Abstract
In this study, a newly established bench-scale thermophilic continuously stirred fluidized bed reactor (CSFBR) was applied for anaerobic co-digestion of food waste (FW) with grease trap waste (GTW). The performance of CSFBR regarding stability and treatment efficiency was inspected through a laboratory contrast experiment with two traditional continuous stirred tank reactors (CSTRs). In the OLR range of 3.19–7.41 g COD/L/d, the methane production rate of the thermophilic CSFBR was about as high as that of the thermophilic CSTR. Nevertheless, the thermophilic CSFBR had much lower VFAs (<1000 mg/L) and LCFA concentrations (<100 mg/L) as compared with the thermophilic CSTR. Unlike the mesophilic CSTR, there was no foaming that occurred in the CSFBR during the whole experimental period. The results all suggested that CSFBR simultaneously provided high treatment capacity and process stability in anaerobic digestion with high-lipid loading.
1. Introduction
As an important part of municipal solid waste, food waste (FW) has become a worldwide problem [1]. Thus, FW disposal is currently of great concern in many countries [2]. Traditional FW disposal methods such as landfills and incineration are sub-satisfactory considering investment, sustainability, and environmental impact [3]. In contrast, anaerobic digestion (AD) is becoming one of the most appealing methods for FW disposal owing to its beneficial characteristics, such as renewable energy power generation, relatively low energy consumption, and valuable materials production [4,5]. In addition, Bernstad Saraiva Schott and Andersson [6] pointed out that landfills and incineration can be replaced by AD or composting in FW treatment, according to their life cycle assessment. Therefore, AD has been extensively used for FW treatment on an industrial scale in many European and developed Asian countries [7].
Grease trap waste (GTW) is collected from grease collectors which are commonly used in eating establishments to prevent FOG (fat, oil, and grease) from accumulating in drainage pipes. It was estimated that roughly 310,000 tons of GTW were generated every year in Japan, from which 110,000 tons of FOG can be potentially gathered [8]. Recently, anaerobic co-digestion of lipidic waste to enhance biogas production has attracted more attention owing to the high biomethane potential of FOG [9,10]. According to literature reports, improved process performance was observed with the addition of GTW to different co-substrates, such as sewage sludge [11], animal manure [12], and FW [13]. Compared with other main-substrates, anaerobic co-digestion of FW with GTW provides an economic option for on-site waste treatment in urban areas because of the close proximity of those two organic wastes [14]. In fact, a tall building in a Japanese city center has recently installed a small biogas generator system for the anaerobic co-digestion of FW with GTW [15]. Nevertheless, anaerobic digestion of lipidic waste can be frequently inhibited by long-chain fatty acids (LCFAs) transformed from FOG [16]. Generally, the slow conversion of LCFAs to lower molecular structures via ß-oxidation makes them easy to accumulate in anaerobic digesters, causing various operational problems such as hindrance, sedimentation clogging, and so on [13].
To mitigate inhibition of LCFAs and improve system stability and efficiency, process monitoring and control are widely applied in AD of lipidic waste [7]. Previous studies have investigated the influence of experimental parameters, such as OLR, digester temperature, and lipid concentration, on the process performance of anaerobic lipidic-waste digestion. In addition, some researchers have focused upon optimizing the structure and function of anaerobic digesters to improve methane production in lipidic-waste fermentation [17]. Chan et al. [18] stated that continuous stirring tank reactors (CSTRs), which have better mixing conditions, gain higher lipid degradation rates when compared with up-flow anaerobic sludge blanket (UASB) reactors. Alves et al. [19] reported a novel inverted anaerobic sludge blanket reactor (IASB) to effectively enhance methane production from LCFA-containing wastewater in AD. In our previous study, a siphon-driven self-agitated anaerobic reactor (SDSAR) was developed for the anaerobic co-digestion of FW and GTW [14]. However, relatively low OLR (1 to 4 g VS/L/d) or long HRT (up to 80 d) are still the few feasible choices for actual FW treatment with traditional digesters to sustain stable AD process and avoid LCFA accumulation [7]. Therefore, more efforts should be made to find some more stable digesters with high performance in anaerobic co-digestion of FW with GTW.
In this paper, we newly established a bench-scale continuously stirred fluidized bed reactor (CSFBR) for thermophilic anaerobic co-digestion of FW with GTW, and assessed the advantages of the CSFBR over the thermophilic and mesophilic CSTR. The effects of OLR on organic removal and methane production of the three reactors were examined, and the advantages and limitations of CSFBR for anaerobic co-digestion were determined.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bioreactors
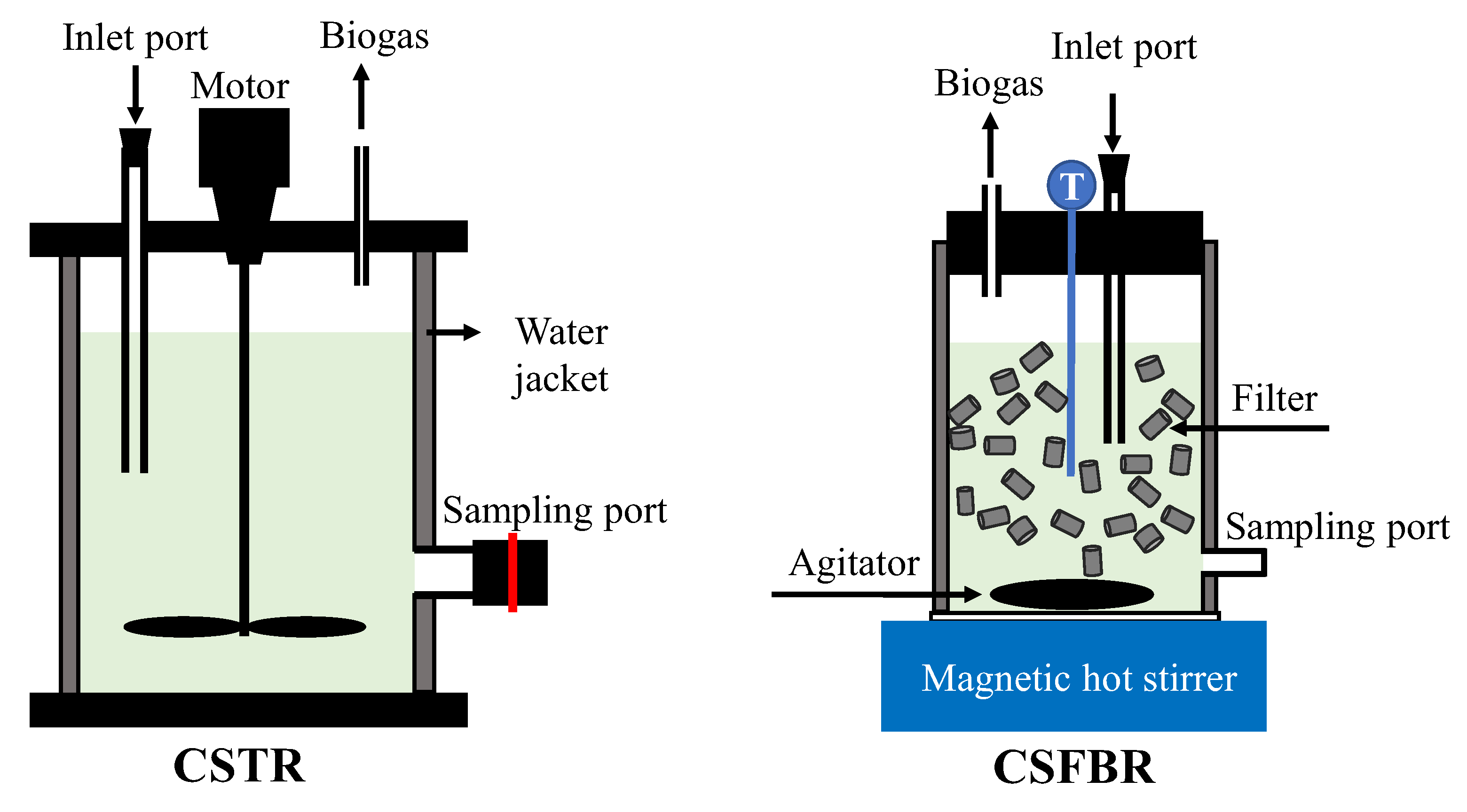
The schematic diagram illustrating reactor structures of the CSTR and CSFBR is shown in Figure 1. The mesophilic and thermophilic CSTR consisted of a polyvinyl chloride (PVC) cylinder-shaped reactor with an effective volume of 1.8 L and heated by an external water jacket. The CSFBR is made from glass with a total working volume of 0.9 L and was heated and stirred with a magnetic hot stirrer (VPHS-190A, AS ONE). The continuously stirred system of the CSFBR is similar to that of a CSTR, except that the CSFBR was also filled with hollow cylinders. The hollow cylinders are made from polypropylene and occupy about 30% of active volume of the reactor. The specific surface area of the medias was 620 m2/m3 with a void space of more than 85%. Like particles in a fluidized-bed reactor (FBR), those medias in the CSFBR provide a suitable environment for microbial growth and move with the fluid. The stirring speeds were 100 rpm in all three reactors. The temperature of the mesophilic CSTR was maintained at 35 ± 1 ℃, while the thermophilic CSTR and CSFBR were maintained at 55 ± 1 ℃.
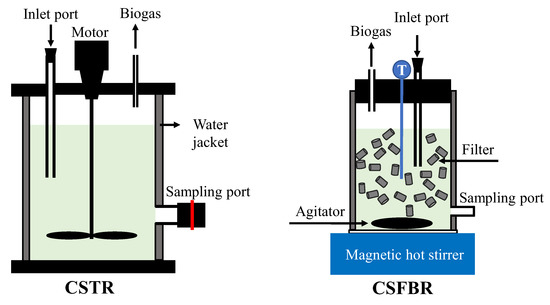
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of the CSTR and CSFBR.
2.2. Substrate and Inoculum
FW was obtained from the staff restaurant of the National Institute for Environmental Studies, Tsukuba, Japan. First, the gathered FW was broken into fine particles (less than 5 mm) with a garbage disposal shredder (Cuisinart, DLC-NXJ2PS). Then, the shredded FW was diluted with running water to reach a desired lipid and VS content of around 24 g/L and 70%. GTW was collected from the oil separator of a biogas system installed in a skyscraper in Osaka, Japan. The GTW residue was stored in the refrigerator before being prepared for use. The VS and lipid concentrations of the GTW were 248.3 and 273.1 g/kg, respectively. Before being added into the reactors, the required ratio of GTW was heated at 60 ℃ for 2 h, and then mixed with the prepared FW completely. Essential trace elements required for microbial growth were added from stock solutions to a final concentration in the substrate of 100 mg Fe/L, 10 mg Co/L, and 10 mg Ni/L, respectively. The mesophilic CSTR was seeded with digestion sludge obtained from an anaerobic food waste treatment plant, while the two thermophilic reactors were seeded with sludge taken from the AD system installed in a skyscraper in Osaka, Japan.
2.3. Operational Conditions
The operational conditions in this study are summarized in Table 1. The mesophilic and thermophilic CSTRs were started from day 1, and the thermophilic CSFBR was started from day 57. The HRT was progressively shortened from 123 to 20 d to increase the OLR from 1.15 to 7.41 g COD/L/d. The TS content of GTW utilized in this study (around 25.5%) falls within a range of 14 to 42% w/w, previously reported for GTW collected from different facilities [20]. In addition, the lipid/VS ratio in the substrate was maintained at around 32%, according to the real lipidic-waste composition in the AD system installed in a skyscraper in Osaka, Japan.

Table 1.
Substrate characteristics and operational conditions for three reactors.
2.4. Analysis Methods
Biogas production was recorded daily using a gas microflow meter (Bioprocess Control AB). The biogas components (including CH4, CO2, and N2) were also determined with the help of a gas chromatograph (GC-8A, Shimadzu, Japan). The effluents of the three reactors were sampled and analyzed twice a week. A pH meter (TOA-DKK, Japan) was used to measure the pH values of liquid samples, while COD, TS, and VS were analyzed following the standard procedure as prescribed by APHA [21]. The lipid in substrate was extracted with a mixture chloroform: methanol 1:2 (v/v) and determined according to Bligh and Dyer [22]. Analysis of volatile fatty acids (VFAs) was conducted by gas chromatography (GC-2014, Shimadzu). The LCFA concentrations were measured with gas chromatography (GC-6890N, Agilent, Santa Clara, CA, USA).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Operational Reactor Performance
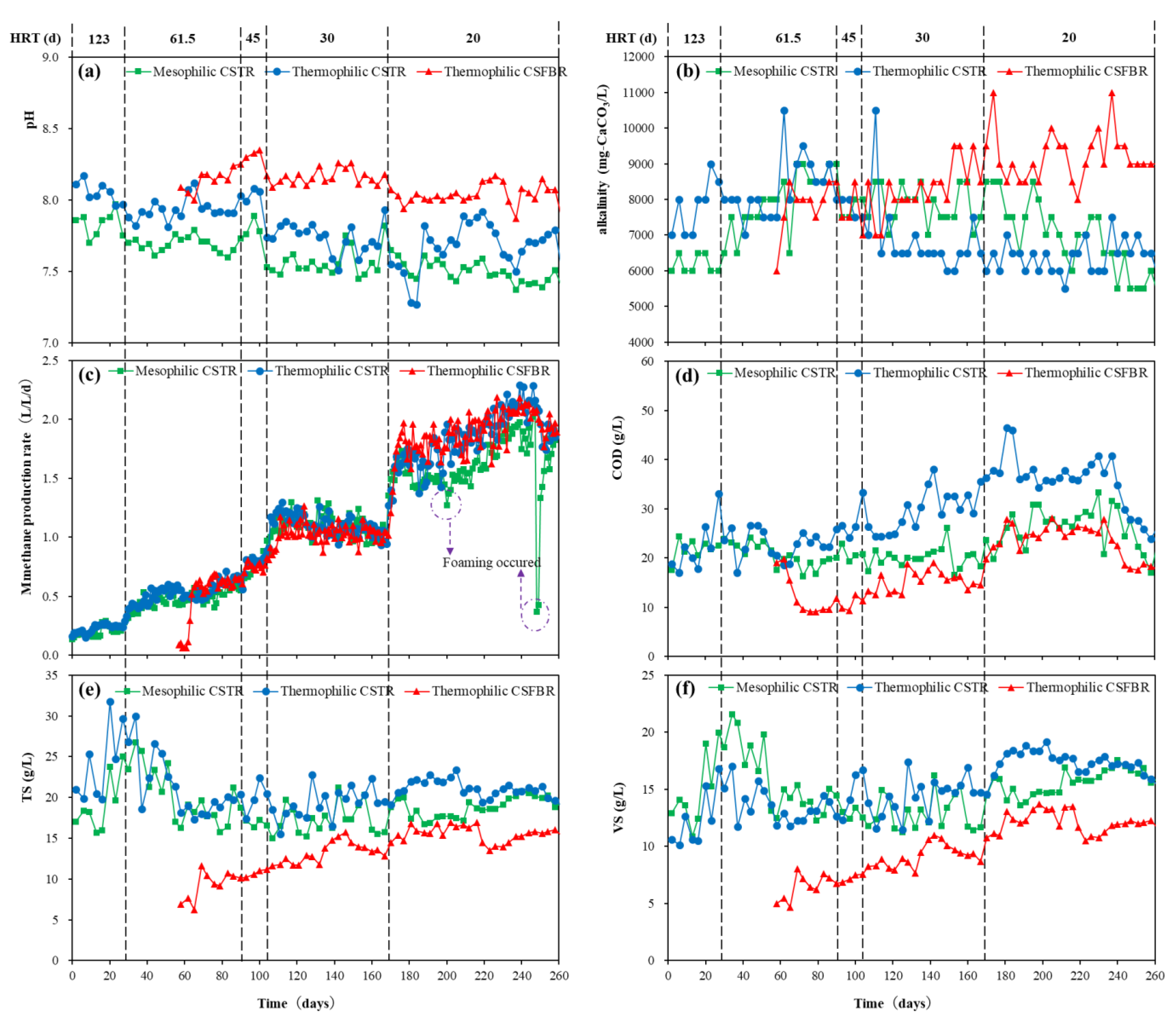
The overall reactor performances of mesophilic CSTR, thermophilic CSTR, and thermophilic CSFBR are shown in Figure 2. There was no significant change in pH observed in the three reactors during the whole experimental period (Figure 2a). However, the pH value was higher in CSFBR compared with that in the two CSTRs. Nevertheless, all three reactors kept an approximately neutral pH in which methanogens can work effectively. Similar results were obtained in alkalinity in the three reactors (Figure 2b). At HRT of 20 d, the alkalinity in the thermophilic reactor was above 8000 mg CaCO3/L, while that in the CSTR reactors were between 6000 to 8000 mg CaCO3/L. Martín-González et al. [23] suggested that total alkalinity (TA) concentrations should remain between 13,000-15,000 mg/L to achieve stable reactor performance in anaerobic digestion. Although relatively low TA concentrations were observed in this study, TA concentration in the thermophilic CSFBR is much closer to the recommended value. For methane production rate, there was no obvious difference among the three reactors with HRT ranging from 123 to 30 d (Figure 2c). However, when HRT further shortened to 20 d, foaming occurred in the mesophilic CSTR on day 207 and day 249. On the other hand, there was no foaming problem observed in the thermophilic CSTR and CSFBR. As shown in Figure 2d, at low HRT conditions, the effluent COD concentration in the thermophilic CSTR was significantly higher than that of the other two reactors, while the lowest effluent COD was maintained in the thermophilic CSFBR. The variations of TS and VS concentrations are shown in Figure 2e,f. In the mesophilic and thermophilic CSTRs, the TS and VS concentrations were maintained at around 20 and 15 g/L at HRT of 20 d. Under the same HRT conditions, the TS and VS concentrations in the thermophilic CSFBR were much lower compared with the CSTRs. Consequently, the CSFBR showed a much higher VS removal of more than 84%, as shown in Table 2.
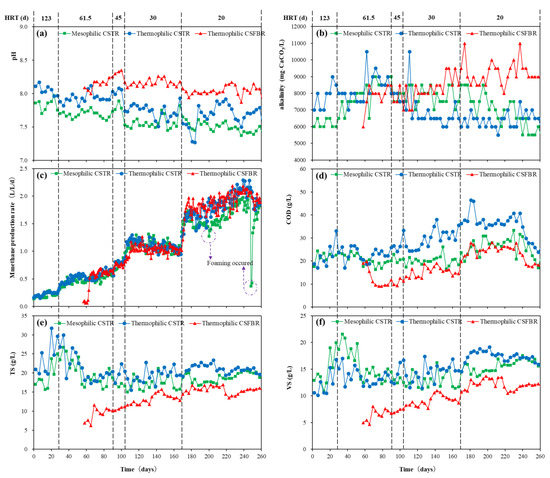
Figure 2.
Overall performance of CSFBR and CSTRs.

Table 2.
Performance and fatty acids in the effluent of three reactors.
3.2. Effects of OLR on the Rector Performance
3.2.1. Effects of OLR on Methane Production
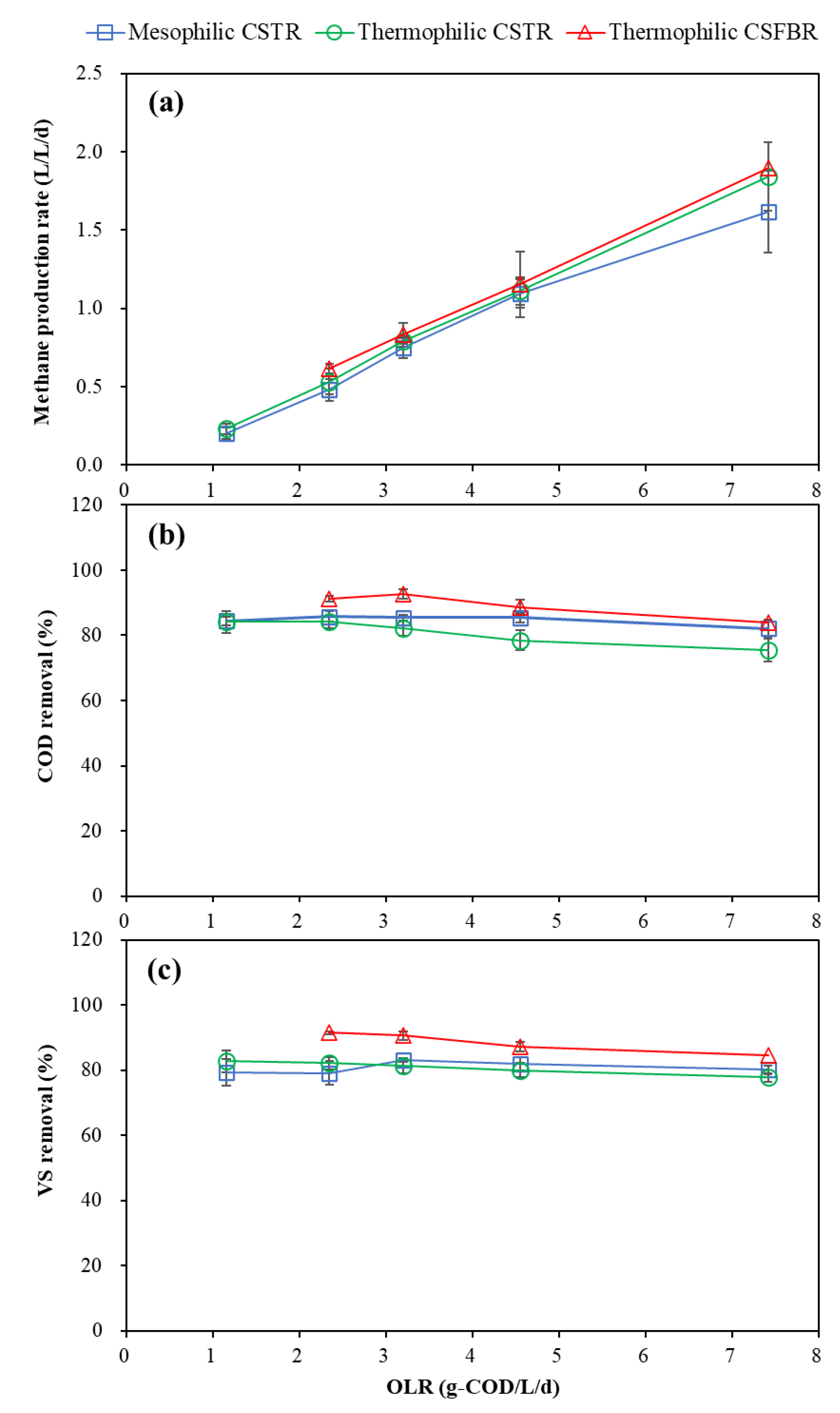
The methane production was greatly affected by HRT and OLR variations, as shown in Figure 3a. The average methane production rate was 0.20 and 0.23 L/L/d in the mesophilic and thermophilic CSTR at an OLR of 1.15 g COD/L/d, which rose to 1.62 and 1.84 L/L/d at an OLR of 7.41 g COD/L/d. In the CSFBR, with OLR increased from 2.34 to 7.41 g COD/L/d, the average methane production rate also increased from 0.61 to 1.89 L/L/d. The methane production rate in the mesophilic CSTR at an OLR of 7.41 was the lowest one among the three reactors due to the foaming problem.
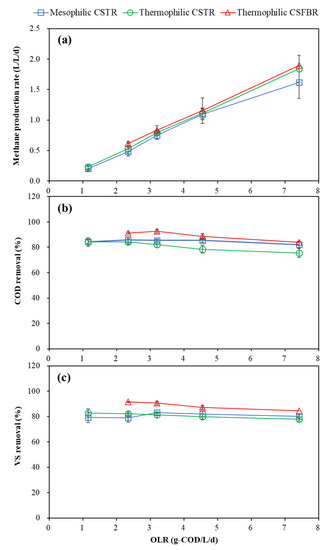
Figure 3.
Effects of OLRs on (a) methane production, (b) COD removal, and (c) VS removal.
The average methane yields (MY) at different operational conditions in the three reactors are summarized in Table 2. The highest methane yield of 496 mL CH4/gVSadded was achieved in the thermophilic CSFBR at a relatively low OLR of 2.34 g COD/L/d. The theoretical MY in wet anaerobic FW digestion typically ranges from 400 to 500 mL CH4/gVSadded [24]. Normally, due to the high methane production potential of lipidic waste (990 mL CH4/glipid) [19], GTW addition as a co-substrate can improve the MY. In our previous study, the MY in FW and GTW co-digestion increased 18.5%, 32.2%, and 2.64% at lipid/TS ratios of 19.7%, 40.9%, and 50.2%, compared with wet mono-digestion of FW [14]. In this research, the MY of the thermophilic CSFBR improved by 15.3%, 4.9%, 3.9%, and 2.8% over the thermophilic CSTR at 2.34, 3.19, 4.55, and 7.41 g COD/L/d OLR conditions.
3.2.2. Effects of OLR on Organic Removal
The effects of OLR on COD and VS removal are presented in Figure 3b,c. The mesophilic CSTR and thermophilic CSFBR maintained high COD removal of above 80% under all OLR conditions applied, while the COD removal dropped to 75.5% at an OLR of 7.41 g COD/L/d in the thermophilic CSTR. The average VS removal in the mesophilic and thermophilic CSTR was maintained around 80% in the OLR range of 1.15 to 7.41 g COD/L/d. Similar results were reported by Wu et al. [9] in that the COD and VS removal was maintained at approximately 85% and 77% at an OLR of 7.41 g COD/L/d in FW and GTW co-digestion using a mesophilic CSTR. In our previous study, high COD removal of 87.5% was obtained in the thermophilic siphon-driven self-agitated anaerobic reactor (SDSAR) with an average OLR of 14.4 kg COD/m3/d, while scum occurred in the mesophilic SDSAR at an average OLR of 7.3 kg COD/m3/d [25]. Generally, shorter HRT often led to lower VS and COD reduction due to the limited contact time between microorganisms and substrates [26]. However, according to our studies, temperature and reactor type also play an important role in the anaerobic FW and GTW co-digestion. The highest average VS removal obtained in the CSFBR, ranging from 84.6% to 91.5%, in this study indicates that CSFBR provided a novel platform for organic waste degradation.
3.2.3. Effects of OLR on Fatty Acids Accumulation
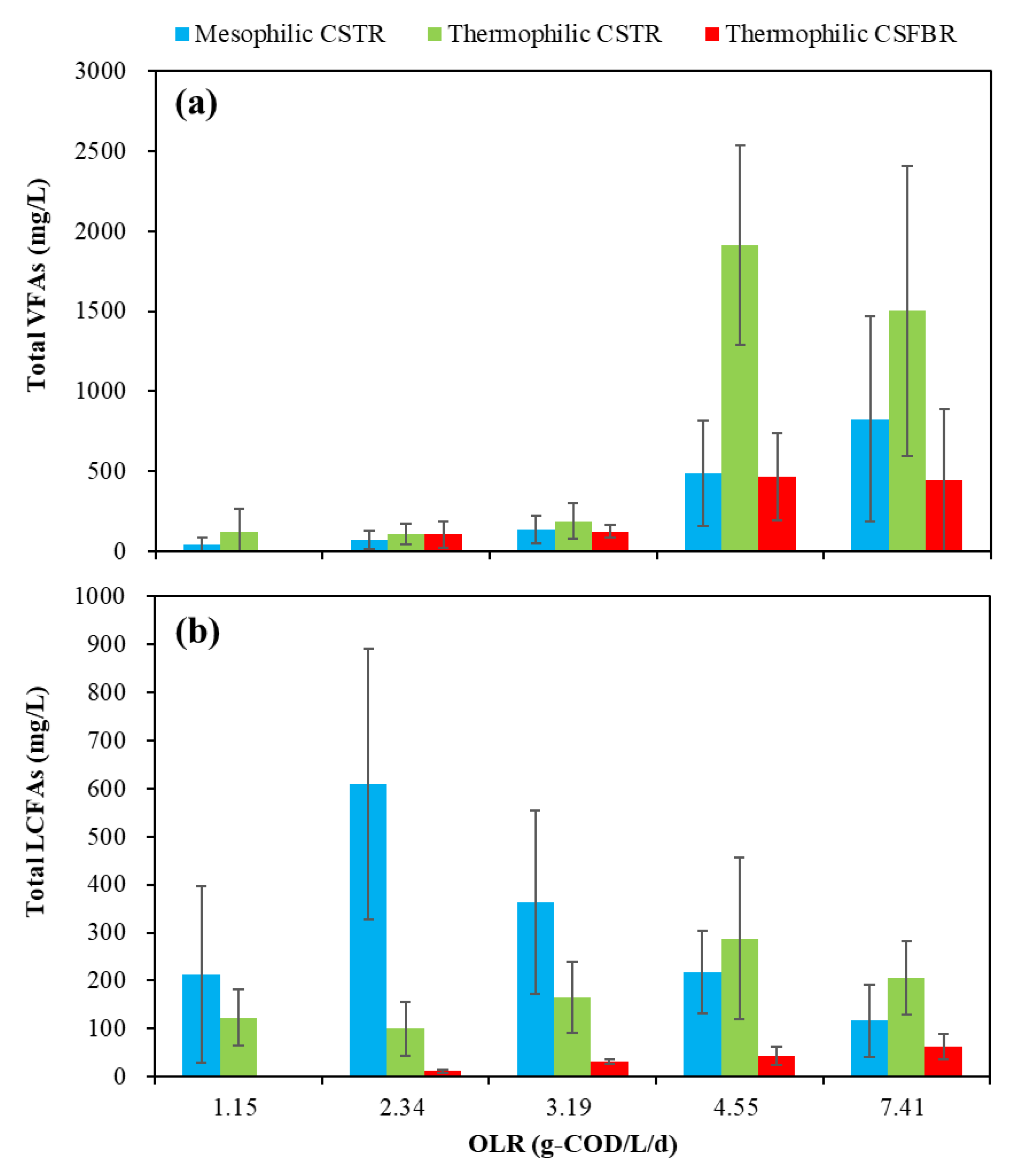
The effects of OLRs on the total VFAs and LCFAs remaining in the effluent are presented in Figure 4a,b.
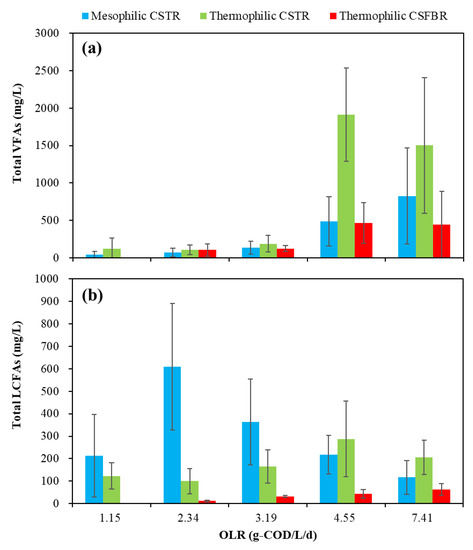
Figure 4.
Effects of OLRs on the VFAs and LCFAs production.
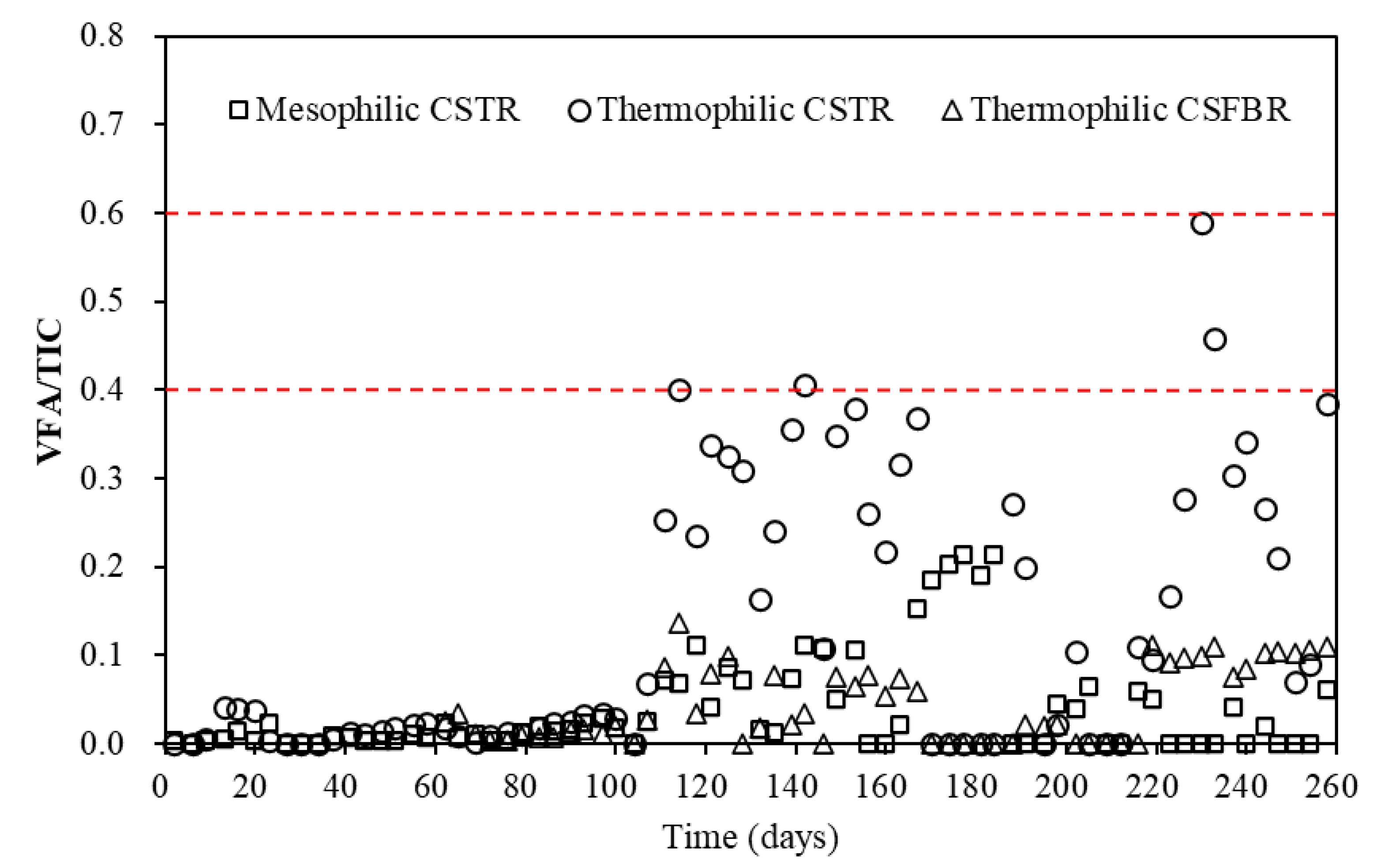
For the total VFAs (Figure 4a), with OLR in the range of 1.15 to 3.19 g COD/L/d, low total VFA concentrations of less than 400 mg/L was observed in all three reactors. However, with OLR increased to 4.55 g COD/L/d, the average total VFA concentration in the thermophilic CSTR significantly increased to 1913 mg/L. Meanwhile, the VFA concentration in the mesophilic CSTR and thermophilic CSFBR also increased to 484 and 466 mg/L. With OLR further increased to 7.41 g COD/L/d, the average total VFA concentration in the mesophilic CSTR increased to 826 mg/L, while that in the thermophilic CSFBR was maintained at a relatively low level of 446 mg/L. It was reported that under thermophilic conditions, endergonic reactions like acetogenesis are enhanced, while exergonic reactions like methanogenesis are diminished [27]. This explains why VFAs accumulated in the thermophilic CSTR. However, it is worth noting that the total VFA concentration obtained in the thermophilic CSFBR was below 1000 mg/L during the whole experimental period. This is likely because some VFAs were absorbed by the carrier materials filled in the CSFBR. It is well-acknowledged that the VFA concentration plays an important role in indicating the actual state of AD. In this study, the VFA concentrations in the three reactors were much lower than the reported values of 2500–3500 mg/L for achieving stable reactor performance in FW wet digestion [23]. In addition to VFA concentration, researchers normally use alkalinity or total inorganic carbon (TIC) to measure buffer capacity and VFA/TIC to evaluate stability of AD systems [28]. Wilches et al. [29] concluded that VFA/TIC values less than 0.3 implied stable process in AD. Lossie and Pütz [30] reported that VFA/TIC values between 0.2 and 0.6 indicated stable process without significant acidification risk. In this experiment, the VFA/TIC variations in the three anaerobic reactors are shown in Figure 5.
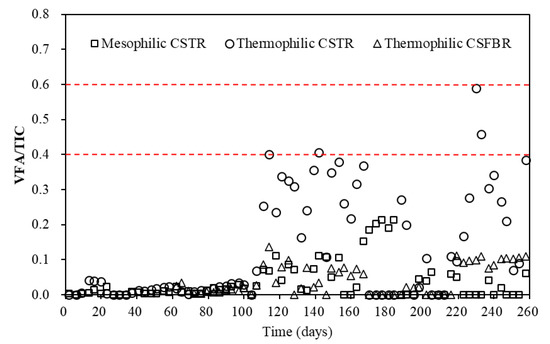
Figure 5.
VFA/TIC variations in three anaerobic reactors.
During the whole experimental period (day 1–258), the VFA/TIC ratios in the reactors were less than 0.6. Particularly, the VFA/TIC ratio in the CSFBR was less than 0.1, which means the anaerobic co-digestion of FW with GTW in this reactor is very stable and without any risk of acidification. However, the VFA/TIC ratio in the thermophilic CSTR once reached a high value of 0.58 at a high OLR of 7.41 g COD/L/d. The VFA/TIC ratio trend observed in the thermophilic CSTR was in accordance with a previous finding stating that the VFA/TIC value rose to more than 0.4 with the increase in VFA concentrations in two CSTRs [31]. Thus, further increase in OLR may possibly put the thermophilic CSTR at a risk of acidification and decrease the stability of the AD system. These results indicate that there was more stability in the CSFBR compared with traditional CSTR in the anaerobic co-digestion of FW with GTW.
Figure 4b also shows the variation of total LCFAs under different OLR conditions. The total average LCFA concentrations in three reactors were less than 1000 mg/L. The highest total average LCFA concentration of 609 mg/L was obtained in the mesophilic CSTR at an OLR of 2.34 g COD/L/d. However, this concentration decreased to 116 mg/L with OLR increased to 7.41 g COD/L/d. In the CSFBR, although the total LCFA concentration increased from average 11 mg/L to 63 mg/L with OLR increased from 1.15 to 7.41 g COD/L/d, it still kept the lowest total LCFAs among all three reactors. It is well-accepted that high concentration of LCFAs can inhibit methanogenesis during AD. Angelidaki and Ahring [32] reported a heavy inhibitory effect at 0.2 g oleate/L, and completely inhibited biogas production at 0.5 g oleate/L. Pereira et al. [33] reported the 50% inhibition of methanogenesis caused at different LCFA concentrations (70 ± 10 mg/L for oleate and 1100 ± 50 mg/L for palmitic acid). Nonetheless, it is worth noting that the LCFA concentrations in the CSFBR stay at a safe level that does not cause any inhibitory effect on the methanogenesis.
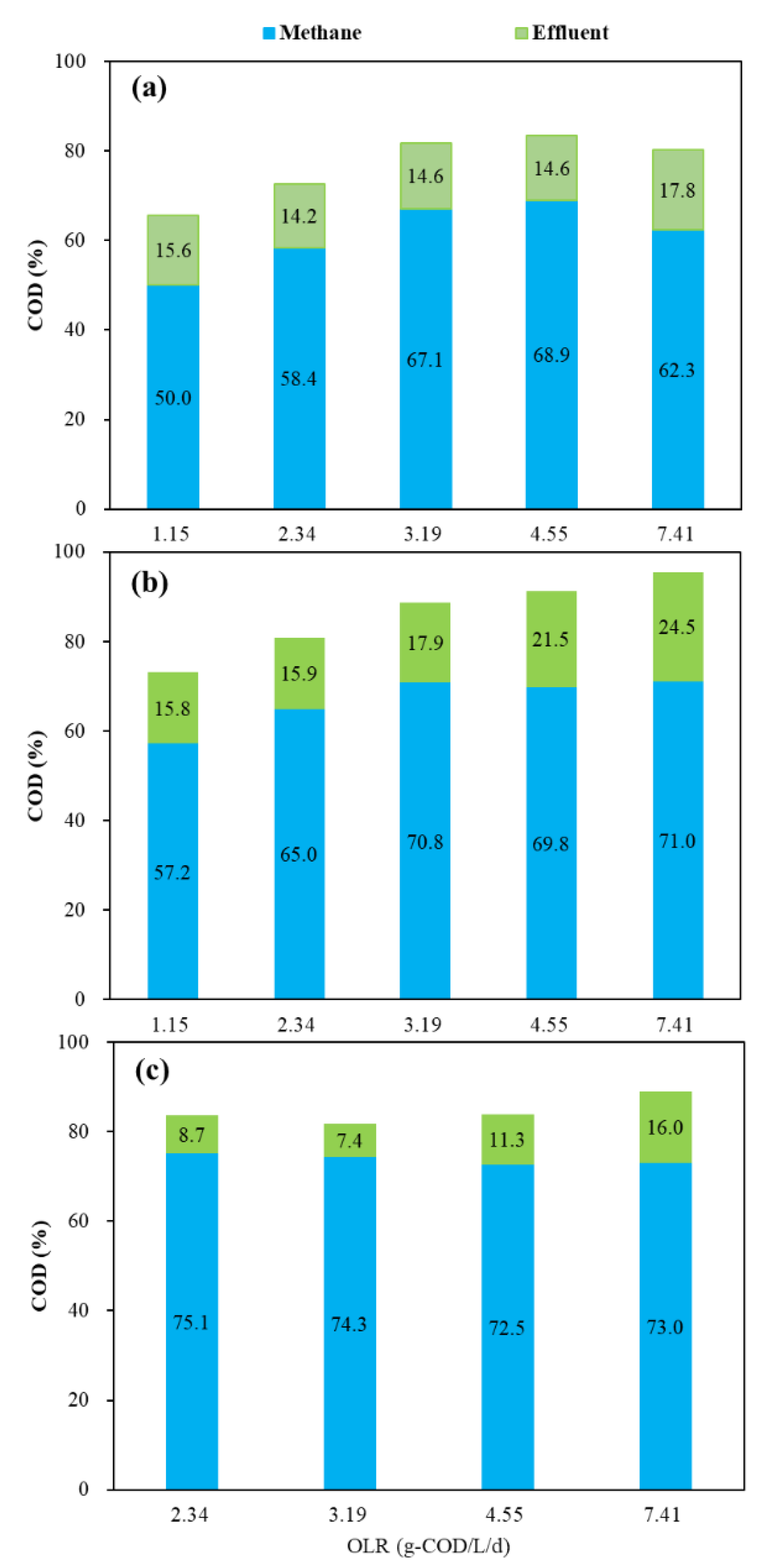
3.2.4. Effects of OLR on COD Balance during Anaerobic Digestion
Figure 6 shows the COD balance of the three reactors under different OLR conditions. At an OLR of 1.15 g COD/L/d, only around 50% of the influent COD was converted into methane in both mesophilic and thermophilic CSTRs. With OLR increased to 4.55 g COD/L/d, this proportion increased to around 70%. However, at an OLR of 7.41 g COD/L/d, only 62.3% of the influent COD was converted into methane in the mesophilic CSTR. On the contrary, the conversion of influent COD to methane in the thermophilic CSFBR was more than 72% at an OLR of 7.41 g COD/L/d. From COD conversion analysis, CSFBR showed high efficiency for co-digestion of FW and GTW at high organic loads.
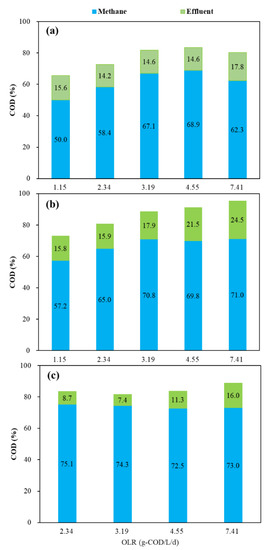
Figure 6.
COD balance under different OLR conditions (a) mesophilic CSTR, (b) thermophilic CSTR, (c) thermophilic CSFBR.
The present study proved that the CSFBR has obvious advantages in maintaining the process stability in anaerobic co-digestion of FW and GTW compared with CSTR. Highest methane yield of 496 mL CH4/gVSadded and VS removal of 91.5% were obtained in the thermophilic CSFBR with OLR increased from 3.19 to 7.41 g COD/L/d. All these experimental results strongly suggest that digester improvement is a feasible alternative for anaerobic co-digestion of FW and GTW. In the meantime, further studies are needed to better understand the interactions between microorganisms and filters within the CSFBR.
4. Conclusions
A continuous experiment was performed to study the stability and treatment efficiency of a CSFBR. It proved that the CSFBR has obvious advantages in anaerobic co-digestion of FW and GTW compared with CSTR. Highest methane yield of 496 mL CH4/gVSadded and VS removal of 91.5% were obtained in the thermophilic CSFBR with OLR increased from 3.19 to 7.41 g COD/L/d. In addition, lower VFA concentration (<1000 mg/L), VFA/TIC ratio (<0.1), and LCFA concentrations (<100 mg/L) were also obtained in the thermophilic CSFBR as compared with the mesophilic and thermophilic CSTRs. All these results suggest that CSFBR has a better performance in process stability and treatment efficiency than the traditional CSTR. This study provides an alternative option to enhancing energy efficiency in the anaerobic co-digestion system of FW with GTW. Meanwhile, further studies are needed to better understand the interactions between microorganisms and filters within the CSFBR.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.H. and T.K.; methodology, Y.H.; software, H.M.; validation, Y.H. and J.W.; formal analysis, H.M.; investigation, H.M.; resources, T.K.; data curation, K.-Q.X.; writing—original draft, Y.H.; writing—review and editing, T.K.; visualization, J.W. and K.-Q.X.; supervision, T.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the JSPS KAKENHI [Grant Number 20K04764]; the National Natural Science Foundation of China [Grant Number 52170037].
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest to disclose.
References
- Capson-Tojo, G.; Trably, E.; Rouez, M.; Crest, M.; Steyer, J.-P.; Delgenès, J.-P.; Escudié, R. Dry anaerobic digestion of food waste and cardboard at different substrate loads, solid contents and co-digestion proportions. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 233, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thi, N.B.D.; Kumar, G.; Lin, C.-Y. An overview of food waste management in developing countries: Current status and future perspective. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 157, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, F.; Li, Y.; Ge, X.; Yang, L.; Li, Y. Anaerobic digestion of food waste—Challenges and opportunities. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 247, 1047–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziels, R.M.; Sousa, D.Z.; Stensel, H.D.; Beck, D.A.C. DNA-SIP based genome-centric metagenomics identifies key long-chain fatty acid-degrading populations in anaerobic digesters with different feeding frequencies. ISME J. 2018, 12, 112–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.; Hu, Y.; Li, S.; Huang, J.; Nie, Q.; Zhao, H.; Tang, J. Simultaneous dark fermentative hydrogen and ethanol production from waste bread in a mixed packed tank reactor. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 141, 608–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schott, A.B.S.; Andersson, T. Food waste minimization from a life-cycle perspective. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 147, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Peng, X.; Wang, X.; Wu, D. Anaerobic digestion of food waste: A review focusing on process stability. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 248, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, T.; Kuramochi, H.; Xu, K.-Q. Variable oil properties and biomethane production of grease trap waste derived from different resources. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2017, 119, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.-J.; Kobayashi, T.; Kuramochi, H.; Li, Y.-Y.; Xu, K.-Q.; Lv, Y. High loading anaerobic co-digestion of food waste and grease trap waste: Determination of the limit and lipid/long chain fatty acid conversion. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 338, 422–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salama, E.-S.; Saha, S.; Kurade, M.B.; Dev, S.; Chang, S.W.; Jeon, B.-H. Recent trends in anaerobic co-digestion: Fat, oil, and grease (FOG) for enhanced biomethanation. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2019, 70, 22–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvestre, G.; Rodríguez-Abalde, A.; Fernández, B.; Flotats, X.; Bonmatí, A. Biomass adaptation over anaerobic co-digestion of sewage sludge and trapped grease waste. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 6830–6836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves, L.; Oliveira, R.; Alves, M. Fate of LCFA in the co-digestion of cow manure, food waste and discontinuous addition of oil. Water Res. 2009, 43, 5142–5150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amha, Y.M.; Sinha, P.; Lagman, J.; Gregori, M.; Smith, A.L. Elucidating microbial community adaptation to anaerobic co-digestion of fats, oils, and grease and food waste. Water Res. 2017, 123, 227–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Kobayashi, T.; Zhen, G.; Shi, C.; Xu, K.-Q. Effects of lipid concentration on anaerobic co-digestion of food waste and grease waste in a thermophilic siphon-driven self-agitated anaerobic reactor. Biotechnol. Rep. 2018, 9, e00269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, T.; Kuramochi, H.; Xu, K.-Q.; Maeda, K. Simple solvatochromic spectroscopic quantification of long-chain fatty acids for biological toxicity assay in biogas plants. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 27, 17596–17606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabouris, J.C.; Tezel, U.; Pavlostathis, S.G.; Engelmann, M.; Todd, A.C.; Gillette, R.A. The Anaerobic Biodegradability of Municipal Sludge and Fat, Oil, and Grease at Mesophilic Conditions. Water Environ. Res. 2008, 80, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Yu, M.; Wu, C.; Wang, Q.; Gao, M.; Huang, Q.; Liu, Y. A comprehensive review on food waste anaerobic digestion: Research updates and tendencies. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 247, 1069–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, P.C.; de Toledo, R.A.; Shim, H. Anaerobic co-digestion of food waste and domestic wastewater—Effect of intermittent feeding on short and long chain fatty acids accumulation. Renew. Energy 2018, 124, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, M.M.; Pereira, M.A.; Sousa, D.Z.; Cavaleiro, A.; Picavet, M.; Smidt, H.; Stams, A. Waste lipids to energy: How to optimize methane production from long-chain fatty acids (LCFA). Microb. Biotechnol. 2009, 2, 538–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakourifar, N.; Krisa, D.; Eskicioglu, C. Anaerobic co-digestion of municipal waste sludge with grease trap waste mixture: Point of process failure determination. Renew. Energy 2020, 154, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APHA. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 22nd ed.; APHA: Washington, DC, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Bligh, E.G.; Dyer, W.J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can. J. Biochem. Physiol. 1959, 37, 911–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martín-González, L.; Font, X.; Vicent, T. Alkalinity ratios to identify process imbalances in anaerobic digesters treating source-sorted organic fraction of municipal wastes. Biochem. Eng. J. 2013, 76, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagao, N.; Tajima, N.; Kawai, M.; Niwa, C.; Kurosawa, N.; Matsuyama, T.; Yusoff, F.M.; Toda, T. Maximum organic loading rate for the single-stage wet anaerobic digestion of food waste. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 118, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Kobayashi, T.; Qi, W.; Oshibe, H.; Xu, K.-Q. Effect of temperature and organic loading rate on siphon-driven self-agitated anaerobic digestion performance for food waste treatment. Waste Manag. 2018, 74, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidsson, Å.; Lövstedt, C.; Jansen, J.L.C.; Gruvberger, C.; Aspegren, H. Co-digestion of grease trap sludge and sewage sludge. Waste Manag. 2008, 28, 986–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, G.; Yang, B.; Dong, M.; Zhu, R.; Yin, F.; Zhao, X.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, W.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, W.; et al. The effect of temperature on the microbial communities of peak biogas production in batch biogas reactors. Renew. Energy 2018, 123, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awe, O.W.; Lu, J.; Wu, S.; Zhao, Y.; Nzihou, A.; Lyczko, N.; Minh, D.P. Effect of Oil Content on Biogas Production, Process Performance and Stability of Food Waste Anaerobic Digestion. Waste Biomass-Valorization 2018, 9, 2295–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilches, C.; Vaske, M.; Hartmann, K.; Nelles, M. Representative Sampling Implementation in Online VFA/TIC Monitoring for Anaerobic Digestion. Energies 2019, 12, 1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lossie, U.; Pütz, P. Targeted Control of Biogas Plants with the Help of FOS/TAC. Pract Rep. Hach-Lange 2008. Available online: https://bg.hach.com/asset-get.download.jsa?id=25593611361 (accessed on 25 October 2022).
- Raposo, F.; De la Rubia, M.A.; Fernández-Cegrí, V.; Borja, R. Anaerobic digestion of solid organic substrates in batch mode: An overview relating to methane yields and experimental procedures. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2012, 16, 861–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelidaki, I.; Ahring, B. Effects of free long-chain fatty acids on thermophilic anaerobic digestion. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1992, 37, 808–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, M.A.; Pires, O.; Mota, M.; Alves, M. Anaerobic biodegradation of oleic and palmitic acids: Evidence of mass transfer limitations caused by long chain fatty acid accumulation onto the anaerobic sludge. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2005, 92, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).