Sensorless Control of High-Speed Motors Subject to Iron Loss
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Model and Sensorless Control of HPMSM
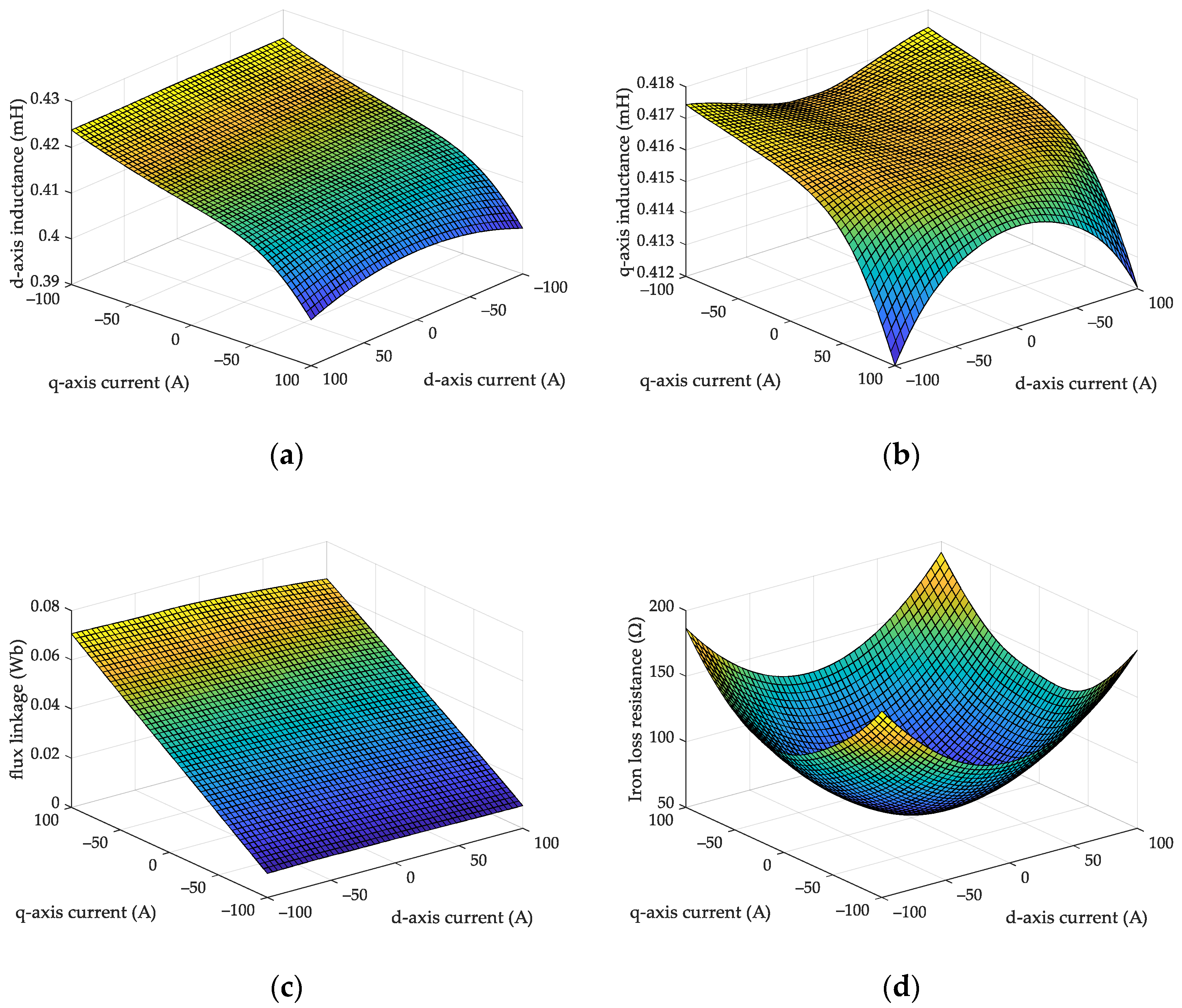
2.1. Model of HSPMSM with Iron Loss
2.2. Design of the Sliding Mode Observer
3. Design of the Adaptive Robust Controller Based on the Characteristic Model
3.1. Characteristic Model of HSPMSM
3.2. Parameter Projection and Parameter Adaptation
3.3. Controller Design
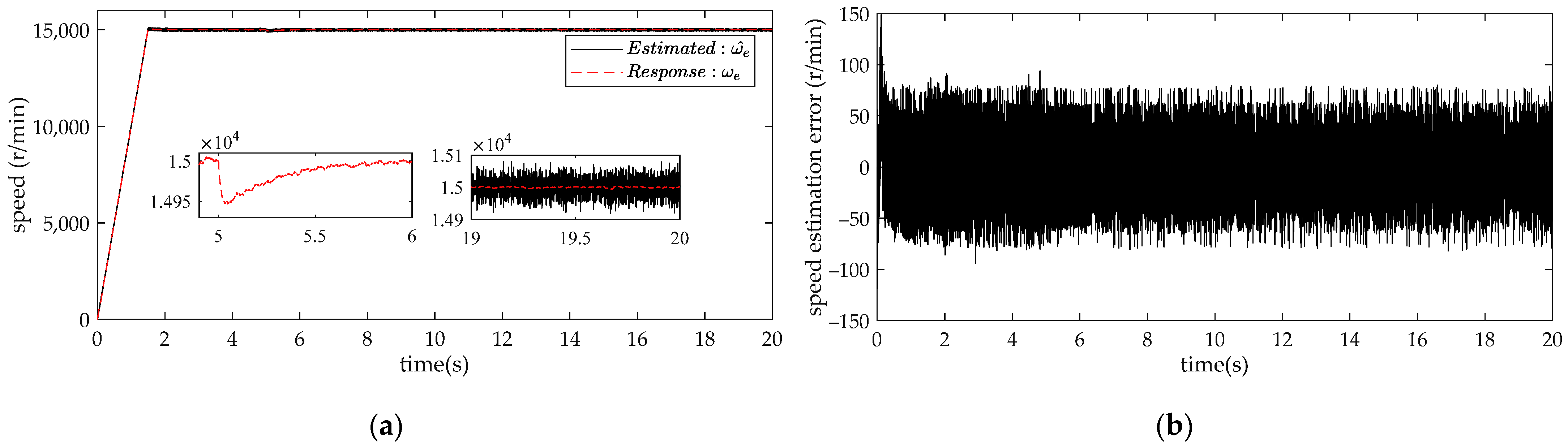
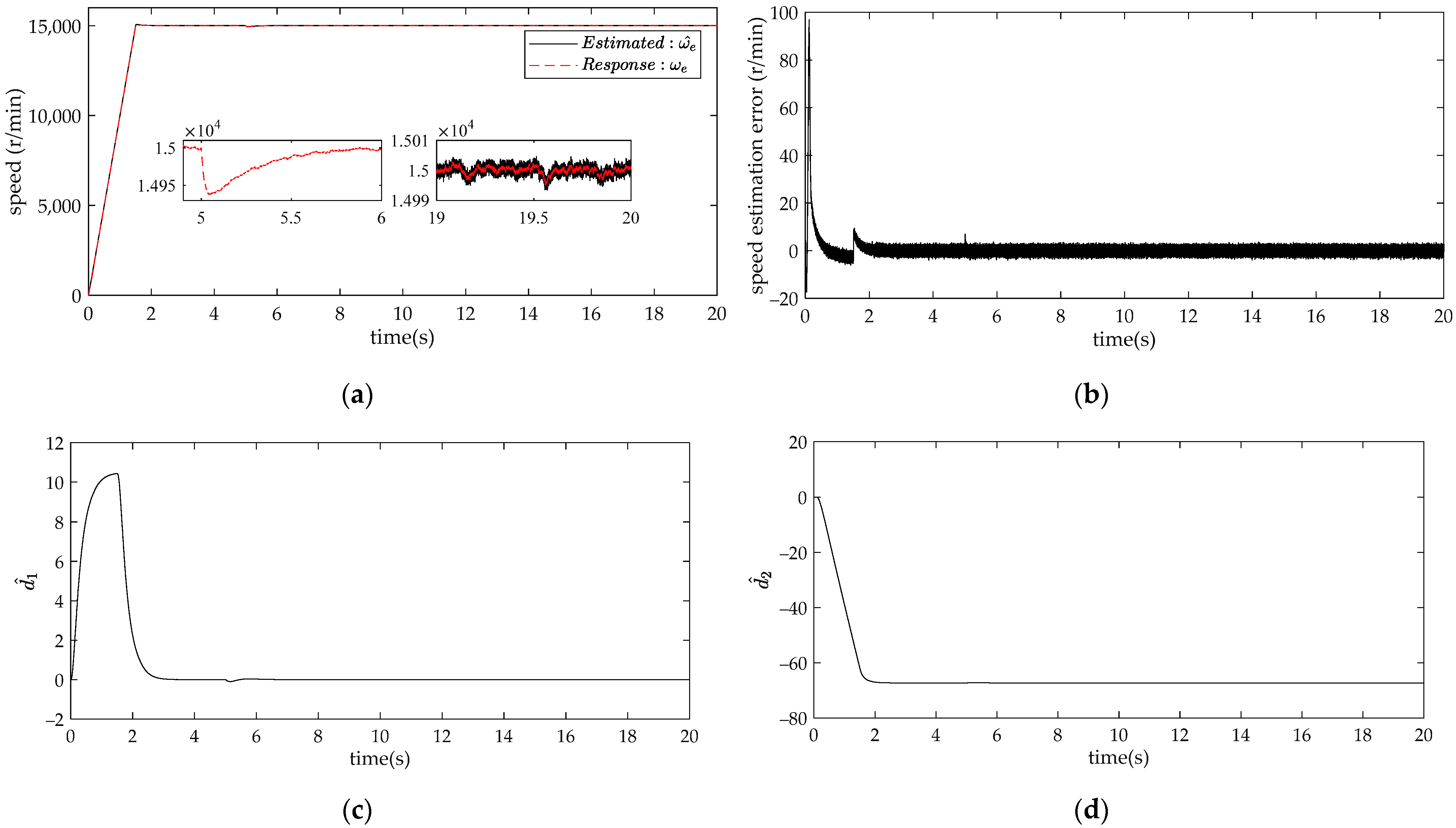
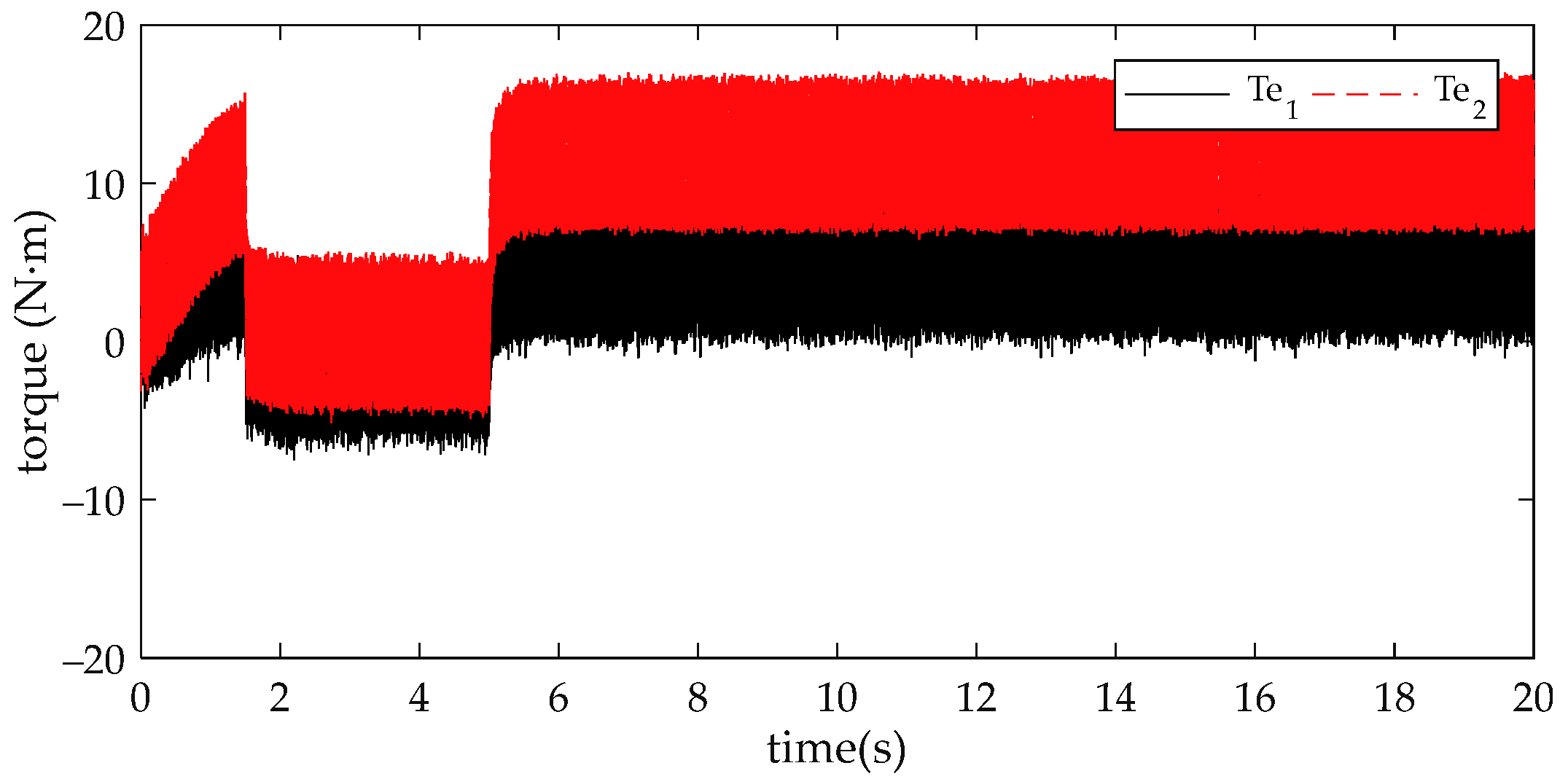
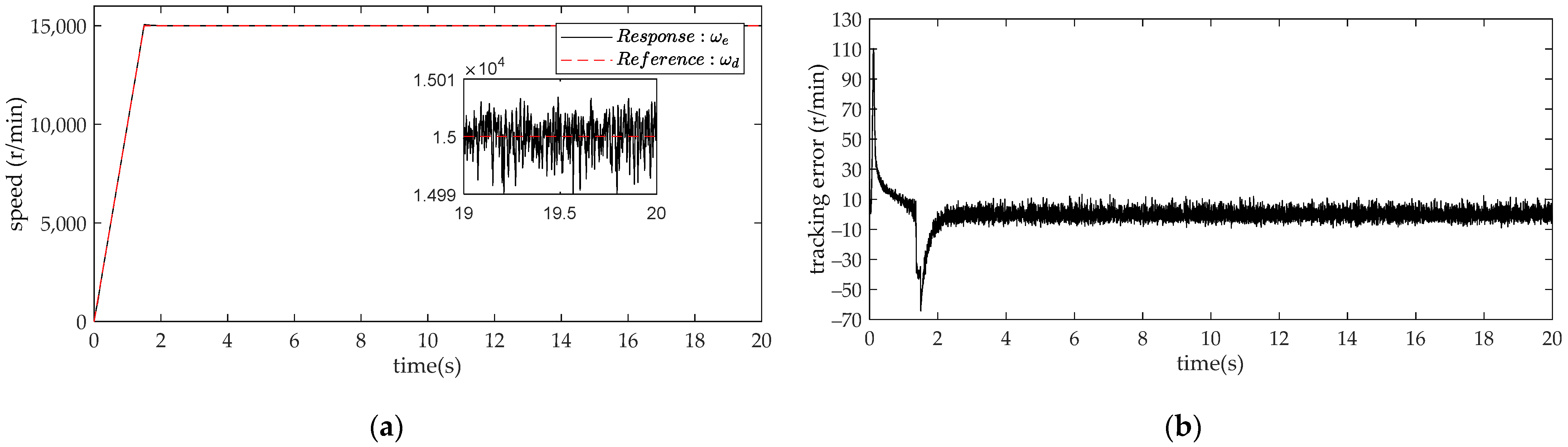
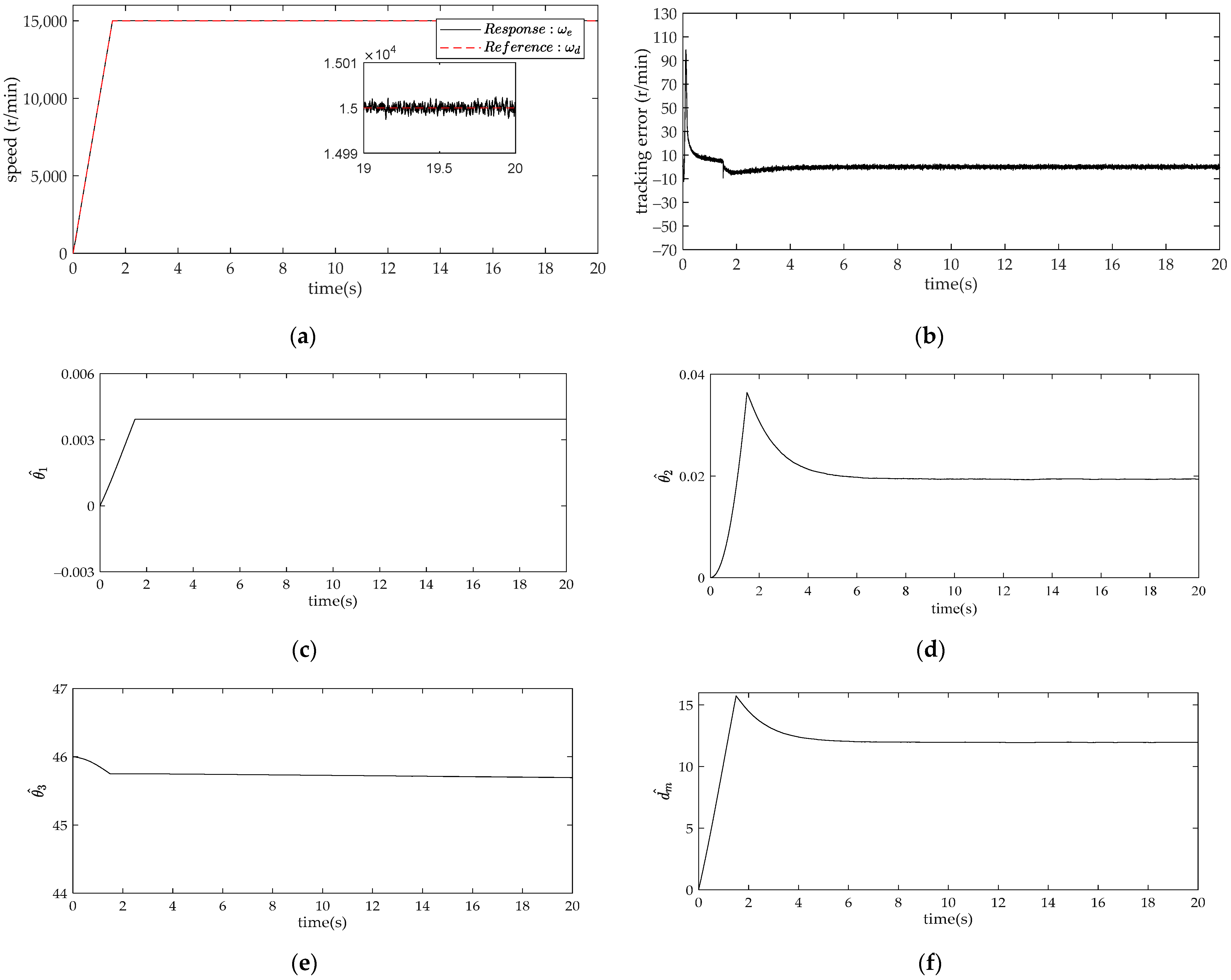
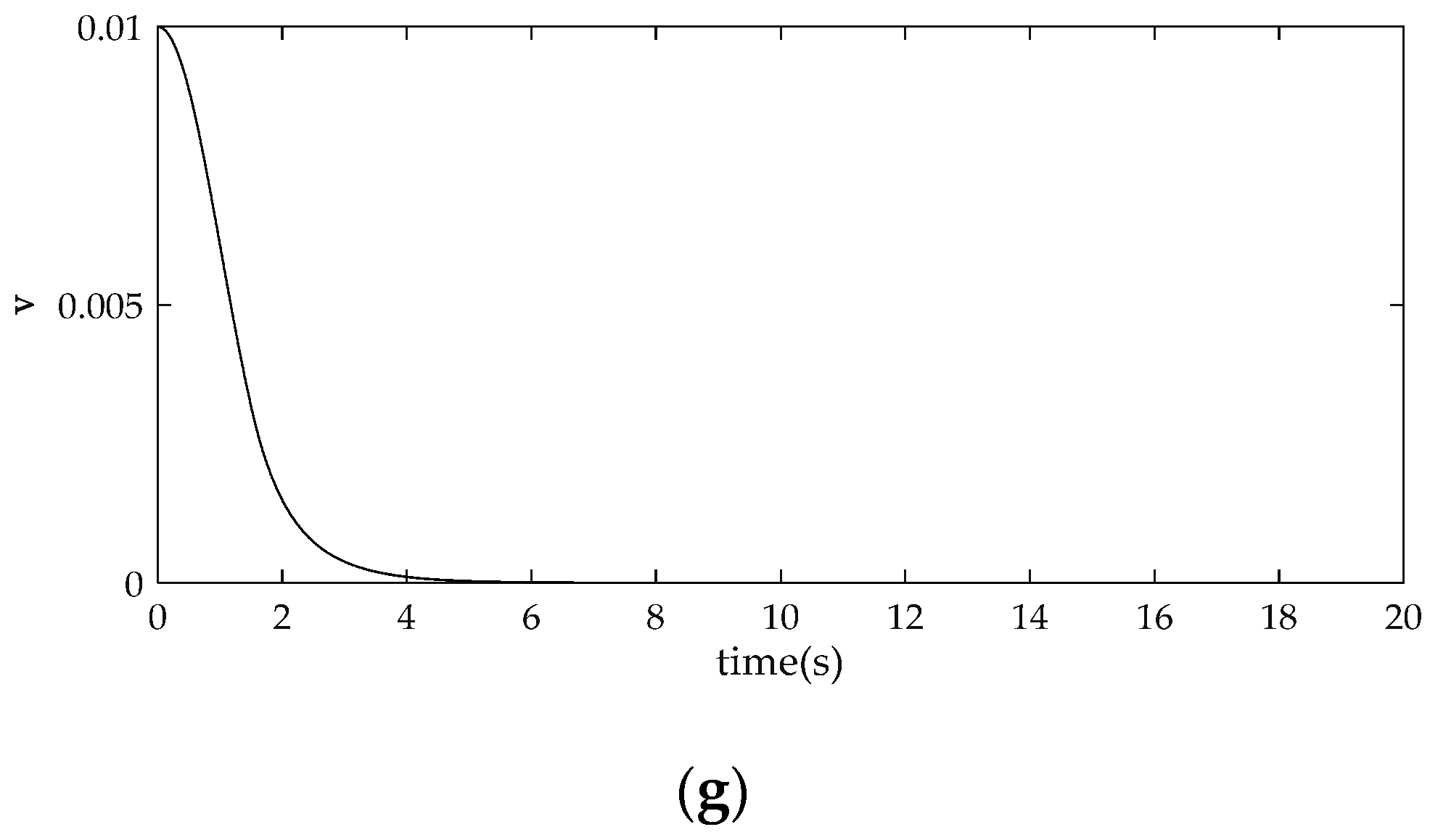
4. Comparison and Analysis of Simulation Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Antivachis, M.; Niklaus, P.S.; Bortis, D.; Kolar, J.W. Input/output EMI filter design for three-phase ultra-high speed motor drive gan inverter stage. CPSSTPEA 2021, 6, 74–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Jeong, I.; Nam, K.; Yang, J.; Hwang, T. Sensorless Control of PMSM in a High-Speed Region Considering Iron Loss. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 62, 6151–6159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Wang, J.; Shen, W. High-performance PMSM self-tuning speed control system with a low-order adaptive instantaneous speed estimator using a low-cost incremental encoder. AJC 2020, 23, 1870–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.; Liang, D.L.; Luo, Z.Q. Position sensorless control of PMSM using sliding mode observer with two-stage filter. Electr. Mach. Control 2012, 11, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Fang, J.; Tan, K.; Huang, B.; He, W. Sliding Mode Observer with Adaptive Parameter Estimation for Sensorless Control of IPMSM. Energies 2020, 13, 5991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veluvolu, K.C.; Soh, Y.C. High-gain observers with sliding mode for state and unknown input estimations. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2009, 56, 3386–3393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Zhang, J.; Chai, B. Adaptive super-twisting sliding mode observer based robust backstepping sensorless speed control for IPMSM. ISA Trans. 2019, 92, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morimoto, S.; Kawamoto, K.; Sanada, M.; Takeda, Y. Sensorless control strategy for salient-pole PMSM based on extended EMF in rotating reference frame. Conference Record of the 2001 IEEE Industry Applications Conference. In Proceedings of the 36th IAS Annual Meeting (Cat. No.01CH37248), Chicago, IL, USA, 30 September–4 October 2001; pp. 2637–2644. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, W.; Qu, S.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, H. An Improved Adaptive Sliding Mode Observer for Middle- and High-Speed Rotor Tracking. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2020, 36, 1043–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, S.; Hirahara, H.; Tanaka, A.; Ara, T.; Matsuse, K. Universal sensorless vector control of induction and permanent magnet synchronous motors considering equivalent iron loss resistance. In Proceedings of the Industry Applications Society Meeting, Lake Buena Vista, FL, USA, 6–11 October 2013; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, P.; Bhaskar, D.V.; Muduli, U.R.; Beig, A.R.; Behera, R.K. Iron-Loss Modeling With Sensorless Predictive Control of PMBLDC Motor Drive for Electric Vehicle Application. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2020, 7, 1506–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, W.; Zhang, F.-X. A Novel Sensorless Rotor Position Estimation Method for PMSM Based on High-Frequency Square-Wave Voltage Injection with Less Iron Loss. Electr. Power Components Syst. 2018, 46, 1872–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, K.-L.; Kim, J.-M.; Hwang, K.-B.; Kim, K.-H. Sensorless control of PMSM in high speed range with iterative sliding mode observer. In Proceedings of the Nineteenth Annual IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition, 2004. APEC ‘04, Anaheim, CA, USA, 22–26 February 2004; pp. 1111–1116. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, X.; Zhu, Q. Attitude control of rigid spacecraft with disturbance generated by time varying exosystems. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2014, 19, 2423–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayacan, E.; Fossen, T.I. Feedback Linearization Control for Systems with Mismatched Uncertainties via Disturbance Observers. Asian J. Control 2019, 21, 1064–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, A.; Yao, B. Integrated Direct/Indirect Adaptive Robust Control of Hydraulic Manipulators With Valve Deadband. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatronics 2010, 16, 707–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Fan, Y.; Li, K.; Liu, W.; Tong, S. Adaptive Optimized Backstepping Control-Based RL Algorithm for Stochastic Nonlinear Systems With State Constraints and Its Application. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2021, 99, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecati, C. Position Control of the Induction Motor Using a Passivity-Based Controller. IEEE TIA 2000, 36, 1277–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, B.; Tomizuka, M. Adaptive robust control of SISO nonlinear systems in a semi-strict feedback form. Automatica 1997, 33, 893–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, B.; Bu, F.; Reedy, J.; Chiu, G.-C. Adaptive robust motion control of single-rod hydraulic actuators: Theory and experiments. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2000, 5, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.-J.; Tsai, M.-C. Robust Scalar Control of Synchronous Reluctance Motor With Optimal Efficiency by MTPA Control. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 32599–32612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quang, L.H.; Putov, V.; Sheludko, V. Adaptive robust control of a multi-degree-of-freedom mechanical plant with resilient properties. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2021, 186, 611–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Jiao, Z.; Ma, D. Extended-State-Observer-Based Output Feedback Nonlinear Robust Control of Hydraulic Systems With Backstepping. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 61, 6285–6293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Hu, J.; Xie, Y. Intelligent Adaptive Control Based on Characteristic Model; China Science and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 2009; pp. 45–76. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H. Research and prospect on the control theory and method in the engineering. Control Theory Appl. 2014, 31, 1626–1631. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, E.; Guo, J.; Chen, Q. Adaptive terminal sliding-mode controller based on characteristic model for gear transmission servo systems. Trans. Inst. Meas. Control 2018, 41, 219–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, Q. Characteristic Model-based Adaptive Control with Genetic Algorithm Estimators for Four-PMSM Synchronization System. Int. J. Control Autom. Syst. 2020, 18, 1605–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urasaki, N.; Senjyu, T.; Uezato, K. Relationship of Parallel Model and Series Model for Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors Taking Iron Loss Into Account. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2004, 19, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallsgrove, R.J.; Akella, M. Globally Stabilizing Saturated Attitude Control in the Presence of Bounded Unknown Disturbances. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 2005, 28, 957–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
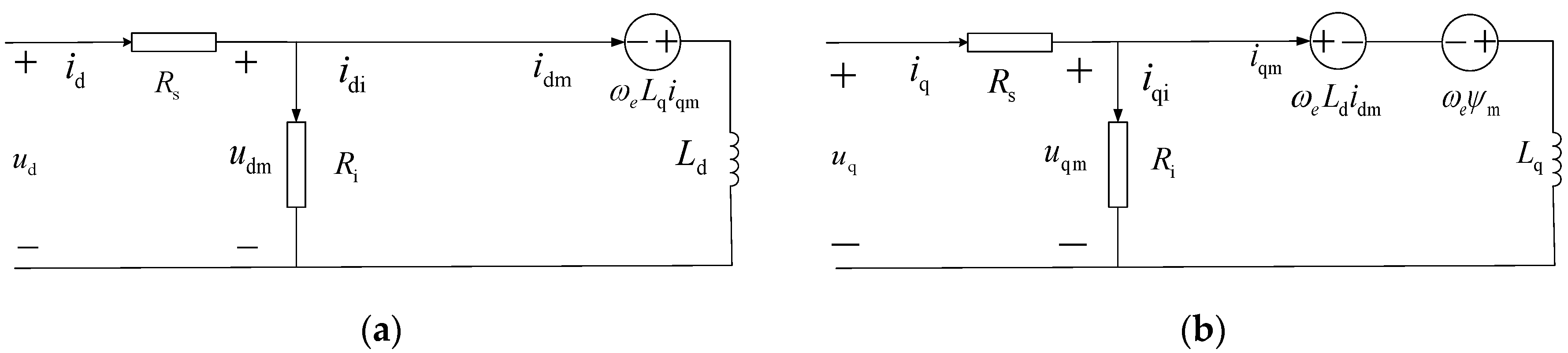




| pole | 1 |
| number of conductors per slot | 8 |
| number of parallel branches | 2 |
| inner diameter of stator | 70 mm |
| outer diameter of stator | 130 mm |
| inner diameter of rotor | 15 mm |
| outer diameter of rotor | 64 mm |
| length of iron core | 130 mm |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cao, Y.; Guo, J. Sensorless Control of High-Speed Motors Subject to Iron Loss. Energies 2022, 15, 7615. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15207615
Cao Y, Guo J. Sensorless Control of High-Speed Motors Subject to Iron Loss. Energies. 2022; 15(20):7615. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15207615
Chicago/Turabian StyleCao, Yang, and Jian Guo. 2022. "Sensorless Control of High-Speed Motors Subject to Iron Loss" Energies 15, no. 20: 7615. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15207615
APA StyleCao, Y., & Guo, J. (2022). Sensorless Control of High-Speed Motors Subject to Iron Loss. Energies, 15(20), 7615. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15207615






