The Impact of Soiling on PV Module Performance in Saudi Arabia
Abstract
1. Introduction
- The following are the primary contributions of this research study: it offers a critical review of the soiling impact on solar PV performance in arid and high solar irradiation regions such as Saudi Arabia for the first time.
- The results and recommendations concluded from this study are essential for enlightening the PV engineering community, investors, and the research community about how soiling may affect regions with significant solar potential, such as Saudi Arabia.
- It describes in detail various soiling mitigation techniques and highlights the benefits and drawbacks of each technique, as well as which one is best suited for maintaining high-performance solar PV projects in such a hot and arid country. Current solar PV projects in Saudi Arabia that have recently been implemented have been considered and discussed.
- This study will encourage researchers to focus more on the need for energy diversification and to broaden research on the effect of dust on PV modules in developing countries like Saudi Arabia, which has a high potential for solar energy deployment but has got limited research on these topics to date.
2. Dust Formation Life Cycle on PV
3. Soiling Impact on Solar PV in Saudi Arabia
3.1. Soiling Generation Sources
3.2. Solar PV Performance under Soiling in Saudi Arabia
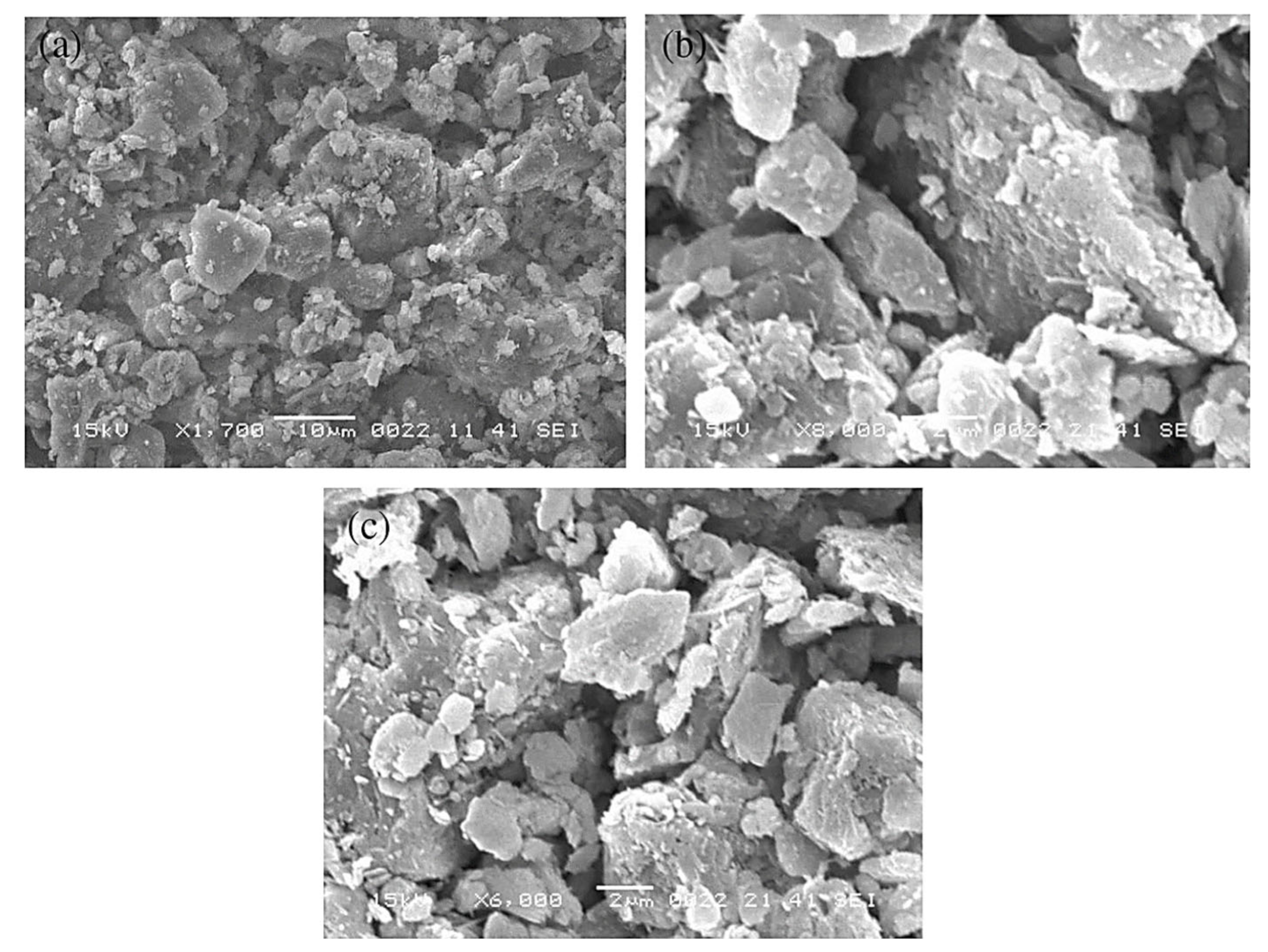
3.3. Dust Particles Size and Composition
4. Mitigation Strategies
4.1. Manual Cleaning
4.2. Natural Cleaning
4.3. Automated Cleaning
4.3.1. Water-Based Cleaning
4.3.2. Mechanized Cleaning
4.4. Automated Cleaning
4.4.1. Super-Hydrophobic Plane (SHOP)
4.4.2. Super Hydrophilic Plane (SHIP)
4.4.3. Electrodynamic Screen (EDS)
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
- Due to Saudi Arabia’s location in a dry, low-precipitation zone with vulnerability to dust storms, the investment in cleaning solutions is advised and worthwhile given the significant influence that soiling has on solar PV performance.
- Soiling will not prevent the widespread deployment of PV plants in Saudi Arabia and other arid regions if the proper cleaning methods are used.
- The recommended cleaning cycles of PV panels for the central region in Saudi Arabia and similar soiling environments are every month or less to avoid a substantial loss in PV performance. Other regions may experience different soiling exposure which may need different cleaning frequencies.
- In the event of a dust storm, it is recommended that the system be cleaned as soon as possible to avoid a significant decrease in PV performance.
- Regarding the fixed solar PV modules, the tilt angle has a strong influence on accumulated dust density. The high tilt angle has improved eliminating dust particles. Nevertheless, this might reduce the output power as a result of missing the optimal tilt angle. Therefore, PV systems designers have to adjust the tilt angle optimally aiming to minimize dust accumulation and attain the maximum amount of power.
- It is recommended that Saudi Arabia consider the solar tracking system because, compared to a fixed solar PV system, the solar tracker reduces dust deposition on PV panels and improves PV performance.
- The solar PV projects have shown a considerably low levelized cost of energy for the central region of Saudi Arabia. It makes use of bi-facial solar panels and is equipped with a tracking system and a robotic cleaning mechanism.
- Self-cleaning strategies, such as superhydrophobic and superhydrophilic planes, could help to further lower the frequency and cost of cleaning. They do, however, need water to clean the PV module adequately. Due to the low yearly precipitation in Saudi Arabia, this type of strategy may be inappropriate to consider.
- Using artificial intelligence and other techniques to forecast dust storms is a promising strategy that will aid plant operators in making plans for the best cleaning operations for solar PV modules.
- The selection of the appropriate cleaning and mitigation techniques should be aided by a deeper understanding of the dust properties and characteristics in the study area.
- The development of soiling prediction models is crucial for feasibility studies and future solar PV plant bidding initiatives.
- More research is needed to determine how environmental factors such as humidity, wind direction, and wind speed impact the efficiency of solar PV systems.
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- REN21. Renewables 2022, Global Status Report; REN21: Paris, France, 2022; ISBN 978-3-948393-04-5. [Google Scholar]
- IEA. Annual Solar PV Capacity Additions by Application Segment, 2015–2022; IEA: Paris, France, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Saudi Vision 2030 Vision, Energy & Sustainability. Available online: https://www.vision2030.gov.sa/thekingdom/explore/energy/ (accessed on 12 March 2022).
- IEA Saudi Arabia—Sudair Solar Plant Project. Available online: https://www.iea.org/policies/14162-saudi-arabia-sudair-solar-plant-project (accessed on 6 September 2022).
- ACWA ACWA Power Connects The First Renewable Energy Project in the Kingdom, Sakaka PV IPP, to the National Electricity Grid, Commencing Initial Production. Available online: https://www.acwapower.com/news/acwa-power-connects-the-first-renewable-energy-project-in-the-kingdom-sakaka-pv-ipp-to-the-national-electricity-grid-commencing-initial-production/ (accessed on 6 September 2022).
- LAYLA SOLAR PV IPP. Available online: https://acwapower.com/en/projects/layla-solar-pv-ipp/ (accessed on 6 September 2022).
- DMS Acwa Power—GIC—Al Babtain Contracting Company—National Renewable Energy Program (NREP)—Al Faisaliah. Available online: https://www.dmsprojects.net/saudi-arabia/projects/acwa-power-gic-al-babtain-contracting-company-national-renewable-energy-program-nrep-al-faisaliah-600-mw-solar-pv-plant/PRJ00025968 (accessed on 6 September 2022).
- Ministry of Energy Renewable Energy. Available online: https://www.moenergy.gov.sa/en/OurPrograms/RenewableEnergy/Pages/Initiatives.aspx (accessed on 2 September 2022).
- Rehman, S.; Aliyu, K.N.; Alhems, L.M.; Mohandes, M.A.; Himri, Y.; Allouhi, A.; Mahbub, M.A. A Comprehensive Global Review of Building Integrated Photovoltaic Systems. FME Trans. 2021, 49, 253–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.; Haq, I.U.; Ullah, F.U.M.; Khan, S.U.; Lee, M.Y. Cl-Net: Convlstm-Based Hybrid Architecture for Batteries’ State of Health and Power Consumption Forecasting. Mathematics 2021, 9, 3326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Garni, H.Z.; Awasthi, A. Solar PV Power Plants Site Selection: A Review. In Advances in Renewable Energies and Power Technologies; Yahyaoui, I., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 57–75. ISBN 978-0-12-812959-3. [Google Scholar]
- Al Garni, H.Z.; Awasthi, A. Solar PV Power Plant Site Selection Using a GIS-AHP Based Approach with Application in Saudi Arabia. Appl. Energy 2017, 206C, 1225–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Garni, H.Z.; Awasthi, A.; Wright, D. Optimal Orientation Angles for Maximizing Energy Yield for Solar PV in Saudi Arabia. Renew. Energy 2019, 133, 538–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Hasanuzzaman, M.; Rahim, N.A. Effects of Various Parameters on PV-Module Power and Efficiency. Energy Convers. Manag. 2015, 103, 348–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Garni, H.Z.; Awasthi, A.; Ramli, M.A.M. Optimal Design and Analysis of Grid-Connected Photovoltaic under Different Tracking Systems Using HOMER. Energy Convers. Manag. 2018, 155, 42–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honrubia-Escribano, A.; Ramirez, F.J.; Gómez-Lázaro, E.; Garcia-Villaverde, P.M.; Ruiz-Ortega, M.J.; Parra-Requena, G. Influence of Solar Technology in the Economic Performance of PV Power Plants in Europe. A Comprehensive Analysis. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 82, 488–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Azevedo Dias, C.L.; Branco, D.A.C.; Arouca, M.C.; Legey, L.F.L. Performance Estimation of Photovoltaic Technologies in Brazil. Renew. Energy 2017, 114, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othman, R.; Hatem, T.M. Assessment of PV Technologies Outdoor Performance and Commercial Software Estimation in Hot and Dry Climates. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 340, 130819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowlands, I.H.; Kemery, B.P.; Beausoleil-Morrison, I. Optimal Solar-PV Tilt Angle and Azimuth: An Ontario (Canada) Case-Study. Energy Policy 2011, 39, 1397–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafez, A.Z.; Soliman, A.; El-Metwally, K.A.; Ismail, I.M. Tilt and Azimuth Angles in Solar Energy Applications—A Review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 77, 147–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bingöl, O.; Özkaya, B. Analysis and Comparison of Different PV Array Configurations under Partial Shading Conditions. Sol. Energy 2018, 160, 336–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramabadran, R.; Mathur, B. Effect of Shading on Series and Parallel Connected Solar PV Modules. Mod. Appl. Sci. 2009, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayrak, F.; Ertürk, G.; Oztop, H.F. Effects of Partial Shading on Energy and Exergy Efficiencies for Photovoltaic Panels. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 164, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, S.A.M.; Hassan, G.; Walwil, H.M.; Al-Aqeeli, N. The Effect of Environmental Factors and Dust Accumulation on Photovoltaic Modules and Dust-Accumulation Mitigation Strategies. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 82, 743–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agyekum, E.B.; PraveenKumar, S.; Alwan, N.T.; Velkin, V.I.; Shcheklein, S.E. Effect of Dual Surface Cooling of Solar Photovoltaic Panel on the Efficiency of the Module: Experimental Investigation. Heliyon 2021, 7, e07920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Praveenkumar, S.; Agyekum, E.B.; Alwan, N.T.; Mohammed, A.; Velkin, V.I.; Shcheklein, S.E. Experimental Assessment of Thermoelectric Cooling on the Efficiency of PV Module. Int. J. Renew. Energy Res. 2022, 12, 1670–1681. [Google Scholar]
- Praveenkumar, S.; Gulakhmadov, A.; Agyekum, E.B.; Alwan, N.T.; Velkin, V.I.; Sharipov, P.; Safaraliev, M.; Chen, X. Experimental Study on Performance Enhancement of a Photovoltaic Module Incorporated with CPU Heat Pipe—A 5E Analysis. Sensors 2022, 22, 6367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PraveenKumar, S.; Agyekum, E.B.; Alwan, N.T.; Velkin, V.I.; Yaqoob, S.J.; Adebayo, T.S. Thermal Management of Solar Photovoltaic Module to Enhance Output Performance: An Experimental Passive Cooling Approach Using Discontinuous Aluminium Heat Sink. Int. J. Renew. Energy Res. 2021, 11, 1700–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agyekum, E.B.; Praveenkumar, S.; Alwan, N.T.; Velkin, V.I.; Adebayo, T.S. Experimental Study on Performance Enhancement of a Photovoltaic Module Using a Combination of Phase Change Material and Aluminum Fins—Exergy, Energy and Economic (3e) Analysis. Inventions 2021, 6, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agyekum, E.B.; Praveenkumar, S.; Alwan, N.T.; Velkin, V.I.; Shcheklein, S.E.; Yaqoob, S.J. Experimental Investigation of the Effect of a Combination of Active and Passive Cooling Mechanism on the Thermal Characteristics and Efficiency of Solar Pv Module. Inventions 2021, 6, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adinoyi, M.J.; Said, S.A.M. Effect of Dust Accumulation on the Power Outputs of Solar Photovoltaic Modules. Renew. Energy 2013, 60, 633–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimber, A.; Mitchell, L.; Nogradi, S.; Wenger, H. The Effect of Soiling on Large Grid-Connected Photovoltaic Systems in California and the Southwest Region of the United States. In Proceedings of the Conference Record of the 2006 IEEE 4th World Conference on Photovoltaic Energy Conversion, WCPEC-4, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 7–12 May 2007; Volume 2, pp. 2391–2395. [Google Scholar]
- Conceição, R.; González-Aguilar, J.; Merrouni, A.A.; Romero, M. Soiling Effect in Solar Energy Conversion Systems: A Review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 162, 112434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laarabi, B.; El Baqqal, Y.; Rajasekar, N.; Barhdadi, A. Updated Review on Soiling of Solar Photovoltaic Systems Morocco and India Contributions. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 311, 127608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazem, H.A.; Chaichan, M.T. The Effect of Dust Accumulation and Cleaning Methods on PV Panels’ Outcomes Based on an Experimental Study of Six Locations in Northern Oman. Sol. Energy 2019, 187, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, A.; Amin, A.; Haider, T.; Saleem, M.; Butt, N.Z. Investigation of Soiling Effects, Dust Chemistry and Optimum Cleaning Schedule for PV Modules in Lahore, Pakistan. Renew. Energy 2020, 150, 456–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanchangi, Y.N.; Ghosh, A.; Baig, H.; Sundaram, S.; Mallick, T.K. Soiling on PV Performance Influenced by Weather Parameters in Northern Nigeria. Renew. Energy 2021, 180, 874–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felipe A Mejia, J.K. Soiling Losses for Solar Photovoltaic Systems in California. Sol. Energy 2013, 95, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Ambient Air Pollution: A Global Assessment of Exposure and Burden of Disease; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Kazem, H.A.; Chaichan, M.T. Experimental Analysis of the Effect of Dust’s Physical Properties on Photovoltaic Modules in Northern Oman. Sol. Energy 2016, 139, 68–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciaccioli, A.; Griffo, G.; Visconti, P.; Andria, G. Effects of Dust on Photovoltaic Measurements: A Comparative Study. Measurement 2017, 113, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, R.A.; Farooqui, S.A.; Khan, M.H. Dust Deposition on PV Module and Its Characteristics Dust Deposition on PV Module and Its. In The Effects of Dust and Heat on Photovoltaic Modules: Impacts and Solutions; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; ISBN 9783030846350. [Google Scholar]
- Moutinho, H.R.; Jiang, C.; To, B.; Perkins, C.; Muller, M.; Simpson, L. Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells Adhesion Mechanisms on Solar Glass: Effects of Relative Humidity, Surface Roughness, and Particle Shape and Size. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2017, 172, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Shehri, A.; Parrott, B.; Carrasco, P.; Al Saiari, H.; Taie, I. Impact of Dust Deposition and Brush-Based Dry Cleaning on Glass Transmittance for PV Modules Applications. Sol. Energy 2016, 135, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilbas, B.S.; Ali, H.; Al-Aqeeli, N.; Khaled, M.M.; Said, S.; Abu-Dheir, N.; Merah, N.; Youcef-Toumi, K.; Varanasi, K.K. Characterization of Environmental Dust in the Dammam Area and Mud After-Effects on Bisphenol-A Polycarbonate Sheets. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fares, E.; Buffiere, M.; Figgis, B.; Haik, Y.; Isaifan, R.J. Soiling of Photovoltaic Panels in the Gulf Cooperation Council Countries and Mitigation Strategies. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2021, 231, 111303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilbas, B.S.; Hassan, G.; Ali, H.; Al-aqeeli, N. Environmental Dust Effects on Aluminum Surfaces in Humid Air Ambient. Nat. Publ. Group 2017, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehman, S.; Bader, M.A.; Al-Moallem, S.A. Cost of Solar Energy Generated Using PV Panels. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2007, 11, 1843–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GeoModel Solar. Validation of SolarGIS GHI and DNI Data for the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia; GeoModel Solar: Bratislava, Slovakia, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Hepbasli, A.; Alsuhaibani, Z. A Key Review on Present Status and Future Directions of Solar Energy Studies and Applications in Saudi Arabia. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2011, 15, 5021–5050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.Y.; Chiba, M. A Numerical Study of the Contributions of Dust Source Regions to the Global Dust Budget. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2006, 52, 88–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, M.J.; Mashat, A.S. MODIS Satellite Data Evaluation for Sand and Dust Storm Monitoring in Saudi Arabia. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villiers, D.; Heerden, V. Dust Storms and Dust at Abu Dhabi International Airport. Weather 2007, 62, 339–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arishi, A.A. Classification of Sandstorms in Saudi Arabia. Atmos. Clim. Sci. 2021, 11, 177–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labban, A.H.; Butt, M.J. Analysis of Sand and Dust Storm Events over Saudi Arabia in Relation with Meteorological Parameters and ENSO. Arab. J. Geosci. 2021, 14, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notaro, M.; Alkolibi, F.; Fadda, E.; Bakhrjy, F. Trajectory Analysis of Saudi Arabian Dust Storms. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 6028–6043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilse, K.K.; Figgis, B.W.; Naumann, V.; Hagendorf, C.; Csp, S.; Saale, H. Fundamentals of Soiling Processes on Photovoltaic Modules. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 98, 239–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, S.A.M. Effects of Dust Accumulation on Performances of Thermal and Photovoltaic Flat-Plate Collectors. Appl. Energy 1990, 37, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, S.A.M.; Walwil, H.M. Fundamental Studies on Dust Fouling Effects on PV Module Performance. Sol. Energy 2014, 107, 328–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, R.K.; Baras, A.; Al Saeeri, A.; Al Qahtani, A.; Al Amoudi, A.O.; Al Shaya, Y.; Alodan, M.; Al-Hsaien, S.A. Optimized Cleaning Cost and Schedule Based on Observed Soiling Conditions for Photovoltaic Plants in Central Saudi Arabia. IEEE J. Photovolt. 2016, 6, 730–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, A. Effect of Shadow and Dust on the Performance of Silicon Solar Cell Effect of Shadow and Dust on the Performance of Silicon Solar Cell. J. Basic Appl. Sci. Res. 2011, 1, 222–230. [Google Scholar]
- Benghanem, M.; Almohammedi, A.; Taukeer Khan, M.; Al-Masraqi, A. Effect of Dust Accumulation on the Performance of Photovoltaic Panels in Desert Countries: A Case Study for Madinah, Saudi Arabia. Int. J. Power Electron. Drive Syst. (IJPEDS) 2018, 9, 1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khayyat, A.M.Z.; Alharthi, A.H.; Almohammadi, F.L.; Almarwani, Z.S.; Kannan, N.; Mobarak, Y. The Soiling Impact Effects on the Performance of the Solar Panels in Rabigh, Saudi Arabia. Adv. Comput. Intell. Technol. 2022, 914, 429–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, J.J.; Warade, S.; Tamizhmani, G.; Kottantharayil, A. Study of Soiling Loss on Photovoltaic Modules with Artificially Deposited Dust of Different Gravimetric Densities and Compositions Collected from Different Locations in India. IEEE J. Photovolt. 2016, 6, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazmerski, L.L.; Al Jardan, M.; Al Jnoobi, Y.; Al Shaya, Y.; John, J.J. Ashes to Ashes, Dust to Dust: Averting a Potential Showstopper for Solar Photovoltaics. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE 40th Photovoltaic Specialist Conference, PVSC 2014, Denver, CO, USA, 8–13 June 2014; pp. 187–192. [Google Scholar]
- Mehmood, U.; Al-Sulaiman, F.A.; Yilbas, B.S. Characterization of Dust Collected from PV Modules in the Area of Dhahran, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, and Its Impact on Protective Transparent Covers for Photovoltaic Applications. Sol. Energy 2017, 141, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelbrecht, J.P.; Mcdonald, E.V.; Gillies, J.A.; Jayanty, R.K.M.; Gertler, A.W. Characterizing Mineral Dusts and Other Aerosols from the Middle East—Part 1: Ambient Sampling. Inhal. Toxicol. 2009, 21, 297–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shenouda, R.; Kandil, H.A. A Review of Dust Accumulation on PV Panels in the MENA and the Far East Regions. J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2022, 69, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanchangi, Y.N.; Ghosh, A.; Sundaram, S.; Mallick, T.K. Dust and PV Performance in Nigeria: A Review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 121, 109704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picotti, G.; Borghesani, P.; Cholette, M.E.; Manzolini, G. Soiling of Solar Collectors—Modelling Approaches for Airborne Dust and Its Interactions with Surfaces. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 81, 2343–2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juzaili, W.; Abdul, H.; Shaari, S.; Salam, Z. Performance Degradation of Photovoltaic Power System: Review on Mitigation Methods. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 67, 876–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.; Sharma, M.; Kumar, R.; Babu, K.N.D. Comprehensive Review on Effect of Dust on Solar Photovoltaic System and Mitigation Techniques. Sol. Energy 2019, 191, 596–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarver, T.; Al-qaraghuli, A.; Kazmerski, L.L. A Comprehensive Review of the Impact of Dust on the Use of Solar Energy: History, Investigations, Results, Literature, and Mitigation Approaches. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 22, 698–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazi, S.; Sayigh, A.; Ip, K. Dust Effect on Flat Surfaces—A Review Paper. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 33, 742–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, D.; Brahmbhatt, N.L. Review of Yield Increase of Solar Panels through Soiling Prevention, and a Proposed Water-Free Automated Cleaning Solution. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 82, 3306–3313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudedmani, M.G.; Joshi, G.; Umayal, R.M.; Revankar, A. A Comparative Study of Dust Cleaning Methods for the Solar PV Panels. Adv. J. Grad. Res. 2017, 1, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Lu, L.; Wang, Y. Numerical Investigation of Dust Pollution on a Solar Photovoltaic ( PV ) System Mounted on an Isolated Building. Appl. Energy 2016, 180, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BOSON Dust Shall Never Shade the Brightness. Available online: https://bosonrobotics.com/en/products/robot (accessed on 14 September 2022).
- Israar Israar. Available online: https://www.israar.com/PVCleaningMachine.php#overview (accessed on 28 September 2022).
- Kumar, N.M.; Sudhakar, K.; Samykano, M.; Jayaseelan, V. On the Technologies Empowering Drones for Intelligent Monitoring of Solar Photovoltaic Power Plants. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2018, 133, 585–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallardo-Saavedra, S.; Hernández-Callejo, L.; Duque-Perez, O. Technological Review of the Instrumentation Used in Aerial Thermographic Inspection of Photovoltaic Plants. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 93, 566–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Housani, M.; Bicer, Y.; Koç, M. Experimental Investigations on PV Cleaning of Large-Scale Solar Power Plants in Desert Climates: Comparison of Cleaning Techniques for Drone Retrofitting. Energy Convers. Manag. 2019, 185, 800–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleandrone Cleandrone. Available online: http://www.cleandrone.com/cleandrone-2/ (accessed on 17 September 2022).
- Dronevolt Dronevolt. Available online: https://www.dronevolt.com/en/expert-solutions/hercules-10-spray/# (accessed on 17 September 2022).
- Aerial Power Aerial Power. Available online: https://www.aerialpower.com/ (accessed on 17 September 2022).
- Williams, R.B.; Tanimoto, R.; Simonyan, A.; Fuerstenau, S. Vibration Characterization of Self-Cleaning Solar Panels with Piezoceramic Actuation. In Proceedings of the Structural Dynamics and Materials Conference, Honolulu, HI, USA, 23–26 April 2007; p. 512. [Google Scholar]
- Indiamart Solar Panels—Super Hydrophobic Coating. Available online: https://www.indiamart.com/proddetail/solar-panels-super-hydrophobic-coating-one-kit-good-for-50-panel-2-mtr-x-1-mtr-22056797862.html (accessed on 18 September 2022).
- Drelich, J.; Chibowski, E.; Meng, D.D.; Terpilowski, K. Hydrophilic and Superhydrophilic Surfaces and Materials. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 9804–9828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bǎlţatu, M.S.; Vizureanu, P.; Bǎlan, T.; Lohan, M.; Ţugui, C.A. Preliminary Tests for Ti-Mo-Zr-Ta Alloys as Potential Biomaterials. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 374, 012023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimoto, S.; Bharat, B. Bioinspired Self-Cleaning Surfaces with Superhydrophobicity, Superoleophobicity, and Superhydrophilicity. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 671–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazumder, M.; Horenstein, M.N.; Stark, J.W.; Girouard, P.; Sumner, R.; Henderson, B.; Sadder, O.; Hidetaka, I.; Biris, A.S.; Sharma, R. Characterization of Electrodynamic Screen Performance for Dust Removal from Solar Panels and Solar Hydrogen Generators. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2013, 49, 1793–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamoto, H. Improved Detachable Electrodynamic Cleaning System for Dust Removal from Soiled Photovoltaic Panels. J. Electrost. 2020, 107, 103481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Jawah, M. A Decision Aiding Framework for Investing in Cleaning Systems for Solar Photovoltaic (PV) Power Plants in Arid Regions. Ph.D. Thesis, George Washington University, Washington, DC, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- KFUPM Forum|Effects of Soiling on Solar Energy Applications: Challenges and Mitigation Techniques. Available online: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-TF5UF7h2oA (accessed on 25 September 2022).
- ACWA SUDAIR PV IPP. Available online: https://acwapower.com/en/projects/sudair-pv-ipp/ (accessed on 24 September 2022).






















Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al Garni, H.Z. The Impact of Soiling on PV Module Performance in Saudi Arabia. Energies 2022, 15, 8033. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15218033
Al Garni HZ. The Impact of Soiling on PV Module Performance in Saudi Arabia. Energies. 2022; 15(21):8033. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15218033
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl Garni, Hassan Z. 2022. "The Impact of Soiling on PV Module Performance in Saudi Arabia" Energies 15, no. 21: 8033. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15218033
APA StyleAl Garni, H. Z. (2022). The Impact of Soiling on PV Module Performance in Saudi Arabia. Energies, 15(21), 8033. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15218033





