Improving Fuel Properties and Hydrocarbon Content from Residual Fat Pyrolysis Vapors over Activated Red Mud Pellets in Two-Stage Reactor: Optimization of Reaction Time and Catalyst Content
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Apparatus
2.3. Methodology
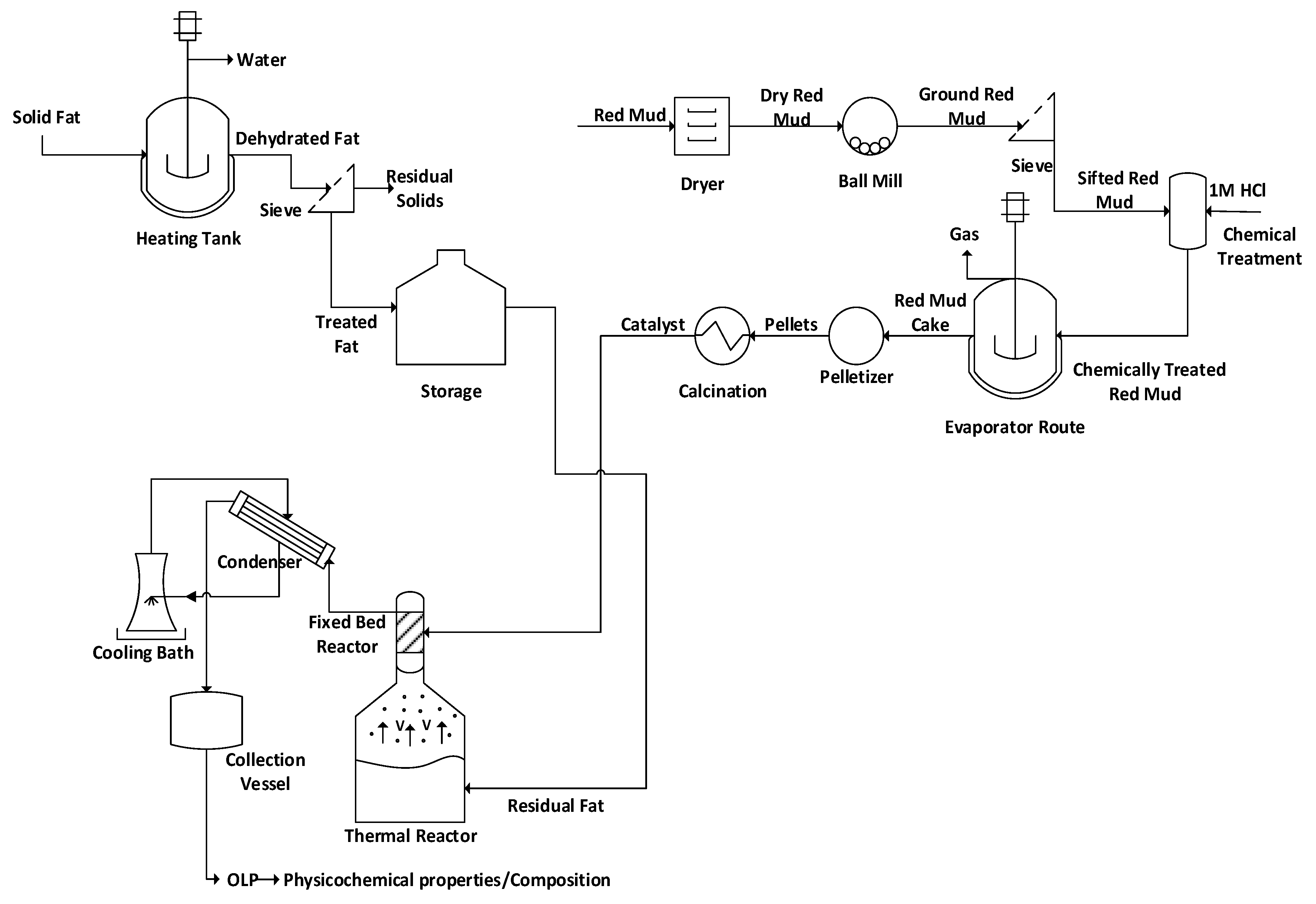
2.3.1. Production of Red Mud Activated Pellets
2.3.2. Chemical Activation of Red Mud
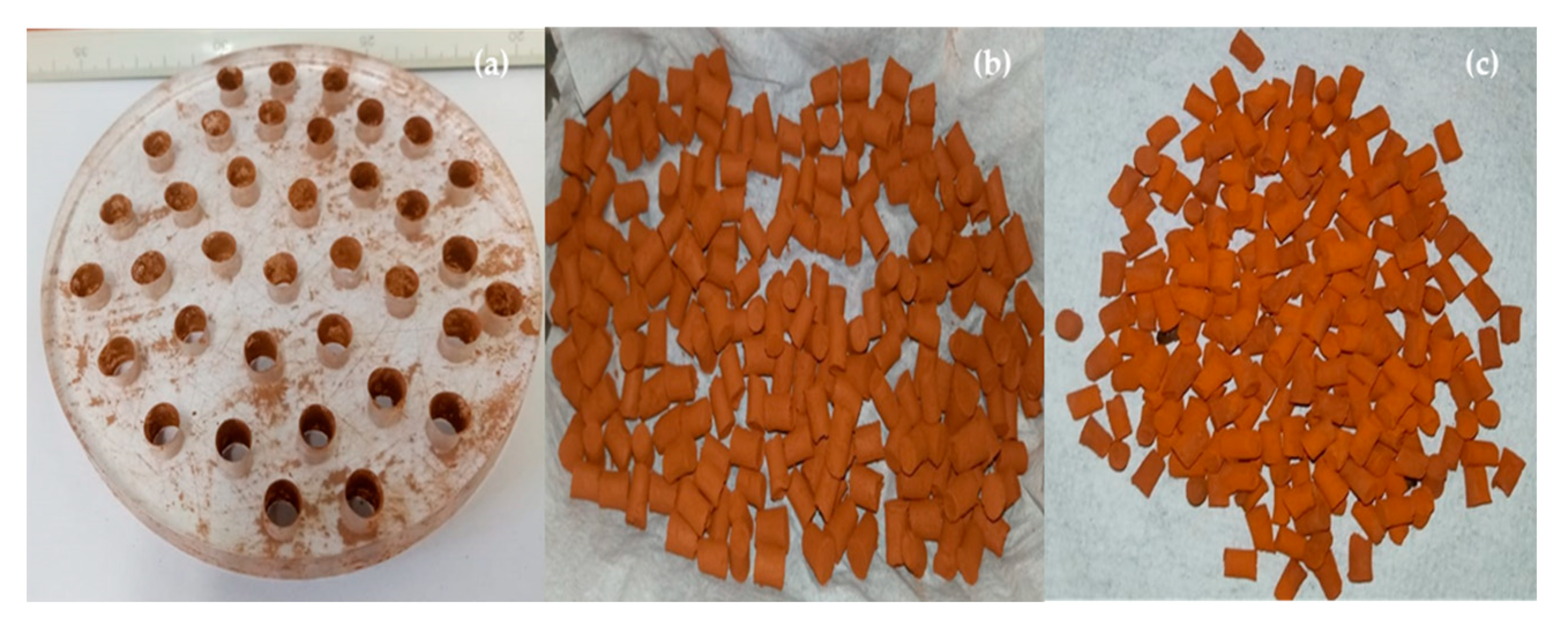
2.3.3. Production of Pellets
2.3.4. Experimental Procedures
Pyrolysis
Thermal Catalytic Cracking
2.3.5. Physical-Chemistry Analysis and Chemical Composition of OLP
Physical-Chemistry Analysis of OLP
Chemical Composition of Organic Liquid Products
2.3.6. Characterization of Activated Red Mud Pellets
SEM and EDX Analysis
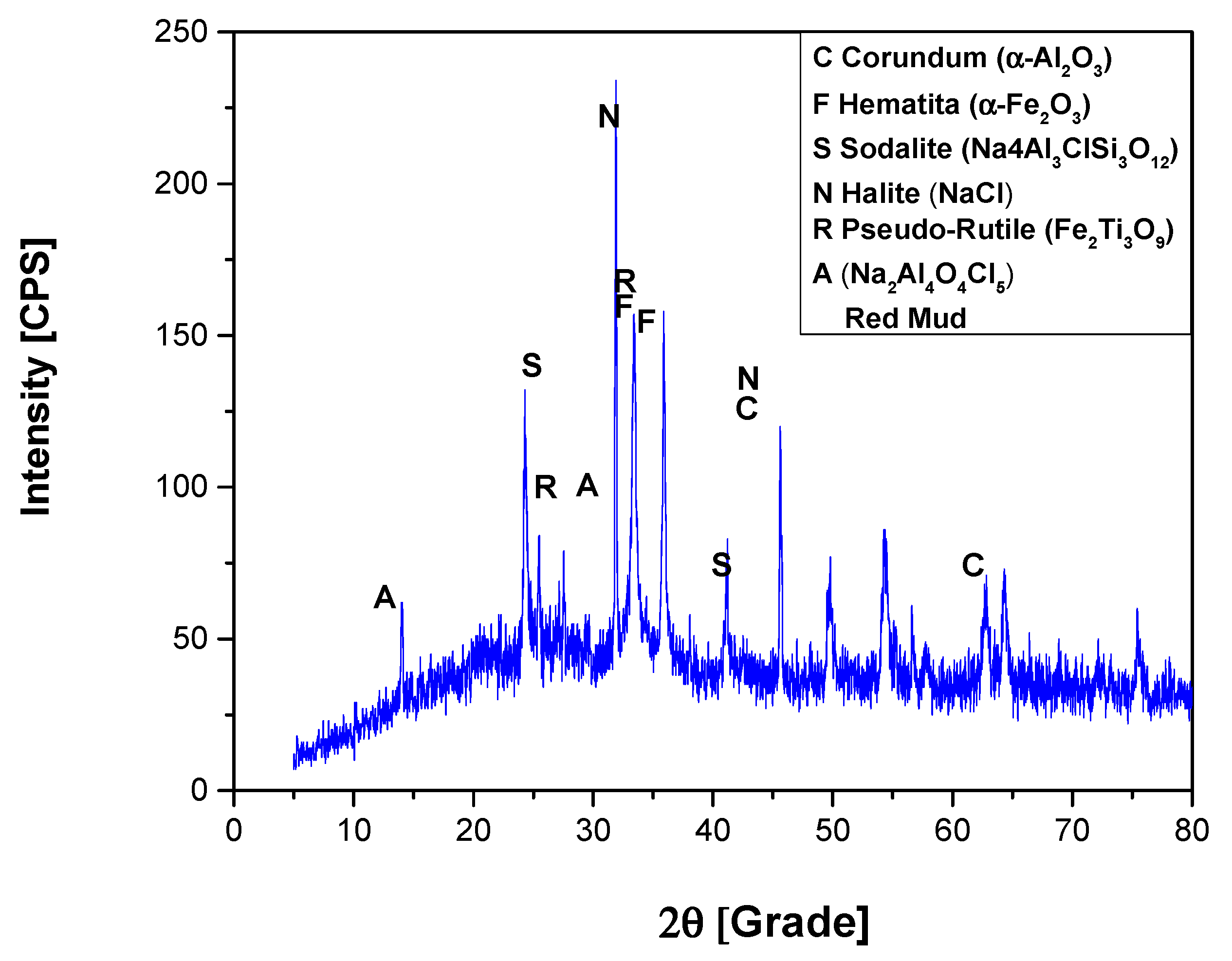
XRD Analysis
2.3.7. Mass Balances by Catalytic Cracking of Vapor Phase Products
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of Catalyst
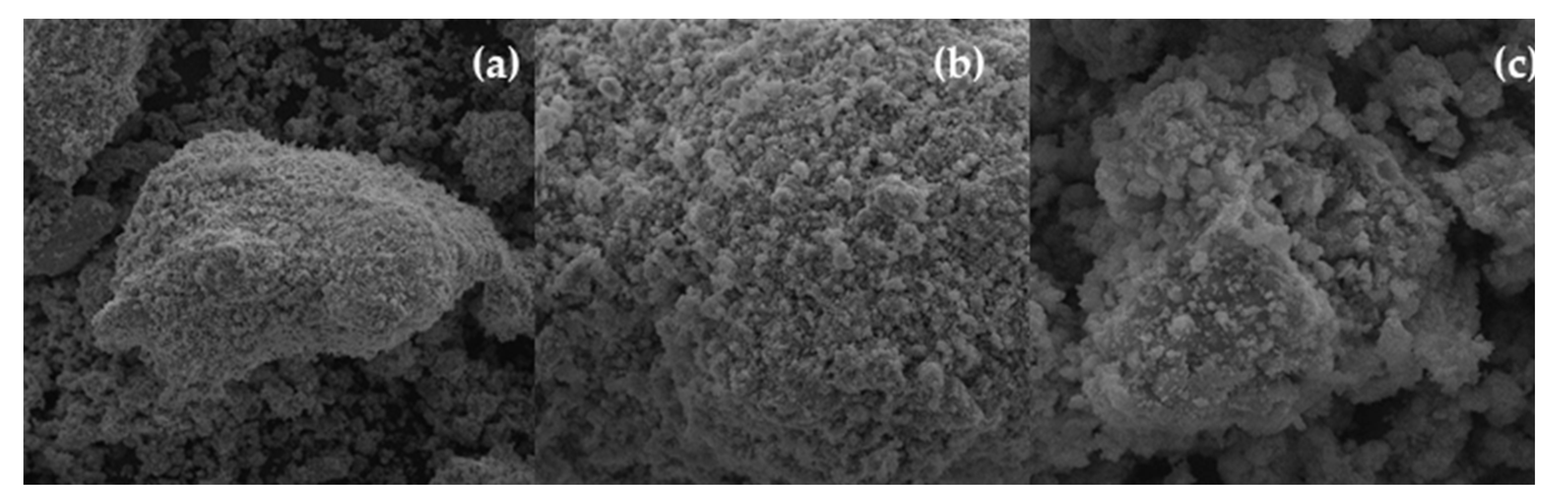
3.1.1. SEM Analysis
3.1.2. EDX Analysis
3.1.3. XRD Analysis
3.2. Upgrading of Residual Fat Pyrolysis Vapors over a Catalyst Fixed Bed Reactor
3.2.1. Process Conditions, Mass Balances, and Yields of Reaction Products
3.2.2. Effect of Catalyst-to-Biomass Ratio on the Yields of Bio-Oils
3.2.3. Effect of Reaction Time on the Yields of Bio-Oil and H2O
3.2.4. Effect of Reaction Time on the Physicochemical Properties of Bio-Oil
Effect of Reaction Time on the Density of Bio-Oil
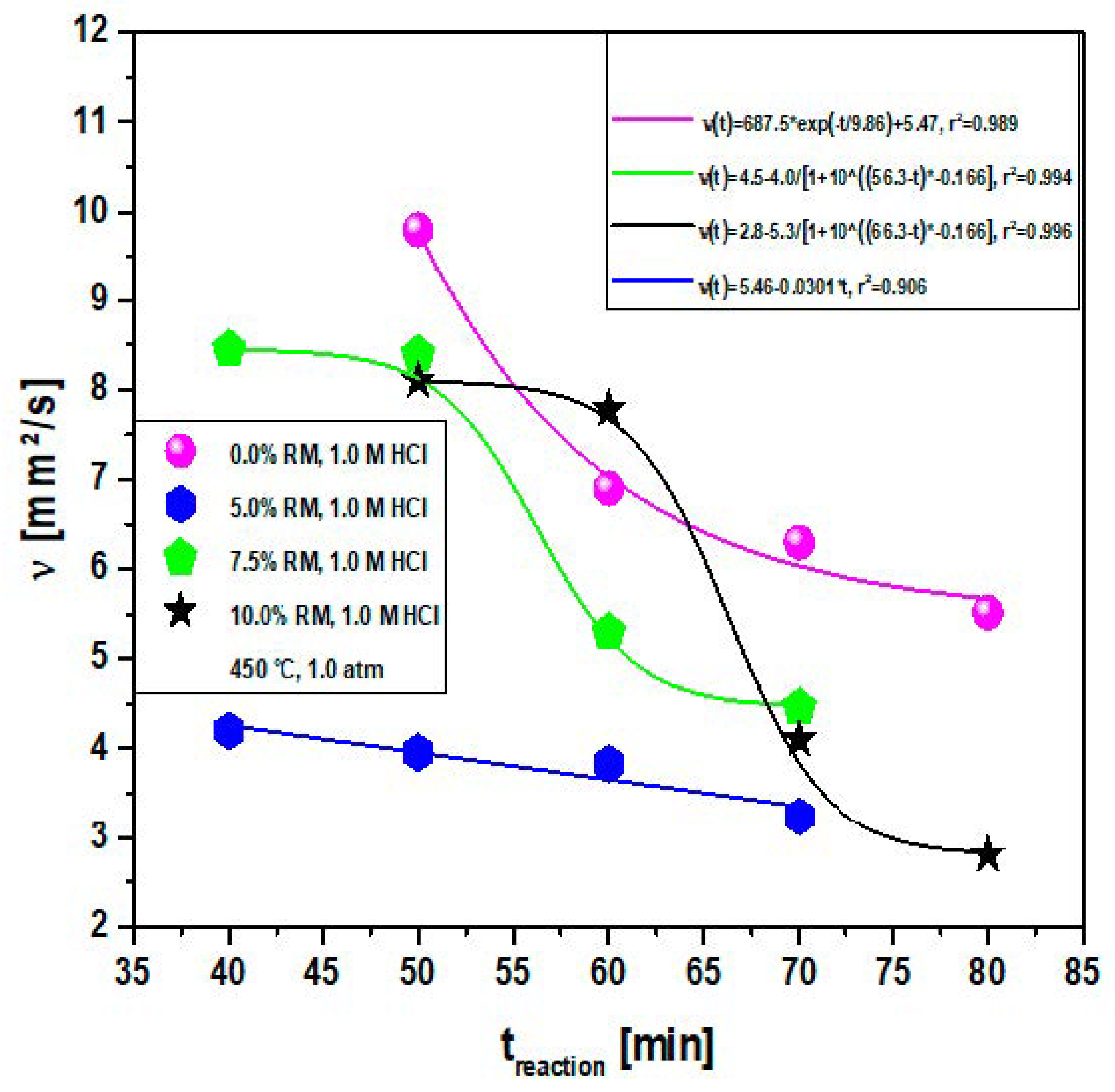
Effect of Reaction Time on the Viscosity of Bio-Oil
Effect of Reaction Time on the Acidity of Bio-Oil
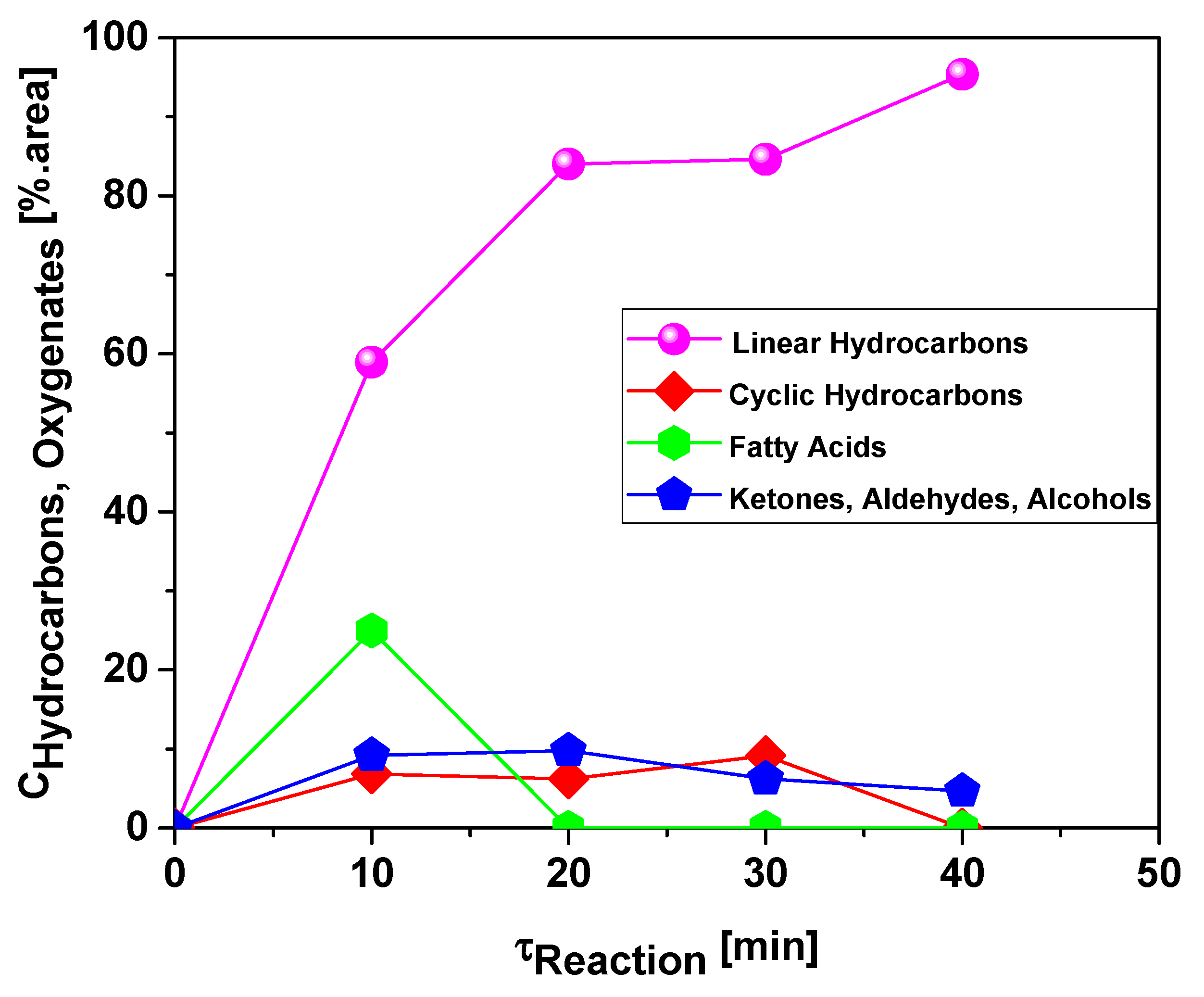
3.2.5. Effect of Reaction Time on the Content of Hydrocarbons and Oxygenates in Bio-Oil
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, Z.; Li, W.Z.; Zhu, X.F. Catalytic Upgrading of Biomass Fast Pyrolysis Vapors with Titania and Zirconia/Titania Based Catalysts. Fuel 2010, 89, 2096–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Yan, L.; Zhao, R.; Li, F. Improving Aromatic Hydrocarbons Yield from Coal Pyrolysis Volatile Products over HZSM-5 and Mo-Modified HZSM-5. Fuel 2014, 130, 154–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.-Y.; Cao, J.-P.; Zhao, X.-Y.; Yang, Z.; Liu, T.-L.; Fan, X.; Zhao, Y.-P.; Wei, X.-Y. Catalytic Upgrading of Pyrolysis Vapors from Lignite over Mono/Bimetal-Loaded Mesoporous HZSM-5. Fuel 2018, 218, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.L.; Cao, J.P.; Zhao, X.Y.; Wang, J.X.; Ren, X.Y.; Fan, X.; Zhao, Y.P.; Wei, X.Y. In Situ Upgrading of Shengli Lignite Pyrolysis Vapors over Metal-Loaded HZSM-5 Catalyst. Fuel Process. Technol. 2017, 160, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.J.; Kong, X.J.; Zhao, R.F.; Li, F.; Xie, K.C. Catalytic Upgrading of Gaseous Tars over Zeolite Catalysts during Coal Pyrolysis. Fuel Process. Technol. 2015, 138, 424–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Cao, J.P.; Ren, X.Y.; Zhao, X.Y.; Liu, S.N.; Guo, Z.X.; Shen, W.Z.; Bai, J.; Wei, X.Y. Preparation of Hierarchical HZSM-5 Based Sulfated Zirconium Solid Acid Catalyst for Catalytic Upgrading of Pyrolysis Vapors from Lignite Pyrolysis. Fuel 2019, 237, 1079–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaman, E.; Yargic, A.S.; Ozbay, N.; Uzun, B.B.; Kalogiannis, K.G.; Stefanidis, S.D.; Pachatouridou, E.P.; Iliopoulou, E.F.; Lappas, A.A. Catalytic Upgrading of Pyrolysis Vapours: Effect of Catalyst Support and Metal Type on Phenolic Content of Bio-Oil. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 185, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Cai, Y.; Li, X.; Yu, N.; Yin, H. Catalytic Upgrading of Pyrolytic Vapors from the Vacuum Pyrolysis of Rape Straw over Nanocrystalline HZSM-5 Zeolite in a Two-Stage Fixed-Bed Reactor. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2014, 108, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koul, M.; Shadangi, K.P.; Mohanty, K. Effect of Catalytic Vapour Cracking on Fuel Properties and Composition of Castor Seed Pyrolytic Oil. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2016, 120, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Wang, F.; Yang, X.; Huang, Y.; Liu, C.; Zheng, Z.; Gu, J. Study on Aromatics Production via the Catalytic Pyrolysis Vapor Upgrading of Biomass Using Metal-Loaded Modified H-ZSM-5. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2017, 126, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.Y.; Cao, J.P.; Zhao, X.Y.; Shen, W.Z.; Wei, X.Y. Increasing Light Aromatic Products during Upgrading of Lignite Pyrolysis Vapor over Co-Modified HZSM-5. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2018, 130, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Fan, Y.; Li, X.; Chen, L.; Wang, J. Preparation of Refined Bio-Oil by Catalytic Transformation of Vapors Derived from Vacuum Pyrolysis of Rape Straw over Modified HZSM-5. Energy 2016, 102, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, H.; Liu, X.; Zhu, S.; Hu, L.; Zhang, Q. Upgrading of Bio-Oil from Catalytic Pyrolysis of Pretreated Rice Husk over Fe-Modified ZSM-5 Zeolite Catalyst. Fuel Process. Technol. 2018, 175, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iliopoulou, E.F.; Stefanidis, S.D.; Kalogiannis, K.G.; Delimitis, A.; Lappas, A.A.; Triantafyllidis, K.S. Catalytic Upgrading of Biomass Pyrolysis Vapors Using Transition Metal-Modified ZSM-5 Zeolite. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2012, 127, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vichaphund, S.; Aht-ong, D.; Sricharoenchaikul, V.; Atong, D. Catalytic Upgrading Pyrolysis Vapors of Jatropha Waste Using Metal Promoted ZSM-5 Catalysts: An Analytical PY-GC/MS. Renew. Energy 2014, 65, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Shao, S.; Dong, L.; Zhang, J.; Hu, C.; Cai, Y. Catalytic Upgrading of Pyrolysis Vapor from Rape Straw in a Vacuum Pyrolysis System over La/HZSM-5 with Hierarchical Structure. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 259, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.S.; Zabeti, M.; Lefferts, L.; Brem, G.; Seshan, K. Catalytic Upgrading of Biomass Pyrolysis Vapours Using Faujasite Zeolite Catalysts. Biomass Bioenergy 2013, 48, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triantafyllidis, K.S.; Iliopoulou, E.F.; Antonakou, E.V.; Lappas, A.A.; Wang, H.; Pinnavaia, T.J. Hydrothermally Stable Mesoporous Aluminosilicates (MSU-S) Assembled from Zeolite Seeds as Catalysts for Biomass Pyrolysis. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2007, 99, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Dong, L.; Zhang, J.; Hu, C.; Zhang, X.; Cai, Y.; Shao, S. In-Situ Catalytic Upgrading of Biomass-Derived Vapors Using HZSM-5 and MCM-41: Effects of Mixing Ratios on Bio-Oil Preparation. J. Energy Inst. 2019, 92, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.-Y.; Feng, X.-B.; Cao, J.-P.; Tang, W.; Wang, Z.-H.; Yang, Z.; Zhao, J.-P.; Zhang, L.-Y.; Wang, Y.-J.; Zhao, X.-Y. Catalytic Conversion of Coal and Biomass Volatiles: A Review. Energy Fuels 2020, 34, 10307–10363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukarakate, C.; Watson, M.J.; ten Dam, J.; Baucherel, X.; Budhi, S.; Yung, M.M.; Ben, H.; Iisa, K.; Baldwin, R.M.; Nimlos, M.R. Upgrading Biomass Pyrolysis Vapors over β-Zeolites: Role of Silica-to-Alumina Ratio. Green Chem. 2014, 16, 4891–4905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engtrakul, C.; Mukarakate, C.; Starace, A.K.; Magrini, K.A.; Rogers, A.K.; Yung, M.M. Effect of ZSM-5 Acidity on Aromatic Product Selectivity during Upgrading of Pine Pyrolysis Vapors. Catal. Today 2016, 269, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ren, X.Y.; Zhao, S.X.; Cao, J.P.; Zhao, X.Y.; Feng, X.B.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Z.H.; Bai, H.C. Effect of Coal Ranks on Light Aromatics Production during Reforming of Pyrolysis Volatiles over HZSM-5 under Ar and H2-Assisted Atmospheres. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2020, 152, 104958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mante, O.D.; Rodriguez, J.A.; Senanayake, S.D.; Babu, S.P. Catalytic Conversion of Biomass Pyrolysis Vapors into Hydrocarbon Fuel Precursors. Green Chem. 2015, 17, 2362–2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasundram, V.; Ibrahim, N.; Kasmani, R.M.; Isha, R.; Hamid, M.K.A.; Hasbullah, H.; Ali, R.R. Catalytic Upgrading of Sugarcane Bagasse Pyrolysis Vapours over Rare Earth Metal (Ce) Loaded HZSM-5: Effect of Catalyst to Biomass Ratio on the Organic Compounds in Pyrolysis Oil. Appl. Energy 2018, 220, 787–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, U.; Vongsvivut, J.; Shahabuddin, M.; Samudrala, S.P.; Srivatsa, S.C.; Bhattacharya, S. A Study on the Performance of Coke Resistive Cerium Modified Zeolite Y Catalyst for the Pyrolysis of Scrap Tyres in a Two-Stage Fixed Bed Reactor. Waste Manag. 2020, 102, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishu; Liu, R.; Rahman, M.M.; Sarker, M.; Chai, M.; Li, C.; Cai, J. A Review on the Catalytic Pyrolysis of Biomass for the Bio-Oil Production with ZSM-5: Focus on Structure. Fuel Process. Technol. 2020, 199, 106301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Chen, P.; Zhou, N.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Omar, M.M.; Peng, P.; Addy, M.; et al. In-Situ and Ex-Situ Catalytic Upgrading of Vapors from Microwave-Assisted Pyrolysis of Lignin. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 247, 851–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, N.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, L.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Chen, P.; Ruan, R. Silicon Carbide Foam Supported ZSM-5 Composite Catalyst for Microwave-Assisted Pyrolysis of Biomass. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 267, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.-Y.; Cao, J.-P.; Li, Y.; He, Z.-M.; Zhao, X.-Y.; Liu, T.-L.; Feng, X.-B.; Zhao, Y.-P.; Bai, H.-C.; Zhang, J.; et al. Formation of Light Aromatics and Coke during Catalytic Reforming of Biopolymer-Derived Volatiles over HZSM-5. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res 2021, 60, 12521–12533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Xiao, R.; Zhang, H. Ex-Situ Catalytic Fast Pyrolysis of Biomass over HZSM-5 in a Two-Stage Fluidized-Bed/Fixed-Bed Combination Reactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 243, 1133–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, P.; Yan, L.; Liu, Y.; Wang, M.; Bao, W.; Li, F. Catalytic Upgrading of Coal Pyrolysis Gaseous Tar over Hierarchical Y-Type Zeolites Synthesized Using a Microwave Hydrothermal Method. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 21817–21826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadieraghi, M.; Ashri Wan Daud, W.M.; Abbas, H.F. Heterogeneous Catalysts for Advanced Bio-Fuel Production through Catalytic Biomass Pyrolysis Vapor Upgrading: A Review. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 22234–22255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.-Y.; Cao, J.-P.; Ren, X.-Y.; Feng, X.-B.; Wang, J.-X.; He, Z.-M.; Liu, T.-L.; Yang, Z.; Zhao, X.-Y.; Bai, H.-C. Catalytic Upgrading of Cellulose Pyrolysis Volatiles over Ce Modified Hierarchical ZSM-5 Zeolite: Insight into the Effect of Acid Properties on Light Aromatics and Catalyst Stability. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2022, 61, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernar, L.P.; Ferreira, C.C.; de Freitas Costa, A.F.; da Silva Ribeiro, H.J.; dos Santos, W.G.; Pereira, L.M.; Pereira, A.M.; Moraes, N.L.; da Costa Assunção, F.P.; da Mota, S.A.P.; et al. Catalytic Upgrading of Residual Fat Pyrolysis Vapors over Activated Carbon Pellets into Hydrocarbons-like Fuels in a Two-Stage Reactor: Analysis of Hydrocarbons Composition and Physical-Chemistry Properties. Energies 2022, 15, 4587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEA. Renewables 2019; International Energy Agency: Paris, France, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.; Jiang, J.; Liu, P.; Zhai, Q.; Wang, F.; Hse, C.; Xu, J. Catalytic Cracking of Triglycerides with a Base Catalyst and Modification of Pyrolytic Oils for Production of Aviation Fuels. Sustain. Energy Fuels 2018, 2, 1206–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ben Hassen-Trabelsi, A.; Kraiem, T.; Naoui, S.; Belayouni, H. Pyrolysis of Waste Animal Fats in a Fixed-Bed Reactor: Production and Characterization of Bio-Oil and Bio-Char. Waste Manag. 2014, 34, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adebanjo, A.O.; Dalai, A.K.; Bakhshi, N.N. Production of Diesel-like Fuel and Other Value-Added Chemicals from Pyrolysis of Animal Fat. Energy Fuels 2005, 19, 1735–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phung, T.K.; Casazza, A.A.; Perego, P.; Capranica, P.; Busca, G. Catalytic Pyrolysis of Vegetable Oils to Biofuels: Catalyst Functionalities and the Role of Ketonization on the Oxygenate Paths. Fuel Process. Technol. 2015, 140, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junming, X.; Jianchun, J.; Yanju, L.; Jie, C. Liquid Hydrocarbon Fuels Obtained by the Pyrolysis of Soybean Oils. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 4867–4870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, T.; Sakurai, Y.; Kakuta, Y.; Sugano, M.; Hirano, K. Biodiesel Production from Waste Animal Fats Using Pyrolysis Method. Fuel Process. Technol. 2012, 94, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratt, L.M.; Kim, J.; Lo, H.Y.; Xiao, D. Brown Grease Pyrolysis under Pressure: Extending the Range of Reaction Conditions and Hydrocarbon Product Distributions. Fuel 2021, 289, 119782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva Almeida, H.; Corrêa, O.A.; Eid, J.G.; Ribeiro, H.J.; de Castro, D.A.R.; Pereira, M.S.; Pereira, L.M.; de Andrade Mâncio, A.; Santos, M.C.; da Silva Souza, J.A.; et al. Production of Biofuels by Thermal Catalytic Cracking of Scum from Grease Traps in Pilot Scale. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2016, 118, 20–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva Almeida, H.; Corrêa, O.A.; Eid, J.G.; Ribeiro, H.J.; de Castro, D.A.R.; Pereira, M.S.; Pereira, L.M.; de Andrade Aâncio, A.; Santos, M.C.; da Mota, S.A.P.; et al. Performance of Thermochemical Conversion of Fat, Oils, and Grease into Kerosene-like Hydrocarbons in Different Production Scales. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2016, 120, 126–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva Almeida, H.; Corrêa, O.A.; Ferreira, C.C.; Ribeiro, H.J.; de Castro, D.A.R.; Pereira, M.S.; de Andrade Mâncio, A.; Santos, M.C.; da Mota, S.A.P.; da Silva Souza, J.A.; et al. Diesel-like Hydrocarbon Fuels by Catalytic Cracking of Fat, Oils, and Grease (FOG) from Grease Traps. J. Energy Inst. 2017, 90, 337–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha de Castro, D.; da Silva Ribeiro, H.; Hamoy Guerreiro, L.; Pinto Bernar, L.; Jonatan Bremer, S.; Costa Santo, M.; da Silva Almeida, H.; Duvoisin, S.; Pizarro Borges, L.; Teixeira Machado, N. Production of Fuel-Like Fractions by Fractional Distillation of Bio-Oil from Açaí (Euterpe Oleracea Mart.) Seeds Pyrolysis. Energies 2021, 14, 3713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Mota, S.A.P.; Mancio, A.A.; Lhamas, D.E.L.; de Abreu, D.H.; da Silva, M.S.; dos Santos, W.G.; de Castro, D.A.R.; de Oliveira, R.M.; Araújo, M.E.; Borges, L.E.P.; et al. Production of Green Diesel by Thermal Catalytic Cracking of Crude Palm Oil (Elaeis Guineensis Jacq) in a Pilot Plant. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2014, 110, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercury, J.M.R.; Galdino, L.G.; Vasconcelos, N.S.L.S.; Paiva, A.E.M.; Cabral, A.A.; Angélica, R.S. Estudo Do Comportamento Térmico e Propriedades Físico-Mecânicas Da Lama Vermelha. Matéria Rio Jan. 2010, 15, 445–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, C.; Luan, Z.; Peng, X.; Zhu, C.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Fan, J.; Jia, Z. Phosphate Removal from Aqueous Solutions Using Raw and Activated Red Mud and Fly Ash. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 137, 374–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, M.K.; Mandal, S.; Dash, S.S.; Badhai, P.; Patel, R.K. Removal of Pb(II) from Aqueous Solution by Acid Activated Red Mud. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2013, 1, 1315–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Wang, S.; Zhu, Z.; Li, L.; Yao, X.; Rudolph, V.; Haghseresht, F. Phosphate Removal from Wastewater Using Red Mud. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 158, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guedes, J. Estudo da Aplicação da Lama Vermelha como Catalisador na Reação de Craqueamento Térmico de Resíduos de Caixa de Gordura. Master’s Thesis, Universidade Federal do Pará , Belém, Brazil, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Benson, T.J.; Hernandez, R.; French, W.T.; Alley, E.G.; Holmes, W.E. Elucidation of the Catalytic Cracking Pathway for Unsaturated Mono-, Di-, and Triacylglycerides on Solid Acid Catalysts. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2009, 303, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appleby, W.G.; Gibson, J.W.; Good, G.M. Coke Formation in Catalytic Cracking. Ind. Eng. Chem. Process Des. Dev. 1962, 1, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.-C.; Wan, S.-W. China’s Motor Fuels from Tung Oil. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1947, 39, 1543–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiggers, V.R.; Meier, H.F.; Wisniewski, A.; Chivanga Barros, A.A.; Wolf Maciel, M.R. Biofuels from Continuous Fast Pyrolysis of Soybean Oil: A Pilot Plant Study. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 6570–6577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lappi, H.; Alén, R. Pyrolysis of Vegetable Oil Soaps—Palm, Olive, Rapeseed and Castor Oils. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2011, 91, 154–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratton Coppos, A.R.; Kahn, S.; Borges, L.E.P. Biofuels Production by Thermal Cracking of Soap from Brown Grease. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2018, 112, 561–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, R.M.; Rodrigues, E.C.; Cardoso, D.N.P.; Santos, W.G.; Machado, N.T. Thermocatalytic Cracking of Fat from Fat Boxes with Activated Red Mud. Braz. J. Dev. 2020, 6, 19876–19887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrão, A.C.M.; Silva, C.M.S.; da Costa Assunção, F.P.; da Silva Ribeiro, H.J.; Santos, M.C.; da Silva Almeida, H.; Duvoisin, S., Jr.; Borges, L.E.P.; de Castro, D.A.R.; Machado, N.T. Análise do processo de pirólise de sementes de Açaí (Euterpe Oleracea, Mart): Influência da temperatura no rendimento dos produtos de reação e nas propriedades físico-químicas do Bio-Óleo. Braz. J.Dev. 2021, 7, 18200–18220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraful, A.M.; Masjuki, H.H.; Kalam, M.A.; Rizwanul Fattah, I.M.; Imtenan, S.; Shahir, S.A.; Mobarak, H.M. Production and Comparison of Fuel Properties, Engine Performance, and Emission Characteristics of Biodiesel from Various Non-Edible Vegetable Oils: A Review. Energy Convers. Manag. 2014, 80, 202–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| Catalyst | Impregnation | References |
|---|---|---|
| Titania/Zirconia based | - | [1,24] |
| Ce | [1,24] | |
| ZrO2 | [24] | |
| Ru/Ce | [1] | |
| Pd/Ce | [1] | |
| Ni | [24] | |
| Pt | [24] | |
| HZSM-5 | - | [2,3,4,6,7,10,11,12,15,19,25] |
| Mo | [2] | |
| Co | [3,4,7,11,15] | |
| Mo | [4] | |
| Ni | [4,7,15] | |
| Mo/Co | [3] | |
| Ni/Co | [3] | |
| Al/Si = 25 to 100 | [8] | |
| P | [12] | |
| Zn | [12] | |
| Ti | [12] | |
| Ce | [25] | |
| Hierarchical HZSM-5 | - | [16] |
| La | [16] | |
| Alkaline Treated HZSM-5 | - | [3] |
| Co | [3] | |
| Mo/Co | [3] | |
| Ni/Co | [3] | |
| - | [6] | |
| Zeolite-Y | - | [5,7,26] |
| Hierarchical | [32] | |
| Al | [5] | |
| 5–10% Al | [7] | |
| 30%–50% Fe | [7] | |
| Ce | [26] | |
| Sulfated Zirconia HZSM-5 | SZr 2:1 to 6:1 | [6] |
| Basic oxides | Kaolin | [9] |
| ZnO | [9] | |
| CaO | [9] | |
| MgO | [24] | |
| Modified ZSM-5 | - | [13,26] |
| Ga | [10] | |
| Ni | [10,14] | |
| Mg | [10] | |
| Co | [10,14] | |
| Zn | [10] | |
| Cu | [10] | |
| Fe 0.5–8% | [13] | |
| Si/Al = 23 to 280 | [22] | |
| Ce | [26,34] | |
| Silicon composite | [29] | |
| Faujasite Zeolite | Na | [17] |
| Na0.2H0.8 | [17] | |
| H | [17] | |
| Aluminosilicates | Hexagonal | [18] |
| Wormhole | [18] | |
| Al-MCM-41 | [18] | |
| MCM-41 | [19] | |
| Beta zeolite | Si/Al = 21 to 250 | [21] |
| Activated carbon | 10.0 M HCl | [35] |
| Catalyst | ||||||||||||
| Red Mud [53] | Red Mud 1000 °C [44] | Red Mud Pellets 2.0 M HCl | Red Mud Pellets after 450 °C | |||||||||
| Chemical Elements | Mass [wt.%] | Atomic Mass [wt.%] | SD | Mass [wt.%] | Atomic Mass [wt.%] | SD | Mass [wt.%] | Atomic Mass [wt.%] | SD | Mass [wt.%] | Atomic Mass [wt.%] | SD |
| C | 15.42 | 24.49 | 0.76 | 13.17 | 23.62 | 0.79 | - | - | - | 26.20 | 38.31 | - |
| O | 44.79 | 53.30 | 0.63 | 43.77 | 55.97 | 0.72 | 56.11 | 71.95 | - | 40.18 | 44.10 | - |
| Na | 7.24 | 5.99 | 0.20 | 4.03 | 3.59 | 0.22 | 7.55 | 6.74 | - | 3.42 | 2.62 | - |
| Al | 7.97 | 5.63 | 1.70 | 3.95 | 2.99 | 0.15 | 12.54 | 9.54 | - | 12.54 | 8.16 | - |
| Ca | 1.09 | 0.52 | 0.07 | 1.15 | 0.59 | 0.09 | 0.65 | 0.33 | - | 0.55 | 0.24 | - |
| Ti | 1.67 | 0.66 | 0.90 | 1.39 | 0.59 | 0.11 | 1.47 | 0.74 | - | 1.14 | 0.42 | - |
| Fe | 15.87 | 5.40 | 0.29 | 29.07 | 10.65 | 0.49 | 12.64 | 4.64 | - | 11.99 | 3.77 | - |
| Si | 5.97 | 4.05 | 0.14 | 2.75 | 2.00 | 0.12 | 7.01 | 5.12 | - | 3.23 | 2.02 | - |
| Cl | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1.47 | 0.85 | - | 0.74 | 0.37 | - |
| K | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.05 | 0.03 | - | - | - | - |
| V | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.06 | 0.02 | - | - | - | - |
| Ba | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.17 | 0.02 | - | - | - | - |
| Process Parameters | 450 (°C) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0 (wt.) | 5.0 (wt.) | 7.5 (wt.) | 10.0 (wt.) | |
| Mass of residual fat (g) | 1000 | 700 | 700 | 700 |
| Cracking time (min) | 80 | 80 | 80 | 80 |
| Initial cracking temperature (°C) | 395 | 380 | 380 | 390 |
| Mechanical system stirring speed (rpm) | 90 | 90 | 90 | 90 |
| Mass of solid (Coke) (g) | 66 | 60.05 | 10.92 | 9.1 |
| Mass of liquid (Bio-oil) (g) | 794.2 | 380.79 | 584.53 | 594.13 |
| Mass of H2O (g) | 115 | 19.63 | 17.45 | 15.5 |
| Mass of gas (g) | 24.81 | 239.53 | 104.55 | 81.27 |
| Yield of Bio-oil (wt.%) | 79.42 | 54.40 | 81.76 | 84.88 |
| Yield of H2O (wt.%) | 11.50 | 2.80 | 2.49 | 2.21 |
| Yield of Coke (wt.%) | 6.60 | 8.60 | 1.56 | 1.30 |
| Yield of Gas (wt.%) | 2.48 | 34.22 | 14.94 | 11.61 |
| Process Parameters | 450 (°C) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.00 (wt.) | ||||
| 50 (min) | 60 (min) | 70 (min) | 80 (min) | |
| Temperature of pyrolysis reactor (°C) | 410 | 445 | 435 | 460 |
| Temperature of fixed bed reactor (°C) | - | - | - | - |
| Mass of H2O (g) | 115 | - | - | - |
| Yield of H2O (wt.%) | 11.5 | - | - | - |
| Mass of Bio-oil (g) | 294 | 311.98 | 176.1 | 12.15 |
| Yield of Bio-oil (wt.%) | 29.4 | 31.2 | 17.6 | 1.22 |
| Process Parameters | 450 (°C) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5.00 (wt.) | ||||
| 40 (min) | 50 (min) | 60 (min) | 70 (min) | |
| Temperature of pyrolysis reactor (°C) | 400 | 417 | 440 | 450 |
| Temperature of fixed bed reactor (°C) | 380 | 365 | 405 | 462 |
| Mass of H2O (g) | 19.63 | - | - | - |
| Yield of H2O (wt.%) | 2.80 | - | - | - |
| Mass of Bio-oil (g) | 160.37 | 109.71 | 99.71 | 11 |
| Yield of Bio-oil (wt.%) | 22.91 | 15.67 | 14.24 | 1.57 |
| Process Parameters | 450 (°C) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7.50 (wt.) | ||||
| 40 (min) | 50 (min) | 60 (min) | 70 (min) | |
| Temperature of pyrolysis reactor (°C) | 374 | 393 | 410 | 450 |
| Temperature of fixed bed reactor (°C) | 371 | 397 | 465 | 470 |
| Mass of H2O (g) | 10.45 | 7 | - | - |
| Yield of H2O (wt.%) | 1.49 | 1 | - | - |
| Mass of Bio-oil (g) | 102.45 | 197.74 | 172.67 | 94.22 |
| Yield of Bio-oil (wt.%) | 14.64 | 28.25 | 24.67 | 13.46 |
| Process Parameters | 450 (°C) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10.0 (wt.) | ||||
| 50 (min) | 60 (min) | 70 (min) | 80 (min) | |
| Temperature of pyrolysis reactor (°C) | 375 | 403 | 423 | 450 |
| Temperature of fixed bed reactor (°C) | 394 | 404 | 428 | 455 |
| Mass of H2O (g) | 14.1 | 1.4 | - | - |
| Yield of H2O (wt.%) | 2.01 | 0.2 | - | - |
| Mass of Bio-oil (g) | 133.86 | 262.95 | 113.12 | 84.2 |
| Yield of Bio-oil (wt.%) | 19.12 | 37.56 | 16.16 | 12.03 |
| Temperature/Catalyst | tReaction [min] | Physical-Chemistry Properties | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ρ [g/cm3] | I.A [mg KOH/g] | I.R [-] | ν [mm2/s] | ||
| 450 °C | 50 | 0.861 | 131.10 | 1.445 | 9.80 |
| 60 | 0.849 | 42.72 | 1.458 | 6.90 | |
| 70 | 0.847 | 33.90 | 1.460 | 6.30 | |
| 80 | 0.841 | 31.64 | 1.445 | 5.52 | |
| 450 °C, 5% red mud (wt.) | 40 | 0.843 | 113.90 | 1.444 | 4.20 |
| 50 | 0.840 | 11.25 | 1.458 | 3.96 | |
| 60 | 0.838 | 6.98 | 1.473 | 3.83 | |
| 70 | 0.813 | 1.13 | 1.439 | 3.24 | |
| 450 °C, 7.5% red mud (wt.) | 40 | 0.871 | 135.27 | 1.445 | 8.45 |
| 50 | 0.857 | 124.41 | 1.451 | 8.39 | |
| 60 | 0.844 | 72.18 | 1.458 | 5.30 | |
| 70 | 0.841 | 8.83 | 1.442 | 4.46 | |
| 450 °C, 10% red mud (wt.) | 50 | 0.874 | 124.41 | 1.408 | 8.10 |
| 60 | 0.853 | 92.09 | 1.409 | 7.78 | |
| 70 | 0.848 | 42.50 | 1.405 | 4.10 | |
| 80 | 0.829 | 26.49 | 1.407 | 2.80 | |
| Experiment | Reaction Time [min] | Weight of Bio-Oil [g] | I.A [mg KOH/g] | Bulk IA [mg KOH/g] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 450 °C | 50 | 294.00 | 131.10 | 73.31 |
| 60 | 311.98 | 42.72 | ||
| 70 | 176.10 | 33.90 | ||
| 80 | 12.15 | 31.64 | ||
| 450 °C, 5% red mud (wt.) | 40 | 160.37 | 113.90 | 53.07 |
| 50 | 109.71 | 11.25 | ||
| 60 | 99.71 | 6.98 | ||
| 70 | 11.00 | 1.13 | ||
| 450 °C, 7.5% red mud (wt.) | 40 | 102.45 | 135.27 | 91.26 |
| 50 | 197.74 | 124.41 | ||
| 60 | 172.67 | 72.18 | ||
| 70 | 94.22 | 8.83 | ||
| 450 °C, 10% red mud (wt.) | 50 | 133.86 | 124.41 | 80.63 |
| 60 | 262.95 | 92.09 | ||
| 70 | 113.12 | 42.50 | ||
| 80 | 84.20 | 26.49 |
| Compounds | 0.0% (No Fixed Bed) [%.Area] | 5.0% [%.Area] |
|---|---|---|
| C5-C10 | 2.6 | 16.6 |
| C11-C15 | 34.9 | 48.3 |
| C16+ | 62.4 | 35.1 |
| Chemical Function | 0.0% [%.Area] | 5.0% [%.Area] |
|---|---|---|
| Alkanes | 27.85 | 42.96 |
| Alkenes | 20.89 | 41.05 |
| Cyclic compounds | 9.85 | 6.19 |
| Carboxylic acids | 20.99 | 0.00 |
| Ketones | 18.42 | 8.02 |
| Aldehydes | 0.00 | 0.86 |
| Alcohols | 2.00 | 0.92 |
| Total | 100.00 | 100.00 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ferreira, C.C.; Bernar, L.P.; de Freitas Costa, A.F.; da Silva Ribeiro, H.J.; Santos, M.C.; Moraes, N.L.; Costa, Y.S.; Baia, A.C.F.; Mendonça, N.M.; da Mota, S.A.P.; et al. Improving Fuel Properties and Hydrocarbon Content from Residual Fat Pyrolysis Vapors over Activated Red Mud Pellets in Two-Stage Reactor: Optimization of Reaction Time and Catalyst Content. Energies 2022, 15, 5595. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15155595
Ferreira CC, Bernar LP, de Freitas Costa AF, da Silva Ribeiro HJ, Santos MC, Moraes NL, Costa YS, Baia ACF, Mendonça NM, da Mota SAP, et al. Improving Fuel Properties and Hydrocarbon Content from Residual Fat Pyrolysis Vapors over Activated Red Mud Pellets in Two-Stage Reactor: Optimization of Reaction Time and Catalyst Content. Energies. 2022; 15(15):5595. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15155595
Chicago/Turabian StyleFerreira, Caio Campos, Lucas Pinto Bernar, Augusto Fernando de Freitas Costa, Haroldo Jorge da Silva Ribeiro, Marcelo Costa Santos, Nathalia Lobato Moraes, Yasmin Santos Costa, Ana Cláudia Fonseca Baia, Neyson Martins Mendonça, Sílvio Alex Pereira da Mota, and et al. 2022. "Improving Fuel Properties and Hydrocarbon Content from Residual Fat Pyrolysis Vapors over Activated Red Mud Pellets in Two-Stage Reactor: Optimization of Reaction Time and Catalyst Content" Energies 15, no. 15: 5595. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15155595
APA StyleFerreira, C. C., Bernar, L. P., de Freitas Costa, A. F., da Silva Ribeiro, H. J., Santos, M. C., Moraes, N. L., Costa, Y. S., Baia, A. C. F., Mendonça, N. M., da Mota, S. A. P., da Costa Assunção, F. P., de Castro, D. A. R., Quaresma, C. C. V., Duvoisin, S., Jr., Borges, L. E. P., & Machado, N. T. (2022). Improving Fuel Properties and Hydrocarbon Content from Residual Fat Pyrolysis Vapors over Activated Red Mud Pellets in Two-Stage Reactor: Optimization of Reaction Time and Catalyst Content. Energies, 15(15), 5595. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15155595






