Abstract
The origin of deep-water mounds has been a topic of debate in recent years. In this study, newly collected seismic data were employed to characterize the mounds within the Meishan Formation in the Qiongdongnan Basin and a novel model was proposed. The result showed that pervasive mounds and ‘V’-shaped troughs were alternately distributed at the top of the Meishan Formation. They appeared as elongated ridges flanked by similarly elongated gullies, with the trending parallel with the strike of the basinward slope. The mounded features were considered to be formed in response to the tectonically induced seabed deformation. The differential subsidence steepened the slope that was equivalent to the top of the Meishan Formation (ca. 10.5 Ma), which offered sufficient driving forces triggering the slope’s instability. Correspondingly, the uppermost deposits glided along a bedding-parallel detachment surface, creating a number of listric detachment faults that ceased downward to this surface. The uppermost layer was cut into a range of tilted fault blocks with tops constituting a seemingly mounded topography. Some of the downfaulted troughs between mounds steered the gravity flows and were filled by sand-rich lithologies. The differential subsidence played a decisive role in the formation of a mounded stratigraphy, which in turn acted as clues to the important tectonic phase since the late Miocene.
1. Introduction
Extensive attention has been paid to the formation of deep-water mounds in recent decades [1,2]. The presence of mounds within the strata can cause dome-like bedforms with mounded seismic reflections [3,4]. Various origins of deep-water mounds in debates mainly involved the carbonate reefs [5,6], mud diapirs or mud volcanoes [4,7], deep-water wave sediments [8], sand bars related to differential compaction [9,10,11], and remnant mounds originated from channel incision [12,13,14,15].
In recent years, pervasive mounded seismic reflections were detected in the Miocene Meishan Formation (Fm.) in the Qiongdongnan Basin (QDNB) [13,16]. Numerous models were proposed over the years to interpret their origins but there is no unified conclusion [4,5,14,15,16,17,18]. A widely accepted view in prior studies was that the middle Miocene was the dominant reef-building period in the northern South China Sea, and the mounded reflections were then thought to be the carbonate reefs [5,16,19]. Nevertheless, recent drilling revealed that some mounds were mainly composed of mud-rich lithology rather than reefs [18,20]. Channel incision has also been considered the possible controlling factor in the formation of the Miocene mounds in the study area [4,15]. However, most of the mounds trend roughly parallel with the inferred strike of the slope, which contradicts the principle that remnant mounds generated by the incision have their axes pointing downslope in most situations [14,16,21]. Additionally, these mounds were interpreted as sediment waves generated by bottom currents, but lacked the overwhelming proof supporting the existence of the bottom currents at that time [13]. Therefore, the models developed previously might not be readily applicable to the study area, and other mechanisms are required to explain the formation of mounds. It is worth noting that much of the topographic relief can appear in the structurally disturbed strata [3,22]. For the QDNB, an important tectonic transformation occurred at the turn of the middle and late Miocene, accompanied by intense tectonic activation corresponding to the time equal to the top of the Meishan Fm. [23,24,25]. Whether the formation of the mounds within the uppermost layer of the middle Miocene is related to such tectonic change has not been noticed previously.
In this study, we applied 2D and 3D seismic data to describe the characteristics of the mounds within the uppermost layer of the Miocene Meishan Fm. Combined with the tectonic settings, a novel model was developed to explain the formation process of the mounds. This model accentuates the decisive role played by tectonic activities in the creation of the mounds. The research results may offer a new idea in the interpretation of similar geological phenomena in other areas around the world.
2. Geological Setting
The QDNB is located at the west of the NE-trending extensional system in the northern South China Sea [26,27,28,29] and comprises the Northern Depression, Northern Uplift, Central Depression, and Southern Uplift from the north to south [30,31,32] (Figure 1). The Central Depression is located in the deep-water area, including the Ledong, Lingshui, Songnan, Ganquan, Beijiao, Baodao, and Changchang Sags, as well as the Lingnan and Songnan highs [33,34]. The water depths vary from 500 to 1500 m, with the maximum depth reaching 2500 m [35]. The tectonic evolution of the basin is consistent with a typical passive margin containing rifting and thermal subsidence. The unconformity of T6 that formed at ~21 Ma divided the Cenozoic strata of the basin into the syn-rift and post-rift layers. Faults were extremely developed in the syn-rift stage while seldom active in the post-rift stage [13,27]. Since the late Miocene, tectonic subsidence accelerated, accompanied by intense reactivation of faults in the eastern basin [23,24,36]. Correspondingly, the water depth of the basin increased [16,37]. In addition, since the cessation of submarine expansion (~16 Ma), magma has been widely active in the South China Sea and its adjacent areas [25,38]. There is a high heat flow zone in the Baodao to Changchang Sags, which was closely related to the thermal events involving massive magmatic intrusions and eruptions from the Miocene to Pliocene [37].
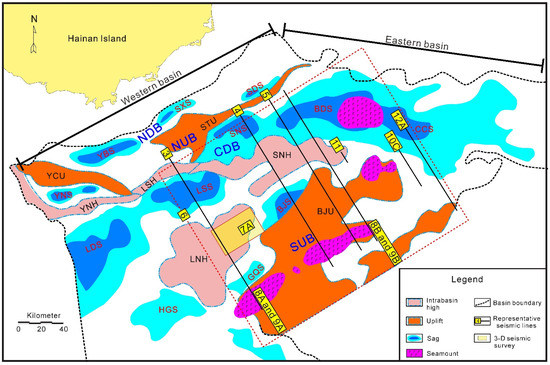
Figure 1.
Tectonic units of the Qiongdongnan Basin (modified from [30,31]). The Qiongdongnan basin is divided into the eastern and western basin according to the direction change of the basin axis. Seamounts composed of basaltic volcanic rocks developed in the south eastern uplifts and eastern sags. NDB = Northern Depression Belt. NUB = Northern Uplift Belt. CDB = Central Depression Belt. SUB = Southern Uplift Belt. YCU = Yacheng Uplift. STU = Songtao Uplift. BJU = Beijiao Uplift. YNH = Yanan High. LSH = Lingshui High. LNH = Lingnan High. SNH = Songnan High. YNS = Yanan Sag. YBS = Yabei Sag. SXS = Songxi Sag. SDS = Songdong Sag. LDS = Ledong Sag. LSS = Lingshui Sag. BJS = Beijiao Sag. SNS = Songnan Sag. BDS = Baodao Sag. CCS = Changchang Sag. GQS = Ganquan Sag. HGS = Huangguang Sag.
The main sequence boundaries of the basin including Tg, T8, T7, T6, T5, T4, T3, and T2 divided the Cenozoic strata into Lingtou (E2l), Yacheng (E3y), Lingshui (E3l), Sanya (N1s), Meishan (N1m), Huangliu (N1h), Yinggehai (N2y) and Ledong (Ql) Fms. (Figure 2). The depositional environment transformed from a coast and shallow sea to a semi-deep and deep sea from the middle to late Miocene [4,18]. The lower member of the Meishan Fm. is composed of mudstones, sandstones, and calcareous sandstones; its upper member mainly consists of mudstones mixed with thin argillaceous siltstones [15,20,39]. The lower member of the Huangliu Fm. is dominantly fine sandstones interbedded with thin mudstones and its upper member primarily comprised sandy limestones and fine sandstones [15]. A large submarine canyon (i.e., Central Canyon) was developed in the late Miocene, with an ‘S’-shaped axis parallel to the shelf break of the basin [18]. The mounded stratigraphy within the Miocene Meishan Fm. is restricted to the Southern Slope (between the Central Depression and Southern Uplift) which has the topography dipping from SE to NW, and is bounded by the Central Canyon to the north and the Xisha Islands to the south [5,18].
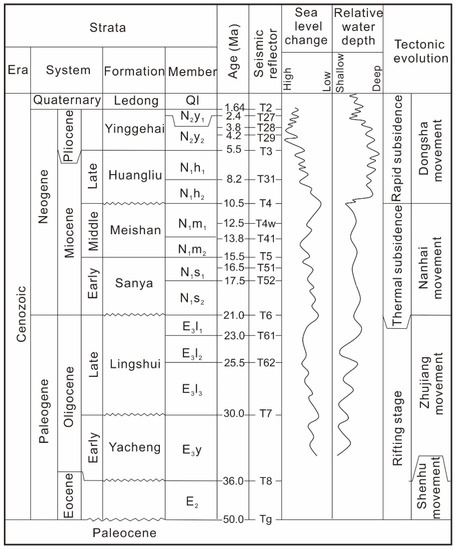
Figure 2.
Generalized stratigraphic column of the Qiongdongnan Basin (modified from [28,29]).
3. Data and Methods
The 2D and 3D seismic data used in this study were acquired over the past several years by Guangzhou Marine Geological Survey (GMGS). The G Gun II type air-gun sources were employed to acquire the seismic lines [40]. The seismic streamer used the Seal 24-digit cable, with a submerged depth of 8 m, and the receiver streamer had 240 traces and 60-fold coverage [41]. The 5700 km of 2D seismic lines covering the QDNB have a dominant frequency of 30 HZ on average, with a vertical resolution of 20 m and a trace interval of 6.25 m. In particular, new multi-channel 3D seismic volumes acquired in 2018 cover an area of ~800 km2 located in the Lingnan High, with the dominant frequency ranging from 30 to 70 Hz. The sampling interval for the 3D seismic data is 1 ms, with a bin size of 3.125 m × 18.75 m. The seismic data were processed by the Institute of Processing in the GMGS using the GeoCluster (a product of CGG®) processing system. The processing procedures including data input, trace editing, static correction, prestack noise attenuation, amplitude compensation, prestack deconvolution, CMP sorting, velocity analysis, dynamic correction, residual static correction, dip moveout (DMO) correction, prestack time migration, quality control in processing, poststack noise attenuation, and poststack time migration have been described by Wang et al. (2010) and Zhang (2020) [41,42].
The interpretation of seismic data was carried out by the Geoframe® software (a product of Schlumberger®) to construct the seismic stratigraphic framework. The seismic data were zero-phased and displayed normal polarity, indicating a positive event on the seismic profiles which is shown as a red reflection [25]. The identification of seismic facies differences and contact relationships between strata supported the tracking of sequence boundaries [43]. Eight main seismic sequence boundaries including Tg, T8, T7, T6, T5, T4, T3, and T2 were identified (Figure 3, Figure 4 and Figure 5). Faults can be identified in seismic profiles in the form of the offset of seismic events or zones of poor seismic signal across which reflectors are offset [3,44]. Fault interpretation was conducted by adopting appropriate geometric and kinematic models, e.g., the listric normal fault, domino-type fault, and flower structure [45]. Based on this, the seismic interpretation emphasized describing the geometric characteristics of the mounds within the uppermost layer of the Meishan Fm. The width and height of the mounds and their distribution range were determined based on the 2D seismic profiles. In addition, the isopach map of the Huangliu Fm., prepared based on seismic surfaces T3 and T4, was used to recover the paleogeomorphology corresponding to the end of the Meishan deposition. Moreover, the seismic attribute map of the curvature was extracted by the Geoframe® to reveal the plan-view characters of the mounded topography. Curvature calculates the bending degree of the stratum, which can effectively reflect geomorphic features such as valleys, ridges, and domes [46,47].
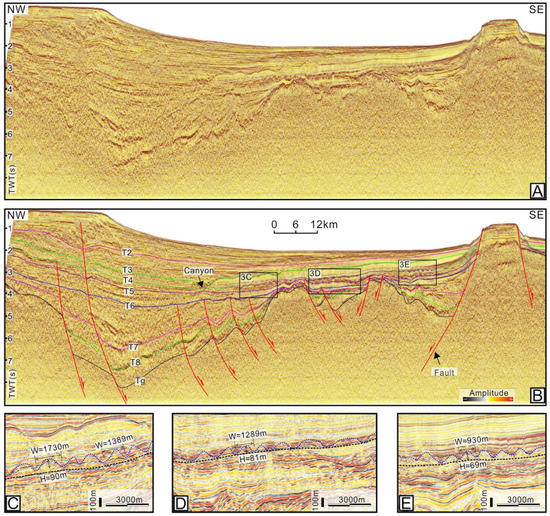
Figure 3.
(A,B) Uninterpreted and interpreted seismic section traversing the Lingshui Sag, showing the stratigraphic and structural characteristics (for location, see Figure 1). (C–E) Seismic profiles and their interpretations showing the mounded topography at the top of Meishan Fm (for locations, see Figure 3A). W = width; H = height; TWT = two-way traveltime.
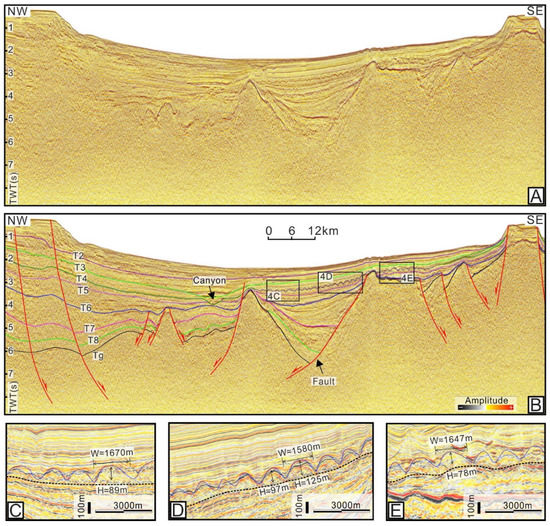
Figure 4.
(A,B) Uninterpreted and interpreted seismic section traversing the Beijiao Sag, showing the stratigraphic and structural characteristics (for location, see Figure 1). (C–E) Seismic profiles and their interpretations showing the mounded topography at the top of Meishan Fm (for locations, see Figure 4A). W = width; H = height; TWT = two-way traveltime.
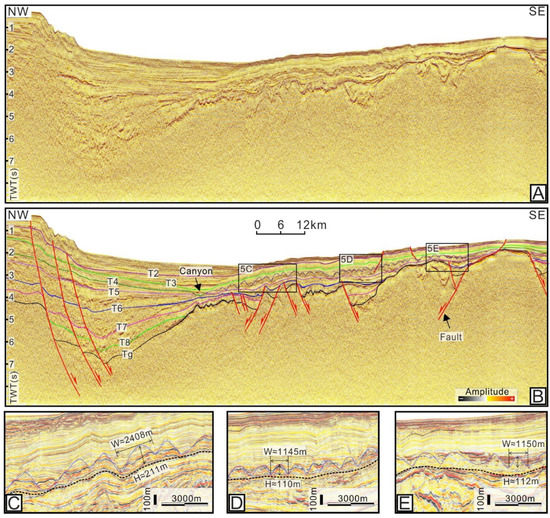
Figure 5.
(A,B) Uninterpreted and interpreted seismic section traversing the Baodao Sag, showing the stratigraphic and structural characteristics (for location, see Figure 1). (C–E) Seismic profiles and their interpretations showing the mounded topography at the top of Meishan Fm (for locations, see Figure 5A). W = width; H = height; TWT = two-way traveltime.
To determine the tectonic histories, backstripping was employed to reconstruct the amount and rate of tectonic subsidence in different stages [48,49]. Back-stripping employs the tectonic subsidence equation presented by Steckler and Watts (1978) [50]. The method is based on the crustal isostatic principle to backstrip the present stratigraphy layer by layer and to obtain the true basement subsidence caused by the tectonic driving forces [48]. Tectonic subsidence reconstruction was performed by dividing and dating the sequence boundary of the seismic profiles. The ages of the sequence boundary are shown in Figure 2. In the process, the seismic sequence boundaries were time-depth conversed by using the formula provided by the GMGS. There is a decrease in the porosity of sediment with an increase in overlying strata thickness during the compaction process [49]. To remove the effect of compaction, the original amount of subsidence in each stratum can be recovered by the relationship between porosity and depth that fits an exponential function to recover the original thicknesses of strata [51]. Additionally, considering that the depositional thickness is not equivalent to the subsidence when the sedimentary interface remains below the water surface, the accurate paleo-water depths and eustatic variations were taken into consideration [48,52]. The paleowater depth data were collected from the previous research results of Zhai et al. (2013) and Zuo et al. (2022) (Table 1) [32,53]. The eustatic variations are shown in Figure 2.

Table 1.
Reference value of paleo heat flow and water depth during different periods (referenced from [32,53]). HF = Heat flow; PWD = Paleowater depth. HF1, HF2, and PWD1 apply to the northern slope; HF3, HF4, and PWD2 apply to the central depression; HF5, HF6, and PWD3 apply to the southern uplift.
4. Results
4.1. Seismic Stratigraphy
The seismic reflector T4 corresponds to the regional unconformity which represented the Dongsha movement in the South China Sea [16]. In the Southern Slope, the reflector T4 truncated the underlying strata and was onlapped by overlying sediments [4,15], as shown in Figure 3, Figure 4 and Figure 5. The underlying Meishan Fm. can be divided into upper and lower members by an obvious interface. The upper member is characterized by strong-moderate amplitudes, moderate frequency, and mounded reflections, and the lower member shows subparallel sheet-shaped reflections with moderate-strong amplitudes and moderate frequency (Figure 3, Figure 4 and Figure 5). The overlying Huangliu Fm. is dominated by moderate amplitude, moderate-weak frequency, and parallel-subparallel reflections (Figure 3, Figure 4 and Figure 5). The Huangliu Fm. gradually thins onto the southern margin of the basin. A large submarine canyon (Central Canyon) was developed in the post-rift sequence of the QDNB, which is distributed in the Central Depression from west to east (Figure 3, Figure 4, Figure 5 and Figure 6). The large magmatic body between Songnan and Baodao Sags divides the canyon into two sections, the west section trending NE and the east section trending nearly EW (Figure 6).
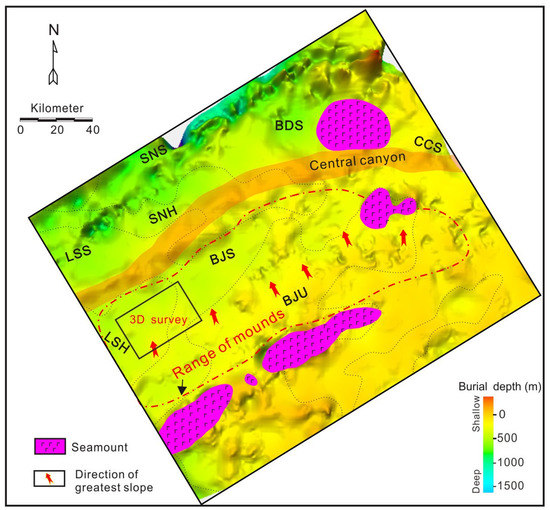
Figure 6.
Paleogeomorphology at the beginning of the deposition of the Huangliu Fm., showing the directions of the greatest slope in the southern area. The red dashed line indicates the range of the mounds. LSS = Lingshui Sag. BJS = Beijiao Sag. SNS = Songnan Sag. BDS = Baodao Sag. CCS = Changchang Sag. LNH = Lingnan High. SNH = Songnan High. BJU = Beijiao Uplift.
4.2. Characteristics of Mounded Stratigraphy
The NW–SE oriented seismic profiles show that the top of the Meishan Fm. is characterized by the elevations alternating with ‘V’-shaped troughs, displaying undulated morphologies (Figure 3, Figure 4 and Figure 5). The elevations tend to be present as lenticular seismic reflectors that are thickest in the middle part and thin toward both wings, showing dome-like bedforms, which are common not only in the QDNB but also in the Pearl River Basin in the northern South China Sea [5,16,18]. Similar elevations were described as ‘mounds’ previously, and strata characterized by the presence of mounds are commonly said to have ‘mounded topography’ [3,18]. The mounded stratigraphy was constrained between the T4 and the boundary of the upper and lower member of the Meishan Fm. (i.e., T5) (Figure 3, Figure 4 and Figure 5). The mounds distributed in the Lingnan High have heights varying from 70 to 90 m, with the widths ranging from 0.9 to 1.7 km (Figure 3C–E). The heights of a single mound in the Beijiao area vary from 90 to 125 m, and their average width is greater than 1.5 km (Figure 4C–E). The mounds in the south of the Baodao Sag have heights of about 110~210 m, with widths ranging from 1.0 to 2.4 km (Figure 5C–E). On the whole, the scale of the single mound in the eastern area seems larger. The internal reflectors of the mounds show strong-moderate amplitudes and moderate frequency, which are characterized by obvious fold structures and disturbed bedding (Figure 3, Figure 4 and Figure 5). The seismic reflections within the troughs vary greatly in different areas, displaying strong-moderate amplitudes and moderate frequency in the Lingnan High (Figure 3C–E and Figure 7B,C), and moderate-weak amplitudes and low frequency in the Beijiao area and the south of the Baodao Sag (Figure 4 and Figure 5). The reflector T4 commonly truncated the flanks of the mounds and was onlapped, filled, and leveled by subsequent seismic strata corresponding to the Huangliu Fm. (Figure 3, Figure 4 and Figure 5). Spatially, the mounds were most developed in the middle of the Southern Slope and disappeared in the Central Depression and South Uplift (Figure 3, Figure 4, Figure 5 and Figure 6). The mounded stratigraphy covers an area restricted to the east of the Huaguang Sag, west of the Changchang Sag, north of the Beijiao Uplift, and south of the Central Canyon (Figure 6). Additionally, the curvature attribute map calculated for the top of the Meishan Fm. shows that the mounded topography is characterized by coupled elongated ridges and gullies, with most of their axes predominantly oriented SWW–NEE and SW-NE (Figure 7A). These elongated ridges and gullies show a subparallel configuration with a few intersections.
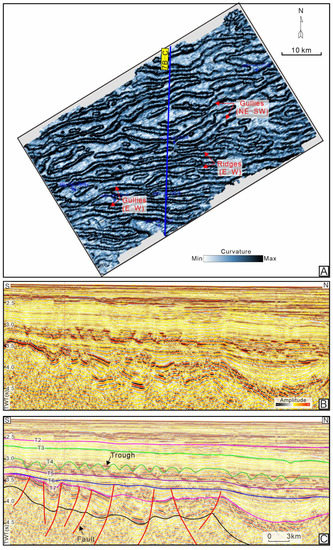
Figure 7.
(A) Characteristics of mounded topography revealed by curvature analysis based on 3D seismic data (See Figure 6 for the location of the 3D survey). The mounded topography is characterized by the alternating distribution of nearly EW-trending elongate troughs and ridges. (B,C) The top of the Miocene Meishan Formation has a mounded topography characterized by the mounds alternating with troughs (for location, see Figure 7A). TWT = two-way traveltime.
4.3. Tectonic Subsidence
The balanced cross-sections were created by using the backstripping technique to determine the tectonic subsidence in different stages [48,49]. The result shows that the sedimentary centers were controlled by the boundary faults in the Paleogene, during which the sedimentary thickness and subsidence rate in the depression centers are larger than those in the uplift belts (Figure 8 and Figure 9). The Eocene is relatively thin and the subsidence rate is low. The sedimentary thickness and subsidence rate in the early Oligocene significantly increased. The sedimentary thickness in the late Oligocene is relatively thick while the subsidence rate decreased. The faults were almost inactive when the basin entered the post-rift stage and its evolution was mainly controlled by thermal subsidence (Figure 8). During the depositional period of Sanya and Meishan Fms., the sedimentary thickness is relatively thin and the subsidence rate was extremely low, with an average value of less than 150 m/myr (Figure 9). In addition, there was little difference in tectonic subsidence between the Central Depression and the Southern Slope. During the deposition of the Huangliu Fm., the sedimentary thickness increased slightly and the subsidence rate in the Central Depression was ~200 m/myr and gradually decreased southward (Figure 9). During the depositional period of the Yinggehai Fm., sedimentary thickness and subsidence increased sharply, with a maximum cumulative rate approaching ~1100 m/myr in the Lingshui Sag and ~1600 m/myr in the Baodao Sag (Figure 8 and Figure 9). The difference in subsidence between the Central Depression and the Southern Slope and Southern Uplift became more obvious. During the deposition of the Ledong Fm., the deposition thickness was still large, and the Baodao and Lingshui Sags had a subsidence rate of ~800 m/myr and ~950 m/myr, respectively (Figure 9). At the same time, the subsidence of the Southern Uplift was much less than that of the Central Depression. Overall, the most obvious feature of the basin is that since 10.5 Ma, the subsidence began to accelerate, showing higher subsidence in the depressions and lower subsidence in the Southern Uplift.
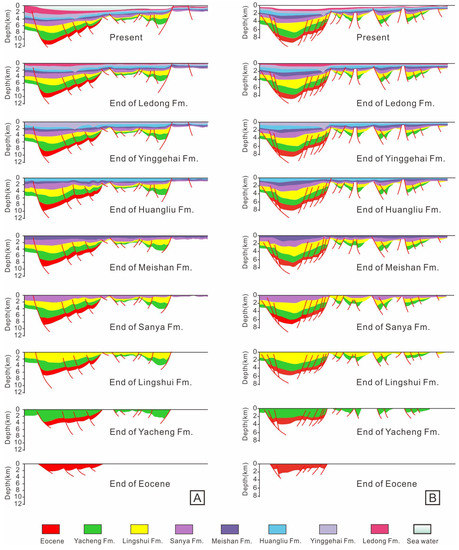
Figure 8.
(A,B) Balanced cross-sections created based on the two profiles traversing the Lingshui and the Baodao Sag, respectively (for location, see Figure 1).
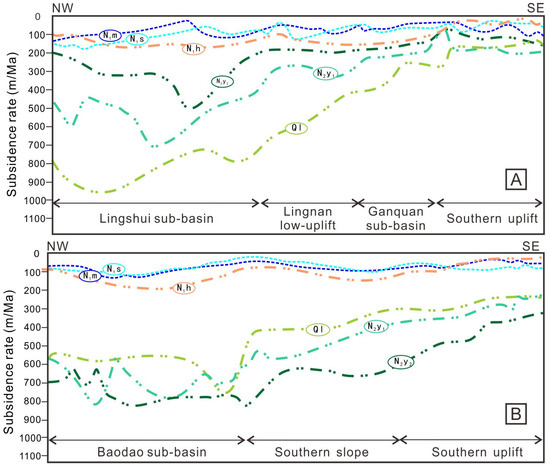
Figure 9.
(A,B) Subsidence curves created based on the two sections traversing the Lingshui and the Baodao Sags, respectively (for location, see Figure 1). The subsidence rate was low in the period of the Sanya and Meishan deposition, then increased slightly during the period of the Huangliu Deposition, and increased sharply from the period of the Yinggehai Deposition. Moreover, the subsidence rate of the depressions is higher than that of the Southern Uplift after the period of the Huangliu Deposition. N1s = Sanya Fm., N1m = Meishan Fm.; N1h = Huangliu Fm.; N2y1 = Lower Yinggehai Fm.; N2y2 = Upper Yinggehai Fm.; Ql = Ledong Fm. Ma = Megaannus.
5. Discussion
The mounded topography in the study area was previously supposed to be the result of the incision of bottom currents or channels [14,15]. The main evidence supporting this view is that some troughs between the mounds are characterized by high amplitude reflections marking the sand-prone lithologies which may be a clue to the incision [4,14,15], as shown in Figure 3C–E and Figure 7B,C. However, quite a few troughs distributed over a wider area are characterized by weak amplitudes, probably marking the bathyal–abyssal deposits [5,18] (Figure 4C and Figure 5C). Additionally, the internal reflectors within most of the mounds have folded seismic patterns, which might be related to other forces rather than the incision (Figure 3, Figure 4 and Figure 5). Moreover, paleogeomorphology indicated that the seabed over the Southern Slope roughly inclined toward NNW after the deposition of the Meishan Fm (Figure 6). If the troughs were indeed derived from the incision, their axes should have tended to the downdip of slope (NNW) in most situations [21]. However, it is not consistent with the result shown in Figure 7, with most of the troughs tending to be parallel to the strike of the slope (SWW–NEE and SW-NE). These doubts implied that the origin of the mounded topography cannot be simply explained solely by incision. In the examples from the Gulf of Mexico, the Brazilian margin, and the Central North Sea, the undulated morphologies can appear over tectonically active slopes [3,21,22,54,55,56,57]. Similar geological phenomena were observed at the seabed of the Shenhu Sea (Figure 10A) [40] and the south of the QDNB (Figure 10B), featured by seemingly mounded topography related to the disturbance of strata by detachment faults. These phenomena are commonly explained by the gravity gliding of sediments down a slope, which can generate a type of listric detachment fault (flattening downward) with associated rotated blocks to cause seabed relief [21,56,57,58,59]. Such a process can be triggered by rapid deposition, earthquakes, seafloor steepening, and excess pore pressure [58,60]. These studies provided an important insight into discovering the origin of a mounded topography in the study area.
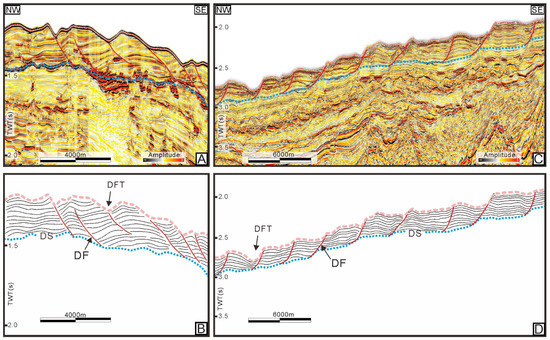
Figure 10.
(A,B) Seismic profile and its geological interpretation showing the seemingly mounded topography on the seabed caused by submarine landslides in the Shenhu Sea in the northern South China Sea (profile quoted from [40]). (C,D) Seismic profile and its interpretation showing the seemingly mounded topography on the seabed in the Southern Slope (for location, see Figure 1). DS = detachment surface; DF = detachment fault; DFT = downfaulted trough; TWT = two-way traveltime.
In this study, the mounded features were interpreted to result from the gravity gliding that was induced by tectonic activities. Firstly, detailed examinations of seismic data revealed that the uppermost layer of the Meishan Fm. was dismembered into a series of moderately deformed blocks by a number of faults with listric geometries which ceased downward to a unified surface (Figure 11A–C). The blocks resting upon the fault planes have shown clockwise rotation, with their internal beds perpendicular to the concave upward fault planes (Figure 11A–C). Secondly, soft-sediment deformation associated with gravity gliding might have occurred in the mounds (blocks) with their internal reflections showing convex-up fold structures and disturbed bedding (Figure 3, Figure 4 and Figure 5 and Figure 11A–C) [61]. Such phenomenon can be related to the rollover anticlines unique to the listric growth faults or associated with the local compressive stresses pervasive in slide blocks which cause internal beds to buckle [22,62,63]. These features are consistent with the gravity slide tectonics shown in some important examples documented previously [3,21,22,54,55,56,57]. It can be inferred that, after the end of Meishan deposition, the uppermost unconsolidated deposits composed of mudstones mixed with thin argillaceous siltstones glided along an underlying shear plane which is probably the top of deep lithified strata [3,15,20,21,39]. Finally, the unbalanced subsidence corresponding to the time equal to the top of the Meishan Fm. was likely to trigger the gravity gliding of sediments which created the mounds. Specifically, the subsidence of the basin shows a decreasing trend from the Central Depression to the southern margin since 10.5 Ma, which immediately steepened the Southern Slope with an NNW inclination (Figure 6 and Figure 9). Studies indicated that the occurrence of a steepening slope induced by the basement-driven differential subsidence was an important aspect of creating sufficient driving forces to drive the gravity gliding [3]. Some scholars suggested that the differential subsidence triggered an intense erosion of the turbidity currents, which created the embryo of the Central Canyon in the late Miocene [64,65,66,67,68]. Therefore, it can be inferred that the differential subsidence across the Southern Slope since 10.5 Ma might have generated sufficient forces to drive the gravity gliding that created the mounds.
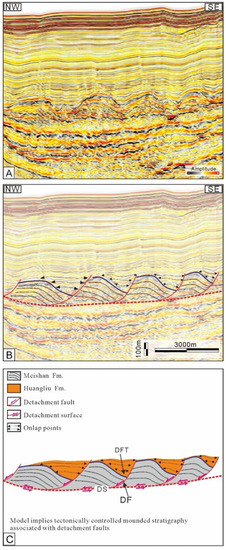
Figure 11.
(A) Uninterpreted seismic profiles, (B) interpretations, and (C) their geological models showing the formation of the mounded stratigraphy (for locations, see Figure 1). The tilted fault blocks rest on the fault plane of detachment faults, with their tops constituting the seemingly mounded topography. DS = detachment surface; DF = detachment fault; DFT = downfaulted trough; TWT = two-way traveltime.
Further analysis indicated a time–space coupling relationship between the formation of mounds and the tectonic events including accelerated subsidence, magmatic activity, and fault reactivation. The accelerated subsidence in the post-rift stage has been observed in many rifted basins, which was considered to be related to the deep thermal anomaly [23,69,70,71]. Detailed examination of seismic data revealed a large number of magmatic intrusions distributed near the deeply rooted faults (Figure 12B). These faults likely extend deeply into magma chambers beneath the Central Depression to provide primary pathways for magma migration [25]. Studies indicated that massive magmas invading up to the cold upper crust through the faults might contribute to the decay of a deep thermal source and the cooling of the asthenosphere, which would cause rapid subsidence [72,73,74]. The samples from adjacent areas indicated that the magmatism typically occurred in the Miocene and more recently [25,37]. Therefore, the accelerated subsidence since 10.5 Ma was likely related to the magmatic activities. In addition, such subsidence showed a higher rate at the crustal thinning zone beneath the Central Depression and decreased to the north and south of the basin (Figure 9). Under the influence of differential subsidence, the stratum of the basin was folded into a syncline, which induced extensional strain at the flanks of the syncline [74] (Figure 13A). Many Neogene faults extended upward to the interface T4 (Figure 12C,D), indicating that their formation age dated 10.5 Ma. It can be inferred the extensional strain induced by differential subsidence was accommodated by the generation of faults in the deep rigid layers, as well as the gravity slide tectonics in the shallow soft layers (Figure 12D and Figure 13A) [75]. Although it is a speculation, local seismic disturbance caused by magmatic activity and fault reactivation might also have triggered slope instability and gravitational sliding [57,60,76,77,78,79].
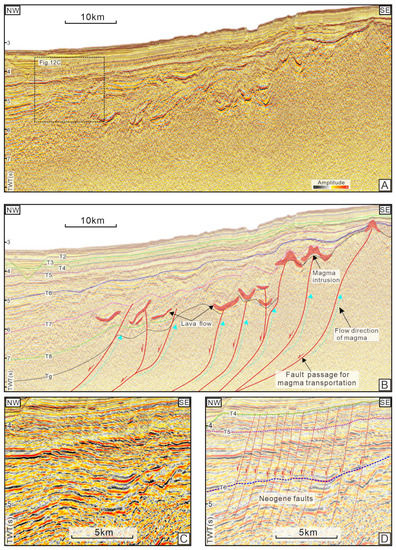
Figure 12.
(A) Seismic profile and (B) its interpretation showing the magmatic intrusions associated with the deeply rooted faults (for location, see Figure 1). (C,D) Seismic profile and its interpretation show the dense post-rift faults developed in the eastern depression (for location, see Figure 12A). TWT = two-way traveltime.
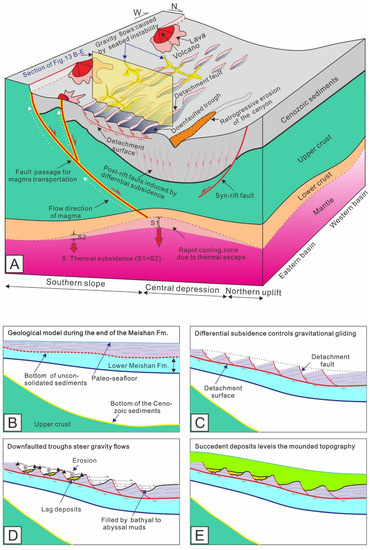
Figure 13.
(A) Model to explain the formation of mounded morphologies in the study area of the Qiongdongnan Basin. Escape of massive magmas through the faults contributed to the cooling of the hot mantle material beneath the crustal thinning zone, resulting in quicker subsidence in the overlying Central Depression. The differential subsidence caused the gravitational gliding of the uppermost layers and the generation of faults in the deep rigid layers. The downfaulted troughs steered the gravity flows along their axes. (B–E) Diagrams illustrating the geological processes responsible for the creation of mounded stratigraphy.
Here, the processes responsible for the formation of mounded stratigraphy are summarized. Firstly, differential subsidence associated with magmatic activities steepened the slope at the end of the Meishan deposition, leading to the gravity gliding of the uppermost unconsolidated layer along a detachment surface (Figure 13B,C). Such a process generated a series of listric detachment faults with numerous tilted fault blocks resting on their fault planes (Figure 13C). The arcuate fault planes and the flanks of blocks together formed the undulated topography. Studies indicated that the denudation of some structural highs in the southern margin at the turn of the middle and late Miocene generated sedimentary sources, which were transported farther into the basin by gravity flows [15]. Then, there might have been some downfaulted troughs steering the gravity flows along their axes, with the unloading of sand-rich deposits at the bottom (Figure 13D). Deposition of other troughs without passing of gravity flows was predominantly from the succeeding bathyal–abyssal muds (Figure 13D). Finally, the Huangliu Fm. onlapped onto and leveled the mounded topography with its final shape adjusted by compaction (Figure 13E). The results of this study do not deny the existence of the erosion of gravity flows, which is also one of the processes that enhanced the relief amplitude of the mounded geometries. It is worthwhile to mention that gravity gliding derived from differential subsidence is decisive for the creation of mounded topography, while erosion and other processes are considered to be of secondary importance and will embellish such topography rather than create it. The differential subsidence associated with magmatic activities led to the development of mounds, which in turn became important clues implying revolutionary changes in tectonic movement that took place at the time equivalent to T4.
6. Conclusions
Detailed examination of seismic data revealed a unique mounded topography corresponding to the top of the Meishan Fm. in the Southern Slope of the QDNB. Such topography is characterized by the mounds alternating with ‘V’-shaped troughs, which display elongated ridges flanked by similar gullies trending roughly parallel with the strike of the slope (SWW–NEE and SW-NE). The height of the mounds varies from about 70~210 m, and they are about 0.9~2.4 km in width. The internal reflectors within the mounds were truncated by the reflector T4 which is in turn overlain by seismic strata corresponding to the Huangliu Fm. Since the late Miocene (ca. 10.5 Ma), under the influence of magmatism, rapid subsidence occurred, which was manifested by the decreasing of subsidence from the center to the south of the depression. Such differential subsidence induced fault reactivation and steepened the slope. These tectonic events triggered the gliding of the uppermost deposits, which generated a series of listric detachment faults that ceased downwards a unified detachment surface. The top of tilted fault blocks that were constrained by these faults formed the rudiment of mounded topography. The downfaulted troughs steered the gravity flows and leveled by the lag deposits or bathyal–abyssal muds. The genetic model of the mounds established in this study accentuates the decisive contribution of tectonic activities to the creation of the mounded topography.
Author Contributions
Methodology, L.X. and T.Z.; investigation, L.X. and J.R.; formal analysis, L.X., J.R. and H.D.; writing—original draft preparation, L.X.; supervision, W.S., R.W. and Y.H.; conceptualization, R.W.; writing—review and editing, R.W.; software, Y.H., H.D., J.H. and Y.D.; funding acquisition, R.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 42202121).
Data Availability Statement
The data relevant with this study can be accessed by contacting the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
This study was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 42202121). The data acquired in the research process is primarily attributed to Guangzhou Marine Geological Survey, Guangzhou. Thanks to the editor and reviewers for the suggestions and other assistance in improving this manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Hart, P.E.; Hutchinson, D.R.; Gardner, J.; Carney, R.S.; Fornari, D. A photographic and acoustic transect across two deep-water seafloor mounds, Mississippi Canyon, northern Gulf of Mexico. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2009, 25, 969–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meredyk, S.P.; Edinger, E.; Piper, D.J.W.; Huvenne, V.A.I.; Hoy, S.; Ruffman, A. Enigmatic deep-water mounds on the Orphan Knoll, Labrador Sea. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 6, 744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koša, E. Differential subsidence driving the formation of mounded stratigraphy in deep-water sediments; Palaeocene, central North Sea. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2007, 24, 632–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Pu, R.; Niu, N.; Li, B. Characteristics and origins of middle Miocene mounds and channels in the northern South China Sea. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2021, 40, 65–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Yuan, S.; Zhang, G.; Ma, Y.; Mi, L.; Xu, N. Seismic characteristics of a reef carbonate reservoir and implications for hydrocarbon exploration in deepwater of the Qiongdongnan Basin, northern South China Sea. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2009, 26, 817–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindler, E.; Wehrmann, A. Genesis and internal architecture of the Middle to Upper Devonian Gwirat Al Hyssan reef-mound (Western Sahara). Palaeogeogr. Palaeoecol. 2011, 304, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Wu, S.G.; Sun, Q.L.; Huuse, M.; Li, W.; Wang, Z.J. Submarine volcanic mounds in the Pearl River Mouth Basin, northern South China Sea. Mar. Geol. 2014, 355, 162–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wynn, R.B.; Stow, D.A.V. Classification and characterisation of deep-water sediment waves. Mar. Geol. 2002, 192, 7–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purvis, K.; Kao, J.; Flanagan, K.; Henderson, J.; Durant, D. Complex reservoir geometries in a deep water clastic sequence, Gryphon Field, UKCS: Injection structures, geological modelling and reservoir simulation. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2002, 19, 161–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Hao, F.; Xu, C.; Wang, Y.; Zou, H.; Gong, C. Differential compaction faults and their implications for fluid expulsion in the northern Bozhong Subbasin, Bohai Bay Basin, China. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2015, 63, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, N.I.P.; Alves, T.M.; Blenkinsop, T.G. Differential compaction over Late Miocene submarine channels in SE Brazil: Implications for trap formation. GSA Bull. 2018, 130, 208–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eschard, R.; Albouy, E.; Deschamps, R.; Euzen, T.; Ayub, A. Downstream evolution of turbiditic channel complexes in the Pab Range outcrops (Maastrichtian, Pakistan). Mar. Pet. Geol. 2003, 20, 691–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Pu, R.; Qu, H.; Zhang, G.; Liang, J.; Feng, Y. An origin discussion of mound-shaped reflections in Miocene, southern Qiongdongnan Basin. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2013, 35, 112–120, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Q.; Cartwright, J.; Wu, S.; Zhong, G.; Wang, S.; Zhang, H. Submarine erosional troughs in the northern South China Sea: Evidence for Early Miocene deepwater circulation and paleoceanographic change. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2016, 77, 75–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, P.; Jiang, T.; Kuang, Z.; Cheng, C.; Ren, J.; Lai, H. Sedimentary characteristics and origin of moundes in Meishan Formation, southern Qiongdongnan Basin. Bull. Geol. Sci. Technol. 2021, 40, 11–21, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Qu, H.; Zhang, G.; Pu, R. Seismic interpretation and hydrocarbon accumulations implication of the Miocene Meishan Formation reefs in southern Qiongdongnan Basin, northern South China Sea. J. Palaeogeogr. 2017, 6, 206–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Ren, Y.; Li, Z.; Jin, L. Geological interpretation and hydrocarbon exploration potential of three types of mound-shaped reflectors in the Meishan Formation, Southern Qiongdongnan Basin. Acta Geol. Sin. 2021, 95, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Wu, S.; Lv, F.; Wang, D.; Wang, B.; Zhang, X.; Ma, B. Middle Miocene mound-shaped sediment packages on the slope of the Xisha carbonate platforms, South China Sea: Combined result of gravity flow and bottom current. Deep-Sea Res. Part II 2015, 122, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Yang, Z.; Wang, D.; Lü, F.; Lüdmann, T.; Fulthorpe, C.; Wang, B. Architecture, development and geological control of the Xisha carbonate platforms, northwestern South China Sea. Mar. Geol. 2014, 350, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, C.; Ren, J.Y. Hyper-extended rift systems in the Xisha Trough, northwestern South China Sea: Implications for extreme crustal thinning ahead of a propagating ocean. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2016, 77, 846–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobbold, P.R.; Szatmari, P. Radial gravitational gliding on passive margins. Tectonophysics 1991, 188, 249–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, T.M. Submarine slide blocks and associated soft-sediment deformation in deep-water basins: A review. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2015, 67, 262–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Müller, R.D.; Li, S.; Gong, Z.; Steinberger, B. Origin of anomalous subsidence along the Northern South China Sea margin and its relationship to dynamic topography. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2006, 23, 745–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Ren, J.; Lei, C.; Wang, S. Postrift rapid subsidence characters in Qiongdongnan Basin, South China Sea. J. Earth Sci. 2011, 22, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Alves, T.M.; Zhao, M.; Sibuet, J.; Calvès, G.; Xie, X. Post-rift magmatism on the northern South China Sea margin. GSA Bull. 2020, 132, 2382–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, Z.; Sun, Z.; Liu, J.; Wang, Z. Structural differences between the western and eastern Qiongdongnan Basin: Evidence of Indochina block extrusion and South China Sea seafloor spreading. Mar. Geophys. Res. 2013, 34, 309–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Wang, L.S.; Yan, W.B.; Liu, S.W.; Cai, D.S.; Zhang, G.C.; Zhong, K.; Pei, J.X.; Sun, B. The tectonic evolution of the Qiongdongnan Basin in the northern margin of the South China Sea. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2013, 77, 163–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Xie, Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, X.; Tong, C. Characteristics of overpressure distribution and its implication for hydrocarbon exploration in the Qiongdongnan Basin. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2013, 66, 150–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Shi, W.; Xie, Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, X.; Tong, C. Identification of low-overpressure interval and its implication to hydrocarbon migration: Case study in the Yanan sub-basin of the Qiongdongnan Basin, South China Sea. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0183676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Sun, Z.; Liu, J.; Pérez-Gussinyé, M.; Zhuo, H. The continental extension discrepancy and anomalous subsidence pattern in the western Qiongdongnan Basin, South China Sea. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2018, 501, 180–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Yin, H.; Gan, J.; Wang, W.; Zhu, J.; Jia, D.; Xiong, X.; Xu, W. Explaining structural difference between the eastern and western zones of the Qiongdongnan Basin, northern South China Sea: Insights from scaled physical models. Tectonics 2022, 41, e2021tc006899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, T.; Wang, R.; He, Y.; Shi, W.; Liang, J.; Xu, L.; Du, H.; Deng, Y.; Xu, X. Natural gas migration pathways and their influence on gas hydrate enrichment in the Qiongdongnan Basin, South China Sea. Geofluids 2022, 2022, 1954931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, C.; Ren, J.; Pei, J.; Lin, H.; Yin, X.; Tong, D. Tectonic Framework and Multiple Episode Tectonic Evolution in Deepwater Area of Qiongdongnan Basin, Northern Continental Margin of South China Sea. Earth Sci. 2011, 36, 151–162, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Z.; Wan, Z.; Wang, X.; Shi, Q.; Cai, S.; Xia, B. The tectonic differences between the east and the west in the deep-water area of the northern South China Sea. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2016, 35, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Xu, L.; Shi, W.; Yang, W.; Wang, R.; He, Y.; Du, H. Shallow overpressure formation in the deep water area of the QiongdongnanBasin, China. Front. Earth Sci. 2022, 10, 922802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Sun, Z.; Yang, J.; Sun, Z.; Zhu, J.; Zhuo, H.; Stock, J. Seismic characteristics and evolution of post-rift igneous complexes and hydrothermal vents in the Lingshui sub-basin (Qiongdongnan basin), northwestern South China Sea. Mar. Geol. 2019, 418, 106043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Jiang, H.; Yang, J.; Yang, X.; Xu, H. Models of the rapid post-rift subsidence in the eastern Qiongdongnan Basin, South China Sea: Implications for the development of the deep thermal anomaly. Basin Res. 2017, 29, 340–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, K.; Xie, X.; Xie, Y.; Ren, J.; Chen, H. Post-rift tectonic reactivation and its effect on deep-water deposits in the Qiongdongnan Basin, northwestern South China Sea. Mar. Geophys. Res. 2015, 36, 227–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Zhai, S.; Xiu, C.; Liu, X.; Zong, T.; Luo, W.; Liu, X.; Chen, K.; Li, N. Geochemical characteristics and their significances of rare-earth elements in deep-water well core at the Lingnan Low Uplift Area of the Qiongdongnan Basin. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2014, 33, 81–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Jiang, T.; Kuang, Z.; Yang, C.; Zhang, C.; He, Y.; Cheng, Z.; Tian, D.; Xiong, P. Characteristics of gas chimneys and their implications on gas hydrate accumulation in the Shenhu area, northern South China Sea. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2020, 84, 103629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wu, S.; Yuan, S.; Wang, D.; Ma, Y.; Yao, G.; Gong, Y.; Zhang, G. Geophysical signatures associated with fluid flow and gas hydrate occurrence in a tectonically quiescent sequence, Qiongdongnan Basin, South China Sea. Geofluids 2010, 10, 351–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Liang, J.; Wei, J.; Lu, J.; Su, P.; Lin, L.; Huang, W.; Guo, Y.; Deng, W.; Yang, X.; et al. Geological and geophysical features of and controls on occurrence and accumulation of gas hydrates in the first offshore gas-hydrate production test region in the Shenhu area, Northern South China Sea. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2020, 114, 104191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X. Seismic Methods for Exploration and Exploitation of Gas Hydrate. J. Earth Sci. 2021, 32, 839–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Xu, S.; Zhuo, H.; Wang, Y.; Wu, S. Coupling relationship between shelf-edge trajectories and slope morphology and its implications for deep-water oil and gas exploration: A case study from the passive continental margin, East Africa. J. Earth Sci. 2020, 31, 820–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, B.; He, D.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, W. 3D geometry and kinematics of the Niudong Fault, Baxian Sag, Bohai Bay Basin, Eastern China—Insights from high-resolution seismic data. J. Struct. Geol. 2021, 146, 104307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marfurt, K.J.; Kirlin, R.L.; Farmer, S.L.; Bahorich, M.S. 3-D seismic attributes using a semblance-based coherency algorithm. Geophysics 1998, 63, 1150–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Yao, Y.; Liu, D.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Cai, Y. Application of seismic curvature attributes in the delineation of coal texture and deformation in Zhengzhuang field, southern Qinshui Basin. AAPG Bull. 2020, 104, 1143–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, P.; Ding, W.; Fang, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Feng, Z. Cenozoic tectonic subsidence in the southern continental margin, South China Sea. Front. Earth Sci. 2017, 11, 427–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, P.; Ding, W.; Zhao, Y.; Lin, X.; Zhao, Z. Detachment-controlled subsidence pattern at hyper-extended passive margin: Insights from backstripping modelling of the Baiyun Rift, northern South China Sea. Gondwana Res. 2022, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steckler, M.S.; Watts, A.B. Subsidence of the Atlantic-type continental margin off New York. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1978, 41, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, H.; Flemings, P.B.; Germaine, J.T.; Saffer, D.M. Consolidation and overpressure near the seafloor in the Ursa Basin, Deepwater Gulf of Mexico. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2011, 305, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, P.; Ding, W.; Lin, X.; Zhao, Z.; Fang, Y.; Li, C. Neogene subsidence pattern in the multi-episodic extension systems: Insights from backstripping modelling of the Okinawa Trough. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2020, 111, 662–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, P.; Chen, H.; Xie, Y.; Wang, Z.; Tong, C. Modelling of evolution of overpressure system and hydrocarbon migration in deepwater area of Qiongdongnan basin, South China Sea. J. Cent. South Univ. 2013, 44, 4187–4201, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Petrobras, P. Campos and Espirito Santo Basins, offshore Brazil. In Seismic Expression of Structural Styles: A Picture and Work Atlas; Bally, A.W., Ed.; American Association of Petroleum Geologists: Tulsa, OK, USA, 1983; Volume 2, pp. 51–58. [Google Scholar]
- Buffler, R.T.; Locker, S.D.; Bryant, W.R.; Hall, S.A.; Pilger, R.H. Gulf of Mexico. In Ocean Margin Drilling Program, Regional Atlas Ser., Atlas 6; Marine Science International: Woods Hole, MA, USA, 1984; 26p. [Google Scholar]
- Alves, T.M.; Lourençob, S.D.N. Geomorphologic features related to gravitational collapse: Submarine landsliding to lateral spreading on a Late Miocene–Quaternary slope (SE Crete, eastern Mediterranean). Geomorphology 2010, 123, 13–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, T.M. Scale-relationships and geometry of normal faults reactivated during gravitational gliding of Albian rafts (Espírito Santo Basin, SE Brazil). Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2012, 331–332, 80–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourgues, R.; Cobbolda, P.R. Sandbox experiments on gravitational spreading and gliding in the presence of fluid overpressures. J. Struct. Geol. 2006, 28, 887–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, G.D.O.; Cooper, R.; Gafeira, J.; Howe, J.A.; Long, D. Morphology of small-scale submarine mass movement events across the northwest United Kingdom. Geomorphology 2020, 365, 107282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biancardi, C.A.; Alves, T.M.; Martins-Ferreira, M.A.C. Unpredictable geometry and depositional stacking patterns of mass-transport complexes in salt minibasins. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2020, 120, 104522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsop, G.I.; Weinberger, R.; Marco, S.; Levi, T. Identifying soft-sediment deformation in rocks. J. Struct. Geol. 2019, 125, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, C.A.L. Three-dimensional seismic analysis of megaclast deformation within a mass transport deposit; implications for debris flow kinematics. Geology 2011, 39, 203–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imber, J.; Childs, C.; Nell, P.A.R.; Walsh, J.J.; Hodgetts, D.; Flint, S. Hanging wall fault kinematics and footwall collapse in listric growth fault systems. J. Struct. Geol. 2003, 25, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Fairweather, L.; Wu, S.; Ren, J.; Zhang, H.; Quan, X.; Jiang, T.; Zhang, C.; Su, M.; He, Y.; et al. Morphology, sedimentary features and evolution of a large palaeo submarine canyon in Qiongdongnan basin, Northern South China Sea. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2013, 62, 685–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, M.; Xie, X.; Xie, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, C.; Jiang, T.; He, Y. The segmentations and the significances of the Central Canyon System in the Qiongdongnan Basin, northern South China Sea. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2014, 79, 552–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, M.; Xie, X.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, T.; Zhang, C.; He, Y. Sedimentary evolution of the Central Canyon System in the Qiongdongnan Basin, northern South China Sea. Pet. Res. 2016, 1, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, M.; Wu, C.; Chen, H.; Li, D.; Jiang, T.; Xie, X.; Jiao, H.; Wang, Z.; Sun, X. Late Miocene provenance evolution at the head of Central Canyon in the Qiongdongnan Basin, Northern South China Sea. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2019, 110, 787–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, M.; Lin, Z.; Wang, C.; Kuang, Z.; Liang, J.; Chen, H.; Liu, S.; Zhang, B.; Luo, K.; Huang, S.; et al. Geomorphologic and infilling characteristics of the slope-confined submarine canyons in the Pearl River Mouth Basin, northern South China Sea. Mar. Geol. 2020, 424, 106166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, P.A.; Cloetingh, S. Dynamic processes controlling evolution of rifted basins. Earth Sci. Rev. 2004, 64, 1–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.; Franke, D.; Li, J.; Steuer, S. Seismic stratigraphy and tectonic structure from a composite multi-channel seismic profile across the entire Dangerous Grounds, South China Sea. Tectonophysics 2013, 582, 162–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franke, D.; Savva, D.; Pubellier, M.; Steuer, S.; Mouly, B.; Auxietre, J.; Meresse, F.; Chamot-Rooke, N. The final rifting evolution in the South China Sea. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2014, 58, 704–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z. The deep mantle upwelling beneath the northwestern South China Sea: Insights from the time-varying residual subsidence in the Qiongdongnan Basin. Geosci. Front. 2021, 12, 101246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, J.H.; Bunge, H.P. Are splash plumes the origin of minor hotspots? Geology 2006, 34, 349–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, Z.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Xu, Y.; Li, X. Identification of an ancient mantle reservoir and young recycled materials in the source region of a young mantle plume: Implications for potential linkages between plume and plate tectonics. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2013, 377, 248–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berra, F.; Carminati, E. Differential compaction and early rock fracturing in high-relief carbonate platforms: Numerical modelling of a Triassic case study (Esino Limestone, Central Southern Alps, Italy). Basin Res. 2012, 24, 598–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsop, G.I.; Weinberger, R.; Marco, S.; Levi, T. Distinguishing coeval patterns of contraction and collapse around flow lobes in mass transport deposits. J. Struct. Geol. 2020, 134, 104013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conforti, M.; Ietto, F. Influence of Tectonics and Morphometric Features on the Landslide Distribution: A Case Study from the Mesima Basin (Calabria, South Italy). J. Earth Sci. 2020, 31, 393–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Shi, W.; Xie, X.; Zhang, W.; Qin, S.; Liu, K.; Busbey, A.B. Clay mineral content, type, and their effects on pore throat structure and reservoir properties: Insight from the Permian tight sandstones in the Hangjinqi area, north Ordos Basin, China. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2020, 115, 104281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Xu, C.; Qi, W.; Huang, Y.; Cheng, J.; Xu, X.; Yao, Q.; Lu, Y.; Dai, B. Landslides Triggered by the 2020 Qiaojia Mw5.1 Earthquake, Yunnan, China: Distribution, Influence Factors and Tectonic Significance. J. Earth Sci. 2021, 32, 1056–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).