Modified Particle Swarm Optimization Based Powertrain Energy Management for Range Extended Electric Vehicle
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
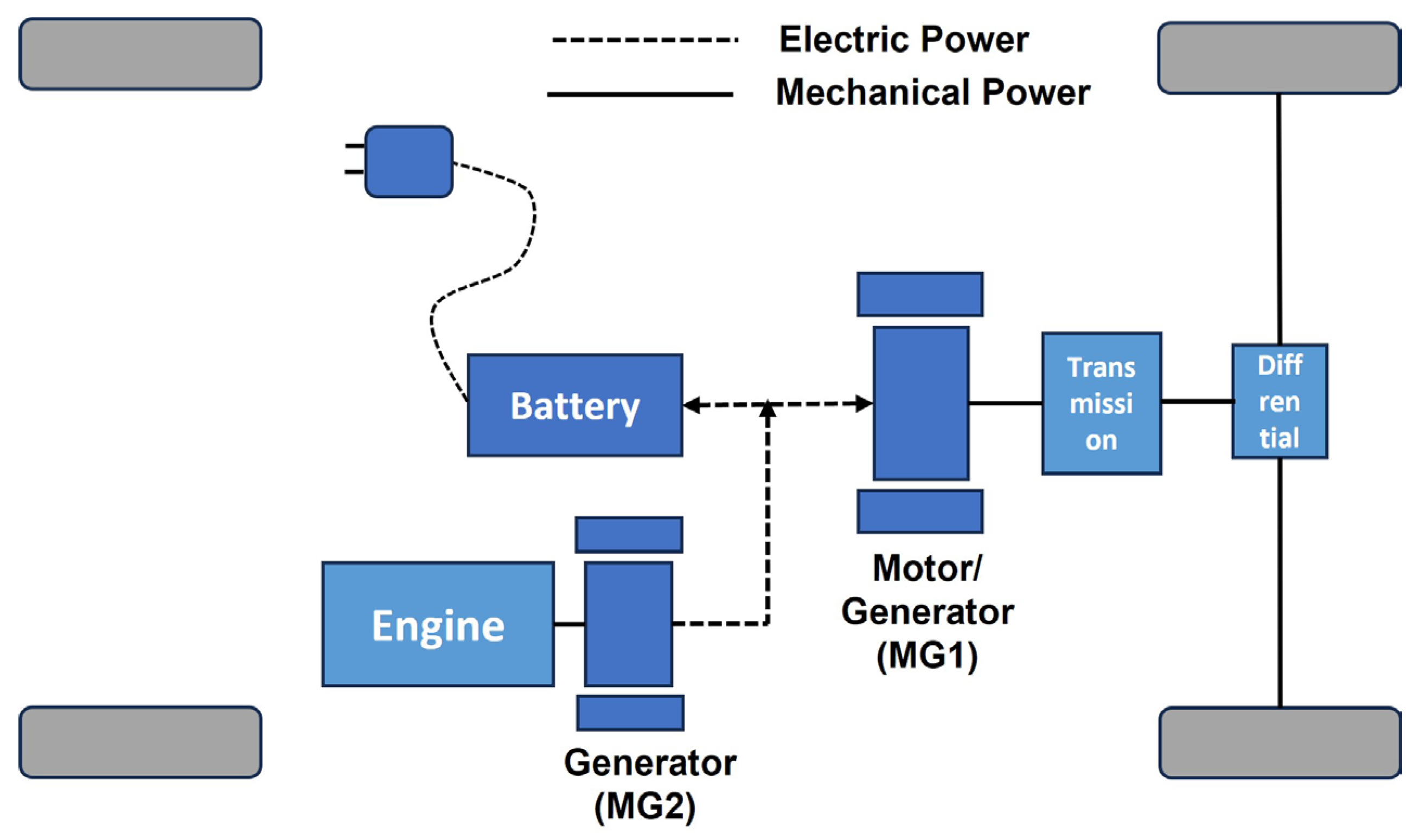
2.1. Model Development
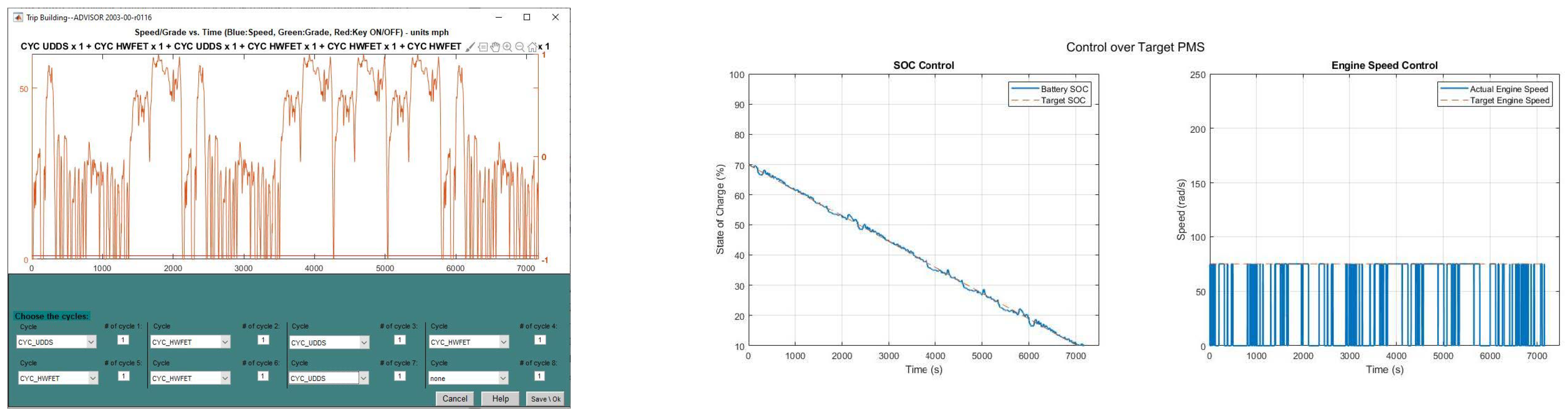
2.2. Model Validation and Comparison
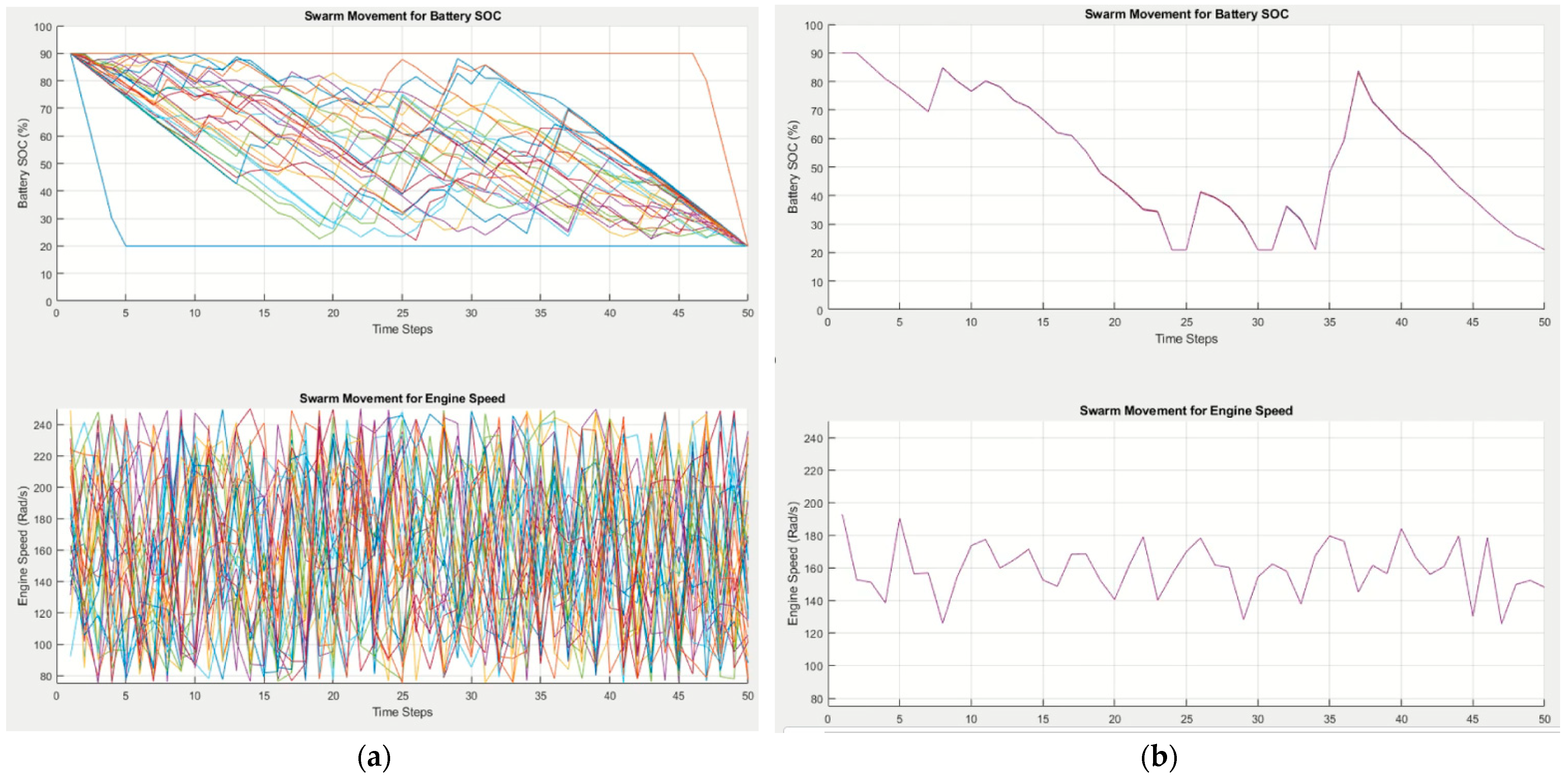
2.3. Modified Particle Swarm Optimization
- is the velocity of th particle,
- is position of th particle,
- is the index of iteration,
- is personal best of particle found till iteration ,
- is global best of the swarm found till iteration ,
- is Inertia Coefficient,
- is Cognitive Coefficient,
- is Social Coefficient,
- are random numbers in range [0, 1].
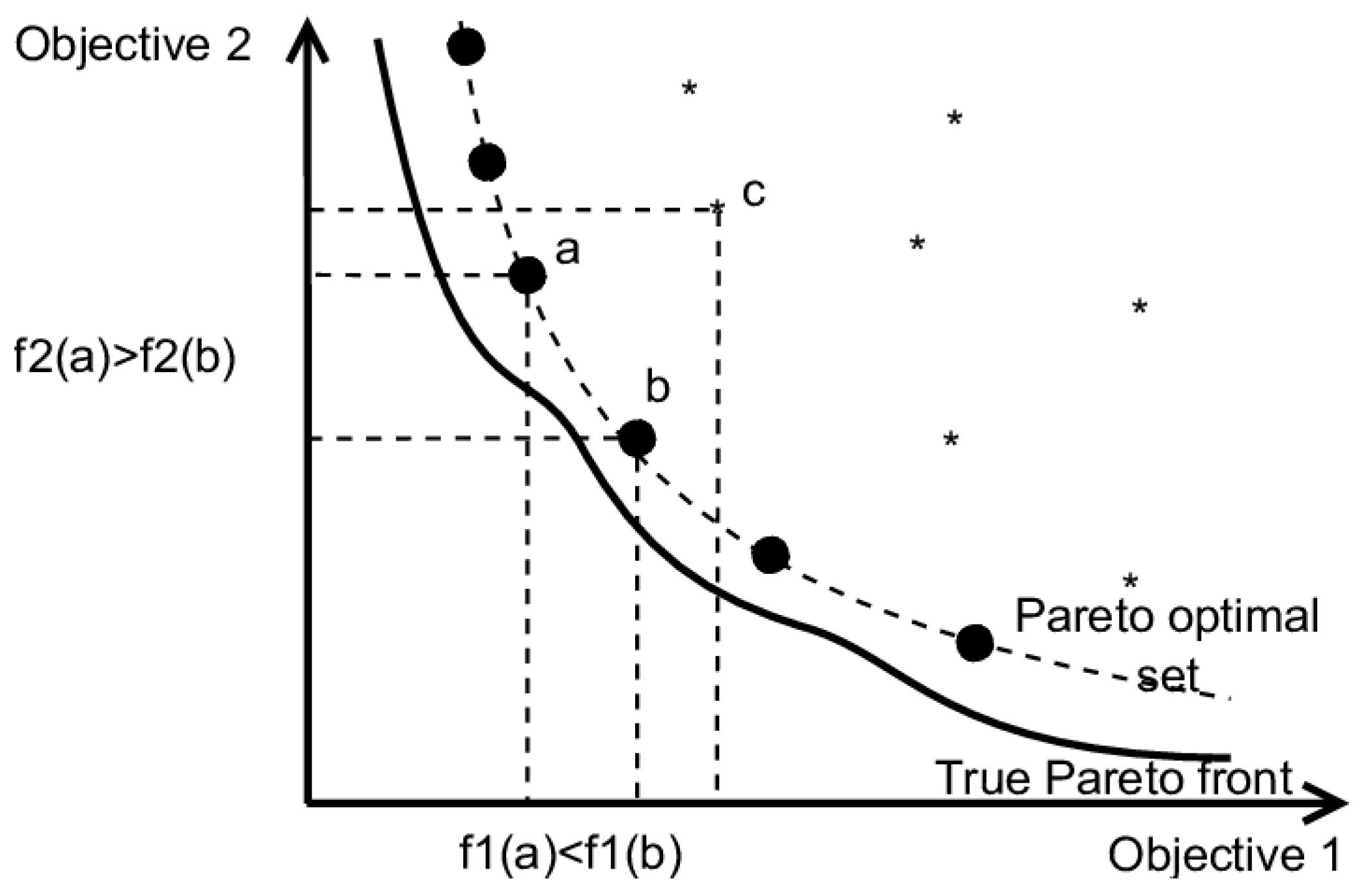
2.4. Multi-Objective Optimization by Pareto Optimality
- is the cumulative cost,
- i is the identifier of the cost,
- n is the total number of costs,
- is the numerical weight of ith cost,
- is the function for ith cost,
- is the ith control variable,
- j is the total number of control variables.
3. Results
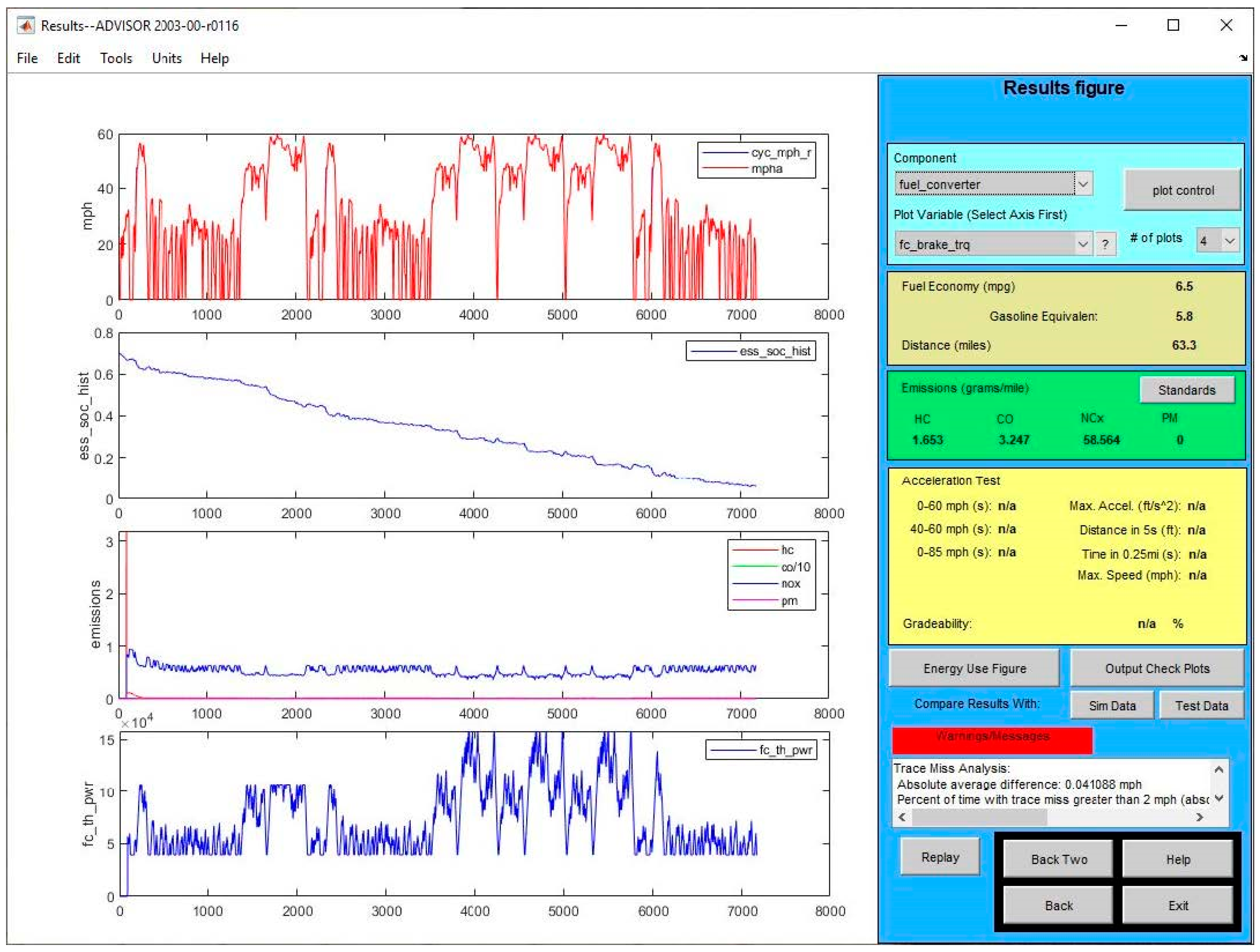
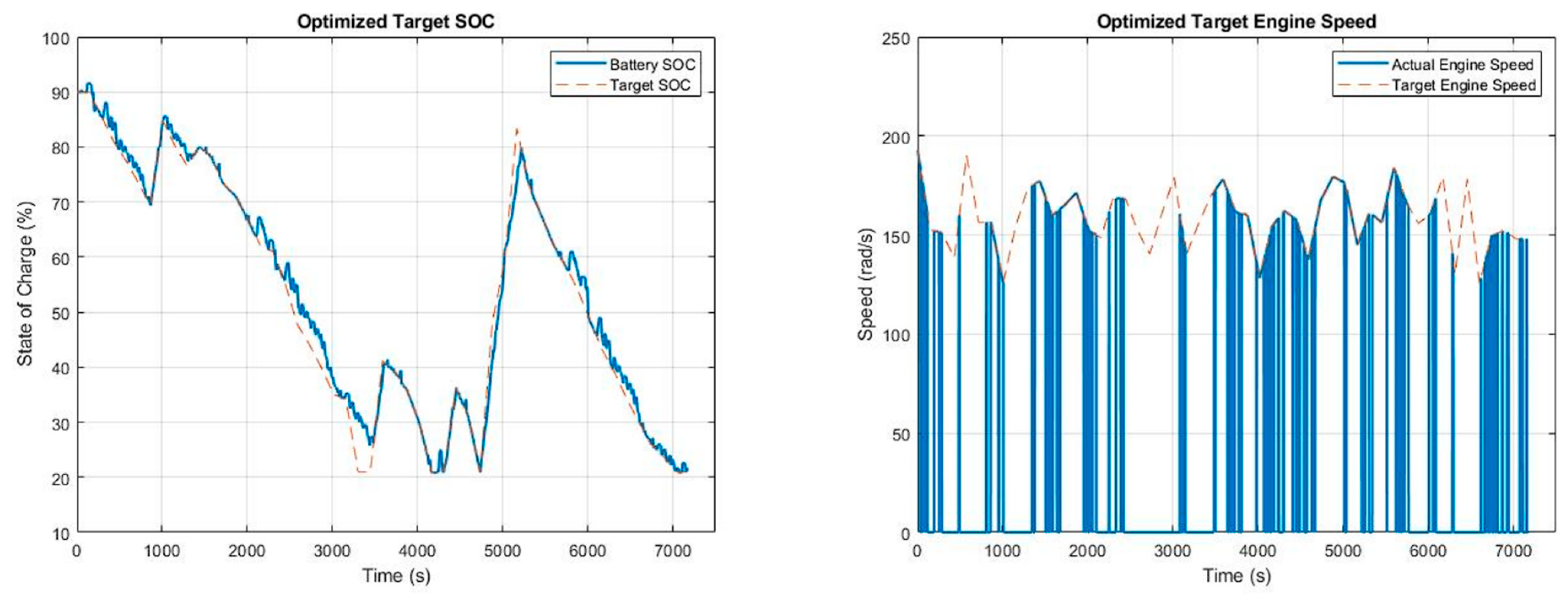
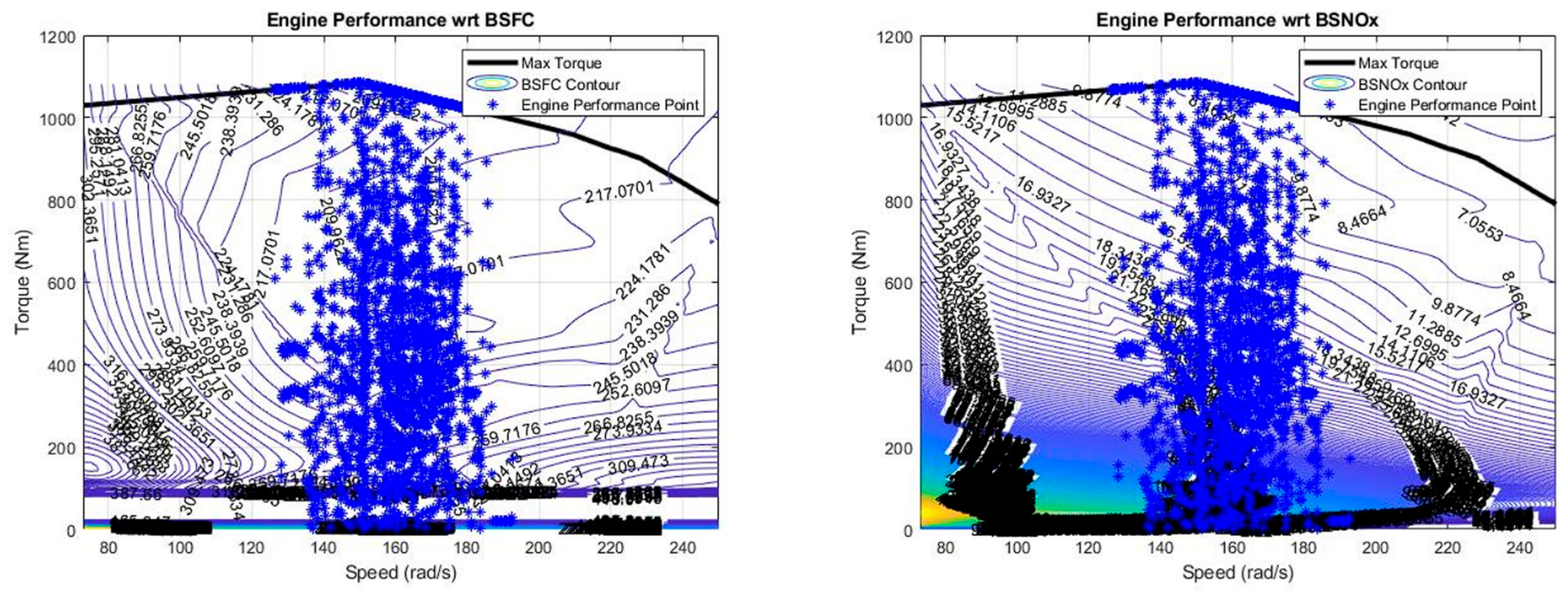
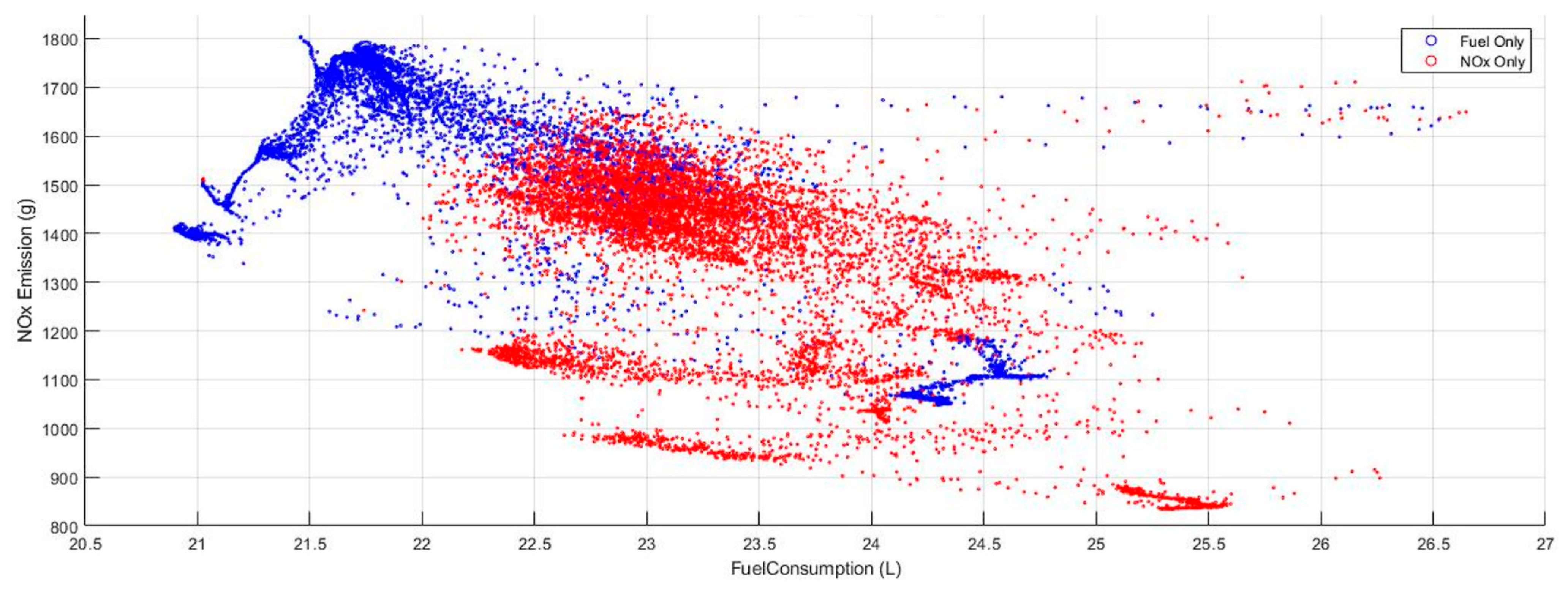
3.1. Minimization of Fuel Consumption
3.2. Minimization of NOx Emission
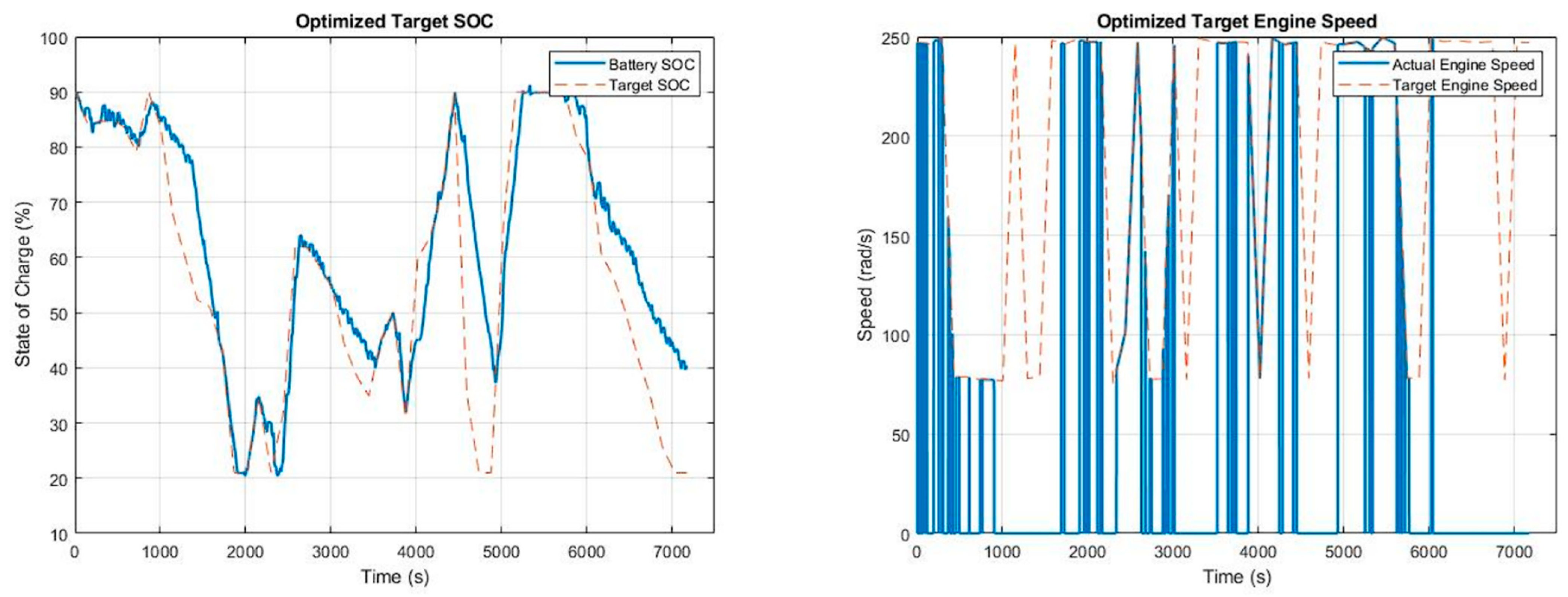
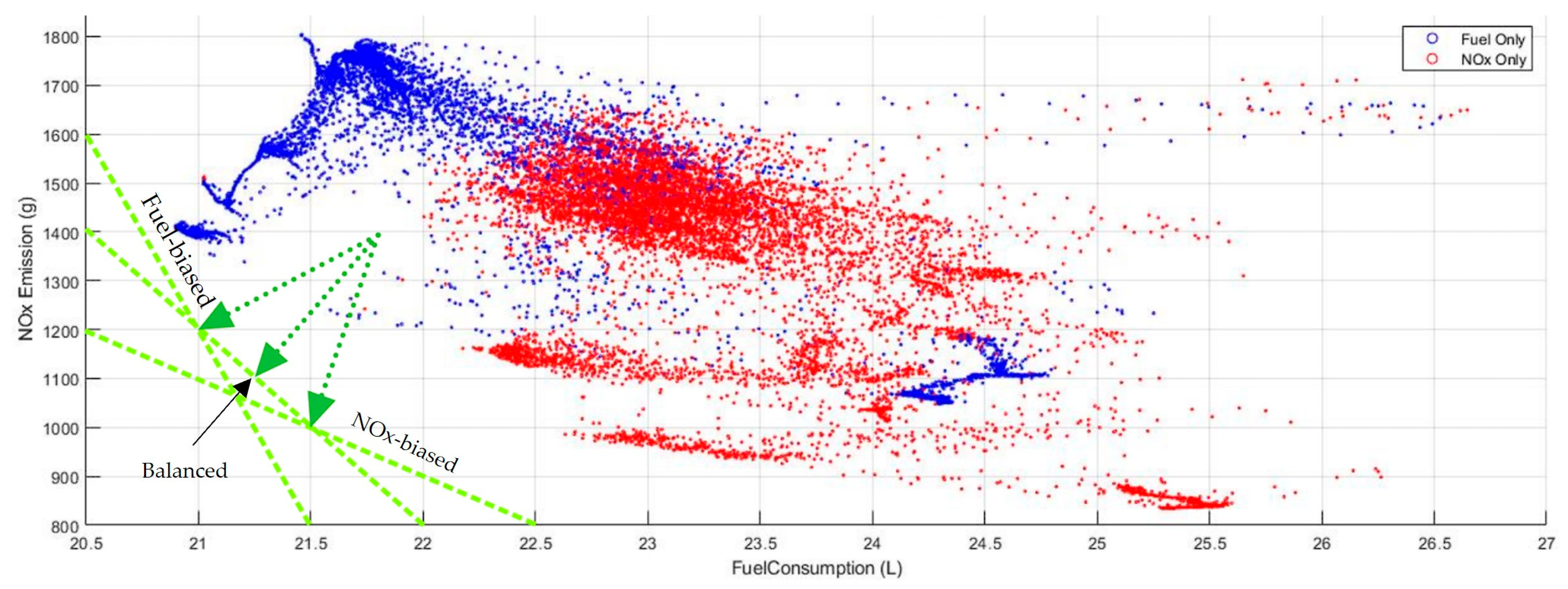
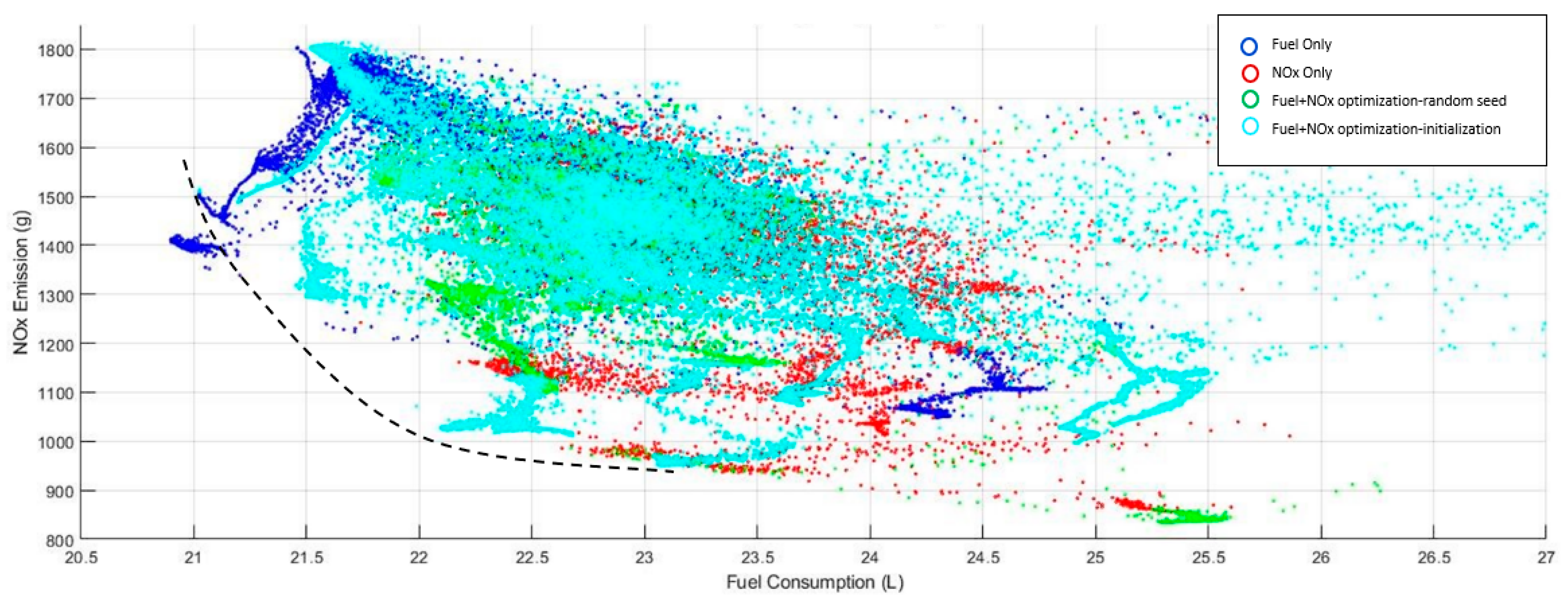
3.3. Optimizing Both Fuel Cost and NOx Emissions
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Singh, K.V.; Bansal, H.O.; Singh, D. A comprehensive review on hybrid electric vehicles: Architectures and components. J. Mod. Transp. 2019, 27, 77–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enang, W.; Bannister, C. Modelling and control of hybrid electric vehicles (A comprehensive review). Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 74, 1210–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirasingha, S.G.; Emadi, A. Classification and Review of Control Strategies for Plug-In Hybrid Electric Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2011, 60, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.-Y.; Hung, Y.-H.; Wu, C.-H.; Huang, S.-T. Optimal energy management of a hybrid electric powertrain system using improved particle swarm optimization. Appl. Energy 2015, 160, 132–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabali, A.; Ghofrani, M.; Etezadi-Amoli, M.; Fadali, M.S.; Baghzouz, Y. Genetic-Algorithm-Based Optimization Approach for Energy Management. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2012, 28, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Mi, C.C.; Xiong, R.; Xu, J.; You, C. Energy management of a power-split plug-in hybrid electric vehicle based on genetic algorithm and quadratic programming. J. Power Sources 2014, 248, 416–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-C.; Peng, H.; Grizzle, J.W.; Kang, J.-M. Power management strategy for a parallel hybrid electric truck. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2003, 11, 839–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brahma, A.; Guezennec, Y.; Rizzoni, G. Optimal energy management in series hybrid electric vehicles. In Proceedings of the 2000 American Control Conference, Chicago, IL, USA, 28–30 June 2000; ACC (IEEE Cat. No. 00CH36334). Volume 1, pp. 60–64. [Google Scholar]
- Borhan, H.; Vahidi, A.; Phillips, A.M.; Kuang, M.L.; Kolmanovsky, I.V.; Di Cairano, S. MPC-Based Energy Management of a Power-Split Hybrid Electric Vehicle. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2012, 20, 593–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.; Cha, S.; Peng, H. Optimal Control of Hybrid Electric Vehicles Based on Pontryagin’s Minimum Principle. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2011, 19, 1279–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrao, L.; Onori, S.; Rizzoni, G. A Comparative Analysis of Energy Management Strategies for Hybrid Electric Vehicles. J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. Control 2011, 133, 031012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrao, L.; Rizzoni, G. Optimal control of power split for a hybrid electric refuse vehicle. In Proceedings of the 2008 American Control Conference, Seattle, WA, USA, 11–13 June 2008; pp. 4498–4503. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Lei, Y.; Fu, Y.; Li, X. A novel hybrid-point-line energy management strategy based on multi-objective optimization for range-extended electric vehicle. Energy 2022, 247, 123357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, M.; Zhu, B.; Zhang, N. Adaptive real-time optimal control for energy management strategy of extended range electric vehicle. Energy Convers. Manag. 2021, 234, 113874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moura, S.J.; Fathy, H.K.; Callaway, D.S.; Stein, J.L. A Stochastic Optimal Control Approach for Power Management in Plug-In Hybrid Electric Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2011, 19, 545–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhang, X. Study on energy management strategy and dynamic modeling for auxiliary power units in range-extended electric vehicles. Appl. Energy 2017, 194, 363–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorrentino, M.; Rizzo, G.; Arsie, I. Analysis of a rule-based control strategy for on-board energy management of series hybrid vehicles. Control Eng. Pract. 2011, 19, 1433–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wu, Z.; Hu, X.; Qian, W.; Li, Z. Trajectory Optimization-Based Auxiliary Power Unit Control Strategy for an Extended Range Electric Vehicle. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2017, 66, 10866–10874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Lou, D.; Zhang, Y.; Fang, L. Optimization and Realization of the Coordination Control Strategy for Extended Range Electric Vehicle. Machines 2022, 10, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lou, D.; Xu, N.; Fang, L.; Tan, P. Energy management and emission control for range extended electric vehicles. Energy 2021, 236, 121370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caux, S.; Wanderley-Honda, D.; Hissel, D.; Fadel, M. On-line energy management for HEV based on Particle Swarm Optimization. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Vehicle Power and Propulsion Conference, Lille, France, 1–3 September 2010; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Hegazy, O.; Van Mierlo, J. Optimal power management and powertrain components sizing of fuel cell/battery hybrid electric vehicles based on particle swarm optimisation. Int. J. Veh. Des. 2012, 58, 200–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehdizadeh, E.; Soheil, S.-N.; Tavakkoli-Moghaddam, R. Optimization of fuzzy clustering criteria by a hybrid PSO and fuzzy c-means clustering algorithm. Iran. J. Fuzzy Syst. 2008, 5, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Dahou, A.; Elaziz, M.A.; Chelloug, S.A.; Awadallah, M.A.; Al-Betar, M.A.; Al-qaness, M.A.; Forestiero, A. Intrusion Detection System for IoT Based on Deep Learning and Modified Reptile Search Algorithm. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2022, 2022, 6473507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehsani, M.; Gao, Y.; Longo, S.; Ebrahimi, K. Modern Electric, Hybrid Electric, and Fuel Cell Vehicles, 3rd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018; ISBN 978-0-429-50488-4. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, J.; Ma, J.; Bai, K. Enhanced Coulomb Counting Method for State-of-Charge Estimation of Lithium-ion Batteries based on Peukert’s Law and Coulombic Efficiency. J. Power Electron. 2018, 18, 910–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booker, A.; Haraldsson, K.; Hendricks, T.; Johnson, V.; Kelly, K.; Kramer, B.; Markel, T.; O’Keefe, M.; Sprik, S.; Wipke, K.; et al. ADVISOR Advanced Vehicle Simulator. Available online: https://adv-vehicle-sim.sourceforge.net/ (accessed on 13 March 2023).
- Kennedy, J.; Eberhart, R. Particle swarm optimization. In Proceedings of the ICNN’95—International Conference on Neural Networks, Perth, Australia, 27 November–1 December 1995; Volume 4, pp. 1942–1948. [Google Scholar]
- Ratnaweera, A.; Halgamuge, S.K.; Watson, H.C. Self-organizing hierarchical particle swarm optimizer with time-varying acceleration coefficients. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2004, 8, 240–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oca, M.A.M.; Stützle, T.; Birattari, M.; Dorigo, M. Frankenstein’s PSO: An Engineered Composite Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm; Technical Report TR/IRIDIA/2007-006; IRIDIA, CoDE; Université Libre de Bruxelles: Brussels, Belgium, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Pareto, V. Ophelimity in nonclosed cycles. In Giornale degli Economisti; Preferences, Utility, and Demand; Kirman, A.P., Chipman, J.S., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1906; pp. 370–385. [Google Scholar]
- Calborean, H.; Jahr, R.; Ungerer, T.; Vintan, L. Optimizing a superscalar system using multi-objective design space exploration. In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Control Systems and Computer Science (CSCS), Bucharest, Romania, 24–27 May 2011; Editura Politehnica Press: Bucharest, Romania, 2011; Volume 1, pp. 339–346. [Google Scholar]



| Obj. Function | Fuel Only | Fuel Heavy | Balanced | NOx Heavy | NOx Only | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weights | Actual | Norm. | Actual | Norm. | Actual | Norm. | Actual | Norm. | Actual | Norm. |
| Fuel | 1 | 1 | 300 | 0.997 | 100 | 0.99 | 33.33 | 0.97 | 0 | 0 |
| NOx | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0.003 | 1 | 0.01 | 1 | 0.03 | 1 | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Parkar, O.; Snyder, B.; Rahi, A.; Anwar, S. Modified Particle Swarm Optimization Based Powertrain Energy Management for Range Extended Electric Vehicle. Energies 2023, 16, 5082. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16135082
Parkar O, Snyder B, Rahi A, Anwar S. Modified Particle Swarm Optimization Based Powertrain Energy Management for Range Extended Electric Vehicle. Energies. 2023; 16(13):5082. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16135082
Chicago/Turabian StyleParkar, Omkar, Benjamin Snyder, Adibuzzaman Rahi, and Sohel Anwar. 2023. "Modified Particle Swarm Optimization Based Powertrain Energy Management for Range Extended Electric Vehicle" Energies 16, no. 13: 5082. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16135082
APA StyleParkar, O., Snyder, B., Rahi, A., & Anwar, S. (2023). Modified Particle Swarm Optimization Based Powertrain Energy Management for Range Extended Electric Vehicle. Energies, 16(13), 5082. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16135082







