Demagnetization Analysis of Modular SPM Machine Based on Coupled Electromagnetic-Thermal Modelling
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Demagnetization Analysis
2.1. Mechanism of Magnet Irreversible Demagnetization
2.2. Demagnetization without EM-Thermal Coupling
- PM field only: the MMF generated by PMs (Fm) can demagnetize the magnets.
- Armature field only: the MMF generated by 3-phase armature currents (Fc), particularly under flux weakening operation or during short-circuit fault, can lead to magnet demagnetization.
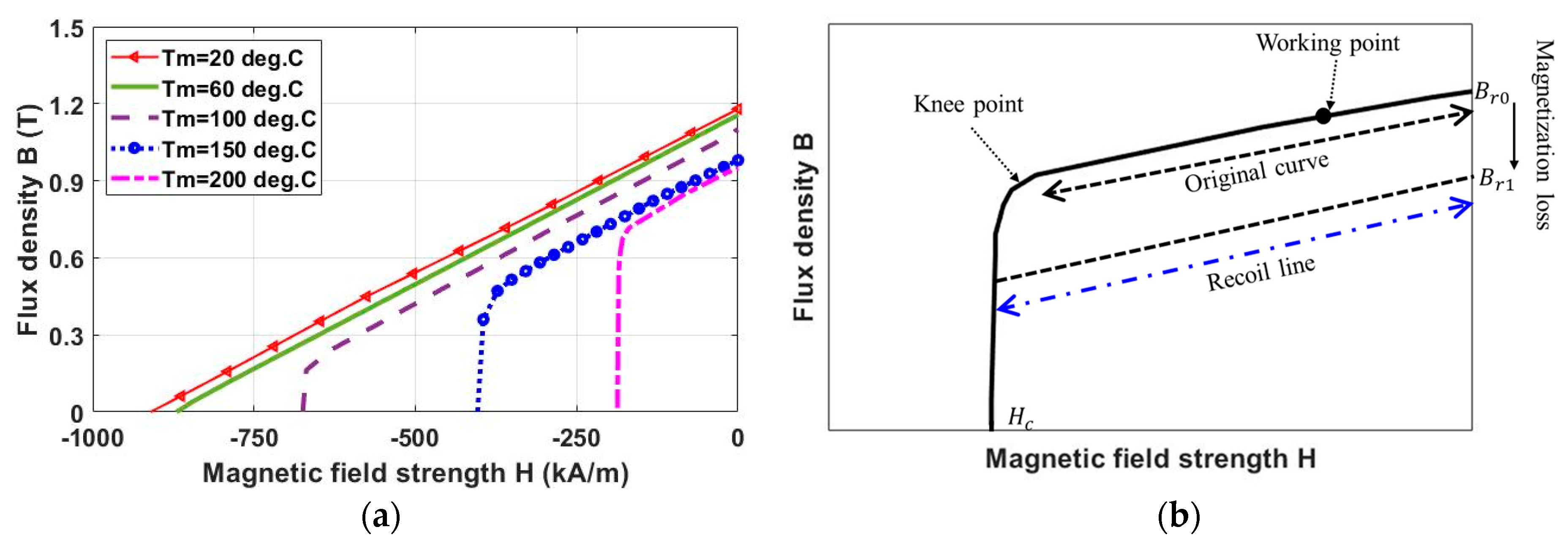
- Temperature rise: as mentioned previously, the coercivity of most magnets (except for Ferrite) reduces while the knee point increases to be closer to the magnet working point, making the magnets prone to irreversible demagnetization.
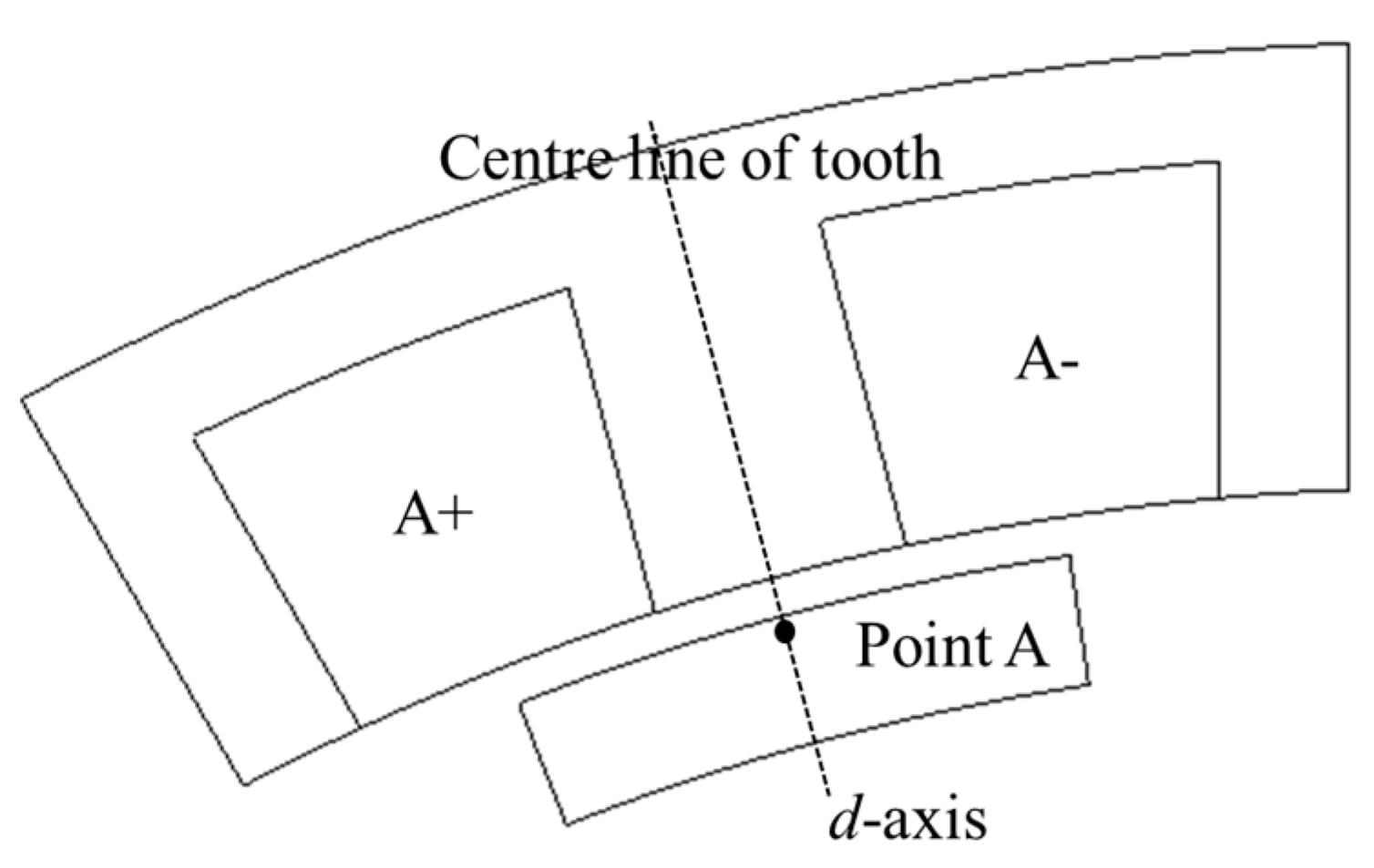
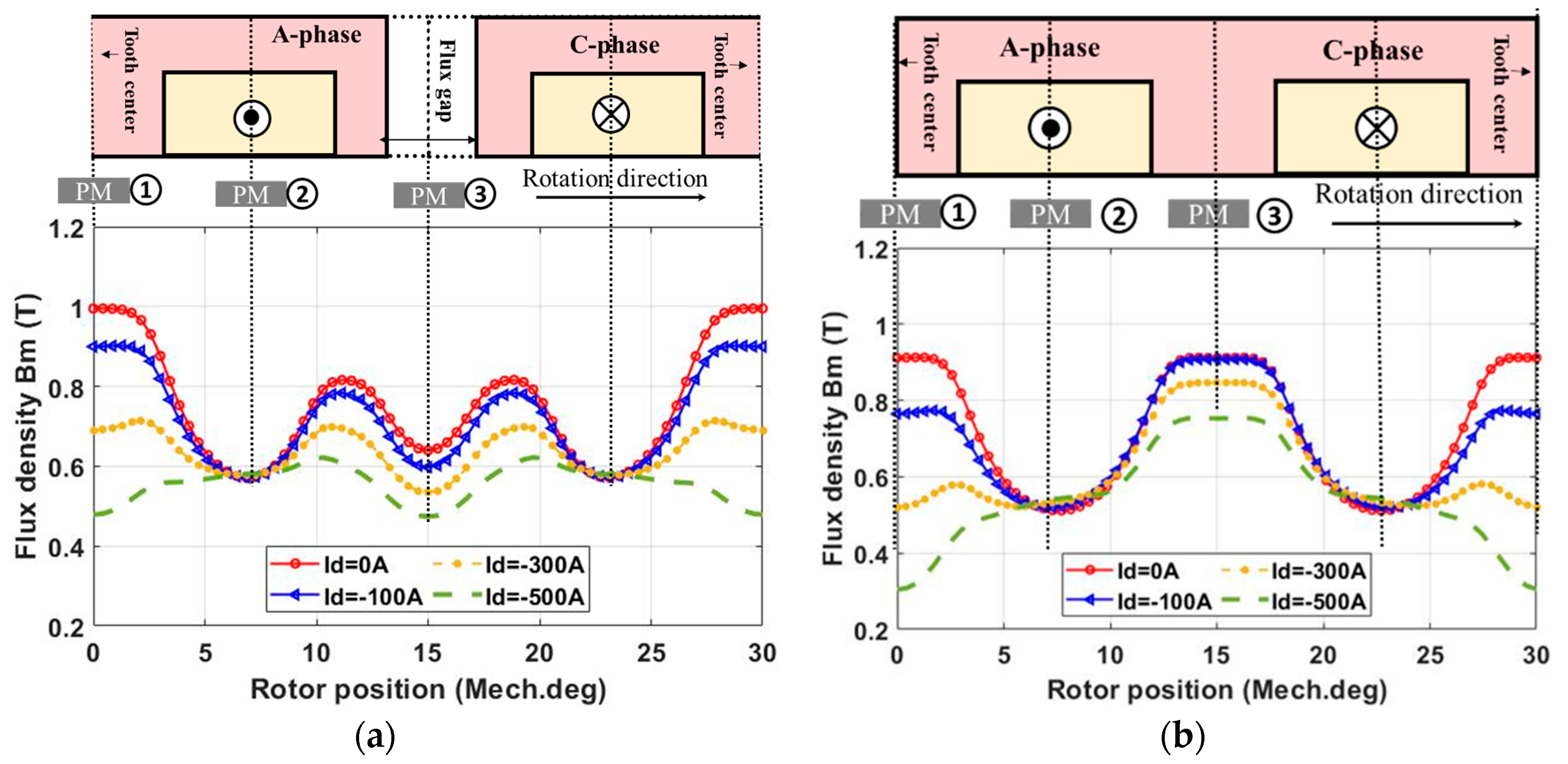
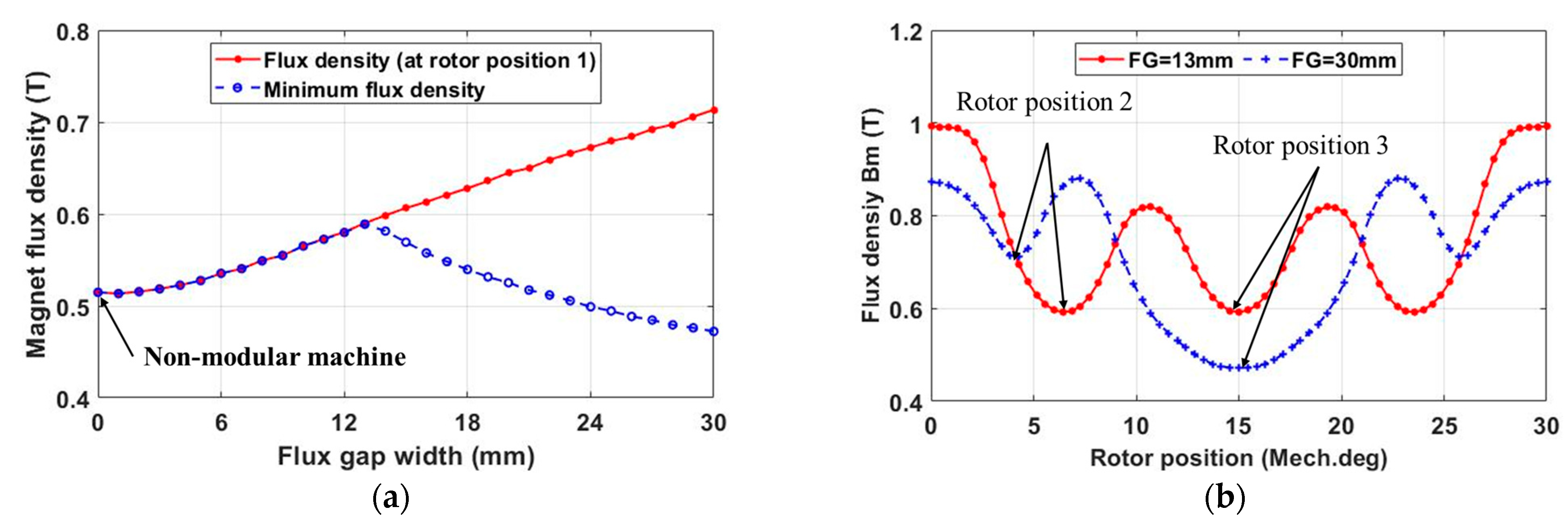
2.2.1. PM Field Only
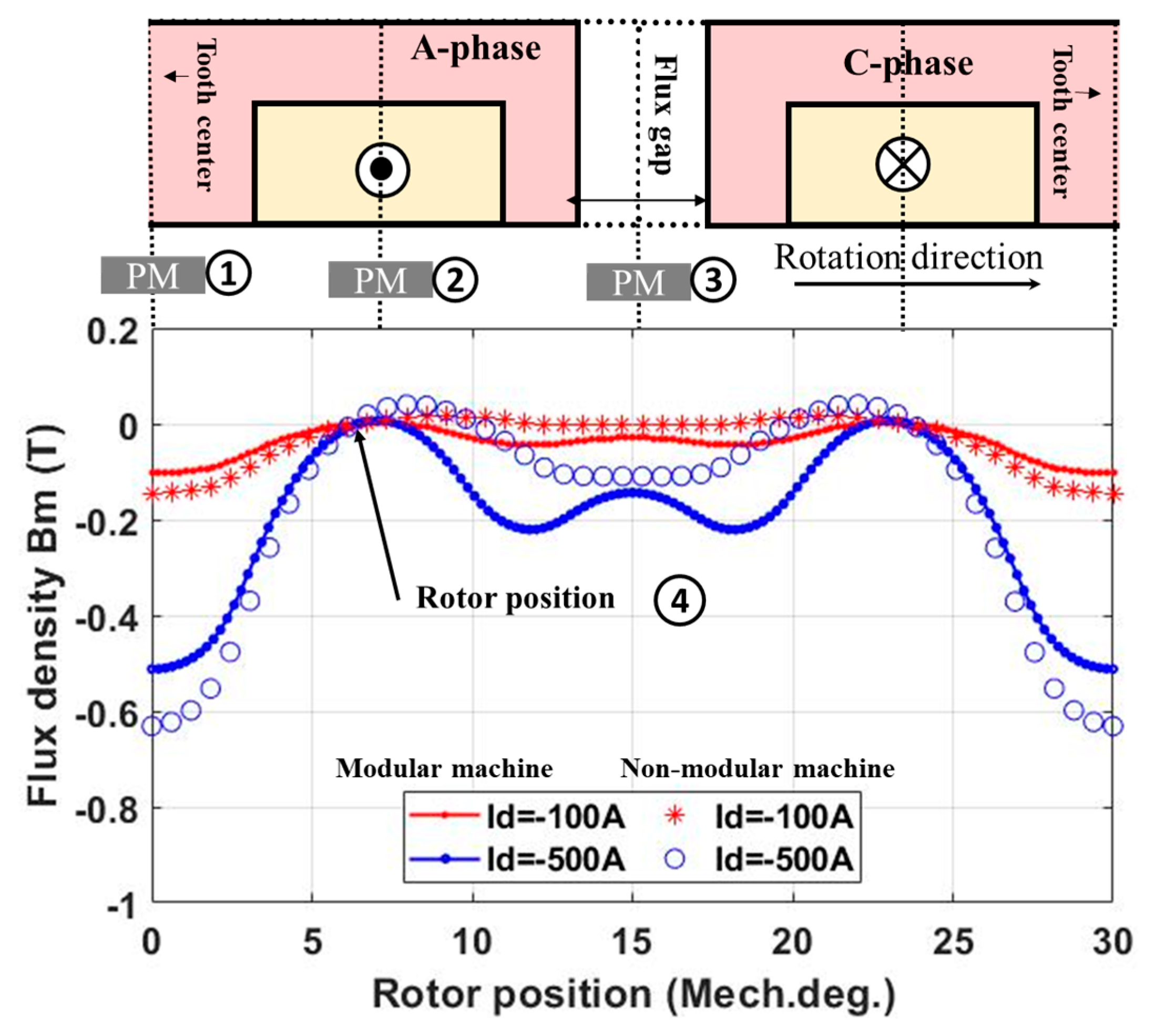
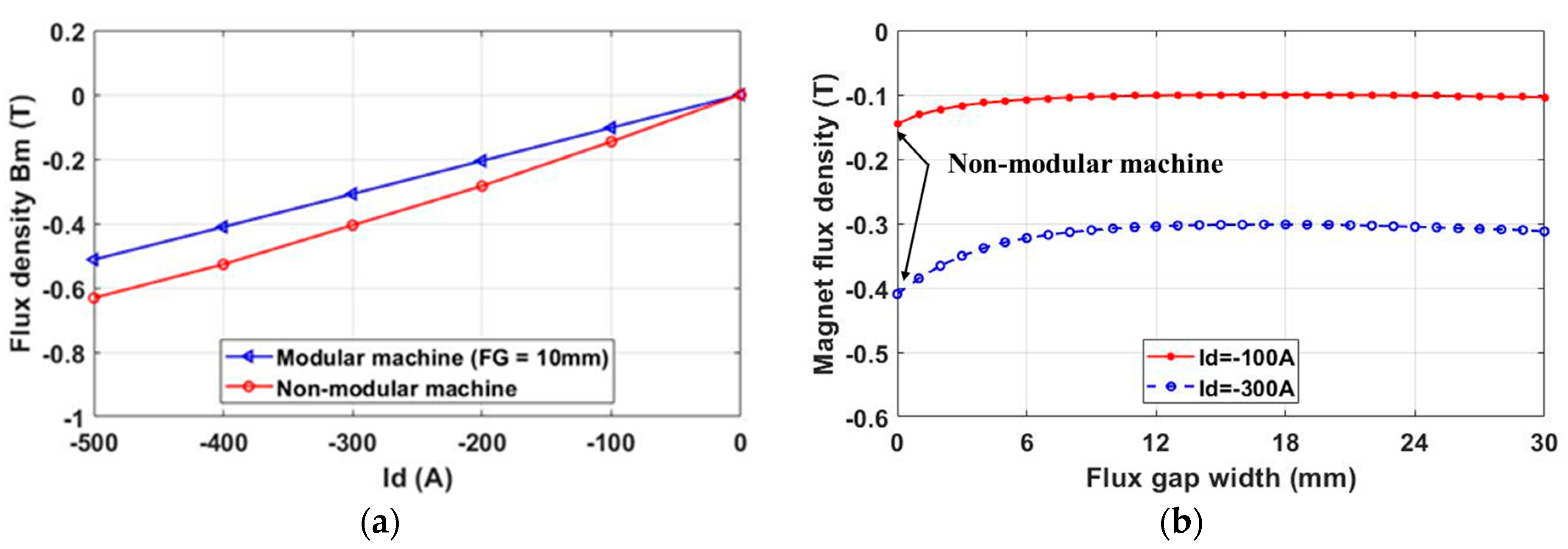
2.2.2. Armature Field Only
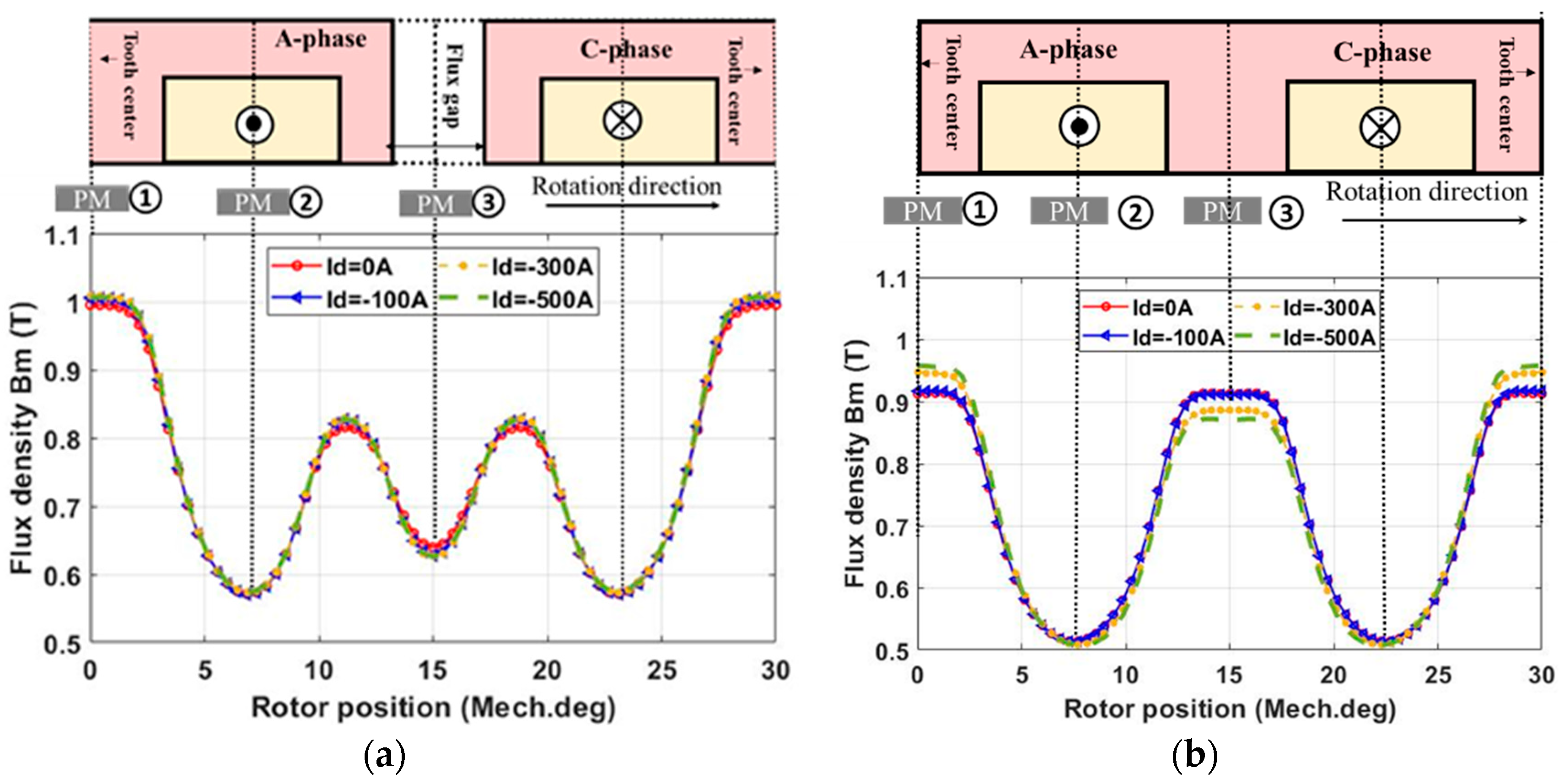
2.2.3. Demagnetization with Temperature Rise
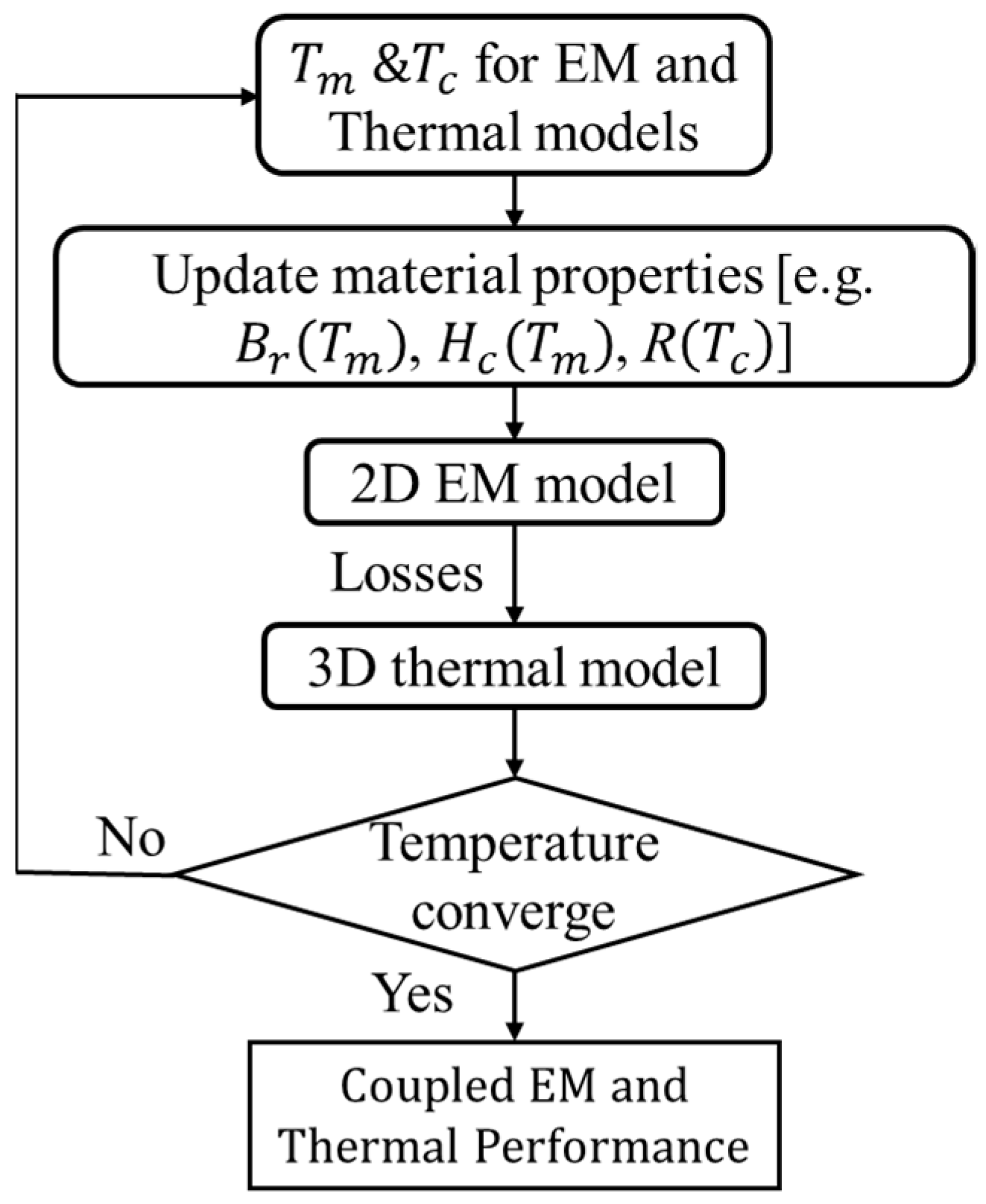
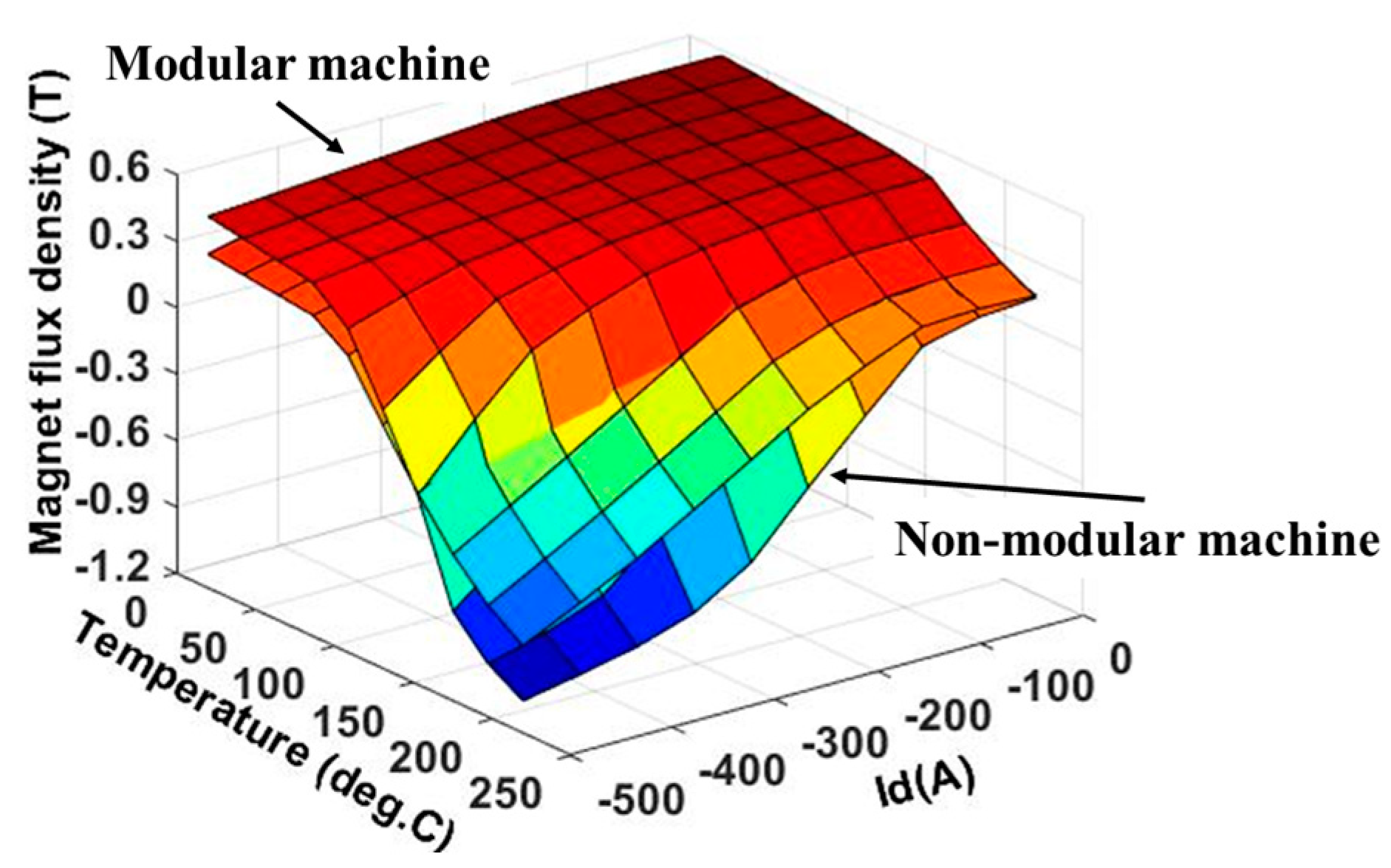
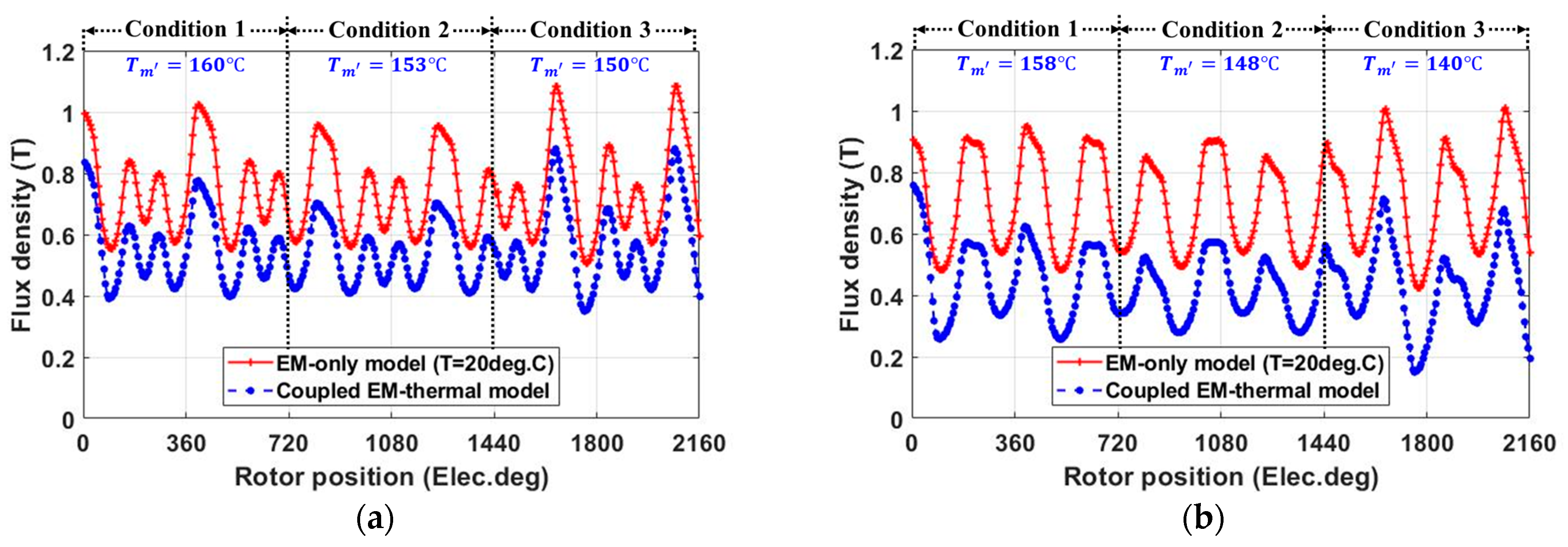
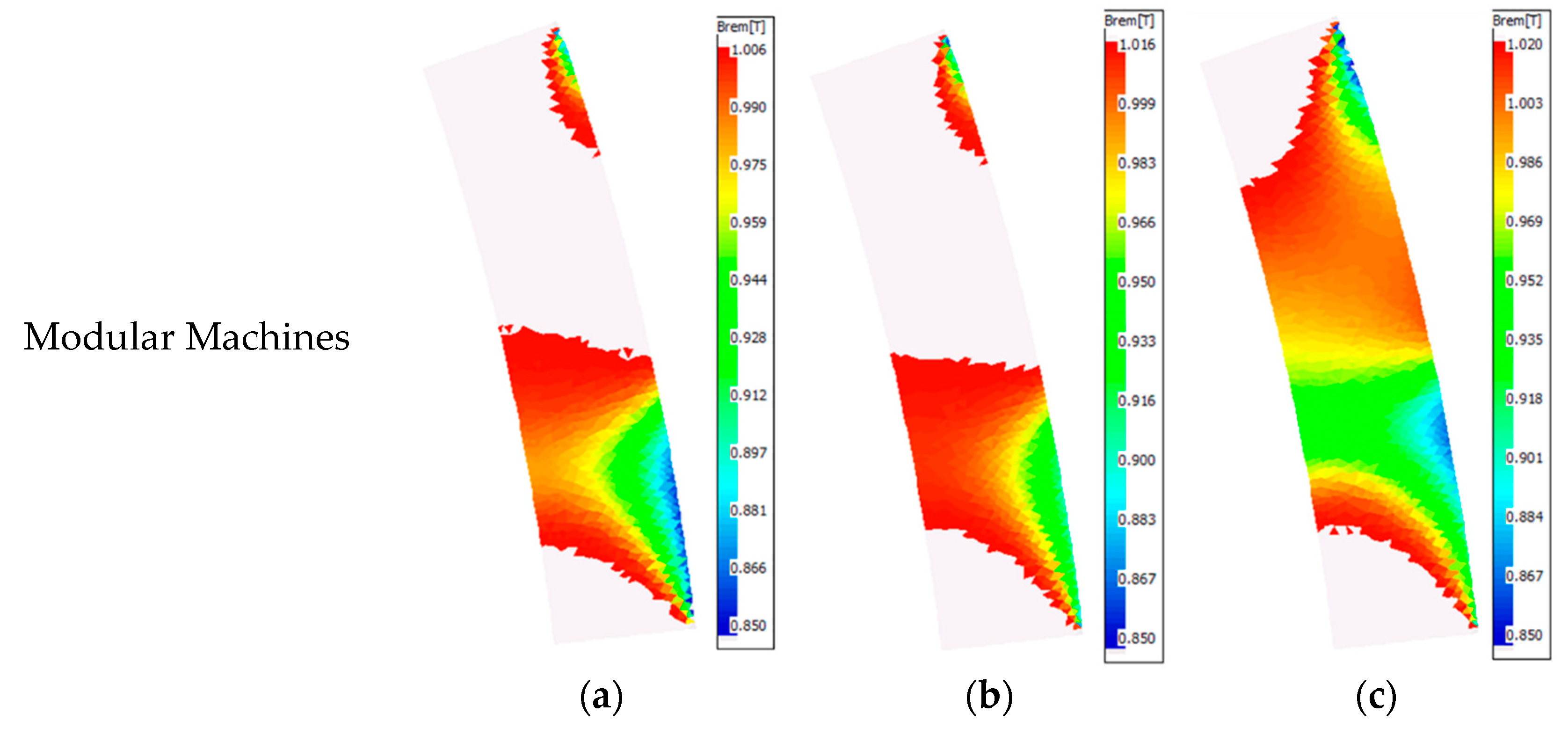
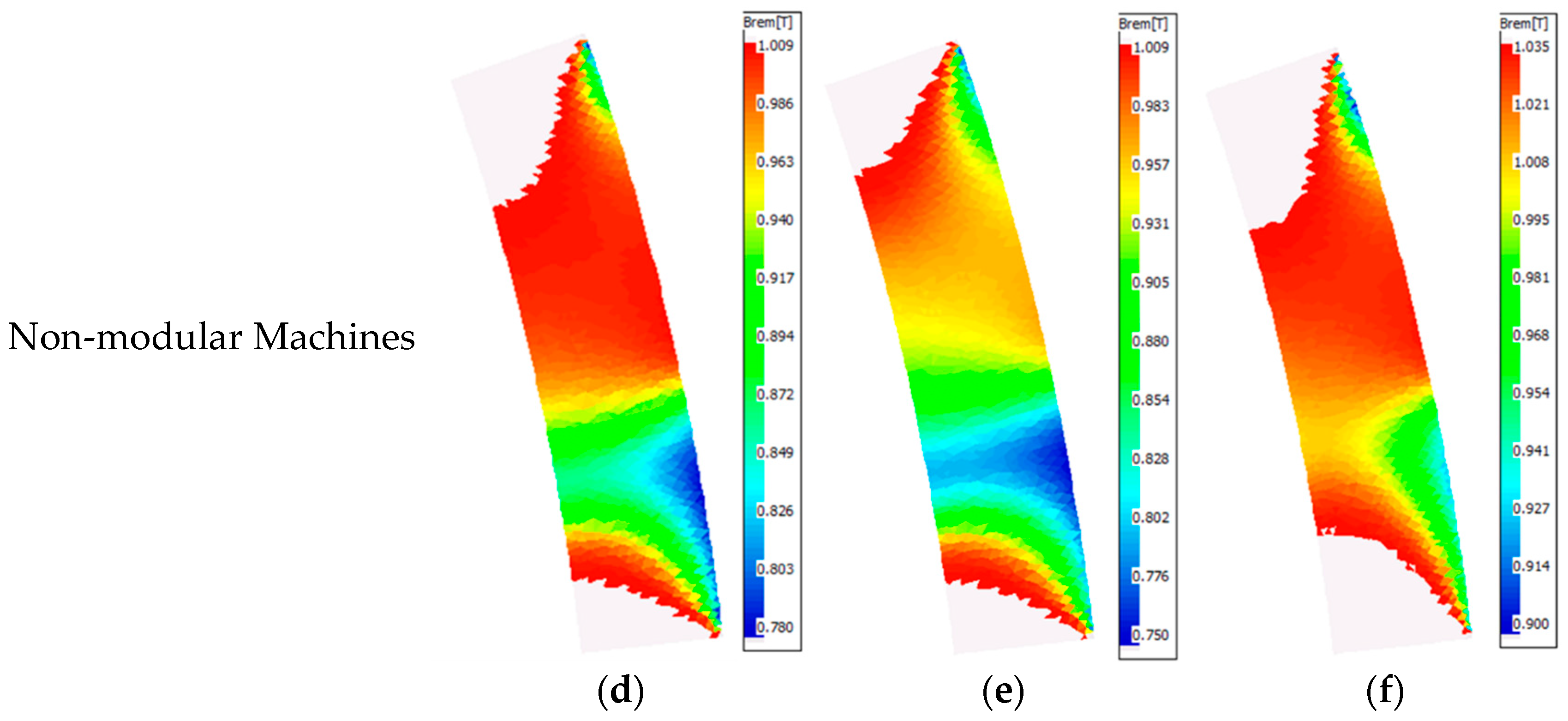
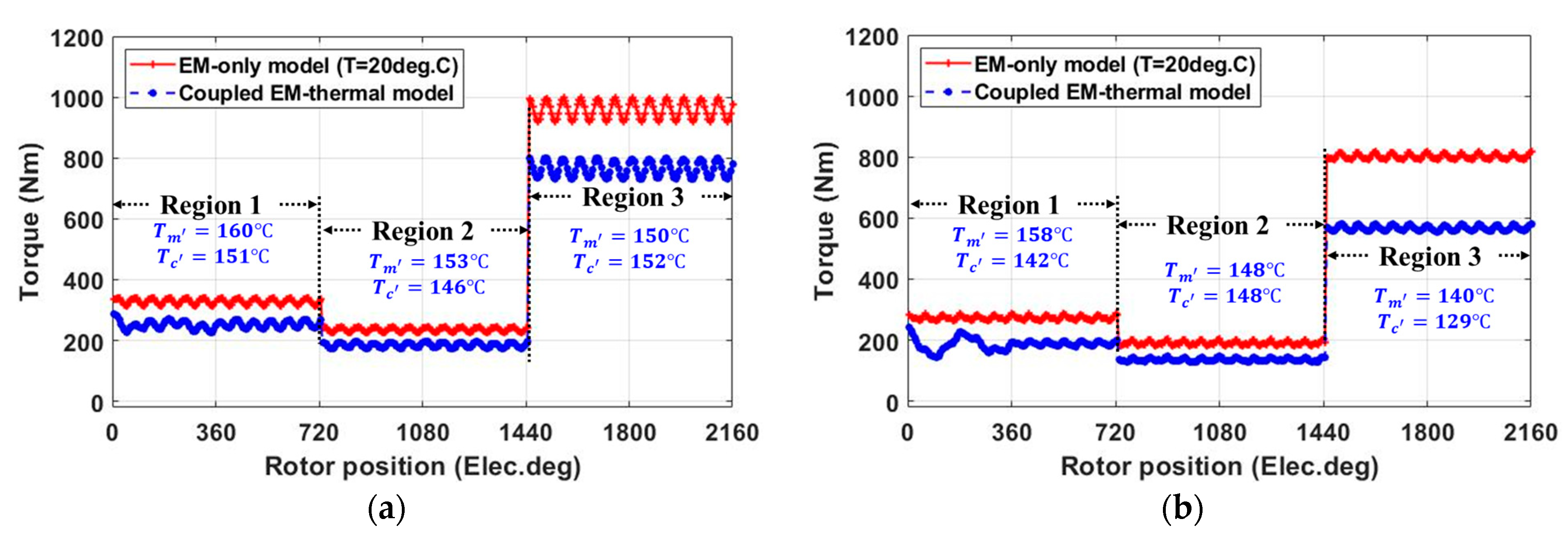
2.2.4. Demagnetization with Coupled EM-Thermal Modelling
- The electrical resistivity of the PM and iron core are independent of the temperature rise. This is because the increase in resistivity of the PM and iron core are negligible when the temperature rise is lower than 300 °C [19].
- For different operating conditions, only steady-state performance is considered to simplify the analyses.
- In order to avoid the change of magnet polarity, as shown in Figure 13, the investigated machines are assumed to operate less than 30 min when they are operated under three times the rated current.
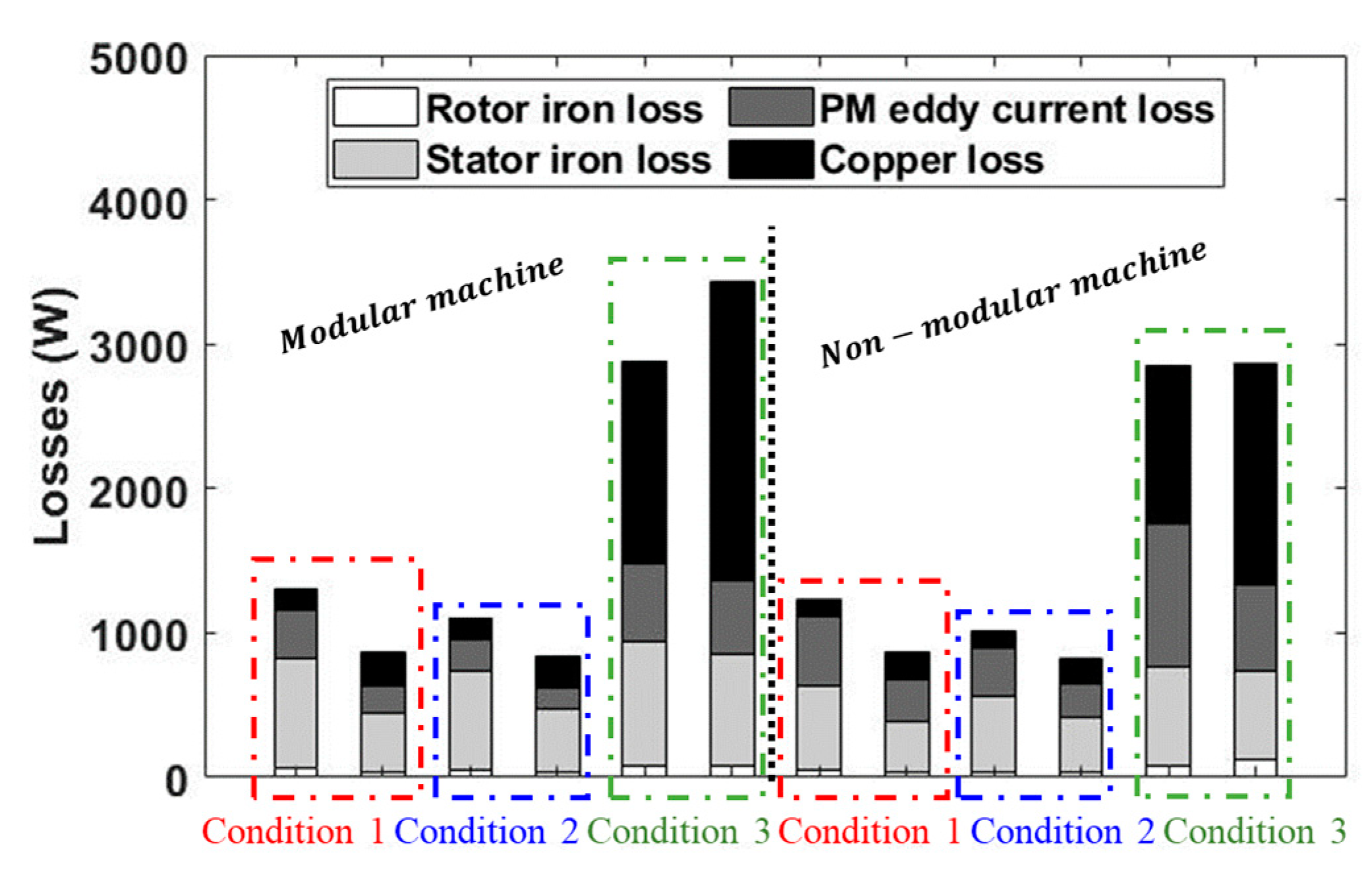
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Spooner, E.; Williamson, A.; Catto, G. Modular design of permanent-magnet generators for wind turbines. IEE Proc.-Electr. Power Appl. 1996, 143, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akita, H.; Nakahara, Y.; Miyake, N.; Oikawa, T. New core structure and manufacturing method for high efficiency of permanent magnet motors. In Proceedings of the 38th IAS Annual Meeting on Conference Record of the Industry Applications Conference, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 12–16 October 2003; pp. 367–372. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Li, G.; Zhu, Z.; Ren, B.; Michon, M. Optimization of Modular SPM Machines Considering Stator Modularity. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Electric Machines & Drives Conference (IEMDC), Hartford, CT, USA, 17–20 May 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.; Zhu, Z.; Chu, W.; Foster, M.; Stone, D. Influence of flux gaps on electromagnetic performance of novel modular PM machines. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2014, 29, 716–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Ren, B.; Zhu, Z.; Foster, M.; Stone, D. Demagnetization withstand capability enhancement of surface mounted PM machines using stator modularity. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2017, 54, 1302–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lyu, S.; Yang, H.; Lin, H.; Zhu, Z.; Zheng, H.; Pan, Z. Influence of design parameters on on-load demagnetization characteristics of switched flux hybrid magnet memory machine. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2019, 55, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McFarland, J.D.; Jahns, T.M. Investigation of the rotor demagnetization characteristics of interior PM synchronous machines during fault conditions. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2013, 50, 2768–2775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, G.; Jahns, T. Interior permanent magnet synchronous machine rotor demagnetization characteristics under fault conditions. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition, Denver, CO, USA, 15–19 September 2013; pp. 2500–2507. [Google Scholar]
- McFarland, J.D.; Jahns, T.M.; El-Refaie, A.M. Demagnetization performance characteristics of flux switching permanent magnet machines. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Electrical Machines (ICEM), Berlin, Germany, 2–5 September 2014; pp. 2001–2007. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.J.; Taras, P.; Zhu, Z.Q.; Ojeda, J.; Gabsi, M. Investigation of irreversible demagnetisation in switched flux permanent magnet machines under short--circuit conditions. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2017, 11, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-K.; Hur, J. Dynamic characteristic analysis of irreversible demagnetization in SPM-and IPM-type BLDC motors. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2016, 53, 982–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebastian, T. Temperature effects on torque production and efficiency of PM motors using NdFeB magnets. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 1995, 31, 353–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dellinger, J.H. The Temperature Coefficient of Resistance of Copper; US Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1911.
- Taras, P.; Li, G.-J.; Zhu, Z.-Q.; Foster, M.P.; Stone, D.A. Combined multiphysics model of switched flux PM machines under fault operations. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 66, 6737–6745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, B. Electromagnetic-thermal coupled simulation under various fault conditions of a triple redundant 9-phase PMASynRM. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2019, 56, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, D.-K.; Jeong, B.H. Irreversible demagnetization of permanent magnet in a surface-mounted permanent magnet motor with overhang structure. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2015, 52, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Pang, Y.; Howe, D.; Iwasaki, S.; Deodhar, R.; Pride, A. Analysis of electromagnetic performance of flux-switching permanent-magnet machines by nonlinear adaptive lumped parameter magnetic circuit model. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2005, 41, 4277–4287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Lin, D.; Xiao, Y.; Lambert, N.; Rahman, M. Temperature-dependent demagnetization model of permanent magnets for finite element analysis. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2012, 48, 1031–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Yao, Y.; Klik, I. Electrical and magnetic properties of NdFeB films. Appl. Surf. Sci. 1997, 113, 174–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezani, S.; Takorabet, N.; Laporte, B. A combined electromagnetic and thermal analysis of induction motors. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2005, 41, 1572–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
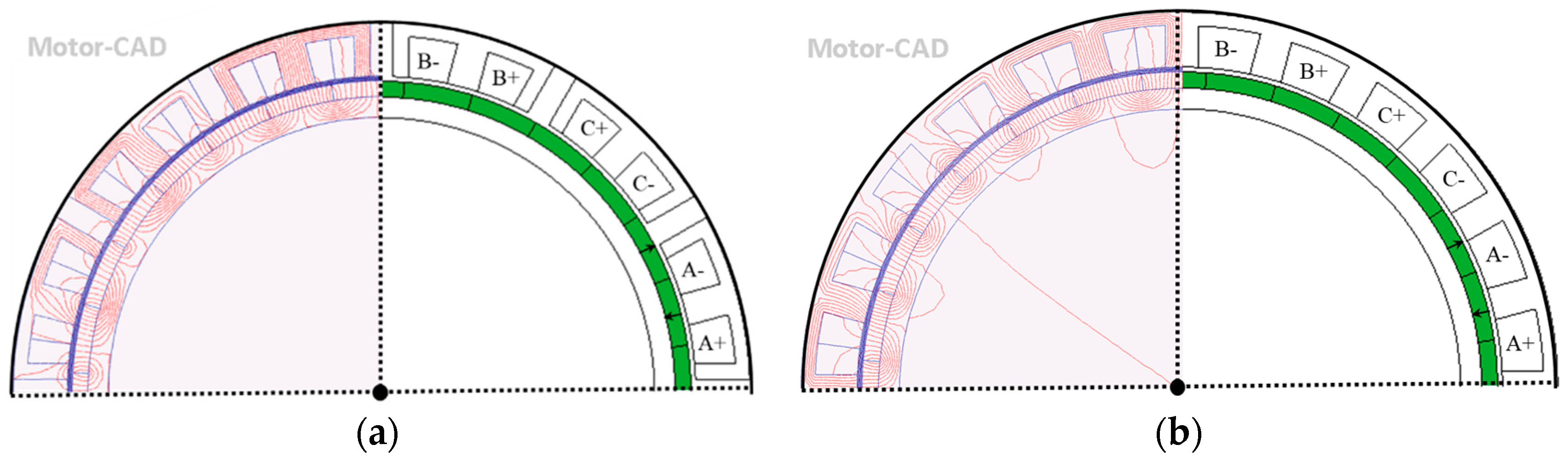

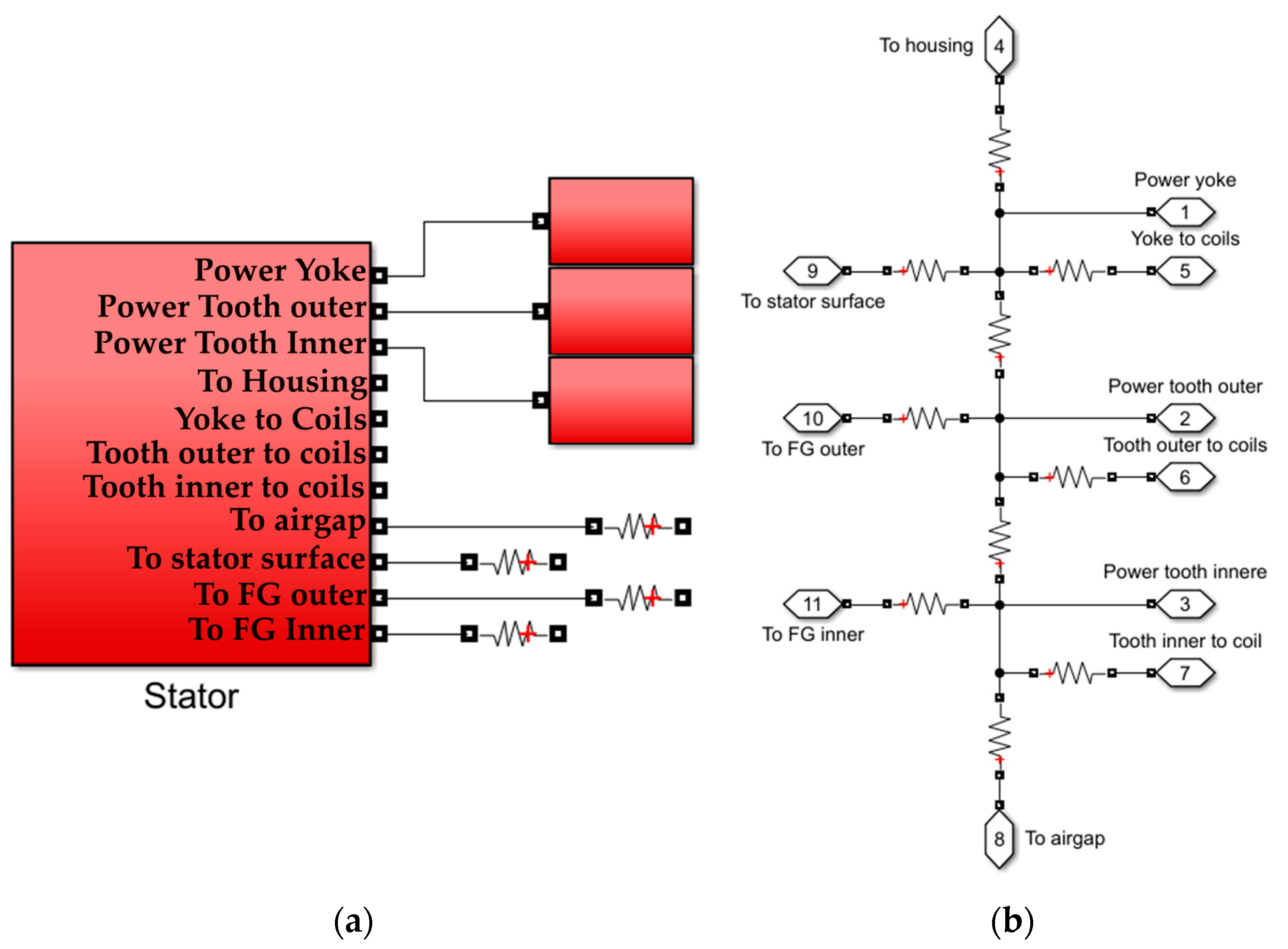
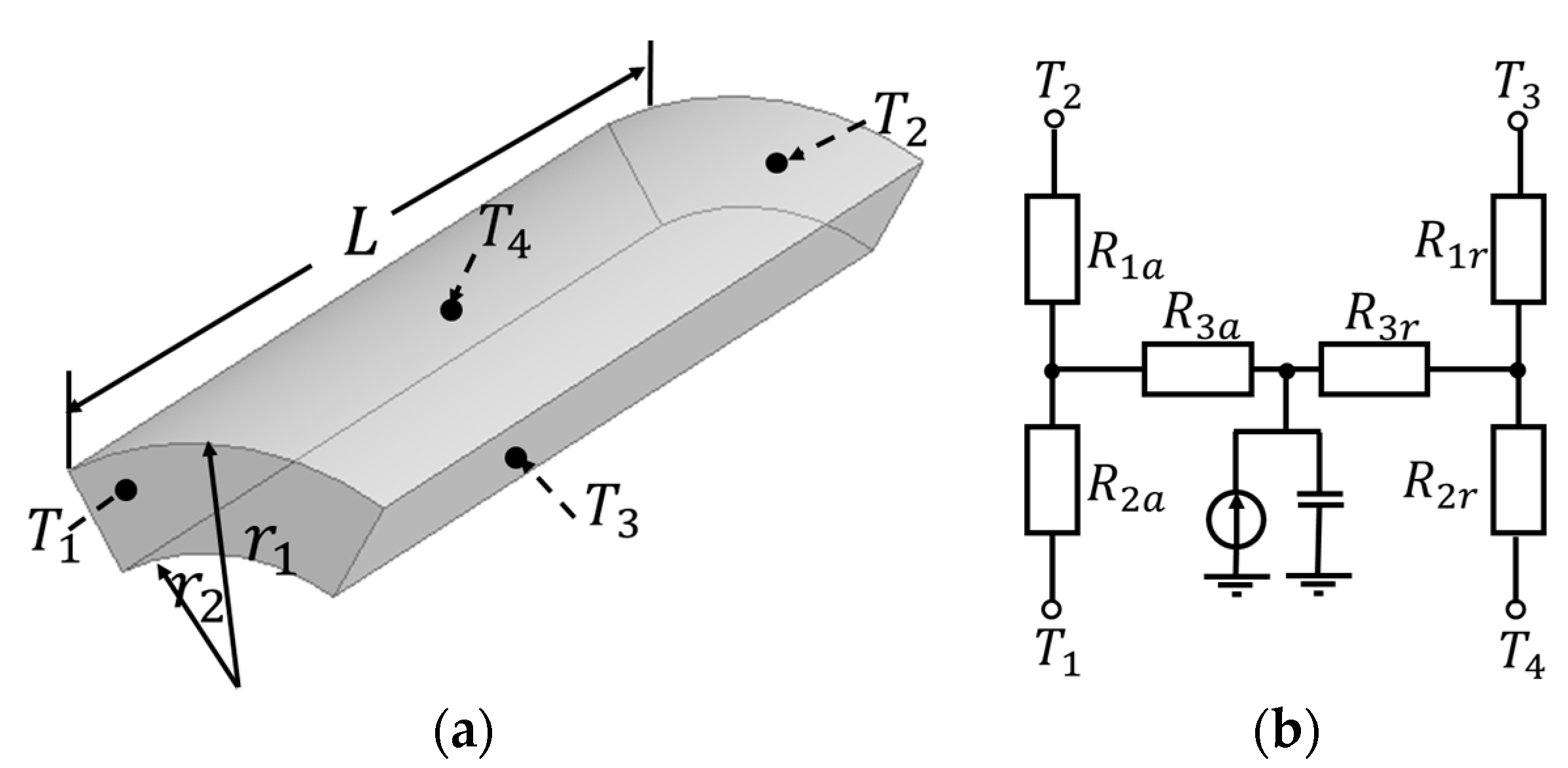
| Slot number | 24 | Rotor outer radius (mm) | 129.4 |
| Pole number | 28 | Rotor yoke thickness (mm) | 8.6 |
| Stator outer radius (mm) | 154 | Stack length (mm) | 210 |
| Stator yoke height (mm) | 5.6 | DC voltage (V) | 800 |
| Tooth width (mm) | 13.2 | Rated phase current () | 100 |
| Flux gap width (mm) | 10 | Number of turns per coil | 10 |
| Airgap length (mm) | 2 | Rate speed (rpm) | 1500 |
| Magnet thickness (mm) | 6.6 |
| Non-Modular Machine | Modular Machine | |
|---|---|---|
| Mass of active winding (kg) | 9.1 | 7.1 |
| Mass of stator steel (kg) | 16.7 | 15.7 |
| Mass of rotor steel (kg) | 10 | 10 |
| Mass of permanent (kg) | 8.2 | 8.2 |
| Slot fill factor | 0.6 | 0.47 |
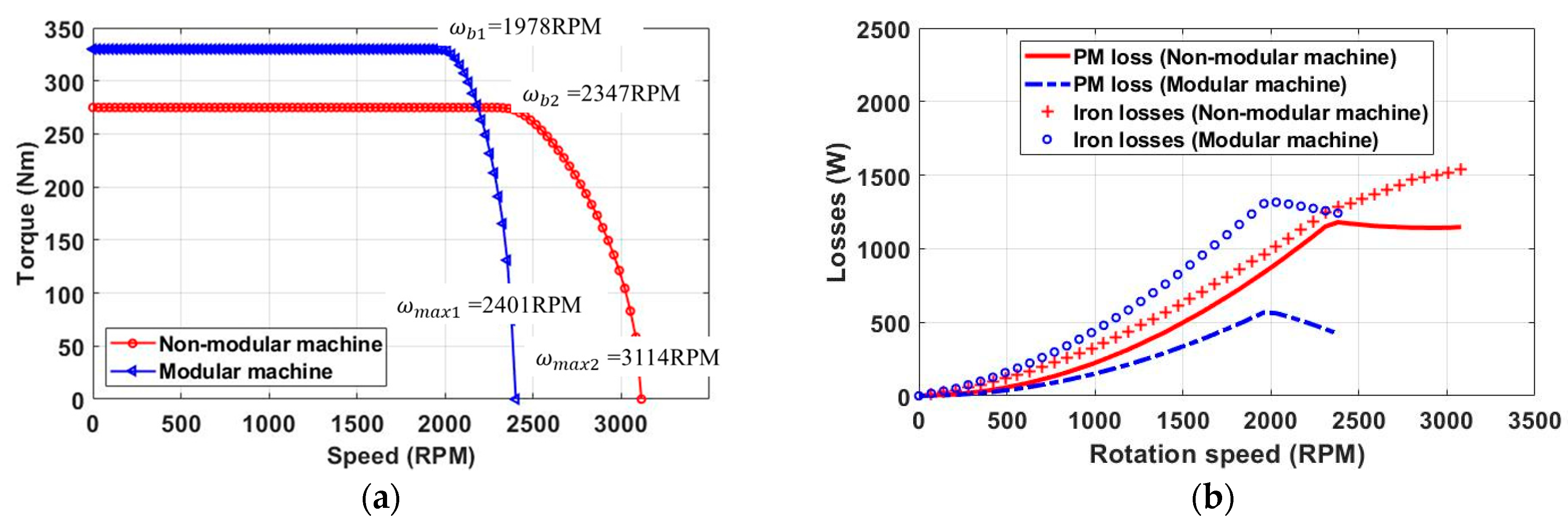
| Torque (Nm) | 273 | 330 |
| Power (kW) | 43 | 52 |
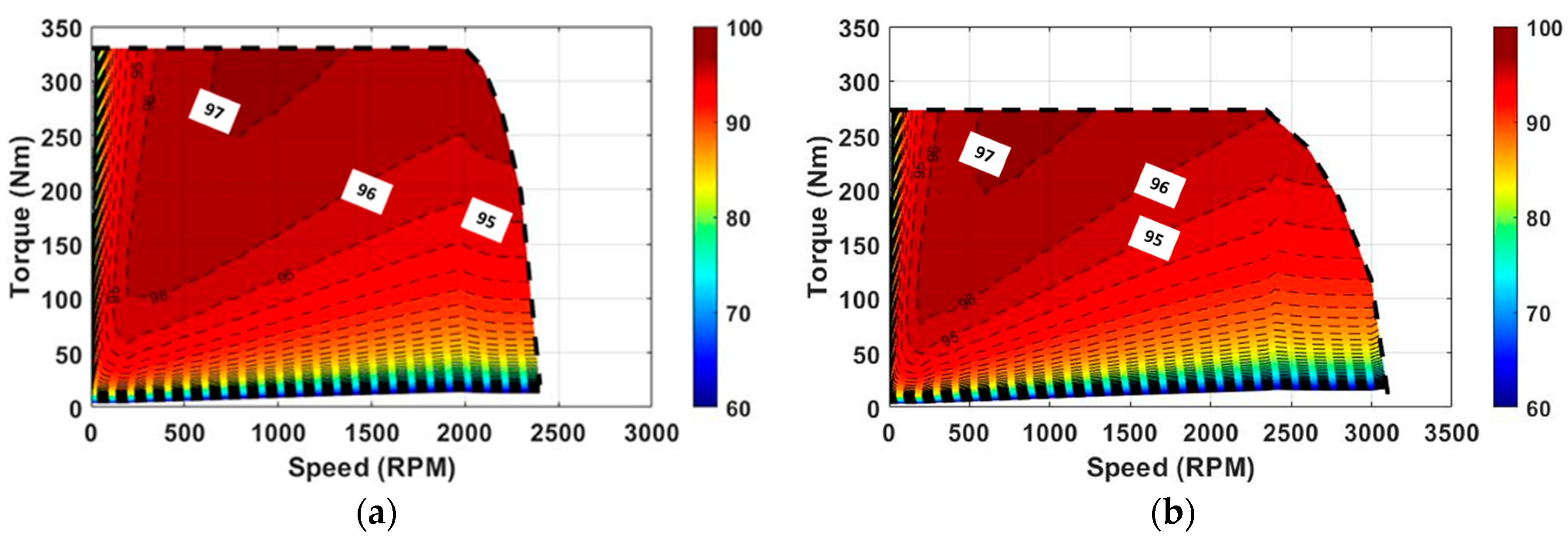
| Efficiency (%) | 96.9 | 96.8 |
| Modular Machine | Non-Modular Machine | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tm (°C) | Tc (°C) | Tm (°C) | Tc (°C) | |
| Condition 1 | 160 | 151 | 158 | 142 |
| Condition 2 | 153 | 146 | 148 | 148 |
| Condition 3 | 150 | 152 | 140 | 129 |
| Torque (Nm) | Power (kW) | Efficiency (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Modular machine | 326 | 51.2 | 97.1 |
| Non-modular machine | 270 | 42.4 | 95.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, W.; Li, G.-J.; Zhu, Z.-Q.; Ren, B.; Chong, Y.C.; Michon, M. Demagnetization Analysis of Modular SPM Machine Based on Coupled Electromagnetic-Thermal Modelling. Energies 2023, 16, 131. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16010131
Zhang W, Li G-J, Zhu Z-Q, Ren B, Chong YC, Michon M. Demagnetization Analysis of Modular SPM Machine Based on Coupled Electromagnetic-Thermal Modelling. Energies. 2023; 16(1):131. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16010131
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Wei, Guang-Jin Li, Zi-Qiang Zhu, Bo Ren, Yew Chuan Chong, and Melanie Michon. 2023. "Demagnetization Analysis of Modular SPM Machine Based on Coupled Electromagnetic-Thermal Modelling" Energies 16, no. 1: 131. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16010131
APA StyleZhang, W., Li, G.-J., Zhu, Z.-Q., Ren, B., Chong, Y. C., & Michon, M. (2023). Demagnetization Analysis of Modular SPM Machine Based on Coupled Electromagnetic-Thermal Modelling. Energies, 16(1), 131. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16010131








