Energy harvesting guarantees continuous recharging of storage devices, ensuring that the wearable device’s building blocks receive an adequate power amount in all operating conditions. This section will introduce the attempts and discoveries of numerous research groups regarding the most efficient energy harvester technology applied to the human body.
3.1. Piezoelectric Wearable-Based Energy Harvester
A piezoelectric polymer generates a potential difference due to a mechanical deformation, which, properly gathered by a properly designed energy harvesting section, can power wearable applications. Since the main prerogatives of such applications concern their lightweight, biocompatibility, and the ability to conform to the human body, several advances were carried out to develop new flexible and stretchable piezoelectric materials (e.g., hybrid composite materials) and stretchable structures (e.g., kirigami designs, serpentine mesh patterns, and buckling forms, etc.) [
57]. The piezoelectric polymer can be used to develop a flexible and lightweight nanogenerator constituted of polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF)/LiCl electrospun nanofibers. In [
58], the authors showed that LiCl could improve the nanogenerator’s output voltage from 1.3 V to 5 V by increasing the β phase, to which the piezoelectric properties of the polymeric material are attributable [
59]. They developed a single-step process to create piezoelectric fabrics that involved electrospinning PVDF/LiCl nanofibers from a liquid solution. Applying an external electrical field to the PVDF/LiCl mixture during electrospinning deposition, the ions of different charges move on opposite sides, resulting in stretching and elongation. The addition of LiCl involves the separation of the positive ions from the negative ones, leading to an increase in electrical conductivity [
60]. Additionally, the authors verified the effect of different web thicknesses and temperature variations on PVDF/LiCl nanogenerator performance during the impact and vibration tests. As shown in
Figure 1, two aluminum foils surround the PVDF/LiCl harvester, which is rectangular and measures 3 cm × 1.5 cm. A pair of copper layers are positioned on either side of the aluminum foils to ensure high conductivity. Finally, silicon resin covered the nanogenerator’s surface to protect it from grime and humidity [
60]. The utility of LiCl is evident in
Figure 2, in which the nanogenerator’s output voltage after a tiny ball fall from the same altitude is represented with (a) and without (b) LiCl addition. The resulting device showed a strong temperature dependence. In fact, adding LiCl, as mentioned before, increased the output voltage with a linear increase in the range of 30–90 °C. This process can find easy applications in safety monitoring and medical diagnostic devices for realizing self-powered temperature sensors [
58].
Another study also promotes using a ferroelectric polymer heterostructure for realizing the so-called fabric-WPEH (Wearable Piezoelectric Energy Harvester), enabling the direct application of the transducers to clothes by heat press [
61].
In particular, the fabric-WPEH features a quick, easy, and inexpensive construction method that can be distilled into the three processes shown in
Figure 3a.
The solution has to be poured over a glass plane to obtain a self-supporting P(VDF-TrFE) layer;
A pair of fabric-based electrodes are fixed to the P(VDF-TrFE) layer by hot pressing and annealing after being covered with copper and nickel particles.
Electric poling aligns the P(VDF-TrFE) film’s electric dipoles.
The obtained harvester appears fully bendable and features a high piezoelectric d
33 coefficient of the P(VDF-TrFE) layer, making it suitable for scavenging energy from human movements (curling and pushing). SEM was used to assess the fabric’s shape and interface, as well as the Fourier transform and X-ray diffraction (XRD) to analyze its crystalline structure. SEM views of the cross-section b(i) and the top surface b(ii) of a tape-casted P(VDF-TrFE) film are shown in
Figure 3b. Instead, cross-section c(i,ii) and top views of the hot-pressed and annealed P(VDF-TrFE) layer are reported in
Figure 3c(iii,iv). Furthermore, the flexibility of the developed fabric WPEH was evident in
Figure 3d. The distribution of the z-axis stress e(i), electric displacement field e(ii), and piezoelectric potential are shown in
Figure 3e(iii).
Using the above equation, the energy harvester’s maximum power density (, W/m2) is calculated by accounting for the sample area (, m2), open-circuit voltage (, Volt), and short-circuit current (, Ampere).
Piezoelectric nanoparticles with a large output current were inserted into the P(VDF-TrFE) film to enhance the fabric WPEH, which has weak output current signals compared to output voltage ones. Human stimulation may provide a 5.3 V maximum output voltage and a 69 nA output current, thus corresponding to a 16.83 nW cm
−2 maximum output power density for 55.5 kPa (6N) pressure, according to modeling and experimental data. Finally,
Table 2 reports the adhesion strength data obtained on the developed PVDF-based fabric employing the Surface and Interfacial Cutting Analysis System (SAICAS) before and after 15,000 bending cycles. The obtained results demonstrated that the developed P(VDF-TrFE) film has an adhesion strength greater than similar PVDF-based films, ensuring the mechanical stability of the resulting fabric-WPEH. This study provided one of the most strongly integrated wearable electronics [
61]. The obtained fabric-WPEH shows a very low output current compared with the output voltage signal. Indeed, the experimental results indicated that the proposed fabric-WPEH could reach a 0.0168 µW/cm
2 power density, limiting its capability to supply electronic wearable devices.
According to findings from a different study, PT (PolyThiophene) helps PVDF accumulate charge carriers at their interfaces, leading to high piezoelectric responsiveness and interface polarization. PVDF and its copolymers have been discussed extensively in [
62]; their outstanding effectiveness is widely used in wearable piezoelectric sensors. In particular, the authors proposed a β-phase PVDF/PT layer deposited on a polyurethane (PU) fabric to obtain cheap, highly sensitive, and flexible piezoelectric pressure sensor. Mechanical endurance and biological compatibility are two important factors to consider; PVDFs are categorized into five types: α(TGTG’), β(TTTT), δ, γ, and ε, each produced under different deposition parameters. Each typology can be converted into another under different conditions (e.g., electric field, mechanical stretching, and heat). Due to the parallel orientation of the electric dipoles, the PVDF polar phase is the most commonly used typology in pyroelectric and piezoelectric applications. The PVDF layer’s capacity to generate piezoelectricity may therefore be considerably enhanced by increasing the content of the β-phase. The sensitive piezoelectric film was created by progressively stretching and drying the PU fabric after it had been coated in a PVDF/PT solution and diffused in N-Methylpyrrolidone (NMP). Afterward, using a conductive silver paste, a cross-finger electrode was made utilizing 3D printing technology; the sensitive fabric was wrapped in two Tegaderm films to protect the previously deposited piezoelectric film. The porous network produced by the created PT’s fibrous structure is considered favorable for sensor flexibility.
The PU fibers were evenly coated with a PVDF/PT mixture prepared by dip coating. As the PVDF/PT film is heated, bubbles produced by solvent evaporation cause a high porosity. Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) was used to analyze the effects of additive PT at concentrations of 0.2 wt%, 0.5 wt%, 1 wt%, and 1.5 wt% on the development of PVDF crystals. The percentage of β-phase in pure PVDF film is just 58.5%. The concentration of 1 percent weight of additive PT caused the quantity of β-phase PVDF to reach its maximum. Increasing PT leads to more β-phase, which is consistent with the findings of X-Ray Diffraction (XRD). Another crucial factor is the sensor’s long-term stability. The output voltage only dropped by 2.6% when the linear motor was applied and released 5000 times at a frequency of 1 Hz and a force of 1 N, proving the mechanical stability of this sensor.
In addition, for wearable physiological monitoring, Y. Su et al. presented a nonwoven piezoelectric textile inspired by muscle fibers with tunable mechanical characteristics [
63]. Polydopamine (PDA) is dispersed into electrospun barium titanate/polyvinylidene fluoride (BTO/PVDF) nanofibers to enhance the interfacial adhesion, mechanical strength, and piezoelectric capabilities to imitate muscle fibers. Numerous possible uses for the piezoelectric textile exist, such as active speech recognition, pulse wave measuring, and human motion tracking. Stretching and contracting skeletal muscles, composed of extracellular matrices and have a highly helical design, allow a living thing to move and exert force. Theoretically, the connective tissue surrounding the helical bundles of muscle fibers allows for the transmission of external loads and uniform stress distribution on the muscle-connective component over a range of size scales, significantly increasing the mechanical strength and toughness of muscle tissues. This special soft biotic architecture inspired the construction of the electrospun nanofiber structure, enclosed/modified by PDA particles. The role of the connective tissue that surrounds muscle fibers is intended to be mimicked by PDA to increase the resilience and longevity of the prepared nanofiber structure. The surface modification changed the electrospun piezoelectric fibrous configuration’s interfacial morphologies and characteristics by PDA coating. Some BTO (Barium Titanate) nanoparticles protruding from the surface of untreated BTO/ PVDF nanofibers are nanostructured knots. These knots cannot create piezoelectric potential within the electrospun composite fiber and cannot contribute effectively to the electromechanical coupling process along the fibers. Adding a PDA coating to the nanofibers’ surface makes BTO particles stand out and smooths the fiber’s surface. The PDA@BTO/PVDF composite fiber benefits from a favorable shape for load transmission because it produces a stronger electromechanical coupling effect and a significantly higher piezoelectric response. Additionally, a linear motor carried out cyclic loading and releasing of 5 N at a frequency of 1 Hz to confirm the MFP textile’s durability, stability, and robustness over the long term. After 7400 cycles, there did not seem to be any discernible output voltage reduction of more than 3%, showing good mechanical durability.
The developed device was fastened to numerous body locations for real-time physiological monitoring to demonstrate the potential and practicality of MFP (muscle fiber-inspired piezoelectric) textiles in wearable medical diagnostics. Based on the heart rate and arterial blood pressure analysis, wrist pulse is considered among the most common vital signs for diagnosing cardiovascular disease amidst various physiological signals. The MFP cloth was conformally applied over the tester wrist’s radial artery to monitor any changes in arterial blood pressure under various bioactive situations. The collected results show that the frequency and amplitude of wrist pulses are precisely identified in terms of the distance between two successive peaks and the average peak amplitude. MFP textile can quickly identify the three distinctive peaks of the radial artery pulse waveforms in static and excised states.
The MFP fabric was also placed on a finger to track its bend and stretch to demonstrate the ability to track tiny limb movement. In addition, carotid artery pulse waveforms were recorded when three subjects wore the MFP material in the same position around their necks. As a result of the various uttered phrases, several signal characteristics were found. According to phase-field simulations and tests, adding PDA to electrospun BTO/PVDF nanofibers significantly improves interfacial adhesion and linkage, which improves the mechanical and piezoelectric capabilities of the nanocomposites as made.
Furthermore, piezoelectric smart fabrics are becoming a reality because of recent advancements in electronics, wearable technology, and the Internet of Things [
64,
65]. Recent ones rely on high sensitivity and flexibility in thread-type piezoelectric fibers intertwined to create smart fabrics [
66,
67,
68]. Applications for smart piezoelectric cloths include energy harvesting, human motion detection, real-time fitness monitoring, and the study of human movement patterns. For instance, in [
69], the authors presented a flexible, lightweight, and sensitive PVDF to create a textile-based piezoelectric textile. PVDF is specifically curled with threads in a spiral shape to create the textile structure. The integrated sensor structure exhibits great stability and endurance under repeated mechanical deformation because of the helicoidal design. Additionally, the mechanical deformation of the sensor may be detected utilizing the electrical response of the sensor while keeping flexibility thanks to piezoelectric capabilities paired with the interaction between the electrical charge and mechanical strain. Similarly, PVDF and BT (Barium Titanate) were employed in [
70] to produce nanostructured hybrid piezoelectric fibers kitted to realize a wearable energy generator. The resulting device was able to produce 4 V maximum output voltage and 87 µW cm
−3.
3.2. Triboelectric Generators for Wearable Applications
The triboelectric effect converts the kinetic energy into electrical energy; the first brings two materials with various electron affinities together, generating a surface charge of opposite polarities over the two materials. In particular, Textile-TENGs (T-TENGs) are composed of three components, as described in [
71]:
Triboelectric materials;
Fundamental materials;
Electrodes.
Different strategies were presented in the scientific literature for obtaining the optimal design of TENG wearable devices, comprising the material system, sensitive structure, and multisensory synergy [
72]. In detail, the electrode design and the friction layers must be designed and optimized to improve the sensitivity and the self-cleaning and self-healing device properties. In addition, the sensing structure is enhanced by optimizing the electromechanical coupling with the application scenarios, increasing its sensitivity, speeding up its response time, and largely accomplishing the real-time signal capturing through the design of air cavities, friction-layer microstructure, etc. Finally, multisensor synergy is enabled by employing sophisticated sensing and detection through capturing several correlated signals, playing a role in anti-interference and noise reduction. In detail, woven TENGs, made up of intertwining different triboelectric materials, are widely investigated for obtaining self-powered wearable sensing systems. In fact, this structure is intrinsically featured by lightness, flexibility, and stretchability, following the requirements imposed by wearable devices. Fibers and their agglomerates—natural and synthetic—are commonly used as fundamental materials. They are flexible, permeable, and stretchable. While natural fibers (from animals, plants, and minerals) are soft and easily degradable, synthetic fibers are durable and fast drying. Most textile polymers are triboelectric materials since wearable devices are the primary application, making T-TENG more practical. For the contact surface of TENG, the main textiles are nylon, silk (characterized by degradability and water solubility), and polylactic acid; furthermore, positive electrode materials for triboelectric are metals layer or particles; while PVDF and PTFE are covered on fibers to increase the T-TENG output. Essential features of these materials are good biocompatibility, good air permeability, and high output power. The electrodes are implemented by metal nanowires or thin layers (and their oxides) such as aluminum or gold. T-TENG’s performances are improved thanks to surface modifications obtained, for instance, by doping the triboelectric material to improve its capability to lose electrons; another solution is the realization of microstructures, through micromachining techniques, on the material’s surface to extend the contact area. Zhang et al. suggested a technique for increasing the TENG’s output performance by 278% [
73]; this technique enriched the TPE (thermoplastic elastomer) composite fabric with Cu nanoparticles, enhancing the TENG output up 1.5 times. Instead, Chu et al. employed SF6 plasma chemical alteration to engrave polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) sheets to create nanostructures, resulting in output values ten times more than the initials [
74].
Furthermore, the TENG technology can be used to make a 3D tactile sensor, as shown in [
75]. Indeed, the authors presented a 3D double-faced interlock fabric TENG (3DFIF-TENG) that harvests mechanical energy and monitors human movements, allowing the development of wearable haptic sensors, stretchable, self-powered, and substrate-free [
75]. The interlock fabric’s internal structure comprises PA (Polyamide) composite yarn and cotton yarn, conferring the material flexibility and stretchability [
76]; also, the 3DFIF-TENG fabric is relatively easy to knit, enabling mass production. In addition, to identify a superior structure and enhance output performance, the two yarn systems—crossed and parallel—are compared. Several fabric typologies were looked at to evaluate the performance of the 3DFIF-TENG based on the triboelectric materials (6 sets of oppositely polarized tribo-materials) and structural parameters (i.e., three distinct column widths and four distinct column heights).
Through multiple tests, it was demonstrated that ISC (short-circuit current), VOC (open-circuit voltage), and QSC (short-circuit charge transfer) of 3DFIF-TENG increase linearly with increasing pressure. Considering a 5 cm × 5 cm 3DFIF-TENG sample, ISC remains constant at 0.05 m s−1 while VOC and QSC rise when elongation increases. The TENG can be used as an object recognizer thanks to their different weights; in fact, the VOC is different when tested with a glass bottle empty, half, and full of water. Another application consisted in putting the TENG over a chair and trying to recognize testers from their weights. Furthermore, this fabric can be used as a 3D tactile sensor when applied over a tester shirt; the test revealed a relation between the applied force and VOC.
F-TENG, developed in [
77], is constituted by a fabric-based triboelectric nanogenerator through a sandwiched structure for real-time biometric identification and biomechanical energy harvesting. The authors exploited this structure to generate a self-powered wearable keyboard with high-pressure sensitivity and stretchability; besides, this device supports a biometric authentication system based on analyzing output signals obtained from different users. Additionally, it generates electrical energy via typing movement, making it self-powered and assignment-safe. The combination of silver-plated cloth, CNT (Carbon Nanotube), and PTFE-coated fabric produces the self-powered action.
The F-TENG fabrication consists of three main phases: deposition of the Ag conduction layer, the CNT coating, and the frictional layer (
Figure 4) [
78]. Investigating the F-TENG electrical performance, the V
OC and I
SC reach the maximum value using polyester cloth twice processed with PTFE; however, the PTFE content affects the mechanical flexibility inversely proportional ways. When F-TENG has optimal structural parameters, the V
OC almost maintains its initial state even if followed by variations of frequency, considering the following expression:
where
is the electron charge (Coulomb),
number of transferred electrons (Dimensionless),
electron transport rate (m
−2 s
−1), and
cross-sectional area (m
2). It indicates that F-TENG moves equal triboelectric charges on the friction layer to maintain an equal potential difference. An instantaneous AC (Alternate Current) voltage is produced when human skin and F-TENG make contact, followed by a separation, and a current flows through the external resistance. The F-TENG strengths are surely its fast response time, high detection resolution, and capability to produce 170 µA m
−2 current density. These features make it a good solution for human-computer interfaces and personal user identification systems [
77].
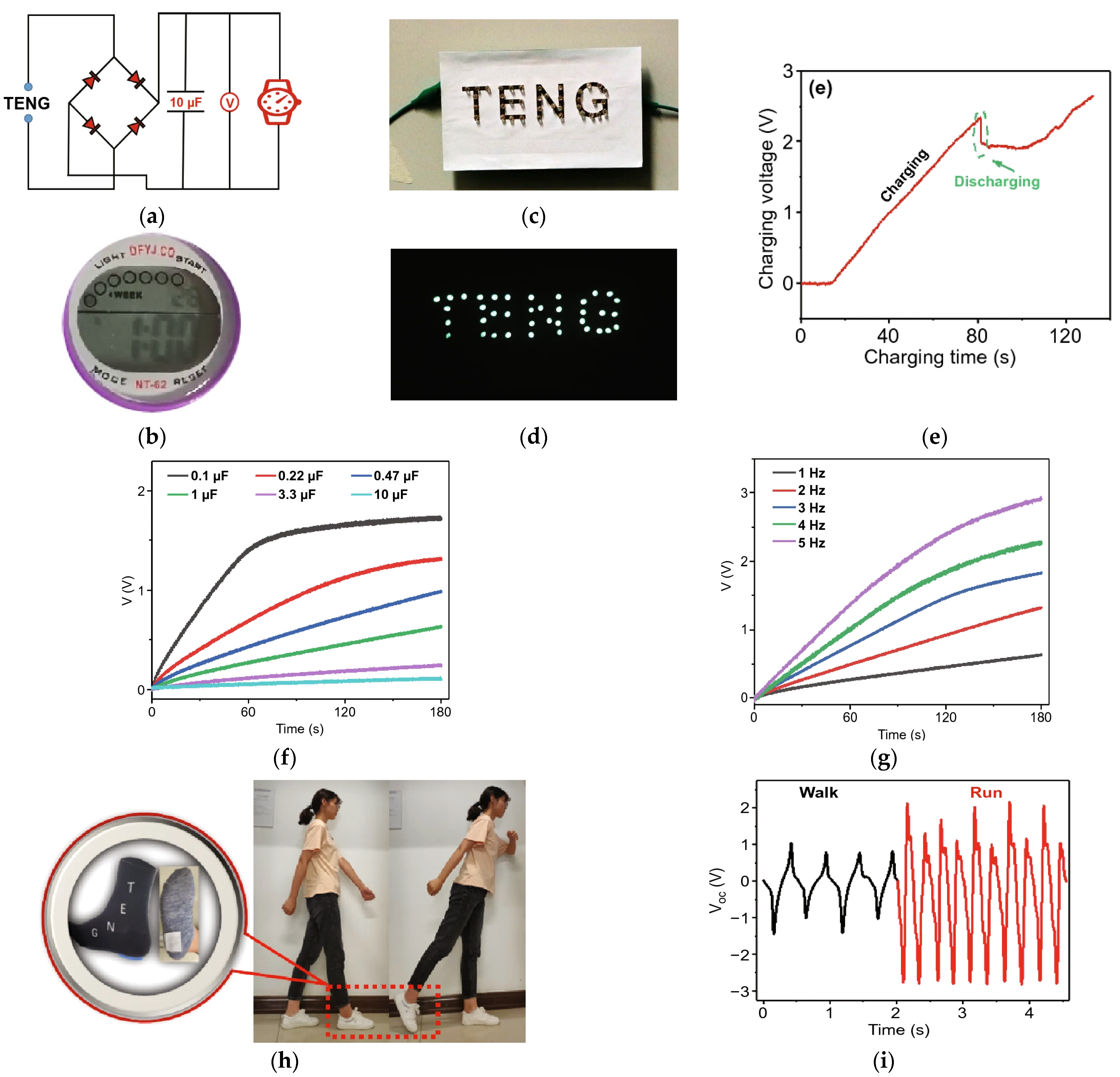
Figure 5a shows the circuit layout of the charging system using the developed F-TENG to charge a commercial watch (
Figure 5b);
Figure 5c,d demonstrate how to light up several LED modules with just one F-TENG. Instead,
Figure 5e shows the time trend of the F-TENG charging voltage, as well as the F-TENG charging capability under storage capacitance from 1 µF to 10 µF (
Figure 5f,g). Finally,
Figure 5h depicts a stepper technology implemented by integrating the F-TENG into a sock;
Figure 5i reports the voltage signal output in the walking and running mode.
Additionally, natural fibers and textiles can be employed to realize triboelectric harvesters. In [
79], the authors described a simple way for fabricating efficient natural textile-based triboelectric nanogenerators (N-TENGs). The TENG was built in a face-to-face arrangement. Fluoroalkylated siloxane grafted fabric (F-fabric) and cyanoalkylated siloxane grafted fabric (CN-fabric) were used to create the negative and positive layers. Each triboelectric layer was fastened to a copper (Cu) cloth electrode using conductive adhesive. Finally, copper tape was used to secure the electrode to the measurement wires. The triboelectric layers of F and CN fabrics were used to create the N-TENGs in a face-to-face configuration. The negative triboelectric layer is provided by the F-fabric, while the equivalent positive triboelectric layer is provided by the CN-fabric.
Additionally, the combination of F-cot and CN-silk produced the greatest electrical output, measuring 216.8 V and 50.3 µA. (0.87 A cm
−2). This study recommends using the N-TENG as a self-powering source in tiny circuits. Previous textile-based TENGs generate energy by vertically compressing and scraping objects. On the other hand, a corrugated textile-based triboelectric generator (CT-TEG) that may generate energy by stretching is presented in [
80]. The CT-TEG comprises two layers: Si-rubber on the bottom and woven conductive textile on top of a silk layer. The corrugated structure on the top layer is sewn to the bottom layer. The CT-TEG may be extended to a maximum of 120 percent. With stretching and releasing actions, the CT-TEG’s maximum output performances may reach 28.13 V and 2.71 A. Furthermore, the tests show the production of enough energy from distinct human body functions to power approximately 54 LEDs.
Finally, in [
81], the authors introduced a new fabric-based TENG that operates in freestanding triboelectric-layer mode. This woven-TENG includes woven electrodes and woven strips of positive and negative triboelectric material, constituting a checkerboard pattern over the electrodes with matching periodicity. The performance of the woven-TENG is greatly enhanced by using positive and negative triboelectric materials. The resulting woven TENG can produce 62.9 V open-circuit voltage, 1.77 µA short-circuit current, and 34.8 µW power under a 2 Hz mechanical oscillator and with a 50 MΩ load. For the practical application of woven-TENG in wearable devices, durability and washability were verified. After 40,000 working cycles, the V
OC marginally decreases from 102 V to 85 V while the I
SC decreases by 12.5%. A minor amount of material transfer, abrasion of the Ag electrodes, and fraying of the nylon fabric was seen after 40,000 operation cycles. Both outputs are steady, indicating that the woven-TENG can withstand this washing regimen. The woven-TENG’s output is also discovered to depend on the temperature and humidity levels outside for wearable devices.
The most powerful and natural action in daily human activity is said to be walking. The bi-directional gearbox-equipped exo-shoe TENG (ES-TENG), which offers enhanced and long-term output performance during regular walking, was described in [
82]. The two-way gearbox efficiently transforms the whole stroke’s low frequency (1 Hz) into a unidirectional high-speed rotation (700 rpm), increasing output performance by a factor of more than 10. The rotating TENG comprises a stator, a flywheel, and a rotator with flexible blades. The dielectric blades connecting the stators and rotators are made of fluorinated ethylene propylene (FEP) and aluminum, both of which have strong triboelectric characteristics. The rotator is connected to the FEP film’s edge, and the deflected film alternately makes contact with electrodes I and II. The ES-TENG, which contains a power transmission module and a rotating TENG section, is mounted outside the shoe to recover wasted biomechanical energy from the ordinary human walking action. Moreover, employing a voltage multiplier circuit to create a boosted open-circuit voltage of more than 3 kV shows how the ES-TENG may be used for electro-stimulation applications. With much better output performance under natural walking motions, the ES-TENG makes biomechanical energy harvesting possible for various applications. Numerous moving parts that move at high speed and are subject to relatively high loads expose the device to rapid wear or failure.
Certain electrical gadgets can operate without an external power source thanks to the biomechanical energy that the stepping movement provides. For instance, the ES-TENG can charge the batteries within a commercial smartwatch using the reliable output provided by the AC/DC converting circuit [
82].
3.3. Thermoelectric (TEG) Wearable-Based Energy Harvesters
TEG, a thermoelectric generator, is a device that generates energy by exploiting the Seeback effect. As represented in
Figure 6, TEG is based on semiconductor bands, P-N junctions (
Figure 6a), which generate a potential difference, then convert into electrical energy. However, several efforts have been made to obtain flexible TEGs, more suitable for wearable applications since they can be adapted to the human body (
Figure 6b) [
83]. Due to the practical restrictions imposed by wearability requirements, achieving an efficiency of 1% is also difficult [
84]. It is more practicable to use a TEG on a limited body portion to optimize effectiveness and reduce wearable system power requirements. A precise design of the TEG at the material, device, and system levels is also required to optimize the amount of energy captured. Any imperfection at these levels has the potential to reduce the output power. Furthermore, when building the system, it is crucial to consider the TEG-body attachment, ease, weight, and dependability.
The materials science community is currently very interested in creating flexible electronics based on conducting polymers [
85]. In general, polymer materials have several appealing qualities, such as being simple to produce, flexible, lightweight, and most importantly for thermoelectric applications-having low heat conductivity by nature. A flexible device has the benefit of conforming to the contour of the human body, which can increase the contact area and hence minimize the parasitic resistances in thermoelectric applications. Numerous doped conjugated polymer systems have been investigated as thermoelectric materials. They may be transformed into textiles using various techniques, such as coating onto pre-made fabric or spinning into mixed or mono-component fibers. A study presented a flexible thermoelectric generator characterized by a lower thermal conductivity due to its composition (
Figure 7a,d) [
83]; it uses a stretchy polymer made of silica aerogel and PDMS, which exploits the insulating capabilities of the material. Although a rigid material, this last produces a conglomerate that is easily castable.
Figure 7b shows the employed system to measure the aerogel-PDMS conductivity; it comprises water-cooling feedthrough, heaters, a measurement channel, a support channel, thermo-couples, a sample, a vacuum chamber, and a z-stage.
Figure 7c shows the composite’s thermal conductivity when the aerogel particle size is 100–700µm and 2–40µm, respectively. The simulations suggest that increasing the fill factor reduces the surfaces for collecting heat, obtaining a higher thermal resistance between the TEG and the body and environment. Less heat loss through the elastomer causes this effect to be more pronounced at lower filler thermal conductivities.
The described devices were made using n-type Bi2Se0.3Te2.7 legs and p-type Bi0.5Sb1.5Te3 legs characterized by a Seeback coefficient of ~220 µV/K and a thermal conductivity value around 1.45 W/(m K).
Figure 8a depicts the steps involved in creating flexible TEGs: first, the thermoelectric legs are deposited on the glass substrate, along with double-sided tape to prevent them from shifting (i); then, to ensure that the uncured compound solely fills the region between the legs, an aerogel-silicone mixture is shed between the legs and compressed with a second glass (ii); finally, cross-sectional microscopy was used to see how the thermoelectric legs are distributed. Using a particular stencil to spray coating the EGaIn, they generated the EGaIn interconnections (iii); then, a thin PDMS encapsulation layer was deposited to cover the realized interconnections, followed by a thick silicone layer (iv–vi). Thanks to this final encapsulation, the device works better as a heat spreader across the device.
Figure 8b,c show the EGaIn interconnects, and a TEG’s cross-sectional view after the legs have been removed, respectively [
83].
A different approach to this technology is presented in [
86], which introduces a metal telluride-based TEG that, at its maximum operating temperature of 120 °C, generates a 34.7 mA cm
−2 current and 8.4 mW cm
−2 power density. In this study, a copper-connected p-SnTe layer and an unconnected n-PbTe layer were sandwiched to produce a TEG to sense body temperature. The resulting device features strong electrical and ultra-low thermal conductivities, contributing to a high merit figure. Sensing the change in voltage and current can detect the touch of a finger thanks to this configuration.
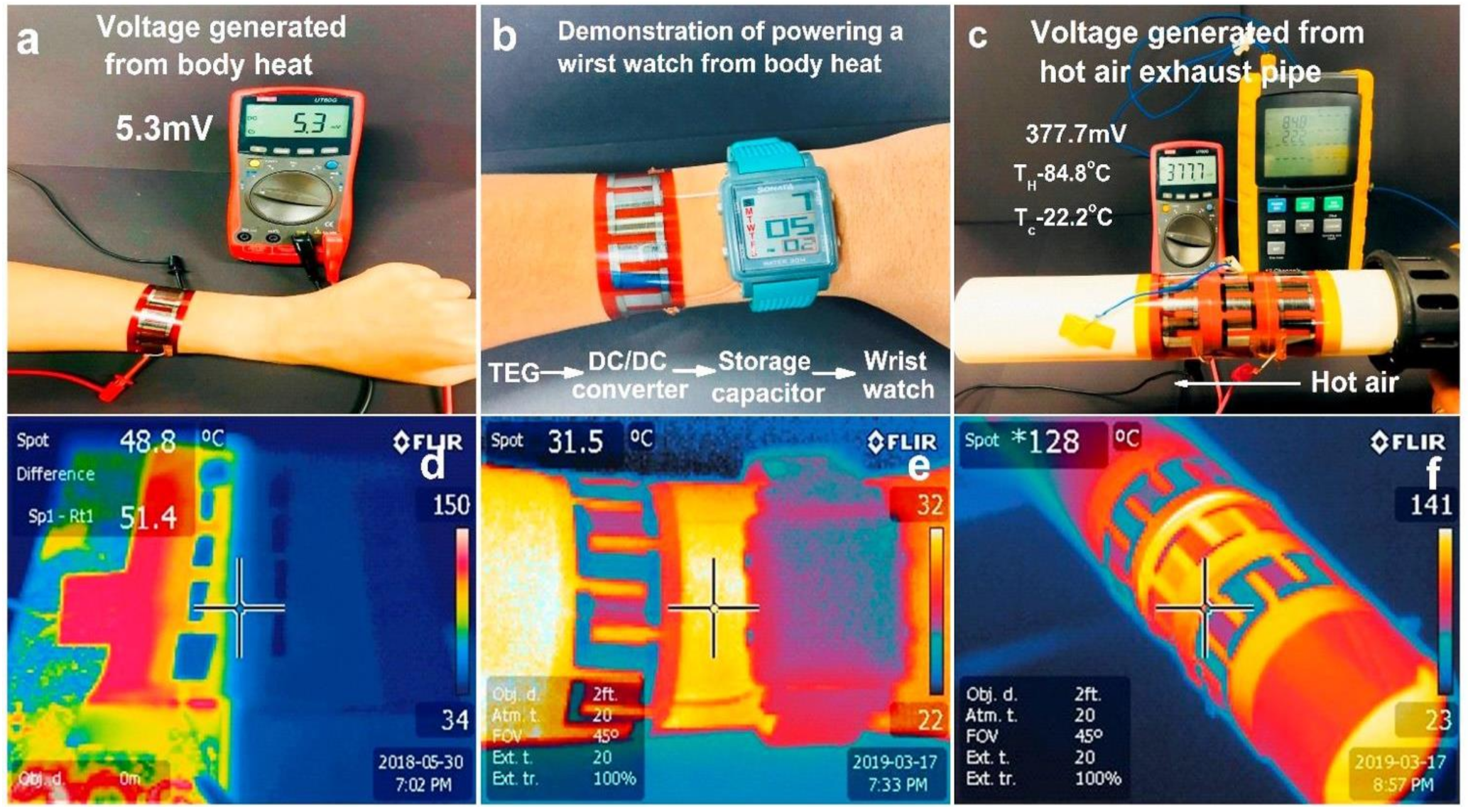
Figure 9 show the results of some experimental tests;
Figure 9a shows the voltage generated from body heat so that, as shown in
Figure 9b, the recharging of a watch is possible.
Figure 9c represents the voltage generated from the hot air exhaust pipe, and the infrared images of TEG for different heating emitters are shown in
Figure 9d–f. Furthermore, the TEG was tested singularly under various temperature gradients (
Figure 9g), serially connected, and exposed to a 120 °C temperature gradient (
Figure 9h). By subjecting the device to over 400 bending cycles, its internal resistance drastically increases with the number of bending cycles, making it difficult to design the next energy harvesting section.
However, optimizing the design of the presented flexible TEG makes it possible to improve their electrical and thermal properties, allowing their operation under lower temperature gradients (ΔT) [
86].
Current wearable f-TEGs are not directly compatible with garments and cannot be bent or stretched without compromising the device’s integrity or thermoelectric performance [
87,
88]. In [
88], the authors introduce ultra-flexible textile thermoelectric generators (uf-TEGs), which include elastic fabric substrates and conductive cloth electrodes. These lasts are fabricated and assembled using a semi-automated method, including pick-and-place assembly, depositing rigid TE cuboids (n-type: Bi
2Te
2.7Se
0.3 and p-type: Bi
0.5Sb
1.5Te
3) and conductive textile-based electrodes over an elastic fabric substrate. The p-type and n-type cuboids are initially put up in the spaces between the TE cuboids on a temporary hard substrate. Then, elastic fabric with holes created by a laser is placed on top of the rigid substrate, and cuboids are forced into the fabric holes. On a polyethylene terephthalate (PET) mask with a design, the cuboids were scraped with solder paste. Then, using a PET thermal-released layer, the serpentine-structured electrodes are deposited on the array of the TE cuboids after being laser-cut into the conductive fabric tape. To align the TE cuboids with the serpentine electrodes, the elastic fabric and thermal released film are aligned throughout this procedure. The bottom electrodes were assembled identically after the elastic fabric, cuboids, thermal-released film, and conductive cloth electrodes were removed from the provisional support. The PET thermal-released films were then automatically reduced and separated from the electrode arrays after being heated with a heat gun set to 120 °C.
Figure 10a shows the characterization of three uf-TEGs with a different number of n-p couples, viz 8, 16, and 48 pairs, respectively. Instead,
Figure 10b displays the output voltage (VL) with load resistance (RL) varying from 10 to 70, together with the open-circuit voltage (V
OC) of uf-TEG with 48 n-p pairs. The V
OC achieved a higher voltage (111.49 mV) than similar flexible TEG devices described in the literature at a temperature differential (T) of 33.24 K. (
Figure 10e).
Figure 10c,d represent voltage-current and power-current correlations graphs for 10.40, 19.83, 26.24, and 33.24 K temperature differences, along with related fitting curves. The uf-TEG generated a 64.10 W maximum power when the temperature differential reached 33.24 K, which was exceptional compared to previously reported fabric-based TEGs (
Figure 10f) [
88]. The 48-pair uf-TEG was up on a hot plate to test the device’s long-term stability before being cooled using an electric fan.
Figure 10g showed the results of ten iterations of heating and cooling, displaying good stability with a maximum V
OC change of 4.09 percent at 33.24 K. In addition, a 12-h curing cycle in a 70 °C oven was used to evaluate the 16-pair uf-TEG resistance after immersing it in water for 30 min (
Figure 10h). When the sample was dried, the uf-TEG resistance dropped from 14.6 to 14.3. The V
OC-ΔT curves were also measured before and after the immersion test.
Figure 10i shows the uf-TE TEG’s performance before and after the immersion test and the possible usage in cloth-assembled electronic skin applications. The resistance fluctuations were minimal when the uf-TEG was bent on acrylic molds with bending radii ranging from 2.5 to 5.0 cm, with 0.5 cm gaps between them in both the x and y directions. At their maximum bending degree, they rose by 5.55% and 2.82%, respectively (bending radius of 2.5 cm).
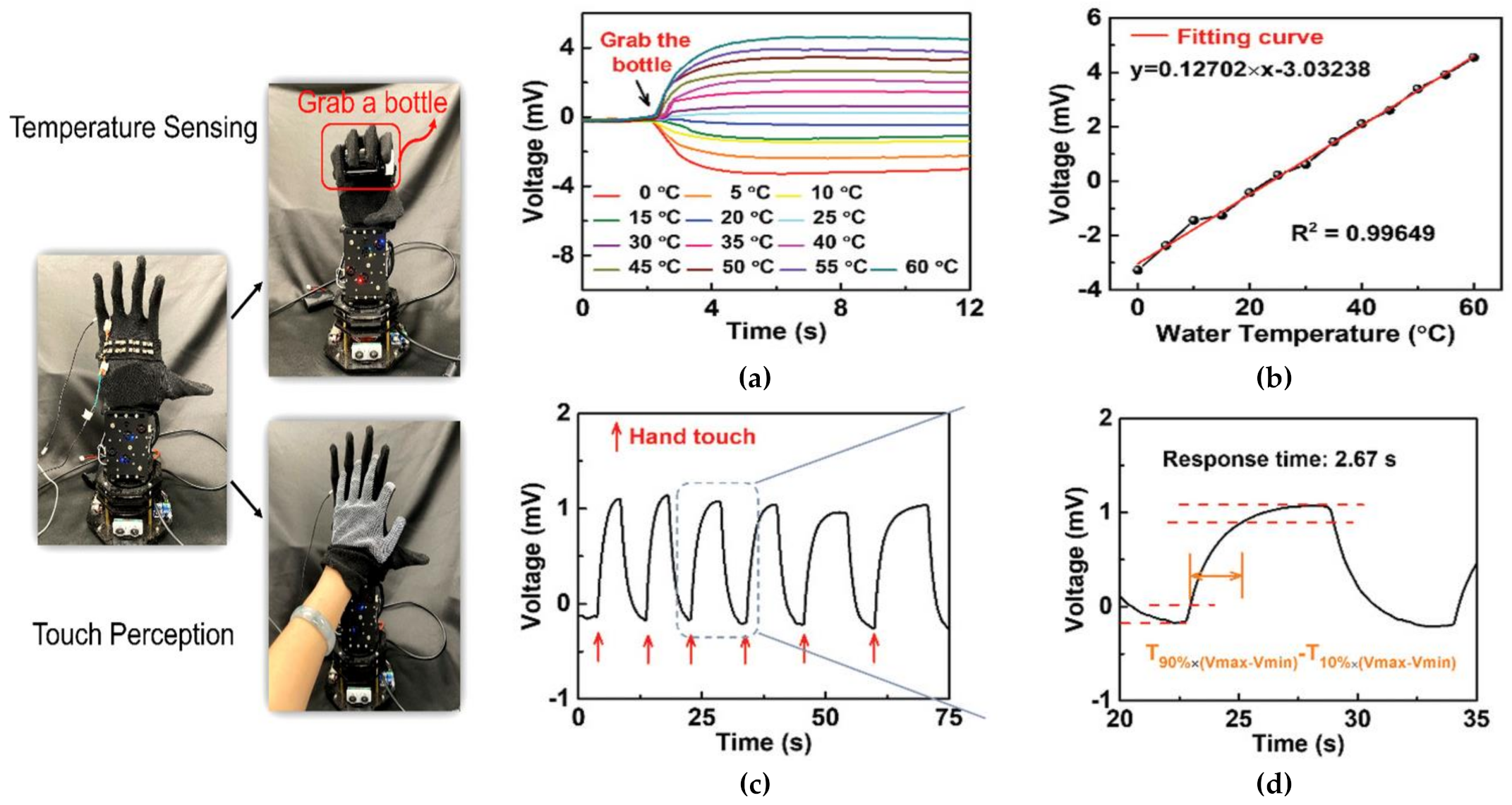
The thermoelectric capability of the uf-TEG allows its application for temperature sensing and tactile perception. The 8-pair uf-TEG, for instance, was attached to a glove and placed on a robotic hand, as shown in
Figure 11. The output voltage (VOUT) increased (25 °C < T
WATER > 60 °C) or decreased (0 °C < T
WATER > 20 °C) when the uf-TEG got in touch with the bottle (
Figure 11a). After the stabilization of VOUT, the linear relationship between VOUT and T
WATER was gathered (
Figure 11b). After two days of aging, the thermoelectric characteristics of both p- and n-type composite fibers remained constant. Although the long-term stability was not examined, passivation techniques may be used to preserve the stability in the air.
As previously mentioned, the uf-TEG may be employed for touch sensing. The robot hand outfitted with the uf-TEG can identify the touch of a user’s hand with a quick reaction time of around 2.67 s, as illustrated in
Figure 11c,d, considerably imitating the biological function of human skin. To track health or mobility, uf-TEGs may be included in common clothes such as fabric, gloves, and wristbands rather than being utilized as an e-skin [
88].
A wearable medical sensor system intended to be used in long-term healthcare applications was presented in [
89]. In real-time, the device monitors the human body’s temperature, heartbeat, SpO
2, and acceleration. The device combines a temperature sensor, a PPG sensor, an inertial sensor, a microcontroller section, and a BLE module. Batteries are required to power this sensor system; however, batteries have a finite lifespan, as discussed in the first section. As a result, a hybrid photovoltaic–thermoelectric energy harvesting section was integrated to feed a wearable health monitoring device. The proposed multi-source energy harvesting section includes a flexible solar panel, a TEG, a step-up converter, and two supercapacitors (50 F total capacitance).
Figure 12 depicts the device architecture, which contains a flexible photovoltaic panel to scavenge energy from solar irradiance, and a TEG module to harvest energy from the body heat as well as monitor its temperature. The flexible PV panel and TEG module are hooked in series to efficiently harvest energy from the sun and body heat.
The sensor system’s firmware flowchart consists of two phases: wake-up and sleep. Firstly, the device is brought into a wake-up state; then, the microcontroller unit acquires the data from sensors and transmits them to the custom mobile app using a BLE transceiver. Afterward, the device goes into a sleep state for 1190 s, reducing its power consumption before waking up for 10 s, starting the acquisition cycle again. The test results demonstrated that the harvesting section produces sufficient energy to extend the device’s lifetime by more than 46 h, providing 2.13 mW overall power [
89].
3.4. Solar Fabrics for Wearable Applications
A useful energy source naturally available is certainly sunlight, which can be scavenged by photovoltaic cells. Due to their excellent mechanical stability/robustness (i.e., bending and compression), high power-to-weight ratios, and affordable manufacturing processes/devices, flexible-wearable solar cells provide viable alternatives to conventional electricity sources [
90]. These photovoltaic devices are the portable power sources of the future that can be fitted to any substrate. More significantly, flexible solar cells may be integrated into various objects, including bags, clothes, shelters, airplanes, vehicles, and more, to provide them with excellent power-to-weight ratios at low production costs compared to other prevalent technologies. Several efforts have been made to integrate them into wearable systems, overcoming their intrinsic rigidity.
A novel technique to use the sun’s energy is through solar fabrics; these lasts are ten times lighter than framed panels, non-toxic, and can be bent or bonded to any surface. Additionally, they have a longer lifespan of up to 20 years. This innovative technology represents a good and promising alternative with respect to conventional PV panels. The high-efficiency rate of conventional cells and panels has been their main selling point, with current technologies capable of well over 20% conversion rates. S. Arumugam et al. described the novel spray-coating method to create organic solar cells on fabrics for wearable energy harvesting applications [
91]. A screen-printed interface layer reduces the surface roughness of the ordinary woven 65/35 polyester cotton fabric utilized in this work to a few microns. Fabric solar cells are made by screen printing an interface layer onto fabric substrates. The screen design ensures that the interface layer is just imprinted where necessary, retaining the fabric’s elasticity and maximizing breathability compared to typical pre-coated textiles. In a standard thermal oven, the interface layer can withstand processing temperatures of 150 °C for up to 45 min without degrading and has surface-free energy of 35 mN/m. It also has a good thermal resistance. The experimental results indicated that the spray-coated PV fabric obtained PCE (0.01%), similar to traditional glass-based panels. Decreasing the thickness of the ZnO-NP layer enhances device performance, while compressing the bottom AgNW layer during the annealing step prevents short circuits and decreases resistance. An all-solid tuneable energy cloth with concurrent solar energy scavenging and storage capability was developed in [
92]. The solar energy harvesting module is an all-solid dye-sensitized solar cell textile (i.e., ZnO-based DSSC). In contrast, the energy storage module is a customizable fiber supercapacitor (TiN-based) with rapid charging abilities and ultrahigh bending resistance. Self-harvesting solar energy can charge the textile sample to 1.2 V in 17 s and discharge it at a 0.1 mA discharge current density in 78 s. This technology enables customization of the multifunctional material into the desired shape without affecting its functionality, leading to stylish smart garments for wearable self-powering systems with enhanced user experience and increased flexibility for fashion design.
In addition, one trouble that researchers are trying to resolve is the permeability of the encapsulation barrier used to protect solar cells from environmental agents such as humidity, water, dust, etc. The study reported in [
93] suggests the introduction of a capping layer of SiO
2-polymer compound that allows the generation of a nano-stratified encapsulation barrier to obtain a washable device. Thanks to its chemical stability, the encapsulation’s water vapor transmission rate (WVTR) is also guaranteed under aqueous environments; in fact, the polymer solar cell (PSC) percentual of degradation after washing 20 times was just 2%. PSC fabrication is based on a barrier-coated textile substrate that has the following structure:
Textile support material;
Bottom encapsulation layer;
Ag cathode (100 nm);
PFN-Poly-Fluorene electron transporting layer (8–10 nm);
PTB7-Th-PolyBisThiophenBenzoDitiophene-Thieno: PC71BM active layer (100–110 nm);
MoO3 hole transporting layer (10 nm);
Ag anode (10 nm);
MoO3 optical protective layer (30 nm).
The acrylic adhesive attaches the encapsulation barrier to the device so that the attachable encapsulation protects the optoelectronic modules made on the textile substrate; then, the conductive paste is used to connect the thermally deposited metal electrodes with the conductive fiber.
There are two different ways of applying the encapsulation barrier; direct encapsulation prevents the infiltration of oxygen and moisture, exposing the device to thermal and ultraviolet damage. These troubles do not happen with the attachable encapsulation, even if it is sensible to the penetration of moister and oxygen that can be overcome with new adhesive materials. The attachable encapsulation method allows the application of the protective layer over wide flexible photovoltaic panels without following process steps. Tests conducted in [
93] show the effectiveness and reliability of the developed capping layer; the Rate of Change (ROT) of the main characteristic parameters of the encapsulated solar cell is almost constant over several washing cycles.
This study shows that the addition of SiO
2-polymer composite goes against the phase transition of Al
2O
3 (during the washing process) and, thus, its decisive role in the next generation of integrated harvesters for wearable E-textiles [
93].
Solar cells are also engaged in charging devices for a limited time; in [
94], the authors presented a solar harvesting cloth comprising 200 tiny solar cells able to charge a 110 mF textile supercapacitor in 37 s. Individually housed in translucent resin micro-pods, the tiny solar cells are coated with a flexible textile sheath made of packing fibers and a tubular knitted structure. The fibrous sheath’s ability to take on any hue, depending on the desired color of the solar-E-yarn and subsequent fabrics, gives it a significant advantage over other solar E-textiles that have been suggested. The performance of the solar-E yarns and the resultant textiles might be further enhanced if the photoactive side of the yarns was soaked with transparent resin.
Figure 13a shows solar-E yarns created from 10 separately soldered and encased solar cells.
Figure 13b depicts a solar energy-harvesting cloth made with 200 solar cells. Then, a comparison between the developed solar energy-harvesting fabrics (
Figure 13c, each equipped with 50 solar cells) with a commercial one was carried out.
The testing findings revealed that the commercially available flexible solar panel had a power density comparable to that of white solar energy harvesting fabric after vertically arranging solar textiles onto a t-shirt. The studies revealed that the resin used in the solar-E-yarns enhanced the power densities for the white solar energy collecting fabric by 35.3% but only by 24.3% for the flexible solar panel. This result demonstrated that solar energy-capturing textiles were acceptable for producing electricity when exposed to natural sunlight since the black and red solar energy harvesting fabrics performed worse in terms of power densities (i.e., −54.4% and −23.5%) than the white ones (
Figure 14) [
94]. The exclusive stiff molecular solar thermal energy storage (MOST) or photothermal materials (PTMs) used by current solar thermal systems result in inadequate solar spectrum utilization and a lack of wearability. In [
95], a team of scientists developed a visual solar storage fabric (VSSF) that combines a wearable contrast photochromic display with UV-Vis-NIR wavelengths. The Azo-PCM@PS nano-capsule and Cs
0.32WO
3 nanoparticle are combined in this VSSF to enable photochemistry and thermophysics related to energy storage and Vis-NIR light harvesting.
The resulting device demonstrated a high heat release (83 °C) and energy efficiency (4.8%) when exposed to sunshine. To develop wearable visual solar storage fabric (VSSF), cotton fabric is covered with Cs
0.32WO
3 nanoparticles and Azo-PCM@PS nanocapsules [
96]. The core/shell mass ratio was tuned between 1:15 to 5:15. The gray factor between the Azo-PCM (dark color) and PS levels affects the core/shell structure of the Azo-PCM@PS nanocapsule (light color). As the Azo-PCM yolk progressively fills up the shell and the Polystyrene (PS) shell thins, the core almost completely fills the nanocapsule when the core/shell mass ratio reaches 5:15 [
97].
Photo-isomerization in the Azo-PCM composite and nanocapsule regulates the energy storage and release of the Azo-PCM@PS nanocapsule [
96]. According to the relationship between absorbance and the percentage of cis-to-trans conversion, blue light causes a greater photo-isomerization in the photostationary state (PSS). Due to the two-way switch caused by photos in monochromatic light, full cis-to-trans conversion is possible [
98]. Although PS, the shell used in Azo-PCM@PS nanocapsules, has strong light transmission, the pace of isomerization is influenced by the thickness of the shell. The photoisomerization kinetics are monitored to determine the isomerization speed, supposing a first-order kinetics process takes place [
26,
28]. The isomerization rate of azo-PCM rises with thinner shells due to lower light transmission losses in propagation at the same core mass with varying core/shell mass ratios.
As examined in [
99], the light intensity and incident light angle are crucial factors for the correct operation of solar panels, which must be considered when designing wearable devices. Textiles made with solar cell-enhanced yarns can resist household washing and maintain 90% of their initial power production after 15 machine wash cycles, according to tests conducted for this study. The three-step procedure of soldering, encapsulating, and covering fibers results in solar-E-yarns.
The linear relationship between light intensity and I
SC explains its significant changes during the yarn production process. On the other hand, V
OC changed just slightly due to its logarithmic dependence on light intensity [
100,
101]. As a result, I
SC may be considered a parameter representing the quantity of light flux received by the embedded SC. Because of the micro pods’ convergent (lensing) and light trapping effects, the I
SC and P
MAX values increased by 18.3% and 21.7%, respectively, when the SCs were encased within the resin micro-pods. An earlier study [
102] explored the performance of photodiodes implanted within thin resin micro pods. The influence of the micro pods’ size, shape, and optical characteristics, as well as the device’s location within the micro pod, were approximated using a theoretical model and physically tested. In this study, the design constraints decided upon the micro pod geometry, size, and SC location to optimize the desirable qualities of the resulting textiles, such as thickness and drapability. The SC within the solar-E-yarn got less light as a result of the fibrous covering. Incident light can pass through the fibrous sheath and into the micro pod in one of two ways: either the fibrous sheath’s porous surroundings would allow for direct passage of some incident light through the structure without interference, or the light might diffuse through the sheath after interference. Light absorption can be further reduced by employing textile fibers with less shine [
103]; on the other hand, scattering can be reduced by using fewer, thicker, or fibers with a lower refraction index fluorinated polyesters or silicones). However, these changes impact the materials’ look, feel, and capacity to trap light.
Three distinct types of electrical device charging capacity of the SC embedded fabric were examined [
99]. The gadget demonstrated its ability to charge various storage devices, as well as feed a mobile phone, a fitness tracker, and LEDs woven into the fabric (supercapacitors, Li-ion, and LiPo batteries). By weaving PV material coated wires or flexible PV tapes into textiles [
104,
105], this novel way of adding solar energy harvesting capabilities outperforms conventional techniques such as laminating, printing, or coating PV onto fabric surfaces in terms of aesthetics, texture, draping, and washability. This ideal textile behavior is provided by the SC embedded yarn’s unique architecture, created by employing electronic yarn technology.
3.5. Hybrid Textile-Based Energy Harvesting Solutions
Hybrid energy harvesting devices have been suggested recently to address the single energy harvester’s energy-sufficiency problem [
106]. In addition to collecting energy from various sources, hybrid harvesting also involves transforming energy into electricity via various transduction methods. A proper hybridization of various energy conversion technologies may greatly increase power production and space utilization efficiency.
Due to its small vertical displacement and ease of integration, hybrid generators combining piezoelectric and triboelectric harvesting sections offer advantages when working in contact mode for applications involving wide-area floor coverings such as runways and carpets [
107,
108,
109]. However, these solutions can be applied to wearable devices, enabling the implementation of self-powered smart garments [
110]. In [
111], Zhang et al. introduce a revolutionary wearable solar energy-driven pyrothermoelectric hybrid generator by combining a high-efficiency solar absorber, a pyroelectric film, and thermoelectric yarns (PTEG). When exposed to sunlight, the solar absorber transforms solar energy to heat energy. While temperatures at the outermost area of the PEDOT: PSS yarns beneath the thermal shielding remain relatively low, temperatures at the PVDF layer and the middle region of the PEDOT: PSS (poly-(styrenesulfonate)) yarns can be greatly raised. An annular ΔT forms because of heat flow conducting from the PTEG’s core outward in this case. PTEG can efficiently capture both dynamic temperature changes and static temperature gradients. The PTEG efficiently charges two commercial capacitors to a cumulative voltage of 3.7 V in under 800 s under a lighting intensity of 1500 W/m
2 (1.5 suns). The total energy can illuminate 73 LED light bulbs.
Hybrid textiles for scavenging both luminous and mechanical energy were also reported in the literature; for example, a textile-based energy harvesting device is presented in [
112], which combines a triboelectric fabric with a fiber-shaped dye-sensitized solar cell. The resulting hybrid power-textile is soft, flexible, wearable, and has great potential for use in smart textiles or wearable electronics. The textile consists of Ni threads coated with a parylene layer, providing triboelectric functionality. Furthermore, the textile integrates a fiber-shaped dye-sensitized solar cell (FDSSC) constituted by Ti wire support wrapped in a Pt wire, acting as a cathode, immersed by a TiO
2 layer. The characterization results indicated that the TENG fabric could achieve 1.9 W m
−2 maximum output power density, whereas the FDSSC-based textiles reached 7% PCE.
The development of wearable technology has recently sparked a lot of interest in hybrid piezoelectric and triboelectric nanogenerators. For instance, the PDMS/graphite composite triboelectric layer, the P(VDFTrFE)/Ag piezoelectric layer, and three fabric electrodes in a cascaded configuration were employed to build the hybrid generators [
113]. Ag nanowires were employed in the piezoelectric layer to increase the piezoelectricity and electric conductivity of P(VDF-TrFE) nanofibers and obtain a high dielectric constant and low dielectric loss. Graphite nanoparticles were employed to improve the dielectric constant of the triboelectric layer. Individual unit output voltage and current, as well as a hybrid generator, were all detected. Two AC/DC converters were employed to avoid output degradation caused by phase mismatch between the output signals from the two units. The results indicated that the hybrid generator’s output power matched the combined output of the two separate units. Besides, in [
114], the authors deploy an elastic, porous, and robust nanofiber composite (LPPS-NFC) (SEBS) for piezoelectric and triboelectric energy harvesting; it was manufactured by the electrospinning technique of lead-free perovskite/poly(vinylidene fluoride-co-hexafluoropropylene) (PVDF-HFP) and styrene-ethylene-butylene-styrene. The efficient electron transfer and reduced charge loss caused by the good energy level matching between Cs
3Bi
2Br
9 and PVDF-HFP improve the electron-trapping process.
Consequently, the presented LPPS-NFC-based energy harvester surpasses the output voltage record for halide-perovskite-based nanogenerators with an outstanding electrical output (400 V, 1.63 A cm
2, and 2.34 W m
2). The LPPS-NFC also provides exceptional elastic properties, waterproofness, and breathability, enabling the creation of strong wearable devices that transform mechanical energy from various biomechanical motions into electrical energy to power conventional electronic devices. For instance, a self-sustainable pulse sensor combining piezoelectric and triboelectric effects is reported in [
115]; this last consists of PDMS-Ecoflex self-arched layer and Al flat layer properly coupled, representing the triboelectric section (
Figure 15a). Besides, the device comprises a metalized PVDF layer, representing the piezoelectric section. The test results indicated that the device has a short-circuit current and open-circuit voltage of 500 nA and 5.2 V, respectively.
Furthermore, a flexible and stretchable PZT-based piezoelectric nanogenerator was presented in [
116]; the device carries out three sequential energy conversion phases to scavenge ambient energy as much as possible (
Figure 15b). This process includes two triboelectrification processes and one piezoelectric electrification process, reaching a 600 V open-circuit voltage and 1.11 W m
−2 power density, respectively. In addition, (PEDOT: PSS)-coated fabric and PZT micro-transducers were combined to obtain a self-powered and self-functional sock [
117] (
Figure 15c). The characterization demonstrated that the triboelectric and piezoelectric contributions could reach 11µW/cm
2 and 128 11µW/cm
2 power densities, respectively. Finally, in [
118], the authors introduced triboelectric and pyroelectric–piezoelectric nanogenerators (PPENGs) based on PVDF film and fluorinated ethylene propylene (FEP)-Cu triboelectric layers. The TENG appears to perform the main role because the output power of the PPENG and TENG can reach up to around 184.32 µW and 4.74 mW.