Energy Management System for Grid-Connected Nanogrid during COVID-19
Abstract
1. Introduction
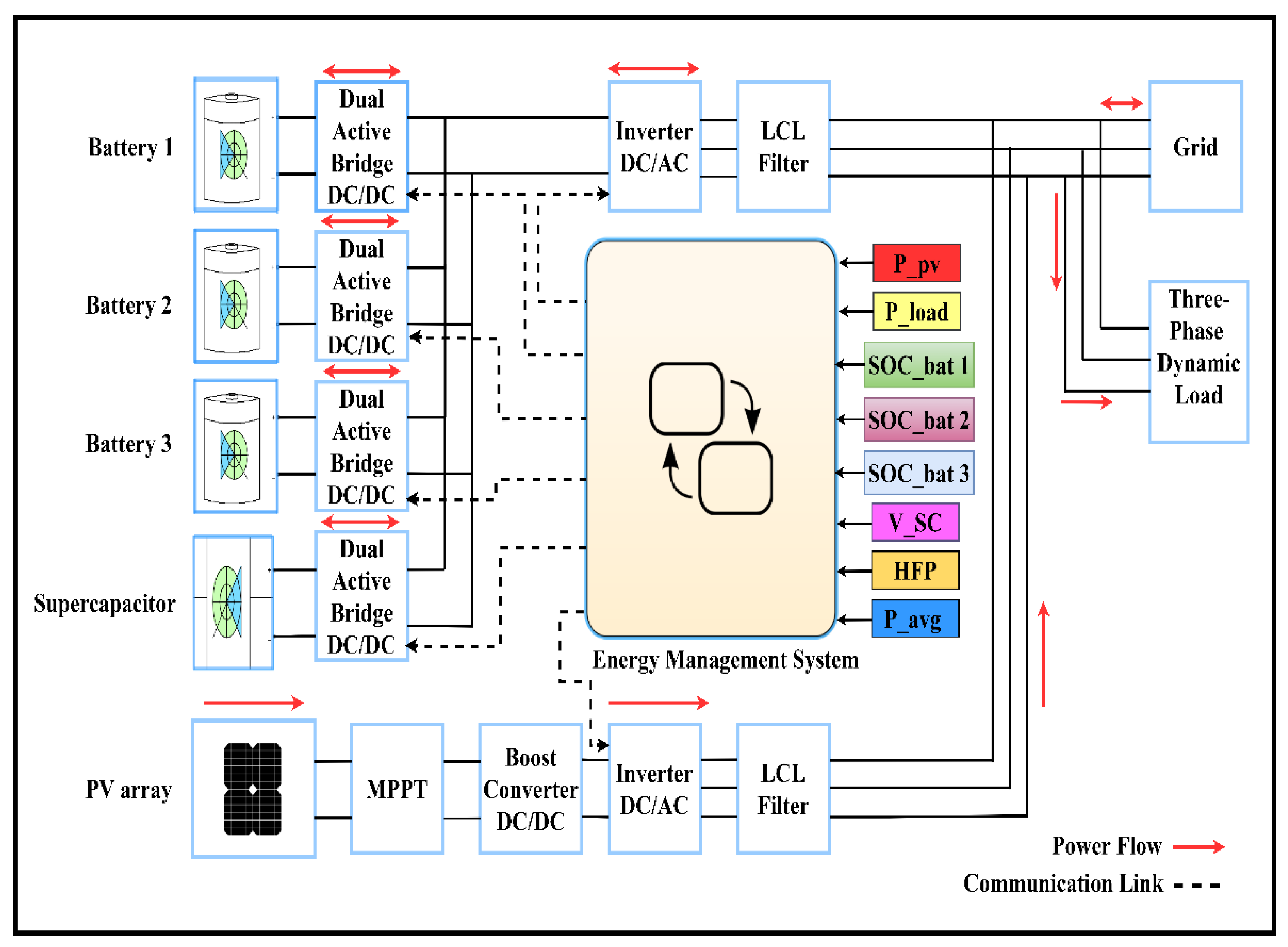
2. Nanogrid Description
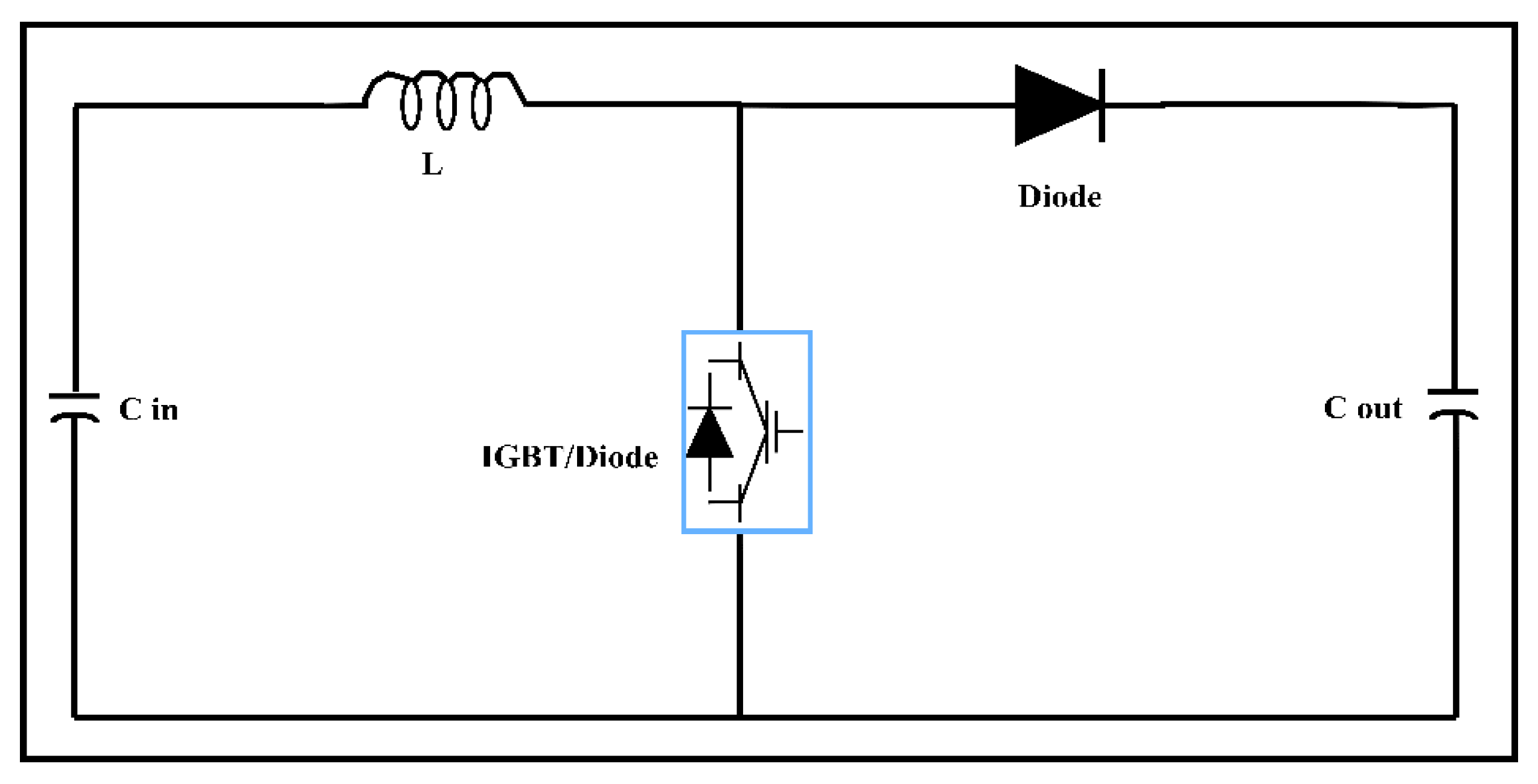
2.1. Photovoltaic (PV) and Boost Converter
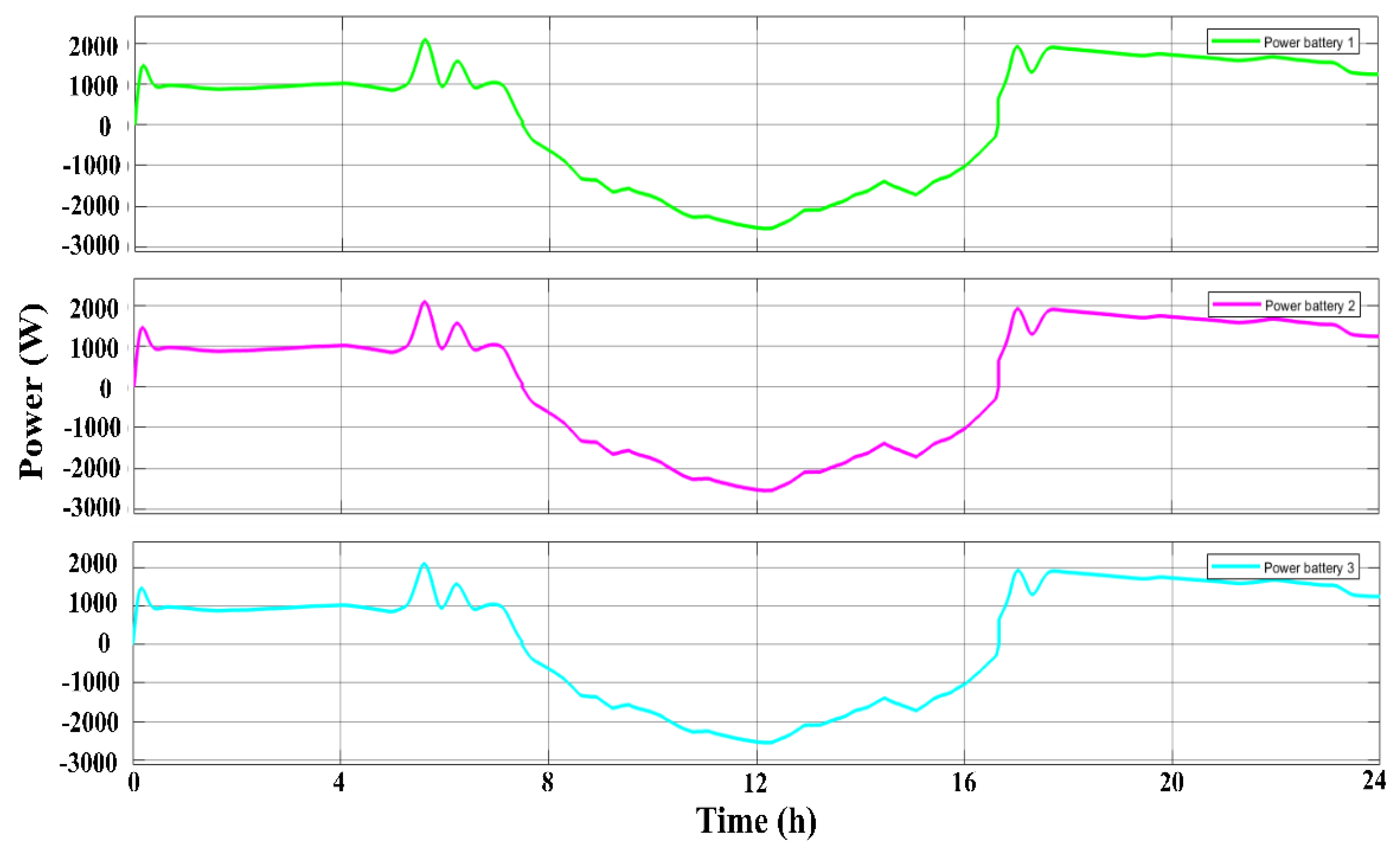
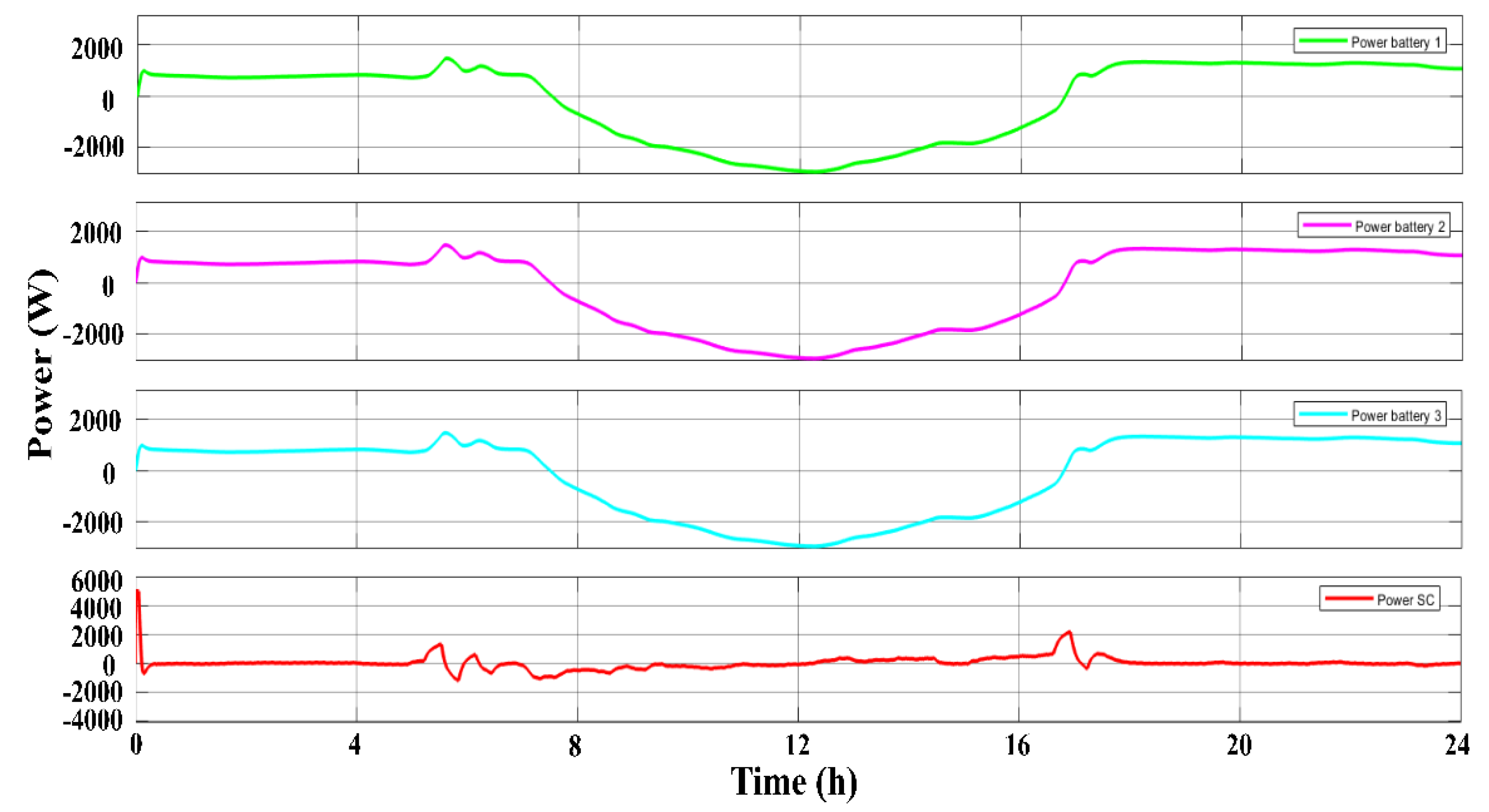
2.2. Energy Storage System with Dual Active Bridge
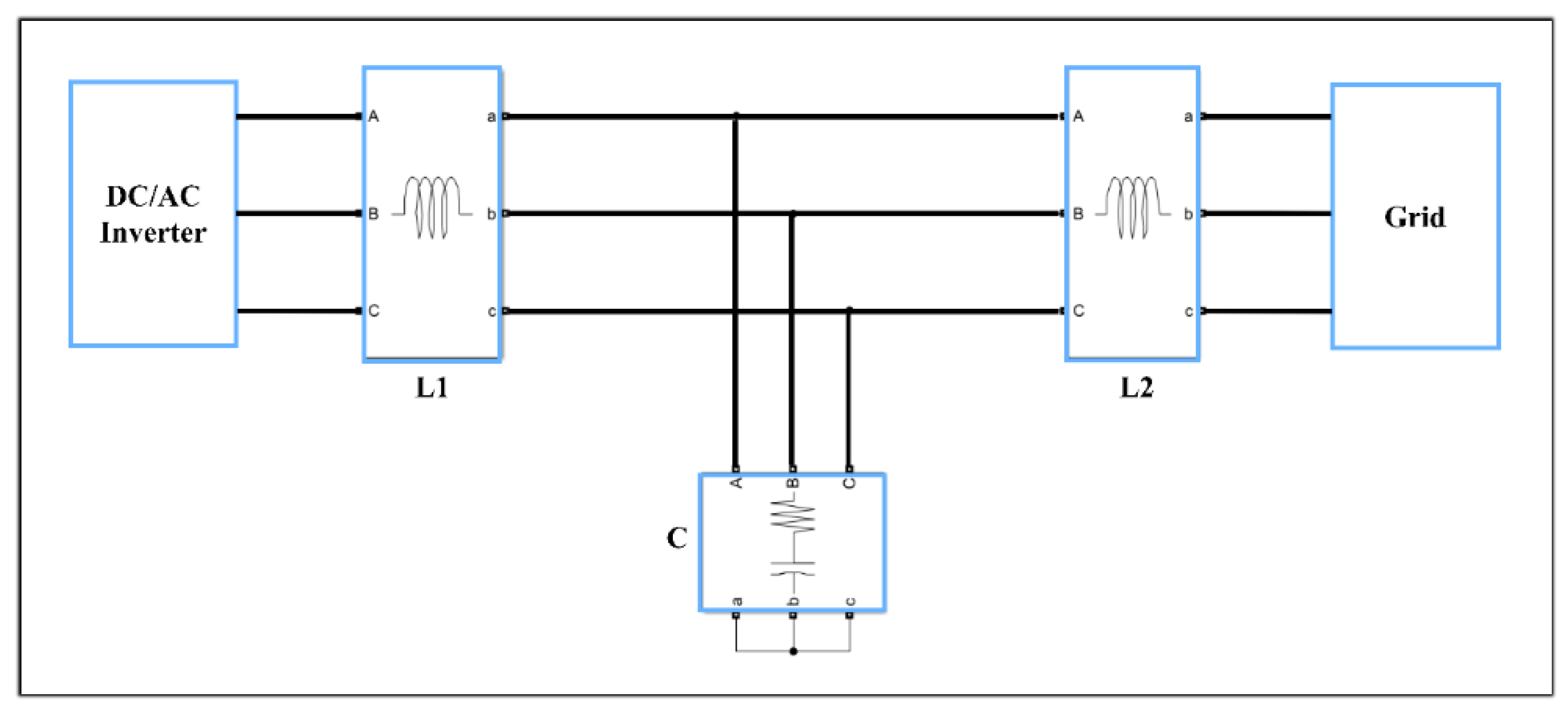
2.3. DC/AC Inverters with LCL Filters
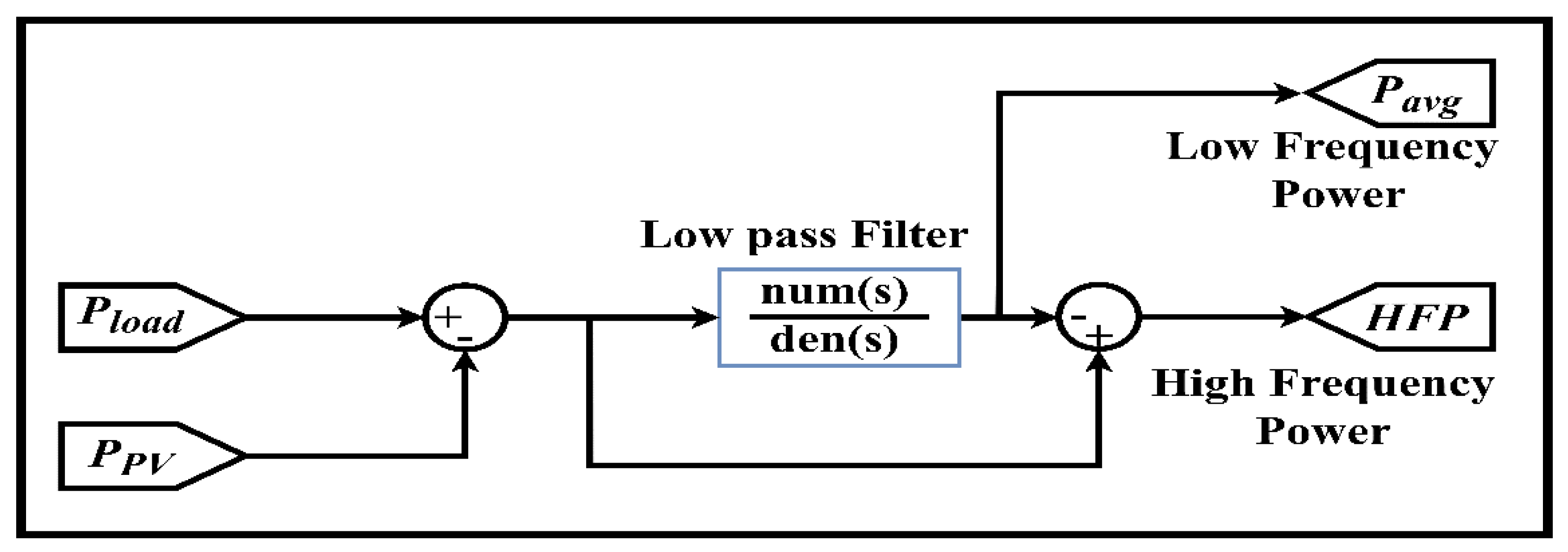
2.4. Energy Management System (EMS) Using Stateflow (SF)
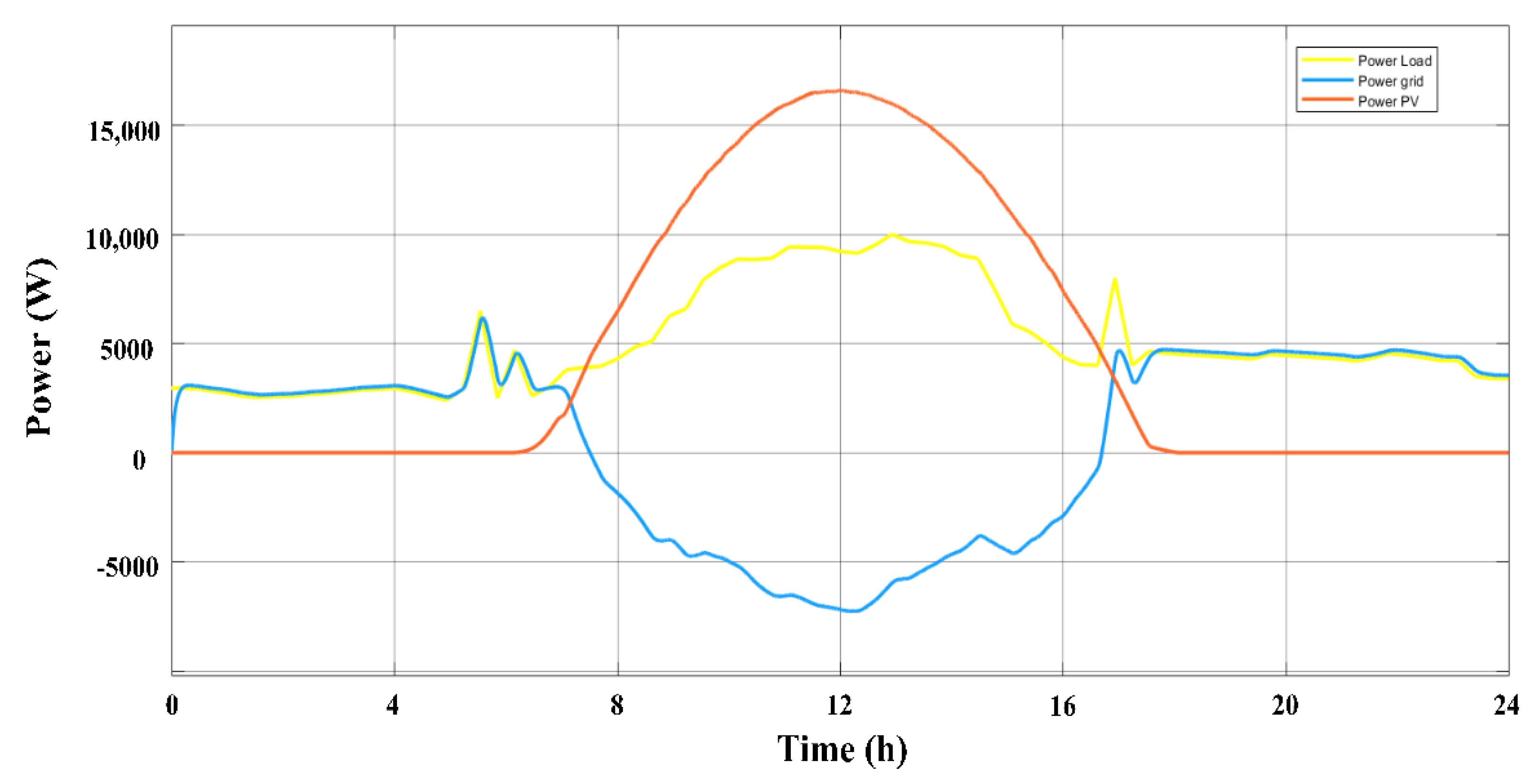
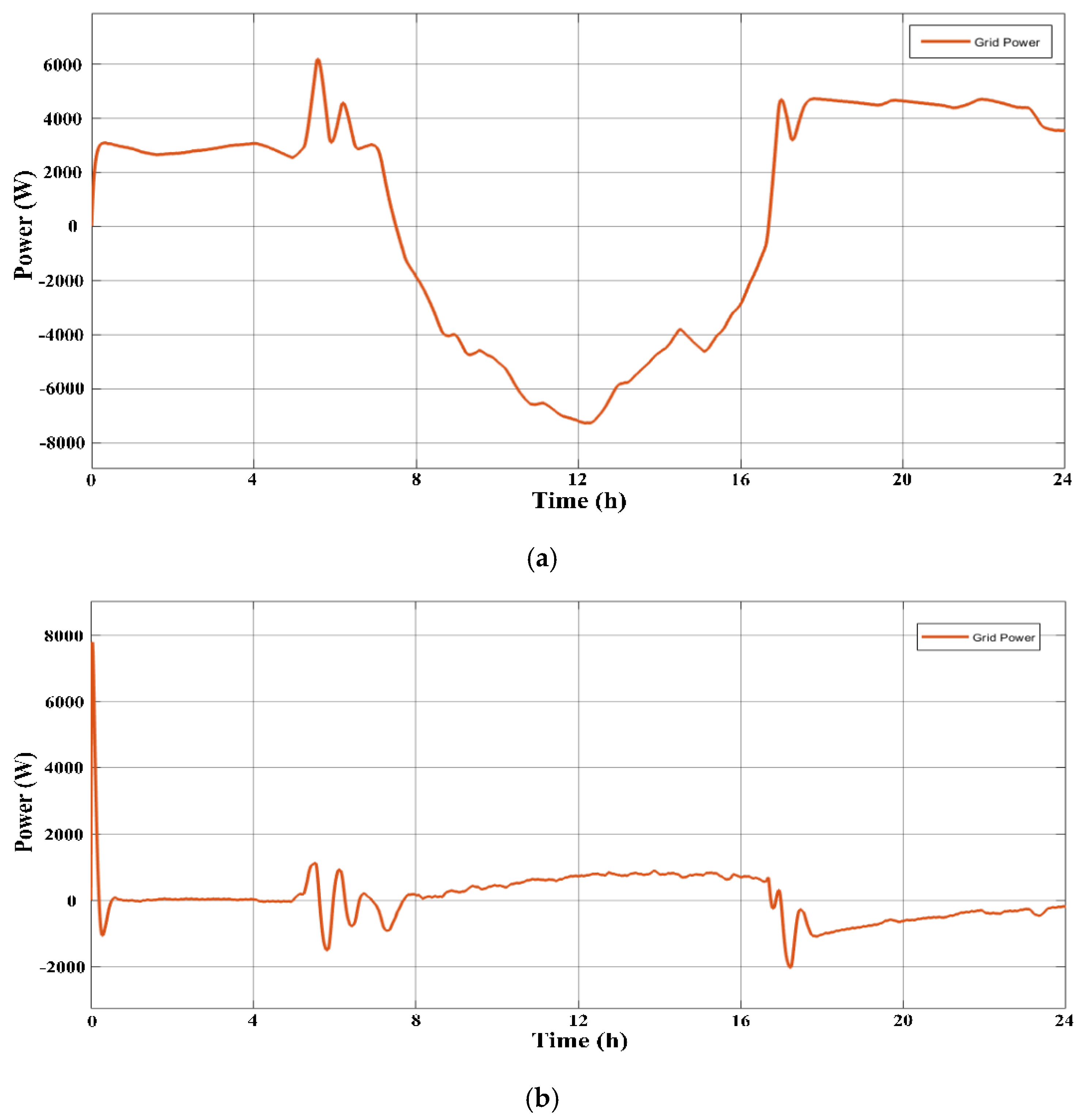
3. Results and Discussions
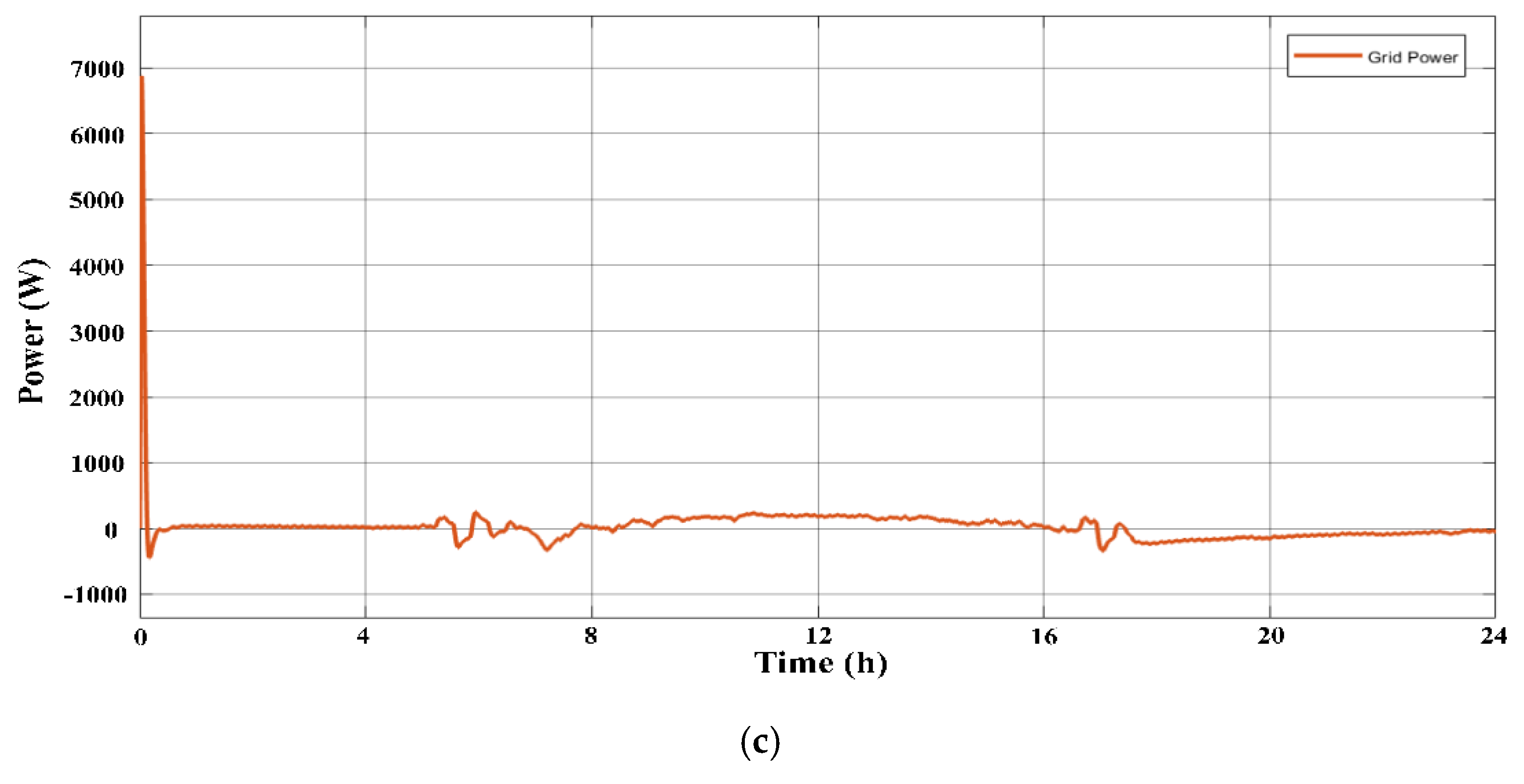
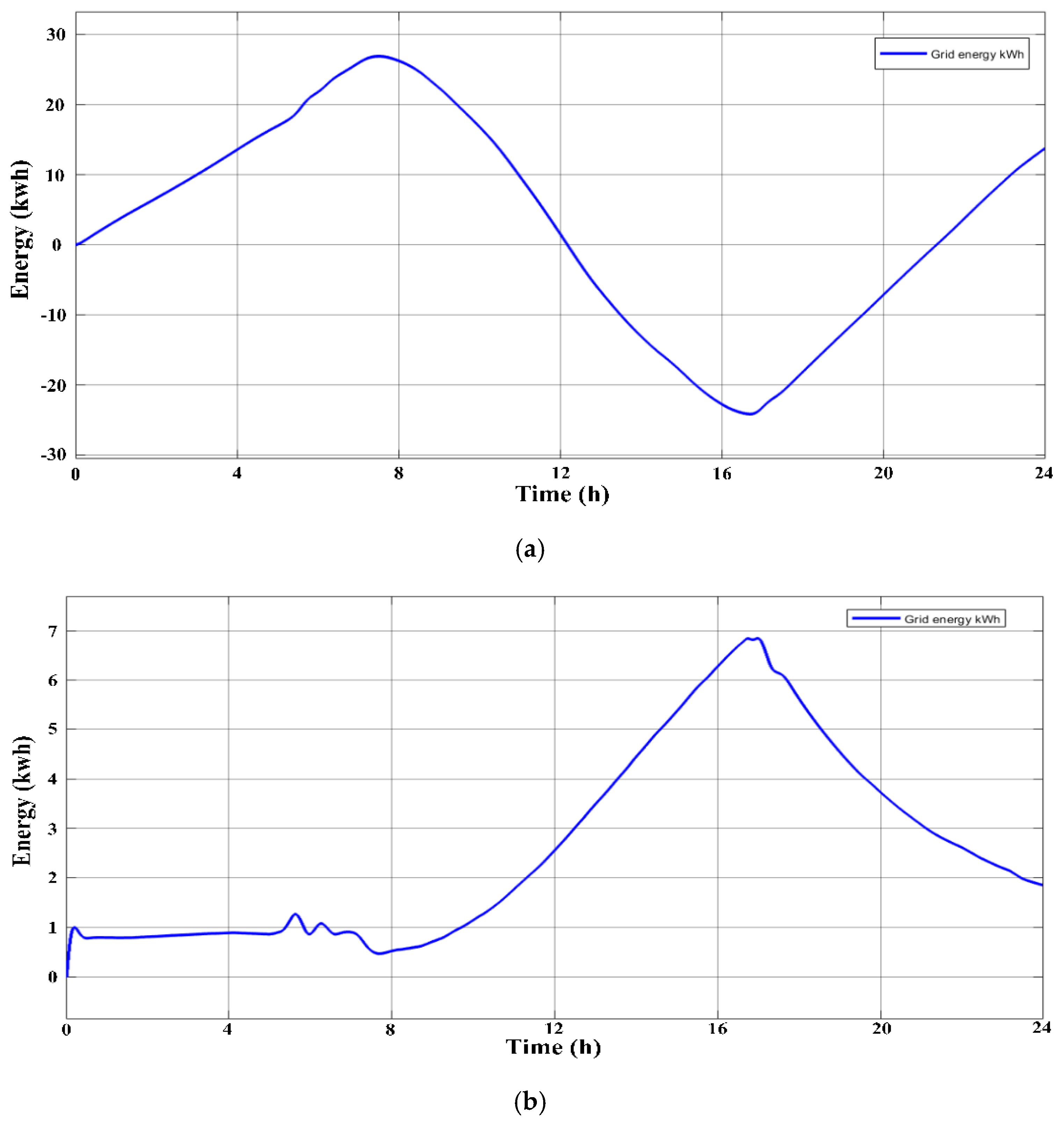
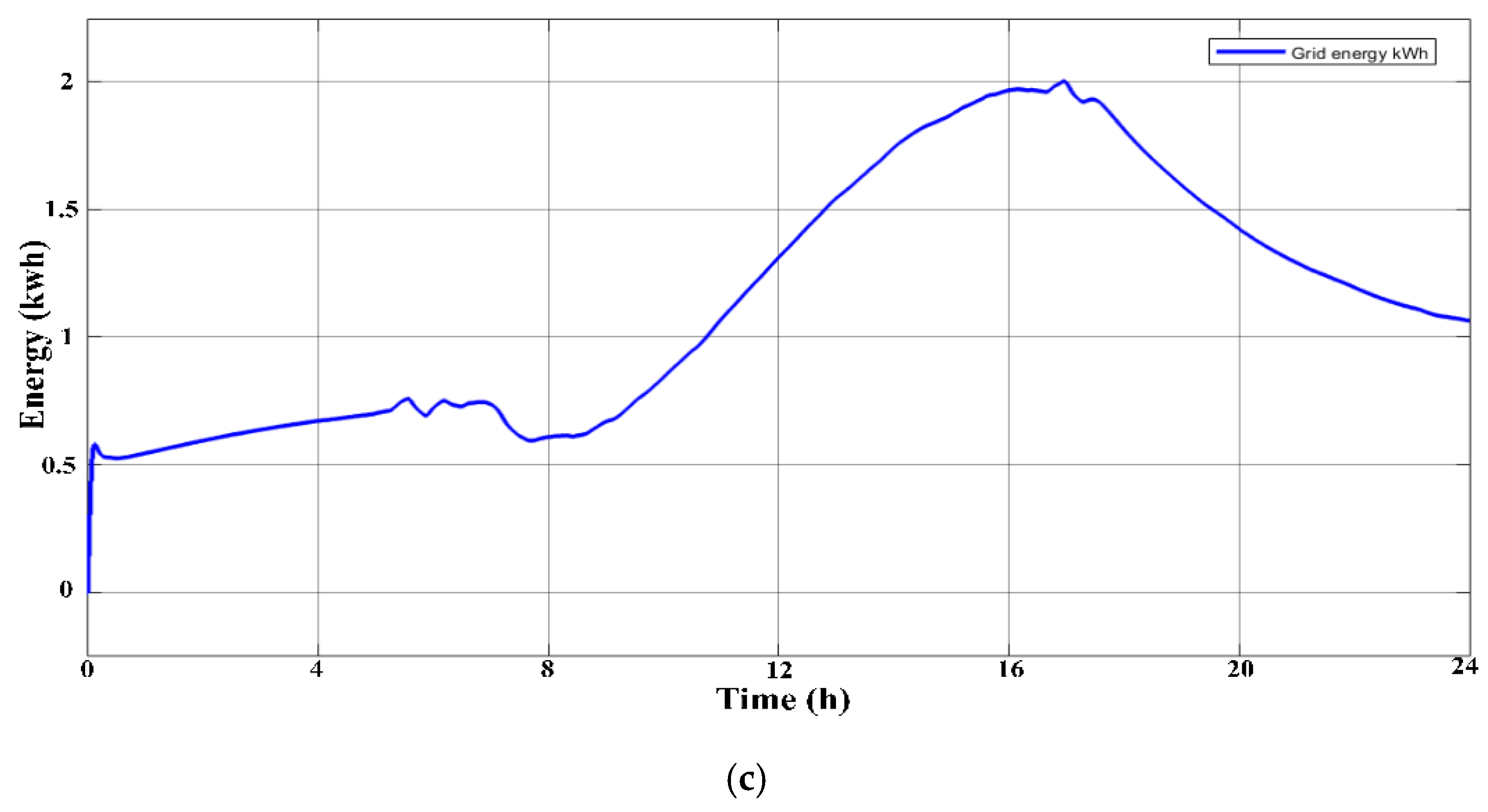
3.1. The Scenarios
3.1.1. First Scenario
3.1.2. Second Scenario
3.1.3. Third Scenario
3.1.4. Fourth Scenario
3.2. Minimization of Energy Consumption and Emissions from the Grid
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A

References
- Jamal, S.; Tan, N.M.L.; Pasupuleti, J. A review of energy management and power management systems for microgrid and nanogrid applications. Sustainability 2021, 13, 10331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakaria, A.; Ismail, F.B.; Lipu, M.S.H.; Hannan, M.A. Uncertainty models for stochastic optimization in renewable energy applications. Renew. Energy 2020, 145, 1543–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, B.; Ertugrul, N.; Chew, H.G. Overview of optimal energy management for nanogrids (end-users with renewables and storage). In Proceedings of the 2016 Australasian Universities Power Engineering Conference (AUPEC), Brisbane, QLD, Australia, 25–28 September 2016; pp. 25–28. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, A.; Bui, V.H.; Kim, H.M. A Resilient and Privacy-Preserving Energy Management Strategy for Networked Mi-crogrids. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2018, 9, 2127–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbungu, N.T.; Naidoo, R.; Bansal, R.C.; Bipath, M. Optimisation of grid connected hybrid photovoltaic-wind-battery system using model predictive control design. IET Renew. Power Gener. 2017, 11, 1760–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Wang, Z.; Liu, S.; Wang, X. Energy Management Strategy of PV Grid-Connected Household Nano-Grid System. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Power & Energy Society General Meeting (PESGM), Atlanta, GA, USA, 4–8 August 2019; pp. 3–7. [Google Scholar]
- Bakht, M.P.; Salam, Z.; Bhatti, A.R.; Anjum, W.; Khalid, S.A.; Khan, N. Stateflow-Based Energy Management Strategy for Hybrid Energy System to Mitigate Load Shedding. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 4601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kermadi, M.; Salam, Z.; Berkouk, E.M. Rule-based Power Management Controller using Stateflow for Grid-Connected PV-Battery Energy System supplying Household load. In Proceedings of the 2018 9th IEEE International Symposium on Power Electronics for Distributed Generation Systems (PEDG), Charlotte, NC, USA, 25–28 June 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Agrawal, A.; Gupta, R. Power Balance for WTG—Solar PV Fed DC Microgrids with Battery and Supercapacitor Support. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Power Electronics, Drives and Energy Systems (PEDES), Chennai, India, 18–21 December 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Manandhar, U.; Ukil, A.; Gooi, H.B.; Tummuru, N.R.; Kollimalla, S.K.; Wang, B.; Chaudhari, K. Energy management and control for grid connected hybrid energy storage system under different operating modes. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2019, 10, 1626–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habeeb, S.A.; Tostado-Véliz, M.; Hasanien, H.M.; Turky, R.A.; Meteab, W.K.; Jurado, F. Dc nanogrids for integration of demand response and electric vehicle charging infrastructures: Appraisal, optimal scheduling and analysis. Electronics 2021, 10, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigalo, M.B.; Pillai, A.C.; Das, S.; Abusara, M. An energy management system for the control of battery storage in a grid-connected microgrid using mixed integer linear programming. Energies 2021, 14, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roslan, M.F.; Hannan, M.A.; Jern Ker, P.; Begum, R.A.; Indra Mahlia, T.M.; Dong, Z.Y. Scheduling controller for microgrids energy management system using optimization algorithm in achieving cost saving and emission reduction. Appl. Energy 2021, 292, 116883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosa, M.A.; Ali, A.A. Energy management system of low voltage dc microgrid using mixed-integer nonlinear programing and a global optimization technique. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2021, 192, 106971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamran, M.; Mudassar, M.; Fazal, M.R.; Asghar, M.U.; Bilal, M.; Asghar, R. Implementation of improved Perturb & Observe MPPT technique with confined search space for standalone photovoltaic system. J. King Saud Univ.-Eng. Sci. 2020, 32, 432–441. [Google Scholar]
- Pradhan, A.; Panda, B. A simplified design and modeling of boost converter for photovoltaic sytem. Int. J. Electr. Comput. Eng. 2018, 8, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Piazza, M.C.; Luna, M.; Pucci, M.; La Tona, G.; Accetta, A. Electrical Storage Integration into a DC Nanogrid Testbed for Smart Home Applications. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Environment and Electrical Engineering and 2018 IEEE Industrial and Commercial Power Systems Europe (EEEIC/I&CPS Europe), Palermo, Italy, 12–15 June 2018; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Mandic, G.; Nasiri, A. Modeling and simulation of a wind turbine system with ultracapacitors for short-term power smoothing. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Symposium on Industrial Electronics, Bari, Italy, 4–7 July 2010; pp. 2431–2436. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, D.; Zhou, T.; Fakham, H.; Francois, B. Design of a power management system for an active PV station including various storage technologies. In Proceedings of the 2008 13th International Power Electronics and Motion Control Conference, Poznan, Poland, 1–3 September 2008; pp. 2142–2149. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, H.; Kimball, J.W. Generalized average modeling of dual active bridge DC-DC converter. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2012, 27, 2078–2084. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, S.; Chen, L.; Shan, Z.; Gao, F.; Chen, H.; Sha, D.; Dragičević, T. Modeling and Advanced Control of Dual-Active-Bridge DC–DC Converters: A Review. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2021, 37, 1524–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ríos, S.J.; Pagano, D.J.; Lucas, K.E. Bidirectional power sharing for dc microgrid enabled by dual active bridge dc-dc converter. Energies 2021, 14, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henao-Bravo, E.E.; Ramos-Paja, C.A.; Saavedra-Montes, A.J.; González-Montoya, D.; Sierra-Pérez, J. Design method of dual active bridge converters for photovoltaic systems with high voltage gain. Energies 2020, 13, 1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, A.; Vázquez, A.; Lamar, D.G.; Hernando, M.M.; Sebastián, J. Different purpose design strategies and techniques to improve the performance of a dual active bridge with phase-shift control. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2015, 30, 790–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafa, S.; Zekry, A.; Youssef, A.; Anis, W.R. Raspberry Pi Design and Hardware Implementation of Fuzzy-PI Controller for Three-Phase Grid-Connected Inverter. Energies 2022, 15, 843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liserre, M.; Blaabjerg, F.; Hansen, S. Design and control of an LCL-filter-based three-phase active rectifier. IEEE Trans. 2005, 41, 1281–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahlooji, M.H.; Mohammadi, H.R.; Rahimi, M. A review on modeling and control of grid-connected photovoltaic inverters with LCL filter. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 81, 563–5782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrane, Z.; Ouassaid, M.; Maaroufi, M. Battery and supercapacitor for photovoltaic energy storage: A fuzzy logic management. IET Renew. Power Gener. 2017, 11, 1157–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| PV array voltage (Vpv) | 513 V |
| Output voltage (Vout) | 800 V |
| Maximum PV array power (Ppv, MAX) | 16.7 kW |
| Current ripple (ΔI) | 3.35 A |
| Voltage ripple of PV (Δvpv) | 5.13 (10% of Vpv) |
| Converter switching frequency (fsw_boost) | 25 kHz |
| Inverter switching frequency (fsw_inverter) | 10 kHz |
| Inductance (L) | 1.53 × 103 H |
| Input capacitor (Cin) | 100 × 106 F |
| Output capacitor (Cout) | 1 × 103 F |
| Output voltage ripple (Δv_out) | 8 V (10% of Vout) |
| Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Operating voltage range for battery | 42 V–54 V |
| Nominal voltage | 48 V |
| Rated capacity | 100 Ah |
| Initial SOC | 40% |
| SOC_max | 80% |
| SOC_min | 20% |
| Rated capacitance of SC | 177 F |
| Rated voltage | 51 V |
| Rated power | 5 kW |
| Number of series capacitors | 18 |
| Number of parallel capacitors | 1 |
| Initial voltage | 50 V |
| Vsc_max | 51 V |
| Vsc_min | 38 V |
| Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Input capacitance (Cin) | 2000 × 106 F |
| Output capacitance (Co) | 2000 × 106 F |
| Leakage inductance (L) | 6 × 106 H |
| Input voltage ripple (Δvi) | 5 V |
| Output voltage ripple (Δvo) | 1.5 V |
| Maximum power (pMAX) | 4.8 kW |
| Switching frequency (Fs) | 25 kHz |
| Input voltage (Vin) | 48 V |
| Output voltage (Vo) | 800 V |
| Maximum duty cycle (dMAX) | 0.35 |
| Turn ratio of the transformer (n) | 5 |
| Parameters | Values of PV Inverter and LCL Filter | Values of ESS Inverter and LCL Filter |
|---|---|---|
| Rated power (Pn) | 16.7 kW | 20 kW |
| ) | 800 V | 800 V |
| Grid voltage (Vg) | 400 V | 400 V |
| Grid frequency (Fg) | 50 HZ | 50 HZ |
| Switching frequency (Fsw) | 10 kHZ | 10 kHZ |
| 4.79 | 4 | |
| Filter capacitor (C) | ||
| Grid maximum current (Imaxg) | 48.4 A | 58 A |
| Current ripple ) | 9% of Imaxg | 9% of Imaxg |
| Inverter-side inductor (L1) | ||
| Grid-side inductor (L2) | ||
| Ratio (r) | 0.0153 | 0.0152 |
| Ripple attenuation (K) | 20% | 20% |
| ESS | Emission Saving per Day (kg) | Emission Saving per Month (kg) | Emission Saving per Year (kg) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Batteries only | 7.623 | 228.69 | 2744.28 |
| Batteries with supercapacitor | 8.1585 | 244.755 | 2937.06 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jamal, S.; Pasupuleti, J.; Rahmat, N.A.; Tan, N.M.L. Energy Management System for Grid-Connected Nanogrid during COVID-19. Energies 2022, 15, 7689. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15207689
Jamal S, Pasupuleti J, Rahmat NA, Tan NML. Energy Management System for Grid-Connected Nanogrid during COVID-19. Energies. 2022; 15(20):7689. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15207689
Chicago/Turabian StyleJamal, Saif, Jagadeesh Pasupuleti, Nur Azzammudin Rahmat, and Nadia M. L. Tan. 2022. "Energy Management System for Grid-Connected Nanogrid during COVID-19" Energies 15, no. 20: 7689. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15207689
APA StyleJamal, S., Pasupuleti, J., Rahmat, N. A., & Tan, N. M. L. (2022). Energy Management System for Grid-Connected Nanogrid during COVID-19. Energies, 15(20), 7689. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15207689






