Effect of Leading/Trailing Edge Swept Impeller on Flow Characteristics of Low Specific Speed Centrifugal Compressor
Abstract
:1. Introduction
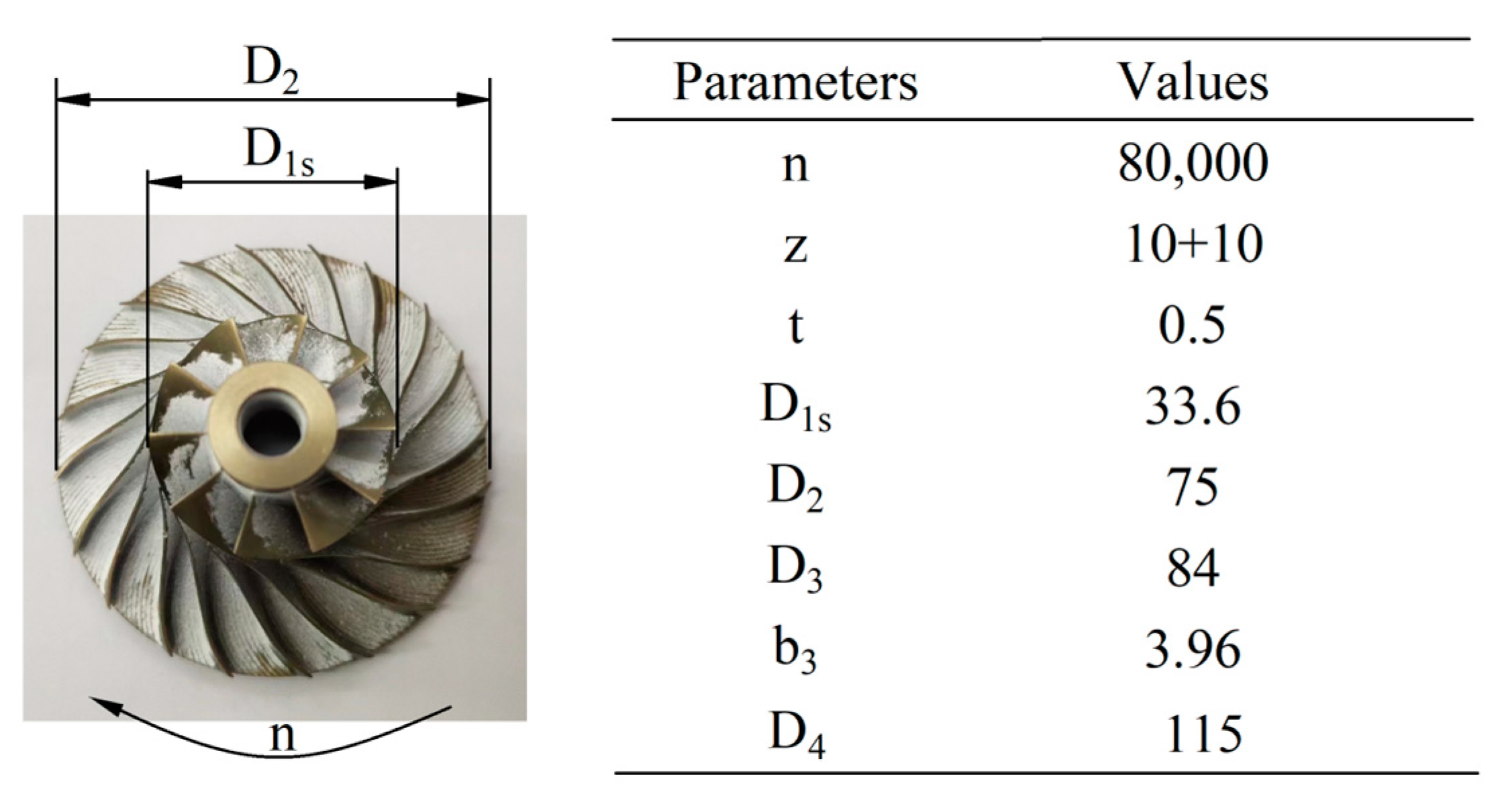
2. Datum Model and Numerical Verification of Compressor
3. Definition of Combined Sweep Blades
3.1. Swept Analysis at Leading Edge, Trailing Edge, and Both Edges
3.2. Combined Swept Impeller Model
4. Results and Analysis
4.1. Overall Performance Comparison
4.2. Detailed Analysis of Impeller Flow Field
4.2.1. Choke Mass Flow Rate
4.2.2. Highest Efficiency Mass Flow Rate
5. Manufacture and Test Rig
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| n | Design rotating speed/r·min−1 |
| z | Number of blades |
| t | Tip clearance/mm |
| D1s | Impeller inlet tip diameter/mm |
| D2 | Impeller outlet diameter /mm |
| D3 | Vaneless diffuser inlet diameter/mm |
| b3 | Vaneless diffuser width/mm |
| D4 | Volute inlet diameter /mm |
References
- Wan, Y.; Guan, J.; Xu, S. Improved empirical parameters design method for centrifugal compressor in PEM fuel cell vehicle application. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 5590–5605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Zhang, Y.; He, H.; Qiu, Z. Design of a centrifugal compressor with low specific speed for automotive fuel cell. In Proceedings of the ASME Turbo Expo 2008: Power for Land, Sea and Air, Berlin, Germany, 9 June 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.T.; Xu, Z. The research development of internal flow in centrifugal turbomachinery. Adv. Mech. 2003, 33, 518–532. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Zhuge, W.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, X.; Tao, L. Performance improvement of a centrifugal compressor for the fuel cell vehicle by tip leak-age vortex control. J. Therm. Sci. 2021, 30, 2099–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cravero, C.; Marsano, D. Criteria for the stability limit prediction of high speed centrifugal compressors with vaneless diffuser: Part I—Flow structure analysis. In Proceedings of the ASME Turbo Expo 2020: Turbomachinery Technical Conference and Exposition, Virtual, 21 September 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cravero, C.; Marsano, D. Criteria for the stability limit prediction of high speed centrifugal compressors with vaneless diffuser: Part II—The development of prediction criteria. In Proceedings of the ASME Turbo Expo 2020: Turbomachinery Technical Conference and Exposition, Virtual, 21 September 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceyrowsky, T.; Hildebrandt, A.; Schwarze, R. Numerical investigation of the circumferential pressure distortion induced by a centrifugal compressor’s external volute. In Proceedings of the ASME Turbo Expo 2014: Power for Land, Sea and Air, Oslo, Norway, 11 June 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiang, X.; Teng, J.; Du, Z. Influence of various volute designs on volute overall performance. J. Therm. Sci. 2010, 19, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Amano, R.S. Aerodynamic and structure considerations in centrifugal compressor design: Blade lean effects. In Proceedings of the ASME Turbo Expo 2012: Power for Land, Sea and Air, Copenhagen, Denmark, 11 June 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Zheng, X. Mechanisms of sweep on the performance of transonic centrifugal compressor impellers. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.D.; Li, C.; Lü, Q.Y.; Zhang, X.M.; Mu, G.Z. The influence of the trailing edge angle of the micro centrifugal impeller on the performance of the centrifugal compressor. Int. J. Appl. Electrom. 2021, 66, 619–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hah, C.; Puterbaugh, S.L.; Wadia, A.R. Control of shock structure and secondary flow field inside transonic compressor rotors through aerodynamic sweep. In Proceedings of the ASME Turbo Expo 1998: Power for Land, Sea and Air, Stockholm, Sweden, 23 December 1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govardhan, M.; Kumar, O.; Sitaram, N. Computational study of the effect of sweep on the performance and flow field in an axial flow compressor rotor. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part A J. Power Energy 2007, 221, 315–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, W.; Xiang, X.; Zhao, Q.; Xu, J. The effect of sweep on flowfields of a highly loaded transonic rotor. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2016, 58, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesh, C.S.; Nagpurwala, Q.H.; Dixit, C.S. Effect of leading edge sweep on the performance of a centrifugal compressor impeller. SAS. Tech-Tech. J. RUAS 2010, 9, 55–62. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, L.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, X.; Cui, Q. Effect of hybrid leading edge sweep on the aerodynamic performance of small scale transonic centrifugal compressor. Trans. CSICE 2016, 34, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Lu, X.; Zhao, G.; Ma, R. Effects of compound sweep and lean on the aerodynamic performances of transonic centrifugal impellers. In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, Dalian, China, 28 September 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.L.; Han, G.; Zhu, J.Q.; Lu, X.G. Flow mechanism of swept controlling internal flow of transonic centrifugal compressor. JASP 2022, 37, 826–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazby, H.; Robinson, C.; Casey, M.; Rusch, D.; Hunziker, R. Free-form versus ruled inducer design in a transonic centrifugal impeller. J. Turbomach. 2018, 140, 011010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Peng, C.; Wu, J. Back swept angle performance analysis of centrifugal compressor. Mechanika 2014, 20, 402–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdmenger, R.R.; Michelassi, V. Impact of main and splitter blade leading edge contour on the performance of high pressure ratio centrifugal compressors. In Proceedings of the ASME Turbo Expo 2014: Power for Land, Sea and Air, Stockholm, Sweden, 18 September 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hildebrandt, A.; Genrup, M. Numerical investigation of the effect of different back sweep angle and exducer width on the impeller outlet flow pattern of a centrifugal compressor with vaneless diffuser. J. Turbomach. 2007, 129, 421–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.J.; Du, L.M.; Guan, T.M. Influence mechanism of impeller trailing edge sweep on aerodynamic performance and internal flow field of a centrifugal compressor. J. Eng. Phys. Thermophys. 2022, 43, 3225–3234. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, H.Y.; Tong, T.; Liu, Y.; Xing, W.D.; Chen, D.F.; Gao, C. The effects of blade trailing edge swept on the performance of centrifugal compressor. J. Eng. Phys. Thermophys. 2021, 42, 399–406. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, H.Y.; Tong, T.; Zhang, J.Y.; Cheng, J.H.; Liu, X.Y. Flow characteristic of transonic centrifugal compressor with free-form sweep impeller at leading and trailing edges. Trans. CSICE 2021, 39, 554–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Methel, J.; Gooding, W.J.; Fabian, J.C.; Key, N.L.; Whitlock, M. The development of a low specific speed centrifugal compressor research facility. In Proceedings of the ASME Turbo Expo 2016: Turbomachinery Technical Conference and Exposition, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 13 June 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Z. Investigations of the performance on vaned diffusers for low specific speed centrifugal compressor. Trans. Beijing Inst. Technol. 2021, 41, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawanishi, T.; Tohbe, Y.; Kanazawa, N. Investigations of the performance on vaned diffusers for low specific speed centrifugal compressor. Int. J. Gas Turbine Propul. Power Syst. 2014, 6, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.H.; Di, L.J.; Cave, M. A CFD study on a base and a flow-trimmed low specific speed centrifugal compressor. In Proceedings of the ASME 2010 International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 12–18 November 2010; Volume 5, pp. 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.F.; Zhang, R.D.; Zhuge, W.L.; Zhang, Y.J.; Wei, J.J. Effect of leading edge swept on low specific speed centrifugal compressor performance. Automot. Saf. Energy 2017, 8, 432–436. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, C.; Chen, L.; Amano, R.S. Design and analysis of energy-efficient low-flow centrifugal compressors. J. Energy Resour. Technol. 2020, 142, 081307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Huang, N.; Chen, G.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Tong, D. Numerical Simulation on the Influence of Inlet Flow Characteristics on the Performance of a Centrifugal Compressor. Energies 2023, 16, 3869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundström, E.; Semlitsch, B.; Mihăescu, M. Similarities and Differences Concerning Flow Characteristics in Centrifugal Compressors of Different Size. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Jets, Wakes and Separated Flows (ICJWSF2015), Stockholm, Sverige, 15 June 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celik, I.B.; Ghia, U.; Roache, P.J.; Freitas, C.J. Procedure for estimation and reporting of uncertainty due to discretization in CFD applications. ASME J. Fluids Eng. 2008, 130, 078001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, C.; Cervantes, M.J.; Gandhi, B.K. Investigation of a High Head Francis Turbine at Runaway Operating Conditions. Energies 2016, 9, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, K.; Xu, Z.; Chen, H.; Xu, H.; Zheng, Y.; Zhou, D.; Maxime, A.; Maxime, B. Energy loss mechanisms of transition from pump mode to turbine mode of an axial-flow pump under bidirectional conditions. Energy 2022, 257, 124630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






















| Boundary Type | Setting |
|---|---|
| Inlet | Total pressure 101,325 Pa, total temperature 298 K axial intake |
| Passage interface | Rotational periodicity |
| Wall | No-slip, adiabatic |
| Rotor-stator interface | Mixing plane |
| Outlet | Mass flow rate/Average static pressure |
| Parameters | Total Pressure Ratio | Isentropic Efficiency |
|---|---|---|
| 1.309 | 1.309 | |
| 1.317 | 1.317 | |
| 1.74986 | 0.71768 | |
| 1.73937 | 0.71424 | |
| 1.64679 | 0.70490 | |
| 8.097 | 3.748 | |
| 1.751 | 0.71958 | |
| /% | 0.599 | 0.479 |
| /% | 0.072 | 0.265 |
| /% | 0.090 | 0.332 |
| Instruments | Range | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|
| Flow Meter with Double Folium Curve | 0.01~0.27 kg/s | ±1.5% |
| 2T-type thermocouple | 0~200 °C | ±0.5 °C |
| High precision pressure scanning valve | −50~500 kpa | ±0.1% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tian, H.; Hou, K.; Tong, D.; Lin, S.; Ma, C. Effect of Leading/Trailing Edge Swept Impeller on Flow Characteristics of Low Specific Speed Centrifugal Compressor. Energies 2023, 16, 4286. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16114286
Tian H, Hou K, Tong D, Lin S, Ma C. Effect of Leading/Trailing Edge Swept Impeller on Flow Characteristics of Low Specific Speed Centrifugal Compressor. Energies. 2023; 16(11):4286. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16114286
Chicago/Turabian StyleTian, Hongyan, Kang Hou, Ding Tong, Sen Lin, and Chicheng Ma. 2023. "Effect of Leading/Trailing Edge Swept Impeller on Flow Characteristics of Low Specific Speed Centrifugal Compressor" Energies 16, no. 11: 4286. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16114286
APA StyleTian, H., Hou, K., Tong, D., Lin, S., & Ma, C. (2023). Effect of Leading/Trailing Edge Swept Impeller on Flow Characteristics of Low Specific Speed Centrifugal Compressor. Energies, 16(11), 4286. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16114286






