Mechanism of Magnetic Nanoparticle Enhanced Microwave Pyrolysis for Oily Sludge
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Apparatus and Methods
2.1. Microwave Thermogravimetric Device
2.2. Pyrolysis Product Staged Collection Device
2.3. Preparation of Oily Sludge
2.4. Reaction Kinetics Equation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Thermogravimetric Curve Analysis
3.1.1. Comparative Analysis of Pyrolysis Temperature
3.1.2. Comparative Analysis of Oily Sludge Weight
3.2. Stage Division of Pyrolysis Process
3.3. Characteristic Analysis of Pyrolysis Products
3.3.1. Gas Products
3.3.2. Liquid Products
3.4. Reaction Kinetics Analysis
3.4.1. Kinetics Simulation in Stage II
3.4.2. Kinetics Simulation in Stage III
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Z.; Gong, Z.; Wang, Z.; Li, X.; Chu, Z. Application and Development of Pyrolysis Technology in Petroleum Oily Sludge Treatment. Environ. Eng. Res. 2020, 26, 190460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yu, H.; Jiang, Z.; Song, Y.; Fang, J. Microwave Pyrolysis of Oily Sludge Under Different Control Modes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 125887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Wang, W.; Lin, L.; Zhang, F.; Zhao, X. A Stepwise Microwave Synergistic Pyrolysis Approach to Produce Sludge-Based Biochars: Feasibility Study Simulated by Laboratory Experiments. Fuel 2020, 272, 117628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; Han, J.; Xiang, H.; Zhan, Y.; Fei, Y. Recovery of Energy and Iron from Oily Sludge Pyrolysis in a Fluidized Bed Reactor. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 154, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.Y. Experimental Study on Low Temperature Thermal Pyrolysis of Oily Sludge in Tahe Oilfield. Environ. Prot. Oil Gas Fields 2015, 25, 9–11. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Yin, J.; Wang, J. Study on the Role of Microwave Absorbent in Microwave Pyrolysis of Oily Sludge. Int. Core J. Eng. 2020, 6, 417–420. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, S.; Wang, Y.; Fumitake, T.; Kouji, T.; Li, A.; Kunio, Y. Effect of Steam and Oil Sludge Ash Additive on the Products of Oil Sludge Pyrolysis. Appl. Energy 2017, 185, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Takahashi, F.; Gao, N.; Yoshikawa, K.; Li, A. Evaluation of Oil Sludge Ash as a Solid Heat Carrier in the Pyrolysis Process of Oil Sludge for Oil Production. Energy Fuels 2016, 30, 5970–5979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.; Song, Z.; Yu, J.; Su, Y.; Wang, W. Study on the Demulsification of Refinery Oily Sludge Enhanced by Microwave Irradiation. Fuel 2020, 279, 118417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalcante, T.; Funcia, E.; Gut, J. Inactivation of Polyphenol Oxidase by Microwave and Conventional Heating: Investigation of Thermal and Non-Thermal Effects of Focused Microwaves. Food Chem. 2020, 340, 127911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luyao, W.; Dong, M.; Lu, L. ‘Heat Effect’ or ‘Non-Heat Effect’-Microwave Heating Reaction Mechanism. Chemistry 2013, 76, 698–703. [Google Scholar]
- Kappe, C.O.; Stadler, A.; Dallinger, D. Microwaves in Organic and Medicinal Chemistry. Weinh. Wiley-VCH 2012, 25, 543–648. [Google Scholar]
- Robinson, J.; Kingman, S.; Irvine, D.; Licence, P.; Smith, A.; Dimitrakis, G.; Obermayer, D.; Kappe, C.O. Electromagnetic Simulations of Microwave Heating Experiments Using Reaction Vessels Made Out of Silicon Carbide. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2010, 12, 10793–10800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Yang, C.; Li, J.; Zhu, Y.; Yan, Z.; Zhang, H. Screening of Inexpensive and Efficient Catalyst for Microwave-Assisted Pyrolysis of Ship Oil Sludge. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2020, 152, 104971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.L.; Tsai, C.H.; Jou, C.J.G. Energy and Resource Utilization of Refining Industry Oil Sludge by Microwave Treatment. Sustainability 2020, 12, 6862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, B.; Huang, L.; Li, S.; Ding, L.; Liu, B.; Zhang, A. Chemical–Microwave–Ultrasonic Compound Conditioning Treatment of Highly-Emulsified Oily Sludge in Gas Fields. Nat. Gas Ind. B 2019, 6, 412–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salema, A.A.; Yeow, Y.K.; Ishaque, K.; Ani, F.N.; Afzal, M.T.; Hassan, A. Dielectric Properties and Microwave Heating of Oil Palm Biomass and Biochar. Ind. Crops Prod. 2013, 50, 366–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, G.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, L.; Fang, L. Experimental Study on Reaction Conditions of Activated Carbon-Assisted Microwave Pyrolysis of Sludge. Ecol. Environ. 2010, 19, 2182–2186. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Y.; Gong, Z.; Wu, X.; Chen, H.; Zuo, W. The Influence Factors of H2S Release from Sewage Sludge Microwave Pyrolysis Process. Environ. Pollut. Amp 2013, 35, 7–10. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.; Hu, J.; Xia, L.; Qu, X. Pyrolysis of Sewage Sludge by Microwave Radiation. J. Shenyang Univ. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2008, 24, 662–666. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.R. Microwave Pyrolysis of Oily Sludge with Activated Carbon. Environ. Technol. Lett. 2016, 37, 3139–3145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domínguez, A.; Menéndez, J.A.; Fernández, Y.; Pis, J.J.; Nabais, J.M.V.; Carrott, P.J.M.; Carrott, M.M.L.R. Conventional and Microwave Induced Pyrolysis of Coffee Hulls for the Production of a Hydrogen Rich Fuel Gas. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2007, 79, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez, A.; Menéndez, J.A.; Inguanzo, M.; Pís, J.J. Production of Bio-Fuels by High Temperature Pyrolysis of Sewage Sludge Using Conventional and Microwave Heating. Bioresour. Technol. 2006, 97, 1185–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menendez, J.A.; Dominguez, A.; Inguanzo, M.; Pis, J.J. Microwave-Induced Drying, Pyrolysis and Gasification (MWDPG) of Sewage Sludge: Vitrification of the Solid Residue. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2005, 74, 406–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menendez, J.A.; Inguanzo, M.; Pis, J.J. Microwave-Induced Pyrolysis of Sewage Sludge. Water Res. 2002, 36, 3261–3264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shie, J.L.; Lin, J.P.; Chang, C.Y.; Lee, D.J.; Wu, C.H. Pyrolysis of Oil Sludge with Additives of Sodium and Potassium Compounds. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2003, 39, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namazi, A.B.; Allen, D.G.; Jia, C.Q. Microwave-Assisted Pyrolysis and Activation of Pulp Mill Sludge. Biomass Bioenergy 2015, 73, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Shi, X.; Song, J.; Fang, S.; Bai, J.; Chang, C. Research Progress of Biomass Microwave Catalytic Pyrolysis for Preparation of High Value-Added Products. Chem. Ind. Eng. Prog. 2021, 41, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Mario, R.H.; Marshall, W.D. Reduction of Hexavalent Chromium Mediated by Micro- and Nano-Sized Mixed Metallic Particles. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 169, 1081–1087. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, N.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, H.; Zaman, W.; Li, X.; Li, W.; Zhang, Q. Interfacially Active and Magnetically Responsive Composite Nanoparticles with Raspberry Like Structure; Synthesis and Its Applications for Heavy Crude Oil/Water Separation. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2015, 472, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, L.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, N.; Du, Y.; Zeng, X.; Zhou, S.; He, Q.; Wu, G. In-Situ Growth of Core-Shell ZnFe2O4 @ Porous Hollow Carbon Microspheres as An Efficient Microwave Absorber. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 581, 475–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Ge, R.; Lu, M.; Xu, R.; Zhang, Z. Graphene-Based Nano-Materials for Lithium–Sulfur Battery and Sodium-Ion Battery. Nano Energy 2015, 15, 379–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongkaew, N.; Simsek, M.; Griesche, C.; Baeumner, A.J. Functional Nanomaterials and Nanostructures Enhancing Electrochemical Biosensors and Lab-on-a-Chip Performances: Recent Progress, Applications, and Future Perspective. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 120–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prashanth, P.F.; Burada, S.; Vinu, R.; Lavanya, M.; Prabu, V.R. Production of Diesel Range Hydrocarbons from Crude Oil Sludge via Microwave-Assisted Pyrolysis and Catalytic Upgradation. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2020, 146, 383–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saitov, R.I.; Abdeev, R.G.; Fatykhov, M.A.; Abdeev, E.R.; Khasanova, A.F. Development of Energy-resource-efficient Equipment and Technologies of Environmentally Safe Microwave Processing of Oil Sludges. KnE Mater. Sci. 2020, 9, 1683–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nariya, P.; Das, M.; Shukla, F.; Thakore, S. Synthesis of Magnetic Silver Cyclodextrin Nanocomposite as Catalyst for Reduction of Nitro Aromatics and Organic Dyes. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 300, 112279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coutinho, T.C.; Malafatti, J.; Paris, E.C.; Tardioli, P.W.; Farinas, C.S. Hydroxyapatite-CoFe2O4 Magnetic Nanoparticle Composites for Industrial Enzyme Immobilization, Use, and Recovery. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2020, 3, 12334–12345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Liu, J.G.; Nie, Y.F. Influencing Factors and Product Property of Low Temperature Pyrolysis of Oil Sludge. China Environ. Sci. 2008, 28, 340–344. [Google Scholar]
- Shie, J.L.; Chang, C.Y.; Lin, J.P.; Wu, C.H.; Lee, D.J. Resources Recovery of Oil Sludge by Pyrolysis: Kinetics Study. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2000, 75, 443–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z. Mechanism of Magnetic Nanoparticles Enhanced Microwave Pyrolysis of Oily Sludge. Master’s Thesis, Xi’an Shiyou University, Xi’an, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Tamizhdurai, P.; Krishnasamy, S.; Nambi, I. Process Optimization for the Recovery of Oil from Tank Bottom Sludge Using Microwave Pyrolysis. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2020, 148, 392–399. [Google Scholar]
- Chiarioni, A.; Reverberi, A.P.; Fabiano, B.; Dovi, V.G. An Improved Model of an ASR Pyrolysis Reactor for Energy Recovery. Energy 2006, 31, 2460–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narnaware, S.L.; Panwar, N.L. Kinetic Study on Pyrolysis of Mustard Stalk Using Thermogravimetric Analysis. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2022, 17, 100942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.F.; Li, G.; Yong, X.Y.; Liu, P.; Zhang, X.F. The Features of Microwave Thermal Conversion of Oil Sludge. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2012, 2047, 788–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Xie, Y.; Jiang, C.; Li, W.; Hou, Y. Products Distribution and Interaction Mechanism During Co-Pyrolysis of Rice Husk and Oily Sludge by Experiments and Reaction Force Field Simulation. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 329, 124822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sergey, V. Determining Preexponential Factor in Model-Free Kinetic Methods: How and Why? Molecules 2021, 26, 3077. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, Y.; Ge, B.; Cao, Q.; Xi, F.; Shi, X.; Si, Y.; Wang, X.; Gao, B.; Yue, Q.; Xu, X. Application of Sectionalized Single-Step Reaction Approach (SSRA) and Distributed Activation Energy Model (DAEM) on the Pyrolysis Kinetics Model of Upstream Oily Sludge: Construction Procedure and Data Reproducibility Comparison. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 774, 145751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Phase and Time of Reaction | Rapid Heating and Water Evaporation (Stage I) | Light Component Evaporation (Stage II) | Primary Cracking of Heavy Component (Stage III) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature range (°C) | 20~150 | 150~240 | 240~300 |
| Heating time of blank sample (s) | 320 | 180 | 460 |
| Heating time of control sample (s) | 280 | 130 | 220 |
| Percentage reduction in time | 12.5% | 27.8% | 52.2% |
| Output energy of blank sample (kJ) | 256 | 144 | 368 |
| Output energy of control sample (kJ) | 224 | 104 | 176 |
| Energy saving percentage | 12.5% | 27.8% | 52.2% |
| Component | Stage II (Volume Fraction %) | Stage III (Volume Fraction %) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blank Sample | Control Sample | Blank Sample | Control Sample | |
| H2 | 0 | 3 | 7.6 | 18 |
| N2 + O2 | 26.8 | 24.3 | 11.4 | 10.2 |
| CO2 | 48.6 | 44.7 | 52.2 | 47.2 |
| CH4 | 3.7 | 7 | 8.1 | 15 |
| C2H6 | 7.2 | 9 | 9.3 | 5.4 |
| CXHY | 13.7 | 12 | 11.5 | 4.2 |
| Component | Stage II (Volume Fraction %) | Stage III (Volume Fraction %) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blank Sample | Control Sample | Blank Sample | Control Sample | |
| C4~C12 | 24.3 | 26.5 | 21.4 | 24.9 |
| C13~C18 | 47.6 | 47.7 | 38.2 | 38.8 |
| C18+ | 28.1 | 25.8 | 40.4 | 36.3 |
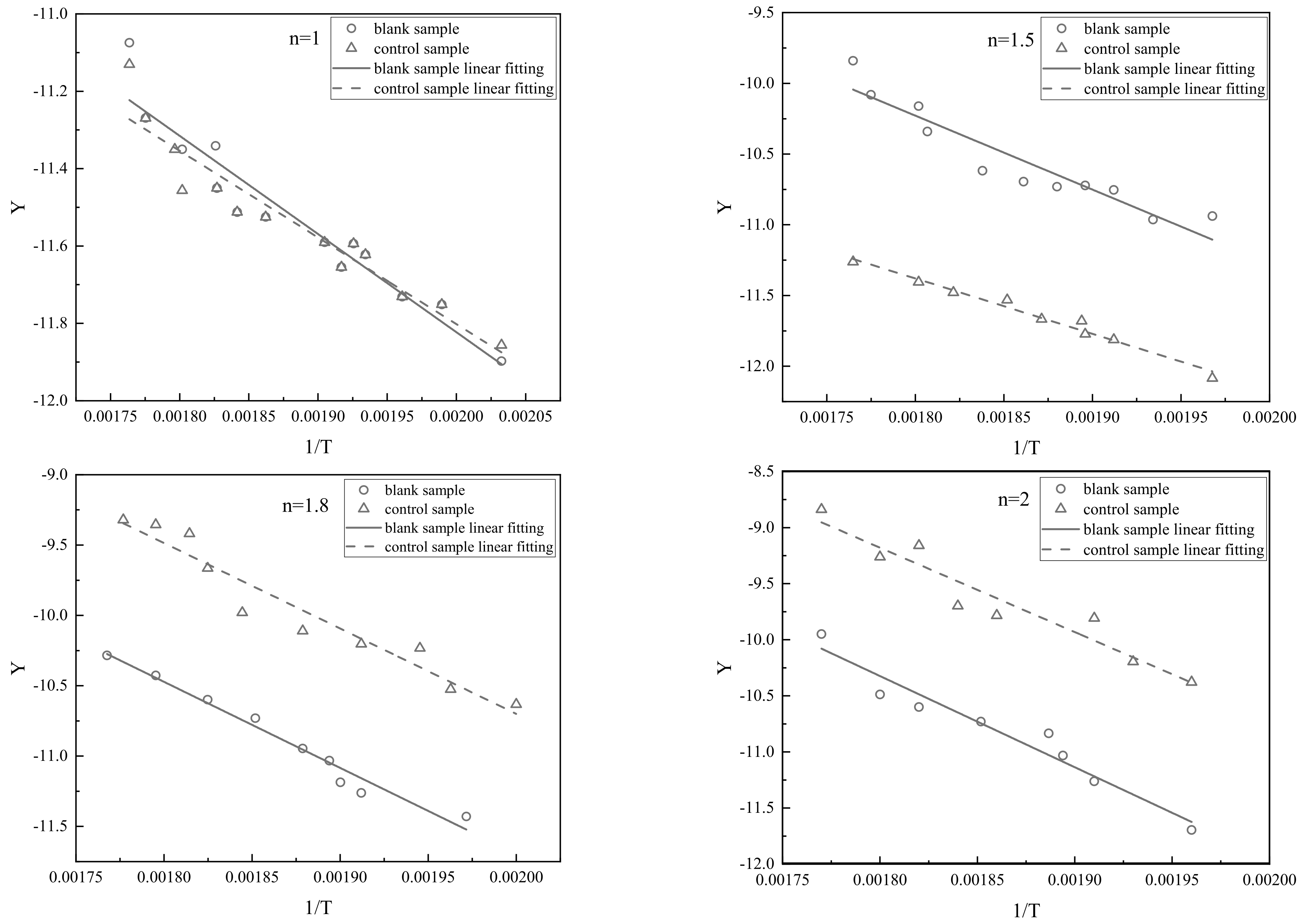
| Reaction Order n | Blank Sample | Control Sample | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fitting Equation | Correlation Coefficient R2 | Fitting Equation | Correlation Coefficient R2 | |
| 1 | Y = −1959.67X − 7.67 | 0.9498 | Y = −1709.21X − 8.02 | 0.9589 |
| 1.5 | Y = −1836.99X − 7.68 | 0.9428 | Y = −2356.19X − 6.87 | 0.9283 |
| 1.8 | Y = −2699.03X − 4.2 | 0.9512 | Y = −2908.36X − 5.33 | 0.8976 |
| 2 | Y = −3840.13X − 2.93 | 0.9257 | Y = −3820.48X − 3.05 | 0.8375 |
| Reaction Order n | Blank Sample | Control Sample | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fitting Equation | Correlation Coefficient R2 | Fitting Equation | Correlation Coefficient R2 | |
| 1 | Y = −2566.95X − 6.69 | 0.9028 | Y = −2239.78X − 7.32 | 0.9067 |
| 1.5 | Y = −4687.77X − 1.81 | 0.8905 | Y = −3917.03X − 3.02 | 0.9738 |
| 1.8 | Y = −6167.03X − 0.63 | 0.9658 | Y = −6202.84X + 1.74 | 0.9161 |
| 2 | Y = −8018.97X + 4.10 | 0.9308 | Y = −6696.26X + 3.03 | 0.8328 |
| Sample | Stage II | Stage III | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reaction Order | E (kJ/mol) | A (s−1) | Reaction Order | E (kJ/mol) | A (s−1) | |
| Blank | 1.8 | 22.44 | 11.34 | 1.8 | 51.27 | 755.64 |
| Control | 1 | 14.21 | 4.48 | 1.5 | 32.56 | 65.05 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qi, H.; Jiang, H.; You, Y.; Hu, J.; Wang, Y.; Wu, Z.; Qi, H. Mechanism of Magnetic Nanoparticle Enhanced Microwave Pyrolysis for Oily Sludge. Energies 2022, 15, 1254. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15041254
Qi H, Jiang H, You Y, Hu J, Wang Y, Wu Z, Qi H. Mechanism of Magnetic Nanoparticle Enhanced Microwave Pyrolysis for Oily Sludge. Energies. 2022; 15(4):1254. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15041254
Chicago/Turabian StyleQi, Hongyuan, Huayi Jiang, Yanzhen You, Juan Hu, Yulong Wang, Zhe Wu, and Hongxin Qi. 2022. "Mechanism of Magnetic Nanoparticle Enhanced Microwave Pyrolysis for Oily Sludge" Energies 15, no. 4: 1254. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15041254
APA StyleQi, H., Jiang, H., You, Y., Hu, J., Wang, Y., Wu, Z., & Qi, H. (2022). Mechanism of Magnetic Nanoparticle Enhanced Microwave Pyrolysis for Oily Sludge. Energies, 15(4), 1254. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15041254





