Solar Photovoltaic Power Estimation Using Meta-Optimized Neural Networks
Abstract
:1. Introduction
Literature Review
- Develop ANN model for PV power prediction;
- Use the optimization method to train the ANN:
- ○
- Genetic algorithm (GA);
- ○
- Particle swarm optimization (PSO);
- ○
- Artificial bee colony (ABC).
- Analyze and compare results.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Genetic Algorithm
2.2. Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO)
- For every particle , perform the following steps:
- ○
- Start with the position of a particle by a random vector with uniform distribution: , where and are the upper boundary and lower boundaries of the search space, respectively;
- ○
- Set the initial value of the particle’s best position to: ;
- ○
- When , change ;
- ○
- Set the initial value of the particle’s velocity:.
- Until a termination condition is met (i.e., the final iteration is met or a solution with adequate objective function value is found):
- ○
- For every particle , perform the following steps:
- ○
- Choose random numbers: ;
- ○
- For every , perform the following steps:
- ○
- Update the velocity of the particle;
- ○
- Update the position of particle:.
- ○
- When , perform the following steps:
- ○
- Update the best-known position of the particle: ;
- ○
- When, update the best-known position of the swarm:.
- Now g represents the best-found solution.
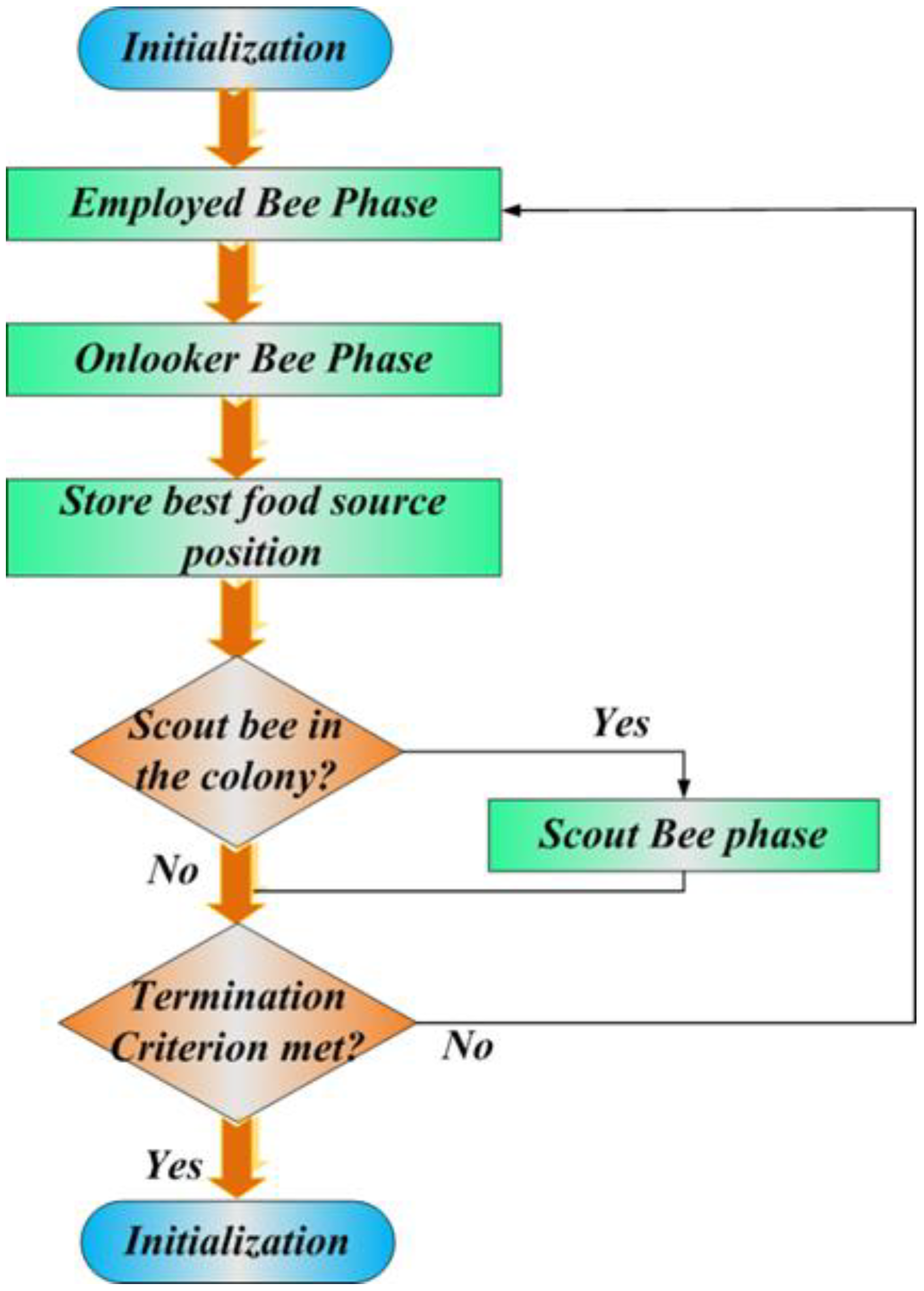
2.3. Artificial Bee Colony (ABC)
- The mobilization of foragers to find and retrieve rich sources of food, which is reconsidered as positive feedback;
- Foragers neglecting poor food sources, leading to negative feedback.
- Employed: which are associated with finding specific sources of food;
- Onlookers: which watch the movements of Employed bees in the hive to select sources of foods;
- Scouts: which randomly look for sources of food.
- Initialization Phase
- REPEAT
- Employed Bees Phase
- Onlooker Bees Phase
- Scout Bees Phase
- Memorize the best solution achieved so far
- UNTIL (Cycle = Maximum Cycle Number)
2.4. Validation Metrics
2.4.1. Mean Square Error
2.4.2. Mean Absolute Percentage Error
2.4.3. Coefficient of Determination
3. Simulation Results
3.1. Data Processing
3.2. Traditional ANN
3.3. ANN with the Genetic Algorithm
3.4. ANN with PSO
3.5. ANN with ABC
3.6. Results Comparisons
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Filik, Ü.B.; Filik, T.; Gerek, Ö.N. New electric transmission systems: Experiences from Turkey. In Handbook of Clean Energy Systems; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Zazoum, B. Solar photovoltaic power prediction using different machine learning methods. Energy Rep. 2021, 8, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Hendouzi, A.; Bourouhou, A. Solar Photovoltaic Power Forecasting. J. Electr. Comput. Eng. 2020, 2020, 8819925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordell, B. Thermal pollution causes global warming. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2003, 38, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, K. COVID-19: How GOGLA is Helping the Off-Grid Solar Industry Deal with the Crisis. Available online: https://www.gogla.org/about-us/blogs/covid-19-how-gogla-ishelping-the-off-grid-solar-industry-deal-with-the-crisis (accessed on 5 October 2022).
- Burnett, J.W.; Hefner, F. Solar energy adoption: A case study of South Carolina. Electr. J. 2021, 34, 106958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eroğlu, H. Effects of Covid-19 outbreak on environment and renewable energy sector. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2020, 23, 4782–4790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Huang, X. An Evaluation Method of the Photovoltaic Power Prediction Quality. Math. Probl. Eng. 2018, 2018, 9049215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, H.; Lu, L.; Sun, K. Experimental investigation of the impact of airborne dust deposition on the performance of solar photovoltaic (PV) modules. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 4299–4304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pi, M.; Jin, N.; Chen, D.; Lou, B. Short-Term Solar Irradiance Prediction Based on Multichannel LSTM Neural Networks Using Edge-Based IoT System. Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2022, 2022, 2372748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, W. Improved Probability Prediction Method Research for Photovoltaic Power Output. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, K.; Cao, S.; Wang, L.; Li, W.; Lv, M. A new ultra-short-term photovoltaic power prediction model based on ground-based cloud images. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 200, 731–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, Y.; Jung, J.; Kim, B.; Han, S. Long short-term memory recurrent neural network for modeling temporal patterns in long-term power forecasting for solar PV facilities: Case study of South Korea. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 250, 119476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias, M.B.; Bae, S. Solar Photovoltaic Power Prediction Using Big Data Tools. Sustainability 2021, 13, 13685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agga, A.; Abbou, A.; Labbadi, M.; El Houm, Y.; Ali, I.H.O. CNN-LSTM: An efficient hybrid deep learning architecture for predicting short-term photovoltaic power production. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2022, 208, 107908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, M.-Y.; Lee, C.-H.; Chang, J.-M. Application of Parallel ANN-PSO to Hourly Solar PV Estimation. Preprints 2021, 2021100112. [Google Scholar]
- Geetha, A.; Santhakumar, J.; Sundaram, K.M.; Usha, S.; Thentral, T.T.; Boopathi, C.; Ramya, R.; Sathyamurthy, R. Prediction of hourly solar radiation in Tamil Nadu using ANN model with different learning algorithms. Energy Rep. 2021, 8, 664–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, S.M.A.; Cari, E.P.T.; Hajimirza, S. A Comparative Analysis of Artificial Neural Networks for Photovoltaic Power Forecast Using Remotes and Local Measurements. J. Sol. Energy Eng. 2021, 144, 021007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashunao, S.; Sunku, H.; Mehta, R.K. Modelling and Forecasting of Solar Radiation Data: A Case Study. In Modeling, Simulation and Optimization; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Das, R.; Singh, K.; Akay, B.; Gogoi, T.K. Application of artificial bee colony algorithm for maximizing heat transfer in a perforated fin. J. Process Mech. Eng. 2018, 232, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, R.; Akay, B.B.; Singla, R.K.; Singh, K. Application of artificial bee colony algorithm for inverse modelling of a solar collector. Inverse Probl. Sci. Eng. 2016, 25, 887–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.C. Artificial Neural Network. In Interdisciplinary Computing in Java Programming; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2003; pp. 81–100. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, N. Artificial neural network. Netw. Complex Syst. 2013, 3, 24–28. [Google Scholar]
- Kramer, O. Genetic algorithms. In Genetic Algorithm Essentials; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 11–19. [Google Scholar]
- Alam, T.; Qamar, S.; Dixit, A.; Benaida, M. Genetic algorithm: Reviews, implementations, and applications. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2007.12673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Husain, D.; Upreti, N.; Gupta, D. Genetic Algorithm: Review and Application. 2010. Available online: https://ssrn.com/abstract=3529843 (accessed on 10 October 2022).
- Kennedy, J.; Eberhart, R. Particle swarm optimization. In Proceedings of the ICNN’95-International Conference on Neural Networks, Perth, WA, Australia, 27 November–1 December 1995; Volume 4, pp. 1942–1948. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Li, X.; Zhu, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, L.; Jiang SRong, Y. The optimization of accuracy and efficiency for multistage precision grinding process with an improved particle swarm optimization algorithm. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2020, 17, 1729881419893508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karaboga, D. An Idea Based on Honey Bee Swarm for Numerical Optimization; Technical Report-tr06; Erciyes University, Engineering Faculty, Computer Engineering Department: Talas/Kayseri, Turkey, 2005; Volume 200, pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Karaboga, D.; Basturk, B. A powerful and efficient algorithm for numerical function optimization: Artificial bee colony (ABC) algorithm. J. Glob. Optim. 2007, 39, 459–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, H.; Ghazali, R.; Nawi, N.M.; Deris, M.M. Global hybrid Artificial bee colony algorithm for training artificial neural networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computational Science and Its Applications, Salvador de Bahia, Brazil, 18–21 June 2012; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 87–100. [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg, D.E.; Deb, K. A comparative analysis of selection schemes used in genetic algorithms. In Foundations of Genetic Algorithms; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1991; Volume 1, pp. 69–93. [Google Scholar]
- Asrari, A.; Wu, T.X.; Ramos, B. A Hybrid Algorithm for Short-Term Solar Power Prediction—Sunshine State Case Study. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2016, 8, 582–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.; Liu, Z. A Fast Grid Search Method in Support Vector Regression Forecasting Time Series; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 504–511. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Guo, S.; Zhao, H.; Su, C.; Wang, B. Annual electric load forecasting by a least squares support vector machine with a fruit fly optimization algorithm. Energies 2012, 5, 4430–4445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Generation | Best Cost Function | Mean Cost Function |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 10.61 | 445.6 |
| 2 | 10.61 | 617.2 |
| 3 | 10.61 | 725.2 |
| 4 | 10.61 | 726.6 |
| 5 | 10.61 | 819.7 |
| 6 | 10.61 | 896.7 |
| 7 | 10.61 | 795.7 |
| 8 | 10.61 | 753.2 |
| 9 | 10.61 | 771.9 |
| 10 | 10.61 | 761.1 |
| 11 | 9.497 | 834.7 |
| 12 | 9.464 | 828.7 |
| 13 | 9.438 | 775.7 |
| 14 | 7.963 | 733.7 |
| 15 | 7.518 | 772.8 |
| Iteration | Best Cost Function |
|---|---|
| 1 | 43.4098 |
| 2 | 43.4098 |
| 3 | 18.8759 |
| 4 | 1.368 |
| 5 | 1.368 |
| 6 | 1.368 |
| 7 | 1.368 |
| 8 | 1.368 |
| 9 | 1.368 |
| 10 | 1.368 |
| MSE | MAPE | R2 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ANN | 0.00002034 | 0.00040514 | 1 |
| GA–ANN | 6.1440 | 0.6790 | 0.4841 |
| PSO–ANN | 0.4607 | 0.0524 | 0.9971 |
| ABC–ANN | 35.1428 | 0.7890 | 0.5004 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gumar, A.K.; Demir, F. Solar Photovoltaic Power Estimation Using Meta-Optimized Neural Networks. Energies 2022, 15, 8669. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15228669
Gumar AK, Demir F. Solar Photovoltaic Power Estimation Using Meta-Optimized Neural Networks. Energies. 2022; 15(22):8669. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15228669
Chicago/Turabian StyleGumar, Ali Kamil, and Funda Demir. 2022. "Solar Photovoltaic Power Estimation Using Meta-Optimized Neural Networks" Energies 15, no. 22: 8669. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15228669
APA StyleGumar, A. K., & Demir, F. (2022). Solar Photovoltaic Power Estimation Using Meta-Optimized Neural Networks. Energies, 15(22), 8669. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15228669








