Performance Improvement of a Switched Reluctance Motor and Drive System Designed for an Electric Motorcycle
Abstract
:1. Introduction
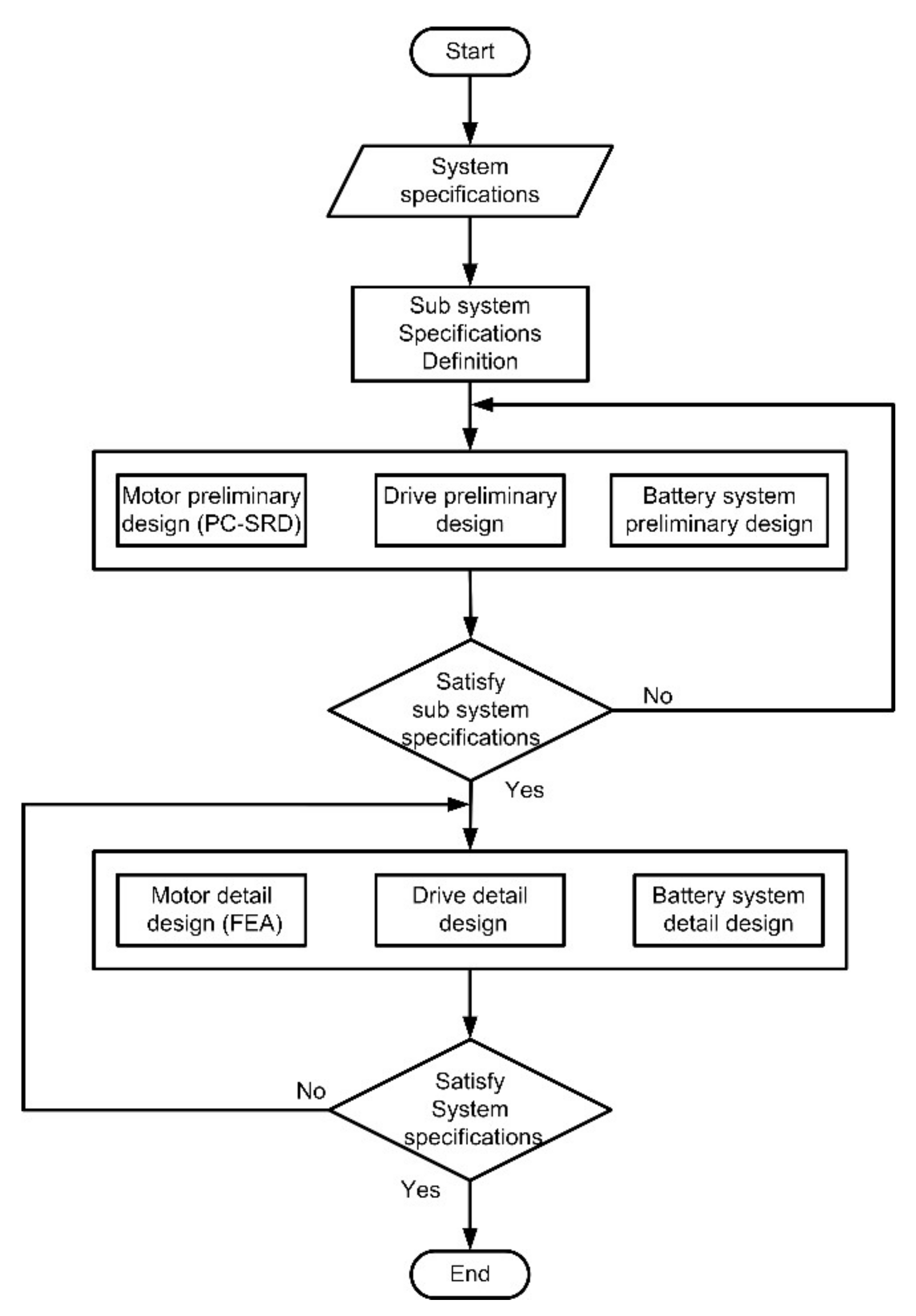
2. Design Methodology
2.1. Specification of the Electric Motorcycle
2.2. Traction Motor Design Consideration
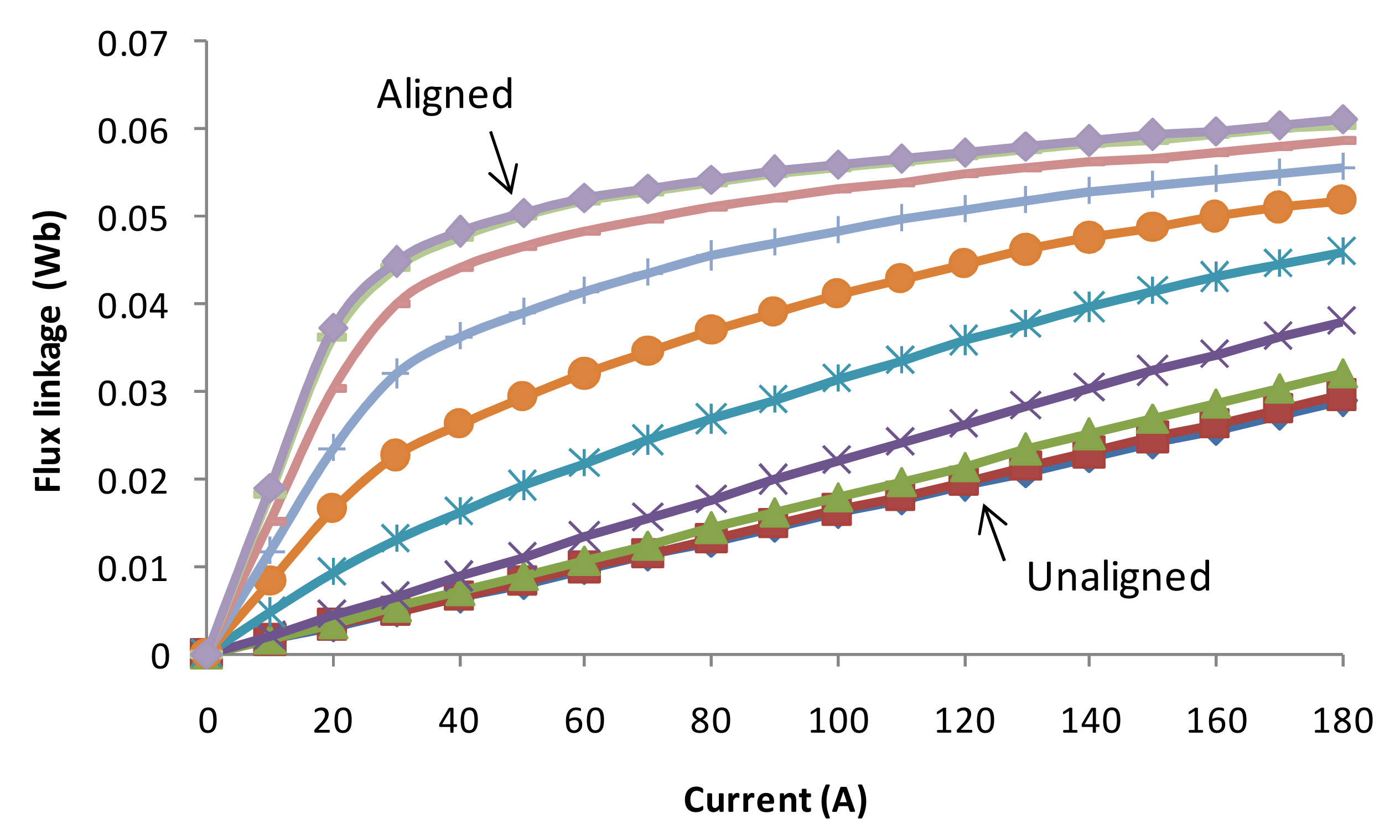
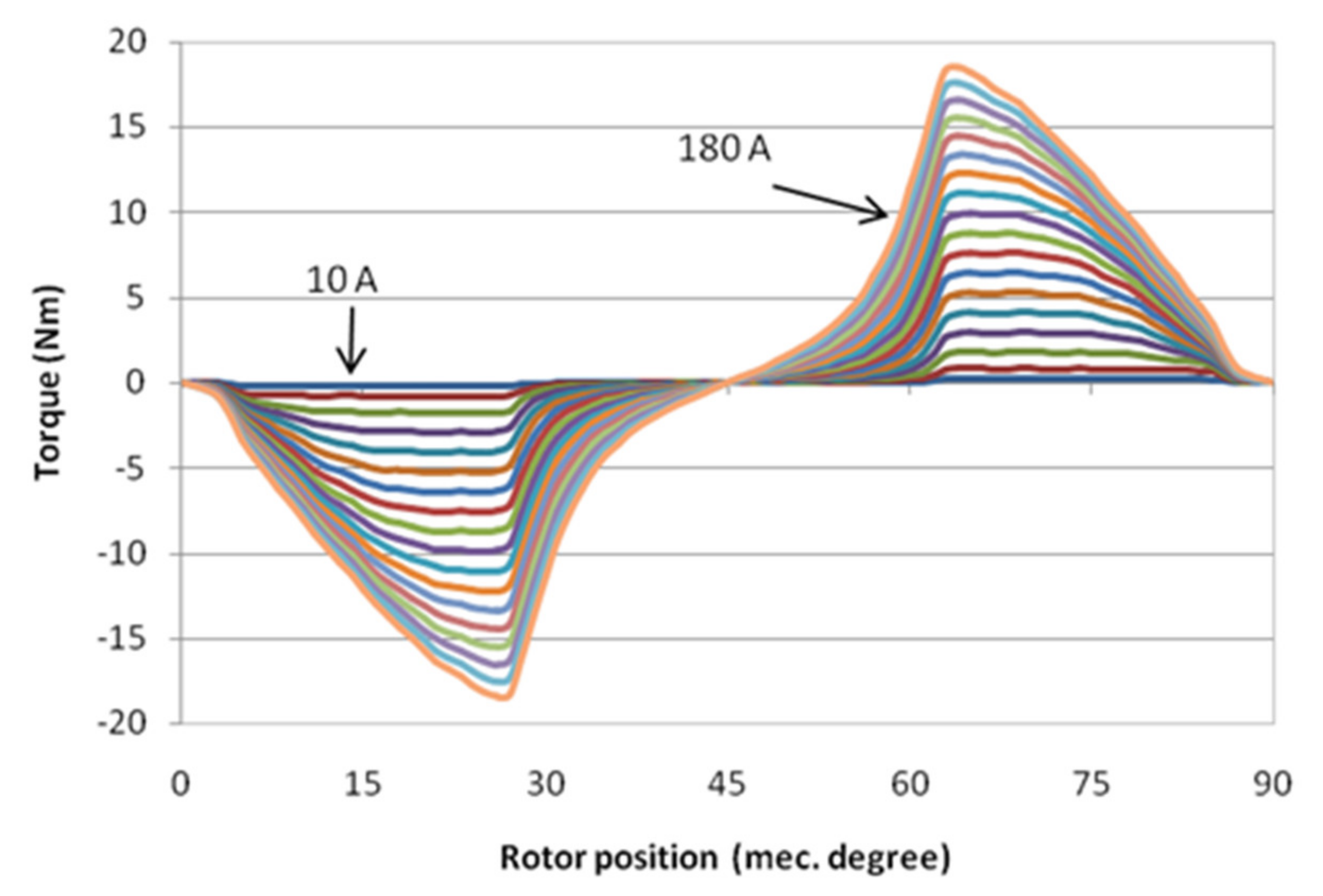
2.3. Static Performance Consideration
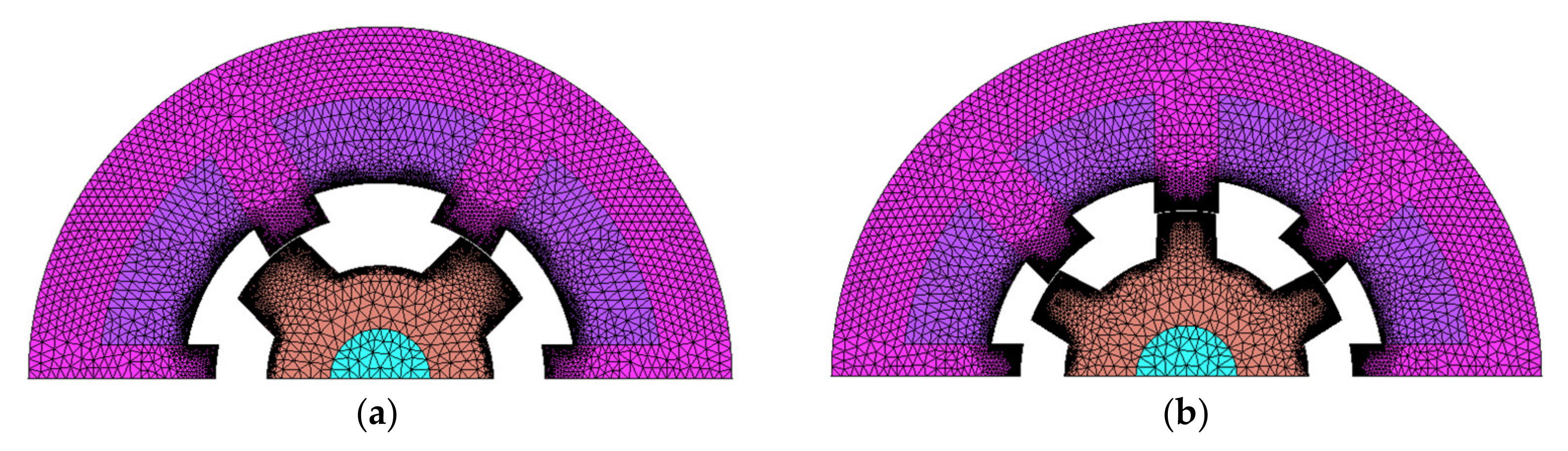
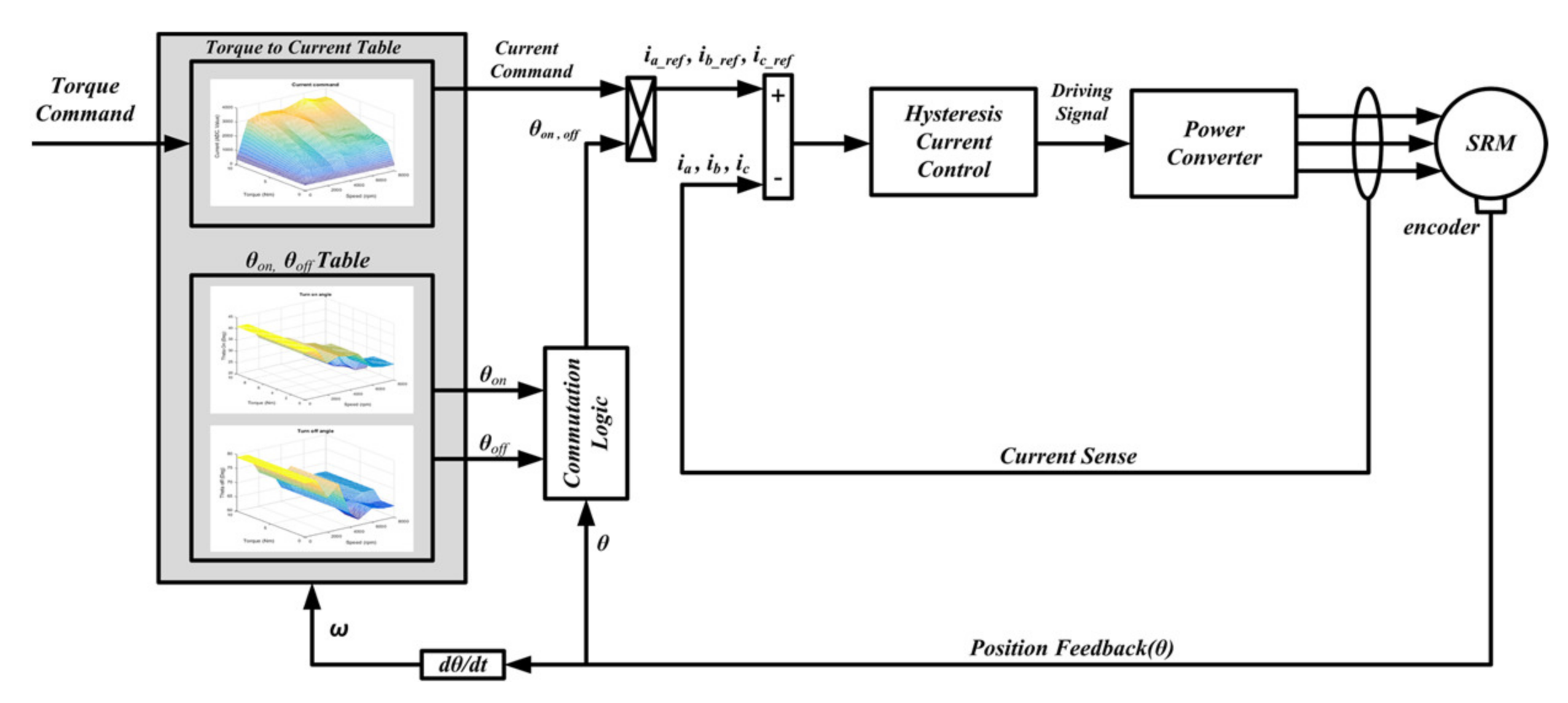
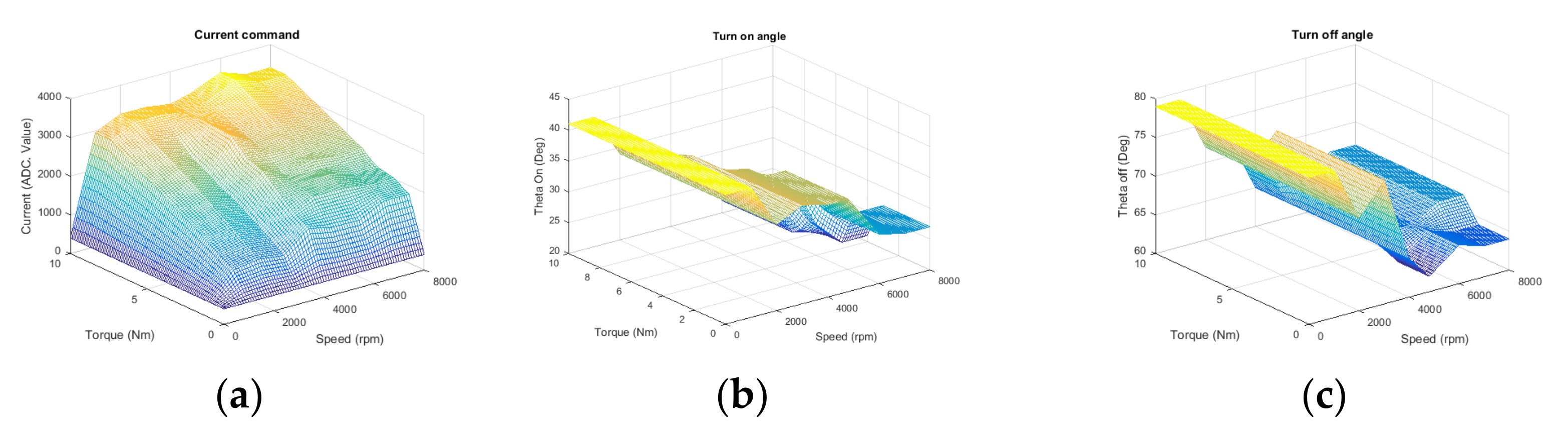
2.4. Dynamic Performance Consideration
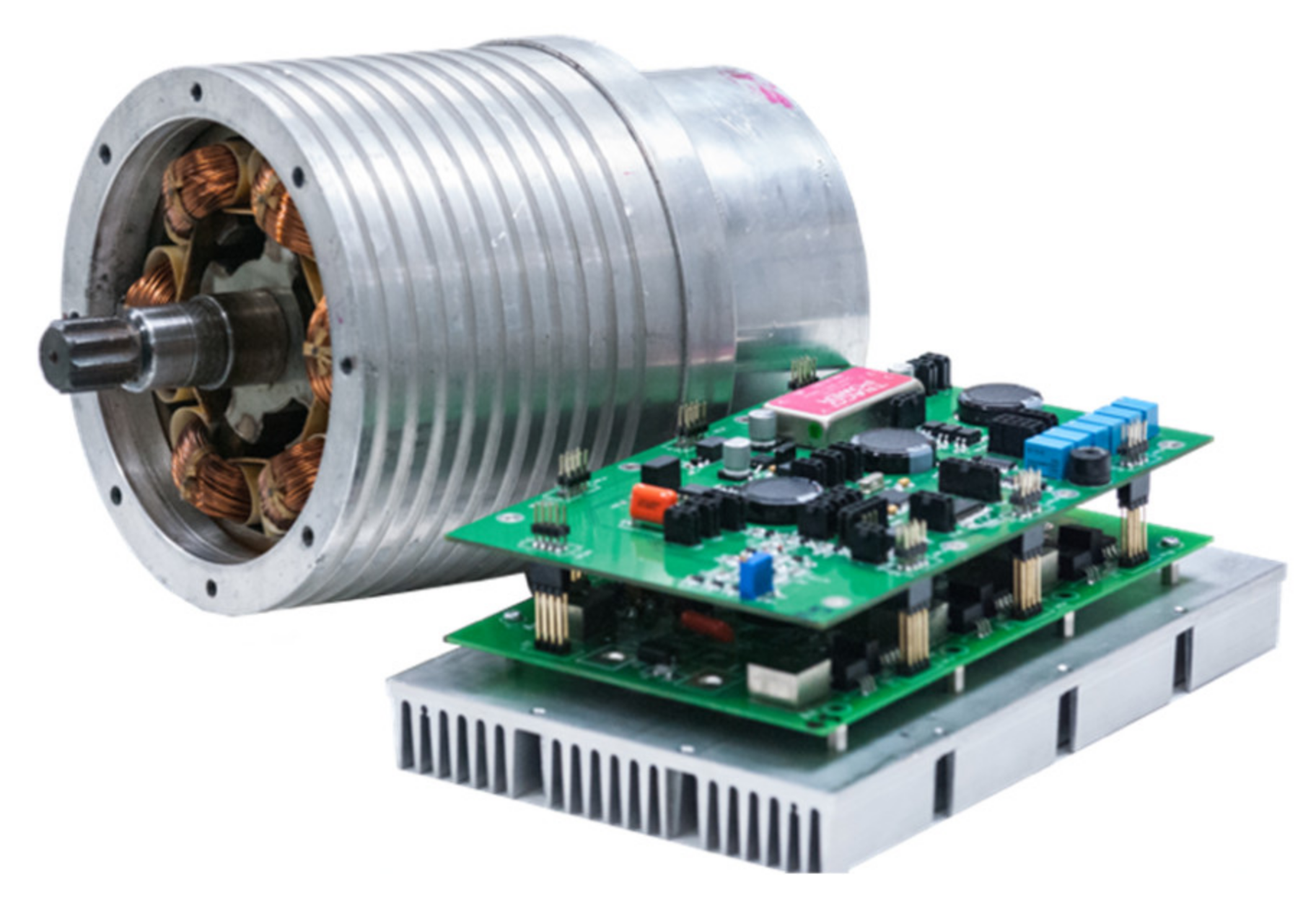
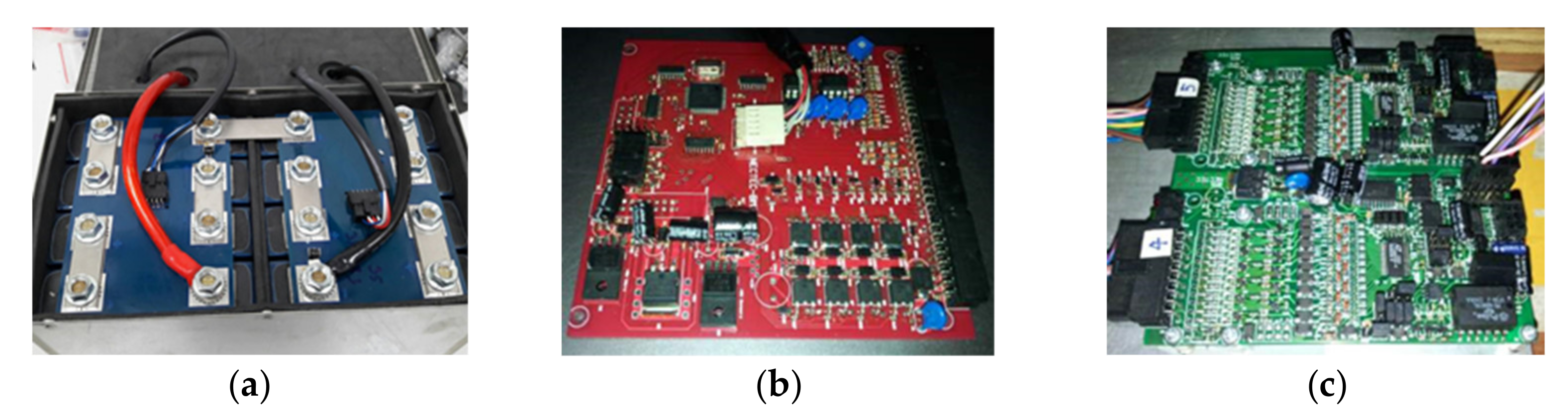
3. Construction of the Motor and Drive System
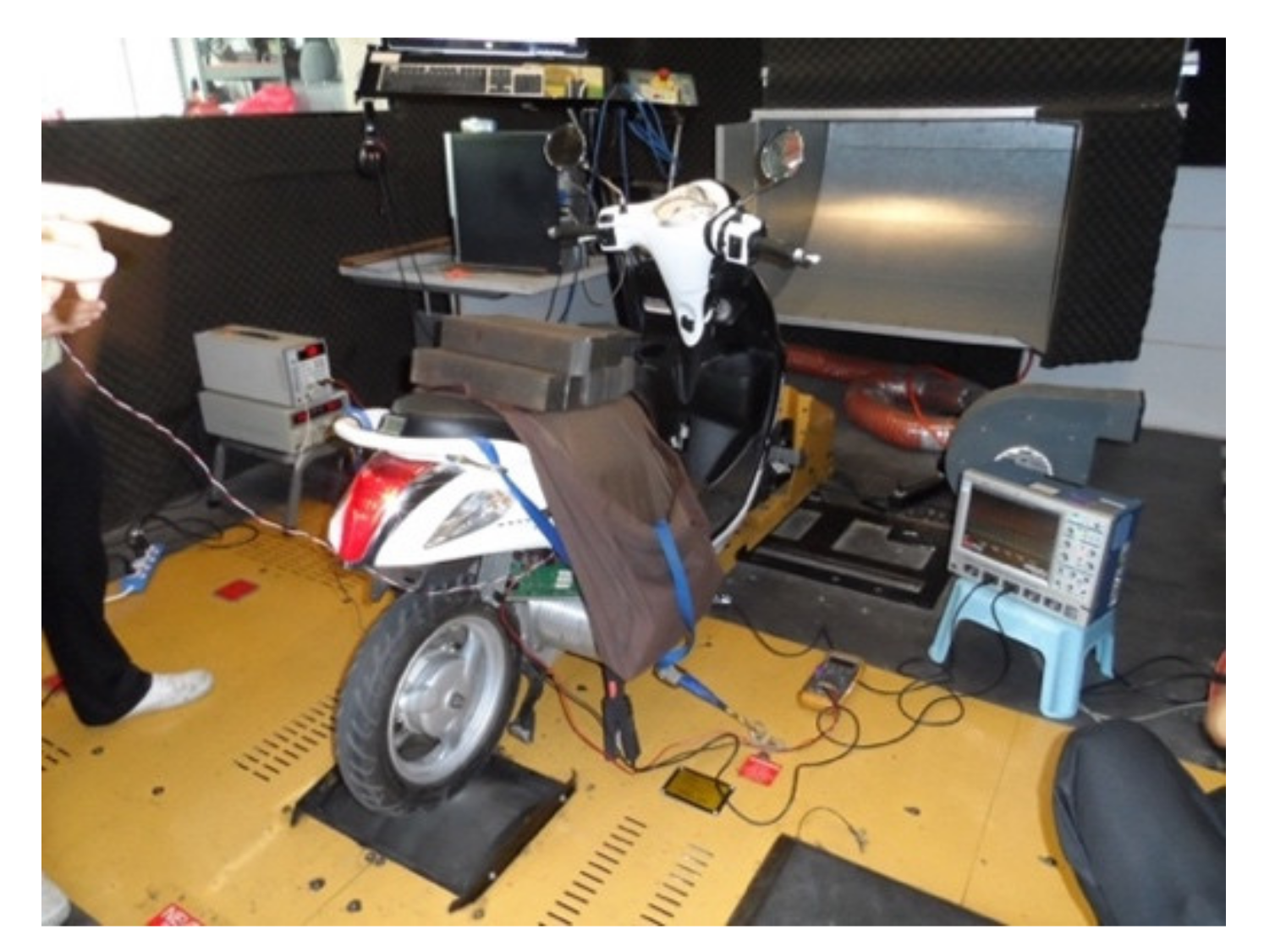
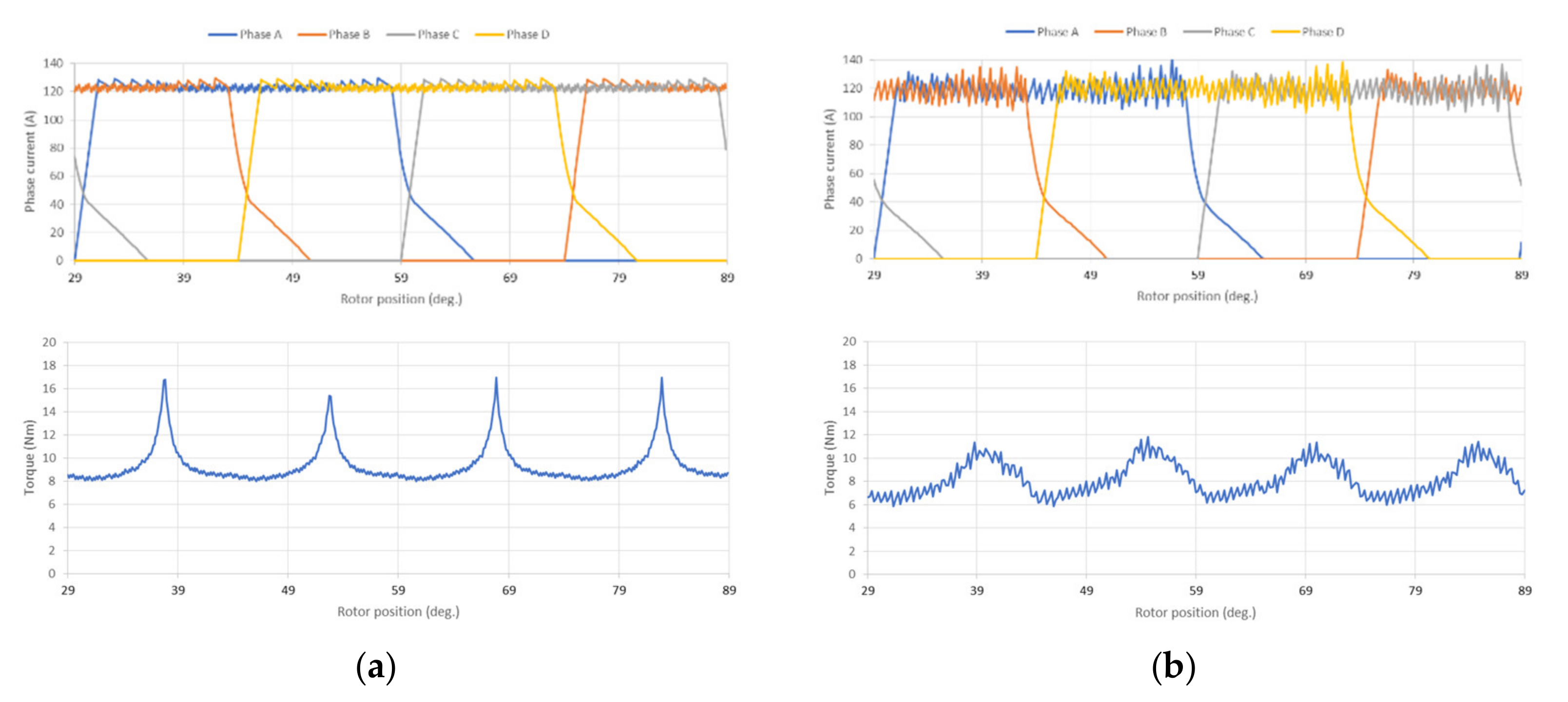
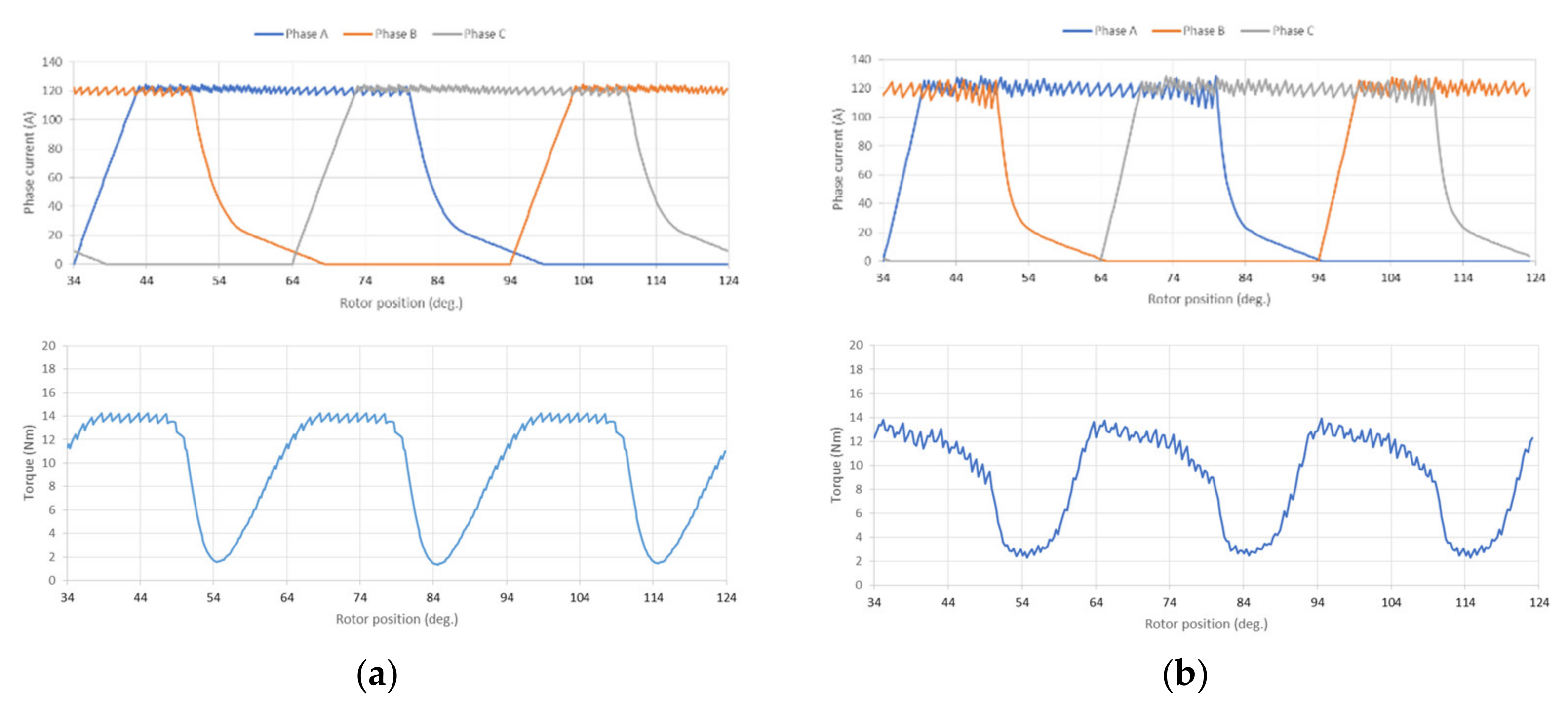
4. Experiment Results
4.1. Motor and Drive System Test Result
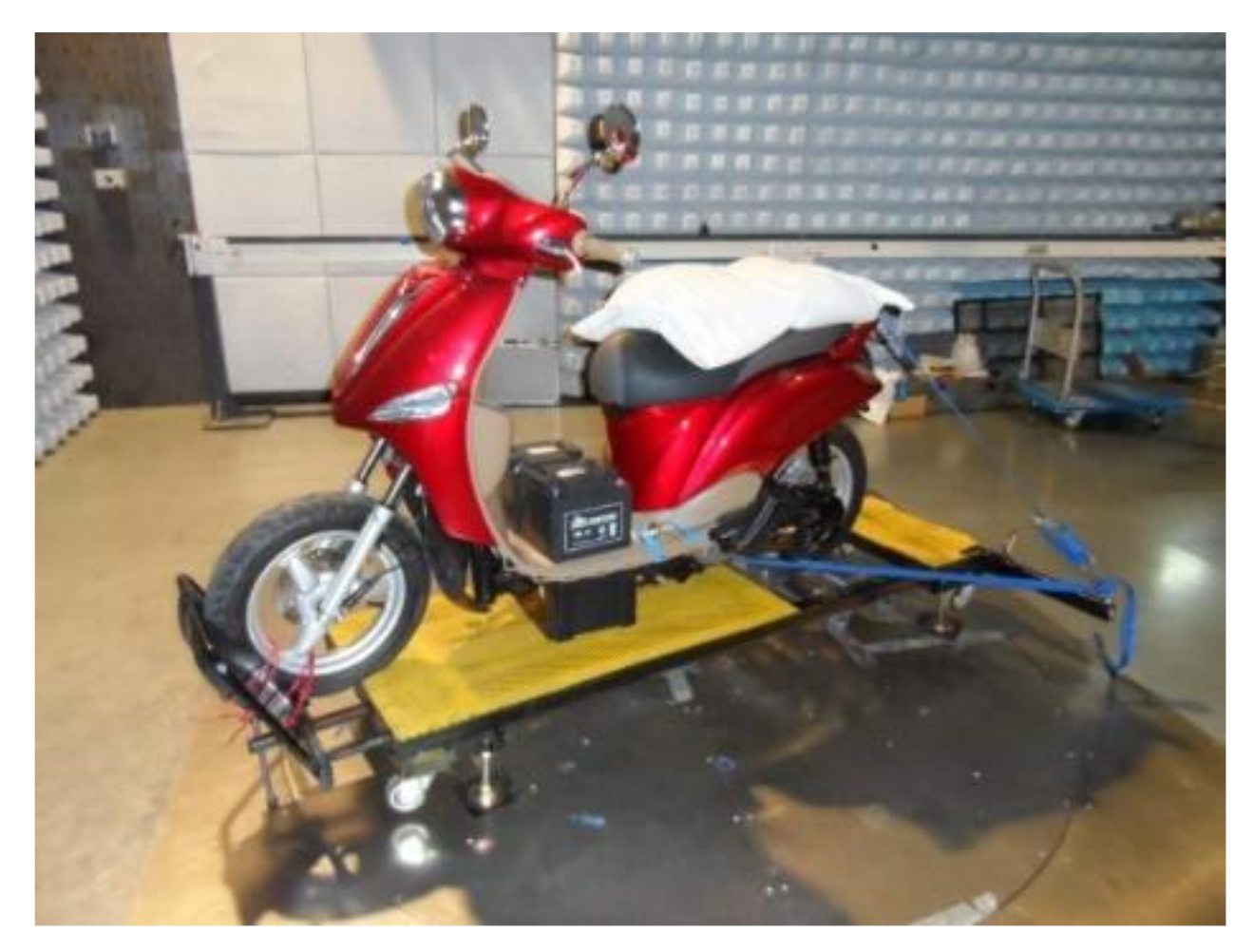
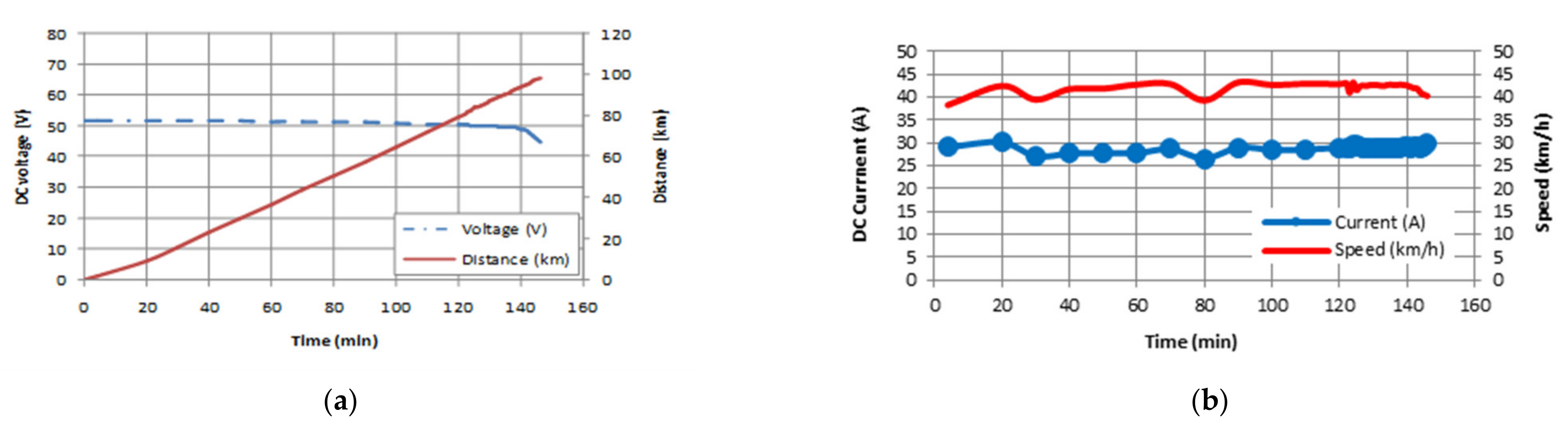
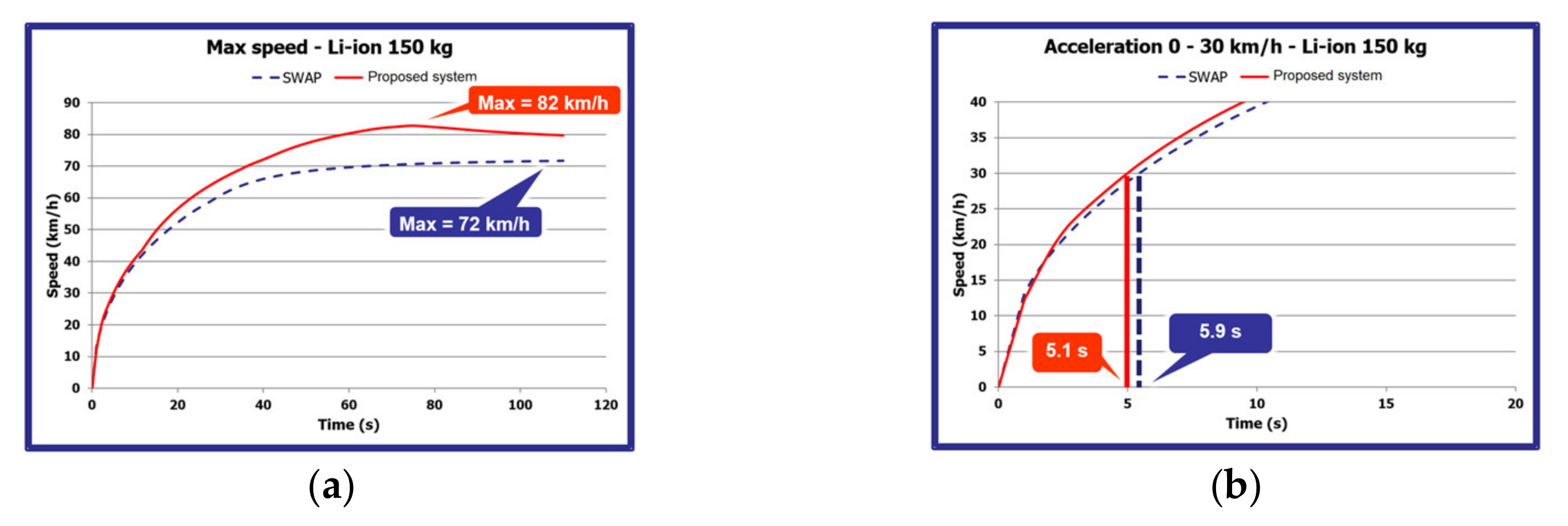
4.2. Electric Motorcycle Performance Test Result
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kerdlap, P.; Gheewala, S.H. Electric motorcycles in Thailand—A life cycle perspective. J. Ind. Ecol. 2016, 20, 1399–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bostanci, E.; Moallem, M.; Parsapour, A.; Fahimi, B. Opportunities and challenges of switched reluctance motor drives for electric propulsion: A comparative study. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2017, 3, 58–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, K.M.; Fahimi, B.; Suresh, G.; Rajarathnam, A.V.; Ehsani, M. Advantages of switched reluctance motor applications to EV and HEV: Design and control issues. IEEE Tran. Ind. Appl. 2000, 36, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, Y.; Benomar, Y.; Deepak, K.; Aksoz, A.; Baghdadi, M.; Bostanci, E.; Hegazy, O. Switched reluctance motors and drive systems for electric vehicle powertrains: State of the art analysis and future trends. Energies 2021, 14, 2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.W.; Bilgin, B.; Emadi, A. Three-phase 24/16 Switched Reluctance Machines for a Hybrid Electric Powertrain. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2017, 3, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiyota, K.; Chiba, A. Design of switched reluctance motor competitive to 60-kW IPMSM in third-generation hybrid electric vehicle. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2012, 48, 2303–2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhan, Q.; Ma, Z.; Zhou, L. Implementation of a 50-kW four-phase switched reluctance motor drive system for hybrid electric vehicle. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2005, 41, 501–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Schofield, N.; Emadi, A. External rotor 6-10 switched reluctance motor for an electric bicycle. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2015, 1, 348–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Terzic, M.V.; Bilgin, B.; Emadi, A. Switched reluctance motor design for a forklift traction application. In Proceedings of the 2018 XIII International Conference on Electrical Machines (ICEM), Alexandroupoli, Greece, 3–6 September 2018; pp. 812–818. [Google Scholar]
- Andrada, P.; Blanque, B.; Capo, M.; Gross, G.; Montesinos, D. Switched reluctance motor for light electric vehicles. In Proceedings of the 2018 20th European Conference on Power Electronics and Applications (EPE’18 ECCE Europe), Riga, Latvia, 17–21 September 2018; pp. 1383–1388. [Google Scholar]
- Vosswinkel, M.; Lohner, A.; Platte, V.; Hirche, T. Design, production, and verification of a switched-reluctance wheel hub drive train for battery electric vehicles. World Electr. Veh. J. 2019, 10, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, C.H. Switched reluctance motor drive for electric motorcycle using HFNN controller. In Proceedings of the 2007 7th International Conference on Power Electronics and Drive Systems, Bangkok, Thailand, 27–30 November 2007; pp. 1383–1388. [Google Scholar]
- Tomczewski, K.; Wrobel, K.; Rataj, D.; Trzmiel, G. A switched reluctance motor drive controller based on an FPGA device with a complex PID regulator. Energies 2021, 14, 1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anvari, B.; Toliyat, H.A.; Fahimi, B. Simultaneous optimization of geometric and firing angles for in-wheel switched reluctance motor drive. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2018, 4, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehsani, M.; Gao, Y.; Longo, S.; Ebrahimi, K.M. Modern Electric, Hybrid Electric, and Fuel Cell Vehicles Fundamentals, Theory, and Design, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- SPEED Consortium University of Glasgow. User’s Manual: PC-SRD; Version 8.8, CD-Adapco; SPEED Consortium University of Glasgow: Glasgow, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Vijayraphavan, P. Design of Switched Reluctance Motors and Development of a Universal Controller for Switched Reluctance and Permanent Magnet Brushless DC Motor Drives. Ph.D. Thesis, Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University, Blacksburg, VA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, T.J.E. Switched Reluctance Motors and Their Control; Magna Physics Publishing and Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Zhu, Z.Q.; Hasegawa, M.; Pride, A.; Deodhar, R.; Maruyama, T.; Chen, Z. Performance comparison between unipolar and bipolar excitations in switched reluctance machine with sinusoidal and rectangular waveforms. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition, Phoenix, AZ, USA, 17–22 September 2011; pp. 1590–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tungpimolrut, K.; Jitkreeyarn, P.; Kachapornkul, S.; Somsiri, P.; Chiba, A. Initial rotor position estimation of a SRM drive installed in an electric vehicle. IEEJ Trans. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2011, 6, 594–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Parameter | Unit | 1 Passenger | 2 Passenger |
|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum speed | km/h | 80 | 70 |
| Acceleration 0–30 km/h | s | 4 | 6 |
| Driving Range at 40 km/h | km | 90 | 80 |
| Payload | kg | 75 | 150 |
| Parameter | Unit | 8/6 Pole SRM | 6/4 Pole SRM |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rated motor voltage (DC) | V | 48 | 48 |
| Outer stator dimension | mm | 140 | 140 |
| Stack length | mm | 70 | 70 |
| Air gap | mm | 0.3 | 0.3 |
| Parameter | Unit | 8/6 Pole SRM | 6/4 Pole SRM |
|---|---|---|---|
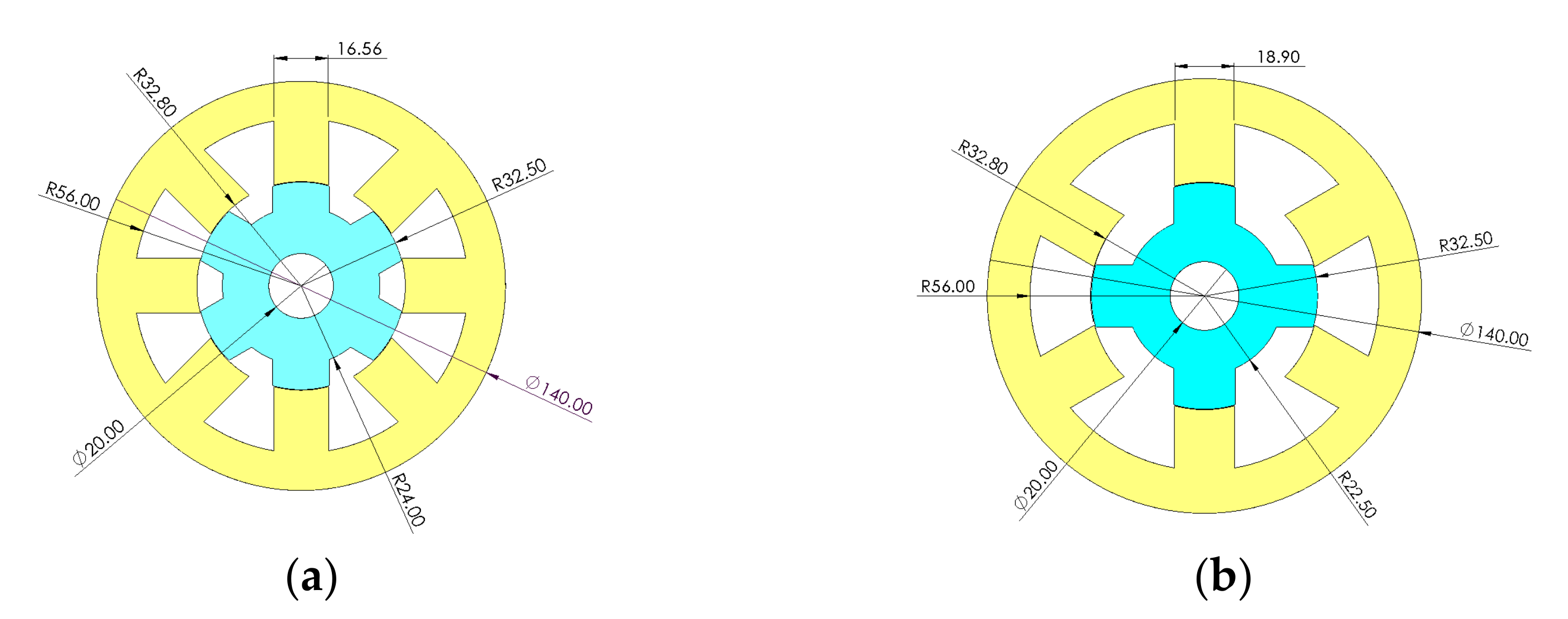
| Radius to the bottom of the rotor slot (R0) | mm | 24 | 22.5 |
| Rotor surface radius (R1) | mm | 32.5 | 32.5 |
| Radius to the bottom of the stator slot (R2) | mm | 56 | 56 |
| Stator outside radius (R3) | mm | 70 | 70 |
| Air gap | mm | 0.3 | 0.3 |
| Stator pole arc (βs) | deg | 22.5 | 24 |
| Rotor pole arc (βr) | deg | 20 | 31.05 |
| Number of turns | - | 9 | 16 |
| Number of strands | - | 11 | 11 |
| Wire diameter | mm | 0.914 | 0.813 |
| Material | - | 35A300 | 35A300 |
| Rotor inertia | kg*·m2 | 4.8777 × 10−4 | 5.1453 × 10−4 |
| Parameter | Unit | 8/6 Pole SRM | 6/4 Pole SRM |
|---|---|---|---|
| Phase resistance | Ohm | 0.012 | 0.032 |
| Aligned inductance | mH | 0.546 | 2.065 |
| Unaligned inductance | mH | 0.062 | 0.264 |
| Theta on | deg | 29 | 34 |
| Theta off | deg | 58 | 80 |
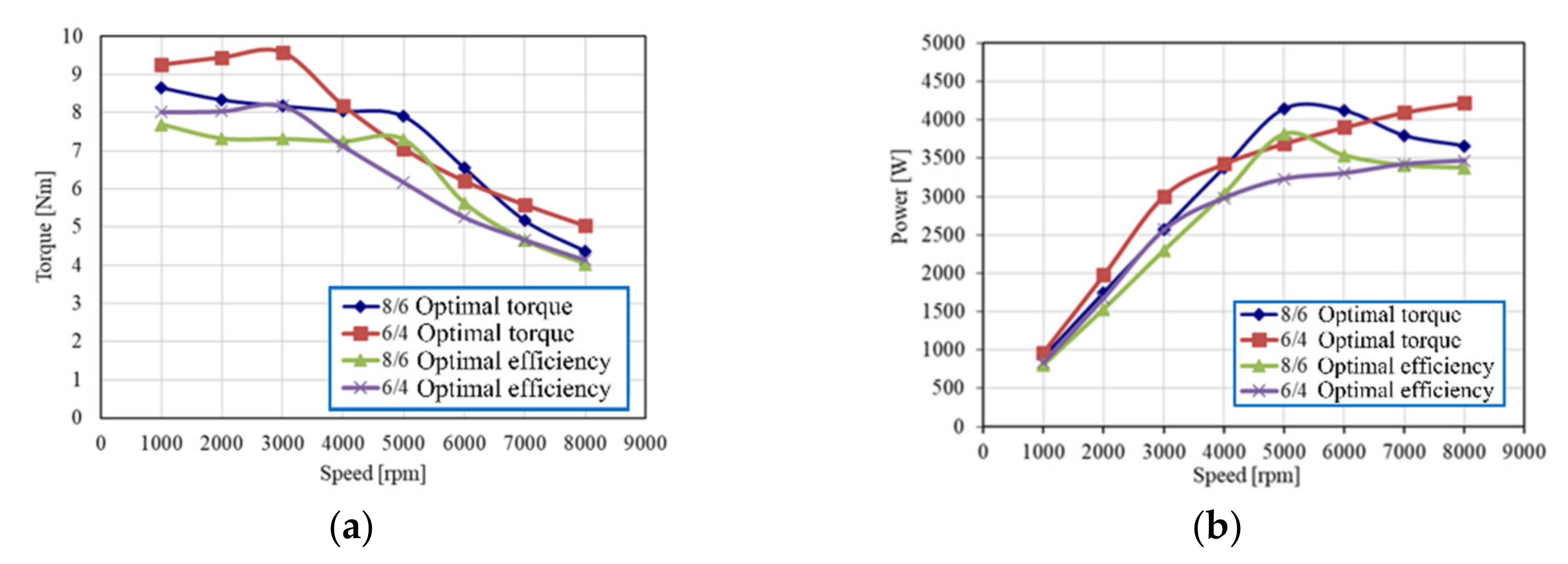
| Average torque | Nm | 8.34 | 9.44 |
| Phase current (rms) | A | 85.62 | 82.8 |
| Shaft power | W | 1746.37 | 1976.89 |
| Overall system efficiency | % | 80.46 | 73.27 |
| Copper loss | W | 362 | 659 |
| Iron loss | W | 55 | 53 |
| Mechanical loss | W | 6 | 8 |
| Flux density at rotor pole | T | 2.179 | 1.723 |
| Flux density at stator pole | T | 1.922 | 2.197 |
| Copper weight | kg | 1.3305 | 1.5959 |
| Iron weight | kg | 5.3165 | 4.9165 |
| Torque per weight | Nm/kg | 1.25 | 1.44 |
| Total copper and iron cost | $ | 52.75 | 56.19 |
| 8/6 Pole SRM | 6/4 Pole SRM | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC-SRD | FEA | PC-SRD | FEA | |
| Average torque (Nm) | 8.34 | 8.23 | 9.44 | 9.15 |
| Torque ripple rate | 0.96 | 0.72 | 1.33 | 1.27 |
| Phase | L-Aligned (mH) | L-Unaligned (mH) | L-Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | 1.9767 | 0.2960 | 6.6774 |
| B | 1.8016 | 0.3342 | 5.3904 |
| C | 1.9385 | 0.2864 | 6.7666 |
| FEA | 2.0652 | 0.2643 | 7.8150 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kachapornkul, S.; Pupadubsin, R.; Somsiri, P.; Jitkreeyarn, P.; Tungpimolrut, K. Performance Improvement of a Switched Reluctance Motor and Drive System Designed for an Electric Motorcycle. Energies 2022, 15, 694. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15030694
Kachapornkul S, Pupadubsin R, Somsiri P, Jitkreeyarn P, Tungpimolrut K. Performance Improvement of a Switched Reluctance Motor and Drive System Designed for an Electric Motorcycle. Energies. 2022; 15(3):694. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15030694
Chicago/Turabian StyleKachapornkul, Seubsuang, Ruchao Pupadubsin, Pakasit Somsiri, Prapon Jitkreeyarn, and Kanokvate Tungpimolrut. 2022. "Performance Improvement of a Switched Reluctance Motor and Drive System Designed for an Electric Motorcycle" Energies 15, no. 3: 694. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15030694
APA StyleKachapornkul, S., Pupadubsin, R., Somsiri, P., Jitkreeyarn, P., & Tungpimolrut, K. (2022). Performance Improvement of a Switched Reluctance Motor and Drive System Designed for an Electric Motorcycle. Energies, 15(3), 694. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15030694






