A Review of the Continuum Theory-Based Stress and Drag Models in Gas-Solid Flows
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Solid Stress Models
2.1. Kinetic-Collisional Law
2.1.1. Solid Pressure and Viscosity
2.1.2. Equation for Granular Temperature
2.1.3. Restitution Coefficient and Radial Distribution Function
2.2. Frictional Law
2.2.1. Frictional Stress Model
2.2.2. η(Is)-Rheology Model
2.3. Combination of Kinetic-Collisional Law and Frictional Law
2.4. Wall Boundary Condition
3. Gas-Solid Drag Models
3.1. Microscale Drag Model
3.1.1. Experiment-Based Drag Model
3.1.2. DNS-Based Model
3.2. Mesoscale Drag Model
3.2.1. Filtered Drag Model
3.2.2. EMMS Drag Model
4. Summary and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Latin symbols | |
| Velocity vector for gas and solid, respectively | |
| Favre filtering gas and solid velocities in Filtered drag model | |
| Slip velocity between particles and wall | |
| Specularity coefficient | |
| time | |
| Pressure for gas and solid | |
| Resolved gas pressure | |
| Particle diameter | |
| kinetic-collision pressure and frictional pressure for solid phase | |
| Drag coefficient for single particle | |
| Particle Reynolds number | |
| Fr | Froude numbers |
| Radial distribution function | |
| Gas-solid drag coefficient | |
| , Is | Unit tensor, inertial number |
| Restitution coefficient and effective restitution coefficient | |
| Deviatoric rate-of-strain tensor of solid phase | |
| Mass specific energy consumption | |
| Superficial fluid and particle velocity in EMMS drag model | |
| Superficial fluid velocity at minimum fluidization | |
| Greek symbols | |
| Concentration for gas and solid phases, respectively | |
| Resolved concentration for gas and solid phase, respectively | |
| Density for gas and solid phase, respectively | |
| Stress tensor for gas and solid phase, respectively | |
| Kinetic-collisional and the frictional stress tensor | |
| Gas viscosity | |
| Bulk, kinetic-collisional and frictional viscosity | |
| Maximum solid volume fraction at packing | |
| Yield friction coefficient | |
| Internal friction coefficient | |
| Granular temperature | |
| Conductivity of granular fluctuating energy | |
| Collisional dissipation | |
| Particle friction coefficient | |
| Blending function | |
| Drag factor | |
| Subscript | |
| Gas phase | |
| Solid phase | |
| c | Particle in dense phase |
| f | Particle in dilute phase |
| i | Cluster phase |
| eff | Effective variable |
References
- Papadikis, K.; Bridgwater, A.; Gu, S. CFD modelling of the fast pyrolysis of biomass in fluidised bed reactors, Part A: Eulerian computation of momentum transport in bubbling fluidised beds. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2008, 63, 4218–4227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Q.; Heindel, T.; Fox, R. A CFD model for biomass fast pyrolysis in fluidized-bed reactors. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2011, 66, 2440–2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rokkam, R.G.; Fox, R.O.; Muhle, M.E. Computational fluid dynamics and electrostatic modeling of polymerization fluidized-bed reactors. Powder Technol. 2010, 203, 109–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schatz, A. Lump Ore, Pellets, and Dead Men: Mathematical Modelling and Numerical Simulation of the COREX Reduction Shaft. Ph.D. Thesis, Johannes Kepler University, Linz, Austria, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Jaeger, H.M.; Nagel, S.R.; Behringer, R.P. Granular solids, liquids, and gases. Rev. Mod. phys. 1996, 68, 1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ancey, C. Plasticity and geophysical flows: A review. J. Non-Newton. Fluid Mech. 2007, 142, 4–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gidaspow, D. Hydrodynamics of fiuidizatlon and heat transfer: Supercomputer modeling. Appl. Mech. Rev. 1986, 39, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gidaspow, D.; Ettehadieh, B. Fluidization in two-dimensional beds with a jet. 2. Hydrodynamic modeling. Ind. Eng. Chem. Fundam. 1983, 22, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, Y.; Gidaspow, D.; Wasan, D. Hydrodynamics of sedimentation of multisized particles. Powder Technol. 1987, 50, 201–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouillard, J.; Lyczkowski, R.; Gidaspow, D. Porosity distributions in a fluidized bed with an immersed obstacle. AIChE J. 1989, 35, 908–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Gidaspow, D. Computation of circulating fluidized-bed riser flow for the fluidization VIII benchmark test. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1999, 38, 787–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lun, C.K.K.; Jeffrey, D.; Chepurniy, N. Kinetic theories for granular flow: Inelastic particles in Couette flow and slightly inelastic particles in a general flow field. J. Fluid Mech. 1984, 140, 223–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Wachem, B.G.M. Derivation, implementation, and validation of computer simulation models for gas-solid fluidized beds. Ph.D. Thesis, Delft University, Delft, Netherlands, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Savage, J.J.S. A theory for the rapid flow of identical, smooth, nearly elastic particles. J. Fluid Mech 1983, 130, 187. [Google Scholar]
- Chapman, S.; Cowling, T.G. The Mathematical Theory of Non-Uniform Gases: An Account of the Kinetic Theory of Viscosity, Thermal Conduction and Diffusion in Gases; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Gidaspow, D. Multiphase Flow and Fluidization: Continuum and Kinetic Theory Descriptions; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Garzó, V.; Dufty, J. Dense fluid transport for inelastic hard spheres. Phys. Rev. E 1999, 59, 5895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chamkha, A.; Peddieson, J. Boundary layer theory for a particulate suspension. J. Fluids Eng. 1994, 116, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamkha, A.J. Hydromagnetic two-phase flow in a channel. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 1995, 33, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chamkha, A.J. Compressible two-phase boundary-layer flow with finite particulate volume fraction. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 1996, 34, 1409–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chamkha, A.J. Compressible dusty-gas boundary-Layer flow over a flat surface. J. Fluids Eng. 1996, 118, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chamkha, A.J. Particulate viscous effects on the compressible boundary-layer two-phase flow over a flat plate. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 1998, 25, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chamkha, A.J. Unsteady laminar hydromagnetic fluid–particle flow and heat transfer in channels and circular pipes. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 2000, 21, 740–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Ozel, A.; Kolehmainen, J.; Sundaresan, S. Computationally generated constitutive models for particle phase rheology in gas-fluidized suspensions. J. Fluid Mech. 2019, 860, 318–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalalinejad, F.; Bi, X.T.; Grace, J.R. Effect of electrostatic charges on single bubble in gas–solid fluidized beds. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 2012, 44, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolehmainen, J.; Ozel, A.; Sundaresan, S. Eulerian modelling of gas–solid flows with triboelectric charging. J. Fluid Mech. 2018, 848, 340–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, P.; Hrenya, C.M. Cluster-induced deagglomeration in dilute gravity-driven gas-solid flows of cohesive grains. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2018, 121, 238001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jenkins, J.T.; Zhang, C. Kinetic theory for identical, frictional, nearly elastic spheres. Phys. Fluids 2002, 14, 1228–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delannay, R.; Louge, M.; Richard, P.; Taberlet, N.; Valance, A. Towards a theoretical picture of dense granular flows down inclines. Nat. Mater. 2007, 6, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-H.; Huang, Z.; Chiew, Y.-M. A three-dimensional continuum model incorporating static and kinetic effects for granular flows with applications to collapse of a two-dimensional granular column. Phys. Fluids 2015, 27, 113303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chialvo, S.; Sundaresan, S. A modified kinetic theory for frictional granular flows in dense and dilute regimes. Phys. Fluids 2013, 25, 070603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duan, Y.; Feng, Z.-G. Incorporation of velocity-dependent restitution coefficient and particle surface friction into kinetic theory for modeling granular flow cooling. Phys. Rev. E 2017, 96, 062907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, Y.; Li, Y.; Chen, X.; Duan, F.; Zhou, Q. Improvement of the Coarse-Grained Discrete Element Method for Frictional Particles. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2021, 60, 5651–5664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carnahan, N.F.; Starling, K.E. Equation of state for nonattracting rigid spheres. J. Chem. Phys. 1969, 51, 635–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagnold, R.A. Experiments on a gravity-free dispersion of large solid spheres in a Newtonian fluid under shear. Proc. R. Soc. London. Ser. A Math. Phys. Sci. 1954, 225, 49–63. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmadi, G.; Ma, D. A thermodynamical formulation for dispersed multiphase turbulent flows—1: Basic theory. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 1990, 16, 323–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savage, S. Analyses of slow high-concentration flows of granular materials. J. Fluid Mech. 1998, 377, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaeffer, D.G. Instability in the evolution equations describing incompressible granular flow. J. Differ. Equ. 1987, 66, 19–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Syamlal, M.; Rogers, W.; OBrien, T.J. MFIX Documentation Theory Guide; USDOE Morgantown Energy Technology Center: Morgantown, WV, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava, A.; Sundaresan, S. Analysis of a frictional–kinetic model for gas–particle flow. Powder Technol. 2003, 129, 72–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, P.C.; Jackson, R. Frictional-collisional constitutive relations for granular materials, with application to plane shearing. J. Fluid Mech. 1987, 176, 67–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passalacqua, A.; Marmo, L. A critical comparison of frictional stress models applied to the simulation of bubbling fluidized beds. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2009, 64, 2795–2806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghgoo, M.R.; Bergstrom, D.J.; Spiteri, R.J. Effect of particle stress tensor in simulations of dense gas–particle flows in fluidized beds. Particuology 2018, 38, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venier, C.M.; Marquez Damian, S.; Nigro, N.M. Assessment of gas-particle flow models for pseudo-2D fluidized bed applications. Chem. Eng. Commun. 2018, 205, 456–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Liu, G.; Li, W.; Yin, X.; Wu, Y.; Wang, C.; Lu, H. A comprehensive stress model for gas-particle flows in dense and dilute regimes. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2020, 226, 115833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Padash, A.; Xi, K.; Kovar, T.M.; Boyce, C.M. Dynamically structured bubbling in vibrated gas-fluidized granular materials. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2021, 118, e2108647118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xi, K.; Guo, Q.; Boyce, C.M. Comparison of Two-Fluid Model Simulations of Freely Bubbling Three-Dimensional Gas-Fluidized Beds with Magnetic Resonance Imaging Results. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2021, 60, 7429–7442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benyahia, S. Validation study of two continuum granular frictional flow theories. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2008, 47, 8926–8932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocone, R.; Sundaresan, S.; Jackson, R. Gas-particle flow in a duct of arbitrary inclination with particle-particle interactions. AIChE J. 1993, 39, 1261–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jop, P.; Forterre, Y.; Pouliquen, O. A constitutive law for dense granular flows. Nature 2006, 441, 727–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pouliquen, O.; Cassar, C.; Jop, P.; Forterre, Y.; Nicolas, M. Flow of dense granular material: Towards simple constitutive laws. J. Stat. Mech. Theory Exp. 2006, 2006, P07020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forterre, Y.; Pouliquen, O. Flows of dense granular media. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2008, 40, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schneiderbauer, S.; Aigner, A.; Pirker, S. A comprehensive frictional-kinetic model for gas–particle flows: Analysis of fluidized and moving bed regimes. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2012, 80, 279–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chialvo, S.; Sun, J.; Sundaresan, S. Bridging the rheology of granular flows in three regimes. Phys. Rev. E 2012, 85, 021305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Da Cruz, F.; Emam, S.; Prochnow, M.; Roux, J.-N.; Chevoir, F. Rheophysics of dense granular materials: Discrete simulation of plane shear flows. Phys. Rev. E 2005, 72, 021309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patil, D.; van Sint Annaland, M.; Kuipers, J. Critical comparison of hydrodynamic models for gas–solid fluidized beds—Part I: Bubbling gas–solid fluidized beds operated with a jet. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2005, 60, 57–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, D.; van Sint Annaland, M.; Kuipers, J. Critical comparison of hydrodynamic models for gas–solid fluidized beds—Part II: Freely bubbling gas–solid fluidized beds. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2005, 60, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Sun, D.; Lu, H.; Bouillard, J.; Bai, Y.; Wang, S. Computations of fluid dynamics of a 50 MWe circulating fluidized bed combustor. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2010, 49, 5132–5140. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Z.-G.; Ponton, M.E.C.; Michaelides, E.E.; Mao, S. Using the direct numerical simulation to compute the slip boundary condition of the solid phase in two-fluid model simulations. Powder Technol. 2014, 265, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaelides, E. Particles, Bubbles & Drops: Their Motion, Heat and Mass Transfer; World Scientific: Singapore, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Sommerfeld, M.; Huber, N. Experimental analysis and modelling of particle-wall collisions. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 1999, 25, 1457–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Benyahia, S. Revisiting Johnson and Jackson boundary conditions for granular flows. AIChE J. 2012, 58, 2058–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benyahia, S.; Syamlal, M.; O’Brien, T.J. Evaluation of boundary conditions used to model dilute, turbulent gas/solids flows in a pipe. Powder Technol. 2005, 156, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloete, J.H.; Cloete, S.; Radl, S.; Amini, S. Evaluation of wall friction models for riser flow. Powder Technol. 2016, 303, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soleimani, A.; Pirker, S.; Schneiderbauer, S. Solid boundary condition for collisional gas–solid flows at rough walls. Powder Technol. 2015, 281, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Gao, J.; Xu, C.; Lan, X. Effect of wall boundary condition on CFD simulation of CFB risers. Particuology 2013, 11, 556–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, Z.; Peng, G.; Wang, J.; Zhang, N.; Li, S.; Lin, W. Comparative CFD analysis of heterogeneous gas–solid flow in a countercurrent downer reactor. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 3378–3384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, K.; Chen, S.; Wang, W.; Li, J. Fine-grid two-fluid modeling of fluidization of Geldart A particles. Powder Technol. 2016, 296, 2–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamkha, A. Effects of particulate diffusion on the thermal flat plate boundary layer of a two-phase suspension. J. Heat Transfer. 1994, 116, 236–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamkha, A. Effect of combined particle-phase diffusivity and viscosity on the compressible boundary layer of a particulate suspension over a flat plate. J. Heat Transfer. 1999, 121, 420–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamkha, A.J. Effects of particulate diffusion on the compressible boundary-layer flow of a two-phase suspension over a horizontal surface. J. Heat Transfer. 1998, 120, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tripathy, P.K.; Mishra, S.K.; Chamkha, A.J. Simulation of particle diffusion and heat transfer in a two-phase turbulent boundary layer using the Eulerian-Eulerian approach. J. Math. Model. 2016, 3, 169–187. [Google Scholar]
- Ergun, S. Fluid flow through packed columns. Chem. Eng. Prog. 1952, 48, 89–94. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, C.Y.; Yu, Y.H. Mechanics of fluidization. Chem. Eng. Prog. Symp. Ser. 1966, 62, 100–111. [Google Scholar]
- Di Felice, R. The voidage function for fluid-particle interaction systems. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 1994, 20, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Gidaspow, D. Hydrodynamics of binary fluidization in a riser: CFD simulation using two granular temperatures. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2003, 58, 3777–3792. [Google Scholar]
- Dahl, S.; Hrenya, C. Size segregation in gas-solid fluidized beds with continuous size distributions. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2005, 60, 6658–6673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Guo, X.; Yin, X.; Zhao, J.; Lu, H. Inertial Number-Based Drag Model and Its Application in Simulating the Fluidization of Geldart B and D Particles. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2022, 61, 13734–13748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syamlal, M.; O’brien, T. Simulation of granular layer inversion in liquid fluidized beds. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 1988, 14, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Hoef, M.A.; van Sint Annaland, M.; Deen, N.; Kuipers, J. Numerical simulation of dense gas-solid fluidized beds: A multiscale modeling strategy. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2008, 40, 47–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balachandar, S.; Eaton, J. Dispersed turbulent multiphase flow. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2010, 42, 111–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenneti, S.; Subramaniam, S. Particle-resolved direct numerical simulation for gas-solid flow model development. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2014, 46, 199–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, R.J.; Koch, D.L.; Ladd, A.J. Moderate-Reynolds-number flows in ordered and random arrays of spheres. J. Fluid Mech. 2001, 448, 243–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Hoef, M.A.; Beetstra, R.; Kuipers, J. Lattice-Boltzmann simulations of low-Reynolds-number flow past mono-and bidisperse arrays of spheres: Results for the permeability and drag force. J. Fluid Mech. 2005, 528, 233–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beetstra, R.; van der Hoef, M.A.; Kuipers, J. Drag force of intermediate Reynolds number flow past mono-and bidisperse arrays of spheres. AIChE J. 2007, 53, 489–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, A.; Milioli, F.E.; Ozarkar, S.; Li, T.; Sun, X.; Sundaresan, S. Filtered sub-grid constitutive models for fluidized gas-particle flows constructed from 3-D simulations. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2016, 152, 443–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yin, X.; Sundaresan, S. Fluid-particle drag in low-Reynolds-number polydisperse gas–solid suspensions. AIChE J. 2009, 55, 1352–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, L.W.; Dong, K.J.; Yu, A. Lattice-Boltzmann simulation of fluid flow through packed beds of uniform spheres: Effect of porosity. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2013, 99, 44–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubinstein, G.J.; Derksen, J.J.; Sundaresan, S. Lattice Boltzmann simulations of low-Reynolds-number flow past fluidized spheres: Effect of Stokes number on drag force. J. Fluid Mech. 2016, 788, 576–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, Y.; Peters, E.; Kuipers, J.; Kriebitzsch, S.; van der Hoef, M. A new drag correlation from fully resolved simulations of flow past monodisperse static arrays of spheres. AIChE J. 2015, 61, 688–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tavanashad, V.; Passalacqua, A.; Subramaniam, S. Particle-resolved simulation of freely evolving particle suspensions: Flow physics and modeling. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 2021, 135, 103533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenneti, S.; Garg, R.; Subramaniam, S. Drag law for monodisperse gas–solid systems using particle-resolved direct numerical simulation of flow past fixed assemblies of spheres. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 2011, 37, 1072–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaidi, A.A.; Tsuji, T.; Tanaka, T. A new relation of drag force for high Stokes number monodisperse spheres by direct numerical simulation. Adv. Powder Technol. 2014, 25, 1860–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogner, S.; Mohanty, S.; Rüde, U. Drag correlation for dilute and moderately dense fluid-particle systems using the lattice Boltzmann method. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 2015, 68, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sheikh, B.; Qiu, T. Pore-scale simulation and statistical investigation of velocity and drag force distribution of flow through randomly-packed porous media under low and intermediate Reynolds numbers. Comput. Fluids 2018, 171, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaidi, A.A. Study of particle inertia effects on drag force of finite sized particles in settling process. Chem. Eng. Res. Design 2018, 132, 714–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igci, Y.; Pannala, S.; Benyahia, S.; Sundaresan, S. Validation studies on filtered model equations for gas-particle flows in risers. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 2094–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igci, Y.; Sundaresan, S. Verification of filtered two-fluid models for gas-particle flows in risers. AIChE J. 2011, 57, 2691–2707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, A. Common property institutions and sustainable governance of resources. World Dev. 2001, 29, 1649–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews IV, A.T.; Loezos, P.N.; Sundaresan, S. Coarse-grid simulation of gas-particle flows in vertical risers. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2005, 44, 6022–6037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igci, Y.; Sundaresan, S. Constitutive models for filtered two-fluid models of fluidized gas–particle flows. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2011, 50, 13190–13201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneiderbauer, S.; Pirker, S. Filtered and heterogeneity-based subgrid modifications for gas–solid drag and solid stresses in bubbling fluidized beds. AIChE J. 2014, 60, 839–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milioli, C.C.; Milioli, F.E.; Holloway, W.; Agrawal, K.; Sundaresan, S. Filtered two-fluid models of fluidized gas-particle flows: New constitutive relations. AIChE J. 2013, 59, 3265–3275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.-T.; Xie, L.; Xiao, J.; Luo, Z.-H. Filtered model for the cold-model gas–solid flow in a large-scale MTO fluidized bed reactor. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2016, 143, 369–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmentier, J.F.; Simonin, O.; Delsart, O. A functional subgrid drift velocity model for filtered drag prediction in dense fluidized bed. AIChE J. 2012, 58, 1084–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozel, A.; Fede, P.; Simonin, O. Development of filtered Euler–Euler two-phase model for circulating fluidised bed: High resolution simulation, formulation and a priori analyses. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 2013, 55, 43–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ozel, A.; Gu, Y.; Milioli, C.C.; Kolehmainen, J.; Sundaresan, S. Towards filtered drag force model for non-cohesive and cohesive particle-gas flows. Phys. Fluids 2017, 29, 103308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schneiderbauer, S. A spatially-averaged two-fluid model for dense large-scale gas-solid flows. AIChE J. 2017, 63, 3544–3562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Kwauk, M. Exploring complex systems in chemical engineering—The multi-scale methodology. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2003, 58, 521–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, N.; Wang, W.; Ge, W.; Li, J. CFD simulation of concurrent-up gas–solid flow in circulating fluidized beds with structure-dependent drag coefficient. Chem. Eng. J. 2003, 96, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, K.; Shi, Z.; Wang, W.; Li, J. A structure-dependent multi-fluid model (SFM) for heterogeneous gas–solid flow. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2013, 99, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Wang, W.; Li, J. A bubble-based EMMS model for gas–solid bubbling fluidization. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2011, 66, 5541–5555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Chandraker, M. Robust scale estimation in real-time monocular SFM for autonomous driving. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 July 2014; pp. 1566–1573. [Google Scholar]
- Du, M.; Hu, S.; Chen, J.; Liu, X.; Ge, W. Extremum characteristics of energy consumption in fluidization analyzed by using EMMS. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 342, 386–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.; Niu, Y.; Chen, F.; Ahmad, N.; Wang, W.; Li, J. Energy-minimization multiscale based mesoscale modeling and applications in gas-fluidized catalytic reactors. Rev. Chem. Eng. 2019, 35, 879–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
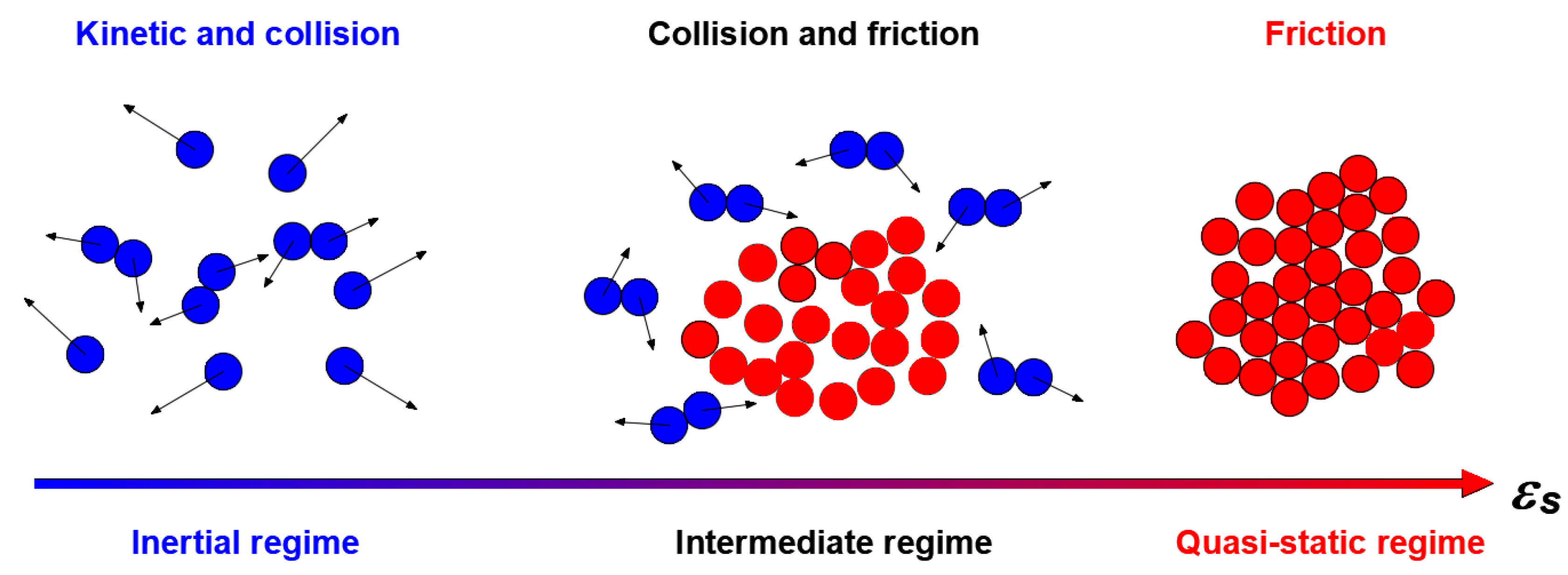

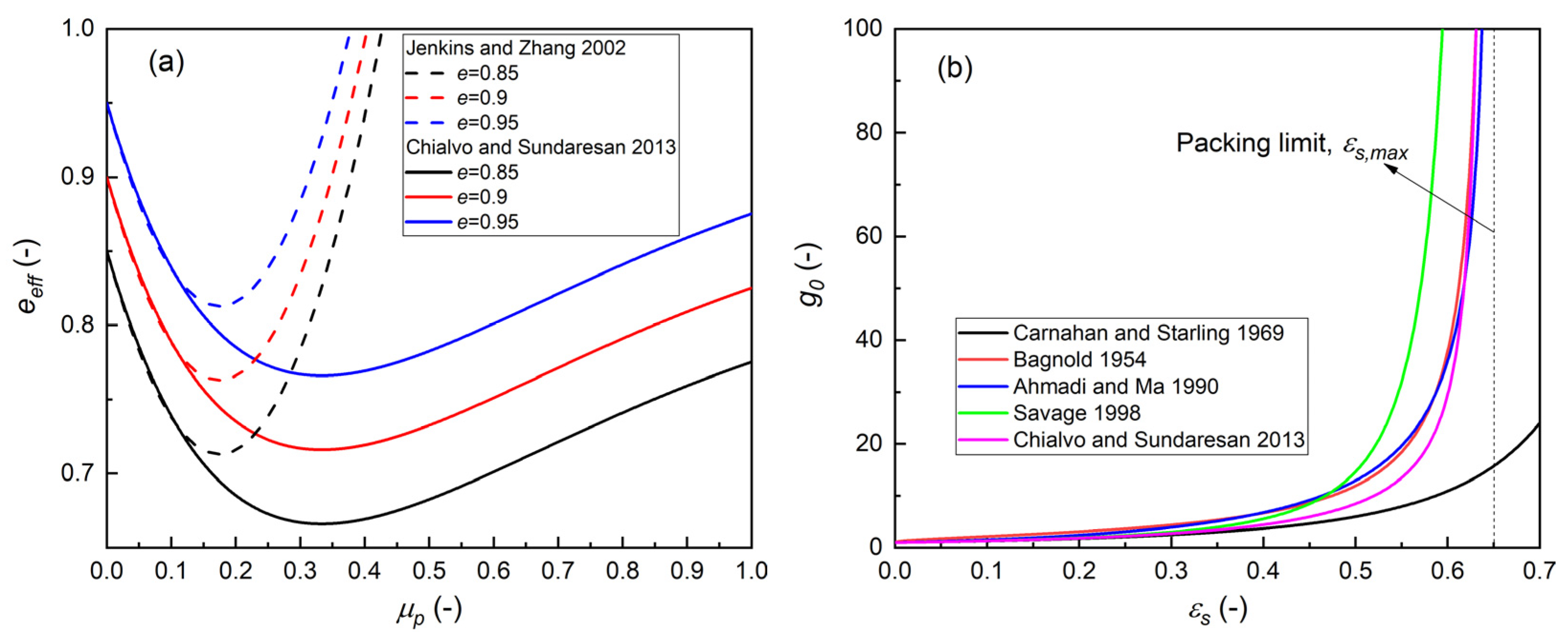
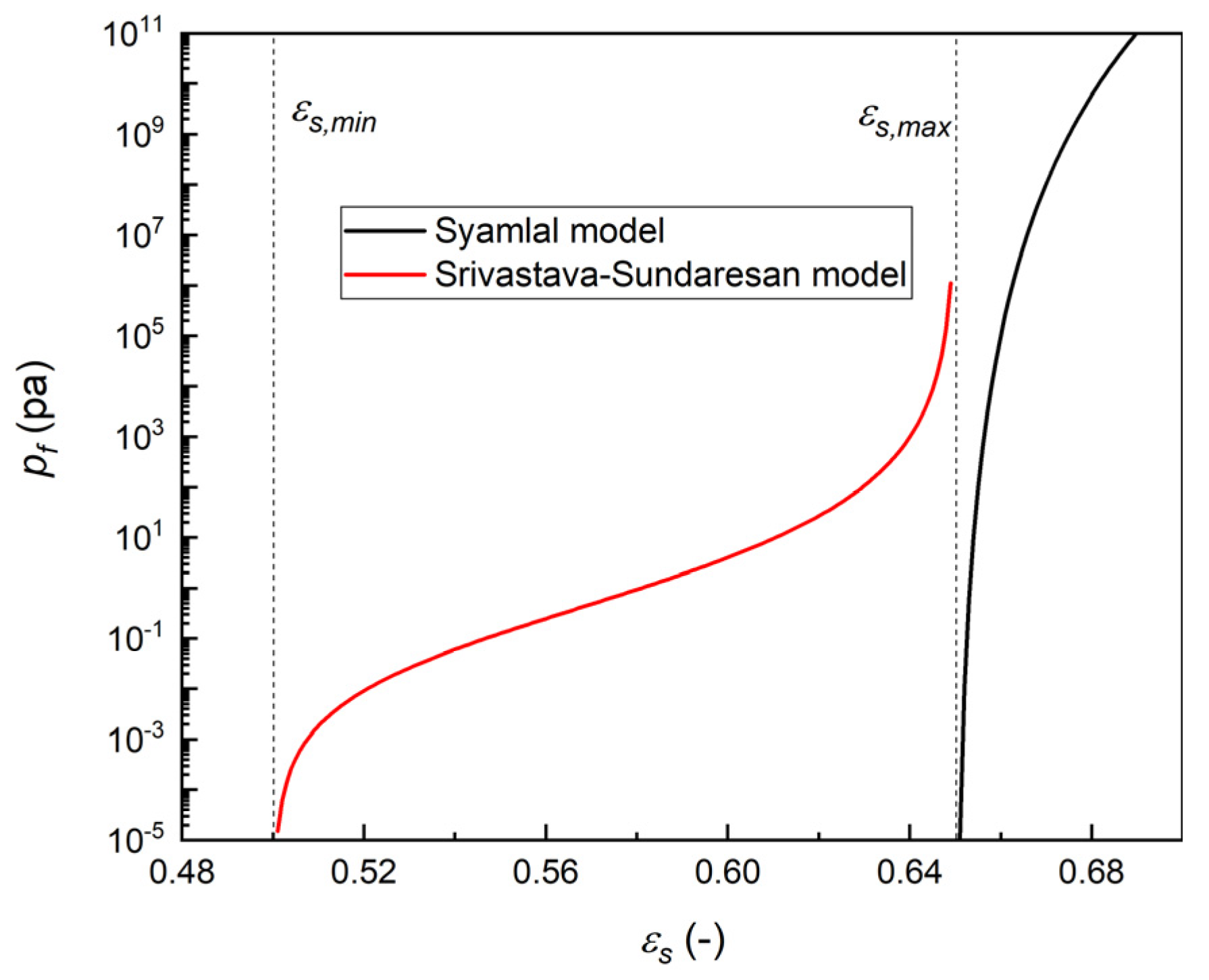

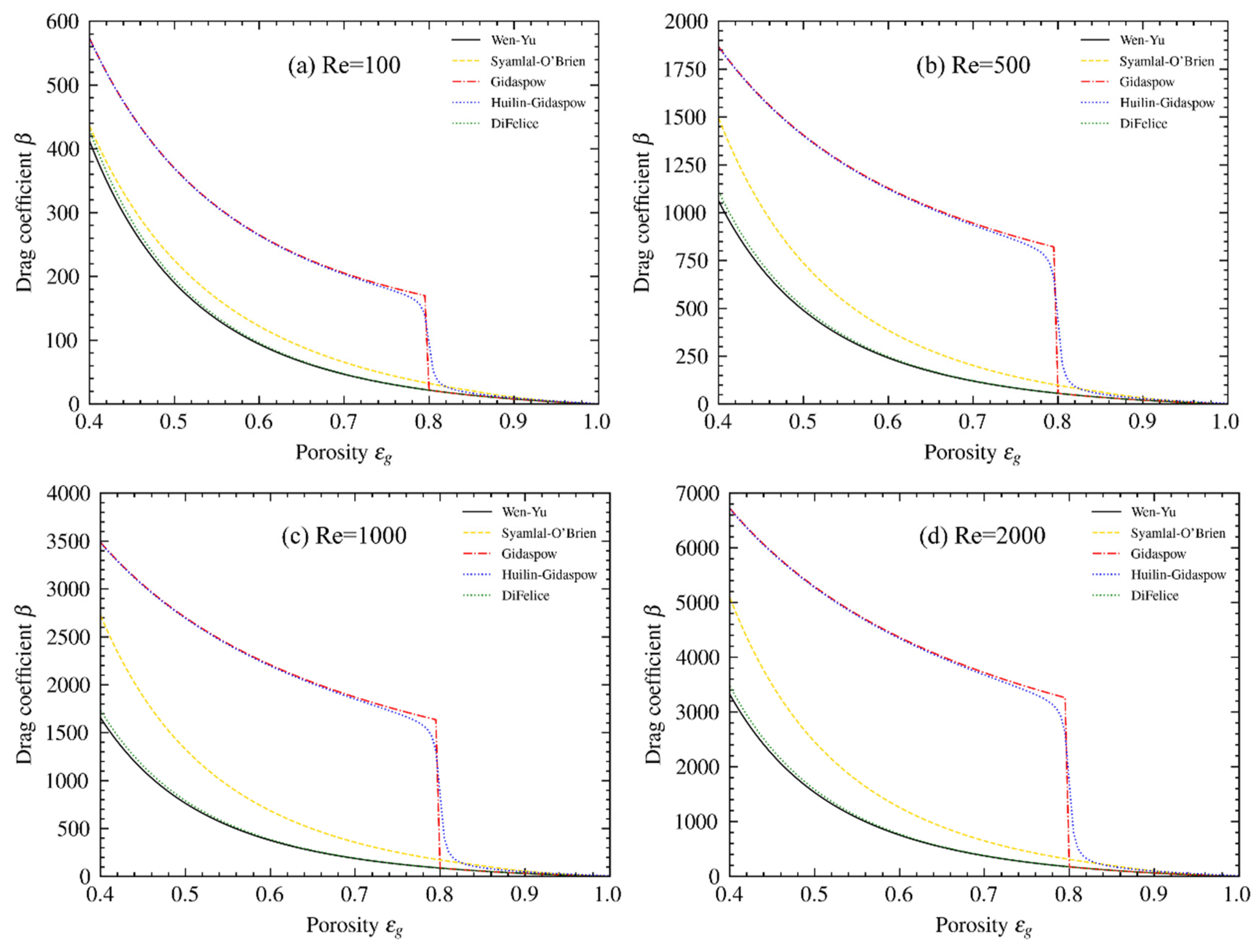
| Continuity Equations: | |
| (1) | |
| (2) | |
| Momentum Equations: | |
| (3) | |
| (4) |
| Lun et al. [12]: | |
with α=1.6 | (9) |
| Gidaspow [16]: | |
| (10) | |
| Garzó and Dufty [17]: | |
| (11) |
| Lun et al. [12]: | |
with α=1.6 | (12) |
| Gidaspow [16]: | |
| (13) | |
| Garzó and Dufty [17]: | |
| (14) |
| Algebraic Equation: | |
| (18) | |
| Lun et al. [12] (PDE) | |
| (19) | |
| Gidaspow [16] (PDE) | |
| (20) |
| Jenkins and Zhang [28]: | |
| (21) | |
| Chialvo and Sundaresan [31]: | |
| (22) |
| Carnahan and Starling [34] | |
| (23) | |
| Bagnold [35] | |
| (24) | |
| Ahmadi and Ma [36] | |
| (25) | |
| Savage [37] | |
| (26) | |
| Chialvo and Sundaresan [31] | |
| (27) |
| Syamlal model | |
| Frictional pressure (Syamlal et al. [39]) | (29) |
| Frictional viscosity (Schaeffer [38]) | (30) |
| Srivastava–Sundaresan model | |
| Frictional pressure (Johnson and Jackson [41]) with Fr = 0.05 N/m2, r = 2 and s = 3 (Ocone et al. [49]) | (31) |
| Frictional viscosity (Srivastava and Sundaresan [40]) | (32) |
| Da Cruz et al. [55]: | |
with ηyield = 0.25 and b = 1.1 | (37) |
| Jop et al. [50]: | |
with ηyield = tan (21°), ηc = tan (33°), I0 = 0.3 (Forterre and Pouliquen [42]) | (38) |
| Chialvo et al. [54]: | |
with α1 = 0.37, β1 = 1.5, I0 = 0.32 | (39) |
| Liu et al. [58]: | |
| (42) | |
| Chialvo and Sundaresan [31]: | |
| (43) |
| Johnson and Jackson [41] | |
| Particle slip velocity at the wall: | (44) |
| Granular energy at the wall: | (45) |
| Schneiderbauer et al. [53] | |
| Particle slip velocity at the wall: where | (46) |
| Granular energy at the wall: | (47) |
| Wen and Yu [74] | |
where , | (48) |
| Syamlal and O’Brien [79] | |
| (49) | |
| Gidaspow [16] | |
| (50) | |
| Di Flice [75] | |
| (51) | |
| Lu and Gidaspow [76] | |
| (52) | |
| Liu et al. [78] | |
| (53) |
| Hill et al. [83] | |
and | (54) |
| Beetstra et al. [85] | |
| (55) | |
| Tenneti et al. [92] | |
| (56) | |
| Rong et al. [88] | |
with | (57) |
| Zaidi et al. [93] | |
| (58) | |
| Bogner et al. [94] | |
| (59) | |
| Tang et al. [90] | |
| (60) | |
| Sheikh and Qiu [95] | |
| (61) | |
| Zaidi [96] | |
| (62) |
| (63) |
| The Drag Expression is Expressed as () | |
where | (64) |
| Force balance for particles in the dense phase Force balance for particles in the dilute phase | |
| Pressure drop balance equation | |
| Continuity equation of gas and particle phase | |
| Cluster diameter | |
| The global stability condition |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, J.; Guo, X.; Liu, G.; Wang, R.; Lu, H. A Review of the Continuum Theory-Based Stress and Drag Models in Gas-Solid Flows. Energies 2023, 16, 65. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16010065
Zhao J, Guo X, Liu G, Wang R, Lu H. A Review of the Continuum Theory-Based Stress and Drag Models in Gas-Solid Flows. Energies. 2023; 16(1):65. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16010065
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Junnan, Xinyao Guo, Guodong Liu, Rui Wang, and Huilin Lu. 2023. "A Review of the Continuum Theory-Based Stress and Drag Models in Gas-Solid Flows" Energies 16, no. 1: 65. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16010065
APA StyleZhao, J., Guo, X., Liu, G., Wang, R., & Lu, H. (2023). A Review of the Continuum Theory-Based Stress and Drag Models in Gas-Solid Flows. Energies, 16(1), 65. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16010065







