | 191.9 | 12.0 | 9.5 | 4.4 |
| Variant VII | 1836.01 | 15.32 | 220.26 | 186.2 | 11.0 | 8.8 | 4.1 |
| Variant VIII | 2038.66 | 15.52 | 220.26 | 188.7 | 12.0 | 9.5 | 4.4 |
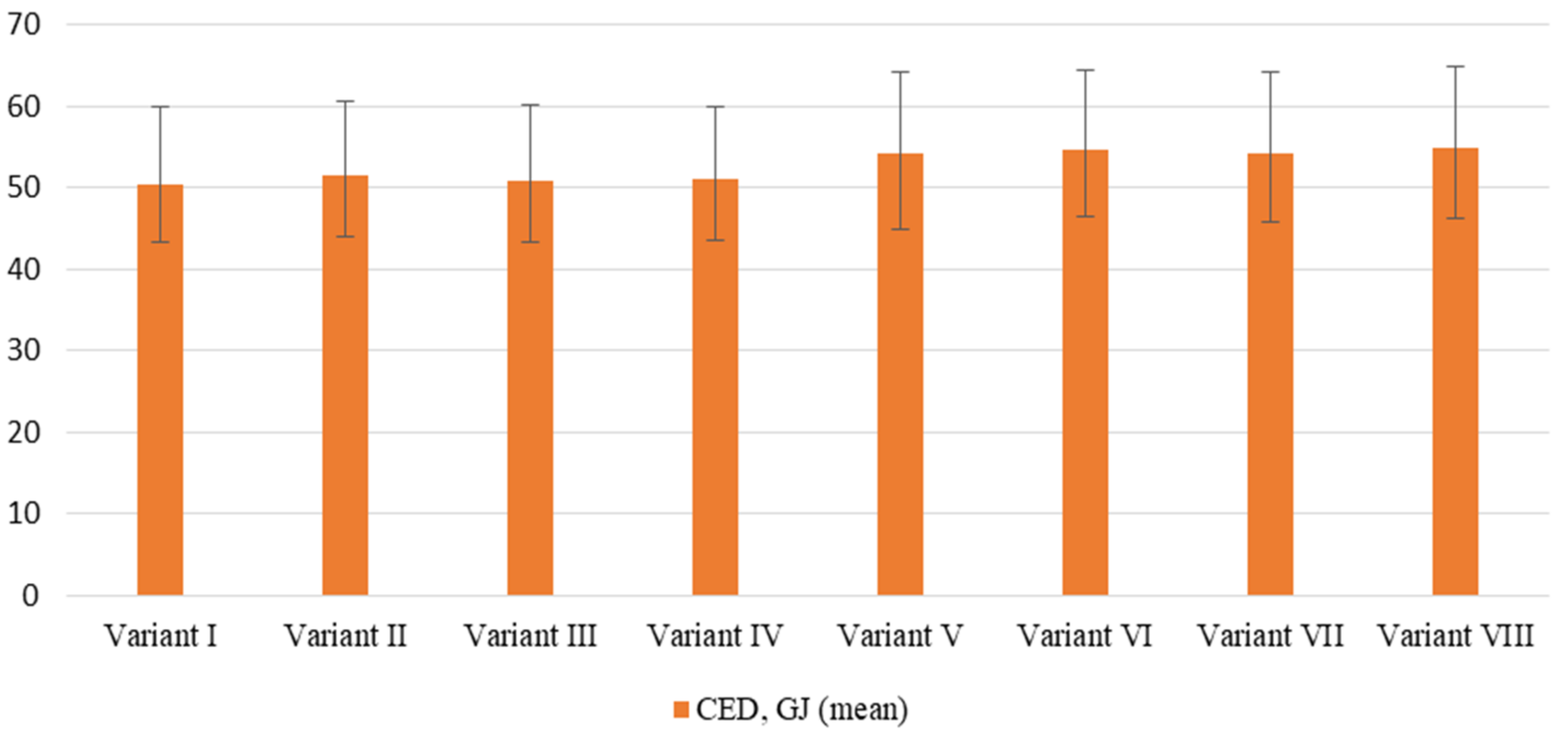
| Variant of Installation | CED | Energy Generated | EPBT |
|---|---|---|---|
| MJ | MJ/yr | Years | |
| Variant I | 50,513.62 | 5767.20 | 8.76 |
| Variant II | 51,545.74 | 5857.20 | 8.80 |
| Variant III | 50,849.69 | 5673.60 | 8.96 |
| Variant IV | 51,364.05 | 5760.00 | 9.00 |
| Variant V | 53,830.63 | 6631.20 | 8.12 |
| Variant VI | 54,819.90 | 6714.00 | 8.17 |
| Variant VII | 54,038.12 | 6516.00 | 8.29 |
| Variant VIII | 55,048.82 | 6602.40 | 8.34 |
| Variant of Installation | SPBT | EPBT | IMPACT 2002+ | WSM Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| - | Years | Years | Pt/kWh | % |
| Variant I | 4.6 | 8.8 | 0.040 | 68% |
| Variant II | 4.9 | 8.8 | 0.040 | 85% |
| Variant III | 4.6 | 9.0 | 0.041 | 83% |
| Variant IV | 4.9 | 9.0 | 0.042 | 100% |
| Variant V | 4.1 | 8.1 | 0.035 | 0% |
| Variant VI | 4.4 | 8.2 | 0.036 | 16% |
| Variant VII | 4.1 | 8.3 | 0.036 | 13% |
| Variant VIII | 4.4 | 8.3 | 0.037 | 29% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Żelazna, A.; Gołębiowska, J. Designing for the Environment: An Example of Multi-Criteria Analysis Used for Solar Hot Water System Selection. Energies 2022, 15, 65. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15010065
Żelazna A, Gołębiowska J. Designing for the Environment: An Example of Multi-Criteria Analysis Used for Solar Hot Water System Selection. Energies. 2022; 15(1):65. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15010065
Chicago/Turabian StyleŻelazna, Agnieszka, and Justyna Gołębiowska. 2022. "Designing for the Environment: An Example of Multi-Criteria Analysis Used for Solar Hot Water System Selection" Energies 15, no. 1: 65. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15010065
APA StyleŻelazna, A., & Gołębiowska, J. (2022). Designing for the Environment: An Example of Multi-Criteria Analysis Used for Solar Hot Water System Selection. Energies, 15(1), 65. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15010065







