Research on Hydrogen Production by Water Electrolysis Using a Rotating Magnetic Field
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Theories
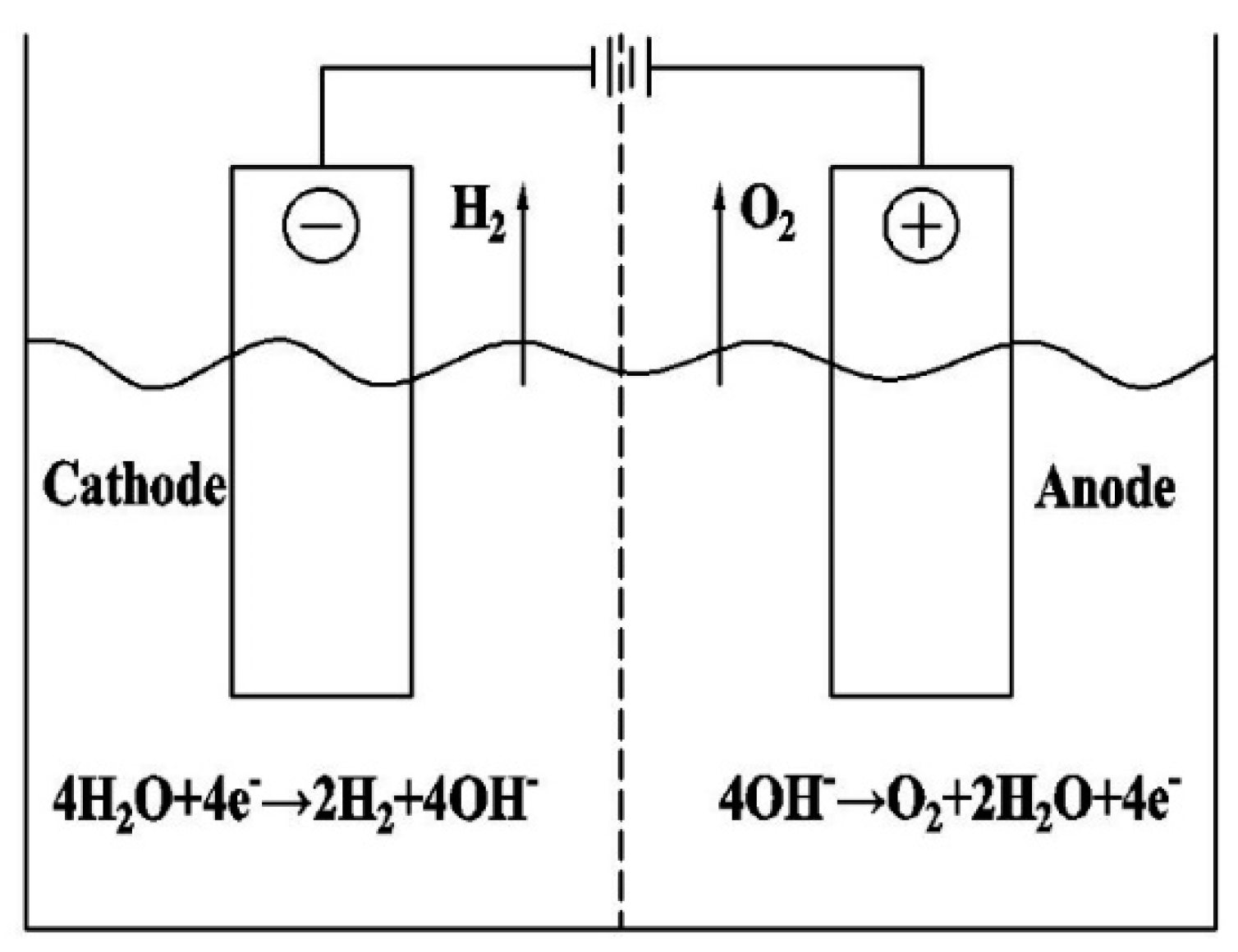
2.1. Water Electrolysis Theory
Total reaction formula: 2H2O → 2H2 + O2
2.2. Fleming’s Right-Hand Rule and Faraday’s Law of Electromagnetic Induction
3. Experiment
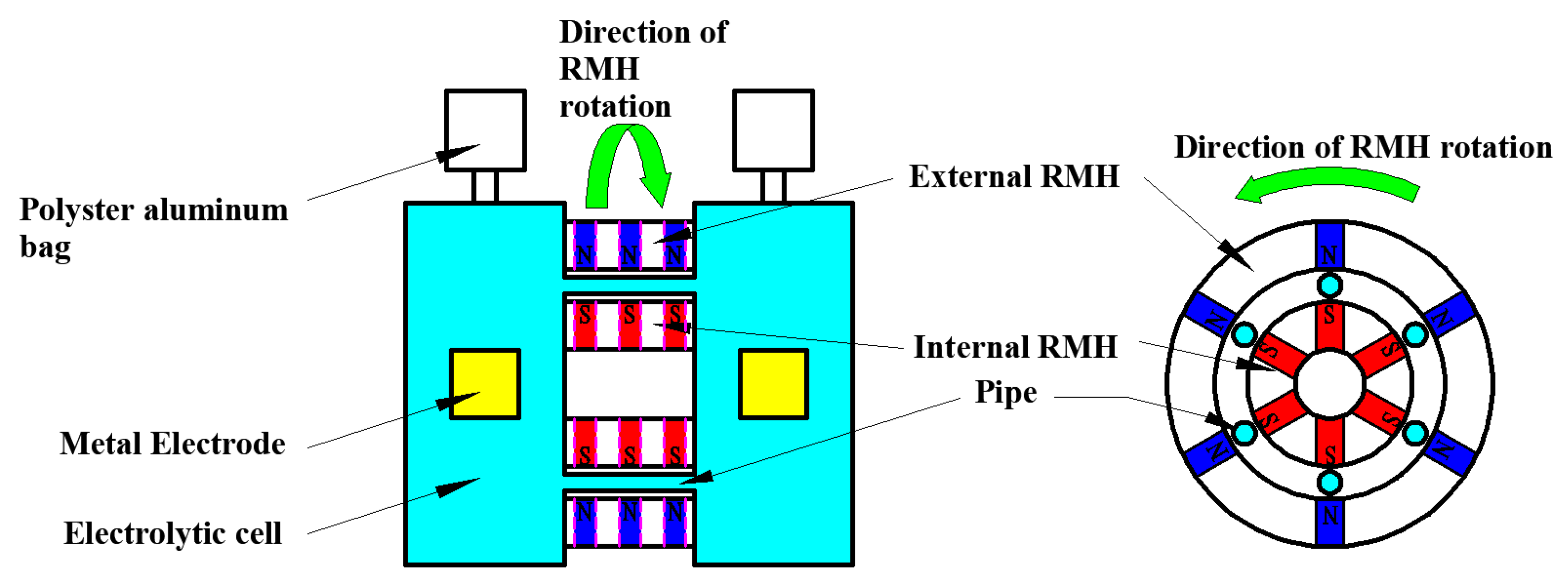
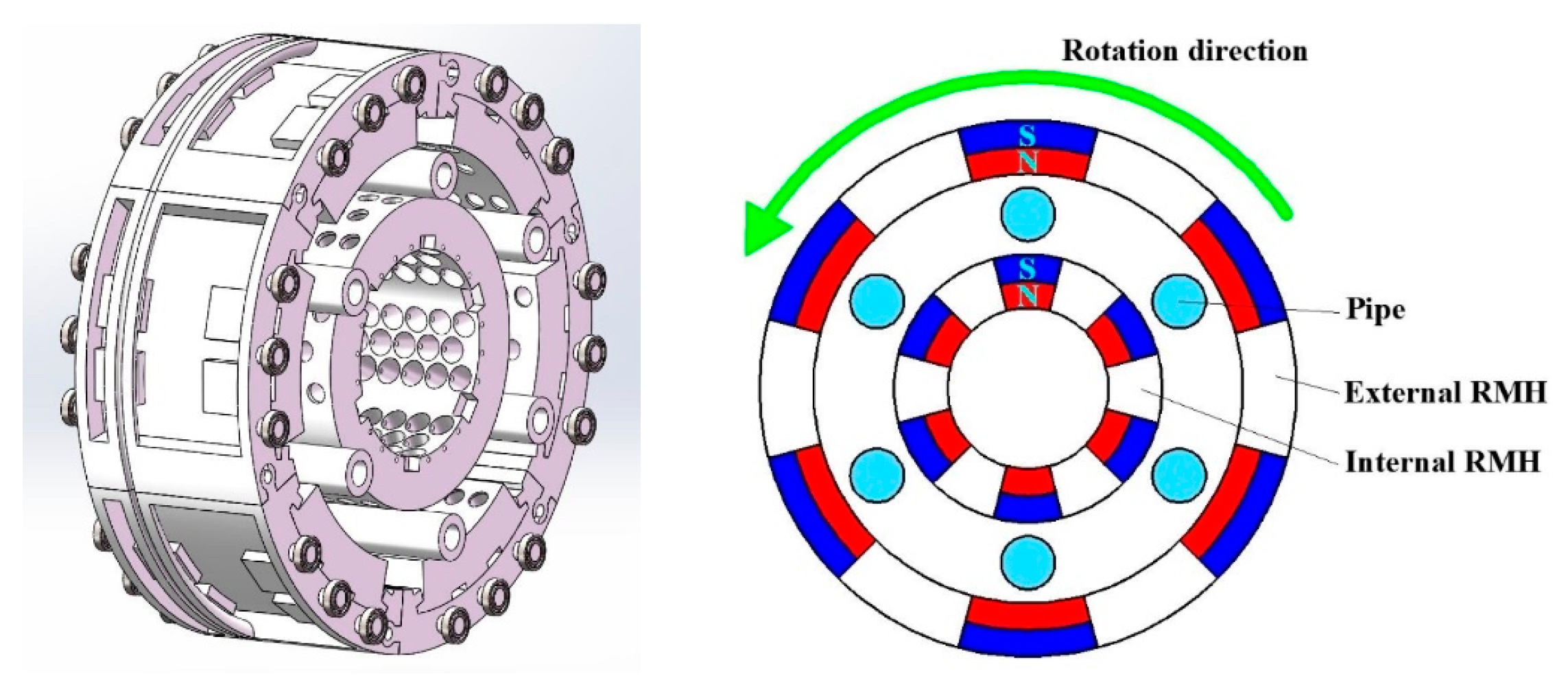
3.1. Experimental Apparatus
3.2. Experimental Methods
4. Results and Discussion
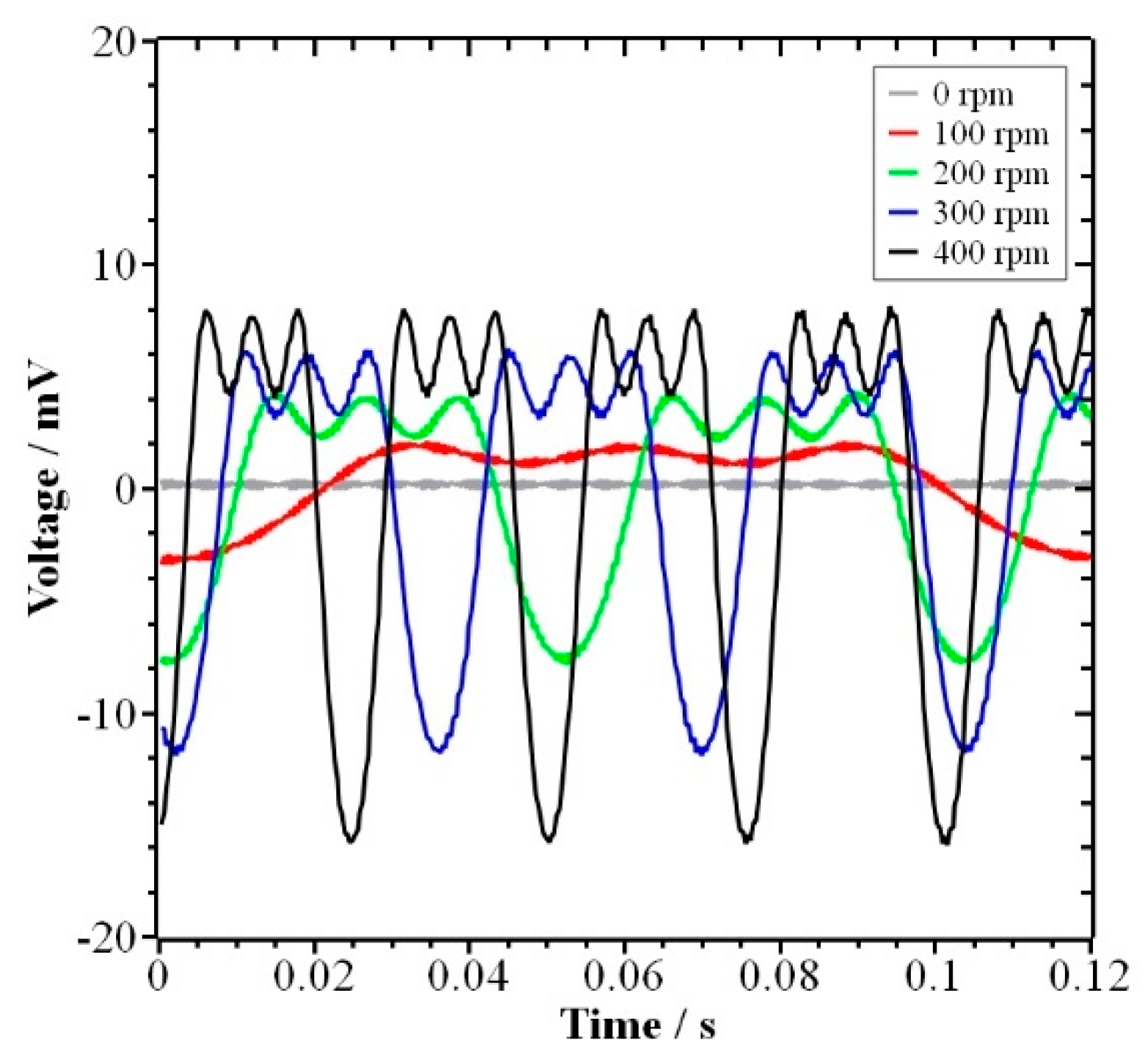
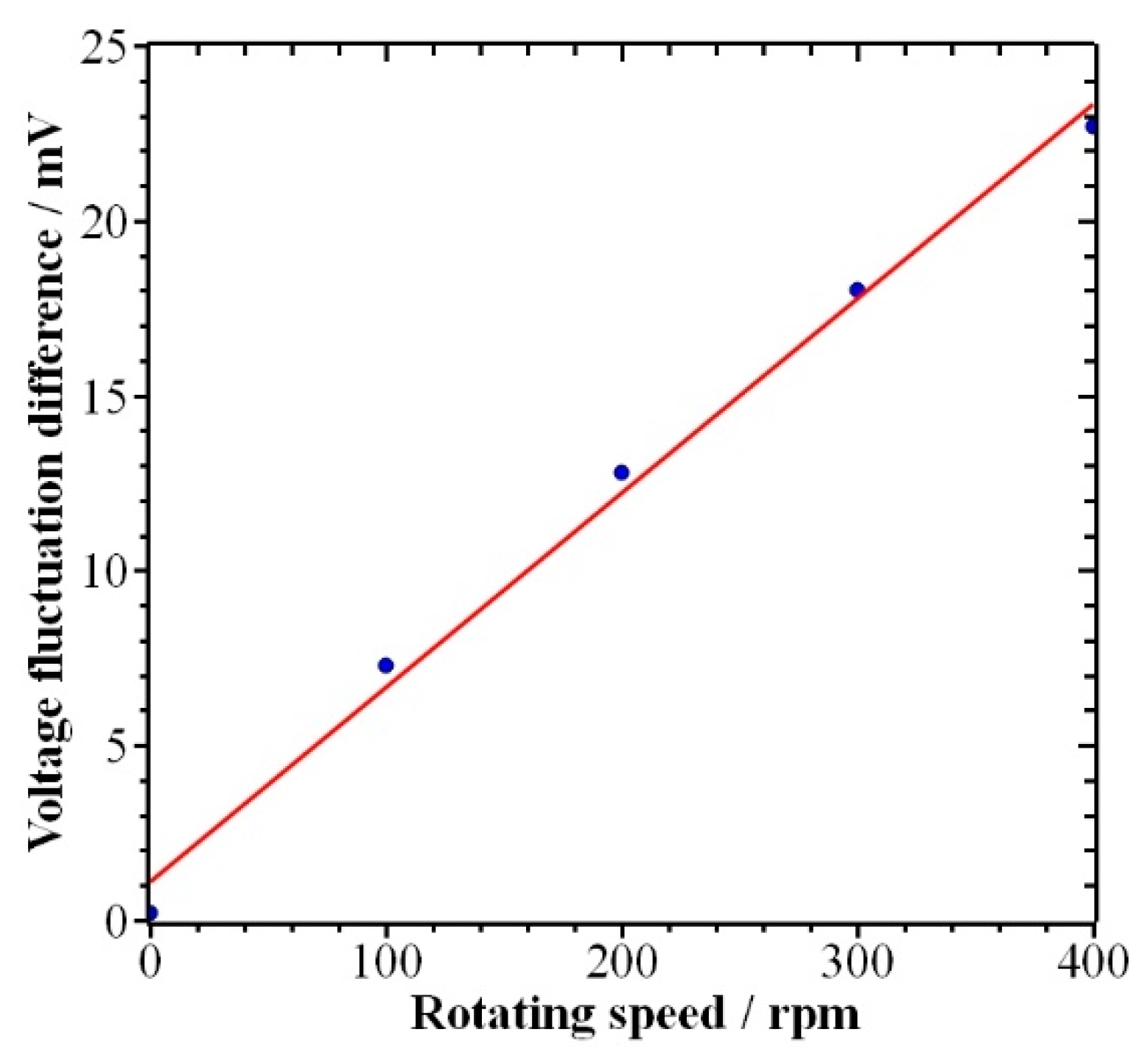
4.1. Results
4.2. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- The rotating magnetic field is used to make the cations and anions in the solution move toward the metal electrode and induce the water electrolysis reaction on the electrode surface.
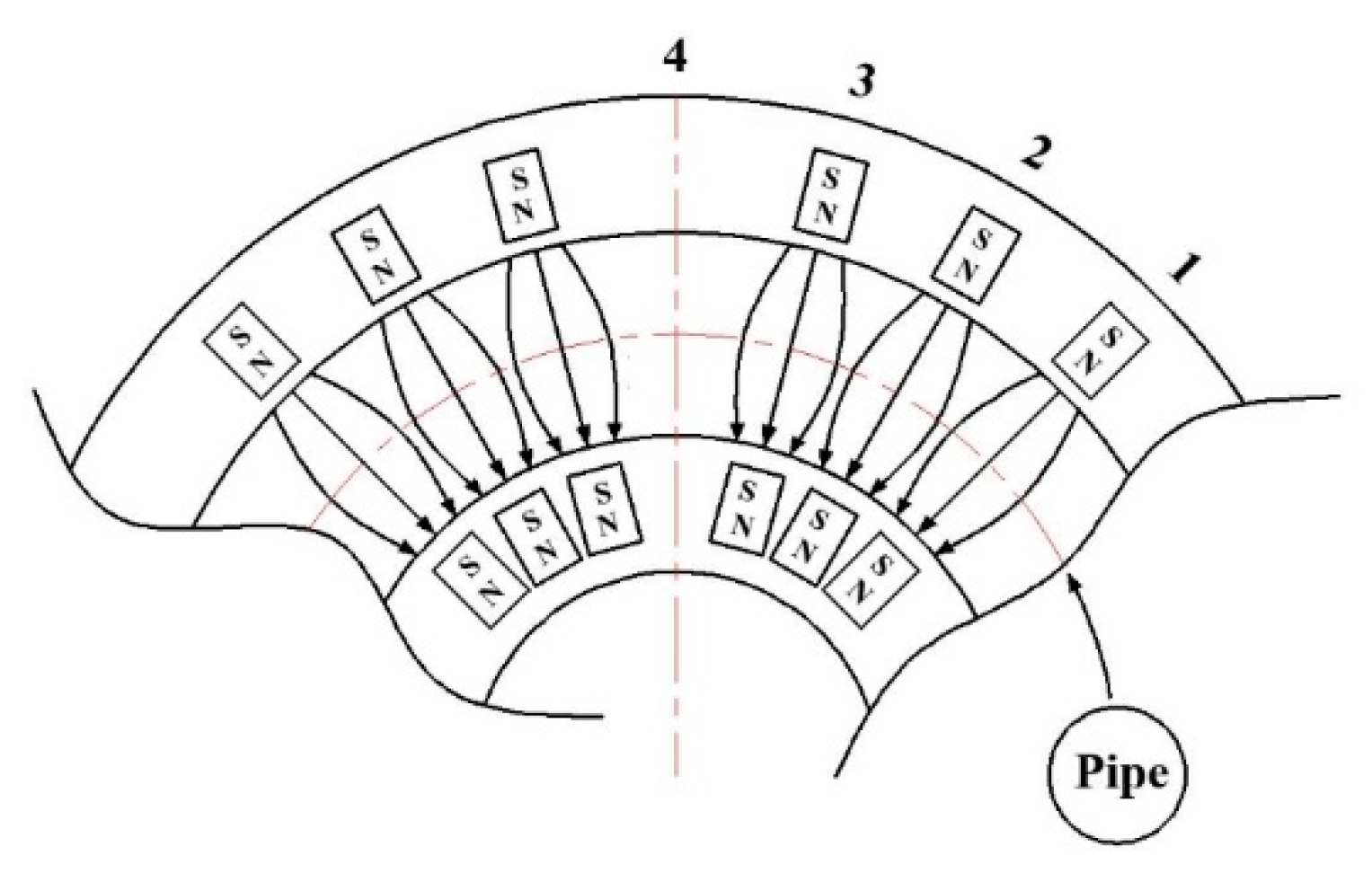
- The special arrangement of the magnetic field (7-6-7, 15°-15°-30°) is used to form the PPM, which causes the ions to move on-axis and off-axis when passing through the RMH, resulting in fluctuating voltage data. At the same time, the migration rate of ions increases, which increases the concentration of ions around the electrode and promotes the electrolysis reaction.
- By analyzing the relationship between the voltage fluctuation and the current density fluctuation, i.e., the increase in voltage fluctuation means the fluctuation of current density is also increasing, and based on the observation of the bubble generation phenomenon, it is found that the electrolysis rate of water also increases.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kudria, S.; Ivanchenko, I.; Tuchynskyi, B.; Petrenko, K.; Karmazin, O.; Riepkin, O. Resource potential for wind-hydrogen power inUkraine. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2021, 46, 157–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brauns, J.; Turek, T. Alkaline water electrolysis powered by Renewable Energy: A Review. Processes 2020, 8, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- David, M.; Ocampo-Martínez, C.; Sánchez-Peña, R. Advances in alkaline water electrolyzers: A Review. J. Energy Storage 2019, 23, 392–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schmidt, O.; Gambhir, A.; Staffell, I.; Hawkes, A.; Nelson, J.; Few, S. Future cost and performance of water electrolysis: An expert elicitation study. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 30470–30492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buttler, A.; Spliethoff, H. Current status of water electrolysis for energy storage, grid balancing and sector coupling via power-to-gas and power-to-liquids: A Review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 82, 2440–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Götz, M.; Lefebvre, J.; Mörs, F.; McDaniel Koch, A.; Graf, F.; Bajohr, S.; Reimert, R.; Kolb, T. Renewable power-to-gas: A technological and Economic Review. Renew. Energy 2016, 85, 1371–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marini, S.; Salvi, P.; Nelli, P.; Pesenti, R.; Villa, M.; Berrettoni, M.; Zangari, G.; Kiros, Y. Advanced alkaline water electrolysis. Electrochim. Acta 2012, 82, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, D.; Cho, H.-S.; Kang, S. Numerical Modeling and analysis of the effect of pressure on the performance of an alkaline water electrolysis system. Appl. Energy 2021, 287, 116554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allebrod, F.; Chatzichristodoulou, C.; Mogensen, M.B. Alkaline electrolysis cell at high temperature and pressure of 250 °C and 42 bar. J. Power Sources 2013, 229, 22–31. [Google Scholar]
- Burton, N.A.; Padilla, R.V.; Rose, A.; Habibullah, H. Increasing the efficiency of hydrogen production from solar powered water electrolysis. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 135, 110255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.Y.; Hourng, L.W.; Kuo, C.W. The effect of magnetic force on hydrogen production efficiency in water electrolysis. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2012, 37, 1311–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, M.F.; Demir, N.; Albawabiji, M.S.; Taş, M. Investigation of alkaline water electrolysis performance for different cost effective electrodes under magnetic field. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 17583–17592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Pan, L.M.; Liu, H.B. Water electrolysis using plate electrodes in an electrode-paralleled non-uniform magnetic field. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2021, 46, 3329–3336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y. The left-right-hand rule and comparison of Chinese and foreign textbooks. Teach. Ref. Middle Sch. Phys. 2011, 40, 12–14. [Google Scholar]
- Giuliani, G. A general law for electromagnetic induction. EPL 2008, 81, 60002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abi-Abdallah, D.; Prel, C. Induced voltage by a conducting fluid flowing in a static magnetic field: An experimental study. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Eng. 2010, 13, 13–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arfken, G.B.; Griffing, D.F.; Kelly, D.C.; Priest, J. University Physics; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1984; pp. 650–666, ISBN-13: 9780120598601. [Google Scholar]
- Dobo, Z.; Palotas, A.B. Impact of the voltage fluctuation of the power supply on the efficiency of alkaline water electrolysis. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 11849–11856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, R.-J. Set of Faraday’s Law of Electromagnetic Induction. Mod. Chem. Res. 2017, 5, 171–172. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, T.-T. Analysis on the Microcosmic Essence of Conductor Rod Cutting magnetic induction lines. J. Phys. Teach. 2020, 38, 43–44. [Google Scholar]
- Du, G.-X.; Qian, B.-L. Side focusing fields generated by offset-pole periodic cusped magnets. High Power Laser Part. Beams 2011, 23, 826–830. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Y.-Z.; Li, S.-F.; Wang, Z.-L.; Huang, H.; Liu, Z.-B.; He, H.; Gong, Y.-B. Periodic permanent focusing magnet of relativistic klystron. High Power Laser Part. Beams 2018, 30, 86–92. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, R.-N.; Li, X.-Q.; Kong, L.; Liu, Q.X.; Wang, S.-M. Analysis of transmission characteristics of the intense relativistic electron beam under PPM focusing system. Inf. Technol. 2017, 12, 14–17. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, J.-X. Study of the Periodic Focusing System Using Permanent Magnet in Traveling Wave Tubes. Vac. Electron. 2005, 2, 20–23. [Google Scholar]
- Anwar, S.; Khan, F.; Zhang, Y.; Djire, A. Recent development in electrocatalysts for hydrogen production through water electrolysis. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2021, 46, 32284–32317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.Z.; Quan, Y. Engineering Electromagnetic Field, 3rd ed.; Tsinghua University Press: Beijing, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, Q.-Z.; Chen, D.-Z. Electromagnetic Field; China Machine Press: Beijing, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Lehn, C. Chemical Solution Dispenser Apparatus and Method of Use Thereof; Ecolab Inc.: Saint Paul, MI, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, H.; Yu, F.; Zhu, Q.; Sun, J.; Qin, F.; Yu, L.; Bao, J.; Yu, Y.; Chen, S.; Ren, Z. Water splitting by electrolysis at high current densities under 1.6 volts. Energy Environ. Sci. 2018, 11, 2858–2864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Gao, Y.; Kong, H.; Kim, J.; Choi, S.; Ciucci, F.; Hao, Y.; Yang, S.; Shao, Z.; Lim, J. Non-precious-metal catalysts for alkaline water electrolysis: Operando characterizations, theoretical calculations, and recent advances. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 9154–9196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, H.; Kim, H.-J.; Kim, S.-Y. Research on Hydrogen Production by Water Electrolysis Using a Rotating Magnetic Field. Energies 2023, 16, 86. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16010086
Guo H, Kim H-J, Kim S-Y. Research on Hydrogen Production by Water Electrolysis Using a Rotating Magnetic Field. Energies. 2023; 16(1):86. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16010086
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Hao, Hyeon-Jung Kim, and Sang-Young Kim. 2023. "Research on Hydrogen Production by Water Electrolysis Using a Rotating Magnetic Field" Energies 16, no. 1: 86. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16010086
APA StyleGuo, H., Kim, H.-J., & Kim, S.-Y. (2023). Research on Hydrogen Production by Water Electrolysis Using a Rotating Magnetic Field. Energies, 16(1), 86. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16010086






