The Effect of Thermal and Moisture Stress on Insulation Deterioration Law of Ionic Contaminated High-Voltage Printed Circuit Board of Electronic Power Conditioner
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experiment Design
2.2. Test Sample Preparation
2.2.1. Divider Resistor
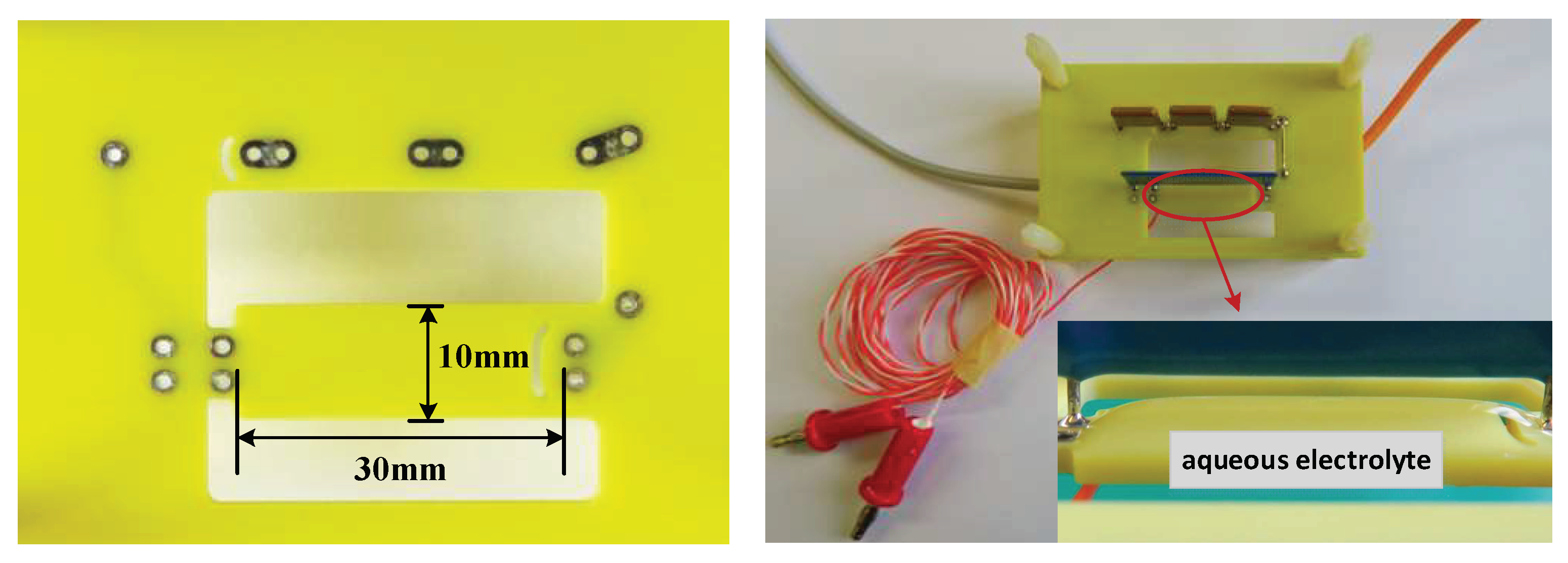
2.2.2. Preparation of the Test Boards
2.3. Testing Circuit
2.4. Testing Condition
2.4.1. Damp Heat Test
2.4.2. Alternating Damp Heat Test
2.5. Testing Platform
3. Results
3.1. Boundaries of Deterioration of Insulation Properties
3.2. Effect of Humidity and Ionic Contamination
3.3. Effect of Temperature and Ionic Contamination
3.4. Surface Discharge of HV-PCB
3.5. Effect of Condensation on Uncontaminated Samples
3.6. Encapsulaion Protection
4. Discussion
4.1. Analysis of the Influence of Temperature and Humidity on SIR
4.2. Analysis of Surface Discharge
4.3. Analysis of Clean Surface
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, Z.-C. The current status and developmental trends of space travelling wave tube amplifier. Space Electron. Technol. 2012, 4, 28–34. [Google Scholar]
- Pequet, E.; Delporte, P.; Fayt, P.; Gak, M.; Canon, T. ESA qualified EPC for telecommunication satellites TWTA. In Proceedings of the Abstracts. International Vacuum Electronics Conference 2000 (Cat. No. 00EX392), Monterey, CA, USA, 2–4 May 2000; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Secretariat, E.C.S.S. Space Engineering High-Voltage Engineering and Design Handbook; ESA Special Publication: Noordwijk, The Netherlands, 2014; p. 133. [Google Scholar]
- Tegehall, P.-E. Impact of humidity and contamination on surface insulation resistance and electrochemical migration. In The ELFNET Book on Failure Mechanisms, Testing Methods, and Quality Issues of Lead-Free Solder Interconnects; Springer: London, UK, 2011; pp. 227–253. [Google Scholar]
- Verdingovas, V.; Jellesen, M.S.; Ambat, R. Impact of NaCl contamination and climatic conditions on the reliability of printed circuit board assemblies. IEEE Trans. Device Mater. Reliab. 2013, 14, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, K.S.; Jellesen, M.S.; Moller, P.; Westermann, P.J.S.; Ambat, R. Effect of solder flux residues on corrosion of electronics. In Proceedings of the 2009 Annual Reliability and Maintainability Symposium, Fort Worth, TX, USA, 26–29 January 2009; pp. 502–508. [Google Scholar]
- Piotrowska, K.; Verdingovas, V.; Ambat, R. Humidity-related failures in electronics: Effect of binary mixtures of weak organic acid activators. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2018, 29, 17834–17852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdingovas, V.; Jellesen, M.S.; Ambat, R. Relative effect of solder flux chemistry on the humidity related failures in electronics. Solder. Surf. Mt. Technol. 2015, 27, 146–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, B.; Azarian, M.H.; Pecht, M.G. Effect of temperature and relative humidity on the impedance degradation of dust-contaminated electronics. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2013, 160, C97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Xie, Q. Effect of dust pollution on temperature characteristics of electrochemical migration. In Proceedings of the 2017 Prognostics and System Health Management Conference (PHM-Harbin), Harbin, China, 9–12 July 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Song, B.; Azarian, M.H.; Pecht, M.G. Impact of dust on printed circuit assembly reliability. In Proceedings of the IPC APEX EXPO, San Diego, CA, USA; 2012; Volume 3, pp. 1643–1659. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, C.; Tang, X.; Song, B.; Jin, J. Study on the Effect of Moisture Stress on Printed Circuit Board of Numerical Control System. In Proceedings of the 2012 Second International Conference on Instrumentation, Measurement, Computer, Communication and Control, Harbin, China, 8–10 December 2012; pp. 1661–1665. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, X.; Yu, S.; Chen, L.; Hu, J.; Zhang, Z. Test methods for electrochemical migration: A review. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2017, 28, 2279–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medgyes, B.; Illés, B.; Harsányi, G. Electrochemical migration behaviour of Cu, Sn, Ag and Sn63/Pb37. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2012, 23, 551–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medgyes, B.; Illés, B.; Harsányi, G. Effect of water condensation on electrochemical migration in case of FR4 and polyimide substrates. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2013, 24, 2315–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minzari, D.; Jellesen, M.S.; Moller, P.; Wahlberg, P.; Ambat, R. Electrochemical migration on electronic chip resistors in chloride environments. IEEE Trans. Device Mater. Reliab. 2009, 9, 392–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Medgyes, B.; Zhong, X.; Harsányi, G. The effect of chloride ion concentration on electrochemical migration of copper. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2015, 26, 2010–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tegehall, P.E.; Dunn, B.D. Evaluation of Cleanliness Test Methods for Spacecraft PCB Assemblies; ESA Publications: Auckland, New Zealand, 2006; Volume 275. [Google Scholar]
- Verdingovas, V.; Jellesen, M.S.; Ambat, R. Solder flux residues and humidity-related failures in electronics: Relative effects of weak organic acids used in no-clean flux systems. J. Electron. Mater. 2015, 44, 1116–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdingovas, V.; Jellesen, M.S.; Ambat, R. Influence of sodium chloride and weak organic acids (flux residues) on electrochemical migration of tin on surface mount chip components. Corros. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2013, 48, 426–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tegehall, P.E.; Dunn, B.D. Influence of flux residues and conformal coatings on the surface resistance properties of spacecraft circuit boards. ESA J. 1992, 16, 255–273. [Google Scholar]
- Hunt, C.; Zou, L. The impact of temperature and humidity conditions on surface insulation resistance values for various fluxes. Solder. Surf. Mt. Technol. 1999, 11, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Y.-L.; Lan, D.-F. Effects of soluble salts in dust on insulation failure of printed circuit boards. Trans. China Electrotech. Soc. 2016, 31, 114–119. [Google Scholar]
- Bahrebar, S.; Ambat, R. Investigation of critical factors effect to predict leakage current and time to failure due to ECM on PCB under humidity. Microelectron. Reliab. 2021, 127, 114418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahrebar, S.; Ambat, R. Time to Failure Prediction on a Printed Circuit Board Surface Under Humidity Using Probabilistic Analysis. J. Electron. Mater. 2022, 51, 4388–4406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, S.; Azarian, M.H.; Pecht, M.G. Surface insulation resistance of conformally coated printed circuit boards processed with no-clean flux. IEEE Trans. Electron. Packag. Manuf. 2006, 29, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancke, R. A moisture protection screening test for hybrid circuit encapsulants. IEEE Trans. Compon. Hybrids Manuf. Technol. 1981, 4, 492–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, P.; Dong, C.-F.; Xiao, K.; Wei, D. Current status and prospects of electrochemical migration research. Sci. Technol. Rev. 2018, 36, 64–73. [Google Scholar]
- Du, B.-X.; Xu, H.; Li, Y.-P.; Li, Z.-L. Study on characteristics of tracking resistance of silicon rubber composite insulators with high thermal conductivity for UHVDC transmission lines. High-Volt. Eng. 2013, 39, 2910–2915. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.-L.; Wang, P.; Ge, S.-C.; Li, F. Investigation on Dust Contamination of Aerospace Electrical Connector after Long-Term Storage. Trans. China Electrotech. Soc. 2014, 29, 269–276. [Google Scholar]
- Conseil-Gudla, H.; Jellesen, M.S.; Ambat, R. Printed circuit board surface finish and effects of chloride contamination, electric field, and humidity on corrosion reliability. J. Electron. Mater. 2017, 46, 817–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmon, C.W.; Grimm, R.L.; McIntire, T.M.; Peterson, M.D.; Njegic, B.; Angel, V.M.; Alshawa, A.; Underwood, J.S.; Tobias, D.J.; Gerber, R.B.; et al. Hygroscopic growth and deliquescence of NaCl nanoparticles mixed with surfactant SDS. J. Phys. Chem. B 2010, 114, 2435–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Korson, L.; Drost-Hansen, W.; Millero, F.J. Viscosity of water at various temperatures. J. Phys. Chem. 1969, 73, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-H.; Zhong, L.-S. Handbook of Electrical Electronic Insulation Technology; China Machine Press: Beijing, China, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, X.-D. High-Voltage Engineerin; Tsinghua University Press: Beijing, China, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Awakuni, Y.; Calderwood, J.H. Water vapour adsorption and surface conductivity in solids. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 1972, 5, 1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harsanyi, G. Irregular effect of chloride impurities on migration failure reliability: Contradictions or understandable? Microelectron. Reliab. 1999, 39, 1407–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sbar, N.L.; Kozakiewicz, R.P. New acceleration factors for temperature, humidity, bias testing. In Proceedings of the 16th International Reliability Physics Symposium, San Diego, CA, USA, 18–20 April 1978; pp. 161–178. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, B.D.; Meilink, S.; Warren, G.; Wynblatt, P. Water adsorption and surface conductivity measurements on alpha-alumina substrates. IEEE Trans. Compon. Hybrids Manuf. Technol. 1987, 10, 247–251. [Google Scholar]
- Sato, M.; Kumada, A.; Hidaka, K.; Yamashiro, K.; Hayase, Y.; Takano, T. On the nature of surface discharges in silicone-gel: Prebreakdown discharges in cavities. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Conference on Electrical Insulation and Dielectric Phenomena (CEIDP), Des Moines, IA, USA, 19–22 October 2014; pp. 19–22. [Google Scholar]






















| Device Name | Device Model | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature and Humidity Chamber | Espec-GPS-5 | Provides test conditions |
| DC high-voltage power supply | Iseg Hpn-300-106 | Provides the voltage required for the test |
| Ammeter | FLUKE 289C | Detects the current in the test circuit |
| Multimeter | UNI-T UT71C | Tests the sampling value |
| Digital microscope | KEYENCE VHX-5000 | Observes the appearance of the samples |
| SEM | JEOL JSM ▪ 6510 | Observes the microscopic morphology of the samples |
| Water drop angle tester | SEO Phoenix300 | Tests the contact angle on the surface of the samples |
| Sample | Temperature (°C) | Relative Humidity (%) | Voltage (kV) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 μg/cm2 | 30 | 75 | 4 |
| 10 μg/cm2 | 30 | 75 | 4 |
| 20 μg/cm2 | 30 | 75 | 4 |
| 30 μg/cm2 | 30 | 75 | 4 |
| 50 μg/cm2 | 30 | 75 | 4 |
| Uncontaminated | 85 | 90 | 4 |
| Sample | Temperature (°C) | Relative Humidity (%) | Voltage(kV) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 μg/cm2 | /* | /* | /* |
| 10 μg/cm2 | 85 | 95 | 10 |
| 20 μg/cm2 | 85 | 95 | 10 |
| 30 μg/cm2 | 85 | 90 | 7 |
| 30 μg/cm2 | 65 | 95 | 7 |
| 50 μg/cm2 | 85 | 85 | 7 |
| 50 μg/cm2 | 65 | 90 | 7 |
| 50 μg/cm2 | 45 | 95 | 7 |
| Uncontaminated | /* | /* | /* |
| TEST | Test Project | Test Condition | Voltage (kV) |
|---|---|---|---|
| TEST-1 | Humidity (steady State) | MIL-STD-202 103-A | 4, 7, and 10 |
| TEST-2 | Moisture Resistance | MIL-STD-202 106 | 4, 7, and 10 |
| TEST-3 | Thermal shock | MIL-STD-202 107-B-1 | 4, 7, and 10 |
| TEST-4 | Alternating hot and humid | 2.4.2 | 4, 7, and 10 |
| Sample | Minimum Deviation from the Sampling Value | Maximum Deviation of the Sampling Value |
|---|---|---|
| encapsulated samples | 0 | 0 |
| unencapsulated samples (non-contamination) | 0.03 1 | 0.44 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, C.; Zheng, W.; Zhao, B.; Fan, Y.; Li, H.; Zheng, K.; Wang, G. The Effect of Thermal and Moisture Stress on Insulation Deterioration Law of Ionic Contaminated High-Voltage Printed Circuit Board of Electronic Power Conditioner. Energies 2022, 15, 9616. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15249616
Hu C, Zheng W, Zhao B, Fan Y, Li H, Zheng K, Wang G. The Effect of Thermal and Moisture Stress on Insulation Deterioration Law of Ionic Contaminated High-Voltage Printed Circuit Board of Electronic Power Conditioner. Energies. 2022; 15(24):9616. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15249616
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Cong, Wei Zheng, Bin Zhao, Yu Fan, Hong Li, Kun Zheng, and Gang Wang. 2022. "The Effect of Thermal and Moisture Stress on Insulation Deterioration Law of Ionic Contaminated High-Voltage Printed Circuit Board of Electronic Power Conditioner" Energies 15, no. 24: 9616. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15249616
APA StyleHu, C., Zheng, W., Zhao, B., Fan, Y., Li, H., Zheng, K., & Wang, G. (2022). The Effect of Thermal and Moisture Stress on Insulation Deterioration Law of Ionic Contaminated High-Voltage Printed Circuit Board of Electronic Power Conditioner. Energies, 15(24), 9616. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15249616






