Abstract
The microgrid (MG) is a popular concept to handle the high penetration of distributed energy resources, such as renewable and energy storage systems, into electric grids. However, the integration of inverter-interfaced distributed generation units (IIDGs) imposes control and protection challenges. Fault identification, classification and isolation are major concerns with IIDGs-based active MGs where IIDGs reveal arbitrary impedance and thus different fault characteristics. Moreover, bidirectional complex power flow creates extra difficulties for fault analysis. This makes the conventional methods inefficient, and a new paradigm in protection schemes is needed for IIDGs-dominated MGs. In this paper, a machine-learning (ML)-based protection technique is developed for IIDG-based AC MGs by extracting unique and novel features for detecting and classifying symmetrical and unsymmetrical faults. Different signals, namely, 400 samples, for wide variations in operating conditions of an MG are obtained through electromagnetic transient simulations in DIgSILENT PowerFactory. After retrieving and pre-processing the signals, 10 different feature extraction techniques, including new peaks metric and max factor, are applied to obtain 100 features. They are ranked using the Kruskal–Wallis H-Test to identify the best performing features, apart from estimating predictor importance for ensemble ML classification. The top 18 features are used as input to train 35 classification learners. Random Forest (RF) outperformed all other ML classifiers for fault detection and fault type classification with faulted phase identification. Compared to previous methods, the results show better performance of the proposed method.
1. Introduction
New DG (Distributed Generation) technologies are being developed, and more DGs are entering the distribution system as the conventional power grid approaches its maximum capacity and concerns about the glasshouse gas emissions by traditional power plants grow. This has allowed microgrids to emerge as an essential element of the modern distribution system. While it offers many advantages, there are a number of concerns to be resolved, among which fault protection is a major challenge. Protection devices in existing DN (Distribution network) consist of non-directional overcurrent (OC) protective relays, reclosers, fuses and sectionalisers [1] and are mostly radial. The protection schemes were initially designed for the unidirectional flow of power, but with the increase in bidirectional power flow, coordination between fault protection devices can be compromised [2], especially when the microgrid is in an autonomous (AUTO) mode of operation. Additionally, achieving correct selectivity and sensitivity poses a great challenge in the practical application of microgrids [3]. As a result, conventional protection techniques will not offer satisfactory protection in the future. Moreover, future intelligent grids will require precise single- and double-pole tripping to boost overall resilience and economic benefits. This requires correct fault type classification (FTC) and faulted phase (FP) identification to avoid tripping of healthy phases in fault events [4].
A common tool for analysing non-stationary, noisy, aperiodic, transient and intermittent signals is wavelet transform (WT). WT can examine the signal in time-frequency domains which give it superiority over Fourier and short-time Fourier transform [5]. WT unhides features within the original signal for detailed analysis. Additionally, applying machine learning (ML) to detect and classify faults offers a promising solution.
To detect microgrid islanding and fault disturbances, refs. [6,7] proposed methods based on WT. Both studies used Daubechies (dB) as the mother wavelet. The former considered only the negative-sequence component, dB5 and line-to-line (LL) faults, while the latter considered the positive- and zero-sequence component, dB10 and double-line-to-ground (LLG) faults. After extracting the signal, discrete wavelet transform (DWT) is applied to decompose it. By detecting variations in different parameters and comparing them to the pre-fault or threshold values, it is claimed that islanded mode and power quality issues can be identified. Furthermore, a DT-based protection scheme is proposed in [8] for FD and FTC. For FE, Discrete Fourier transform is used to extract features from voltage and current phasors.
On the other hand, ML-based microgrid fault protection methods are proposed in [9,10]. Wavelet Packet Transform and Multiresolution decomposition of WT are respectively used to pre-process the current and voltage signals to extract features based on negative sequence components and total harmonics distortion (THD) to train and evaluate the ML classifier. Likewise, a microgrid fault identification and classification method is proposed in [11], which processes line current using Haar wavelet to generate various coefficients. Detail coefficient d3 was selected to calculate different features to train the decision tree (DT) to detect and classify faults. Additionally, a Brownboost (BB) ensemble approach is used for FD and FTC in [12]. Hilbert–Huang transform is adopted for feature extraction from signals. Signals used are the current differential between the two ends of the line.
Similarly, a combination of Maximal Overlap Discrete Wavelet Transform and Extreme Gradient Boost is applied for FD and FTC in [13]. FejerKorovkin is used as the mother wavelet to extract features from the three-phase current and its zero-sequence current component. Further, ref. [14] proposed a technique for identifying various fault types in a microgrid by applying DWT to calculate the wavelet coefficients that are fed to different ML classifiers. Conversely, a high impedance fault detection approach using empirical wavelet transform is proposed in [15]. Different time-frequency components are first acquired using the WT to decompose the differential coefficient of wavelet energy. Feature components with the highest permutation entropy are then selected, which are used to identify high impedance faults.
In ref. [16], the authors used actual fault signals instead of normalising and extracting features. Although this gives high efficiency, a significant drawback of using the raw signals instead of transforming them into numerical features is that the ML model becomes prone to overfitting. Similarly, using a large number of features increases processing time. Hence, there is a need to extract unique features that result in high accuracy.
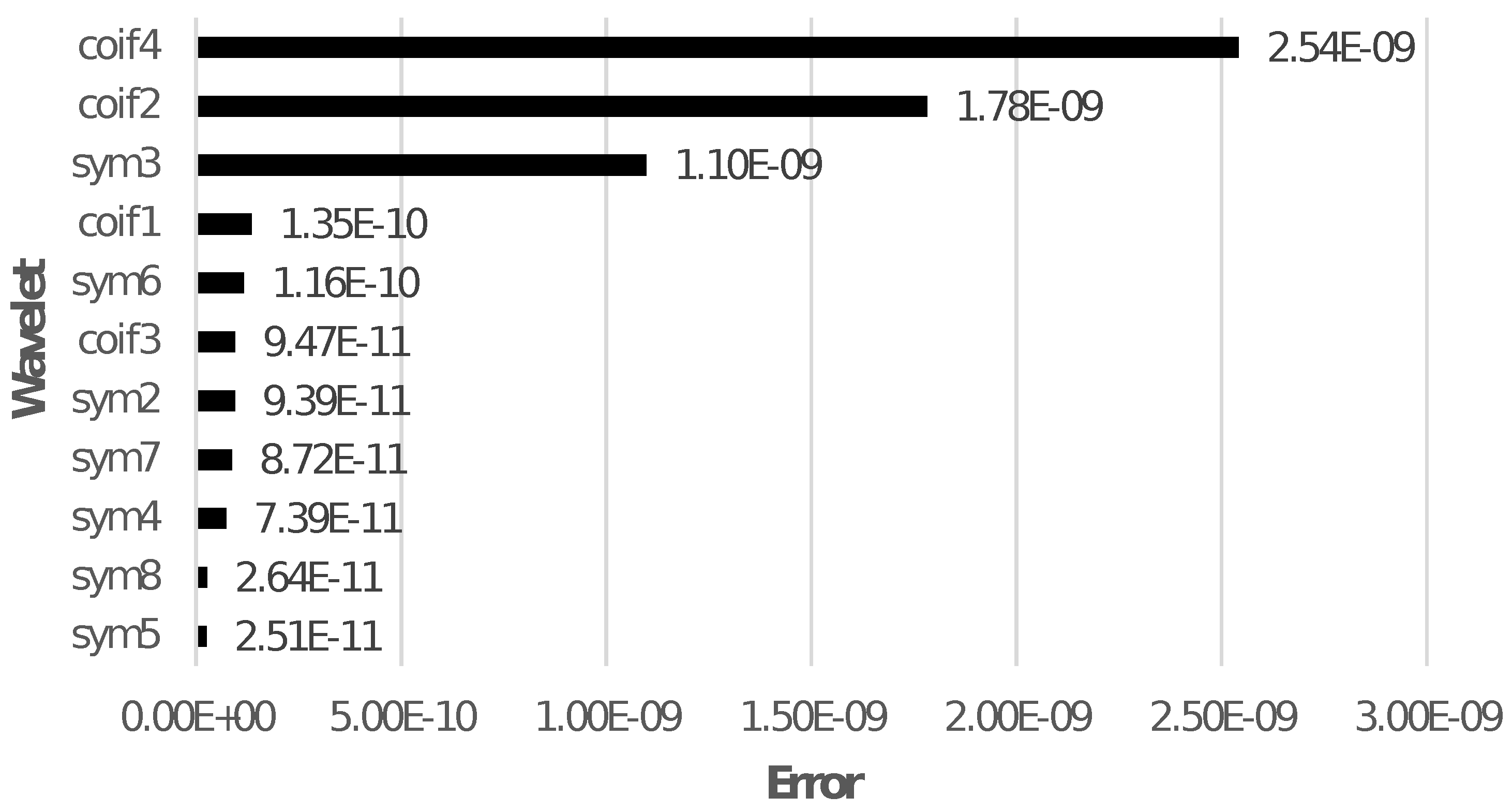
From the literature, it can be noticed that WT is commonly used for feature extraction. The main shortcoming of protection schemes using WT for feature extraction for ML is selecting an optimal mother wavelet basis function. Applying various mother wavelets to the signal may produce a variety of outcomes [17,18,19] that can cause protection system misoperation. Additionally, the type of chosen mother wavelet significantly impacts DWT, producing quite varied outcomes. Moreover, fault inception angle and sampling rate affect DWT response. As a result, most DWT-based protection techniques or derived features are efficient for specific parameters and cannot be generalised without using a different mother wavelet [20]. Figure 1 demonstrates the WT shortcoming by comparing the root-mean-square error (RMSE) for the reconstructed current signals using all the approximate and detail coefficients of a few wavelets for a low-resistance LG fault on phase A.
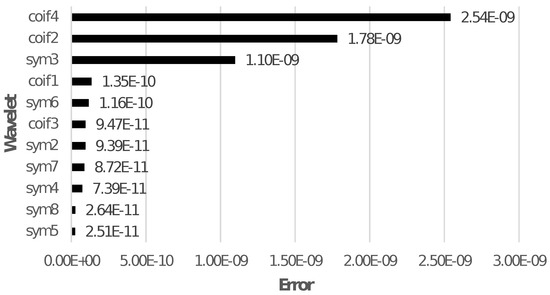
Figure 1.
RMSE for the reconstructed signals using all the coefficients of different wavelets.
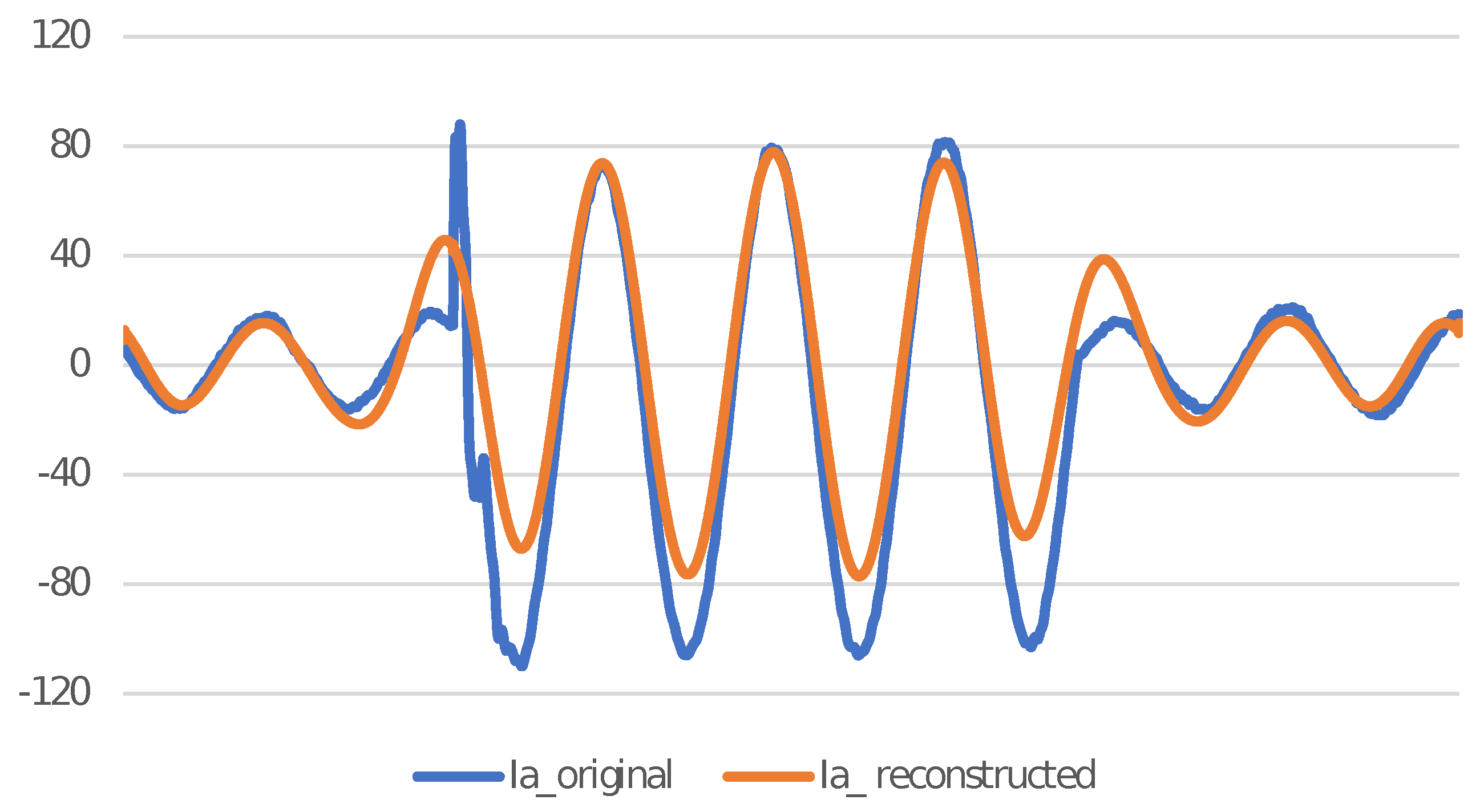
The RMSE seems to be negligible when all the approximate and detail coefficients are used to reconstruct the signal, but it is not feasible to use all the coefficients. When only one of the detail level coefficients corresponding to maximum relative energy is used to reconstruct the signal, there is a significant change in RMSE for different wavelets. Figure 2 shows a comparison of Level 9 detail coefficient of a current signal and reconstructed signal for a low resistance LG fault on phase A using Symlets 5 () as MW.
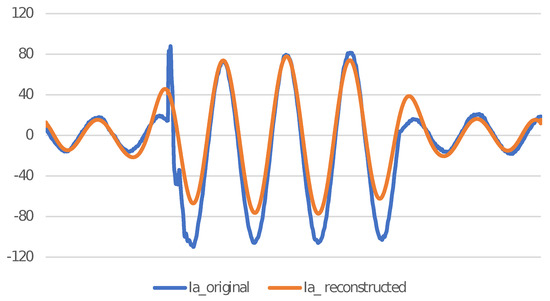
Figure 2.
and reconstructed signal using Level 9 detail coefficient for a low resistance LG fault on phase A.
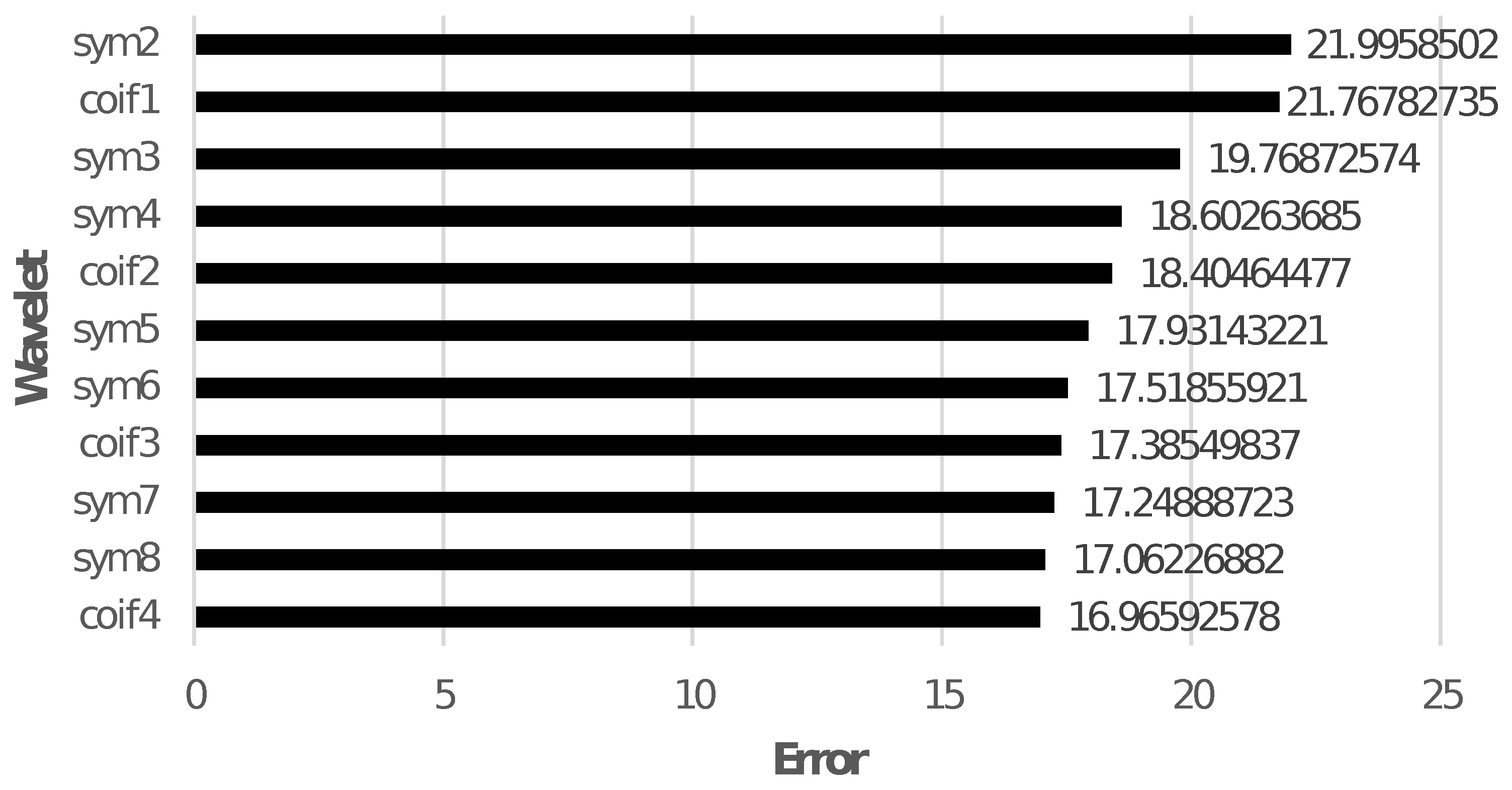
When only Level 9 detail coefficient is used to reconstruct the signal, comparison of RMSE for different wavelets is shown in Figure 3.
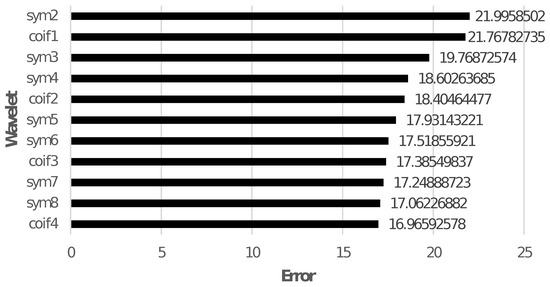
Figure 3.
RMSE for the reconstructed signals using Level 9 detail coefficient of different wavelets.
Unlike most researchers who have used WT to extract features, this research proposes new feature extraction methods and examines dimensionality reduction techniques, statistical tools, and impulsive and signal processing metrics to extract unique features for ML classifiers, to overcome the challenges associated with the selection of the optimal mother wavelet.
The most common type of asymmetrical faults is a line-to-ground fault (LG), accounting for 65 to 70% of all faults in an electric power system, followed by LLG faults that occur around 15 to 20% of the time, while LL faults make up 5 to 10% of all faults [21]. Symmetrical faults (LLL) are rare but the most severe of all electrical faults [22]. All these different types of faults are detected and classified in this paper, which is an extension of the research work published in [23].
Many improvements have been made. Previously, only LG faults were classified for faulted phase and variations in fault resistance. Nine signals, line-to-line voltage, phase voltage and short-circuit currents for phases A, B and C were used. Although these signals were enough to classify LG faults, they were not enough for FD. Since there was only LG fault classification, no data was collected to detect the fault and no-fault conditions. A small dataset was used with manual parameter tuning, which can not match the automated optimisation, using every possible variation in order to improve performance. Additionally, features were selected using an iterative process instead of using FS techniques. The main contributions of this paper are:
- A large amount of data is collected for varying fault conditions and no-fault cases. A new 400 × 500 × 10 microgrid fault dataset is built for 400 scenarios, each with 500 samples for 10 signals.
- Two new feature extraction (FE) techniques, Peaks Metric and Max Factor, are formulated and applied.
- Eight other FE methods, most of which have not been used for microgrid fault detection and classification, are investigated for suitability.
- A new 400 × 10 × 10 dataset with unique features for fault detection and classification in AC microgrids is built for 400 cases, 10 FE techniques and 10 signals.
- Various feature ranking techniques have been used to reduce the number of predictors. 35 ML algorithms with optimal hyperparameters have been trained to find the models with the highest possible accuracy for the fewest possible predictors.
- Validation of the trained models is carried out by using unseen data for making predictions.
After the introduction, Section 2 describes the test microgrid model used to record signals through electromagnetic transient (EMT) simulations for wide variations in operating conditions. Different techniques, including new factors proposed for extracting features, are presented in Section 3. Section 4 presents the methods used for feature selection. The proposed method for detecting and classifying faults is described in Section 5. The results and analysis are summarised in Section 6. Section 7 presents the conclusion and future work.
2. Test Microgrid and Simulations
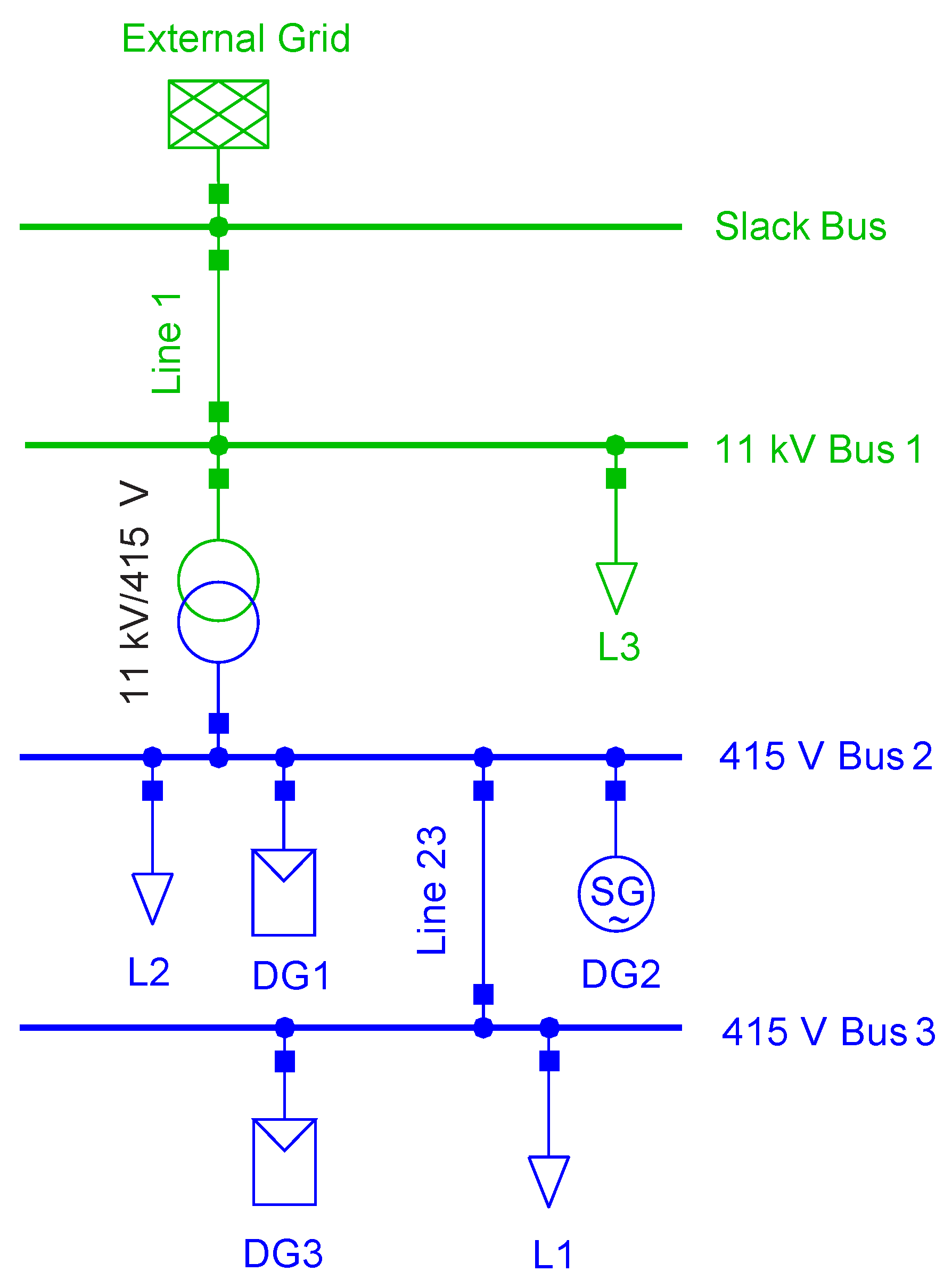
The low voltage AC test microgrid simulated in DIgSILENT PowerFactory shown in Figure 4 is a part of a radial distribution system operating at 415 V, 50 Hz. It is connected to the main grid through an 11 kV/415 V transformer. There are three DG sources, two photovoltaic (PV) systems, which are inverter-interfaced distributed generators (IIDGs) and a synchronous generator-based microturbine to maintain microgrid stability in AUTO mode by providing sufficient damping component and rotational inertia. A commercial load is connected to Bus 1, and domestic loads are connected to Bus 2 and 3. Bus 2 is the point of common coupling (PCC). The circuit breaker after the transformer is used for switching between the two microgrid operational modes.
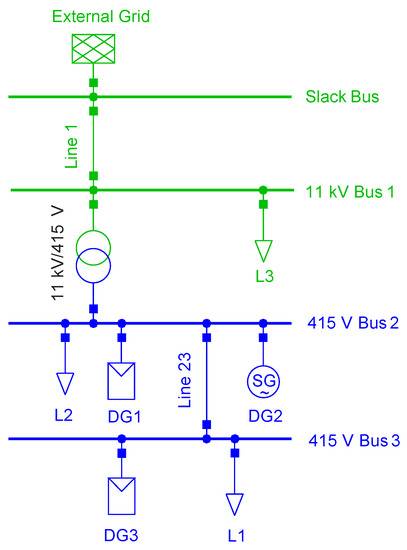
Figure 4.
Test Microgrid.
Data is recorded through EMT simulations for 400 cases. For every case, simulations are carried out for 0.05 s with a step size of 0.0001 s to obtain 500 observations for each of the 10 signals. The signals include three phase voltage in kV, three phase current and short-circuit current in kA and frequency in Hz.
Simulations are carried out for ten faults to collect data for fault detection (FD) and FTC with FP. Apart from variations in fault resistance, reactance, inception angles, number of cycles and locations, all faults are simulated for grid-connected (GC) and AUTO mode to identify the variations in fault current level and other signals. Three cases are used for the LG faults: bolted fault with 0 resistance, low resistance ground fault with 5 resistance, and high resistance fault with a value of 400 . For all other faults, the first case (C1) has no fault resistance or reactance. The second case (C2) has a resistance of 0.1 and a 0.001 reactance. The third and last case (C3) has a resistance of 0.1 and a comparatively greater reactance of 1 .
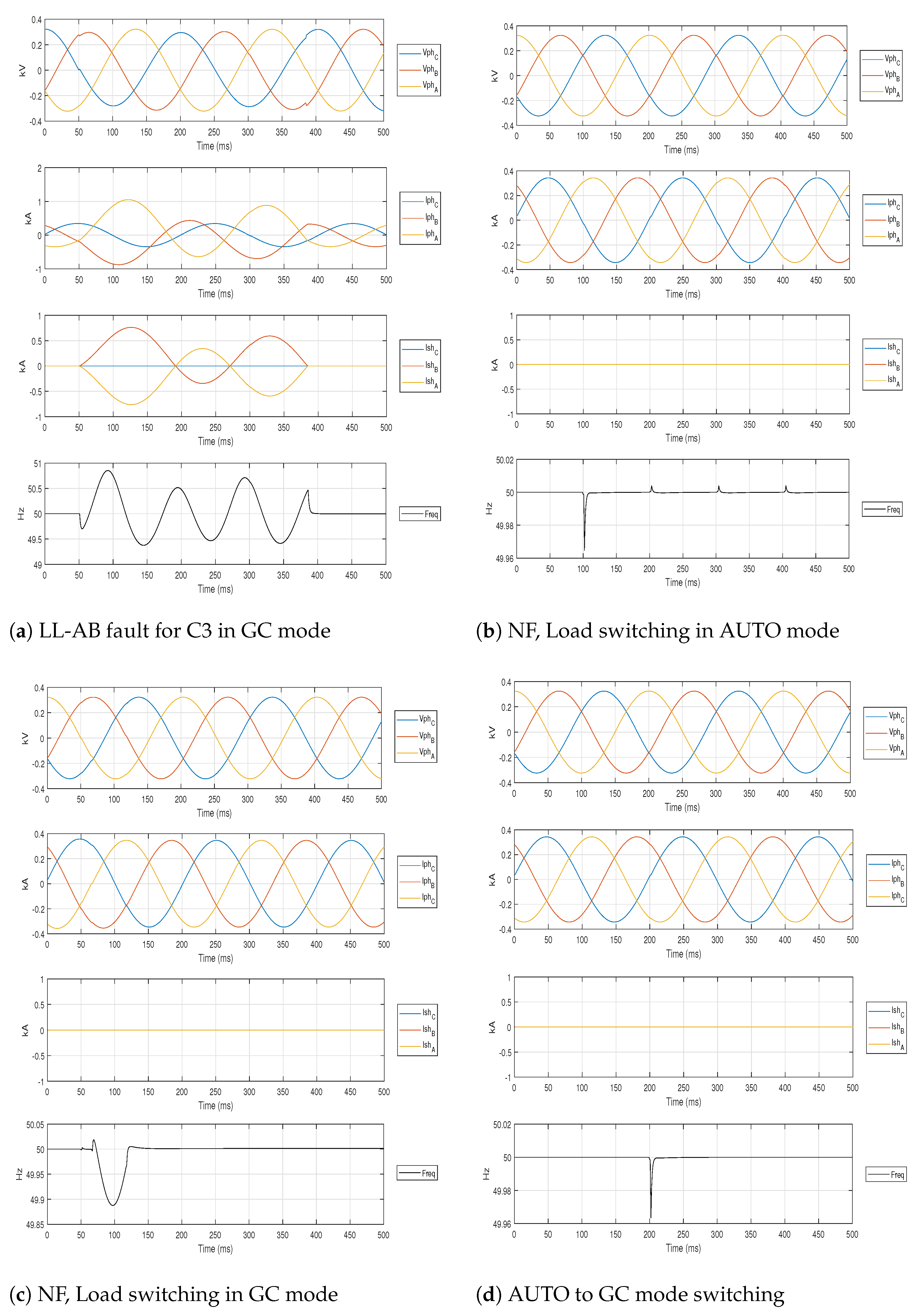
Waveforms of 10 signals: , , and for a fault and three NF cases are shown in Figure 5. Waveforms for LL-AB fault for case C3 in GC mode is shown in Figure 5a. The NF case of loads switching on and off in AUTO mode is shown in Figure 5b; the NF case of load switching off in GC mode is shown in Figure 5c; and the NF case of MG switching from AUTO to GC mode is shown in Figure 5d.
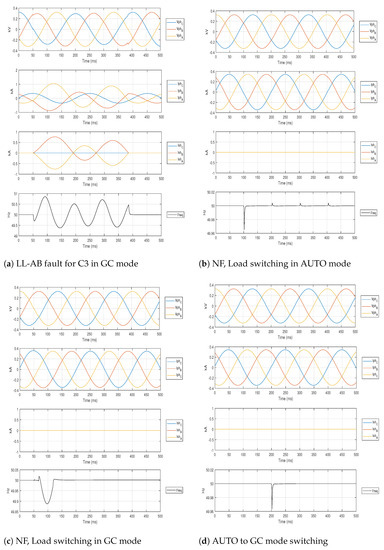
Figure 5.
Ten signals for LL-AB Fault and NF conditions.
For FD, equal sets for different faults are categorised as Fault, while various cases of normal operation, load switching and grig switching are classified as No Fault (NF). On the other hand, FTC data has been organised to classify the fault type and FP. Data for the NF conditions include simulations of connecting and disconnecting 5 kW, 50 kW and 200 kW load in both modes, switching from GC to AUTO and vice versa with and without load switching. Additionally, simulations without any fault, load or grid switching are also included to differentiate between a fault and NF conditions. Data collected for symmetrical faults include LLL, LLLN and LLLNG faults. Due to close similarity in collected signals, all cases of symmetrical faults are categorised as LLL faults.
3. Feature Extraction
Feature extraction (FE) involves transforming raw data into numerical features while retaining the information in the original data. This helps in preventing overfitting and gives better results instead of applying ML to the raw data. Two novel FE techniques, Peaks Metric and Max Factor are proposed and applied in this research. Additionally, the suitability of using Standard Deviation, First and Second Principal Components [23], Total Harmonic Distortion [10], Kurtosis, Crest Factor, Shape Factor and Skewness [24,25] to extract useful features is investigated. A total of 100 unique features are obtained. Kurtosis, Crest Factor, Shape Factor and Skewness are commonly used FE techniques for bearing fault diagnosis but have not been applied before to detect and classify faults in an AC microgrid to the best of the author’s knowledge.
Moreover, using Principal Component Analysis to detect and classify AC microgrid faults is also not common and was previously proposed by the authors of this paper.
3.1. Standard Deviation
The standard deviation , for a variable vector x composed of N scalar observations is defined as
where is the mean of x:
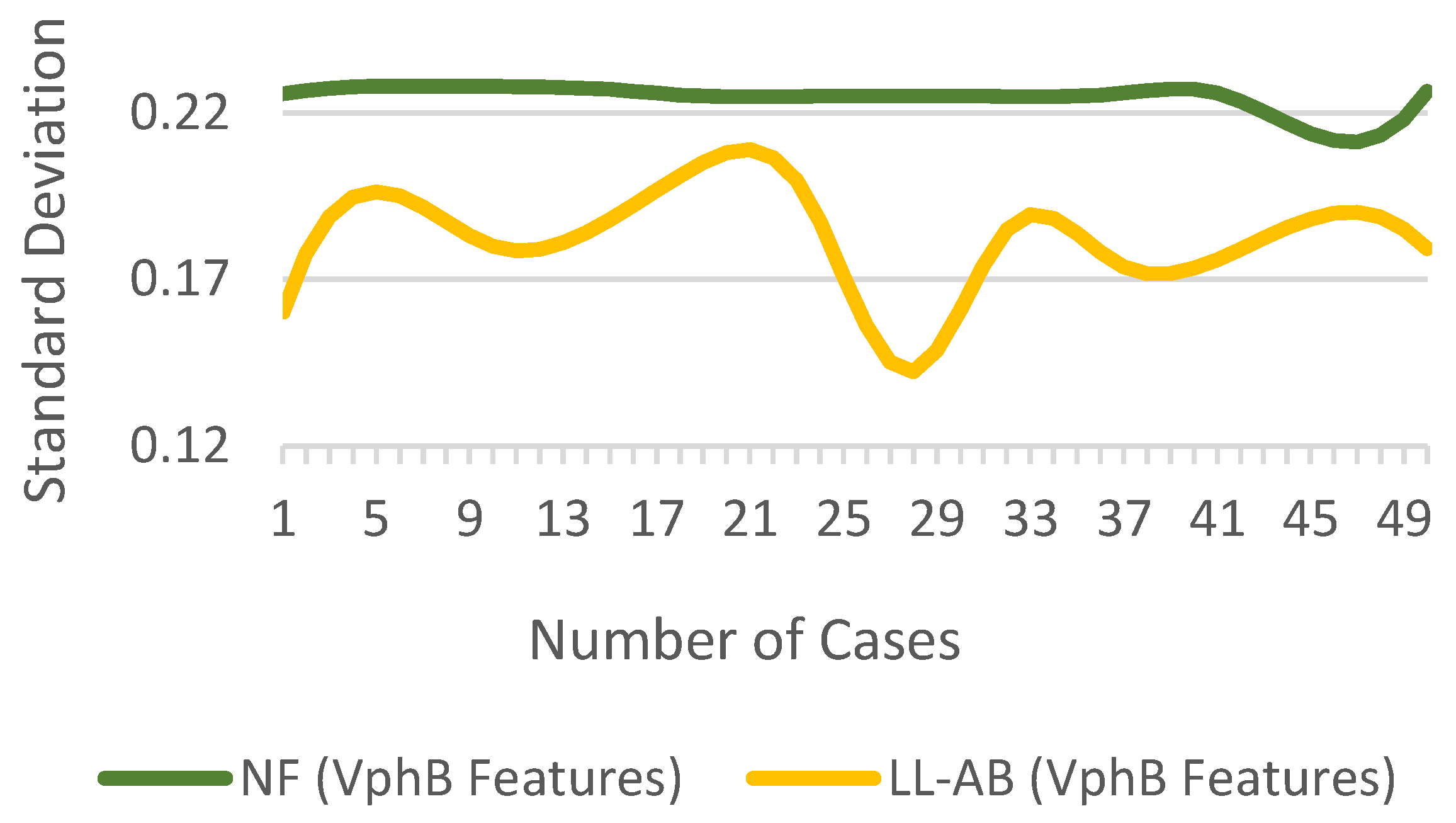
The variation in of for random cases of NF and LL-AB fault is shown in Figure 6. There is a notable difference between fault and NF features, which is desired for training ML classifiers. If the features also called predictors are very closely distributed, the probability of misclassification increases.
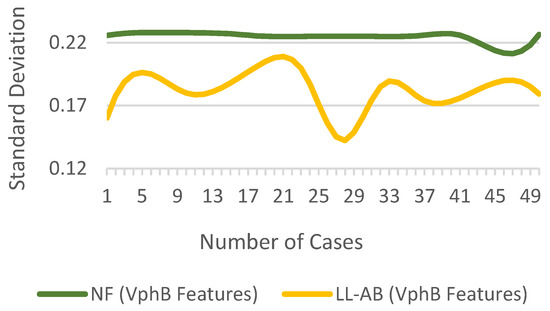
Figure 6.
of for NF and fault cases.
3.2. Peaks Metric
Peaks Metric is a novel metric proposed in this research and is defined as the ratio of the mean of the peak values in the signal to the mean of the signal.
where
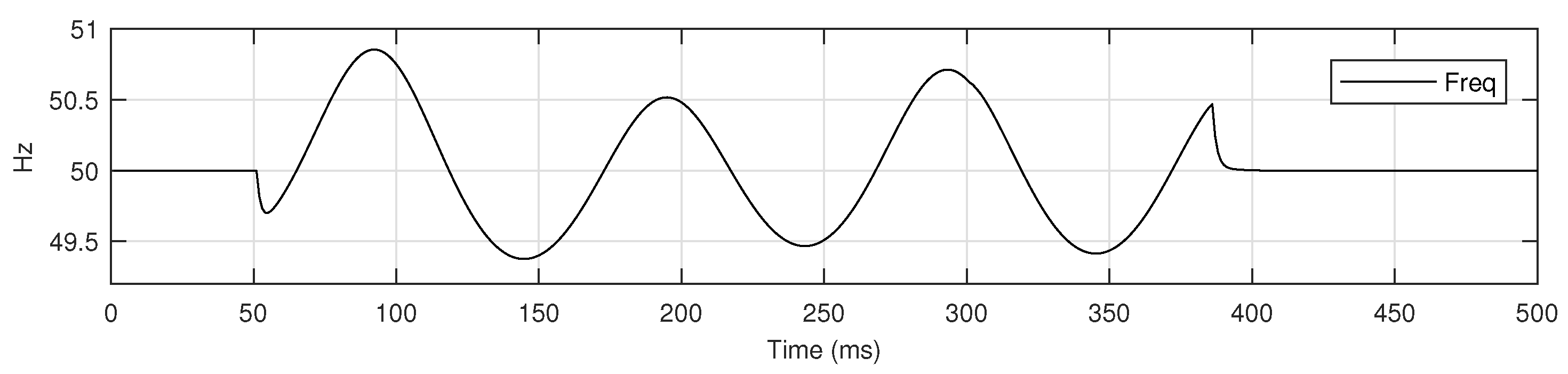
For C3, LL-AB fault in GC mode, the deviation in is shown in Figure 7.
Figure 7.
deviation for C3, LL-AB fault in GC mode.
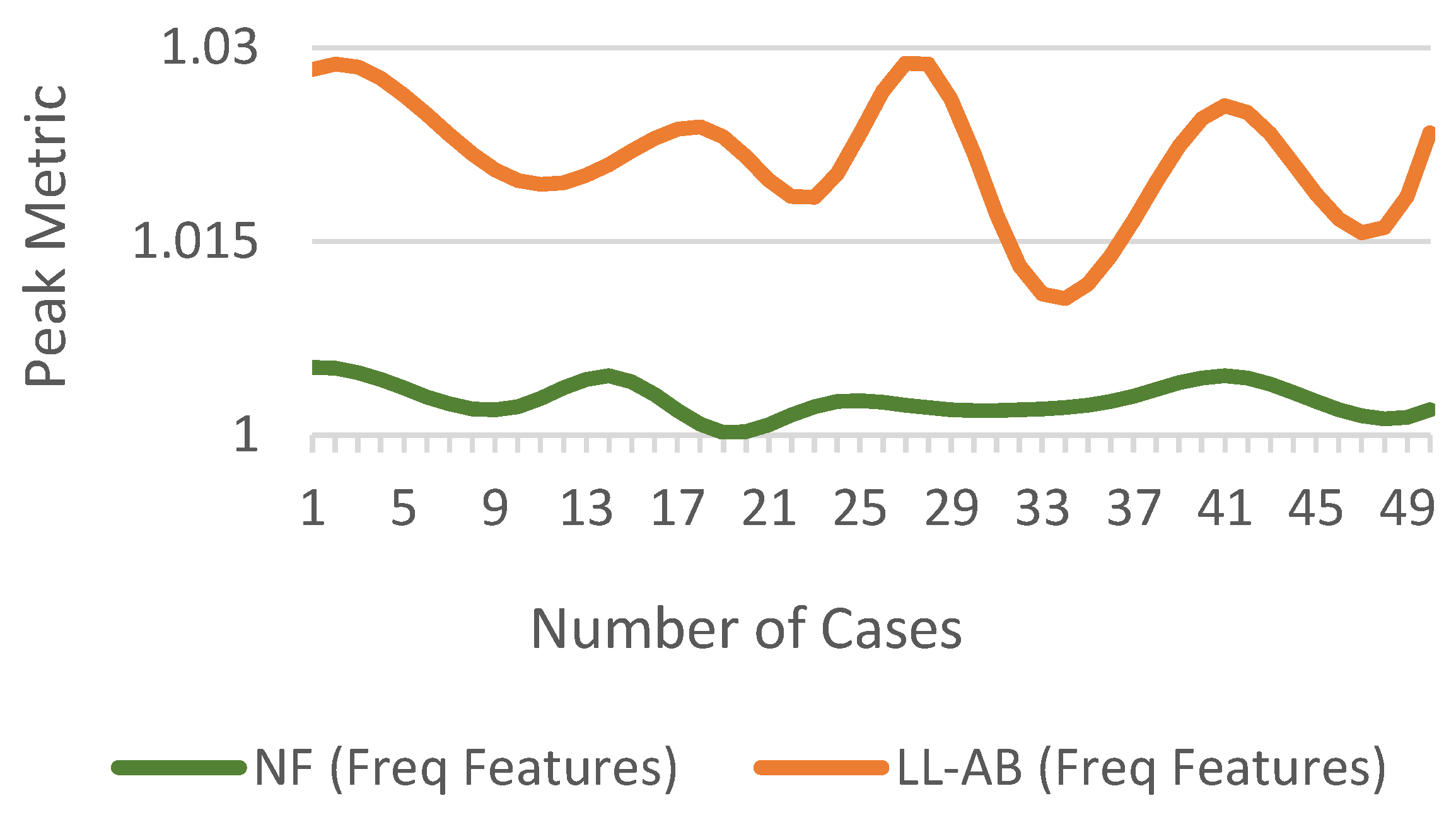
For the above observation, there are four peaks with values 50.8540, 50.5164, 50.7120 and 50.4684. The is 50.6377, while is 50.0130. For the above case, the value of is 1.0125. The difference in of for LL-AB fault and NF conditions is shown in Figure 8.
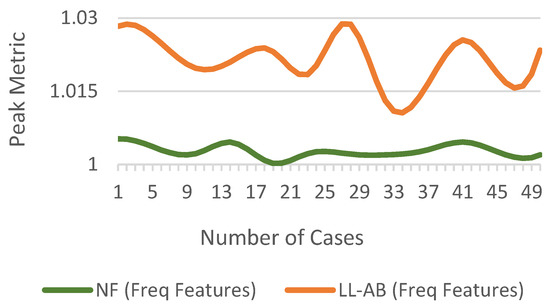
Figure 8.
of for fault and NF conditions.
The proposed considers all the peaks and takes their mean to represent the signal better, instead of just using the max value. When a fault occurs, the peaks of the waveform change before there is any significant change in the signal’s energy. Therefore the can warn of faults when they first initiate.
3.3. Max Factor
Max Factor is the second novel metric proposed in this research and is the ratio of maximum value to the absolute value of mean of the signal.
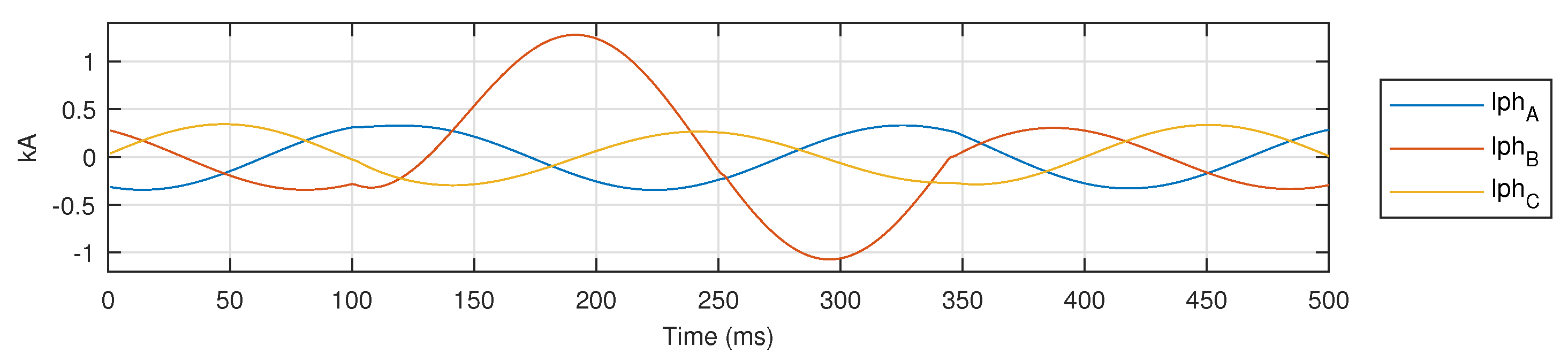
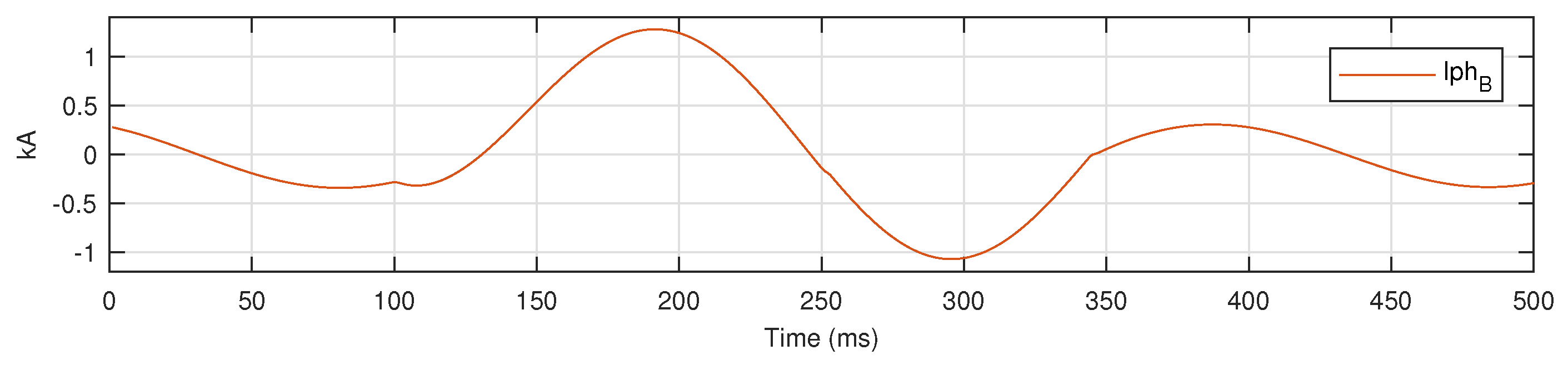
For a bolted LG fault on phase B in AUTO mode, three phase current signals are shown in Figure 9, and the signal for is shown separately in Figure 10 to demonstrate the application of proposed metric .
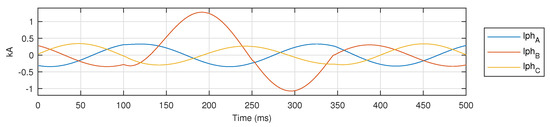
Figure 9.
for a bolted LG fault on phase B in AUTO mode.
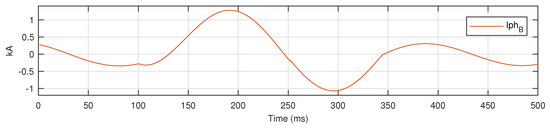
Figure 10.
for a bolted LG fault on phase B in AUTO mode.
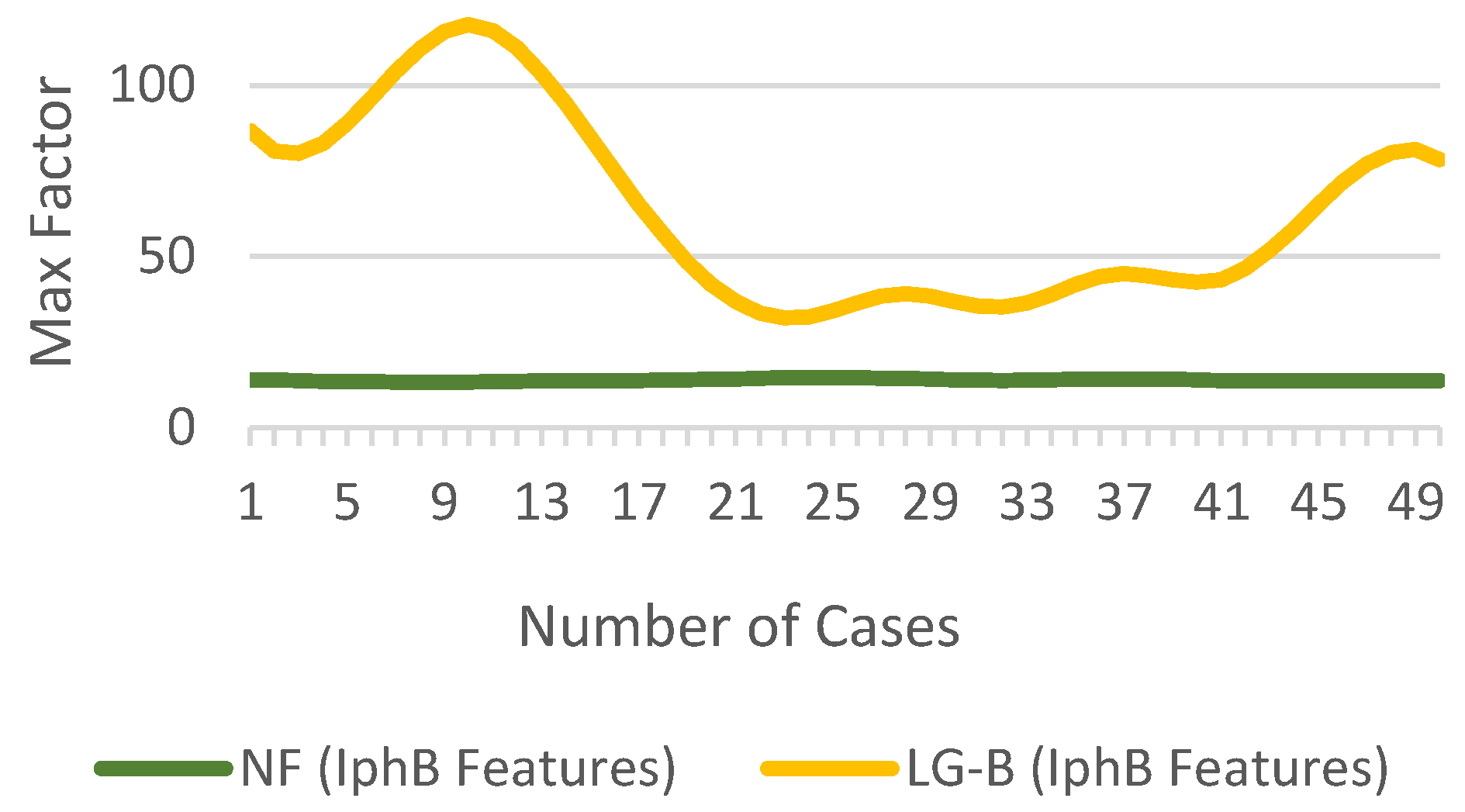
In Figure 10, the max value of the is 1.2775, while is 0.0108. For the above case, the value of is 117.7036. For the no fault case, the max value of the is 0.343, while is 0.026, resulting in of 13.273. The difference in of for NF and LG-B fault cases is shown in Figure 11.
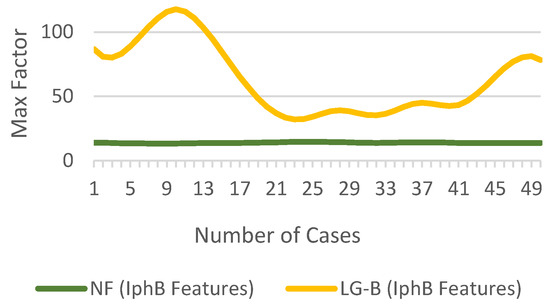
Figure 11.
of for NF and fault conditions.
3.4. Principal Component Analysis
Principal component analysis is mainly applied to reduce dimensionality in order to decrease the processing time and avoid overfitting the model [23]. The first step in is to calculate the covariance matrix. The covariance matrix of any two variables x and y, is the matrix of pairwise covariance calculations between each variable.
where
and are the mean values of x and y, respectively and ∗ denote the complex conjugate. Eigenvalues are used to calculate the eigenvectors for the covariance matrix, which are then used to extract patterns. The first eigenvector represents the eigenvalue that has the highest variance. For the eigenvalue, which has the next highest variance, the second eigenvector corresponds to it, and so on. The matrix that results is as follows…
Only the first and second eigenvectors are selected to obtain the first and second principal components .
The projection of the vectors onto the new base that is consistent with and is used to represent the new features.
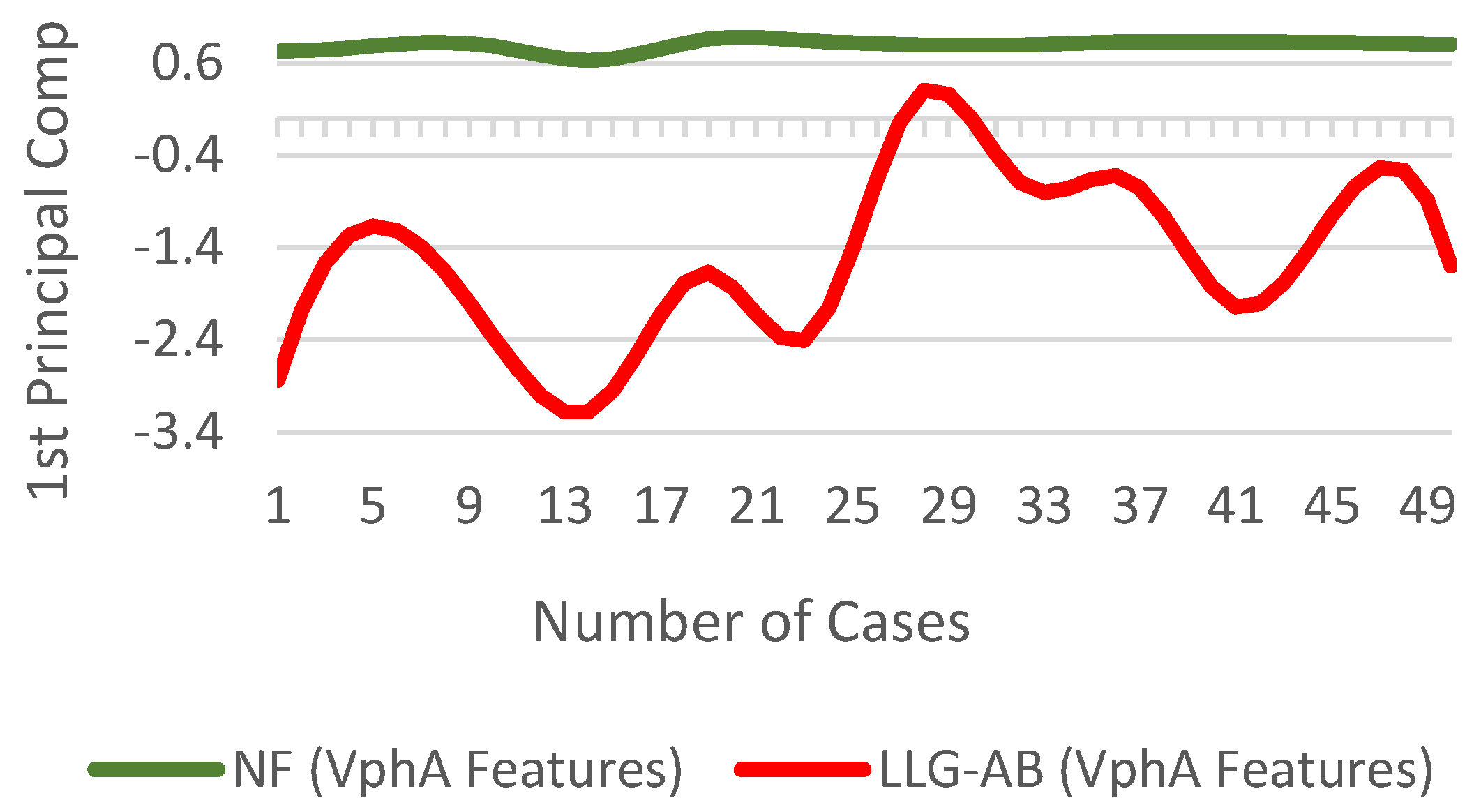
where and respectively represent the variable and the mean vector of the original data, whereas represents new features. The difference in for for NF and LLG-AB fault scenarios is shown in Figure 12.
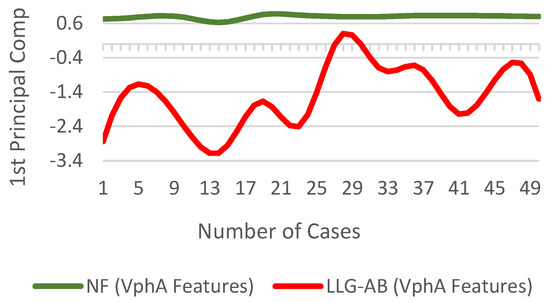
Figure 12.
of for NF and fault scenarios.
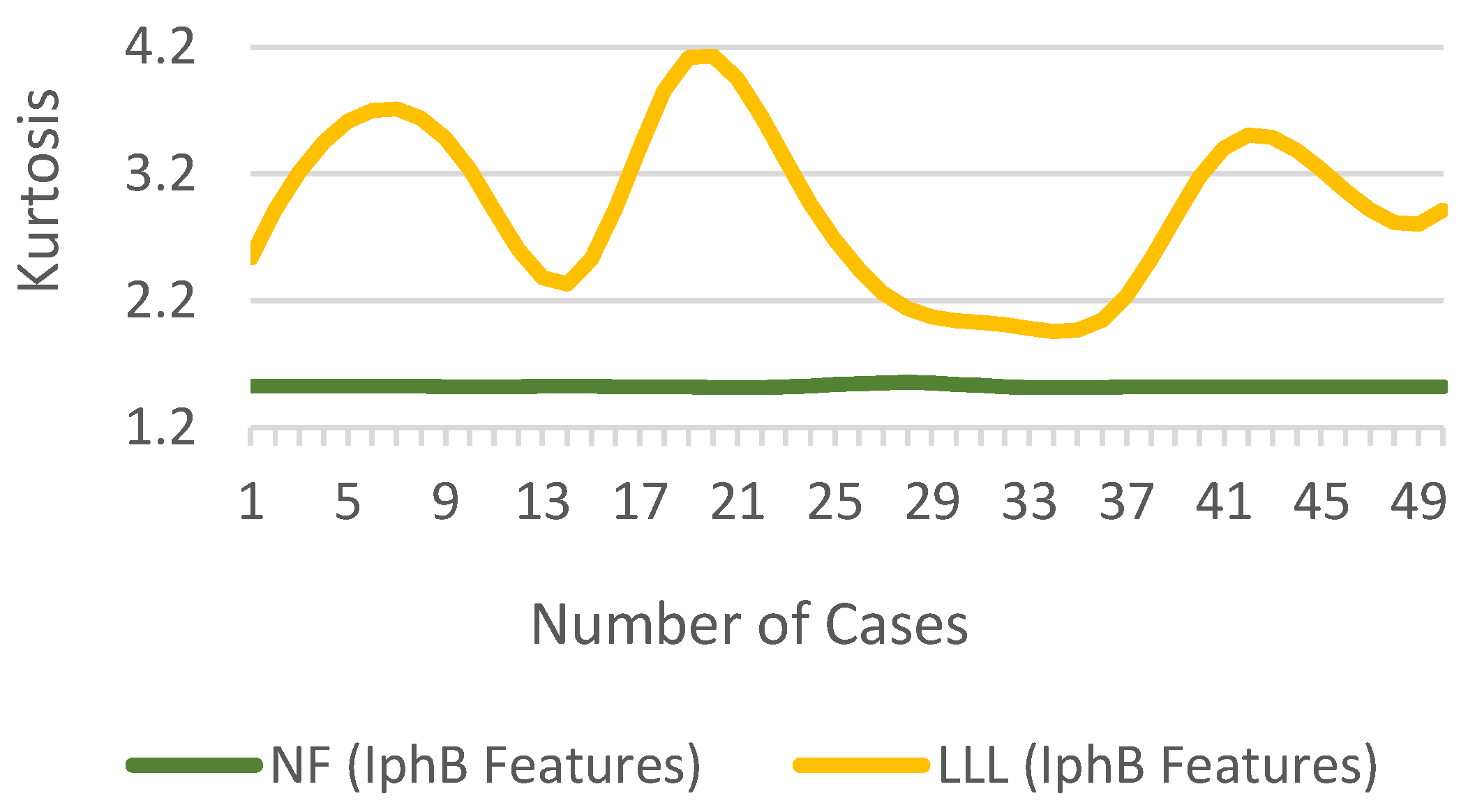
3.5. Kurtosis
The Kurtosis of a signal x is defined in (12) [25].
The of the normal distribution is 3. A fault in the system will change the value, greater than or less than 3. The difference in for for NF and LLL fault cases is shown in Figure 13.
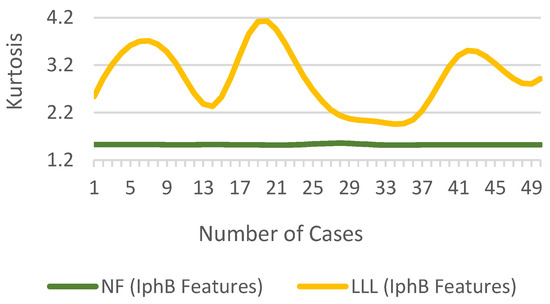
Figure 13.
of for NF and fault cases.
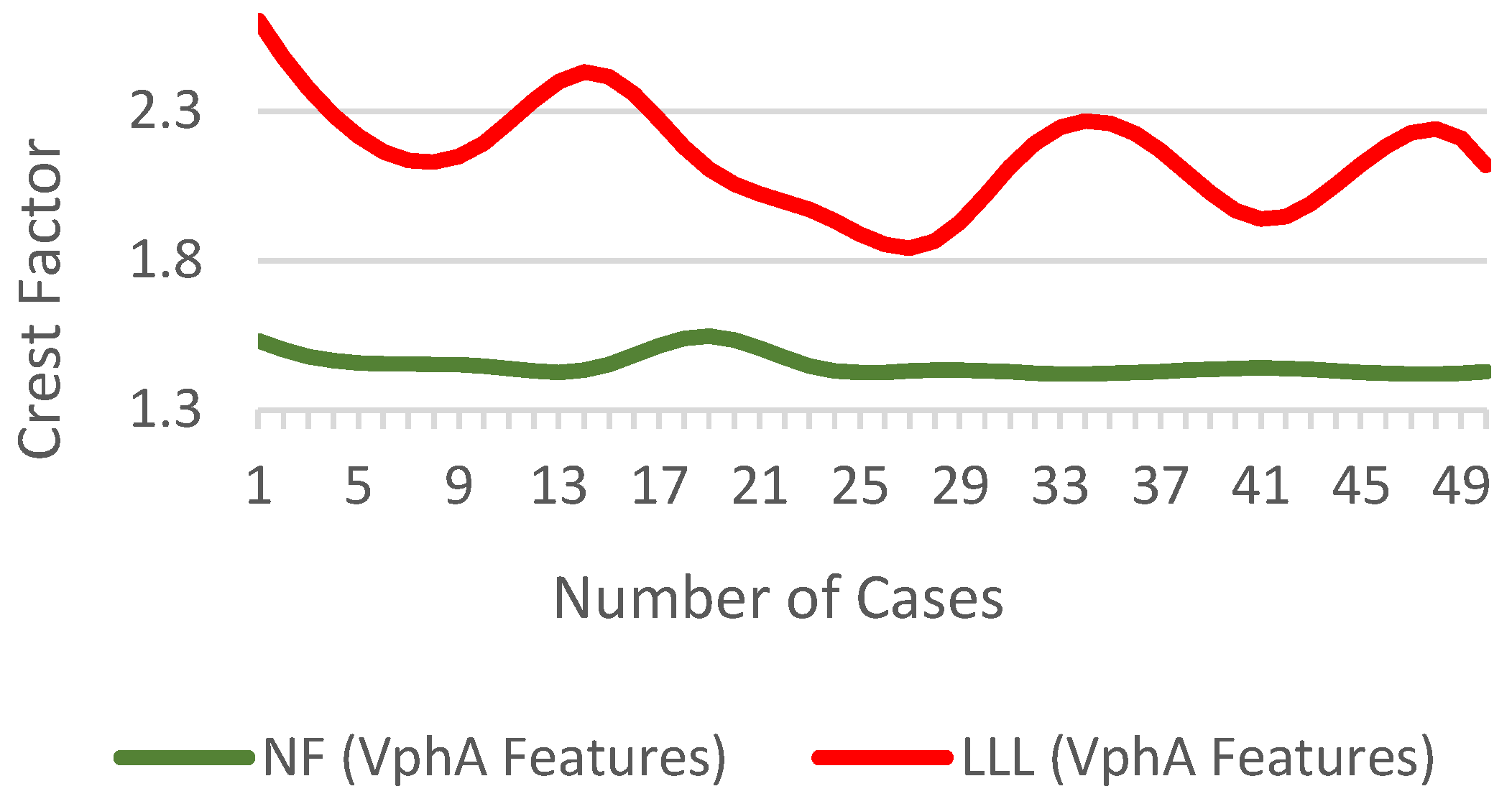
3.6. Crest Factor
Crest Factor is the ratio of the maximum absolute value to the RMS [25].
where is the maximum absolute value of the signal:
and is:
The of a sinusoidal current waveform for purely resistive load is 1.414. Figure 14 show the difference in of for NF and LLL fault condition.
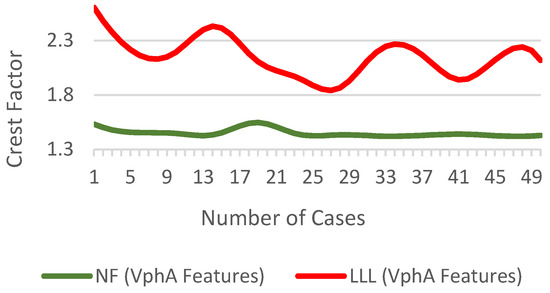
Figure 14.
of for NF and fault conditions.
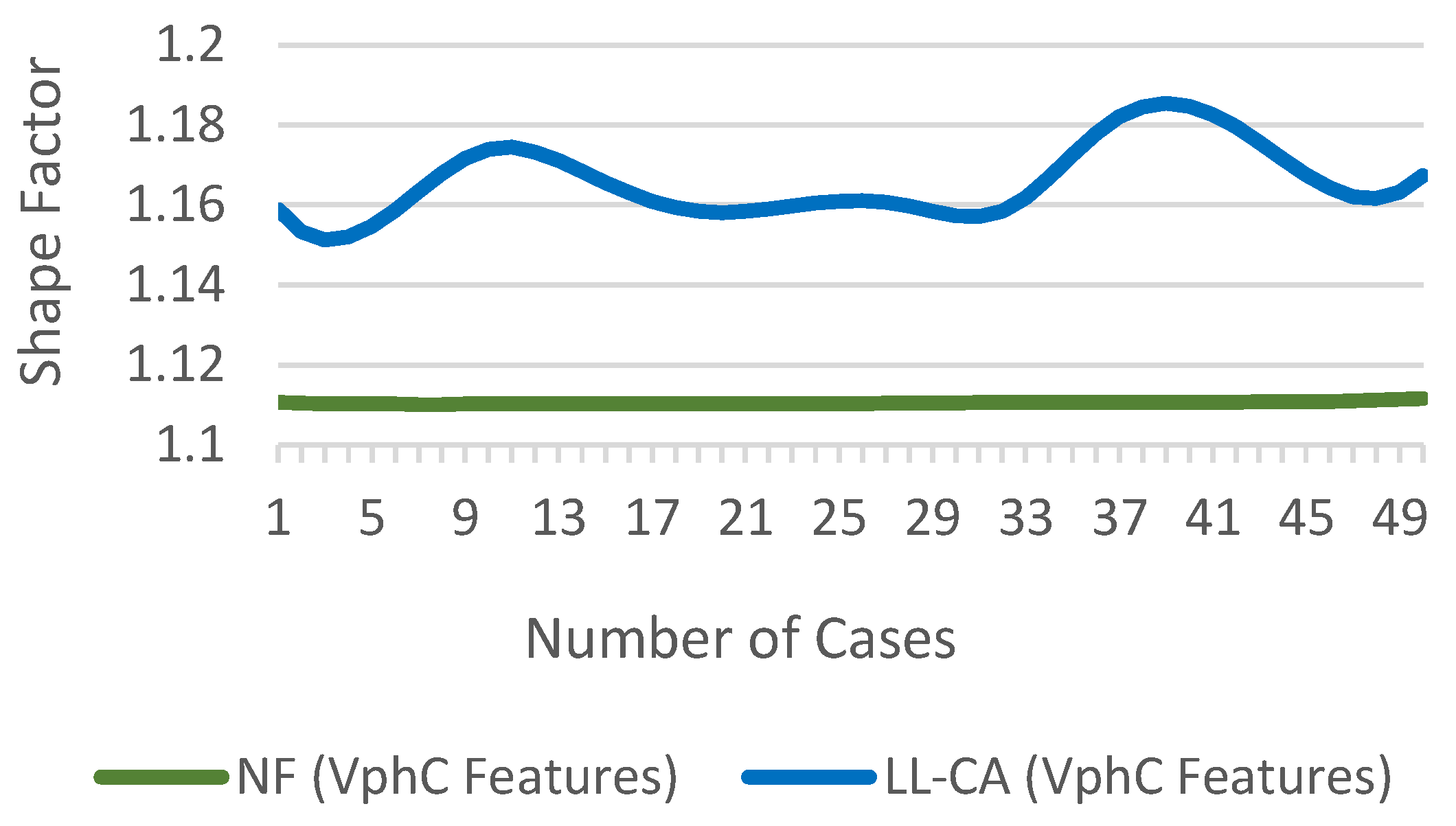
3.7. Shape Factor
Shape Factor is the ratio of RMS to the mean of the absolute value [24]. The is independent of the signal dimensions, but it relies on the signal shape.
Figure 15 show the difference in of for NF and LL-CA fault cases.
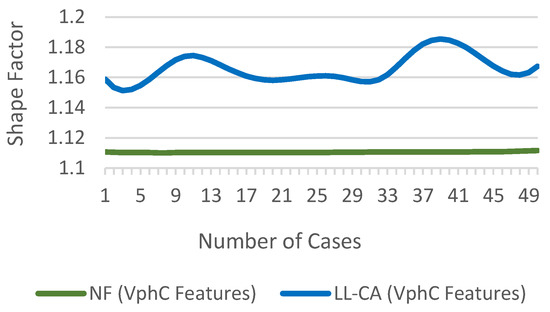
Figure 15.
of for NF and fault cases.
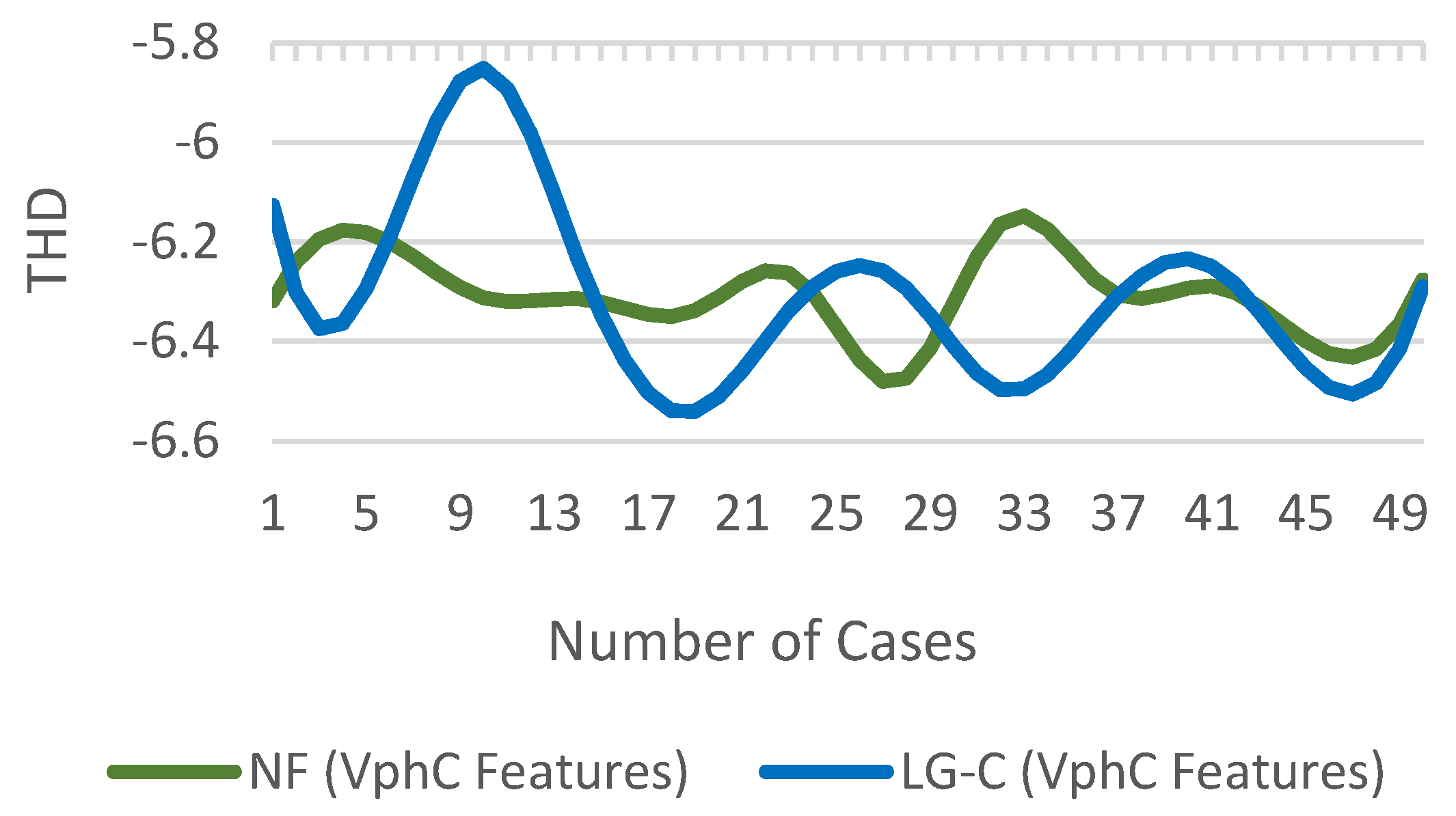
3.8. Total Harmonics Distortion
The is the amount of distortion in the signal compared to the undistorted signal. It is defined as the ratio of the square root of the summation of all harmonics squared (from second harmonic) over the fundamental component [10]. is an essential measure in power systems. A lower value gives lower peak currents, higher power factor and system efficiency.
where is the n-th harmonic of x and is the fundamental component. difference of for NF and LG(C) fault cases is shown in Figure 16.
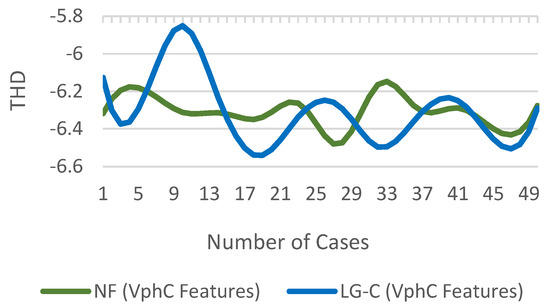
Figure 16.
of for NF and fault cases.
3.9. Skewness
The skewness shows the irregularity of signal distribution [25]. Distribution symmetry can be impacted by faults resulting in an increased level of skewness.
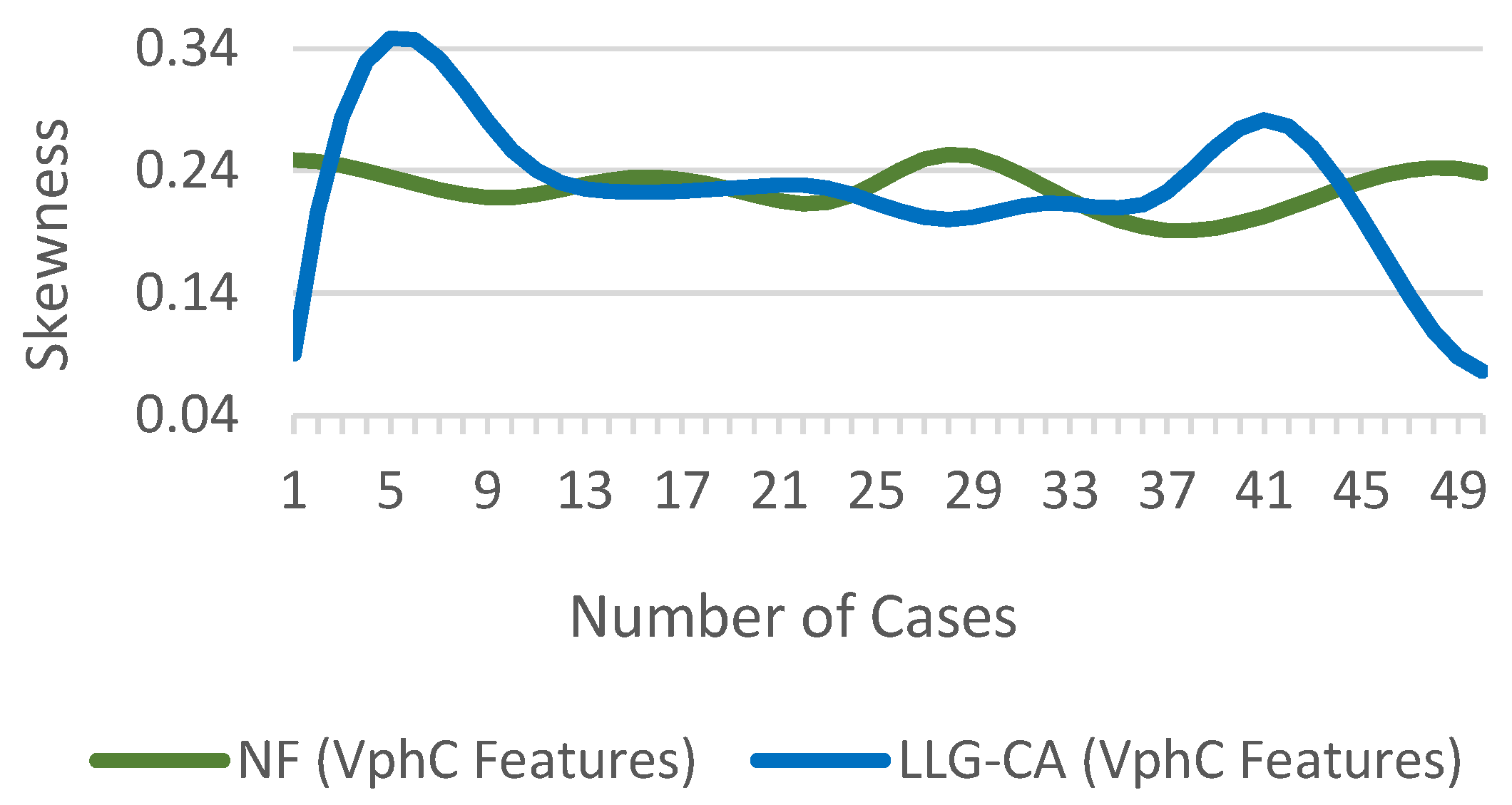
The difference in of phase C for NF and LLG(CA) fault conditions is shown in Figure 17.
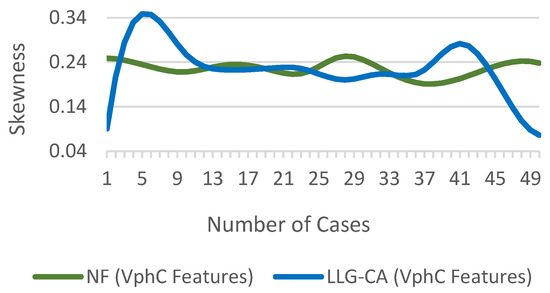
Figure 17.
of for NF and fault scenarios.
4. Feature Selection
Feature selection (FS) is the process of reducing features or predictors to provide the best predictive power in modelling a set of data, as not all features are useful. The goal is to find the fewest possible features with the highest possible accuracy. Finding the best features essentially remains an iterative process and requires deep domain knowledge. Feature selection aids in improving the speed and accuracy of prediction as it:
- Prevents overfitting: modelling with many features can make the model more susceptible to specific observations in training data.
- Reduces model size: fewer features increase computational performance and require less memory for embedded deployment.
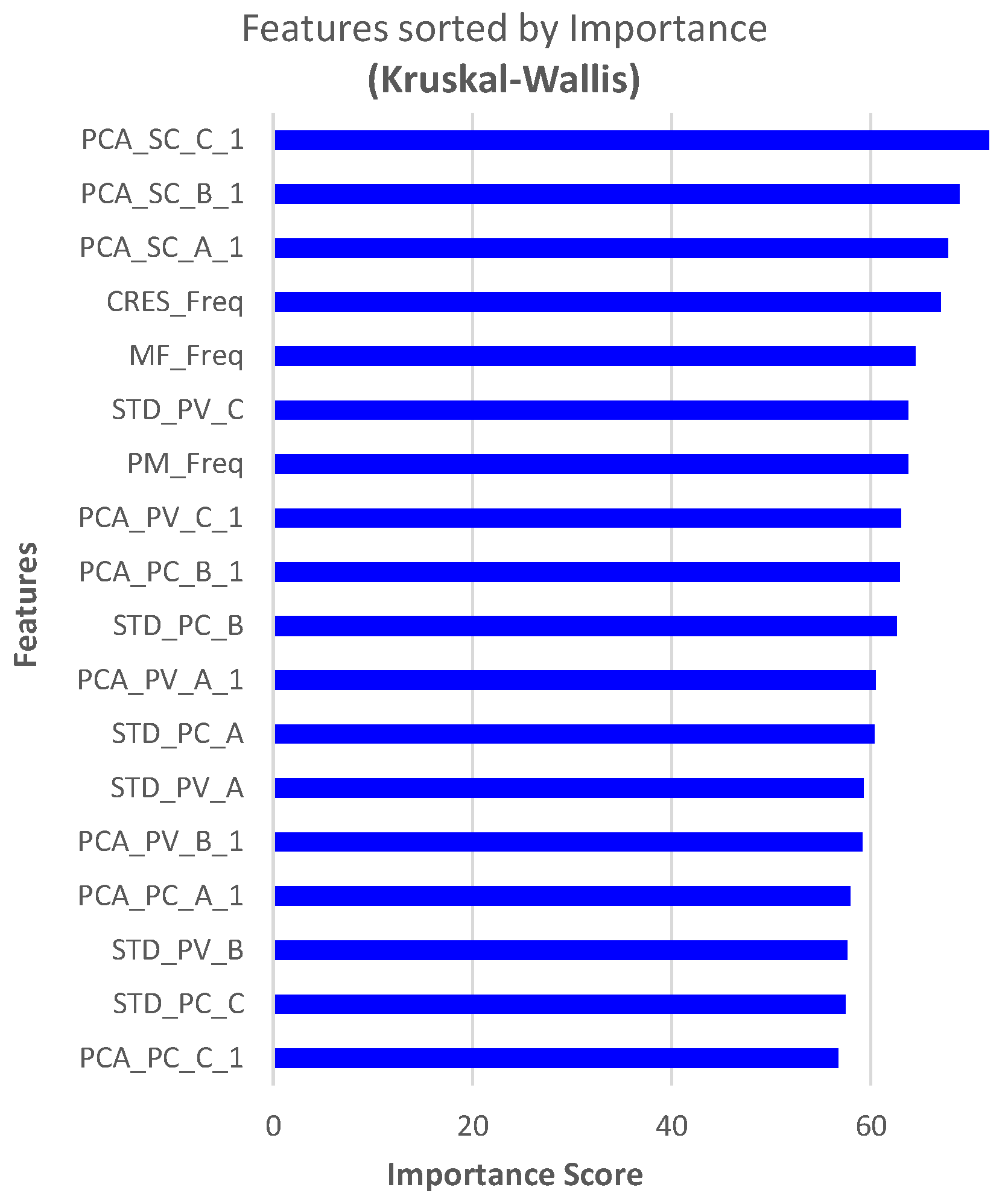
Features are ranked using the Kruskal–Wallis H-Test (KW) [26] for FD and FTC with FP. The top 18 features for FD are shown in Figure 18.
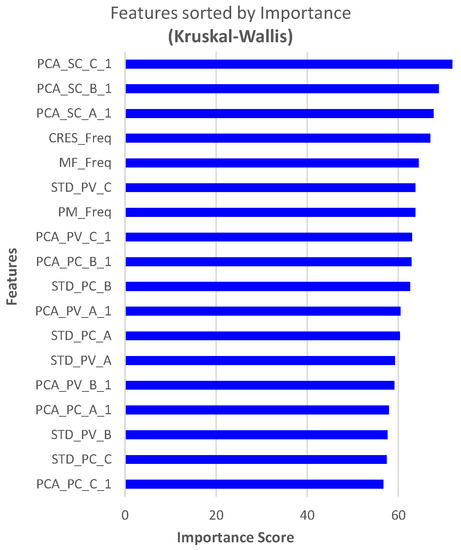
Figure 18.
Feature ranking for FD using KW.
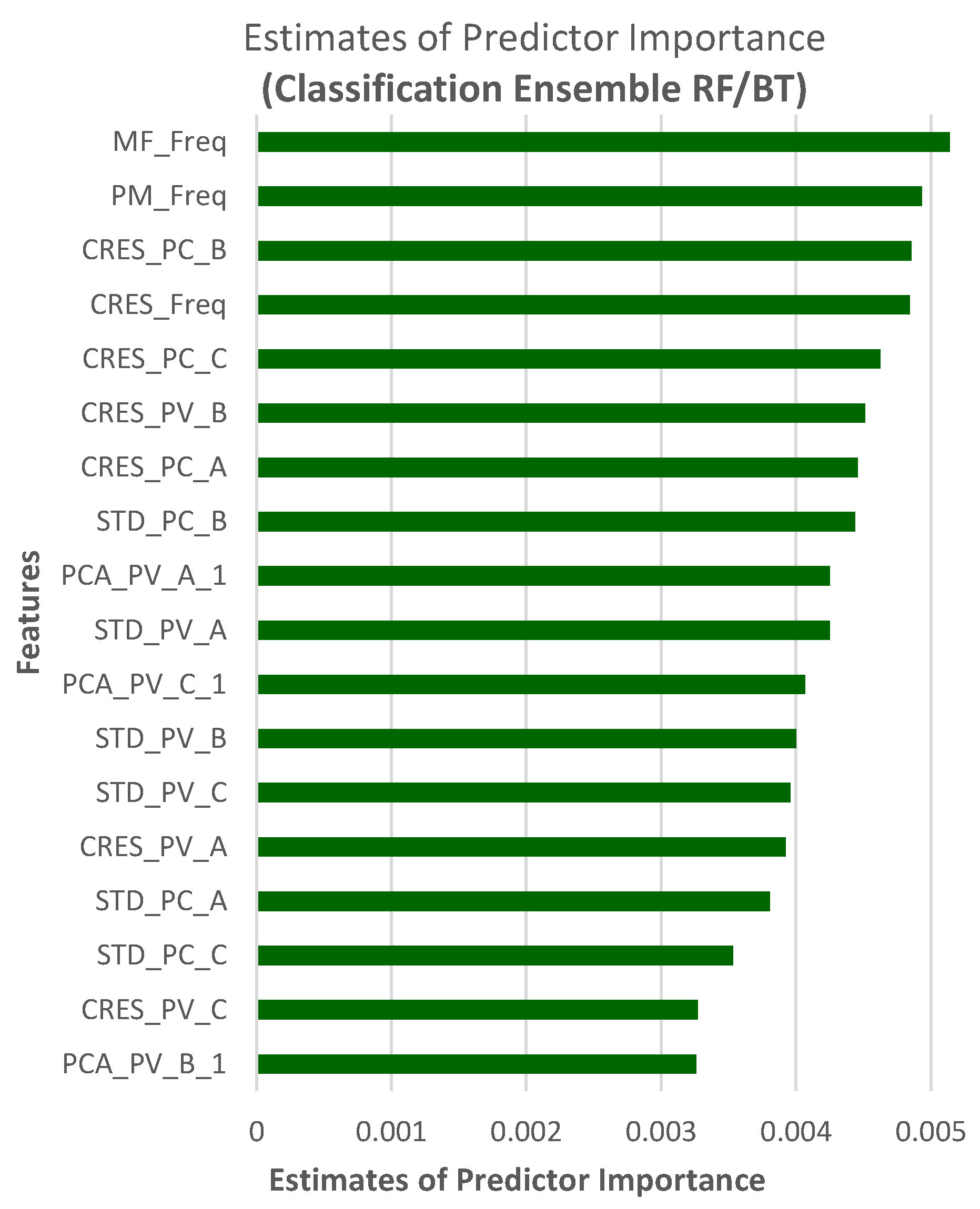
Additionally, estimates of predictor importance for the classification ensemble methods are also computed by summing the estimates over weak learners in the ensemble for each input predictor. A high value indicates that this predictor is important. Predictor importance for FD using Bagged Trees (BT) ensemble, where bagging is short for bootstrap aggregation [27], is shown in Figure 19.
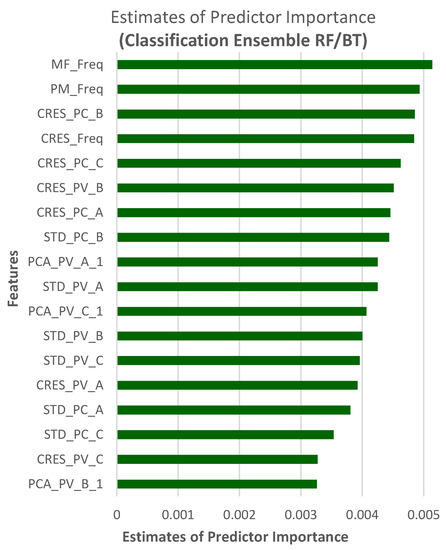
Figure 19.
Predictor importance for FD using BT/RF.
5. Methodology
By applying domain knowledge and FS methods, the top 18 features are selected for FD, and the top 18 features are chosen for FTC with FP. Numerous ML algorithms are trained and tested, as will be discussed in Section VI. Random Forest (RF) [28,29] outperformed all other ML classifiers for FD and FTC with FP.
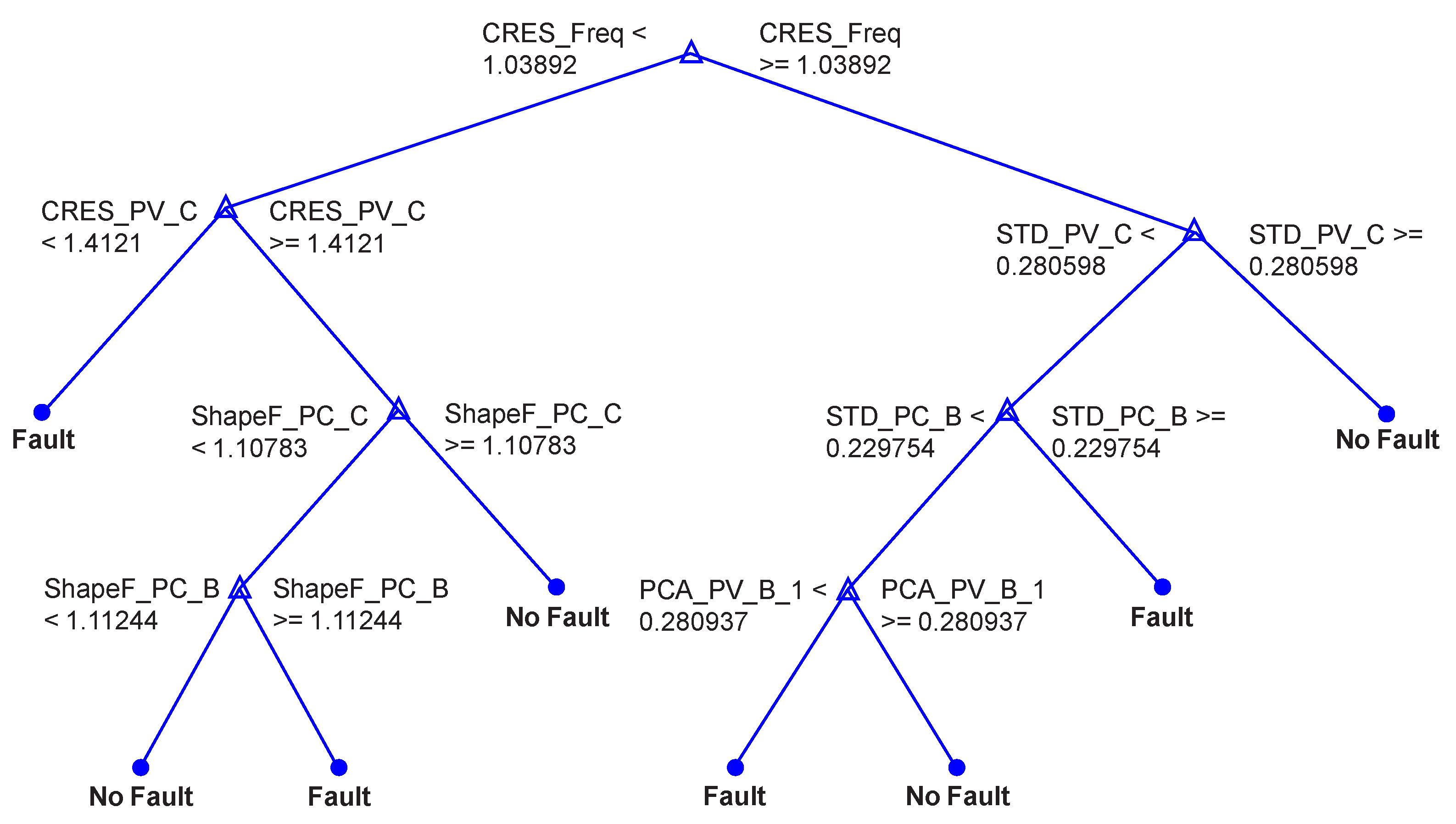
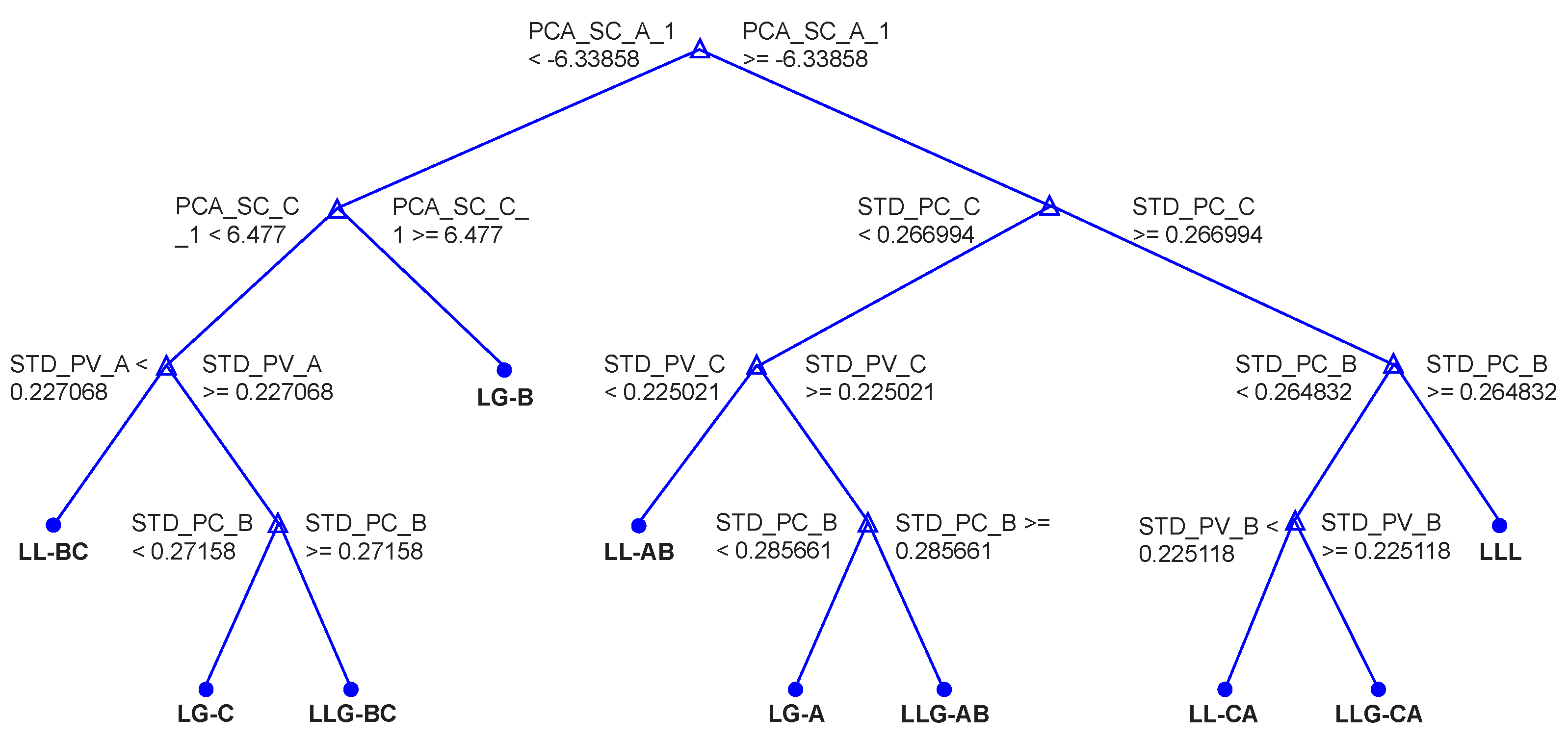
RF is an ensemble method similar to BT but differs in the growing phase. A subset of features is randomly selected for each decision split in RF as shown in Figure 20.
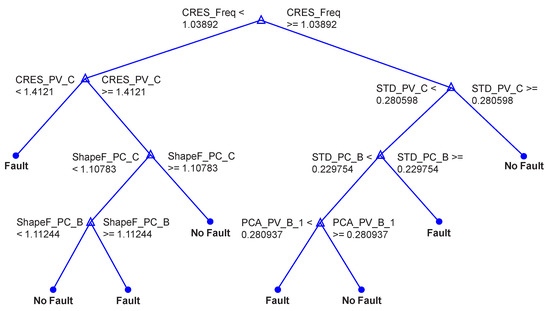
Figure 20.
View of 4th Tree with 7 branches and 15 nodes.
In BT, at each node, all the features are candidates for splitting, which can result in the same features giving the highest accuracy, being used at different nodes and for numerous DTs, as shown in Figure 21. This causes overfitting in the model. On the contrary, in RF, each tree is grown using a separate random subset of data; therefore, every decision tree that makes up a RF is unique. RF has superior accuracy compared to BT, as it minimises overfitting, while BT is better than a single decision tree.
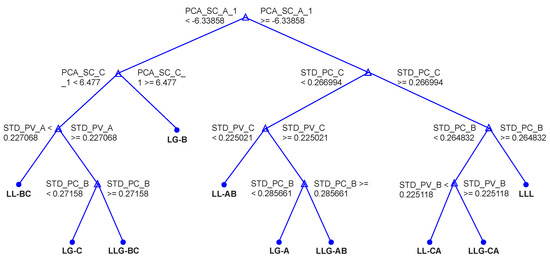
Figure 21.
View of 20th Tree with 9 braches and 19 nodes.
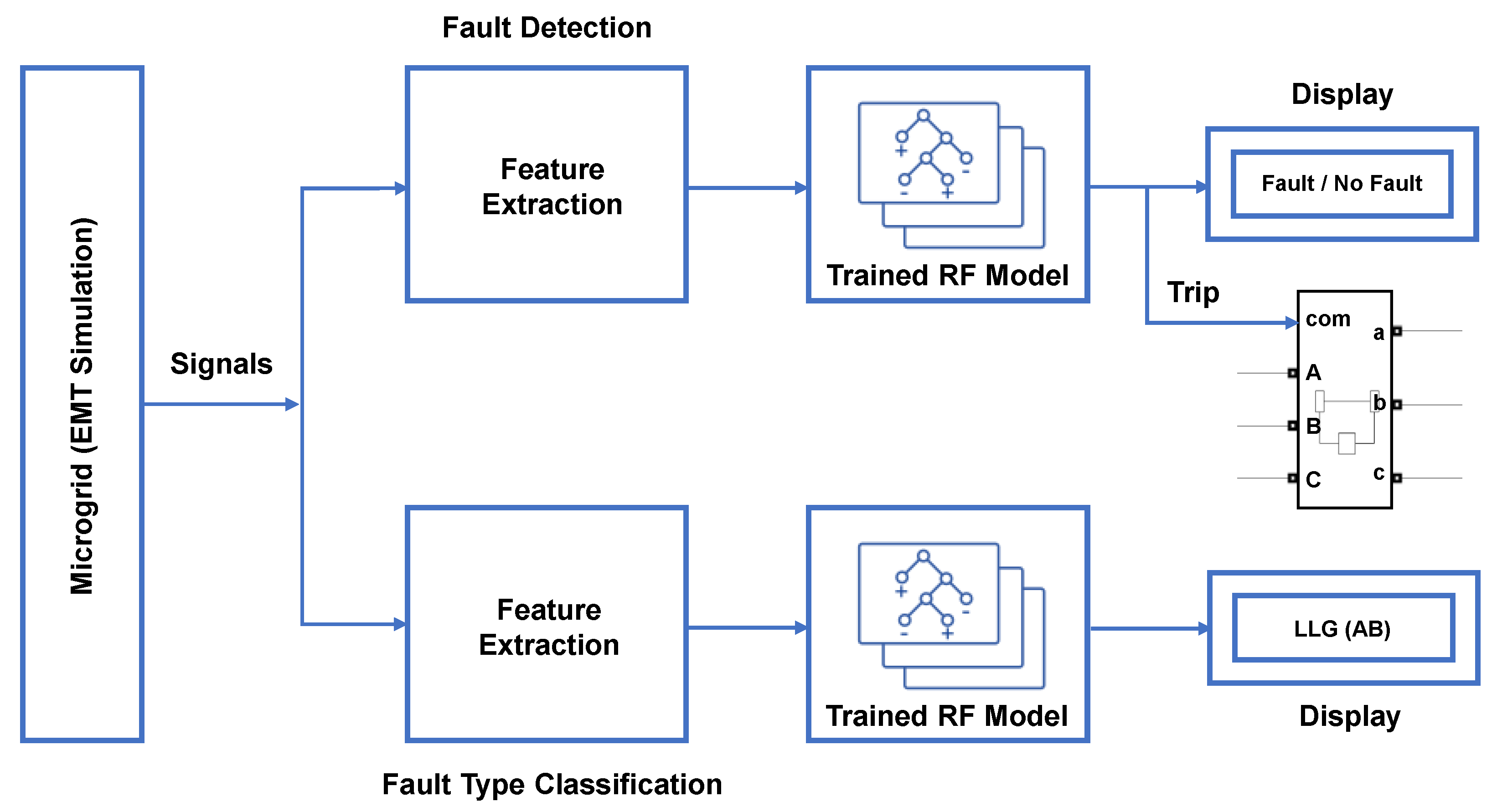
For FD, the RF model with optimal hyperparameters grows 488 individual trees. On the other hand, for FTC with FP, the optimised RF model has 271 trees. The trained RF models are deployed to detect and classify faults. Figure 22 presents a schematic diagram of the proposed protection scheme.
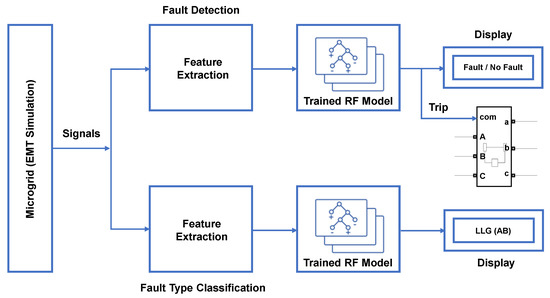
Figure 22.
Proposed methodology.
The process starts with measuring local signals, followed by FE, fed to the trained RF models. A trip signal is issued when a fault is detected by converting the data type of label to the real-world numerical value. Furthermore, FTC with FP is displayed.
6. Results and Analysis
The top 18 features are used as input to train 35 classification learners for FD and FTC with FP. These include Classification Ensembles, Naive Bayes, Neural Networks, Discriminant Analysis, Support Vector Machine (SVM), Classification Trees and k-nearest neighbours (KNN) [30]. Ten-fold cross-validation (CV) is applied to the training dataset to protect against overfitting. Hyperparameter tuning of all models is performed to improve accuracy. Predictions are made using unseen data. The top 5 models with CV and test accuracy for FD are shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Test accuracy of ML models with 18 features for FD.
RF displayed the highest test accuracy. The accuracy of ML models with further reduction in the number of features for FD and FTC with FP is also investigated. Model accuracy dropped sharply for less than 18 predictors. The best combination of 18 predictors for FD includes 3 predictors obtained by of , and 9 using of , and . The remaining 6 include of , , and of .
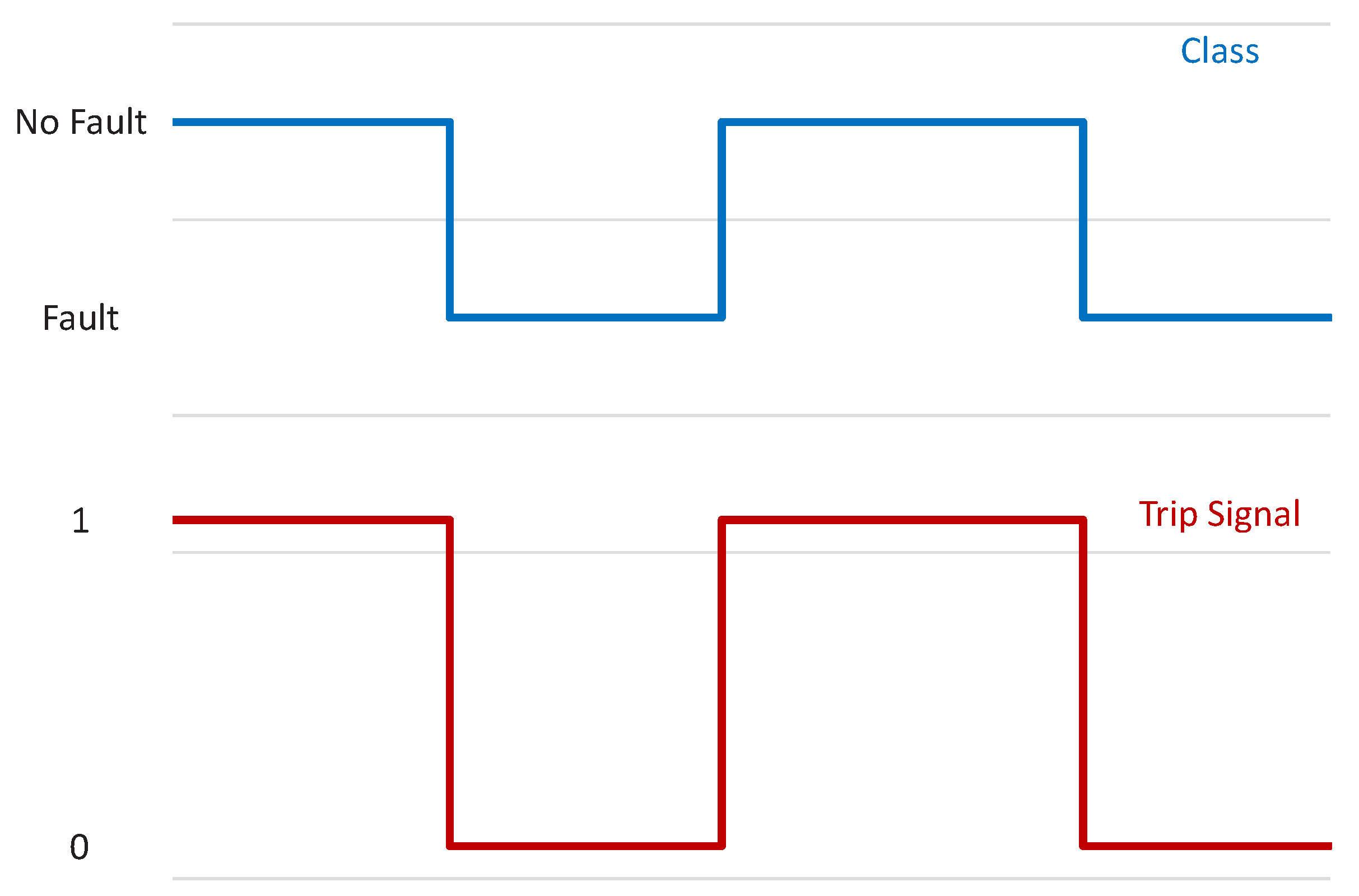
The Simulink Classification Ensemble Predict block with trained RF model is used to validate the model predictions with trip signal issued when fault is detected. For a set of 20 new observations, with alternating 5 NFs followed by fault cases, the model only misclassified once, where it predicted a fault as an NF. The alternating trip signals for the 20 observations are shown in Figure 23.
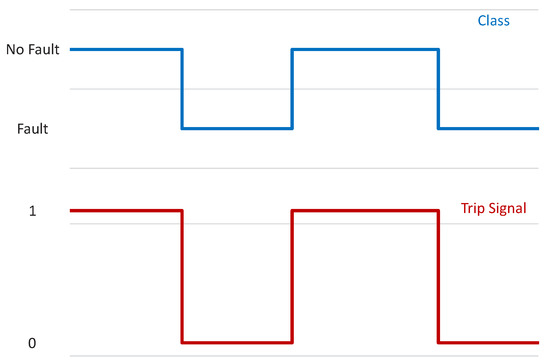
Figure 23.
Fault as a NF detection and respective trip signal.
Likewise, for FTC with FP, the top 18 predictors are used to train 35 classification learners. The top 5 models with 10-fold cross-validation and test accuracy are shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Test accuracy of ML models with 18 features for FTC with FP.
The best combination of 18 predictors for FTC with FP includes 6 obtained by of and , and 9 using of , and . The remaining 3 include of .
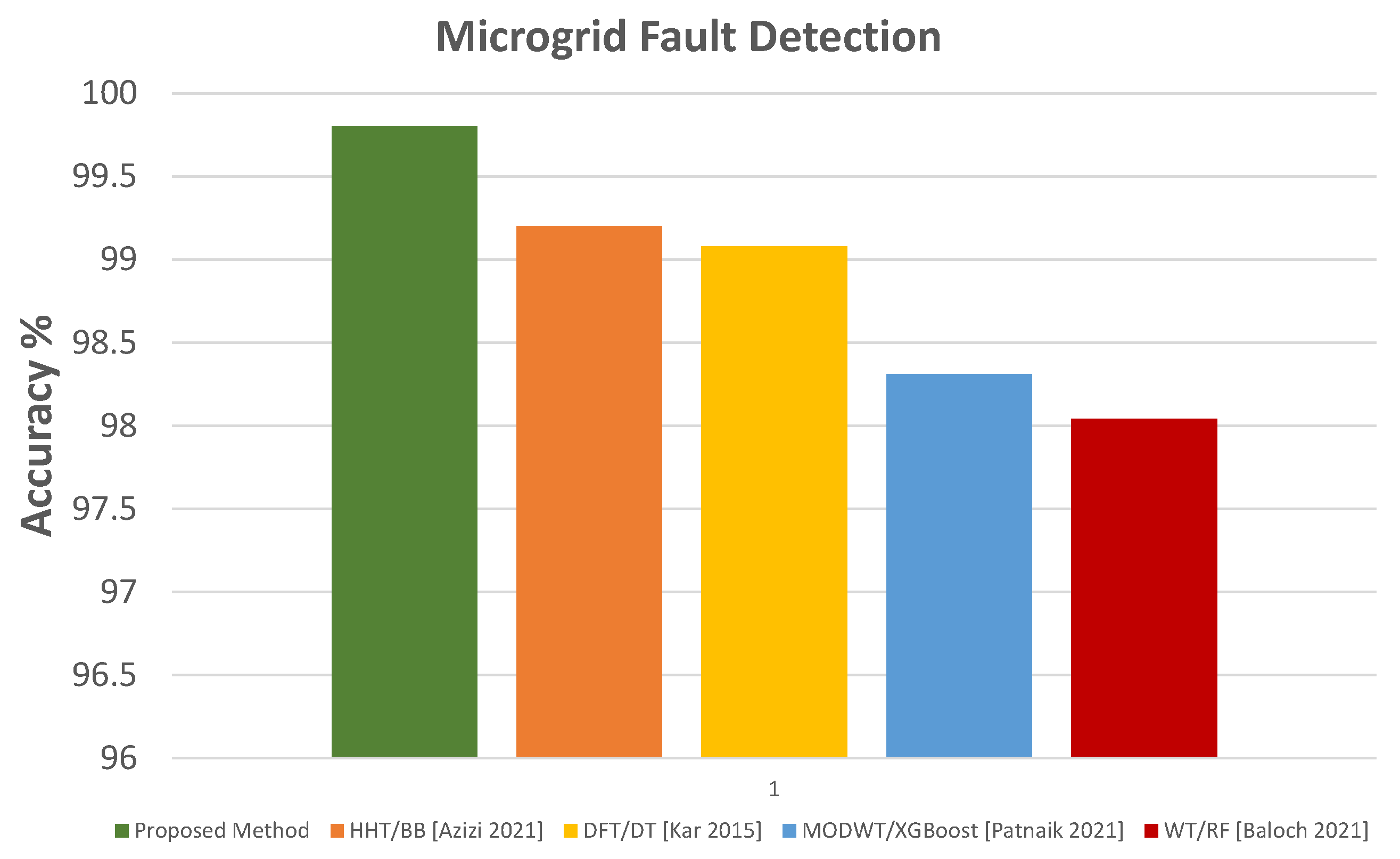
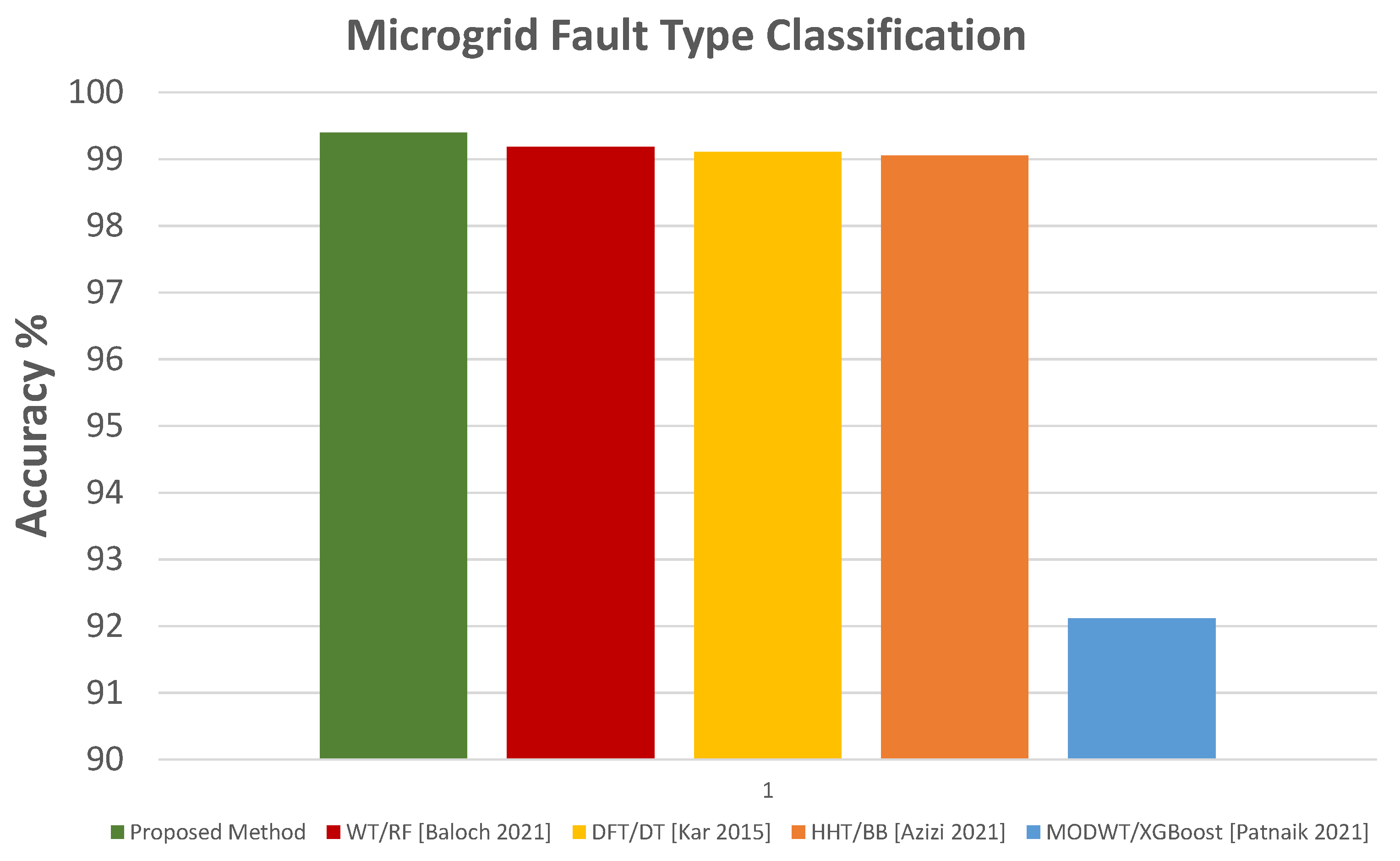
The test accuracy comparison of the proposed method with other FD and FTC methods is shown in Figure 24 and Figure 25.
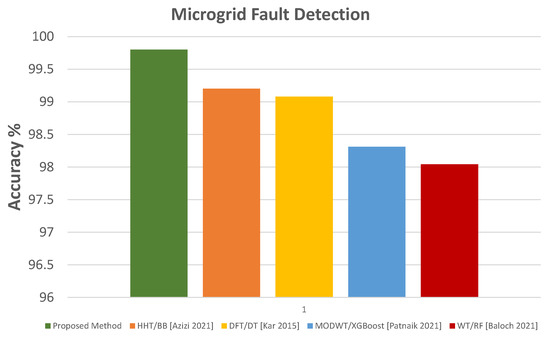
Figure 24.
Accuracy comparison with other FD methods [8,10,12,13].
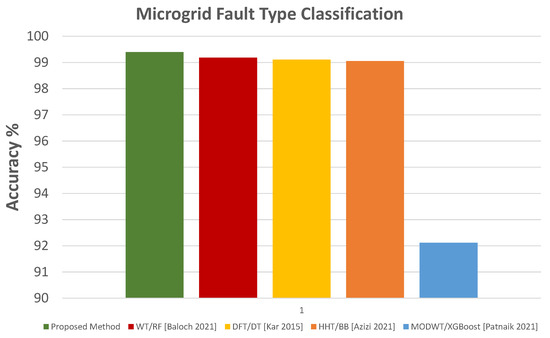
Figure 25.
Accuracy comparison with other FTC methods [8,10,12,13].
The results show excellent performance by the proposed protection scheme compared to previous methods. Apart from achieving very high accuracy for FD and FTC with FP, very high protection sensitivity is also attained for both modes of microgrid operation for various fault types and cases.
7. Conclusions and Future Work
The FD methods based on WT feature extraction can be affected by the type of selected mother wavelet, which may cause the protection system misoperation. Subsequently, most WT based protection techniques are efficient for specific parameters and cannot be generalised without using a different mother wavelet. To overcome this shortcoming of WT, a new protection scheme for AC microgrids is developed in the proposed research. Novel FE techniques, Peaks Metric and Max Factor are applied, apart from exploring other FE methods to examine the suitability for detecting and classifying faults. After the signals are pre-processed, the features are extracted and then the best performing features are selected using FS techniques. Various ML classifiers are trained and tested. For FD and FTC, with 18 predictors, RF outperformed all other ML classifiers for FD and FTC with FP. Simulink is used to validate the model predictions with a trip signal issued when a fault is detected. Accurate FD, FTC with FP identification, and high protection sensitivity for wide variations in operating conditions make the protection scheme superior to earlier methods.
Future work will integrate the proposed FD and FTC method into a multi-agent based protection scheme for meshed microgrid and testing it on a real-time digital simulator to evaluate the performance.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.U.; methodology, M.U.; software, M.U.; validation, M.U., M.E. and L.L.; formal analysis, M.U.; investigation, M.E.; resources, M.U.; data curation, M.U.; writing—original draft preparation, M.U.; writing—review and editing, M.U., M.E. and L.L.; visualization, M.U.; supervision, L.L.; project administration, J.Z.; funding acquisition, M.E. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Nikolaidis, V.C.; Desiniotis, D.; Papaspiliotopoulos, V.A.; Tsimtsios, A.M.; Korres, G.N. Optimal Recloser-Fuse and Distribution Network Protection Coordination including Distributed Generation Relays. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Smart Energy Systems and Technologies (SEST), Eindhoven, The Netherlands, 5–7 September 2022; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, N.; Khayat, Y.; Golestan, S.; Nasir, M.; Vasquez, J.C.; Guerrero, J.M.; Kauhaniemi, K. AC Microgrids Protection: A Digital Coordinated Adaptive Scheme. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 7066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molokomme, D.N.; Onumanyi, A.J.; Abu-Mahfouz, A.M. Edge intelligence in Smart Grids: A survey on architectures, offloading models, cyber security measures, and challenges. J. Sens. Actuator Netw. 2022, 11, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anudeep, B.; Nayak, P.K. Differential power based selective phase tripping for fault-resilient microgrid. J. Mod. Power Syst. Clean Energy 2021, 10, 459–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addison, P.S. The Illustrated Wavelet Transform Handbook: Introductory Theory and Applications in Science, Engineering, Medicine and Finance; CRC Press: London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Panigrahi, B.K.; Ray, P.K.; Rout, P.K.; Sahu, S.K. Detection and location of fault in a micro grid using wavelet transform. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Circuit, Power and Computing Technologies (ICCPCT), Kollam, India, 20–21 April 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Swain, G.; Sinha, P.; Maharana, M. Detection of islanding and power quality disturbance in micro grid connected distributed generation. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Innovative Mechanisms for Industry Applications (ICIMIA), Bengaluru, India, 21–23 February 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 388–393. [Google Scholar]
- Kar, S.; Samantaray, S.; Zadeh, M.D. Data-mining model based intelligent differential microgrid protection scheme. IEEE Syst. J. 2015, 11, 1161–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baloch, S.; Jamali, S.Z.; Shah, S.A.R. A Protection Technique for Microgrid Using Wavelet Packet Transform and Data Mining Classifier. Eng. Proc. 2022, 20, 33. [Google Scholar]
- Baloch, S.; Samsani, S.S.; Muhammad, M.S. Fault Protection in Microgrid Using Wavelet Multiresolution Analysis and Data Mining. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 86382–86391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, D.P.; Samantaray, S.R.; Joos, G. A combined wavelet and data-mining based intelligent protection scheme for microgrid. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2015, 7, 2295–2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizi, R.; Seker, S. Microgrid fault detection and classification based on the boosting ensemble method with the Hilbert-Huang transform. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2021, 37, 2289–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patnaik, B.; Mishra, M.; Bansal, R.C.; Jena, R.K. MODWT-XGBoost based smart energy solution for fault detection and classification in a smart microgrid. Appl. Energy 2021, 285, 116457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelgayed, T.S.; Morsi, W.G.; Sidhu, T.S. A new approach for fault classification in microgrids using optimal wavelet functions matching pursuit. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2017, 9, 4838–4846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Yang, A.; Yuan, H.; Wei, X. A High-Impedance Fault Detection Method for Distribution Systems Based on Empirical Wavelet Transform and Differential Faulty Energy. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2021, 13, 900–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forouzesh, A.; Golsorkhi, M.S.; Savaghebi, M.; Baharizadeh, M. Support vector machine based fault location identification in microgrids using interharmonic injection. Energies 2021, 14, 2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngui, W.K.; Leong, M.S.; Hee, L.M.; Abdelrhman, A.M. Wavelet analysis: Mother wavelet selection methods. In Applied Mechanics and Materials; Trans Tech Publications: Zurich, Switzerland, 2013; Volume 393, pp. 953–958. [Google Scholar]
- Megahed, A.; Moussa, A.M.; Elrefaie, H.; Marghany, Y. Selection of a suitable mother wavelet for analyzing power system fault transients. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE Power and Energy Society General Meeting-Conversion and Delivery of Electrical Energy in the 21st Century, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 20–24 July 2008; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2008; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson, W.A.; Cox, M. Discrete wavelet analysis of power system transients. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 1996, 11, 2038–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darwish, H.A.; Hesham, M.; Taalab, A.M.I.; Mansour, N.M. Close accord on DWT performance and real-time implementation for protection applications. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2010, 25, 2174–2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recioui, A.; Benseghier, B.; Khalfallah, H. Power system fault detection, classification and location using the K-Nearest Neighbors. In Proceedings of the 2015 4th International Conference on Electrical Engineering (ICEE), Boumerdes, Algeria, 13–15 December 2015; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- McGranaghan, M.F.; Mueller, D.R.; Samotyj, M.J. Voltage sags in industrial systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 1993, 29, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzair, M.; Li, L.; Zhu, J.G. Identifying line-to-ground faulted phase in low and medium voltage AC microgrid using principal component analysis and supervised machine-learning. In Proceedings of the 2018 Australasian Universities Power Engineering Conference (AUPEC), Auckland, New Zealand, 27–30 November 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, J.B.; Saidi, L.; Harrath, S.; Bechhoefer, E.; Benbouzid, M. Online automatic diagnosis of wind turbine bearings progressive degradations under real experimental conditions based on unsupervised machine learning. Appl. Acoust. 2018, 132, 167–181. [Google Scholar]
- Van Hecke, B.; Qu, Y.; He, D. Bearing fault diagnosis based on a new acoustic emission sensor technique. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part O J. Risk Reliab. 2015, 229, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacFarland, T.W.; Yates, J.M. Kruskal–Wallis H-test for oneway analysis of variance (ANOVA) by ranks. In Introduction to Nonparametric Statistics for the Biological Sciences Using R; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 177–211. [Google Scholar]
- Breiman, L. Bagging predictors. Mach. Learn. 1996, 24, 123–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R.; Friedman, J. Random forests. In The Elements of Statistical Learning; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 587–604. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, R.C.; Dewi, C.; Huang, S.W.; Caraka, R.E. Selecting critical features for data classification based on machine learning methods. J. Big Data 2020, 7, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).