Optimization Methods of Urban Green Space Layout on Tropical Islands to Control Heat Island Effects
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
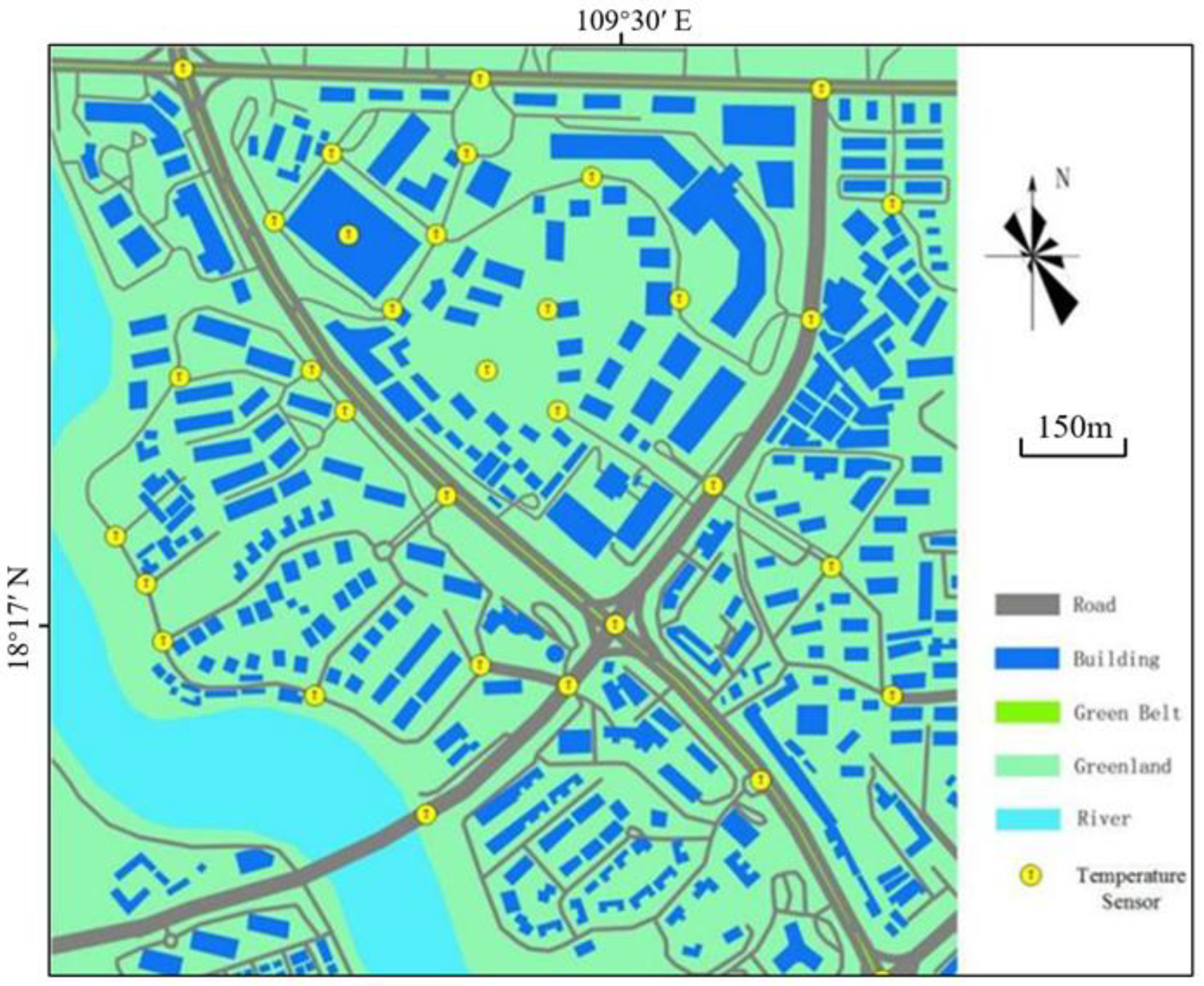
2.1. Study Area
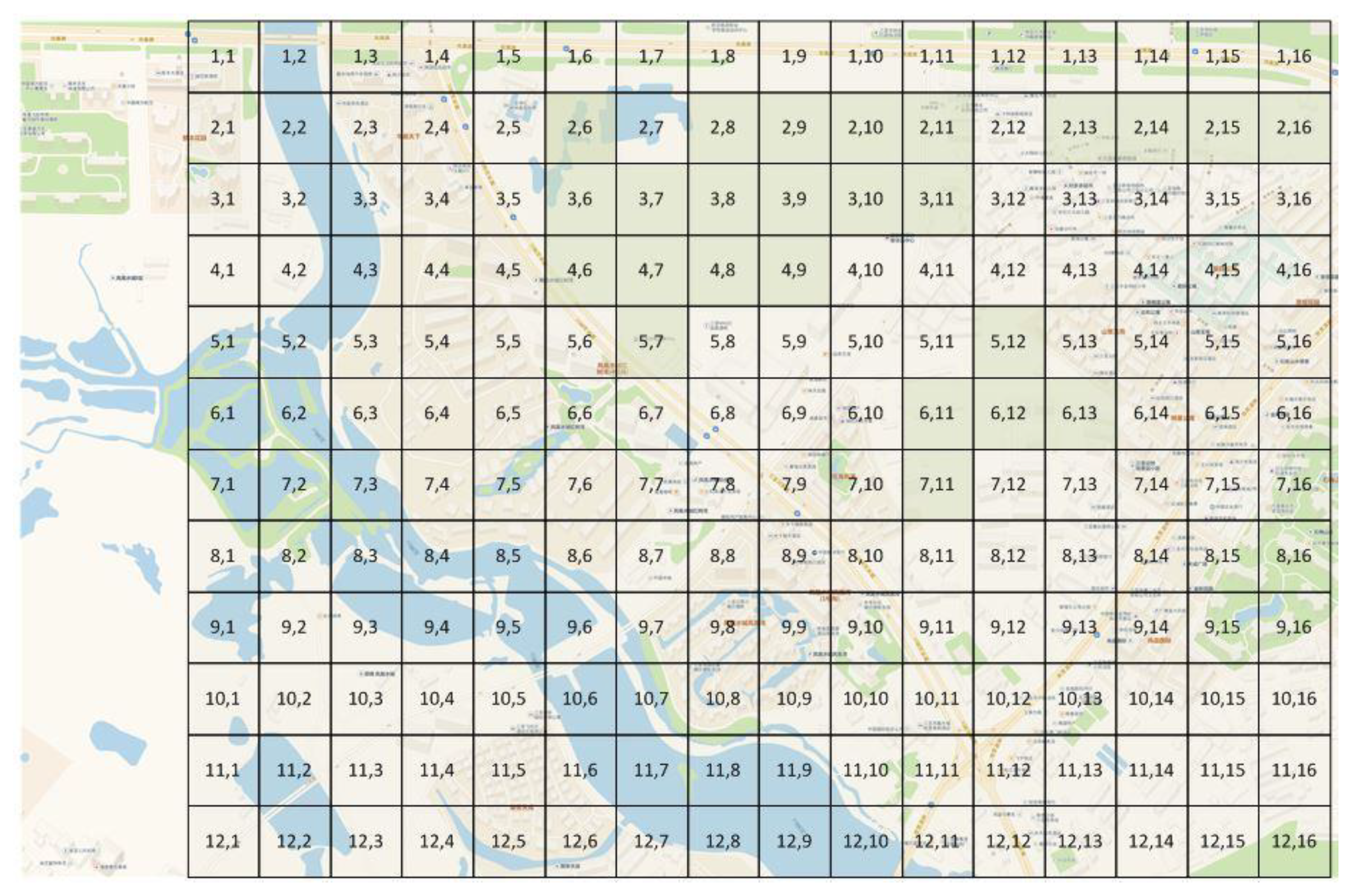
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Green Space Cooling Model
- (1)
- Air temperature of grid green space
- (2)
- Air temperature around grid green space
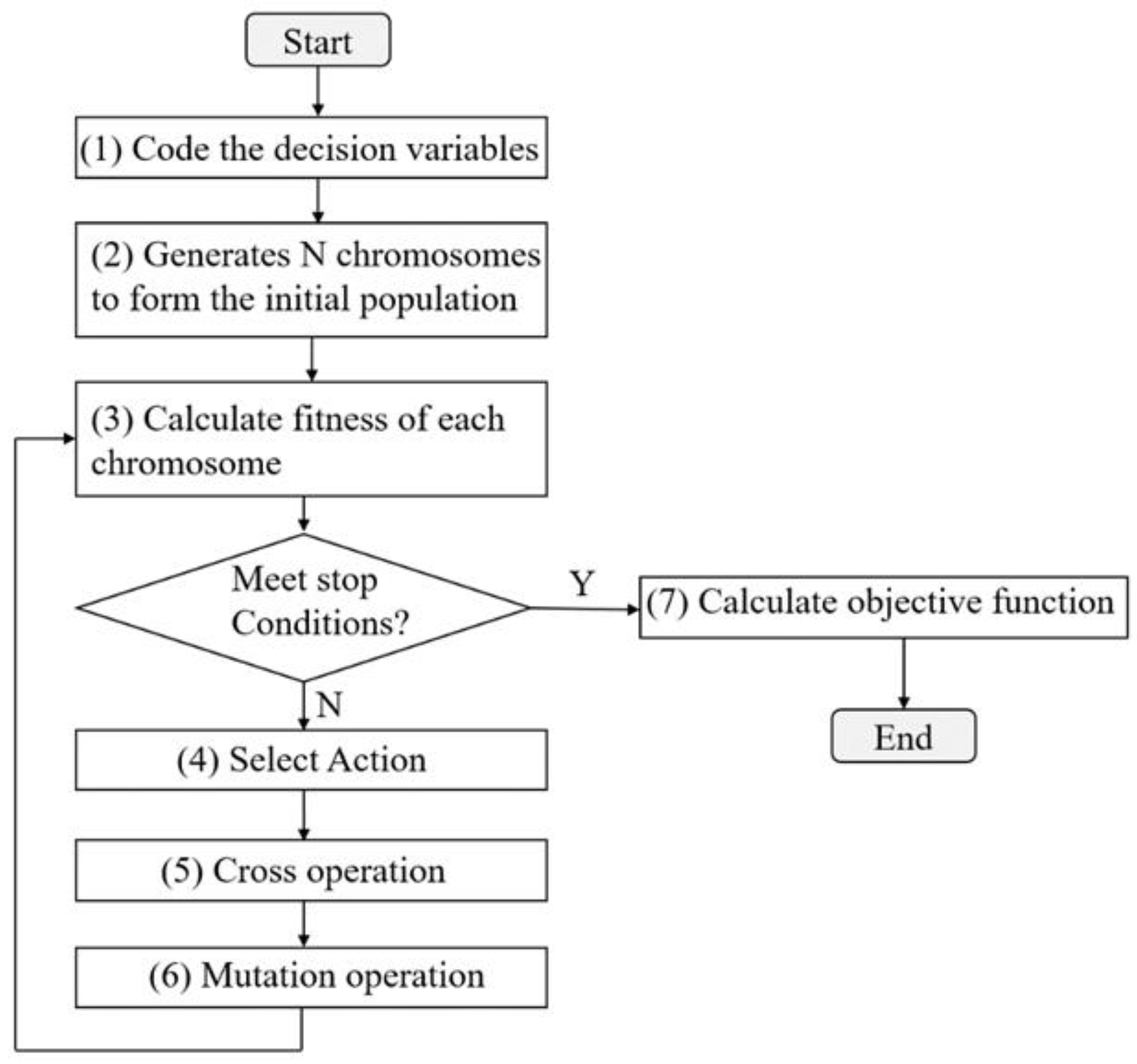
2.4. Objective Function
3. Case Study
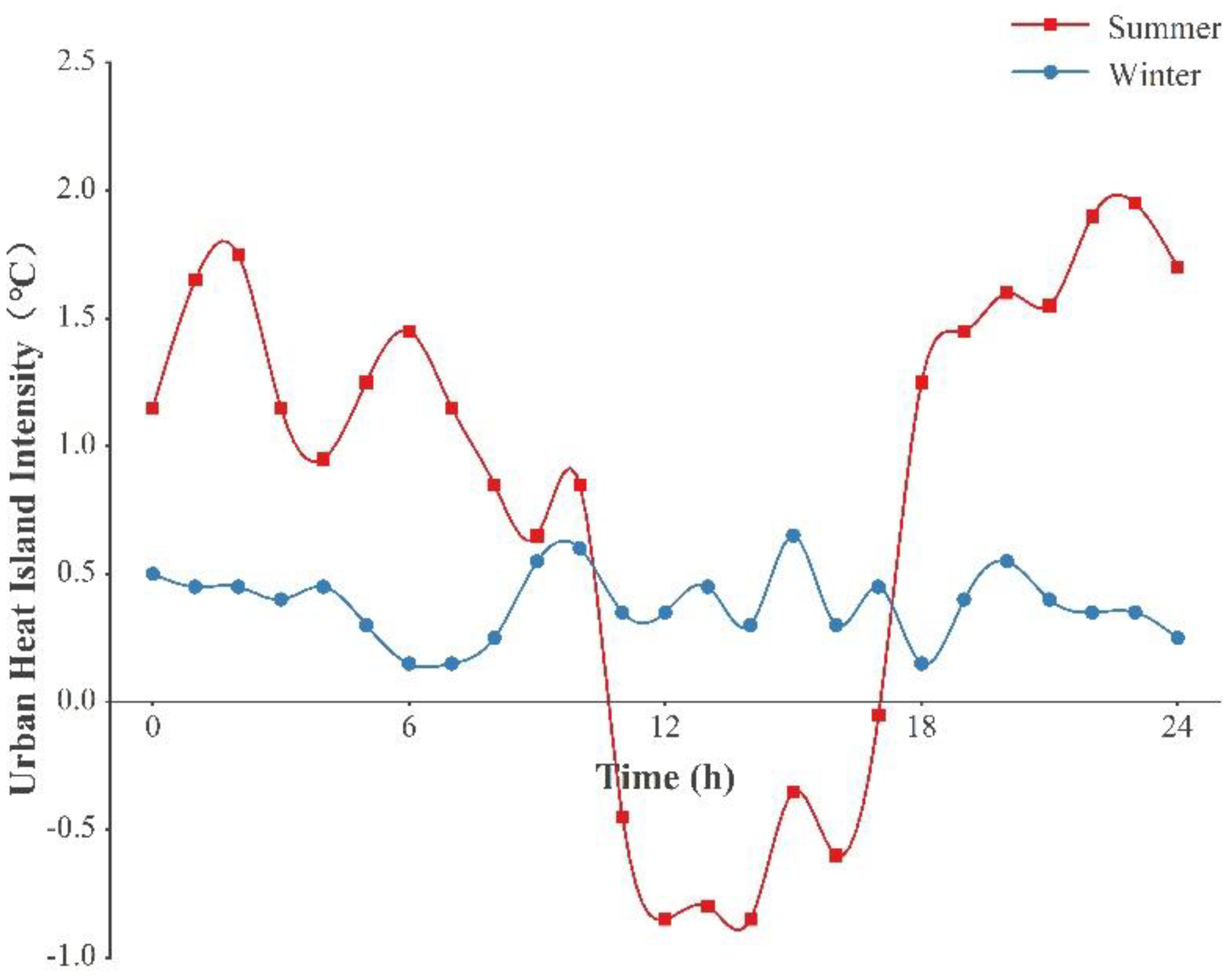
3.1. Experimental Result Analysis
3.2. Establishment of Cooling Model for Green Space
3.3. Analysis of Optimization Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Planning and Design Method for Mitigating the Heat Island Effect
4.2. Limitations and Future Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hu, G.T.; Wang, G.; Yang, C.J. Analysis of green landscape distribution and thermal environment of Yangjiang City. Remote Sens. Inf. 2017, 6, 157–161. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, X.L.; Lin, J.; Yang, Y.C. Mitigation role of urban green space in reducing heat island effect—A case study of central urban area of Baoding City. Landsc. Archit. 2018, 10, 66–70. [Google Scholar]
- Aronson, M.; Lepczyk, C.A.; Evans, K.L.; Goddard, M.A.; Lerman, S.B.; MacIvor, J.S.; Nilon, C.H.; Vargo, T. Biodiversity in the city: Key challenges for urban green space management. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2017, 15, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wolch, J.; Byrne, J.; Newell, J. Urban green space, public health, and environmental justice: The challenge of making cities ‘just green enough’. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2014, 125, 234–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Su, Y.X.; Huang, G.Q.; Chen, X.Z.; Chen, S.; Li, Z. Research progress in the eco-environmental effects of urban green spaces. Acta Ecologica. Sin. 2011, 31, 7287–7300. [Google Scholar]
- Haq, S.M.A. Urban green spaces and an integrative approach to sustainable environment. J. Environ. Prot. 2011, 2, 601–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Georgi, J.; Dimitriou, D. The contribution of urban green spaces to the improvement of environment in cities: Case study of Chania, Greece. Build. Environ. 2010, 45, 1401–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kabisch, N.; Haase, D. Green justice or just green? Provision of urban green spaces in Berlin, Germany. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2014, 122, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aerts, J.; Heuvelink, G. Research Article Using simulated annealing for resource allocation. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2001, 16, 571–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vujcic, M.; Tomicevic-Dubljevic, J.; Zivojinovic, I.; Toskovic, O. Connection between urban green areas and visitors’ physical and mental well-being. Urban For. Urban Green. 2019, 40, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kafy, A.A.; Saha, M.; Faisal, A.A.; Rahaman, Z.A.; Rahman, M.T.; Liu, D.; Fattah, M.A.; Al Rakib, A.; AlDousari, A.E.; Rahaman, S.N.; et al. Predicting the impacts of land use/land cover changes on seasonal urban thermal characteristics using machine learning algorithms. Build. Environ. 2022, 217, 109066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowler, D.E.; Buyung-Ali, L.; Knight, T.M.; Pullin, A.S. Urban greening to cool towns and cities: A systematic review of the empirical evidence. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2010, 97, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Xu, X.; Lao, Z.; Liu, W.; Li, Z.; García, E.H.; He, L.; Zhu, J. Evaluating the impact of urban green space and landscape design parameters on thermal comfort in hot summer by numerical simulation. Build. Environ. 2017, 123, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, P.; Potchter, O.; Matzarakis, A. Daily and seasonal climatic conditions of green urban open spaces in the Mediterranean climate and their impact on human comfort. Build. Environ. 2012, 51, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, W.T.L.; Brennan, D.; Brazel, A.J. Urban Heat Island research in Phoenix, Arizona: Theoretical contributions and policy applications. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2012, 93, 517–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matthews, T.; Lo, A.; Byrne, J. Reconceptualizing green infrastructure for climate change adaptation: Barriers to adoption and drivers for uptake by spatial planners. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2015, 138, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzoulas, K.; Korpela, K.; Venn, S.; Yli-Pelkonen, V.; Kaźmierczak, A.; Niemela, J.; James, P. Promoting ecosystem and human health in urban areas using Green Infrastructure: A literature review. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2007, 81, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alexandri, E.; Jones, P. Temperature decreases in an urban canyon due to green walls and green roofs in diverse climates. Build. Environ. 2008, 43, 480–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaffarian Hoseini, A.H.; Berardi, U.; GhaffarianHoseini, A.; Nastaran, M. Intelligent facades in low-energy buildings. Br. J. Environ. Clim. Chang. 2012, 4, 437–445. [Google Scholar]
- Berardi, U.; GhaffarianHoseini, A.H.; GhaffarianHoseini, A. State-of-the-art analysis of the environmental benefits of green roofs. Appl. Energy 2014, 115, 411–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berardi, U. The outdoor microclimate benefits and energy saving resulting from green roofs retrofits. Energy Build. 2016, 121, 217–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jim, C.Y. Assessing climate-adaptation effect of extensive tropical green roofs in cities. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2015, 138, 54–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jim, C.; Peng, L. Weather effect on thermal and energy performance of an extensive tropical green roof. Urban For. Urban Green. 2012, 11, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, N.; Chen, Y.; Sia, A. Investigation of thermal benefits of rooftop garden in the tropical environment. Build. Environ. 2003, 38, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, N.; Cheong, D.; Yan, H.; Soh, J.; Ong, C.L.; Sia, A. The effects of rooftop garden on energy consumption of a commercial building in Singapore. Energy Build. 2003, 35, 353–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.X.; Norford, L.K. Evaluation of cool roof and vegetation in mitigating urban heat island in a tropical city, Singapore. Urban Clim. 2016, 16, 59–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, N.H.; Yu, C. Study of green areas and urban heat island in a tropical city. Habitat Int. 2005, 29, 547–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, N.; Tan, A.; Chen, Y.; Sekar, K.; Tan, P.Y.; Chan, D.; Chiang, K.; Wong, N.C. Thermal evaluation of vertical greenery systems for building walls. Build. Environ. 2010, 45, 663–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charoenkit, S.; Yiemwattana, S. Living walls and their contribution to improved thermal comfort and carbon emission reduction: A review. Build. Environ. 2016, 105, 82–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.Y.; Cheung, K.K.; Chu, L.M. Thermal performance of a vegetated cladding system on facade walls. Build. Environ. 2010, 45, 1779–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, N.; Tan, A.; Tan, P.; Wong, N.C. Energy simulation of vertical greenery systems. Energy Build. 2009, 42, 1401–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ca, V.; Asaeda, T.; Abu, E. Reductions in air conditioning energy caused by a nearby park. Energy Build. 1998, 29, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abreu-Harbich, L.; Labaki, L.; Matzarakis, A. Effect of tree planting design and tree species on human thermal comfort in the tropics. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2015, 138, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.; Li, M.; Chang, S. A preliminary study on the local cool-island intensity of Taipei city parks. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2007, 80, 386–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, N.H.; Jusuf, S.K.; La Win, A.A.; Thu, H.K.; Negara, T.S.; Wu, X. Environmental study of the impact of greenery in an institutional campus in the tropics. Build. Environ. 2007, 42, 2949–2970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhou, D.; Gao, W.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, W.; Peng, W. Simulation on the impacts of the street tree pattern on built summer thermal comfort in cold region of China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2018, 37, 563–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H. Study on the Temporal and Spatial Changes of Urban Green Space and Land Surface Temperature in Main Urban Areas of Beijing; China University of Geosciences: Beijing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, J.R.; Chen, Z.Z.; Wu, T.T. Spatio-temporal evolution and interrelationship between thermal environment and landscape patterns of Haikou City, 1989~2015. China Environ. Sci. 2019, 4, 1734–1743. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, H.; Liu, H.Z.; Li, Y.M. Actuality of summer urban heat island and the impact of urban planning wedge shaped greenland to reducing the intensity of urban heat island in Beijing. J. Appl. Meteorol. Sci. 2005, 16, 357–366. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, J.; He, J.; Kong, X.; Xu, W.; Kang, Y.; Yu, Z.; Li, X. A field study of CO2 and particulate matter characteristics during the transition season in the subway system in Tianjin, China. Energy Build. 2022, 254, 111620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, H. Study on Urban Heat Island Effect and Cooling Effect of Greenland in Beijing; Beijing Forestry University: Beijing, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y. Research on the Influence Mechanism and Optimization of Urban Green Space Landscape to Its Thermal Environment a Case Study of Taiyuan City; Shanxi Agricultural University: Taiyuan, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.H. Optimization Strategy Research of the Green Space Pattern in Harbin Urban Central Area in Response to Heat Island Effect; Harbin Institute of Technology: Harbin, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Papangelisaaab, G. An urban “green planning” approach utilizing the Weather Research and Forecasting (WRF) modeling system. A case study of Athens, Greece. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2012, 105, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamei, E.; Rajagopalan, P.; Seyedmahmoudian, M. Review on the impact of urban geometry and pedestrian level greening on outdoor thermal comfort. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 54, 1002–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.; Schade, G.W.; Werner, N.D.; Sailor, D.J.; Kim, C.H. Comparative estimates of anthropogenic heat emission in relation to surface energy balance of a subtropical urban neighborhood. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 126, 182–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferreira, M.J.; de Oliveira, A.P.; Soares, J. Diurnal variation in stored energy flux in São Paulo city, Brazil. Urban Clim. 2013, 5, 36–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesan, S.; Lau, S.S.Y. Urban challenges in Hong Kong: Future directions for design. Urban Des. Int. 2000, 5, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giridharan, R.; Ganesan, S.; Lau, S. Nocturnal heat island effect in urban residential developments of Hong Kong. Energy Build. 2005, 9, 964–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonsson, P. Vegetation as an urban climate control in the subtropical city of Gaborone, Botswana. Int. J. Climatol. 2004, 24, 1307–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macedo, J. Maringá: A British Garden City in the tropics. Cities 2011, 28, 347–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, W.; Crompton, G.; Bell, J. Analysis of cool roof coatings for residential demand side management in tropical Australia. Energies 2015, 8, 5303–5318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chakraborty, T.; Sarangi, C. Understanding diurnality and inter-seasonality of a sub-tropical urban heat island. Bound. -Layer Meteorol. 2016, 163, 287–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, G.M.; Chambers, L.E.; Haylock. Change in mean temperature as a predictor of extreme temperature change in the Asia-Pacific region. Int. J. Climatol. 2005, 25, 1301–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.Z.; Zhu, N.; Wang, Q.Q. Modeling and simulation of the urban heat island effect in a tropical seaside city considering multiple street canyons. Indoor Built Environ. 2021, 30, 1124–1141. [Google Scholar]
- Bueno, B.; Norford, L.; Hidalgo, J.; Pigeon, G. The urban weather generator. J. Build. Perform. Simul. 2013, 6, 269–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L. Research on the Spatial Characteristics of the Urban Green Space’s Function of Mitigating Urban Heat Island; Southwest Jiaotong University: Chengdu, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, L.; Cai, W.; Chai, Y.S.; Xie, L. Global optimization for overall HVAC systems—Part I problem formulation and analysis. Energy Convers. Manag. 2005, 46, 999–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morakinyo, T.E.; Kong, L.; Lau, K.; Yuan, C.; Ng, E. A study on the impact of shadow-cast and tree species on in-canyon and neighborhood’s thermal comfort. Build. Environ. 2017, 115, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Yang, H.; Luo, P.; Luo, C.; Li, H.; Liu, M.; Ruan, Y.; Zhang, S.; Xiang, P.; Jia, H.; et al. The Effects of the Cooling Efficiency of Urban Wetlands in an InlandMegacity: A Case Study of Chengdu, Southwest China. Build. Environ. 2021, 204, 108128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Cao, W.; Wu, T.; Zhang, T. The win-win interaction between integrated blue and green space on urban cooling. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 863, 160712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhou, D.; Xu, D.; Cheng, J.; Rogora, A. Influencing factors of the thermal environment of urban green space. Heliyon 2022, 8, e11559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deilami, K.; Kamruzzaman, M.; Liu, Y. Urban heat island effect: A systematic review of spatio-temporal factors, data, methods, and mitigation measures. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2018, 67, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koc, C.B.; Osmond, P.; Peters, A. Evaluating the cooling effects of green infrastructure: A systematic review of methods, indicators and data sources. Sol. Energy 2018, 166, 486–508. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, J.; Dan, Y.; Qiao, R.; Liu, Y.; Dong, J.; Wu, J. How to quantify the cooling effect of urban parks? Linking maximum and accumulation perspectives. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 252, 112135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Fan, Y.; Hang, J.; Li, Y. Interacting urban heat island circulations as affected by weak background wind. Build. Environ. 2019, 160, 106224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, C.K.C.; Weng, J.; Liu, K.; Hang, J. The effects of shading devices on outdoor thermal and visual comfort in Southern China during summer. Build. Environ. 2022, 228, 109743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzeo, D.; Matera, N.; Peri, G.; Scaccianoce, G. Forecasting green roofs’ potential in improving building thermal performance and mitigating urban heat island in the Mediterranean area: An artificial intelligence-based approach. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2022, 119879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



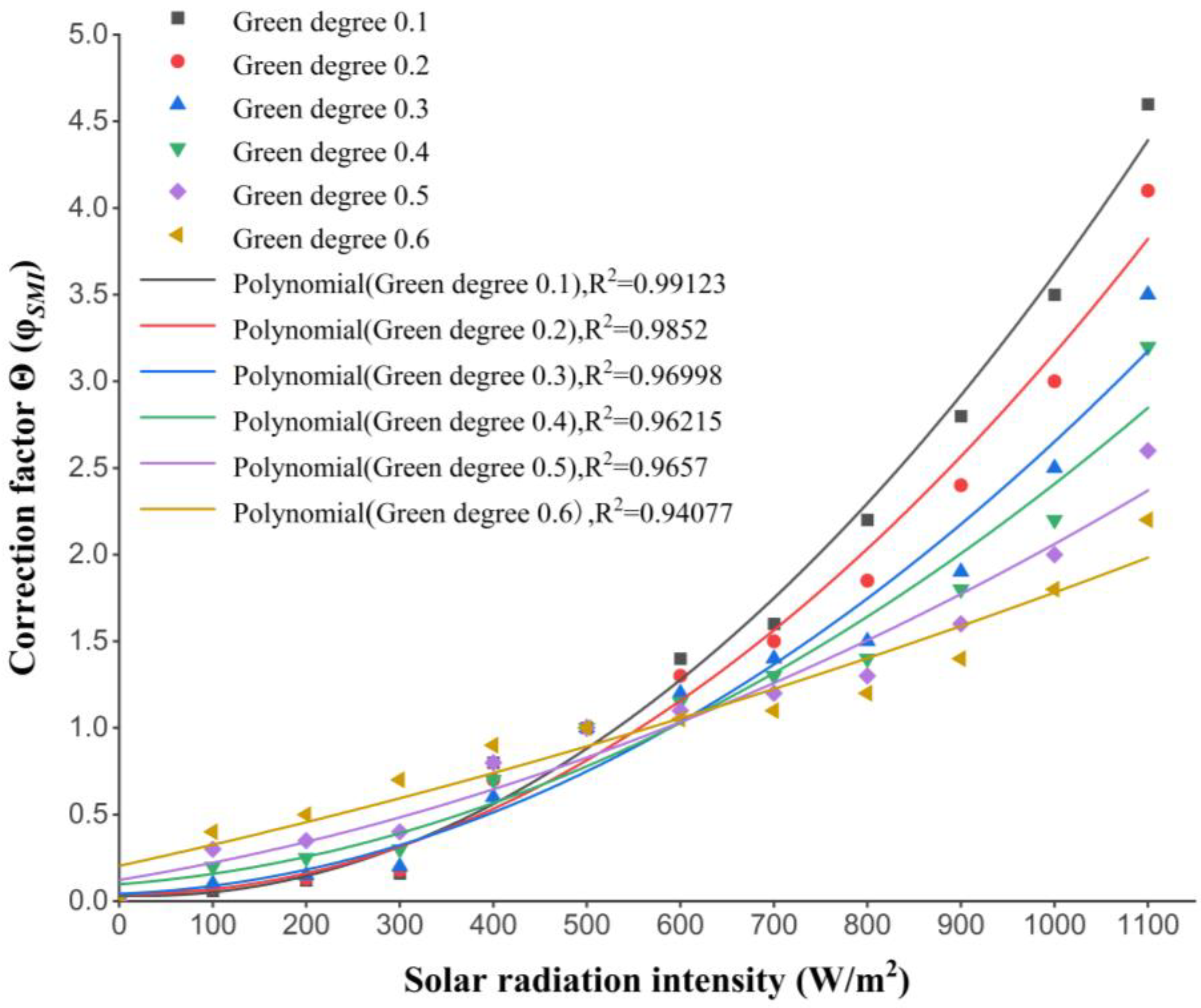
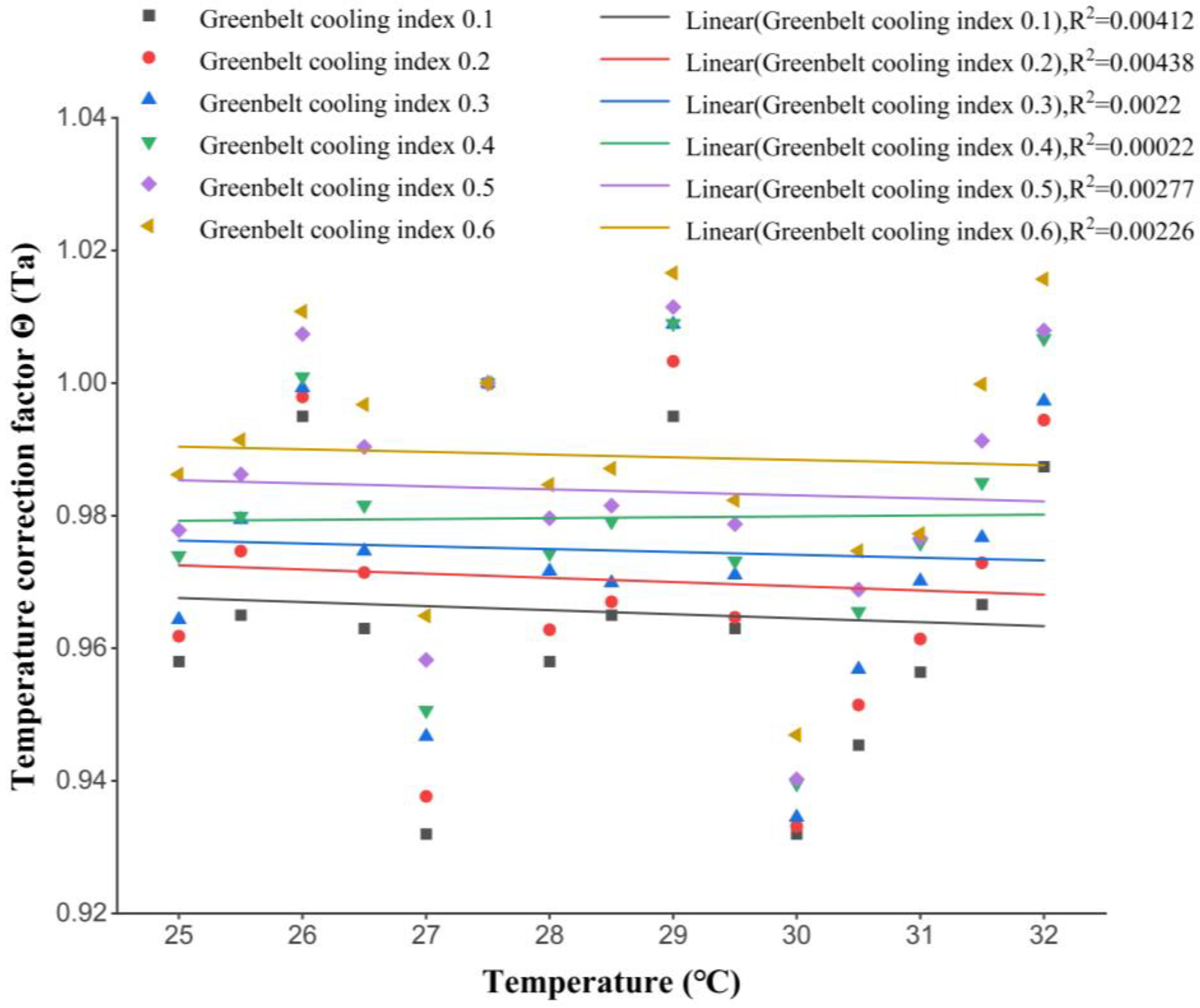


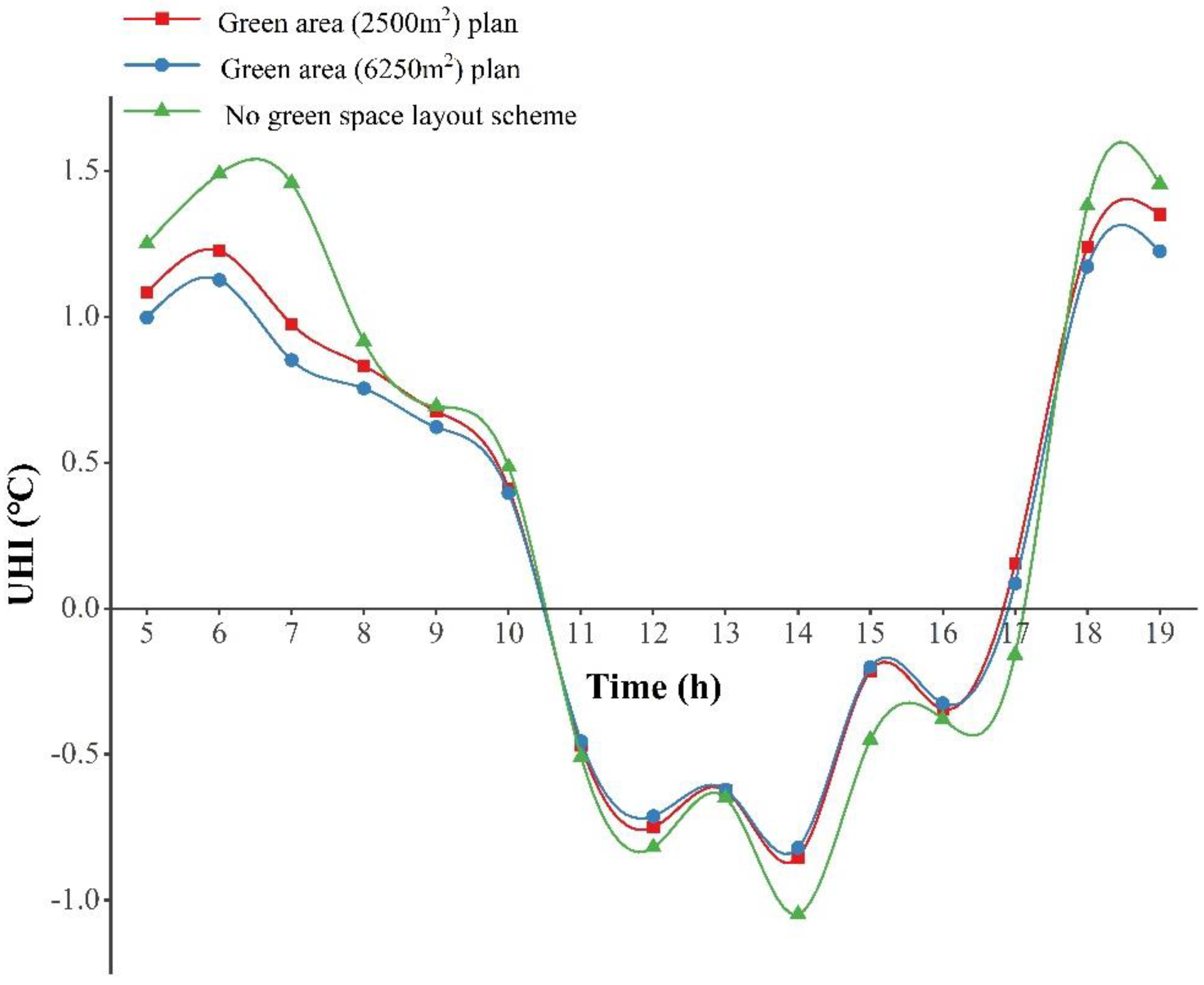
| Measures | Type | Effects |
|---|---|---|
| Increase surface vegetation coverage | Urban roof greening | Reduce the near surface temperature by more than 1 °C [16,17] |
| Light roof greening | Reduce the air temperature of pedestrian floor by 0.4–0.7 °C [18,19,20,21,22,23] | |
| Heavy roof greening | Reduce the air temperature of pedestrian floor by 0.5–1.7 °C [24,25,26] | |
| Road Greening | Reduce air temperature by 0–15 °C [27,28] | |
| wall greening | Reduce carbon emissions by 014–0.98 kg/m2 [29] | |
| wall greening | Reduce surface temperature by 6–10 °C [30,31] | |
| Construction of urban parks | Ambient temperature around the park: 1–1.3 °C [32,33] The temperature inside the park decreased by 0.8 °C [34,35] |
| Equipment | Parameter |
|---|---|
| Temperature and humidity recorder | Measuring range: −40~100 °C Measurement accuracy: Wet ± 2% Temperature: ±0.2 °C |
| Irradiation table | Measuring range: 0~2000 W/m2 Sensitivity: 9.75 uV·W−1·m2 |
| Anemometer | Measuring range: 0~30 m/s Measurement accuracy: 0.5 m/s |
| Thermal resistance | Measuring range: 0~100 °C Measurement error: ±0.01 °C |
| Data acquisition instrument | Measuring range: −50~150 °C Measurement accuracy: ±0.2 °C |
| Objective Function | (6) | |
|---|---|---|
| Decision variables | (7) | |
| Restrictions | (8) | |
| (9) | ||
| (10) | ||
| (11) |
| Season | Grid of Optimization Scheme | The GSCI of Each Grid (°C) | Optimization Index Value I UHI | Not Optimized Index Value I UHI |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Summer | (2, 6), (3, 6), (3, 7), (4, 6), (4, 7), (4, 8), (5, 7), (6, 11), (6, 12), (7, 11) | 0.26, 0.32, 0.31, 0.30, 0.33, 0.31, 0.33, 0.33, 0.33, 0.31 | 0.31 | 0.34 |
| Winter | (2, 6), (2, 8), (2, 9), (2, 10), (2, 11), (2, 12), (2, 14), (2, 15), (2, 16), (3, 6) | 0.32, 0.27, 0.31, 0.33, 0.33, 0.33, 0.25, 0.24, 0.32, 0.33 | 0.49 | 0.52 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, H.; Wang, Q.; Zhu, N.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Zhou, L.; Pei, Y.; Zhang, S. Optimization Methods of Urban Green Space Layout on Tropical Islands to Control Heat Island Effects. Energies 2023, 16, 368. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16010368
Zhou H, Wang Q, Zhu N, Li Y, Li J, Zhou L, Pei Y, Zhang S. Optimization Methods of Urban Green Space Layout on Tropical Islands to Control Heat Island Effects. Energies. 2023; 16(1):368. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16010368
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Haizhu, Qingqin Wang, Neng Zhu, Yitong Li, Jiayu Li, Lining Zhou, Yu Pei, and Shuai Zhang. 2023. "Optimization Methods of Urban Green Space Layout on Tropical Islands to Control Heat Island Effects" Energies 16, no. 1: 368. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16010368
APA StyleZhou, H., Wang, Q., Zhu, N., Li, Y., Li, J., Zhou, L., Pei, Y., & Zhang, S. (2023). Optimization Methods of Urban Green Space Layout on Tropical Islands to Control Heat Island Effects. Energies, 16(1), 368. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16010368








