Catalytic Pyrolysis of Waste Bicycle Tires and Engine Oil to Produce Limonene
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Apparatus and Procedure
2.2.1. TG–FTIR Measurement
2.2.2. Pyrolysis Furnace
2.2.3. Py–GC/MS Measurement
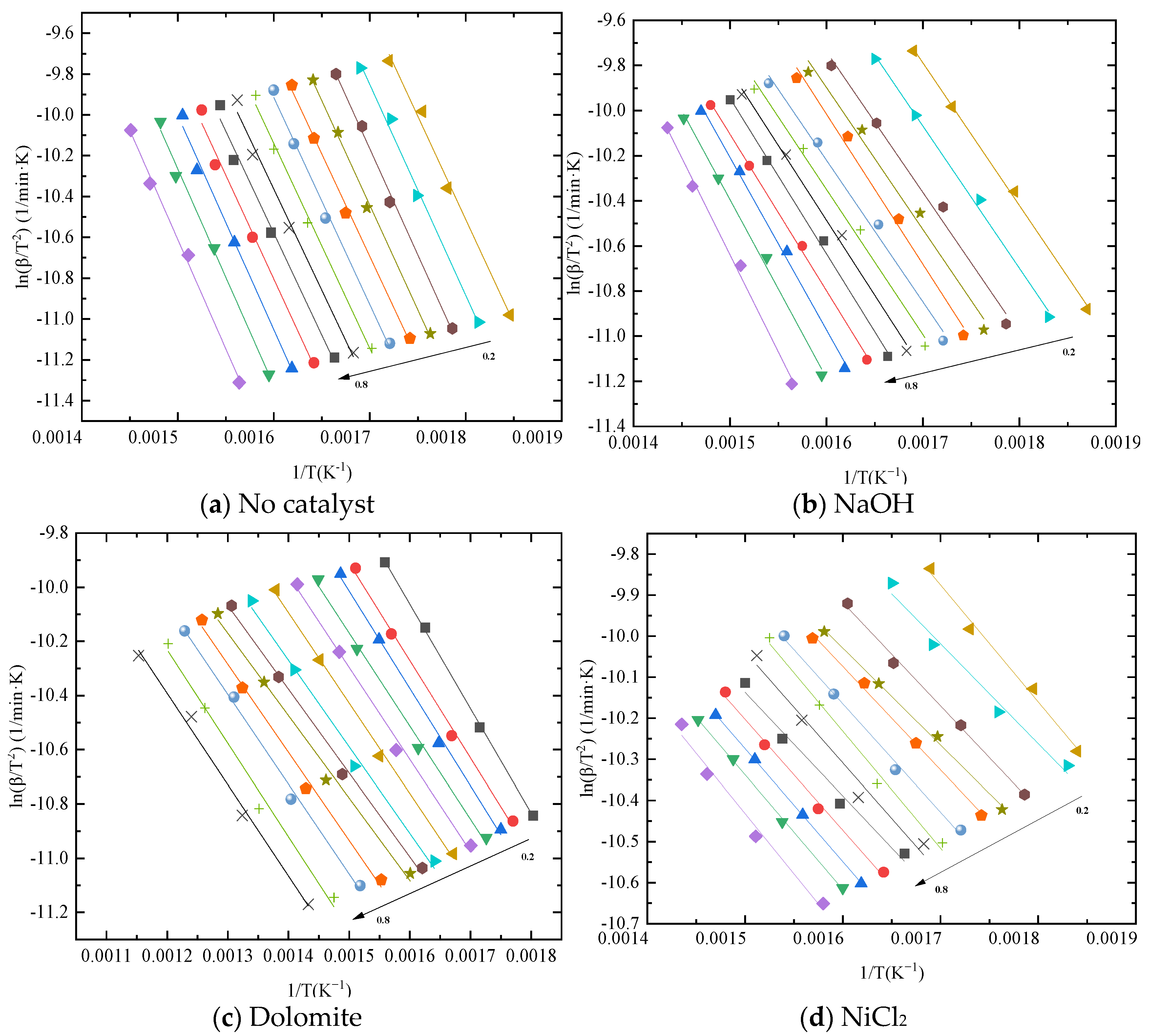
2.3. Kinetic Analysis
3. Results and Discussions
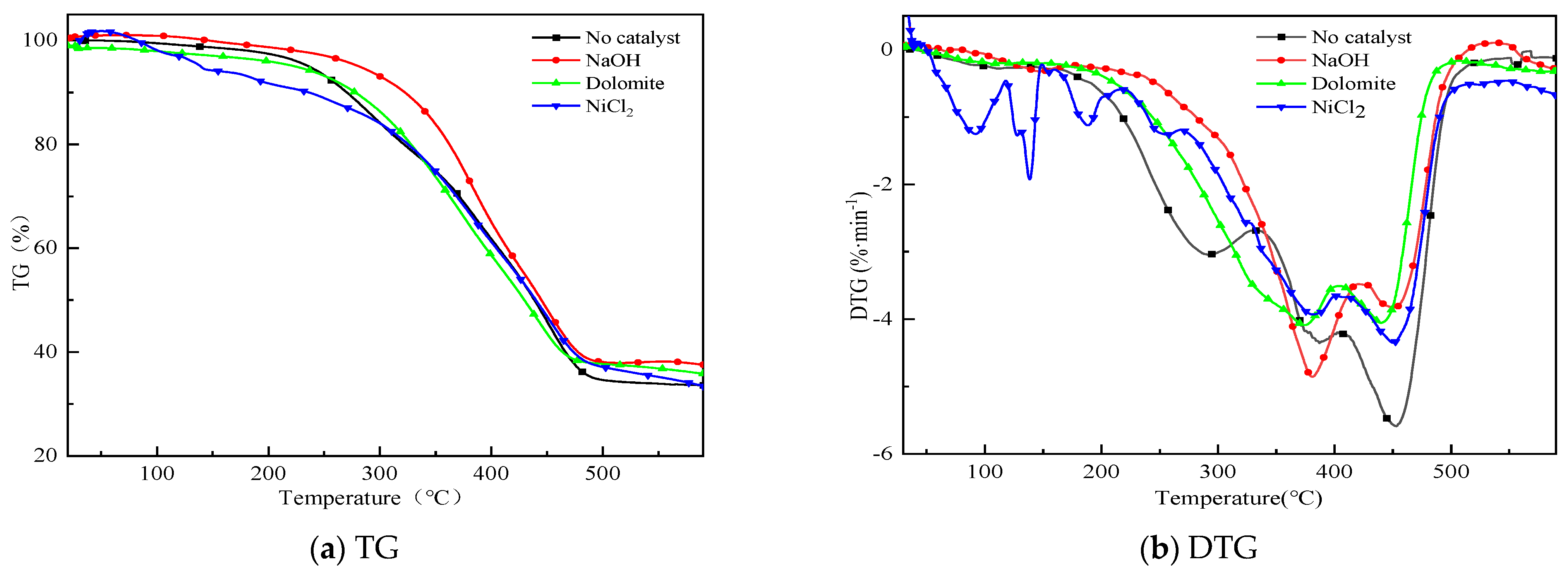
3.1. Thermogravimetric Analysis
3.2. Kinetic Analysis of Catalytic Co–Pyrolysis
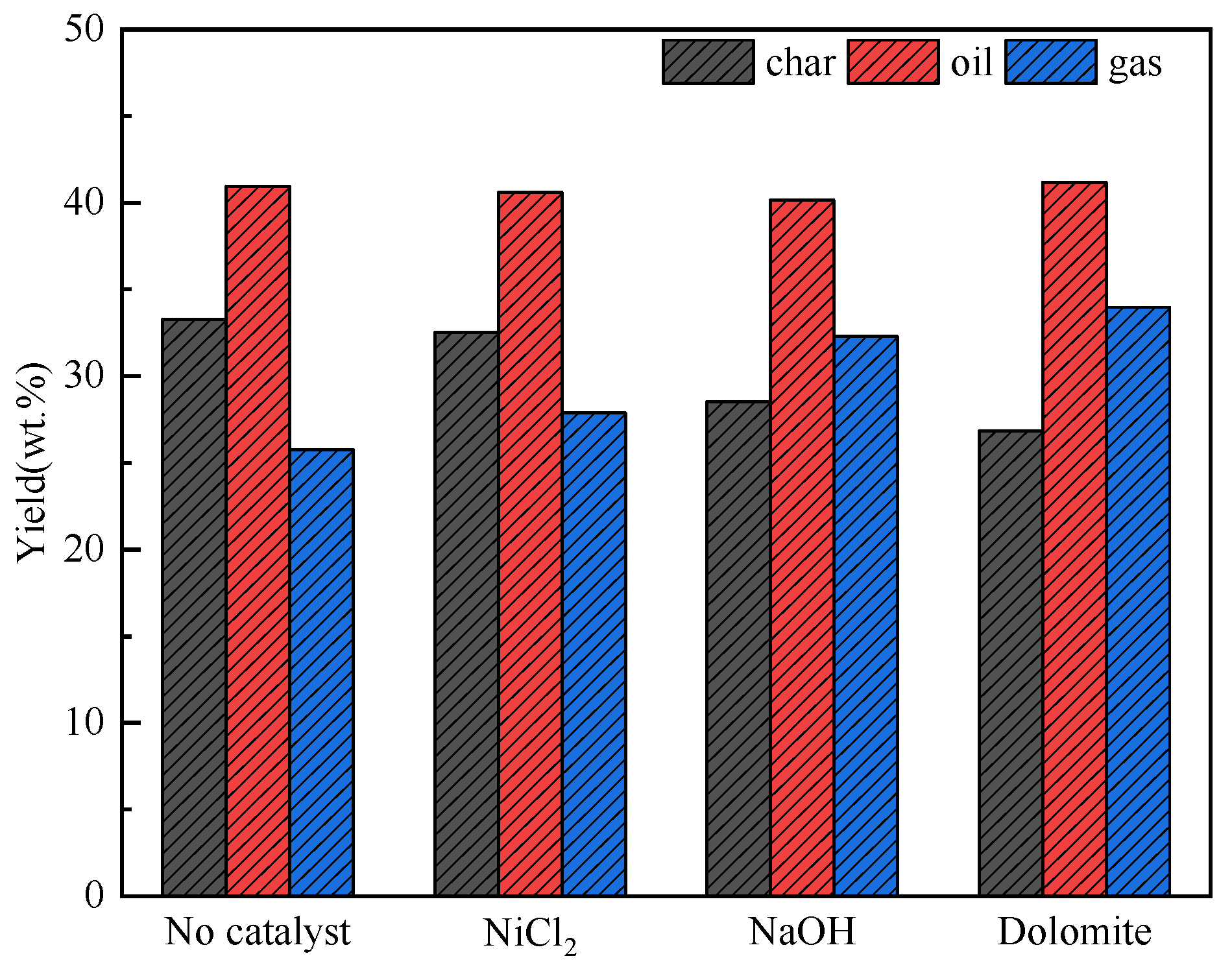
3.3. Distribution of Co–Pyrolysis Products
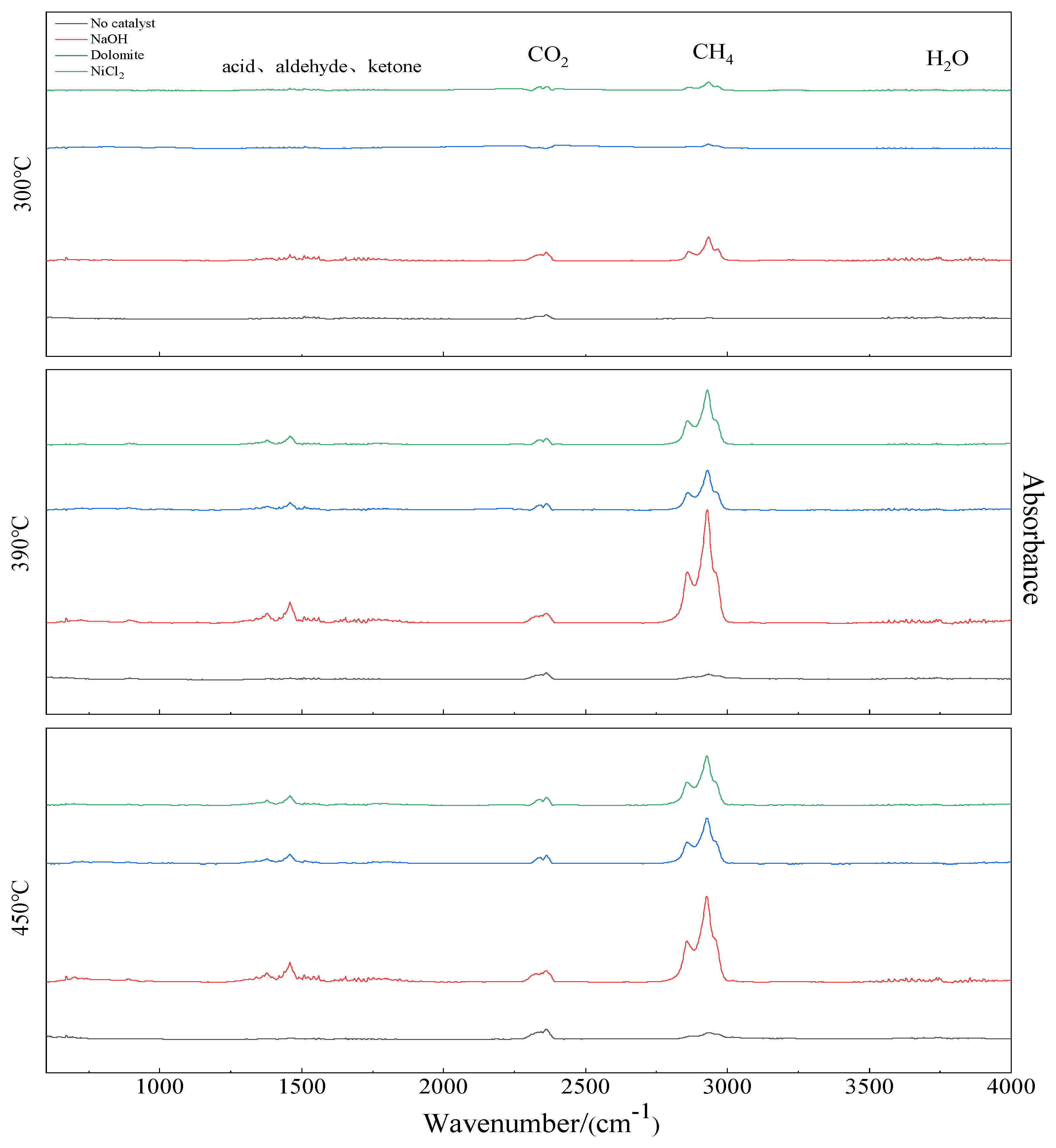
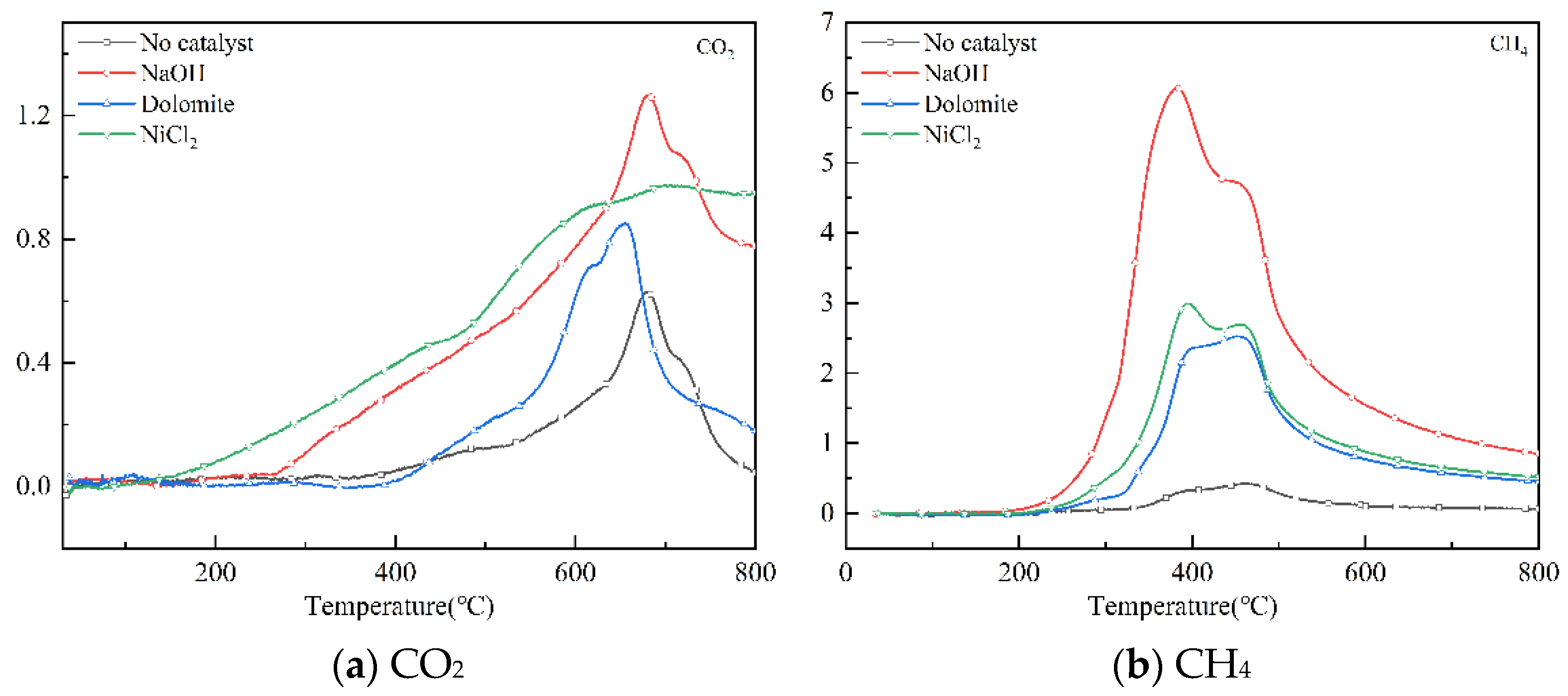
3.4. FTIR Analysis
3.5. Py–GC/MS Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kositkanawuth, K.; Bhatt, A.; Sattler, M.; Dennis, B. Renewable energy from waste: Investigation of Co-pyrolysis between Sargassum macroalgae and polystyrene. Energy Fuels 2017, 31, 5088–5096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kai, X.; Yang, T.; Shen, S.; Li, R. TG-FTIR-MS study of synergistic effects during co-pyrolysis of corn stalk and high-density polyethylene (HDPE). Energy Convers. Manag. 2019, 181, 202–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, A.T.; Le, V.V.; Al-Tawaha, A.R.M.; Nguyen, D.N.; Noor, M.M.; Pham, V.V. An absorption capacity investigation of new absorbent based on polyurethane foams and rice straw for oil spill cleanup. Pet. Sci. Technol. 2019, 36, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarifa, J.M.; Ruiz, C.P.A.; Gomes, V.L.A.; Araújo, J.S. Coke deposition during electromagnetic heating. Liq. Fuels Technol. 2017, 35, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Xu, Y.; Duan, P.; Wang, F.; Xu, Z.-X. Thermo-chemical conversion of scrap tire waste to produce gasoline fuel. Waste Manag. 2019, 86, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Wang, B.; Yang, D.; Ming, X.; Jiang, Y.; Hao, J.; Qiao, Y.; Tian, Y. TG-FTIR and Py-GC/MS study on pyrolysis mechanism and products distribution of waste bicycle tire. Energy Convers. Manag. 2018, 175, 288–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Januszewicz, K.; Kazimierski, P.; Suchocki, T.; Kardaś, D.; Lewandowski, W.; Klugmann-Radziemska, E.; Łuczak, J. Waste Rubber Pyrolysis: Product Yields and Limonene Concentration. Materials 2020, 13, 4435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Liu, L.; Yang, Y.; Sun, J.; Zhao, X.; Wang, W.; Mao, Y.; Yuan, X.; Wang, Q. Characteristics of limonene formation during microwave pyrolysis of scrap tires and quantitative analysis. Energy 2018, 142, 953–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mkhize, N.M.; van der Gryp, P.; Danon, B.; Gorgens, J.F. Effect of temperature and heating rate on limonene production from waste tyre pyrolysis. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2016, 120, 314–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gang, Y.; Pan, L.; Niu, M.; Zhang, X.; Li, D.; Li, W. Catalytic hydrogenation of Low temperature coal tar into jet fuel by using two-reactors system. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2018, 134, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Q.; Zhang, J.; Hu, S.; Ma, S.; Huang, R.; Su, S.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, L.; Xu, J.; Xiang, J. Novel photothermal pyrolysis on waste tire to generate high-yield limonene. Fuel 2022, 329, 125482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanteigne, J.-R.; LaViolette, J.-P.; Tremblay, G.; Chaouki, J. Predictive Kinetics Model for an Industrial Waste Tire Pyrolysis Process. Energy Fuels 2013, 27, 1040–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Qi, X.; Dong, X.; Luo, S.; Feng, Y.; Feng, M.; Guo, X. The co-pyrolysis of waste tires and waste engine oil. Energy Sources Part A Recover. Util. Environ. Eff. 2022, 44, 9764–9778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, U.; Vongsvivut, J.; Shahabuddin, M.; Samudrala, S.P.; Srivatsa, S.C.; Bhattacharya, S. A study on the performance of coke resistive cerium modified zeolite Y catalyst for the pyrolysis of scrap tyres in a two-stage fixed bed reactor. Waste Manag. 2019, 102, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, T.; Ma, L.; Chang, J. Vacuum pyrolysis of waste tires with basic additives. Waste Manag. 2008, 28, 2301–2310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabir, G.; Hameed, B. Recent progress on catalytic pyrolysis of lignocellulosic biomass to high-grade bio-oil and bio-chemicals. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 70, 945–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miskah, S.; Aprianti, T.; Moeksin, R. Potential use of waste rubber tires containing polystyrene to produce gasoline-like hydrocarbon by thermal catalytic cracking. IOP Conf. Series Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 298, 012014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, B.S.; Gupta, R.C. A comprehensive review on the applications of waste tire rubber in cement concrete. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 54, 1323–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, J.; Jan, M.R.; Mabood, F. Catalytic conversion of waste tyres into valuable hydrocarbons. J. Polym. Environ. 2007, 15, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, J.; Rasul, M.; Mabood, F. Catalytic Pyrolysis of Waste Tyre Rubber into Hydrocarbons Via Base Catalysts. Iran. J. Chem. Chem. Eng.-Int. Engl. Ed. 2008, 27, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, J.; Jan, M.; Mabood, F. Recovery of value-added products from the catalytic pyrolysis of waste tyre. Energy Convers. Manag. 2009, 50, 991–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahoor, A.H.; Zandi-Atashbar, N. Fuel production based on catalytic pyrolysis of waste tires as an optimized model. Energy Convers. Manag. 2014, 87, 653–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palza, H.; Aravena, C.; Colet, M. Role of the Catalyst in the Pyrolysis of Polyolefin Mixtures and Used Tires. Energy Fuels 2017, 31, 3111–3120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbaba, I.F.; Williams, P.T. High yield hydrogen from the pyrolysis–catalytic gasification of waste tyres with a nickel/dolomite catalyst. Fuel 2013, 106, 528–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.K.; Ruj, B.; Jana, A.; Mondal, S.; Jana, B.; Sadhukhan, A.K.; Gupta, P. Pyrolysis of three different categories of automotive tyre wastes: Product yield analysis and characterization. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2018, 135, 379–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Wan, J.; Fan, Z.; Hu, Q.; Zhou, N.; Xia, M.; Song, M.; Qi, Z.; Zhou, Z. In-situ catalytic pyrolysis of waste tires over clays for high quality pyrolysis products. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 46, 6937–6944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.B.; De, M. Thermally exfoliated graphene oxide for hydrogen storage. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2019, 239, 122102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Ning, Z.; Li, Z.; Zou, W.; Li, B.; Huang, Y.; Cao, F.; Sun, J. Evolved gas analysis of PEP-SET sand by TG and FTIR. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2017, 127, 490–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.-H.; Horng, R.-F. Experimental study of syngas production from methane dry reforming with heat recovery strategy. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 25213–25224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, G.-G.; Oh, S.-J.; Kim, J.-S. Clean pyrolysis oil from a continuous two-stage pyrolysis of scrap tires using in-situ and ex-situ desulfurization. Energy 2018, 141, 2234–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.-Q.; Yao, Q.; Chi, Y.; Yan, J.-H.; Cen, K.-F. Pilot-Scale Pyrolysis of Scrap Tires in a Continuous Rotary Kiln Reactor. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2004, 43, 5133–5145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mkhize, N.; Danon, B.; Alvarez, J.; Lopez, G.; Amutio, M.; Bilbao, J.; Olazar, M.; van der Gryp, P.; Görgens, J. Influence of reactor and condensation system design on tyre pyrolysis products yields. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2019, 143, 104683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Catalyst | Yield (wt.%) | Temperature (°C) | Data Source | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gas | Oil | Char | |||
| CaC2 | 34.50 | 33.50 | 32.00 | 400 | [18] |
| MgO | 19.30 | 27.00 | 53.50 | 400 | [19] |
| CaCO3 | 31.90 | 29.20 | 38.90 | 400 | [19] |
| Al2O3 | 21.00 | 23.20 | 55.80 | 400 | [20] |
| MgCl2 | 16.20 | 38.20 | 45.60 | 407 | [21] |
| HZSM–5 | 31.00 | 33.00 | 36.00 | 450 | [22] |
| Na2CO3 | 14.60 | 47.80 | 37.60 | 500 | [14] |
| NaOH | 13.30 | 48.10 | 38.60 | 500 | [14] |
| Ni + Dolomite | 40.00 | 30.40 | 29.60 | 500 | [23] |
| Item | Condition | |
|---|---|---|
| TG | carrier gas | N2 |
| temperature range/°C | 20–800 | |
| heating rate/(°C·min−1) | 15 | |
| sample mass/mg | 10 | |
| FTIR | frequency ranger/cm | 4000–400 |
| resolution/cm−1 | 4.0 | |
| scan rate/(scans·s−1) | 8 |
| Item | Condition | |
|---|---|---|
| Pyrolyzer | furnace temperature/°C | 300, 390, 450 |
| sample amount/mg | 10 | |
| Gas chromatograph | column style/μm | 60 × 0.25 × 0.25 |
| column temperature | held 40 °C for 3 min, then programmed to 290 °C at a heating rate of 6 °C·min−1 | |
| inlet temperature of column/°C | 290 | |
| inlet pressure of column/kPa | 50 | |
| split ratio | 1:50 | |
| Mass spectrometer | interface temperature/°C | 290 |
| scanning range/(m·z−1) | 15–550 | |
| scan rate/(scans·s−1) | 5 |
| Parameters | Feedstock | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| WT | WEO | ||
| Proximate Analysis (wt.%) | Moisture | 1.14 | 0.77 |
| Volatiles | 62.24 | 97.01 | |
| Fixed Carbon | 32.28 | 1.32 | |
| Ash | 4.34 | 0.90 | |
| Elemental Analysis (wt.%) | C | 84.35 | 81.28 |
| H | 6.70 | 15.61 | |
| O | 6.95 | 2.56 | |
| N | 0.39 | 0.14 | |
| S | 1.61 | 0.41 | |
| HHV (MJ/kg) | 34.90 | 41.30 | |
| Material | Catalyst | Method | Oil (%) | Limonene (%) | Data Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WT + WEO | No | Pyrolysis | 41.0 | 4.99 | This work |
| WT + WEO | 10%NaOH | Pyrolysis | 41.0 | 19.65 | This work |
| WT + WEO | Dolomite | Pyrolysis | 40.7 | 16.85 | This work |
| WT + WEO | NiCl2 | Pyrolysis | 41.5 | 9.69 | This work |
| WT | No | Pyrolysis | 36.6 | 6.60 | [29] |
| WT | 3%NaOH | Vacuum | 48.1 | 11.95 | [14] |
| WT | 3%Na2CO3 | Vacuum | 42.0 | 12.39 | [14] |
| WT | No | Vacuum | 32.9 | 11.97 | [14] |
| WT | No | Pyrolysis | 43.0 | 5.40 | [30] |
| WT | No | Microwave | 44.0 | 9.92 | [8] |
| WT | No | Pyrolysis | 49.2 | 7.90 | [31] |
| WT | No | Pyrolysis | 43.4 | 6.70 | [32] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Dong, X.; Zuo, Z.; Luo, S. Catalytic Pyrolysis of Waste Bicycle Tires and Engine Oil to Produce Limonene. Energies 2023, 16, 4351. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16114351
Wang J, Dong X, Zuo Z, Luo S. Catalytic Pyrolysis of Waste Bicycle Tires and Engine Oil to Produce Limonene. Energies. 2023; 16(11):4351. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16114351
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Junzhi, Xinjiang Dong, Zongliang Zuo, and Siyi Luo. 2023. "Catalytic Pyrolysis of Waste Bicycle Tires and Engine Oil to Produce Limonene" Energies 16, no. 11: 4351. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16114351
APA StyleWang, J., Dong, X., Zuo, Z., & Luo, S. (2023). Catalytic Pyrolysis of Waste Bicycle Tires and Engine Oil to Produce Limonene. Energies, 16(11), 4351. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16114351






