State-of-the-Art Using Bibliometric Analysis of Wind-Speed and -Power Forecasting Methods Applied in Power Systems
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Methodology for the Systematic Literature Review
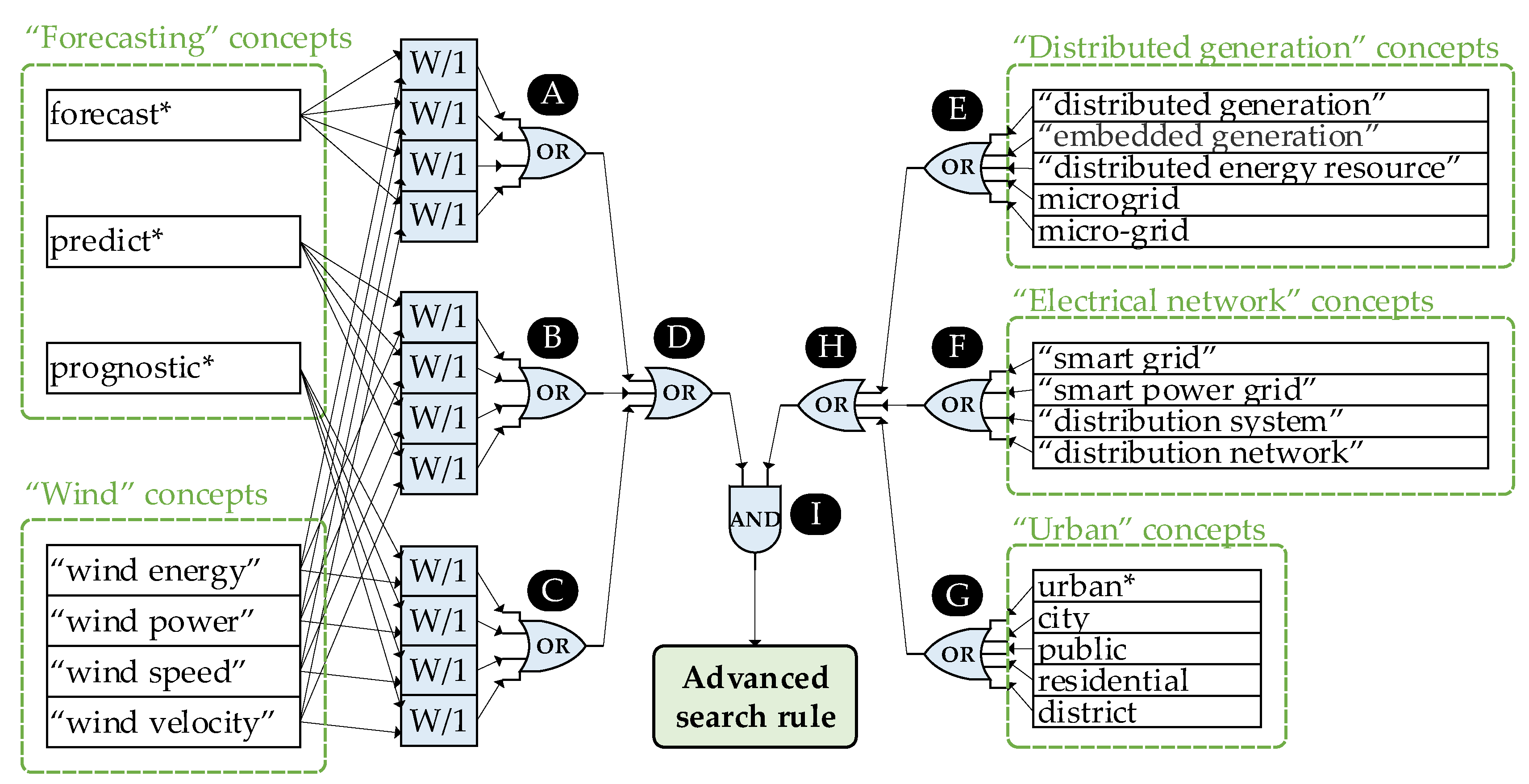
1.1.1. Identification—Search Strategy
- “Forecasting” terms: This set included synonyms that the authors use to refer to the term forecast, and the words derived from it. In the case of the Scopus citation database, to find words that derive from one another, the (*) symbol was used at the end of each word. For example: “forecast*” searches for terms such as forecasting, forecast, etc.
- “Wind” terms: This set described our forecast objective, e.g., wind power, OR wind energy, OR wind speed, OR wind direction were some of the terms used by the authors to refer to the subject.
- “Distributed generation”, “Electrical network” and “Urban” terms: These sets included associated or related terms that have power systems of the urban area implicit within their definitions.
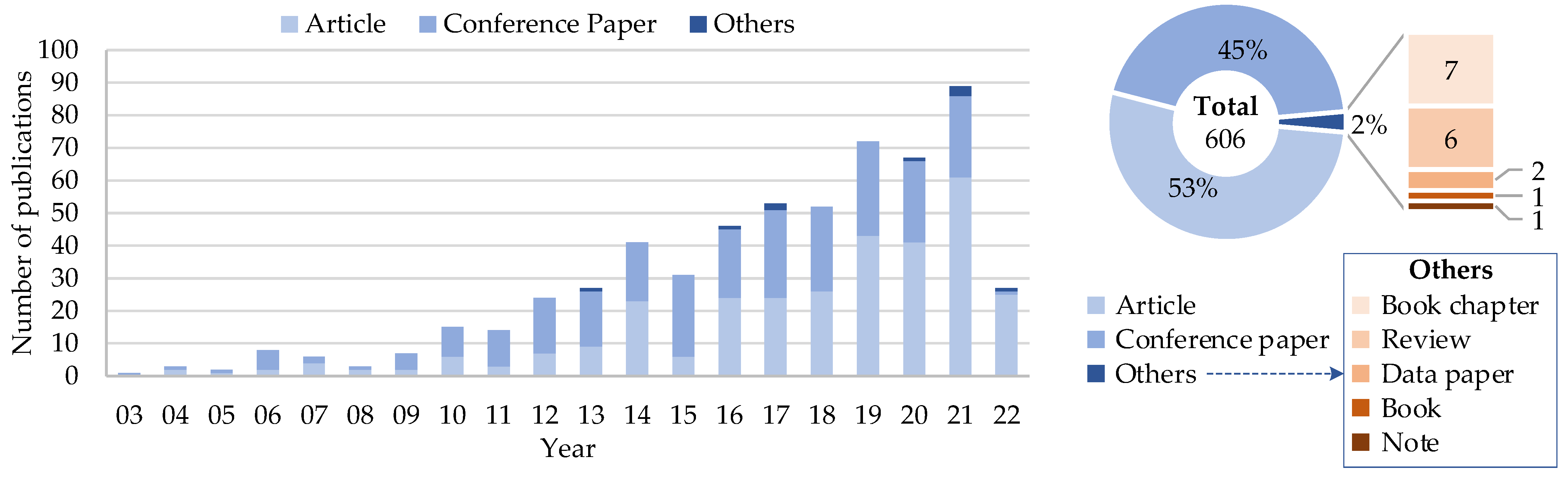
1.1.2. Screening—Quantitative Synthesis
1.1.3. Eligibility—Selection Criteria
1.1.4. Inclusion—Critical Review
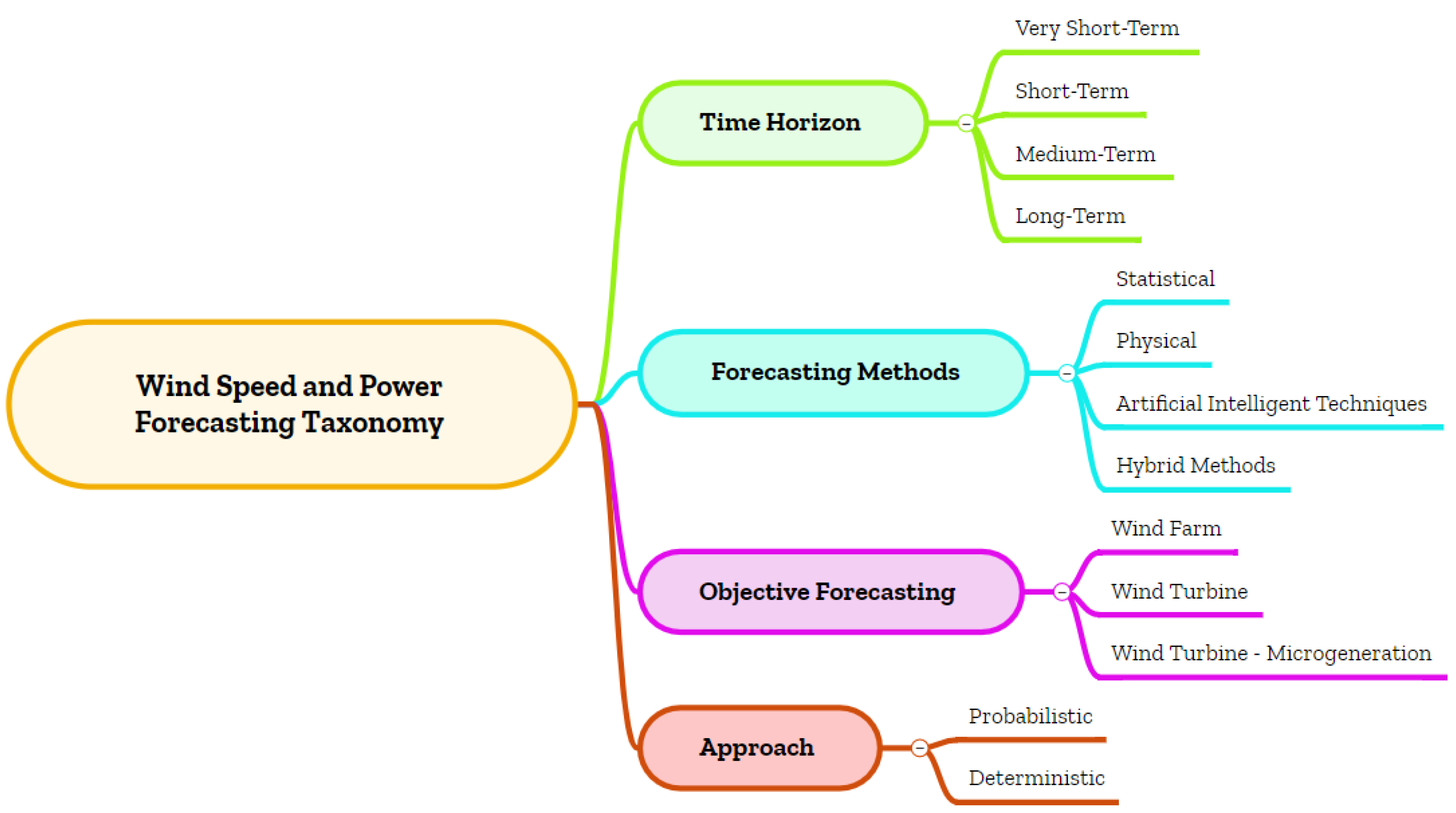
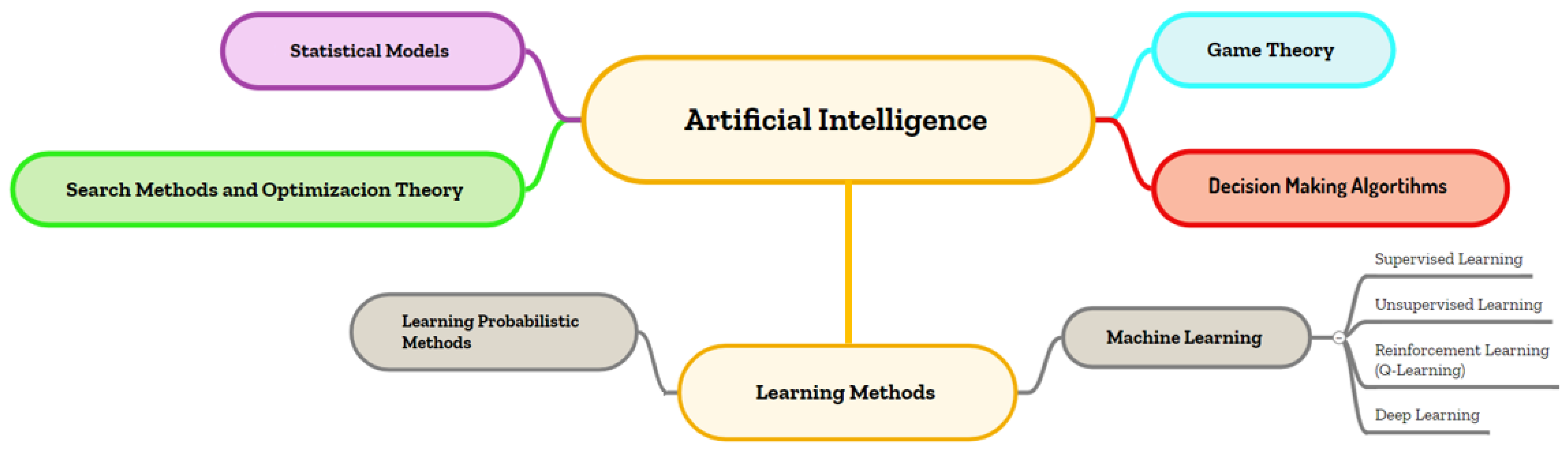
2. Taxonomy of Wind Power and Wind Speed
2.1. Time Horizon
2.1.1. Physical Models
2.1.2. Statistical Models
2.1.3. Artificial Intelligence-Based Models
2.1.4. Hybrid Models
2.2. Objective Forecasting
Wind Power Model
2.3. Uncertainty
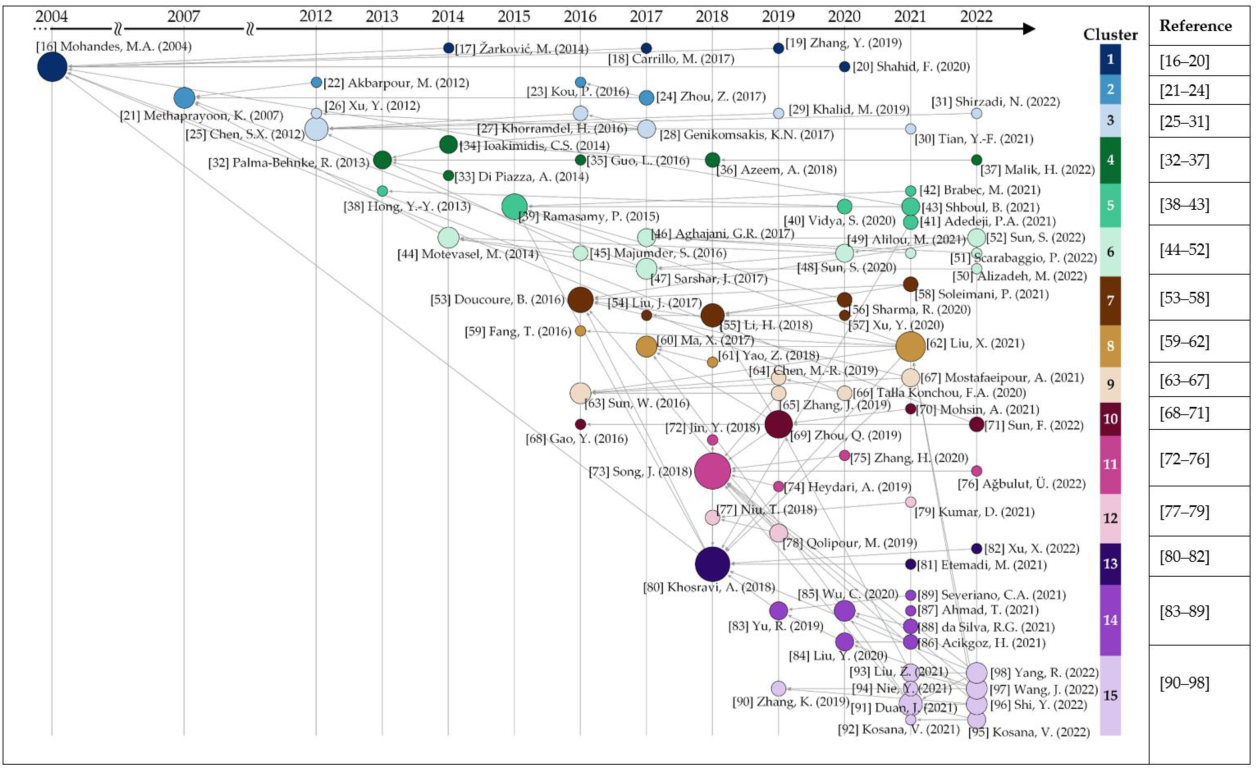
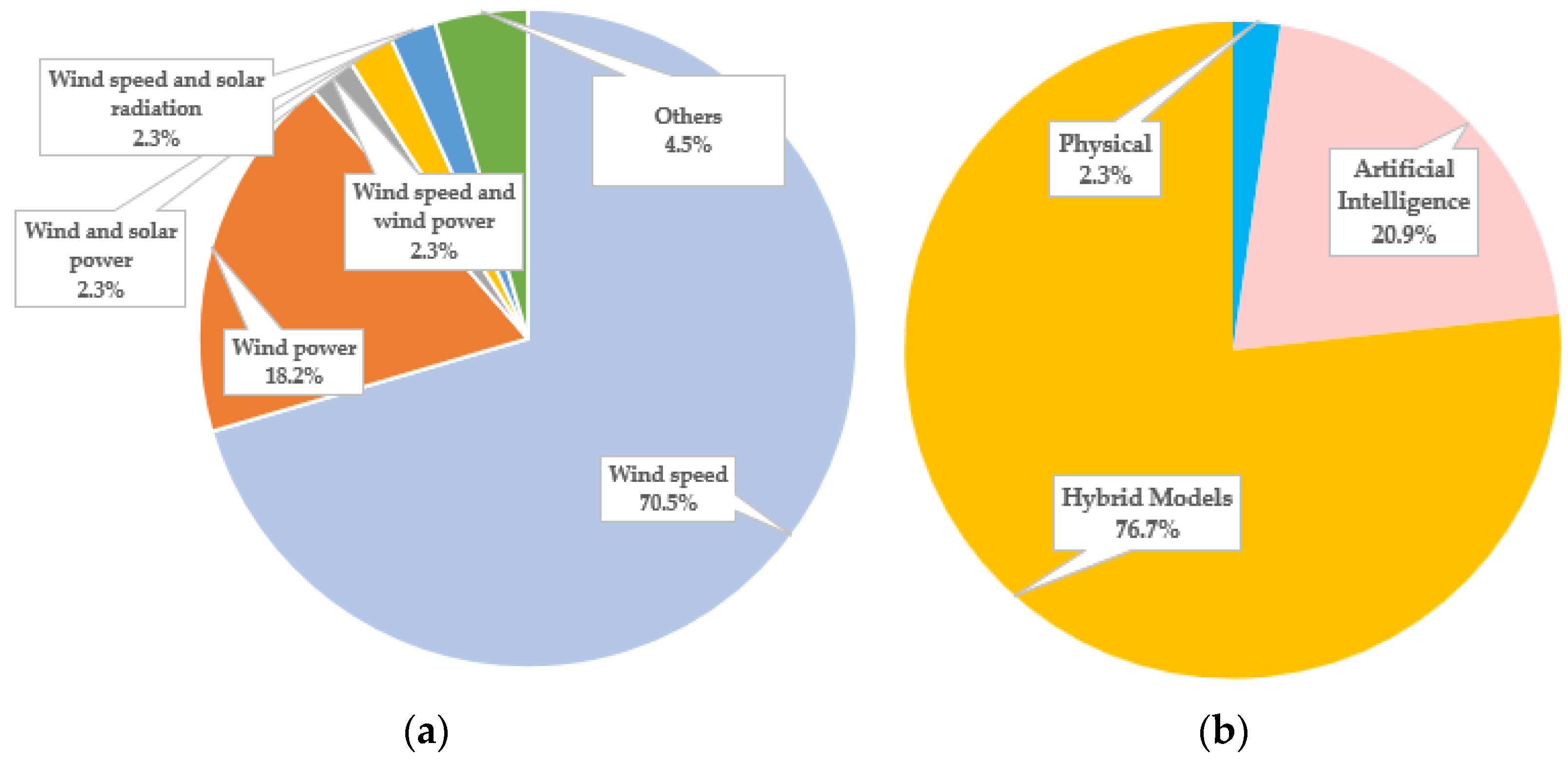
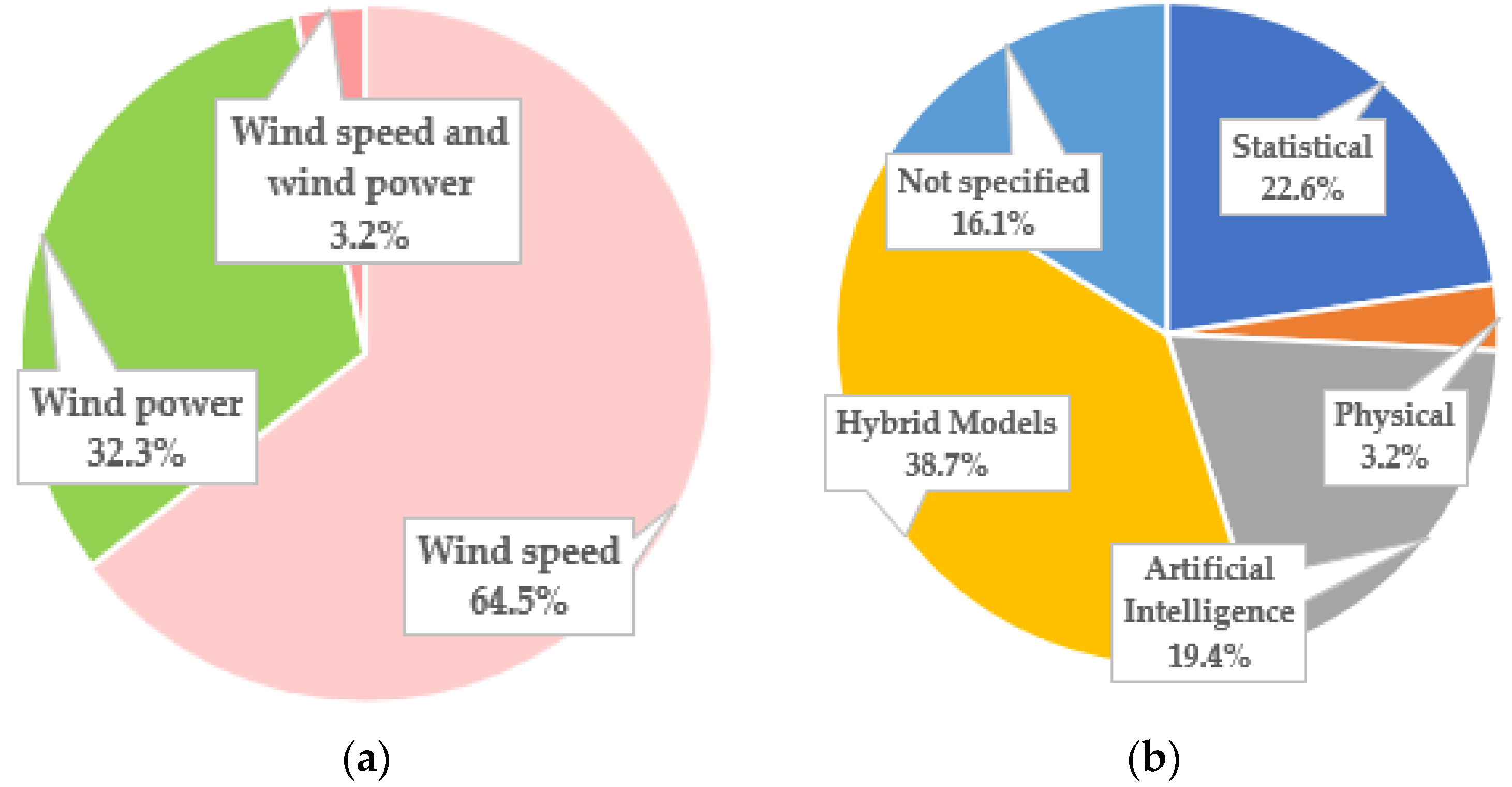
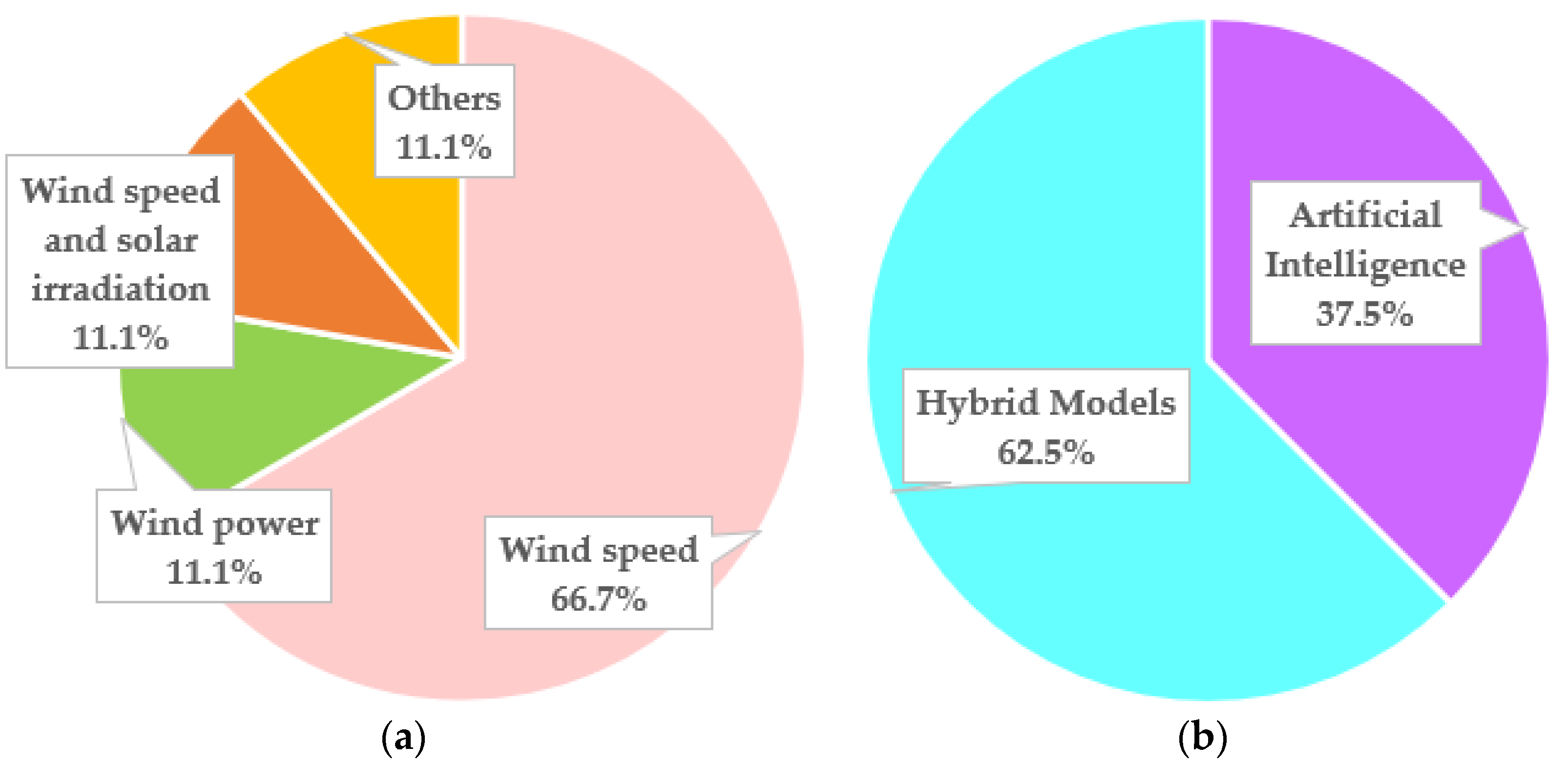
3. Bibliometric Analysis Results
3.1. Cluster 1
3.2. Cluster 2
3.3. Cluster 3
3.4. Cluster 4
3.5. Cluster 5
3.6. Cluster 6
3.7. Cluster 7
3.8. Cluster 8
3.9. Cluster 9
3.10. Cluster 10
3.11. Cluster 11
3.12. Cluster 12
3.13. Cluster 13
3.14. Cluster 14
3.15. Cluster 15
4. Discussion
4.1. Very Short Term
4.2. Short Term
4.3. Medium Term
4.4. Long-Term
4.5. General Discussions
4.5.1. Calculation Time
4.5.2. Model Efficiency
| Indicator | Equation |
|---|---|
| MSE | |
| MAE | |
| MAPE | |
| RMSE |
| Indicator | Equation |
|---|---|
| FINAW | |
| FICP |
4.5.3. Data Sets
4.5.4. Forecast Scenarios
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Technologies. Available online: https://www.irena.org/Statistics/View-Data-by-Topic/Capacity-and-Generation/Technologies (accessed on 8 May 2022).
- Global Wind Energy Council. GWEC-Global-Wind-Report-2021; Global Wind Energy Council: Brussels, Belgium, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Theo, W.L.; Lim, J.S.; Ho, W.S.; Hashim, H.; Lee, C.T. Review of Distributed Generation (DG) System Planning and Optimisation Techniques: Comparison of Numerical and Mathematical Modelling Methods. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 67, 531–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giebel, G.; Kariniotakis, G. The Anemos project. In The State-of-the-Art in Short-Term Forecasting of Wind Power—A Literature Overview; U.S. Department of Energy Office of Scientific and Technical Information: Oak Ridge, TN, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Giebel, G.; Brownsword, R.; Kariniotakis, G.; Denhard, M.; Draxl, C. The State-Of-The-Art in Short-Term Prediction of Wind Power A Literature Overview; Technical Report, ANEMOS.plus; U.S. Department of Energy Office of Scientific and Technical Information: Oak Ridge, TN, USA, 2011.
- Ding, Y. Data Science for Wind Energy; Chapman & Hall: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmadi, M.; Khashei, M. Current Status of Hybrid Structures in Wind Forecasting. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2021, 99, 104133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zou, R.; Liu, F.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Q. A Review of Wind Speed and Wind Power Forecasting with Deep Neural Networks. Appl. Energy 2021, 304, 117766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhayat, G.; Mehmood, R. A Review and Taxonomy of Wind and Solar Energy Forecasting Methods Based on Deep Learning. Energy AI 2021, 4, 100060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, T.; Zhang, H.; Yan, B. A Review on Renewable Energy and Electricity Requirement Forecasting Models for Smart Grid and Buildings. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 55, 102052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, H.; Khosravi, A.; Yang, D.; Srinivasan, D. A Survey of Computational Intelligence Techniques for Wind Power Uncertainty Quantification in Smart Grids. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2020, 31, 4582–4599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urrútia, G.; Bonfill, X. Declaración PRIMSA: Una propuesta para mejorar la publicación de revisiones sistemáticas y metaanálisis. Medicina Clínica. 2010, 135, 507–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waltman, L.; van Eck, N.J.; Noyons, E.C.M. A Unified Approach to Mapping and Clustering of Bibliometric Networks. J. Informetr. 2010, 4, 629–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waltman, L.; van Eck, N.J. A Smart Local Moving Algorithm for Large-Scale Modularity-Based Community Detection. Eur. Phys. J. B 2013, 86, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caicedo, J.E.; Romero, A.A.; Zini, H.C. Evaluación de La Distorsión Armónica En Sistemas de Distribución Residencial: Revisión Literaria. Ing. Investig. 2017, 37, 72–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohandes, M.A.; Halawani, T.O.; Rehman, S.; HuSSain, A.A. Support Vector Machines for Wind Speed Prediction. Renew. Energy 2004, 29, 939–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Žarković, M.; Šošić, D.; Dobrić, G. Fuzzy Based Prediction of Wind Distributed Generation Impact on Distribution Network: Case Study—Banat Region, Serbia. J. Renew. Sustain. Energy 2014, 6, 013120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrillo, M.; del Ser, J.; Nekane Bilbao, M.; Perfecto, C.; Camacho, D. Wind Power Production Forecasting Using Ant Colony Optimization and Extreme Learning Machines. In Intelligent Distributed Computing XI; Springer Nature: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; Volume 737. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Gao, S.; Han, J.; Ban, M. Wind Speed Prediction Research Considering Wind Speed Ramp and Residual Distribution. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 131873–131887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, F.; Zameer, A.; Mehmood, A.; Raja, M.A.Z. A Novel Wavenets Long Short Term Memory Paradigm for Wind Power Prediction. Appl. Energy 2020, 269, 115098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Methaprayoon, K.; Yingvivatanapong, C.; Lee, W.J.; Liao, J.R. An Integration of ANN Wind Power Estimation into Unit Commitment Considering the Forecasting Uncertainty. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2007, 43, 1441–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbarpour, M.; Esmailnia Shirvani, R.; Lohi, M.; Khalilifar, H. Optimal Operation of a Microgrid in the Power Market Environment by PSO Algorithm. Life Sci. J. 2012, 9, 160–170. [Google Scholar]
- Kou, P.; Liang, D.; Gao, L.; Gao, F. Stochastic Coordination of Plug-In Electric Vehicles and Wind Turbines in Microgrid: A Model Predictive Control Approach. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2016, 7, 1537–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Xiong, F.; Huang, B.; Xu, C.; Jiao, R.; Liao, B.; Yin, Z.; Li, J. Game-Theoretical Energy Management for Energy Internet with Big Data-Based Renewable Power Forecasting. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 5731–5746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.X.; Gooi, H.B.; Wang, M.Q. Sizing of Energy Storage for Microgrids. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2012, 3, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Dong, Z.Y.; Xu, Z.; Meng, K.; Wong, K.P. An Intelligent Dynamic Security Assessment Framework for Power Systems with Wind Power. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2012, 8, 995–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorramdel, H.; Aghaei, J.; Khorramdel, B.; Siano, P. Optimal Battery Sizing in Microgrids Using Probabilistic Unit Commitment. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2016, 12, 834–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genikomsakis, K.N.; Lopez, S.; Dallas, P.I.; Ioakimidis, C.S. Simulation of Wind-Battery Microgrid Based on Short-Term Wind Power Forecasting. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, M. Wind Power Economic Dispatch—Impact of Radial Basis Functional Networks and Battery Energy Storage. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 36819–36832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.F.; Liao, R.J.; Farkoush, S.G. Placement and Sizing of EESS Bundled with Uncertainty Modeling by Two-Stage Stochastic Search Based on Improved Shark Smell Optimization Algorithm in Micro-Grids. Energy Rep. 2021, 7, 4792–4808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirzadi, N.; Nasiri, F.; El-Bayeh, C.; Eicker, U. Optimal Dispatching of Renewable Energy-Based Urban Microgrids Using a Deep Learning Approach for Electrical Load and Wind Power Forecasting. Int. J. Energy Res. 2022, 46, 3173–3188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma-Behnke, R.; Benavides, C.; Lanas, F.; Severino, B.; Reyes, L.; Llanos, J.; Saez, D. A Microgrid Energy Management System Based on the Rolling Horizon Strategy. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2013, 4, 996–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- di Piazza, A.; di Piazza, M.C.; Vitale, G. Estimation and Forecast of Wind Power Generation by FTDNN and NARX-Net Based Models for Energy Management Purpose in Smart Grids. Renew. Energy Power Qual. J. 2014, 1, 995–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioakimidis, C.S.; Oliveira, L.J.; Genikomsakis, K.N. Wind Power Forecasting in a Residential Location as Part of the Energy Box Management Decision Tool. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2014, 10, 2103–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Liu, W.; Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Jiao, B.; Wang, W.; Wang, C.; Li, F. Energy Management System for Stand-Alone Wind-Powered-Desalination Microgrid. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2016, 7, 1079–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azeem, A.; Fatema, N.; Malik, H. κ-NN and ANN Based Deterministic and Probabilistic Wind Speed Forecasting Intelligent Approach. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2018, 35, 5021–5031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, H.; Khurshaid, T.; Almutairi, A.; Alotaibi, M.A. Multi-Step Ahead Time-Series Wind Speed Forecasting for Smart-Grid Application. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2022, 42, 633–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.-Y.; Yu, T.-H.; Liu, C.-Y. Hour-Ahead Wind Speed and Power Forecasting Using Empirical Mode Decomposition. Energies 2013, 6, 6137–6152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramasamy, P.; Chandel, S.S.; Yadav, A.K. Wind Speed Prediction in the Mountainous Region of India Using an Artificial Neural Network Model. Renew. Energy 2015, 80, 338–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidya, S.; Srie Vidhya Janani, E. Tabu Search Algorithm Based General Regression Neural Network for Long Term Wind Speed Predictions. Automatika 2020, 61, 657–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adedeji, P.A.; Akinlabi, S.A.; Madushele, N.; Olatunji, O.O. Hybrid Neurofuzzy Wind Power Forecast and Wind Turbine Location for Embedded Generation. Int. J. Energy Res. 2021, 45, 413–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brabec, M.; Craciun, A.; Dumitrescu, A. Hybrid Numerical Models for Wind Speed Forecasting. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 2021, 220, 105669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shboul, B.; AL-Arfi, I.; Michailos, S.; Ingham, D.; Ma, L.; Hughes, K.J.; Pourkashanian, M. A New ANN Model for Hourly Solar Radiation and Wind Speed Prediction: A Case Study over the North & South of the Arabian Peninsula. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2021, 46, 101248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motevasel, M.; Seifi, A.R. Expert Energy Management of a Micro-Grid Considering Wind Energy Uncertainty. Energy Convers. Manag. 2014, 83, 58–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumder, S.; Khaparde, S.A. Revenue and Ancillary Benefit Maximisation of Multiple Non-Collocated Wind Power Producers Considering Uncertainties. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2016, 10, 789–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghajani, G.R.; Shayanfar, H.A.; Shayeghi, H. Demand Side Management in a Smart Micro-Grid in the Presence of Renewable Generation and Demand Response. Energy 2017, 126, 622–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarshar, J.; Moosapour, S.S.; Joorabian, M. Multi-Objective Energy Management of a Micro-Grid Considering Uncertainty in Wind Power Forecasting. Energy 2017, 139, 680–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Fu, J.; Wei, L.; Li, A. Multi-Objective Optimal Dispatching for a Grid-Connected Micro-Grid Considering Wind Power Forecasting Probability. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 46981–46997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alilou, M.; Tousi, B.; Shayeghi, H. Multi-Objective Energy Management of Smart Homes Considering Uncertainty in Wind Power Forecasting. Electr. Eng. 2021, 103, 1367–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh Bidgoli, M.; Ahmadian, A. Multi-Stage Optimal Scheduling of Multi-Microgrids Using Deep-Learning Artificial Neural Network and Cooperative Game Approach. Energy 2022, 239, 122036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarabaggio, P.; Grammatico, S.; Carli, R.; Dotoli, M. Distributed Demand Side Management with Stochastic Wind Power Forecasting. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2022, 30, 97–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, X.; Lu, H. Multi-Objective Optimization Dispatching of a Micro-Grid Considering Uncertainty in Wind Power Forecasting. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 2859–2874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doucoure, B.; Agbossou, K.; Cardenas, A. Time Series Prediction Using Artificial Wavelet Neural Network and Multi-Resolution Analysis: Application to Wind Speed Data. Renew. Energy 2016, 92, 202–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, X.; Lu, Y. A Novel Hybrid Methodology for Short-Term Wind Power Forecasting Based on Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Inference System. Renew. Energy 2017, 103, 620–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, J.; Lu, H.; Guo, Z. Research and Application of a Combined Model Based on Variable Weight for Short Term Wind Speed Forecasting. Renew. Energy 2018, 116, 669–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Shikhola, T.; Kohli, J.K. Modified Fuzzy Q-Learning Based Wind Speed Prediction. J. Wind Eng. Ind. Aerodyn. 2020, 206, 104361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Liu, H.; Long, Z. A Distributed Computing Framework for Wind Speed Big Data Forecasting on Apache Spark. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2020, 37, 100582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soleimani, P.; Emami, B.; Rafei, M.; Shahrasbi, H. Forecasting the Wind Direction by Using Time Series Models with Long-Term Memory (Case Study: Nayer Region). Int. J. Energy Sect. Manag. 2021, 15, 385–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, T.; Lahdelma, R. Evaluation of a Multiple Linear Regression Model and SARIMA Model in Forecasting Heat Demand for District Heating System. Appl. Energy 2016, 179, 544–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Jin, Y.; Dong, Q. A Generalized Dynamic Fuzzy Neural Network Based on Singular Spectrum Analysis Optimized by Brain Storm Optimization for Short-Term Wind Speed Forecasting. Appl. Soft Comput. 2017, 54, 296–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.; Wang, C. A Hybrid Model Based on a Modified Optimization Algorithm and an Artificial Intelligence Algorithm for Short-Term Wind Speed Multi-Step Ahead Forecasting. Sustainability 2018, 10, 1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Lin, Z.; Feng, Z. Short-Term Offshore Wind Speed Forecast by Seasonal ARIMA—A Comparison against GRU and LSTM. Energy 2021, 227, 120492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Liu, M. Wind Speed Forecasting Using FEEMD Echo State Networks with RELM in Hebei, China. Energy Convers. Manag. 2016, 114, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.R.; Zeng, G.Q.; Lu, K.D.; Weng, J. A Two-Layer Nonlinear Combination Method for Short-Term Wind Speed Prediction Based on ELM, ENN, and LSTM. IEEE Internet Things J. 2019, 6, 6997–7010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yan, J.; Infield, D.; Liu, Y.; Lien, F. Short-Term Forecasting and Uncertainty Analysis of Wind Turbine Power Based on Long Short-Term Memory Network and Gaussian Mixture Model. Appl. Energy 2019, 241, 229–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talla Konchou, F.A.; Tiam Kapen, P.; Kenfack Magnissob, S.B.; Youssoufa, M.; Tchinda, R. Prediction of Wind Speed Profile Using Two Artificial Neural Network Models: An Ab Initio Investigation in the Bapouh’s City, Cameroon. Int. J. Energy Sect. Manag. 2020, 15, 566–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafaeipour, A.; Goli, A.; Rezaei, M.; Qolipour, M.; Arabnia, H.R.; Goudarzi, H.; Behnam, E. Performance of Different Hybrid Algorithms for Prediction of Wind Speed Behavior. Wind Eng. 2021, 45, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Qu, C.; Zhang, K. A Hybrid Method Based on Singular Spectrum Analysis, Firefly Algorithm, and BP Neural Network for Short-Term Wind Speed Forecasting. Energies 2016, 9, 757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Wang, C.; Zhang, G. Hybrid Forecasting System Based on an Optimal Model Selection Strategy for Different Wind Speed Forecasting Problems. Appl. Energy 2019, 250, 1559–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohsin, S.; Ramli, S.N.; Imdad, M. Medium-Term Wind Speed Prediction Using Bayesian Neural Network (BNN). Int. J. Syst. Innov. 2021, 6, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.; Jin, T. A Hybrid Approach to Multi-Step, Short-Term Wind Speed Forecasting Using Correlated Features. Renew. Energy 2022, 186, 742–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Ju, P.; Rehtanz, C.; Wu, F.; Pan, X. Equivalent Modeling of Wind Energy Conversion Considering Overall Effect of Pitch Angle Controllers in Wind Farm. Appl. Energy 2018, 222, 485–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Wang, J.; Lu, H. A Novel Combined Model Based on Advanced Optimization Algorithm for Short-Term Wind Speed Forecasting. Appl. Energy 2018, 215, 643–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heydari, A.; Astiaso Garcia, D.; Keynia, F.; Bisegna, F.; de Santoli, L. A Novel Composite Neural Network Based Method for Wind and Solar Power Forecasting in Microgrids. Appl. Energy 2019, 251, 113353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Luo, H. An Advanced Hybrid Forecasting System for Wind Speed Point Forecasting and Interval Forecasting. Complexity 2020, 2020, 7854286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ağbulut, Ü. A Novel Stochastic Model for Very Short-Term Wind Speed Forecasting in the Determination of Wind Energy Potential of a Region: A Case Study from Turkey. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2022, 51, 101853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, T.; Wang, J.; Zhang, K.; Du, P. Multi-Step-Ahead Wind Speed Forecasting Based on Optimal Feature Selection and a Modified Bat Algorithm with the Cognition Strategy. Renew. Energy 2018, 118, 213–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qolipour, M.; Mostafaeipour, A.; Saidi-Mehrabad, M.; Arabnia, H.R. Prediction of Wind Speed Using a New Grey-Extreme Learning Machine Hybrid Algorithm: A Case Study. Energy Environ. 2019, 30, 44–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.; Mathur, H.D.; Bhanot, S.; Bansal, R.C. Forecasting of Solar and Wind Power Using LSTM RNN for Load Frequency Control in Isolated Microgrid. Int. J. Model. Simul. 2021, 41, 311–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosravi, A.; Machado, L.; Nunes, R.O. Time-Series Prediction of Wind Speed Using Machine Learning Algorithms: A Case Study Osorio Wind Farm, Brazil. Appl. Energy 2018, 224, 550–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etemadi, M.; Abdollahi, A.; Rashidinejad, M.; Aalami, H.A. Wind Turbine Output Power Prediction in a Probabilistic Framework Based on Fuzzy Intervals. Iran. J. Sci. Technol.—Trans. Electr. Eng. 2021, 45, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Wei, Y. An Ultra-Short-Term Wind Speed Prediction Model Using LSTM and CNN. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2022, 81, 10819–10837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.; Liu, Z.; Li, X.; Lu, W.; Ma, D.; Yu, M.; Wang, J.; Li, B. Scene Learning: Deep Convolutional Networks for Wind Power Prediction by Embedding Turbines into Grid Space. Appl. Energy 2019, 238, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Qin, H.; Zhang, Z.; Pei, S.; Jiang, Z.; Feng, Z.; Zhou, J. Probabilistic Spatiotemporal Wind Speed Forecasting Based on a Variational Bayesian Deep Learning Model. Appl. Energy 2020, 260, 114259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Wang, J.; Chen, X.; Du, P.; Yang, W. A Novel Hybrid System Based on Multi-Objective Optimization for Wind Speed Forecasting. Renew. Energy 2020, 146, 149–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acikgoz, H.; Budak, U.; Korkmaz, D.; Yildiz, C. WSFNet: An Efficient Wind Speed Forecasting Model Using Channel Attention-Based Densely Connected Convolutional Neural Network. Energy 2021, 233, 121121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, T.; Zhang, D.; Huang, C. Methodological Framework for Short-and Medium-Term Energy, Solar and Wind Power Forecasting with Stochastic-Based Machine Learning Approach to Monetary and Energy Policy Applications. Energy 2021, 231, 120911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, R.G.; Ribeiro, M.H.D.M.; Moreno, S.R.; Mariani, V.C.; Coelho, L. dos S. A Novel Decomposition-Ensemble Learning Framework for Multi-Step Ahead Wind Energy Forecasting. Energy 2021, 216, 119174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Severiano, C.A.; e Silva, P.C.D.L.; Weiss Cohen, M.; Guimarães, F.G. Evolving Fuzzy Time Series for Spatio-Temporal Forecasting in Renewable Energy Systems. Renew. Energy 2021, 171, 764–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Qu, Z.; Dong, Y.; Lu, H.; Leng, W.; Wang, J.; Zhang, W. Research on a Combined Model Based on Linear and Nonlinear Features—A Case Study of Wind Speed Forecasting. Renew. Energy 2019, 130, 814–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.; Zuo, H.; Bai, Y.; Duan, J.; Chang, M.; Chen, B. Short-Term Wind Speed Forecasting Using Recurrent Neural Networks with Error Correction. Energy 2021, 217, 119397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosana, V.; Madasthu, S.; Teeparthi, K. A Novel Hybrid Framework for Wind Speed Forecasting Using Autoencoder-Based Convolutional Long Short-Term Memory Network. Int. Trans. Electr. Energy Syst. 2021, 31, e13072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Jiang, P.; Wang, J.; Zhang, L. Ensemble Forecasting System for Short-Term Wind Speed Forecasting Based on Optimal Sub-Model Selection and Multi-Objective Version of Mayfly Optimization Algorithm. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 177, 114974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Y.; Liang, N.; Wang, J. Ultra-Short-Term Wind-Speed Bi-Forecasting System via Artificial Intelligence and a Double-Forecasting Scheme. Appl. Energy 2021, 301, 117452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosana, V.; Teeparthi, K.; Madasthu, S. Hybrid Wind Speed Prediction Framework Using Data Pre-Processing Strategy Based Autoencoder Network. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2022, 206, 107821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, H. Wind Speed Prediction for Offshore Sites Using a Clockwork Recurrent Network. Energies 2022, 15, 751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, S.; Zeng, B.; Lu, H. A Novel Ensemble Probabilistic Forecasting System for Uncertainty in Wind Speed. Appl. Energy 2022, 313, 118796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Liu, H.; Nikitas, N.; Duan, Z.; Li, Y.; Li, Y. Short-Term Wind Speed Forecasting Using Deep Reinforcement Learning with Improved Multiple Error Correction Approach. Energy 2022, 239, 122128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khamparia, A.; Singh, K.M. A Systematic Review on Deep Learning Architectures and Applications. Expert Syst. 2019, 36, e12400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozcanli, A.K.; Yaprakdal, F.; Baysal, M. Deep Learning Methods and Applications for Electrical Power Systems: A Comprehensive Review. Int. J. Energy Res. 2020, 44, 7136–7157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaee Jordehi, A. Allocation of Distributed Generation Units in Electric Power Systems: A Review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 56, 893–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colson, C.M.; Nehrir, M.H. A Review of Challenges to Real-Time Power Management of Microgrids. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Power and Energy Society General Meeting, PES ’09, Calgary, AB, Canada, 26–30 July 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Ley-21118_17-NOV-2018. Available online: https://www.bcn.cl/leychile/navegar?idNorma=1125560&idParte=0 (accessed on 25 July 2022).
- Resolución No. 174 de 2021. República de Colombia. Available online: https://www.creg.gov.co/sites/default/files/creg174-2021_compressed.pdf (accessed on 25 July 2022).
- IEC 61400-2:2013; Wind Turbines—Part 2, Small Wind Turbines. International Electrotechnical Commission: Geneva, Switzerland; ISBN 9782832212844.
- Zavala, V.M.; Constantinescu, E.M.; Anitescu, M. Economic Impacts of Advanced Weather Forecasting on Energy System Operations. In Proceedings of the Innovative Smart Grid Technologies Conference, ISGT 2010, Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 19–21 January 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Eskandar, H.; Sadollah, A.; Bahreininejad, A.; Hamdi, M. Water Cycle Algorithm—A Novel Metaheuristic Optimization Method for Solving Constrained Engineering Optimization Problems. Comput. Struct. 2012, 110–111, 151–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandana, S.; Mayorga, R.V. The New Rough Neuron. In Proceedings of the 2005 International Conference on Neural Networks and Brain Proceedings, ICNNB’05, Beijing, China, 13–15 October 2005; Volume 1, pp. 13–18. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, J.; Liu, Y.; Han, S.; Wang, Y.; Feng, S. Reviews on Uncertainty Analysis of Wind Power Forecasting. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 52, 1322–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Cluster | Number of Articles | Most-Cited Article/Number of Citations | Oldest Article/Year | Newest Article/Year | Most Linked Articles/Citing Articles/Referenced Articles |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 5 | [16]/593 | [16]/2004 | [20]/2020 | [16]/[17,18,19,20,43,66,71,80]/-- |
| 2 | 4 | [21]/205 | [21]/2007 | [24]/2017 | [21]/[22,24,44,47]/-- |
| 3 | 7 | [25]/664 | [25]/2012 | [31]/2022 | [25]/[27,29,30,31,45]/-- |
| 4 | 6 | [32]/544 | [32]/2013 | [37]/2022 | [32]/[33,34,35]/-- |
| 5 | 6 | [39]/108 | [38]/2013 | [43]/2021 | [39]/[40,42,43,56,62,80]/-- |
| 6 | 9 | [44]/170 | [44]/2014 | [52]/2022 | [44]/[45,47,48]/[21] |
| 7 | 6 | [53]/178 | [53]/2016 | [58]/2021 | [53]/[52,58,62,67,78,80]/-- |
| 8 | 4 | [60]/137 | [59]/2016 | [62]/2021 | [62]/[95,96]/[39,53,59,60,63,80] |
| 9 | 5 | [65]/105 | [63]/2016 | [67]/2021 | [63]/[62,64,65,67]/-- |
| 10 | 4 | [69]/53 | [68]/2016 | [71]/2022 | [69]/[70,71,93]/[55,60,68,73] |
| 11 | 5 | [73]/132 | [72]/2018 | [76]/2022 | [73]/[65,69,74,75,76,78,91,96,97,98]/[72,80] |
| 12 | 3 | [77]/76 | [77]/2018 | [79]/2021 | [78]/--/[53,73,77] |
| 13 | 3 | [80]/113 | [80]/2018 | [82]/2022 | [80]/[41,62,67,73,81,82,83,98]/[16,39,53] |
| 14 | 7 | [85]/79 | [83]/2019 | [89]/2021 | [85]/[86,88,91]/[60] |
| 15 | 9 | [91]/43 | [90]/2019 | [98]/2022 | [91]/[95,96,98]/[62,91,92] |
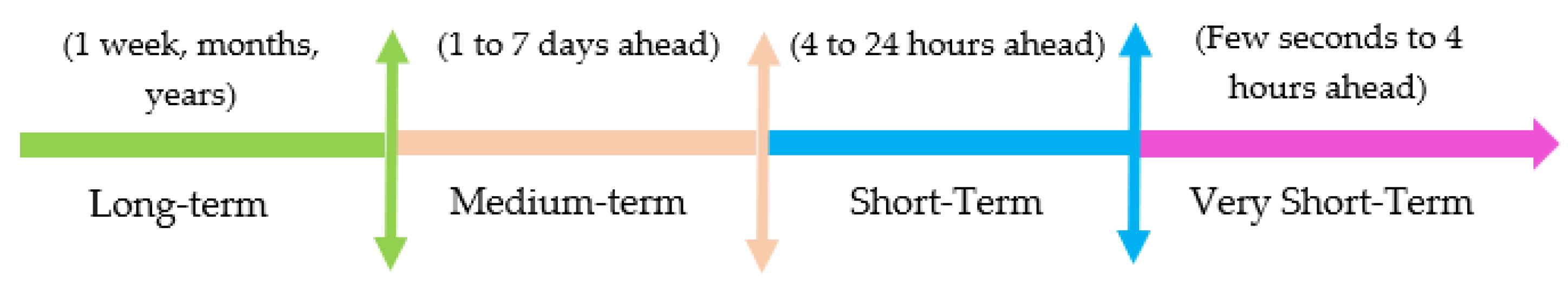
| Category | Scale of Forecast Horizon | Application | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Very short term | A few seconds to 4 h ahead |
| [17,18,20,24,29,32,35,38,41,43,53,54,55,56,57,58,59,60,61,63,64,68,69,71,75,76,77,79,80,82,83,84,85,86,87,88,90,91,93,94,95,96,97,98] |
| Short term | 4 to 24 h ahead |
| [19,20,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,30,32,34,37,39,42,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,62,69,70,71,72,78,86] |
| Medium term | 1 to 7 days ahead |
| [19,20,21,31,32,37,59,65,66,70,73] |
| Long term | 1 week, months, years |
| [16,20,33,36,40,59,63,67,74] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lagos, A.; Caicedo, J.E.; Coria, G.; Quete, A.R.; Martínez, M.; Suvire, G.; Riquelme, J. State-of-the-Art Using Bibliometric Analysis of Wind-Speed and -Power Forecasting Methods Applied in Power Systems. Energies 2022, 15, 6545. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15186545
Lagos A, Caicedo JE, Coria G, Quete AR, Martínez M, Suvire G, Riquelme J. State-of-the-Art Using Bibliometric Analysis of Wind-Speed and -Power Forecasting Methods Applied in Power Systems. Energies. 2022; 15(18):6545. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15186545
Chicago/Turabian StyleLagos, Ana, Joaquín E. Caicedo, Gustavo Coria, Andrés Romero Quete, Maximiliano Martínez, Gastón Suvire, and Jesús Riquelme. 2022. "State-of-the-Art Using Bibliometric Analysis of Wind-Speed and -Power Forecasting Methods Applied in Power Systems" Energies 15, no. 18: 6545. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15186545
APA StyleLagos, A., Caicedo, J. E., Coria, G., Quete, A. R., Martínez, M., Suvire, G., & Riquelme, J. (2022). State-of-the-Art Using Bibliometric Analysis of Wind-Speed and -Power Forecasting Methods Applied in Power Systems. Energies, 15(18), 6545. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15186545







