An Integrated Energy System Operation Optimization Model for Water Consumption Control Analysis in Park Scale from the Perspective of Energy–Water Nexus
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Power–Gas–Water Nexus in Integrated Energy System
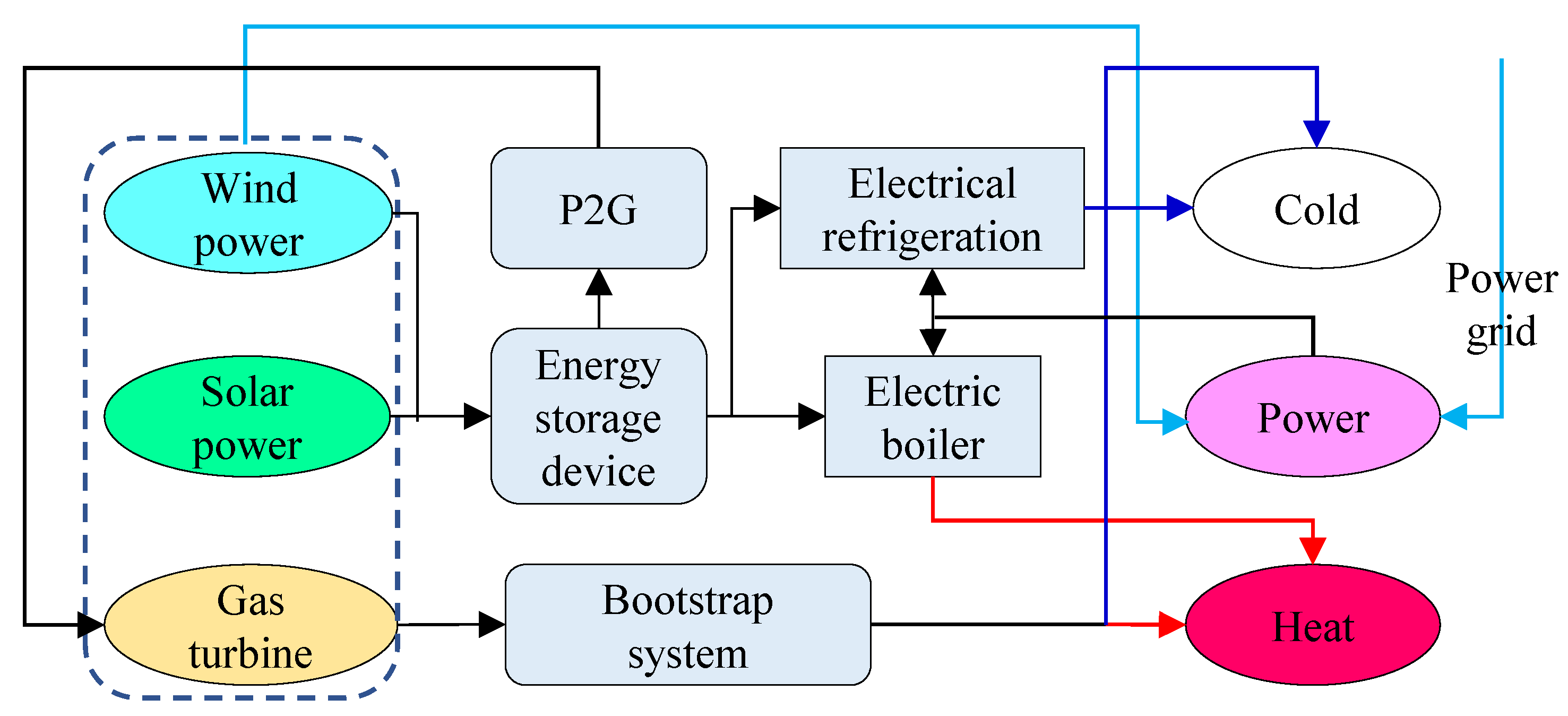
2.1. Integrated Energy System Framework in Park
2.2. Water–Energy Nexus
3. Model Development
3.1. System Cost Model
- (1)
- Operation costs
- (2)
- Gas purchasing costs
- (3)
- Power purchase cost
3.2. System Revenue Model
- (1)
- Revenue from electricity sales
- (2)
- Revenue from heat sales
- (3)
- Revenue from cool sales
3.3. Integrated Energy System Optimization Model
3.3.1. Objective Function
3.3.2. Constraint
- (1)
- Demand and supply balance of cold, heat, and electricity load
- (2)
- Operation constraints of wind power unit
- (3)
- Operation constraints of photovoltaic unit
- (4)
- Operation constraints of the gas tri-generation unit
- (5)
- Operation constraints of P2G
- (6)
- Operation constraints of the electric boiler and electric refrigeration
- (7)
- Operation constraints of energy storage facilities
- (8)
- Water resource constraints
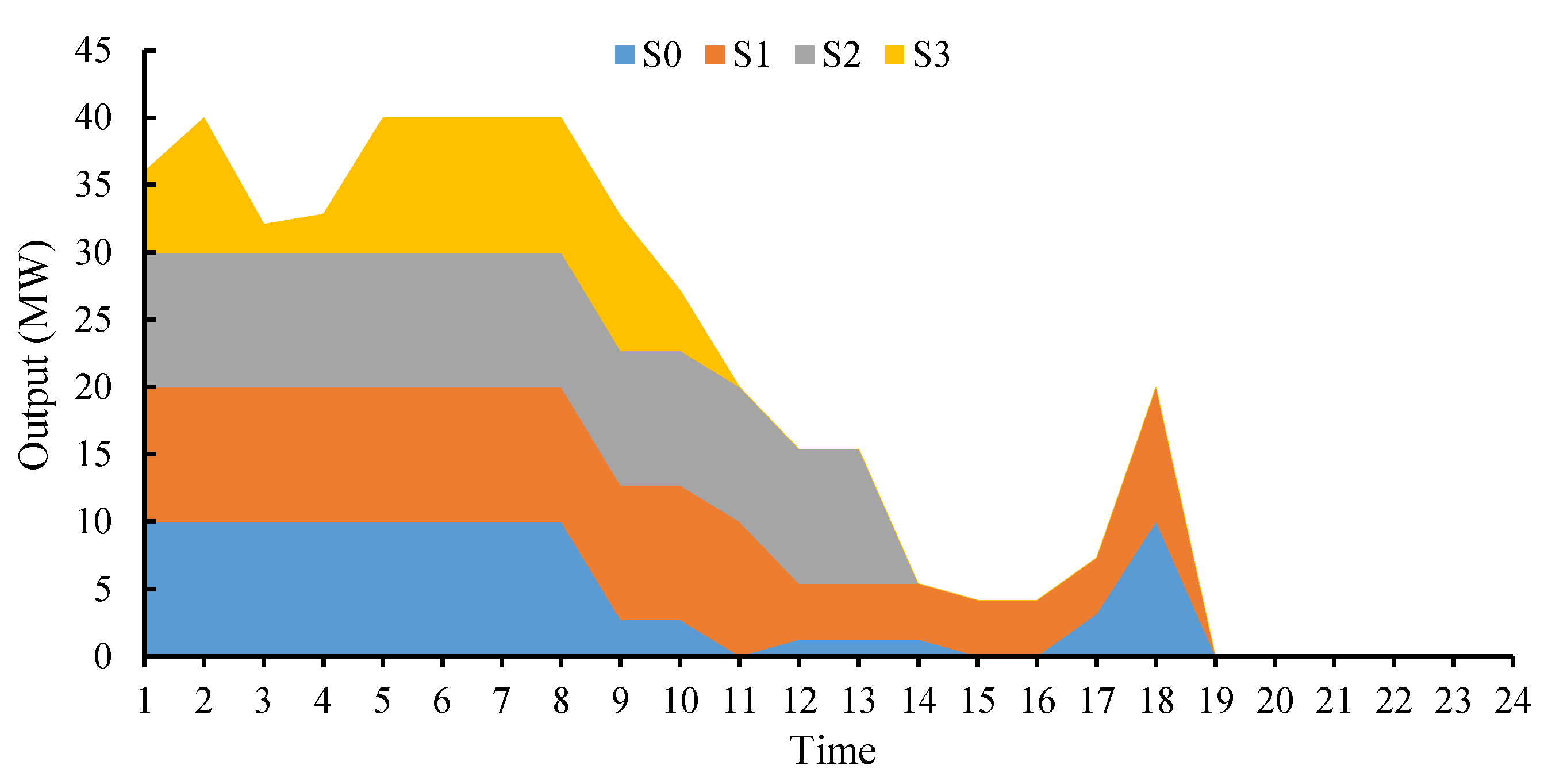
4. Results and Discussion
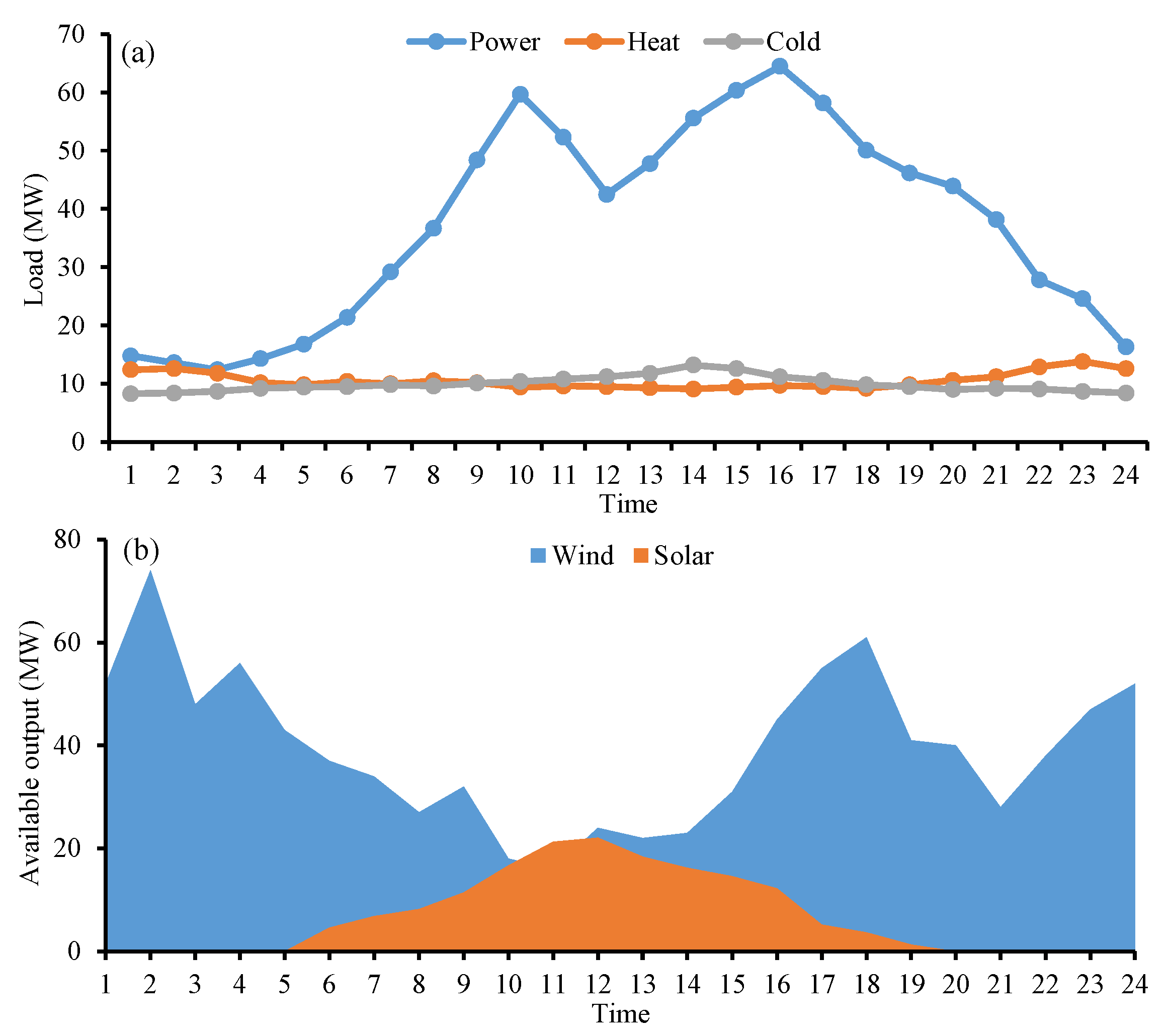
4.1. Overview of the Integrated Energy System
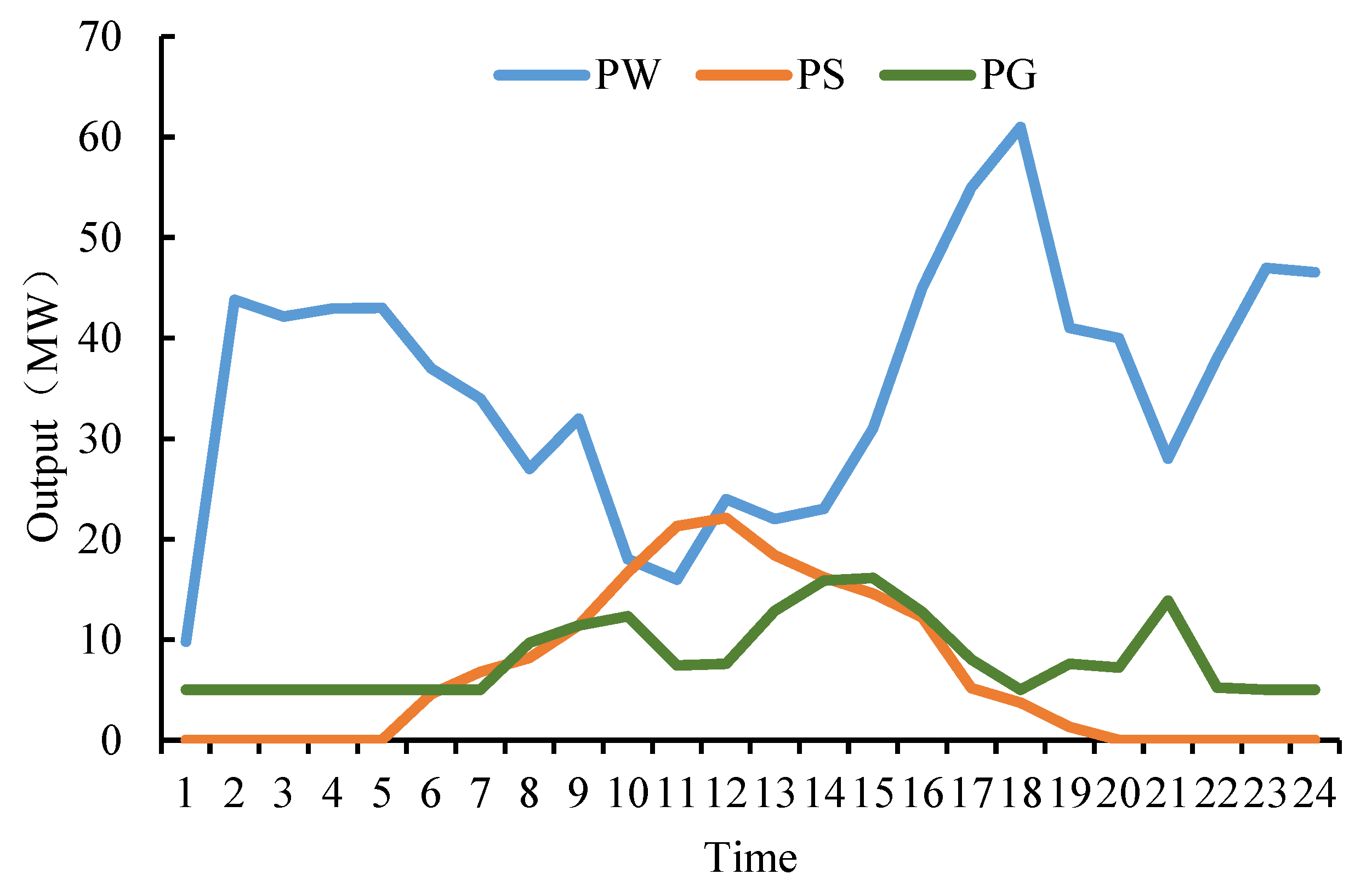
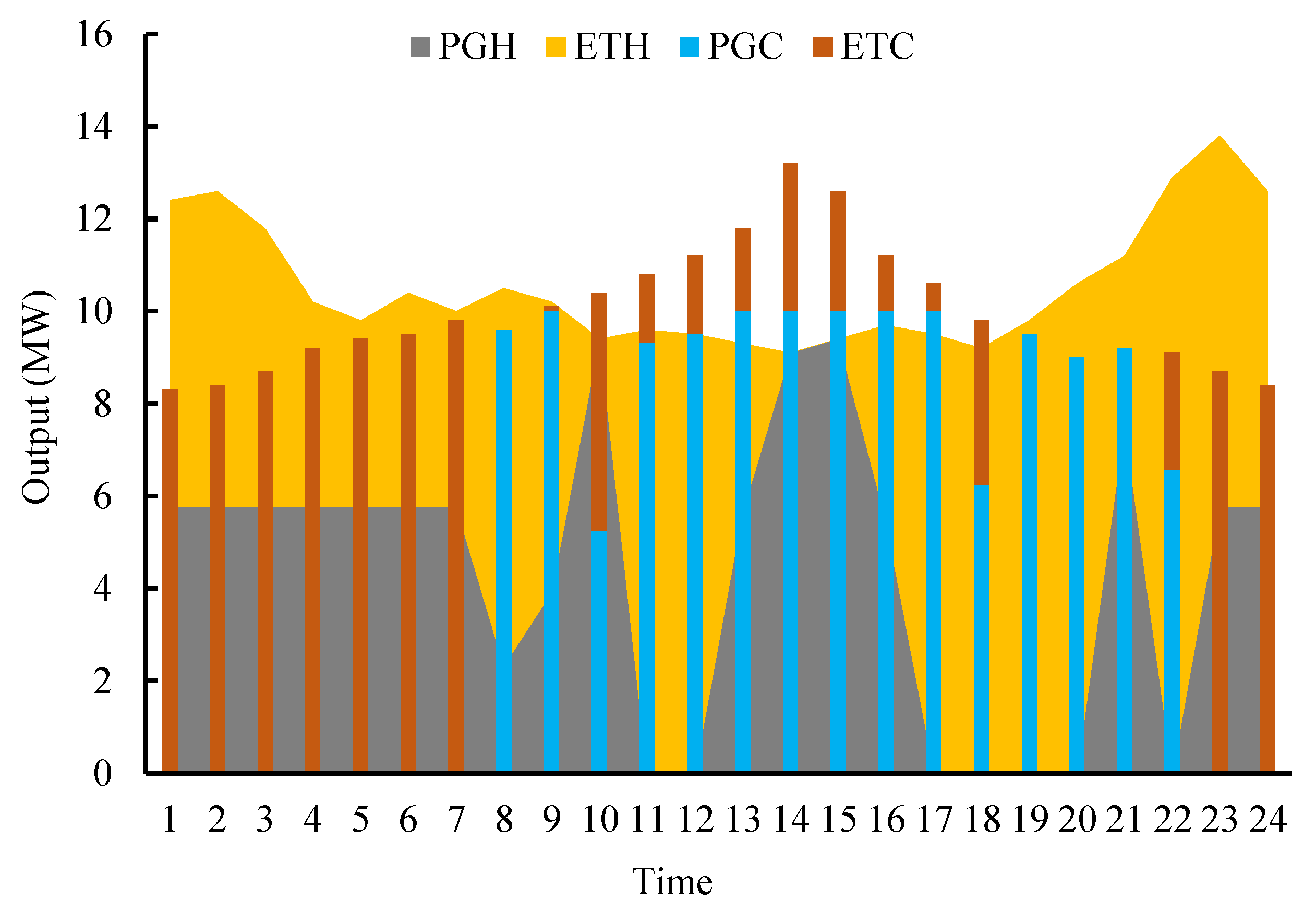
4.2. Results Analysis and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sovacool, B.K.; Sovacool, K.E. Identifying future electricity-water tradeoffs in the United States. Energy Policy 2009, 37, 2763–2773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercedes Garcia, A.V.; López-Jiménez, P.A.; Sánchez-Romero, F.-J.; Pérez-Sánchez, M. Objectives, keys and results in the water networks to reach the sustainable development goals. Water 2021, 13, 1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.H.; Wang, H.C.; Han, J.L.; Liu, W.Z.; Cheng, H.Y.; Liang, B.; Wang, A.J. The application of footprints for assessing the sustainability of wastewater treatment plants: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 277, 124053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macknick, J.; Newmark, R.; Heath, G.; Hallett, K. A Review of Operational Water Consumption and Withdrawal Factors for Electricity Generating Technologies; National Renewable Energy Laboratory: Golden, CO, USA, 2011.
- Xu, W.H.; Xie, Y.L.; Cai, Y.P.; Ji, L.; Wang, B.S.; Yang, Z.F. Environmentally-extended input-output and ecological network analysis for Energy-Water-CO2 metabolic system in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 758, 143931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, L.; Huang, G.H.; Xie, Y.L.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, J.F. Robust cost-risk tradeoff for day-ahead schedule optimization in residential microgrid system under worst-case conditional value-at-risk consideration. Energy 2018, 153, 324–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Q.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X. Stochastic optimization framework of the energy-water-emissions nexus for regional power system planning considering multiple uncertainty. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 281, 124470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, L.; Zheng, Z.X.; Wu, T.H.; Xie, Y.L.; Liu, Z.P.; Huang, G.H.; Niu, D.X. Synergetic optimization management of crop-biomass coproduction with food-energy-water nexus under uncertainties. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 258, 120645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pehnt, M.; Oeser, M.; Swider, D.J. Consequential environmental system analysis of expected offshore wind electricity production in Germany. Energy 2008, 33, 747–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqi, A.; Anadon, L.D. The water-energy nexus in Middle East and North Africa. Energy Policy 2011, 39, 4529–4540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.Q. Governing the energy–water nexus in China: An analysis from the perspective of the science–policy interface. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 272, 111119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llácer-Iglesias, R.M.; López-Jiménez, P.A.; Pérez-Sánchez, M. Energy self-sufficiency aiming for sustainable wastewater systems: Are all options being explored? Sustainability 2021, 13, 5537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Feng, K.S.; Siu, Y.L.; Hubacek, K. Energy-water nexus of wind power in China: The balancing act between CO2 emissions and water consumption. Energy Policy 2012, 45, 440–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.G.; Cao, T.; Chen, B. Urban energy-water nexus based on modified input-output analysis. Appl. Energy 2017, 196, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Y.; Tian, L.; Yu, M. Review of the studies on the water-energy nexus of the electricity sector. China Environ. Sci. 2018, 38, 4742–4748. [Google Scholar]
- Den, W.; Chen, C.H.; Luo, Y.C. Revisiting the water-use efficiency performance for microelectronics manufacturing facilities: Using Taiwan’s Science Parks as a case study. Water-Energy Nexus 2018, 1, 116–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luna, T.; Ribau, J.; Figueiredo, D.; Alves, R. Improving energy efficiency in water supply systems with pump scheduling optimization. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 213, 342–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, K.; Zhu, H.; Wang, S.G. Energy-water nexus in Hubei province based on system input-output analysis and ecological network analysis. J. Nat. Resour. 2018, 33, 1514–1528. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, L.; Zhang, B.B.; Huang, G.H.; Cai, Y.P.; Yin, J.G. Robust regional low-carbon electricity system planning with energy-water nexus under uncertainties and complex policy guidelines. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 252, 119800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergara-Araya, M.; Lehn, H.; Poganietz, W.R. Integrated water, waste and energy management systems—A case study from Curauma, Chile. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 156, 104725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, L.; Zhang, B.B.; Huang, G.H.; Wang, P. A novel multi-stage fuzzy stochastic programming for electricity system structure optimization and planning with energy-water nexus—A case study of Tianjin, China. Energy 2020, 190, 116418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafi, J.; Peiravi, A.; Anvari-Moghaddam, A.; Guerrero, J.M. Resilience improvement planning of power-water distribution systems with multiple microgrids against hurricanes using clean strategies. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 223, 109–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, X.W.; Zhao, X.; Liu, W.F.; Li, R.S.; Wang, X.X.; Wang, W.P.; Tillotson, M.R. Comparing water footprint and water scarcity footprint of energy demand in China’s six megacities. Appl. Energy 2020, 269, 115137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Ma, M.; Kong, F.; Wang, K.; Bi, J. Capturing the co-benefits of energy efficiency in China: A perspective from the water-energy nexus. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 132, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, M.M.; Mahmoud, N.H.; Farahat, M.A. Energy storage system with flat plate solar collector and water-ZnO nanofluid. Sol. Energy 2020, 202, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Suh, S. Environmental impacts of products in China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 4102–4109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, A.; Teng, F.; Wang, Y. China energy-water nexus: Assessing the watersaving synergy effects of energy-saving policies during the eleventh Five-year Plan. Energy Convers. Manag. 2014, 85, 630–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Equipment | Capacity | Equipment | Capacity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wind turbine unit | 24 MW | Gas generator | 20 MW |
| Photovoltaic units | 30 MW | Waste heat cooling | 10 MW |
| P2G | 12 MW | Waste heat heating | 20 MW |
| Energy storage | 10 MW | Electric Boiler | 15 MW |
| Electric refrigeration | 15 MW |
| Period | Price (103/MWh) | |
|---|---|---|
| Electricity | 00:00–06:00 | 0.32 |
| 06:00–10:00 | 1.10 | |
| 10:00–13:00 | 0.67 | |
| 13:00–17:00 | 1.10 | |
| 17:00–22:00 | 0.67 | |
| 22:00–24:00 | 0.32 | |
| Heat | 00:00–05:00 | 0.28 |
| 05:00–08:00 | 0.48 | |
| 08:00–11:00 | 0.65 | |
| 11:00–17:00 | 0.48 | |
| 17:00–20:00 | 0.65 | |
| 20:00–24:00 | 0.28 | |
| Cold | 00:00–24:00 | 0.22 |
| Imported power | 00:00–06:00 | 0.34 |
| 06:00–10:00 | 1.20 | |
| 10:00–13:00 | 0.71 | |
| 13:00–18:00 | 1.20 | |
| 18:00–22:00 | 0.71 | |
| 22:00–24:00 | 0.34 |
| Scenario | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S0 | S1 | S2 | S3 | |
| Benefit (106 RMB¥) | 630.0444 | 626.4859 | 618.2493 | 570.2099 |
| Water amount (m3) | 284.1718 | 282.7917 | 282.7916 | 235.9122 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gou, R.; He, G.; Yu, B.; Xiao, Y.; Luo, Z.; Xie, Y. An Integrated Energy System Operation Optimization Model for Water Consumption Control Analysis in Park Scale from the Perspective of Energy–Water Nexus. Energies 2022, 15, 4410. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15124410
Gou R, He G, Yu B, Xiao Y, Luo Z, Xie Y. An Integrated Energy System Operation Optimization Model for Water Consumption Control Analysis in Park Scale from the Perspective of Energy–Water Nexus. Energies. 2022; 15(12):4410. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15124410
Chicago/Turabian StyleGou, Ruixin, Guiping He, Bo Yu, Yanli Xiao, Zhiwei Luo, and Yulei Xie. 2022. "An Integrated Energy System Operation Optimization Model for Water Consumption Control Analysis in Park Scale from the Perspective of Energy–Water Nexus" Energies 15, no. 12: 4410. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15124410
APA StyleGou, R., He, G., Yu, B., Xiao, Y., Luo, Z., & Xie, Y. (2022). An Integrated Energy System Operation Optimization Model for Water Consumption Control Analysis in Park Scale from the Perspective of Energy–Water Nexus. Energies, 15(12), 4410. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15124410






