Recent Advances in Energy Harvesting from the Human Body for Biomedical Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Biofuel Cells
3. Thermal Generators
4. Biomechanical Energy
4.1. Piezoelectric Nanogenerators
4.2. Triboelectric Nanogenerators
4.3. Electromagnetic Generators
4.4. Electrostatic Nanogenerators
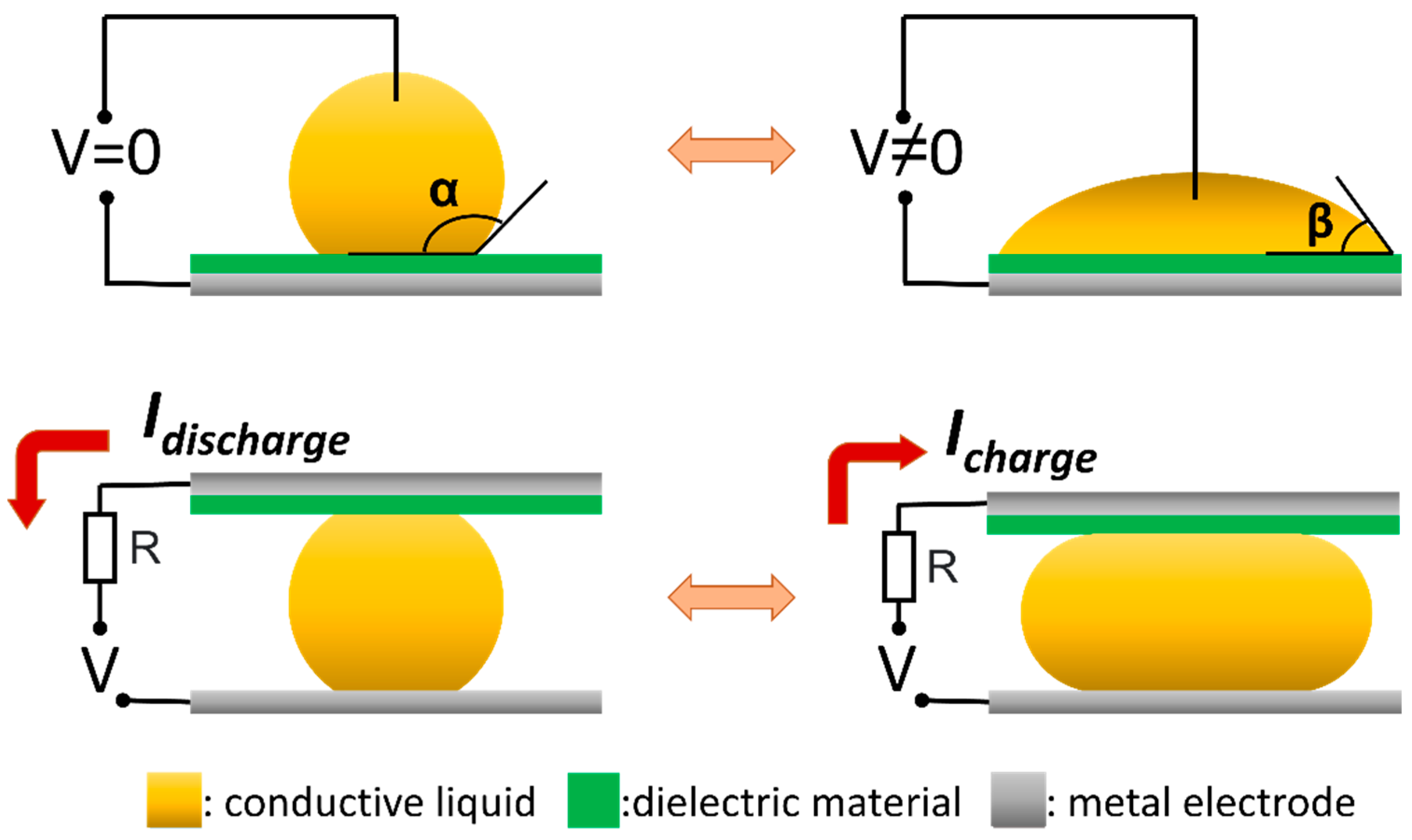
4.5. Reverse Electrowetting on Dielectric Phenomenon (REWOD)
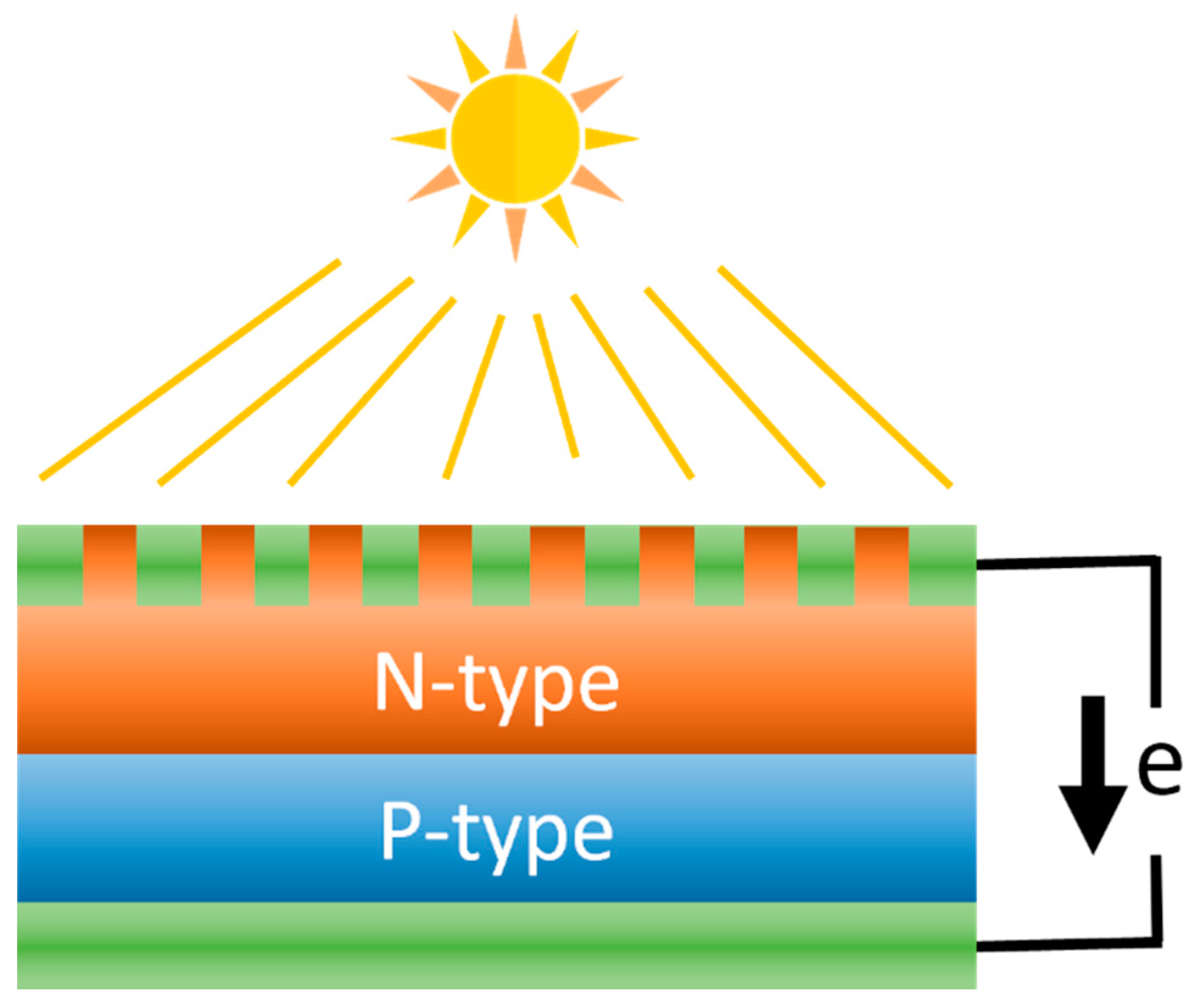
5. Photovoltaic Materials
6. Comparison of Nanogenerators
7. Biomedical Application of Energy Harvesters
8. Discussion on Current Trends
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BFC | Biofuel cell |
| EMG | Electromagnetic generators |
| ESG | Electrostatic generators |
| EWOD | Electrowetting on dielectric |
| ICD | Implantable cardioverter-defibrillators |
| IMD | Implantable medical devices |
| MEMS | Micro-electromechanical system |
| NG | Nanogenerator |
| OC | Open-circuit |
| PENG | Piezoelectric nanogenerator |
| PVDF | Polyvinylidene fluoride |
| PZT | Lead zirconate titanate |
| REWOD | Reverse electrowetting on dielectric |
| TENG | Triboelectric nanogenerator |
References
- Gambhir Sanjiv, S.; Ge, T.J.; Vermesh, O.; Spitler, R.; Gold Garry, E. Continuous health monitoring: An opportunity for precision health. Sci. Transl. Med. 2021, 13, eabe5383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leenen, J.P.L.; Leerentveld, C.; van Dijk, J.D.; van Westreenen, H.L.; Schoonhoven, L.; Patijn, G.A. Current Evidence for Continuous Vital Signs Monitoring by Wearable Wireless Devices in Hospitalized Adults: Systematic Review. J. Med. Internet Res. 2020, 22, e18636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Mukasa, D.; Zhang, H.; Gao, W. Self-Powered Wearable Biosensors. Acc. Mater. Res. 2021, 2, 184–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, P.; Zou, Y.; Fan, Y.; Li, Z. Self-powered wearable electronics. Wearable Technol. 2020, 1, e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina Arias, L.; Iwaniec, J.; Iwaniec, M. Modeling and Analysis of the Power Conditioning Circuit for an Electromagnetic Human Walking-Induced Energy Harvester. Energies 2021, 14, 3367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Liu, L.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, S.; He, T.; Shi, Q.; Lee, C. Technology evolution from micro-scale energy harvesters to nanogenerators. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2021, 31, 093002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.; Guo, X.; Lee, C. Flourishing energy harvesters for future body sensor network: From single to multiple energy sources. iScience 2021, 24, 101934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rong, G.; Zheng, Y.; Sawan, M. Energy Solutions for Wearable Sensors: A Review. Sensors 2021, 21, 3806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Yang, T.; Zhang, M.; Bowen, C.R.; Yang, Y. Recent Progress in Hybridized Nanogenerators for Energy Scavenging. iScience 2020, 23, 101689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Song, Y.; Han, M.; Zhang, H. Portable and wearable self-powered systems based on emerging energy harvesting technology. Microsyst. Nanoeng. 2021, 7, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.L.; Song, J. Piezoelectric nanogenerators based on zinc oxide nanowire arrays. Science 2006, 312, 242–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feynman, R.P. There’s Plenty of Room at the Bottom. Eng. Sci. 1960, 23, 63–76. [Google Scholar]
- Schüssler-Fiorenza Rose, S.M.; Contrepois, K.; Moneghetti, K.J.; Zhou, W.; Mishra, T.; Mataraso, S.; Dagan-Rosenfeld, O.; Ganz, A.B.; Dunn, J.; Hornburg, D.; et al. A longitudinal big data approach for precision health. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 792–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, A.; Badea, M.; Tiwari, S.; Marty, J.L. Wearable Biosensors: An Alternative and Practical Approach in Healthcare and Disease Monitoring. Molecules 2021, 26, 748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, P.M.; Xiong, Z.; Ho, J. Methods for powering bioelectronic microdevices. Bioelectron. Med. 2018, 1, 201–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, S.; Sun, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhai, J.; Dong, S. Recent development of biofuel cell based self-powered biosensors. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 3393–3407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katz, E.; Bollella, P. Fuel Cells and Biofuel Cells: From Past to Perspectives. Isr. J. Chem. 2021, 61, 68–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasar, A.; Perveen, R. Applications of enzymatic biofuel cells in bioelectronic devices—A review. Int. J. Hydrogn Energy 2019, 44, 15287–15312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Singh, G.; Arya, S.K. Biofuel cell nanodevices. Int. J. Hydrogn Energy 2021, 46, 3270–3288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yimamumaimaiti, T.; Lu, X.; Zhang, J.-R.; Wang, L.; Zhu, J.-J. Efficient Blood-toleration Enzymatic Biofuel Cell via In Situ Protection of an Enzyme Catalyst. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 41429–41436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Kjøniksen, A.-L.; Zhou, X.; Zhou, X. Wearable Biofuel Cells: Advances from Fabrication to Application. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2103976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buaki-Sogó, M.; García-Carmona, L.; Gil-Agustí, M.; García-Pellicer, M.; Quijano-López, A. Flexible and Conductive Bioelectrodes Based on Chitosan-Carbon Black Membranes: Towards the Development of Wearable Bioelectrodes. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, X.; Peng, R.; Fan, Z.; Lin, Y. Self-powered and wearable biosensors for healthcare. Mater. Today Energy 2022, 23, 100900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Yao, Y.; Lv, T.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Chen, T. Flexible and Stretchable Enzymatic Biofuel Cell with High Performance Enabled by Textile Electrodes and Polymer Hydrogel Electrolyte. Nano Lett. 2021, 22, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seselj, N.; Engelbrekt, C.; Zhang, J. Graphene-supported platinum catalysts for fuel cells. Sci. Bull. 2015, 60, 864–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivan, I.; Vidaković-Koch, T.; Sundmacher, K. Recent Advances in Enzymatic Fuel Cells: Experiments and Modeling. Energies 2010, 3, 803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, J.; Su, H.; Sun, F.; Lu, Z.; Su, A. A wearable self-powered biosensor system integrated with diaper for detecting the urine glucose of diabetic patients. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 341, 130046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Huang, L.; Chen, J.; Liu, L.; Zhu, X.; Wu, W.; Dong, S. Bionic design of cytochrome c oxidase-like single-atom nanozymes for oxygen reduction reaction in enzymatic biofuel cells. Nano Energy 2021, 83, 105798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayapiriya, U.S.; Goel, S. Influence of cellulose separators in coin-sized 3D printed paper-based microbial fuel cells. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2021, 47, 101535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Hou, Y.; Yu, Z.; Tu, L.; Qin, S.; Lan, D.; Chen, S.; Sun, J.; Wang, S. B-doped graphene quantum dots implanted into bimetallic organic framework as a highly active and robust cathodic catalyst in the microbial fuel cell. Chemosphere 2022, 286, 131908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kano, K.; Shirai, O.; Kitazumi, Y.; Sakai, K.; Xia, H.-Q. Applications to Biofuel Cells and Bioreactors. In Enzymatic Bioelectrocatalysis; Kano, K., Shirai, O., Kitazumi, Y., Sakai, K., Xia, H.-Q., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2021; pp. 115–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Kim, J.; Acharya, S.; Kim, W. Review on the operation of wearable sensors through body heat harvesting based on thermoelectric devices. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2021, 118, 200501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Cai, K.; Gao, M.; Du, Y.; Shen, S. Recent advances in flexible thermoelectric films and devices. Nano Energy 2021, 89, 106309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soleimani, Z.; Zoras, S.; Ceranic, B.; Cui, Y.; Shahzad, S. A comprehensive review on the output voltage/power of wearable thermoelectric generators concerning their geometry and thermoelectric materials. Nano Energy 2021, 89, 106325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abedlhafd, M.; Izman, S.; Noor, A.; Basheer, U.; Rajoo, S. A review of thermoelectric p-type Ca3Co4O9 nanostructured ceramics for exhaust energy recovery. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Symposium on Engine Boosting and Energy Recovery, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 11–13 September 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Surmenev, R.A.; Chernozem, R.V.; Pariy, I.O.; Surmeneva, M.A. A review on piezo- and pyroelectric responses of flexible nano- and micropatterned polymer surfaces for biomedical sensing and energy harvesting applications. Nano Energy 2021, 79, 105442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishore, R.; Priya, S. A Review on Low-Grade Thermal Energy Harvesting: Materials, Methods and Devices. Materials 2018, 11, 1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasan, M.N.; Wahid, H.; Nayan, N.; Mohamed Ali, M.S. Inorganic thermoelectric materials: A review. Int. J. Energy Res. 2020, 44, 6170–6222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caballero-Calero, O.; Ares, J.; Martín-González, M. Environmentally Friendly Thermoelectric Materials: High Performance from Inorganic Components with Low Toxicity and Abundance in the Earth. Adv. Sustain. Syst. 2021, 5, 2100095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Koh, C.S.L.; Lee, Y.H.; Zhang, Y.; Phan-Quang, G.C.; Zhu, C.; Liu, Z.; Chen, Z.; Sim, H.Y.F.; Lay, C.L.; et al. A wearable solar-thermal-pyroelectric harvester: Achieving high power output using modified rGO-PEI and polarized PVDF. Nano Energy 2020, 73, 104723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klochko, N.P.; Barbash, V.A.; Petrushenko, S.I.; Kopach, V.R.; Klepikova, K.S.; Zhadan, D.O.; Yashchenko, O.V.; Dukarov, S.V.; Sukhov, V.M.; Khrypunova, A.L. Thermoelectric textile devices with thin films of nanocellulose and copper iodide. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2021, 32, 23246–23265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, C.; Wang, Z.; Yang, S.; Cui, X.; Li, X.; Yin, Y.; Zhang, M.; Wang, T.; Sang, S.; Zhang, W.; et al. Wearable Electronics Based on the Gel Thermogalvanic Electrolyte for Self-Powered Human Health Monitoring. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 37316–37322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rösch, A.G.; Gall, A.; Aslan, S.; Hecht, M.; Franke, L.; Mallick, M.M.; Penth, L.; Bahro, D.; Friderich, D.; Lemmer, U. Fully printed origami thermoelectric generators for energy-harvesting. Npj Flex. Electron. 2021, 5, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, W.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, D.; Aili, A.; Zhang, S.; Shi, C.; Zhang, J.; Geng, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, L.; et al. High-performance wearable thermoelectric generator with self-healing, recycling, and Lego-like reconfiguring capabilities. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabe0586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, X.; Wei, S.; Lv, H.; Zhou, J.; Peng, P.; Wang, H.; Chen, G. A Wavy-Structured Highly Stretchable Thermoelectric Generator with Stable Energy Output and Self-Rescuing Capability. CCS Chem. 2021, 3, 2404–2414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.X.; Wang, B.L.; Hou, S.H.; Zheng, L. Degeneration of power output of a flexible and wearable thermoelectric module under bending fatigue. Mech. Mater. 2021, 161, 104027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahanty, B.; Ghosh, S.K.; Maity, K.; Roy, K.; Sarkar, S.; Mandal, D. All-fiber pyro- and piezo-electric nanogenerator for IoT based self-powered health-care monitoring. Mater. Adv. 2021, 2, 4370–4379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afroz, A.S.; Romano, D.; Inglese, F.; Stefanini, C. Towards Bio-Hybrid Energy Harvesting in the Real-World: Pushing the Boundaries of Technologies and Strategies Using Bio-Electrochemical and Bio-Mechanical Processes. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Bo, L.; Li, Z. Recent progress in human body energy harvesting for smart bioelectronic system. Fundam. Res. 2021, 1, 364–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Long, Y.; Yang, F.; Wang, X. Respiration driven triboelectric nanogenerators for biomedical applications. EcoMat 2020, 2, e12045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourshaban, E.; Karkhanis, M.U.; Deshpande, A.; Banerjee, A.; Ghosh, C.; Kim, H.; Mastrangelo, C.H. A Magnetically-Coupled Micromachined Electrostatic Energy Harvester Driven by Eye Blinking Motion. In Proceedings of the 2021 21st International Conference on Solid-State Sensors, Actuators and Microsystems (Transducers), Orlando, FL, USA, 20–24 June 2021; pp. 960–963. [Google Scholar]
- Pu, X.; An, S.; Tang, Q.; Guo, H.; Hu, C. Wearable triboelectric sensors for biomedical monitoring and human-machine interface. iScience 2021, 24, 102027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz, L.L.; Lin, V.; Fitzgerald, L.; Zhu, J.; Borish, L.; Quinn, D.; Lach, J. Piezoelectric-Based Respiratory Monitoring: Towards Self-Powered Implantables for the Airways. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 17th International Conference on Wearable and Implantable Body Sensor Networks (BSN), Athens, Greece, 27–30 July 2021; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Khalid, S.; Raouf, I.; Khan, A.; Kim, N.; Kim, H.S. A Review of Human-Powered Energy Harvesting for Smart Electronics: Recent Progress and Challenges. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf.-Green Technol. 2019, 6, 821–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyaz, M.İ. An acoustic blood pressure sensing scheme using time of flight and shear wave elastography techniques. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2021, 330, 112865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yang, Y.; Li, M.; Chen, E.; Mu, W.; Fisher, R.; Yin, R. Wearable Actuators: An Overview. Textiles 2021, 1, 283–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahapatra, S.D.; Mohapatra, P.C.; Aria, A.I.; Christie, G.; Mishra, Y.K.; Hofmann, S.; Thakur, V.K. Piezoelectric Materials for Energy Harvesting and Sensing Applications: Roadmap for Future Smart Materials. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2100864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veronica, A.; Hsing, I.m. An Insight into Tunable Innate Piezoelectricity of Silk for Green Bioelectronics. ChemPhysChem 2021, 22, 2266–2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagaraj, M.J.; Shantha, V.; Nishanth, N.; Parthsarathy, V. Study and Optimization of Piezoelectric Materials for MEMS Biochemical Sensor Applications. In Advances in Renewable Energy and Electric Vehicles; Sanjeevikumar, P., Nagesh, p., Suryanarayana, K., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2022; Volume 767, pp. 419–425. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.-H.; Peng, Y.-H.; Tang, L.-K.; Yu, H.-Q. A multi-chamber piezoelectric pump based on pumping unit with double circular piezoelectric unimorph actuators. Smart Mater. Struct. 2021, 30, 095023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Z.; Hu, H.; Wu, Z.; Xie, S.; Chen, G.; Zhang, S.; Lou, L.; Liu, H. An Ultrasonic Proximity Sensing Skin for Robot Safety Control by Using Piezoelectric Micromachined Ultrasonic Transducers (PMUTs). IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 22, 17351–17361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayakanth, T.; Liptrot, D.J.; Gazit, E.; Boomishankar, R.; Bowen, C.R. Recent Advances in Organic and Organic–Inorganic Hybrid Materials for Piezoelectric Mechanical Energy Harvesting. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2109492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lay, R.; Deijs, G.S.; Malmström, J. The intrinsic piezoelectric properties of materials—A review with a focus on biological materials. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 3657–3673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sultana, A.; Alam, M.M.; Middya, T.R.; Mandal, D. A pyroelectric generator as a self-powered temperature sensor for sustainable thermal energy harvesting from waste heat and human body heat. Appl. Energy 2018, 221, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koroglu, L.; Ayas, E.; Ay, N. 3D Printing of Polyvinylidene Fluoride Based Piezoelectric Nanocomposites: An Overview. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2021, 306, 2100277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montero, K.L.; Laurila, M.M.; Mäntysalo, M. Fully Printed Unobtrusive and Skin-conformable Piezoelectric Energy Harvester. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Flexible and Printable Sensors and Systems (FLEPS), Manchester, UK, 20–23 June 2021; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Yu, X.; Zhao, W.; Qu, D. A piezoelectric vibration energy harvester based on the reverse-rhombus double-bridge force amplification frame. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2021, 54, 365501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Mahale, B.; Muzata, T.S.; Ranjan, R. Energy harvesting with flexible piezocomposite fabricated from a biodegradable polymer. Int. J. Energy Res. 2021, 45, 19395–19404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Guo, H.; Ribera, J.; Wu, C.; Tu, K.; Binelli, M.; Panzarasa, G.; Schwarze, F.W.M.R.; Wang, Z.L.; Burgert, I. Sustainable and Biodegradable Wood Sponge Piezoelectric Nanogenerator for Sensing and Energy Harvesting Applications. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 14665–14674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, L.; Liu, J.; Cui, N.; Xu, Q.; Du, T.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Z.; Long, C.; Qin, Y. Enhancing the current density of a piezoelectric nanogenerator using a three-dimensional intercalation electrode. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Jin, C.; Cabe, A.; Escobedo, D.; Hao, N.; Trase, I.; Closson, A.B.; Dong, L.; Nie, Y.; Elliott, J.; et al. Flexible Energy Harvester on a Pacemaker Lead Using Multibeam Piezoelectric Composite Thin Films. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 34170–34179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thainiramit, P.; Yingyong, P.; Isarakorn, D. Impact-Driven Energy Harvesting: Piezoelectric Versus Triboelectric Energy Harvesters. Sensors 2020, 20, 5828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Wang, N.; Hu, C.; Wang, Z.L.; Yang, Y. Soft triboelectric nanogenerators for mechanical energy scavenging and self-powered sensors. Nano Energy 2021, 84, 105919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Raveendran, V.; Chen, J. Wearable triboelectric nanogenerators for biomechanical energy harvesting. Nano Energy 2020, 77, 105303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pharino, U.; Sinsanong, Y.; Pongampai, S.; Charoonsuk, T.; Pakawanit, P.; Sriphan, S.; Vittayakorn, N.; Vittayakorn, W. Influence of pore morphologies on the mechanical and tribo-electrical performance of polydimethylsiloxane sponge fabricated via commercial seasoning templates. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2021, 189, 109720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.; Hassan, I.; Helal, A.S.; Sencadas, V.; Radhi, A.; Jeong, C.K.; El-Kady, M.F. Triboelectric Nanogenerator versus Piezoelectric Generator at Low Frequency (<4 Hz): A Quantitative Comparison. iScience 2020, 23, 101286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Olin, H. Material choices for triboelectric nanogenerators: A critical review. EcoMat 2020, 2, e12062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.W.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, J.K.; Jeong, U. Material aspects of triboelectric energy generation and sensors. NPG Asia Mater. 2020, 12, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Jie, Y.; Zhu, J.; Zhu, Z.; Chen, H.; Lu, Q.; Zeng, Y.; Cao, X.; Wang, N.; Wang, Z. Paper triboelectric nanogenerator designed for continuous reuse and quick construction. Nano Res. 2021, 15, 1109–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Guan, Q.; Liu, Y.; Sun, X.; Wen, Z. Abrasion and Fracture Self-Healable Triboelectric Nanogenerator with Ultrahigh Stretchability and Long-Term Durability. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2105380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Gao, Z.; Yao, K.; Hou, S.; Liu, Y.; Li, D.; He, J.; Huang, X.; Song, E.; Yu, J.; et al. Thin, soft, skin-integrated foam-based triboelectric nanogenerators for tactile sensing and energy harvesting. Mater. Today Energy 2021, 20, 100657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.; Xu, B.; Huang, J.; Jing, T.; Gao, Y. Fiber-shaped stretchable triboelectric nanogenerator with a novel synergistic structure of opposite Poisson’s ratios. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 427, 131698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, W.; Liu, X.; Li, Y.; Xu, X.; Jiang, J.; Lu, S.; Bao, D.; Wen, Z.; Sun, X. Transparent, stretchable, temperature-stable and self-healing ionogel-based triboelectric nanogenerator for biomechanical energy collection. Nano Res. 2021, 15, 2060–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, F.; Yi, J.; Shen, S.; Cheng, R.; Ning, C.; Ma, L.; Peng, X.; Deng, W.; Dong, K.; Wang, Z.L. Self-Powered Smart Arm Training Band Sensor Based on Extremely Stretchable Hydrogel Conductors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 44868–44877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Chen, L.; He, J.; Hou, X.; Qiao, X.; Xiong, J.; Chou, X. Flexible and Extendable Honeycomb-Shaped Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Effective Human Motion Energy Harvesting and Biomechanical Sensing. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2021, 7, 2100702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, H.; Park, H.-m.; Kim, M.-K.; Kim, B.; Myoung, H.S.; Kim, T.Y.; Yoon, H.-J.; Kwak, S.S.; Kim, J.; Hwang, T.H.; et al. Self-rechargeable cardiac pacemaker system with triboelectric nanogenerators. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iqbal, M.; Nauman, M.M.; Khan, F.U.; Abas, P.E.; Cheok, Q.; Iqbal, A.; Aissa, B. Multimodal Hybrid Piezoelectric-Electromagnetic Insole Energy Harvester Using PVDF Generators. Electronics 2020, 9, 635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Luo, J.; Xie, S.; Xin, L.; Guo, H.; Pu, H.; Yin, P.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, D.; Peng, Y.; et al. Instantaneous peak 2.1 W-level hybrid energy harvesting from human motions for self-charging battery-powered electronics. Nano Energy 2021, 81, 105629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; He, J.; Peng, P.; Chen, L.; Cao, K. Reliability of Microelectromechanical Systems Devices. In Reliability and Maintenance: An Overview of Cases; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, D.; Ouyang, H.; Shi, B.; Zou, Y.; Tan, P.; Qu, X.; Chao, S.; Xi, Y.; Zhao, C.; Fan, Y.; et al. A wearable noncontact free-rotating hybrid nanogenerator for self-powered electronics. InfoMat 2020, 2, 1191–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, Z.; Zheng, G.; Zhong, W.; Jiang, L.; Yang, Y.; Jiang, L.; Chen, Y.; Wong, C.-P. A magnetized microneedle-array based flexible triboelectric-electromagnetic hybrid generator for human motion monitoring. Nano Energy 2020, 69, 104415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.-C.; Lu, H.-W.; Wu, H.-M.; Zhang, D.; Yang, J.; Ma, J.; Shamsi, M.; Vallem, V.; Dickey, M.D. Elastic Multifunctional Liquid–Metal Fibers for Harvesting Mechanical and Electromagnetic Energy and as Self-Powered Sensors. Adv. Energy Mater. 2021, 11, 2100411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, T.-H.; Manakasettharn, S.; Taylor, J.A.; Krupenkin, T. Bubbler: A Novel Ultra-High Power Density Energy Harvesting Method Based on Reverse Electrowetting. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Cao, Z.; Ding, R.; Wang, S.; Chu, Y.; Ye, X. An electrostatic-electromagnetic hybrid generator with largely enhanced energy conversion efficiency. Nano Energy 2021, 89, 106425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boisseau, S.; Despesse, G.; Seddik, B. Electrostatic Conversion for Vibration Energy Harvesting. In Small-Scale Energy Harvesting; BoD–Books: Norderstedt, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourshaban, E.; Karkhanis, M.U.; Deshpande, A.; Banerjee, A.; Ghosh, C.; Kim, H.; Mastrangelo, C.H. Flexible Electrostatic Energy Harvester Driven by Cyclic Eye Tear Wetting and Dewetting. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Flexible and Printable Sensors and Systems (FLEPS), Manchester, UK, 20–23 June 2021; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Erturun, U.; Eisape, A.A.; Kang, S.H.; West, J.E. Energy harvester using piezoelectric nanogenerator and electrostatic generator. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2021, 118, 063902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Nie, D.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; He, R.; Zhao, Z.; Wu, J.; Ji, B.; Xie, J.; Tao, K. Investigation of electrostatic-piezoelectric hybrid vibrational power generators with different frequency broadening schemes. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 16th International Conference on Nano/Micro Engineered and Molecular Systems (NEMS), Xiamen, China, 25–29 April 2021; pp. 528–532. [Google Scholar]
- Boroujeni, F.G.; Raissi, B.; Jafarabadi-Ashtiani, S.; Riahifar, R.; Sahba-Yaghmaee, M. Droplet-based energy harvester considering electrowetting phenomena. Eng. Res. Express 2020, 2, 045028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Mendel, N.; van der Ham, S.; Shui, L.; Zhou, G.; Mugele, F. Charge Trapping-Based Electricity Generator (CTEG): An Ultrarobust and High Efficiency Nanogenerator for Energy Harvesting from Water Droplets. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 2001699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, P.R.; Tasneem, N.T.; Reid, R.C.; Mahbub, I. Electrode and electrolyte configurations for low frequency motion energy harvesting based on reverse electrowetting. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 5030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srinivasan, V.; Pamula, V.K.; Fair, R.B. An integrated digital microfluidic lab-on-a-chip for clinical diagnostics on human physiological fluids. Lab. A Chip 2004, 4, 310–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, J.-Y.; Garrell, R.L. Preventing Biomolecular Adsorption in Electrowetting-Based Biofluidic Chips. Anal. Chem. 2003, 75, 5097–5102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tasneem, N.T.; Biswas, D.K.; Mahbub, I.; Adhikari, P.R.; Reid, R. Self-Powered Motion Tracking Sensor Integrated with Low-Power CMOS Circuitry. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), Daegu, Korea, 22–28 May 2021; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Shiu, B.C.; Li, T.-T.; Liu, X.; Ren, H.-T.; Wang, Y.; Lou, C.-W.; Lin, J.-H. Photo-thermoelectric nanofiber film based on the synergy of conjugated polymer and light traps for the solar-energy harvesting of textile solar panel. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2021, 232, 111353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Kaur, R.; Singh, D. Energy harvesting in wireless sensor networks: A taxonomic survey. Int. J. Energy Res. 2020, 45, 118–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Song, W.; Ge, J.; Tang, B.; Zhang, X.; Wu, T.; Ge, Z. Recent progress of organic photovoltaics for indoor energy harvesting. Nano Energy 2021, 82, 105770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Shiu, B.C.; Li, T.-T.; Liu, X.; Ren, H.-T.; Wang, Y.; Lou, C.-W.; Lin, J.-H. Synergistic work of photo-thermoelectric and hydroelectric effects of hierarchical structure photo-thermoelectric textile for solar energy harvesting and solar steam generation simultaneously. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 426, 131923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Xiang, S.; Tao, H.; Xue, J.; Tao, C.; Li, C.; Zhang, N.; Fan, X. Embroidering a Light and Foldable Photovoltaic Gauze Kerchiefs. Energy Technol. 2021, 9, 2100285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, X.; Yin, J.; Xu, Y.; Fei, W.; Xue, M.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, J.; Guo, W. Emerging hydrovoltaic technology. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2018, 13, 1109–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Zhou, J.; Fang, S.; Guo, W. Hydrovoltaic Energy on the Way. Joule 2020, 4, 1852–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Fang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Yin, J.; Li, L.; Wang, X.; Guo, W. Self-sustained electricity generator driven by the compatible integration of ambient moisture adsorption and evaporation. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganesh, K.V.S.S.; Ruhan Bevi, A. Low-Cost Pulse Oximeter & Heart Rate Measurement for COVID Diagnosis. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 1964, 62035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michard, F.; Shelley, K.; L’Her, E. COVID-19: Pulse oximeters in the spotlight. J. Clin. Monit. Comput. 2020, 35, 11–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhtaruzzaman, A.K.M.; Kamal, M.M.; Parveen, M.; Rabbi, M.; Dhali, R.; Islam, M.S.; Bhowmick, D.K. Remote monitoring of COVID–19 patients using home pulse oximetry and virtual platform: An observational study. Anaesth. Pain Intensive Care 2022, 26, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.-Y. Spectrophotometry and Optical Biosensor. In Introduction to Biosensors; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 121–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsamnah, F.; Bilgaiyan, A.; Affiq, M.; Shim, C.H.; Ishidai, H.; Hattori, R. Comparative Design Study for Power Reduction in Organic Optoelectronic Pulse Meter Sensor. Biosensors 2019, 9, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kossaify, A. Sensing and Detection Functions in Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillators: The Good, the Bad and the Ugly. Acta Cardiol. Sin. 2020, 36, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulpuru, S.K.; Madhavan, M.; McLeod, C.J.; Cha, Y.-M.; Friedman, P.A. Cardiac Pacemakers: Function, Troubleshooting, and Management: Part 1 of a 2-Part Series. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2017, 69, 189–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moerke, C.; Wolff, A.; Ince, H.; Ortak, J.; Öner, A. New strategies for energy supply of cardiac implantable devices. Herzschrittmachertherapie Elektrophysiologie 2022, 33, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Han, X.; Xu, Z.; Closson, A.; Liu, Y.; Wen, C.; Liu, X.; Escobar, G.; Oglesby, M.; Feldman, M.; et al. Flexible Porous Piezoelectric Cantilever on a Pacemaker Lead for Compact Energy Harvesting. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2018, 4, 1800148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammannaya, G.K.K. Implantable cardioverter defibrillators-the past, present and future. Arch. Med. Sci. Atheroscler. Dis. 2020, 5, e163–e170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Closson, A.; Jin, C.; Nie, Y.; Cabe, A.; Escobedo, D.; Huang, S.; Trase, I.; Xu, Z.; Chen, Z.; et al. Multifunctional Pacemaker Lead for Cardiac Energy Harvesting and Pressure Sensing. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2020, 9, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, D.; Barbosa, A.I.; Rebelo, R.; Kwon, I.K.; Reis, R.L.; Correlo, V.M. Skin-Integrated Wearable Systems and Implantable Biosensors: A Comprehensive Review. Biosensors 2020, 10, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zan, G.; Wu, T.; Zhu, F.; He, P.; Cheng, Y.; Chai, S.; Wang, Y.; Huang, X.; Zhang, W.; Wan, Y.; et al. A biomimetic conductive super-foldable material. Matter 2021, 4, 3232–3247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zan, G.; Wu, T.; Zhang, Z.; Li, J.; Zhou, J.; Zhu, F.; Chen, H.; Wen, M.; Yang, X.; Peng, X.; et al. Bioinspired Nanocomposites with Self-Adaptive Stress Dispersion for Super-Foldable Electrodes. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, 2103714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zan, G.; Wu, T.; Dong, W.; Zhou, J.; Tu, T.; Xu, R.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wu, Q. Two-Level Biomimetic Designs Enable Intelligent Stress Dispersion for Super-Foldable C/NiS Nanofiber Free-Standing Electrode. Adv. Fiber Mater. 2022, 4, 1177–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnaud, O. The technological challenges of microelectronics for the next generations of connected sensors. Int. J. Plasma Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 14, e01002. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, A.; Sharma, A.; Ahmed, A.; Sundramoorthy, A.K.; Furukawa, H.; Arya, S.; Khosla, A. Recent Advances in Electrochemical Biosensors: Applications, Challenges, and Future Scope. Biosensors 2021, 11, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

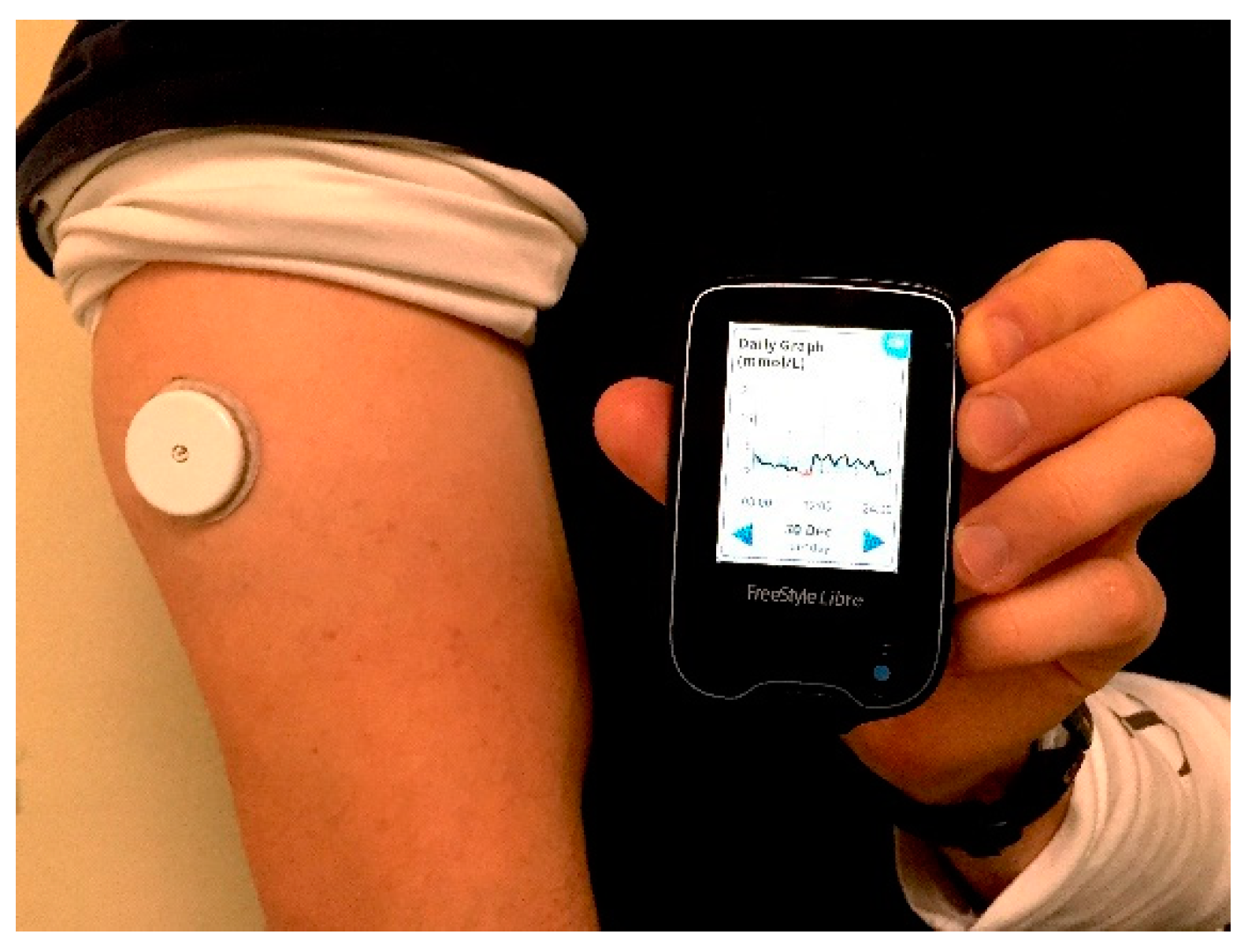


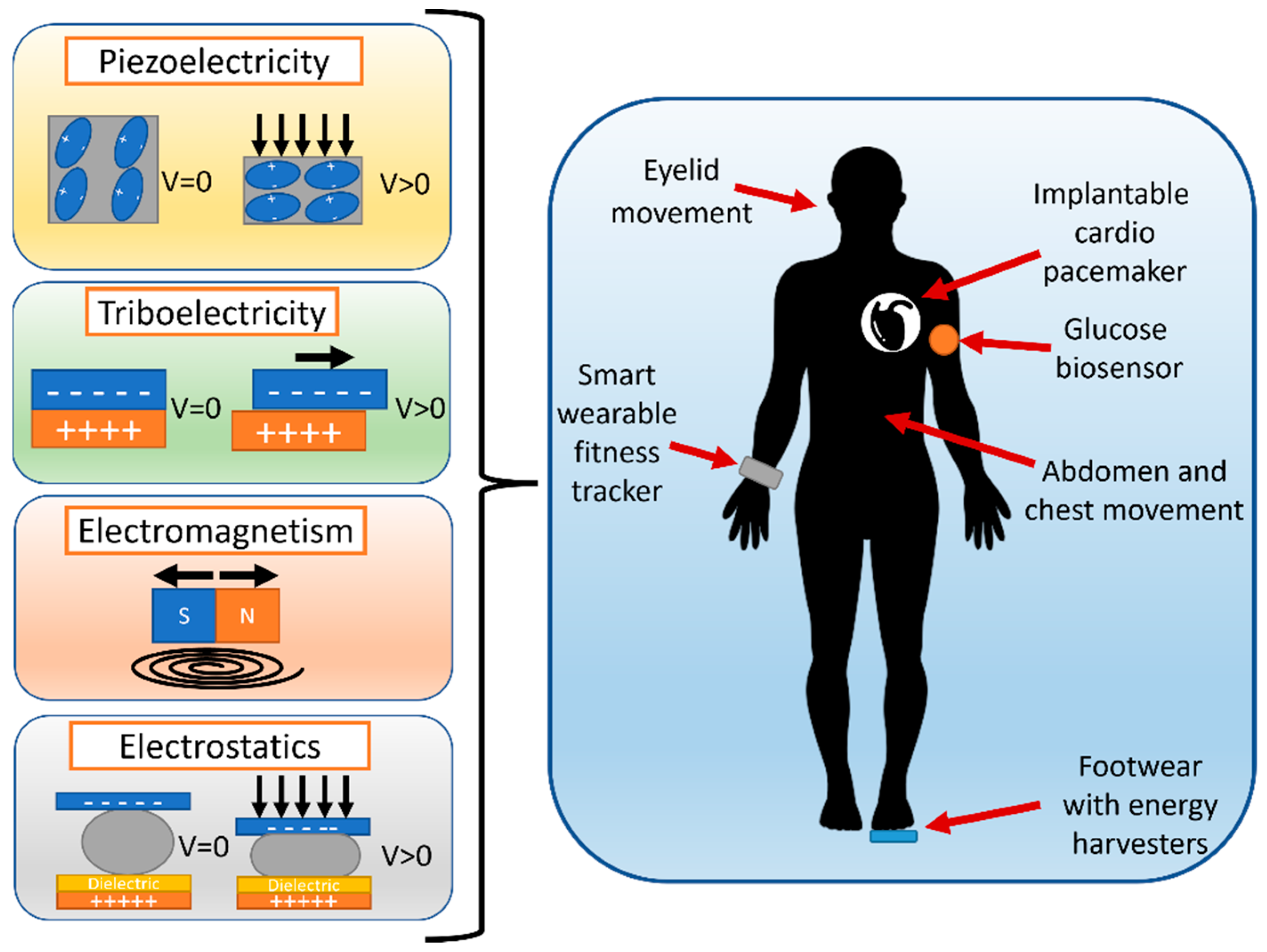

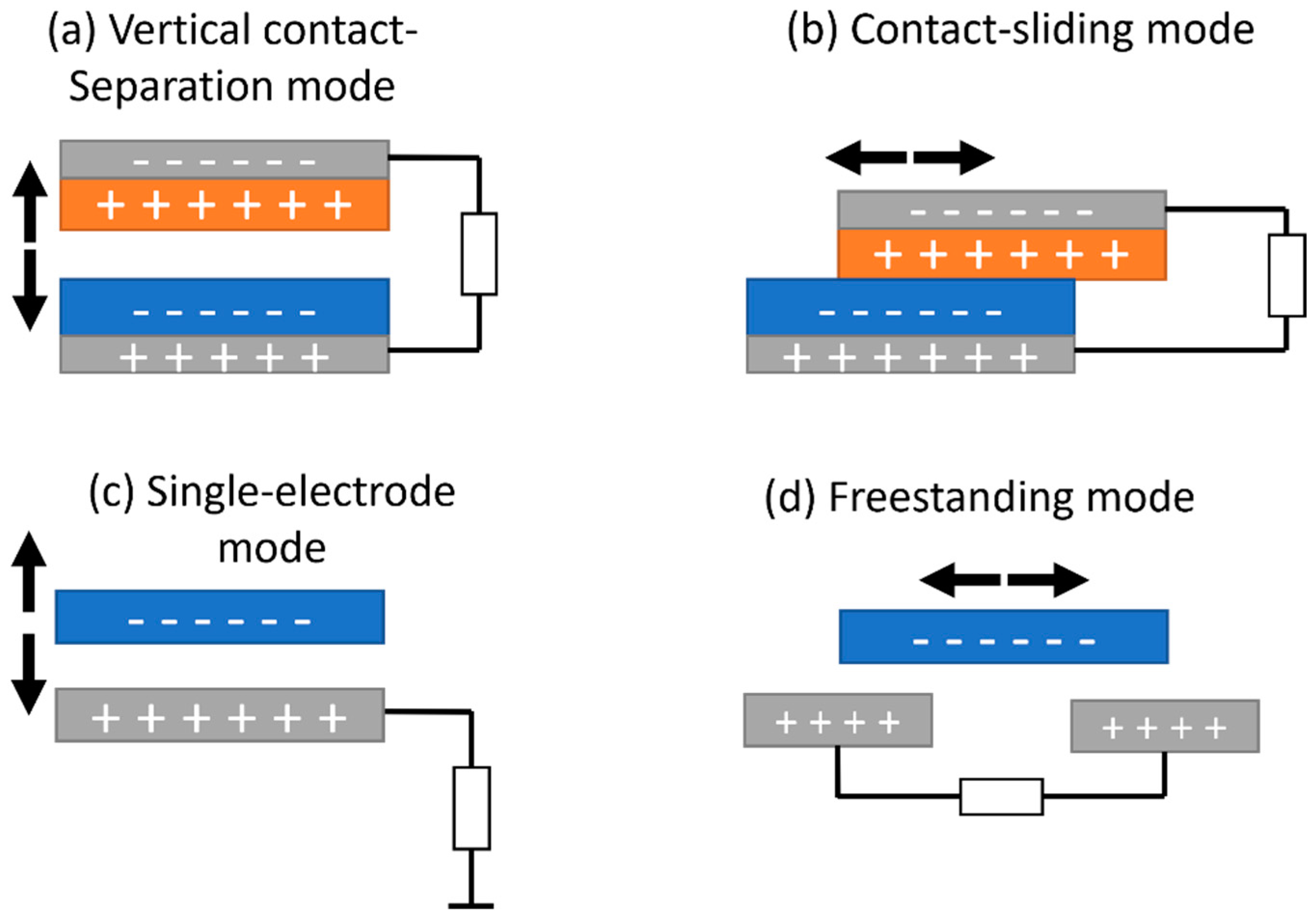

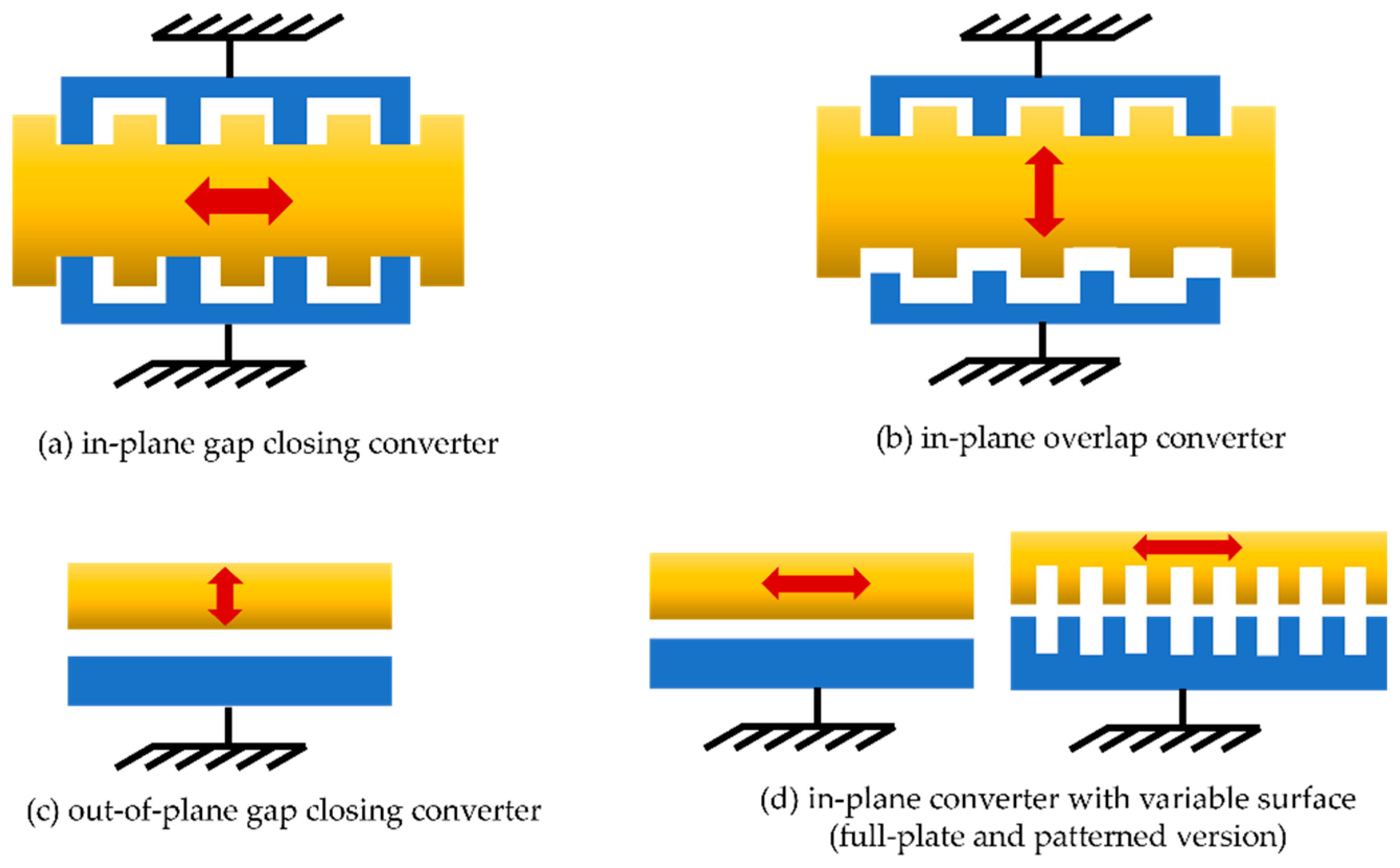


| NG Type | Authors | Features | Voltage, Load, Frequency | Size | Power Output |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| enzymatic BFC | Zhang et al. [27] | Integrated into a diaper | 300 mV (OC) | 6 × 5 cm2 | 220 μW·cm−2 |
| enzymatic BFC | Zhang et al. [28] | artificial enzyme | 400 mV (OC) | n/a | 149.2 μW·cm−2 |
| microbial BFC | Jayapiriya and Goel [29] | 3D printed, paper-based | 480 mV (OC) | Coin size (~2 × 2 cm2) | 11.8 µW·cm−2 |
| enzymatic BFC | Yan et al. [30] | high-power, nano enhancements of materials | ~0.8 V 1000 Ω | ~0.3 nm2 | 703.55 mW·m−2 |
| thermoelectric NG | Klochko et al. [41] | Biodegradable materials | 5 V (OC) | 3 × 2 cm2 | 44 µW·cm−2 |
| thermoelectric NG | Rösch et al. [43] | 3D printed origami-like shape | 534 mV (OC) | 190 cm2 | 47.8 µW·cm−2 |
| thermoelectric NG | Ren et al. [44] | self-healing recyclable material | 5 V | 6 × 5 cm2 | 83 nW·cm−2 |
| thermoelectric NG | Liu et al. [45] | self-healing | 4.15 mV 600 Ω | ~4 × 2 cm2 | 172.9 nW |
| pyro- and PENG | Mahanty et al. [47] | hybrid | 35 V at 3.4 M Ω | 8 × 7 cm2 | 34 μW·cm−2 |
| Solar, thermal and pyroelectric NG | Li et al. [40] | hybrid | 93.1 (OC) | 3 × 9 cm2 | 21.3 mW·m−2 |
| PENG | Montero et al. [66] | 3D printed | 1.1 V 60 Hz 100 MΩ | 18 × 18 cm2 | 0.5 µW·cm−3 |
| PENG | Zhang et al. [67] | integrated into a backpack | ~1.7 V 8 Hz 0.7 MΩ | 3.5 × 3.5 × 9 mm3 | 4.13 μW |
| PENG | Kumar et al. [68] | nano enhancements of materials | 16.67 V (OC) 5 Hz | 12 × 8 mm2 | 2556 μW·cm−3 |
| PENG | Sun et al. [69] | made from wood sponge | 0.63 V ~1 Hz 80 MΩ | 15 × 15 × 14 mm3 | 0.6 nW·cm−2 |
| PENG | Xu et al. [71] | multibeam structure implantable | 0.3 V 1 Hz | n/a | 6.5 μJ |
| TENG | Zhang et al. [79] | paper-based | ~95 V 2 Hz 130 MΩ | 4 × 4 cm2 | 171 mW·m−2 |
| TENG | Jiang et al. [80] | self-healing | 75 V (calc) 2 Hz 5 MΩ | 2 × 2 cm2 | 450 mW·m−2 |
| TENG | Wu et al. [81] | optimized surface porosity | 78.7 V (OC) | 8 × 8 × 0.5 mm3 | 33.75 W·m−2 |
| TENG | Guan et al. [82] | different Poisson-ratio materials | ~25 V 10 MΩ | 20 cm × ø 2 mm | 52.36 mW·m−2 |
| TENG | Liao et al. [83] | ion-gel self-healing | 189 V (OC) 1.5 Hz | 3 × 3 cm2 | 2.17 W·m−2 |
| TENG | Yang et al. [85] | 3D printed honey-comb structure | 1500 V (OC) 3 Hz | 68 × 39 mm2 × 5 | 10.79 W·m−2 |
| TENG | Ryu et al. [86] | implantable stacked TENG structure | 10 MΩ | n/a | 4.9 μW·cm−3 |
| EMG and TENG | Li et al. [91] | hybrid Microscale needles | 10 V (OC) 1 Hz (TENG) | 24 × 24 × 3.2 mm3 | 16.19 μW·m−2 |
| EMG and PENG | Iqbal et al. [87] | hybrid | 7.01 V (OC) | 3.9 × 3.9 × 2.9 cm3 | 4.05 µW·cm−3 |
| EMG and TENG | Lai et al. [92] | hybrid uses ambient magnetic field | 120 V/m 100 MΩ | 5 cm (contact length) | 360 µW·m−1 and 8 µW·m−1 |
| EMG and PENG | Li et al. [88] | hybrid MEMS | 18 V (OC) PENG 22 V (OC) EMG | 4 × 2.5 × 5.8 | 36.21 mW·cm−3 |
| ESG and EMG | Wu et al. [94] | hybrid | ~40 V (OC) EMG ~0.1 V (OC) ESG 50 rpm | ø 50 mm | 2.5 W·m−3 and 107.8 W·m−3 |
| ESG | Pourshaban et al. [96] | contact lens | 450 mV 100 kΩ | 2 × 10 mm2 | 0.265 µW |
| ESG and PENG | Erturun et al. [97] | hybrid | 4.2 V 1 MΩ—PENG 17 V 10 MΩ—ESG 20 Hz | ø 3 × 0.65 cm | 8.8 μW·cm−3 |
| REWOD NG | Adhikari et al. [101] | no bias voltage | 0.103 V 0.15 MΩ 3 Hz | ø 50.5 mm | 53.3 nW·cm−2 |
| REWOD NG | Tasneem et al. [104] | conditioning circuit | 943 mV pp 1.6 MΩ 10 Hz | 4 mm gap between electrodes | 58 nW·cm−2 |
| REWOD NG | Hsu et al. [93] | self-oscillation | bias voltage used 0.877 MΩ | 40 × 40 mm2 (628 mm2) | 100 W·m−2 |
| photo-thermoelectric NG | Zhang et al. [105] | hybrid | 0.56 mV 1.32 kΩ | 4 × 0.3 cm2 | 0.24 nW |
| photo-, thermo-, hydroelectric NG | Zhang et al. [108] | hybrid hydroelectricity | 12.5 mV 15.93 Ω | 1.5 × 1.5 cm2 | 2.45 μW |
| photovoltaic NG | Yu et al. [109] | photovoltaic textile | 0.79 V | 4.5 mm pitch | ~134 μW |
| Energy Harvester Type | Advantages | Disadvantages | Voltage Output | Current Density | Power Density | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BFCs | Microbial | No enzymes Long life span (5 years) DC output voltage | Need special mediators Low power density | 100–500 mV | 10–100 μA×cm−2 | 1–10 μW×cm−2 |
| Enzymatic | Effective use of body liquids (sweat, tears, etc) as fuel DC output voltage | Short life span | 0.1–1 V | 100–500 μA×cm−2 | 10–100 μW×cm−2 | |
| Thermal | Thermoelectric | DC output voltage | Low voltage | 0.1–1 V | 0.1–10 μA×cm−2 | 0.1–10 µW×cm−2 |
| Pyroelectric | Are a sub-class of piezoelectric materials | Require temperature fluctuations | 0.1–10 V | 0.01–10 μA×cm−2 | 0.1–1 µW×cm−2 | |
| Piezoelectric | Availability “of-the-shelf” Can possess pyroelectric properties | Frequency dependent output | 0.1–10 V | 0.01–10 μA×cm−2 | 1–100 µW×cm−2 | |
| Triboelectric | High output High elasticity Low cost | Overvoltage Small current | 10–1000 V | 1–10 μA×cm−2 | 1–100 mW×m−2 | |
| Electromagnetic | Hybridization with TENGs and ESGs Low impedance | MEMS (low reliability) Rigid, non-flexible nature | 0.1–10 V | 1–10 μA×cm−2 | 10 µW×cm−2 (mostly used as a hybrid with TENGs) | |
| Electrostatic | Simple structure | Practical applications involve MEMS | 0.1–1 V | 1–10 μA×cm−2 | 0.1–10 µW×cm−2 | |
| REWOD | High output voltage at high frequencies | Needs bias voltage for high output Frequency dependent | 10–100 mV | 10–100 nA×cm−2 | 0.01–0.1 µW×cm−2 | |
| Photovoltaic | DC current | Needs hybridization for constant energy | 1–100 mV | 1–100 μA×cm−2 | 0.1–10 μW×cm−2 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sobianin, I.; Psoma, S.D.; Tourlidakis, A. Recent Advances in Energy Harvesting from the Human Body for Biomedical Applications. Energies 2022, 15, 7959. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15217959
Sobianin I, Psoma SD, Tourlidakis A. Recent Advances in Energy Harvesting from the Human Body for Biomedical Applications. Energies. 2022; 15(21):7959. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15217959
Chicago/Turabian StyleSobianin, Ihor, Sotiria D. Psoma, and Antonios Tourlidakis. 2022. "Recent Advances in Energy Harvesting from the Human Body for Biomedical Applications" Energies 15, no. 21: 7959. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15217959
APA StyleSobianin, I., Psoma, S. D., & Tourlidakis, A. (2022). Recent Advances in Energy Harvesting from the Human Body for Biomedical Applications. Energies, 15(21), 7959. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15217959







