Open-Winding Permanent Magnet Synchronous Generator for Renewable Energy—A Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
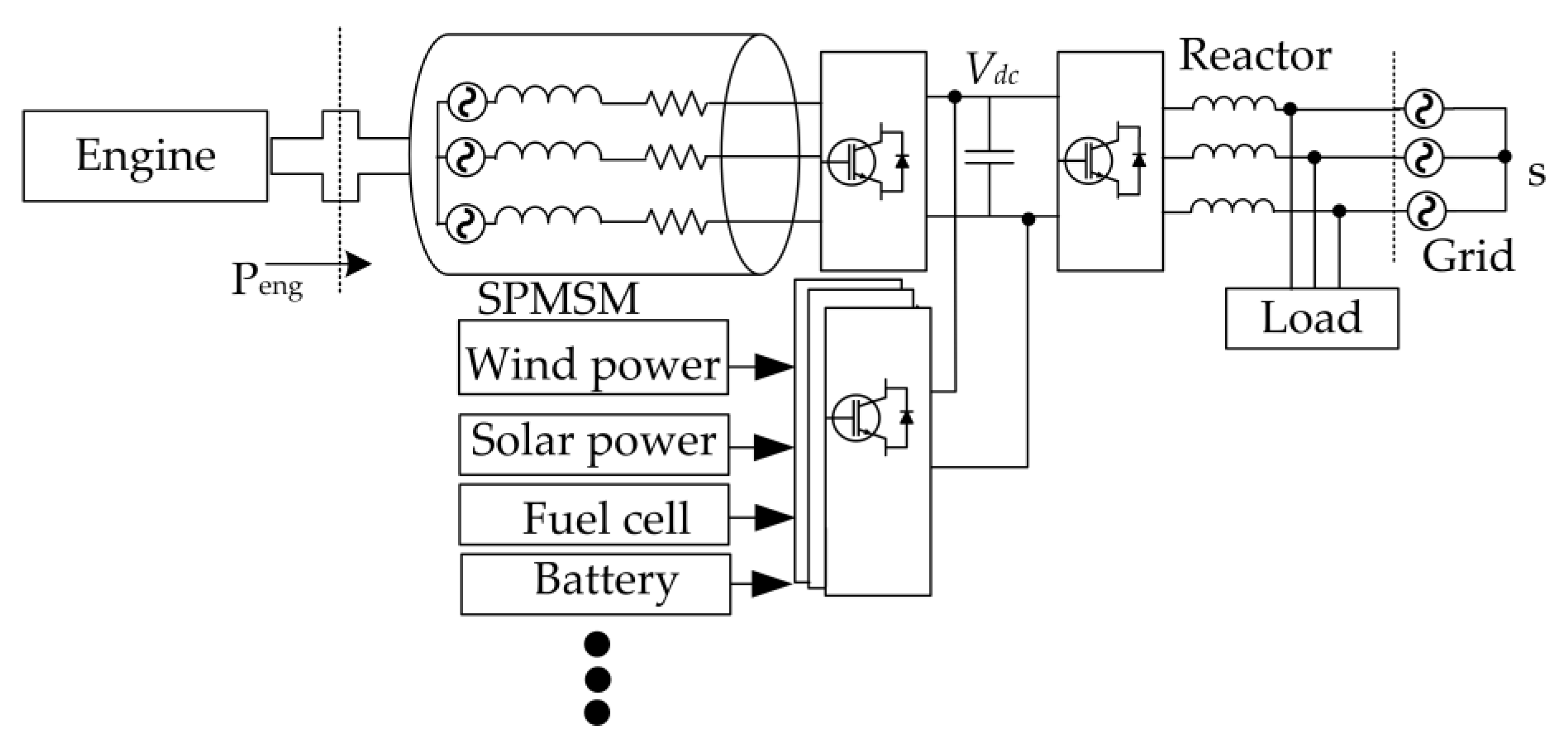
2. OW-PMSM Configurations
2.1. Isolated Two DC Buses
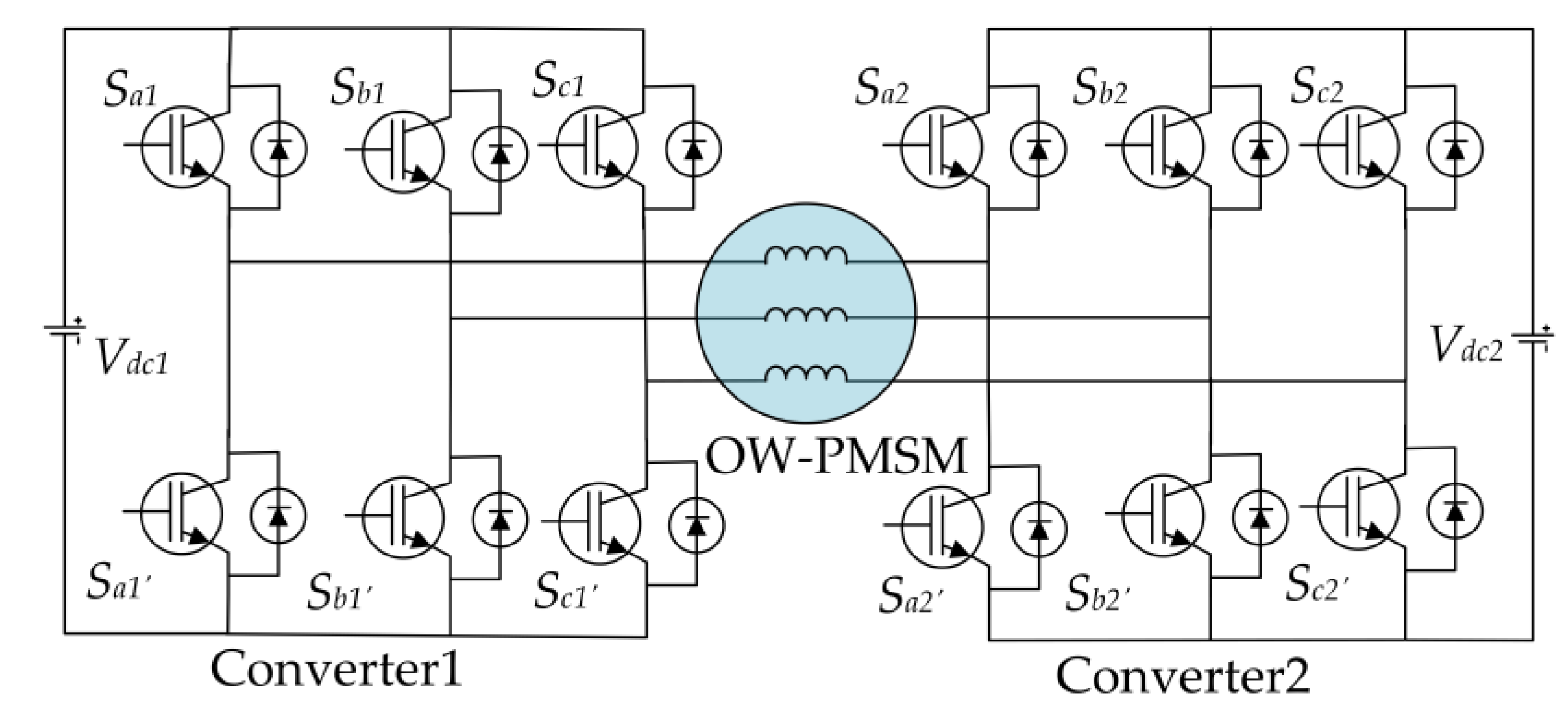
2.2. Common DC Bus
2.3. Floating Capacitor
2.4. Semi-Controlled
3. OW-PMSM with Common DC Bus
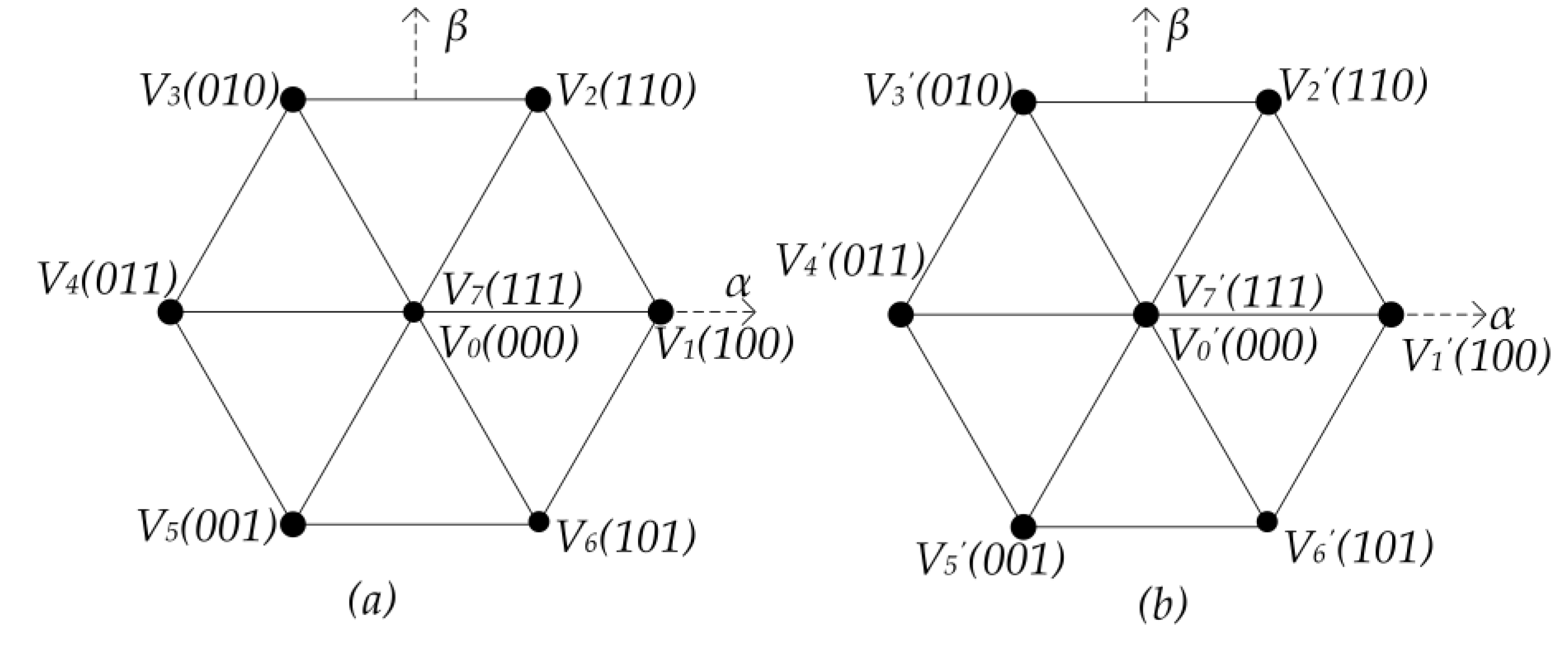
3.1. OW-PMSM Model
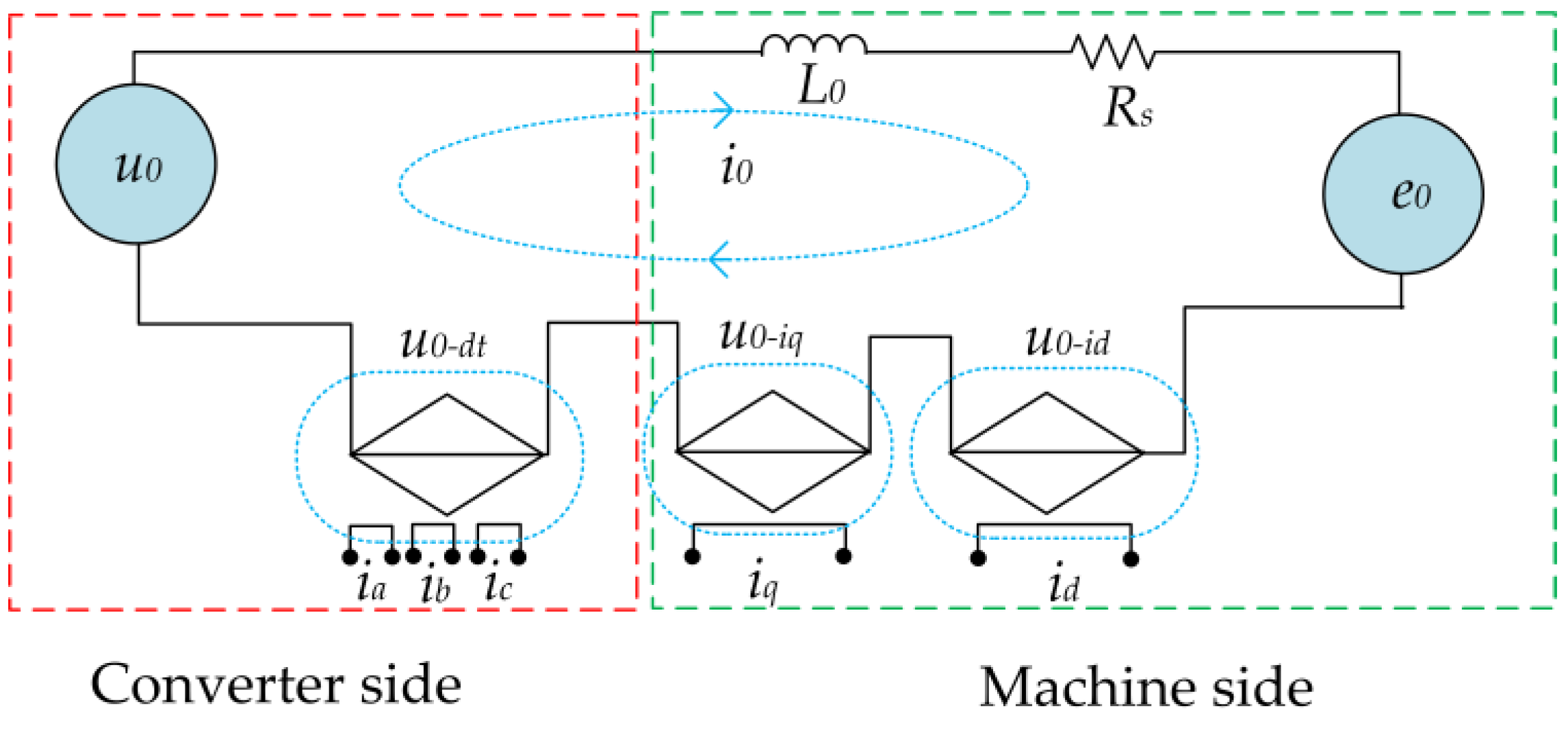
3.2. Zero-Sequence Equivalent Circuit
3.3. PWM Schemes for Eliminating ZSC
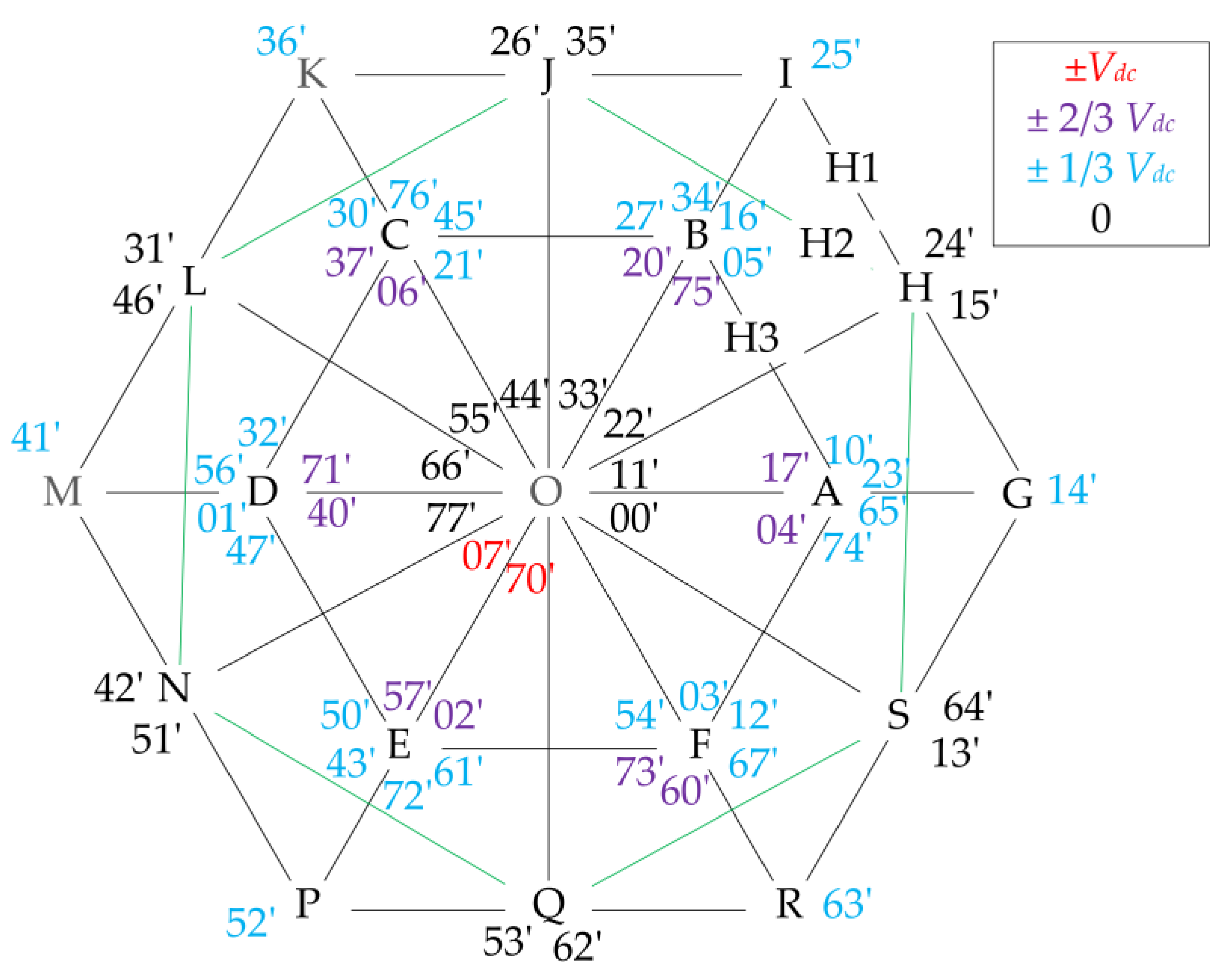

4. Control of OW-PMSM with a Common DC Bus
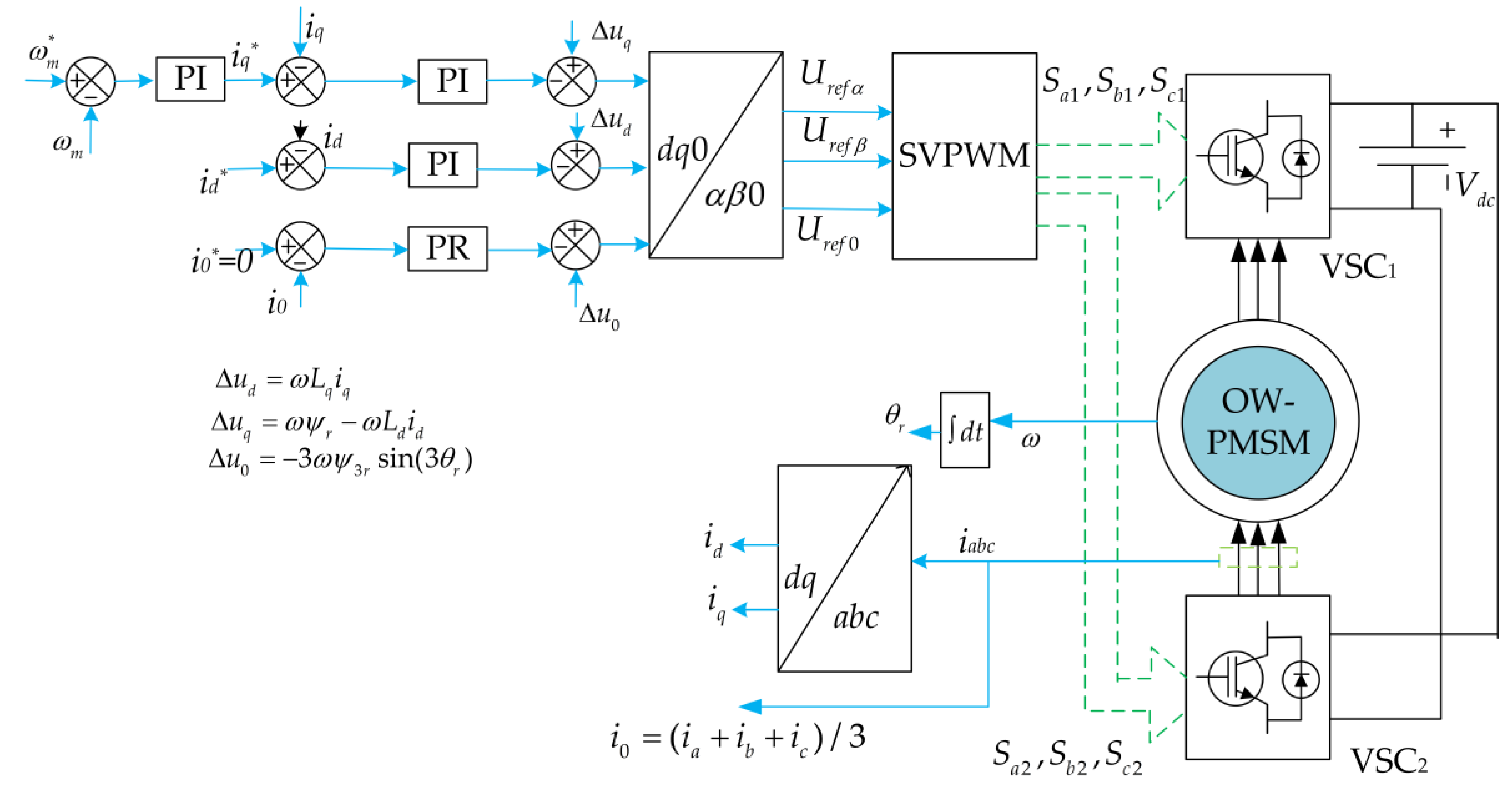
4.1. FOC-Based SVPWM Control
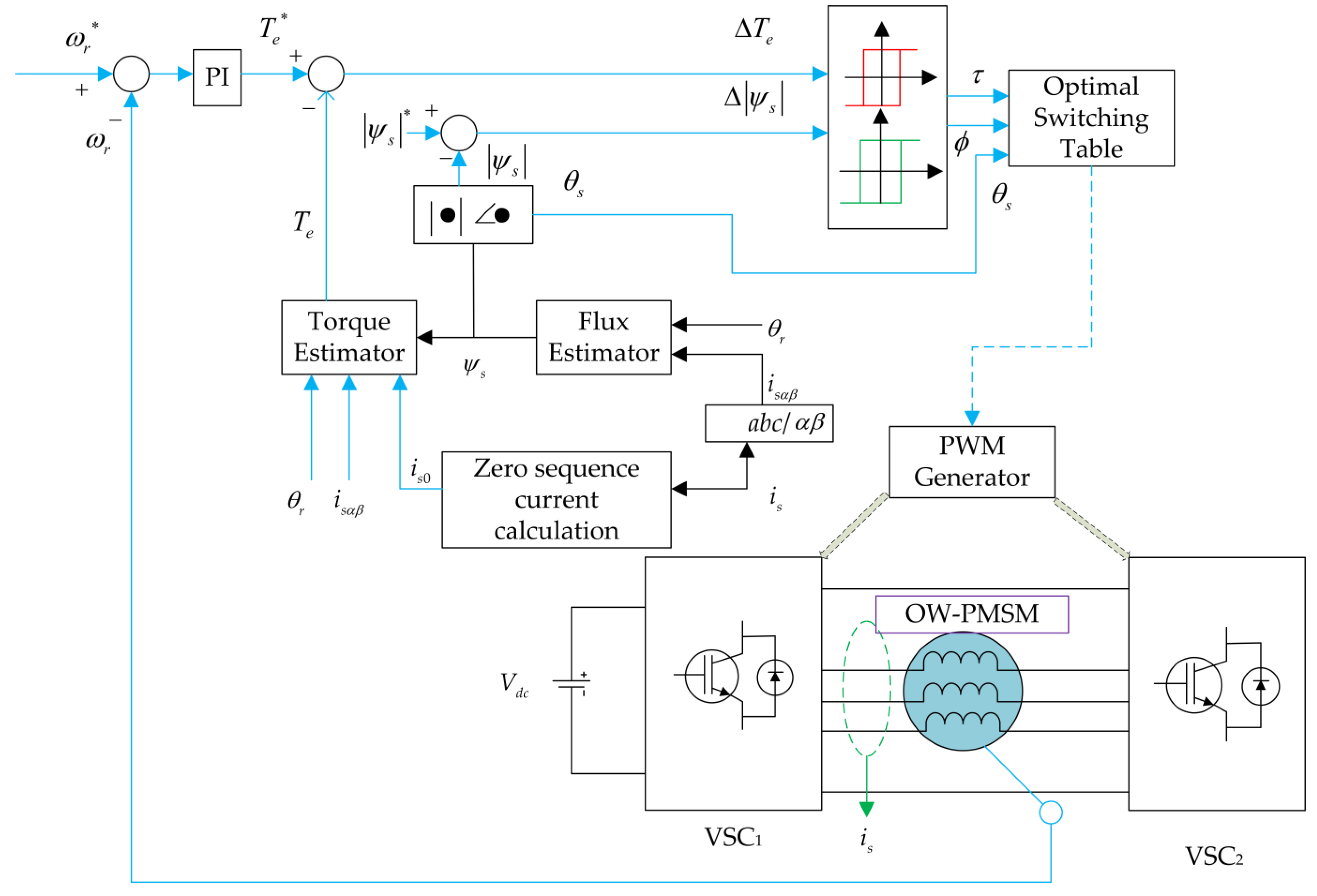
4.2. Direct Torque Control
4.3. MPC
4.4. Fault-Tolerant Control
5. Performance Comparison among Different Methods
6. Challenges and Future Direction for the OW-PMSM
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kawabata, Y.; Nasu, M.; Nomoto, T.; Ejiogu, E.C.; Kawabata, T. High-efficiency and low acoustic noise drive system using open-winding AC motor and two space-vector-modulated inverters. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2002, 49, 783–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corzine, K.A.; Sudhoff, S.D.; Whitcomb, C.A. Performance characteristics of a cascaded two-level converter. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 1999, 14, 433–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welchko, B.A.; Nagashima, J.M. The influence of topology selection on the design of EV/HEV propulsion systems. IEEE Power Electron. Lett. 2003, 1, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watthewaduge, G.; Toulabi, M.S.; Filizadeh, S.; Gole, A.M. Performance Analysis and Operating Limits of a Dual-Inverter Open-Winding IPMSM Drive. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2019, 34, 1655–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, M.; Sul, S. Control of an Open-Winding Machine in a Grid-Connected Distributed Generation System. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2008, 44, 1259–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Panda, D.; Lipo, T.A.; Pan, D. Open-Winding Power Conversion Systems Fed by Half-Controlled Converters. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2013, 28, 2427–2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Yang, T.; Giangrande, P.; Chowdhury, S.; Galea, M.; Wheeler, P. Enhanced performance of dual inverter with a floating capacitor for motor drive applications. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2020, 36, 6903–6916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Yang, T.; Giangrande, P.; Galea, M.; Wheeler, P. Technical review of dual inverter topologies for more electric aircraft applications. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2021, 8, 1966–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, S.; Wheeler, P.W.; Gerada, C.; Patel, C. Model Predictive Control for a Dual-Active Bridge Inverter with a Floating Bridge. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 5558–5568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Nian, H. Zero-sequence current suppression strategy of open-winding PMSG system with common DC bus based on zero vector redistribution. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 62, 3399–3408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Huang, W.; Wang, L. SVPWM Strategy Based on the Hysteresis Controller of Zero-Sequence Current for Three-Phase Open-End Winding PMSM. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2019, 34, 3474–3486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baiju, M.R.; Mohapatra, K.K.; Kanchan, R.S.; Gopakumar, K. A Dual Two-Level Inverter Scheme with Common Mode Voltage Elimination for an Induction Motor Drive. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2004, 19, 794–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Somasekhar, V.; Gopakumar, K.; Shivakumar, E. A space-vector modulation scheme for a dual two-level inverter fed open-end winding induction motor drive for the elimination of zero-sequence currents. EPE J. 2002, 12, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, W.; Nian, H.; Sun, D. Zero-Sequence Current Suppression Strategy With Reduced Switching Frequency for Open-End Winding PMSM Drives With Common DC BUS. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 66, 7613–7623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovere, L.; Formentini, A.; Calzo, G.L.; Zanchetta, P.; Cox, T. Zero-Sequence Voltage Elimination for Dual-Fed Common DC-Link Open-End Winding PMSM High-Speed Starter–Generator—Part I: Modulation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2019, 55, 7804–7812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, H.; Zhu, Z.; Odavic, M.; Li, Y. A novel zero-sequence model-based sensorless method for open-winding PMSM with common DC bus. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 6777–6789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nian, H.; Hu, W. A sensorless drive strategy for open-end winding PMSM with common DC voltage based on lower switching frequency. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2019, 34, 1553–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, H.; Zhu, Z.; Odavic, M. Nonparametric sensorless drive method for open-winding PMSM based on zero-sequence back EMF with circulating current suppression. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2016, 32, 3808–3817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Huang, W.; Jiang, W.; Zhao, Y.; Dong, D.; Wu, X. Direct torque control for three-phase open-end winding PMSM with common DC bus based on duty ratio modulation. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2019, 35, 4216–4232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Chen, W.; Cheng, Y.; Nian, H. Improved direct torque control for open-winding PMSM system considering zero-sequence current suppression with low switching frequency. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2020, 36, 4440–4451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, M.S.; Song, W.; Yu, B.; Xie, Z.; Feng, X. Low-complexity deadbeat model predictive current control for open-winding PMSM drive with zero-sequence current suppression. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2021, 7, 2671–2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Huang, W.; Jiang, W.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, X.; Zhu, S. Predictive torque control for open-end winding PMSM with common DC bus based on weighting factorless and finite control set optimization. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2019, 9, 1479–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, W.; Xu, C.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Gao, D. 3-D vector-based model predictive current control for open-end winding PMSG system with zero-sequence current suppression. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2019, 9, 242–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, K.; Zhang, W.; Gao, D. Model predictive control of the open-winding PMSG system based on three-dimensional reference voltage-vector. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 67, 6312–6322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Localzo, G.; El Murr, G.; Wang, J.; Griffo, A.; Gerada, C.; Cox, T. Overall assessments of dual inverter open winding drives. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Electric Machines & Drives Conference (IEMDC), Coeur d’Alene, ID, USA, 10–13 May 2015; pp. 1029–1035. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Lipo, T.A.; Pan, D. Half-controlled-converter-fed open-winding permanent magnet synchronous generator for wind applications. In Proceedings of the 14th International Power Electronics and Motion Control Conference EPE-PEMC 2010, Ohrid, North Macedonia, 6–8 September 2010; pp. T4-123–T4-126. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, C.; Sun, D.; Zheng, Z.; Nian, H. Simplified Model Predictive Control for Dual Inverter-Fed Open-Winding Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2018, 33, 1846–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casadei, D.; Grandi, G.; Lega, A.; Rossi, C.; Zarri, L. Switching Technique for Dual-Two level Inverter Supplied by Two Separate Sources. In Proceedings of the APEC 07—Twenty-Second Annual IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition, Anaheim, CA, USA, 25 February–1 March 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Ruan, C.; Nian, H.; Sun, D. Zero-Sequence Current Suppression Strategy With Common-Mode Voltage Control for Open-End Winding PMSM Drives with Common DC Bus. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2021, 68, 4691–4702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, H.; Zhu, Z.-Q.; Odavic, M. Analysis and Suppression of Zero Sequence Circulating Current in Open Winding PMSM Drives with Common DC Bus. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2017, 53, 3609–3620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Tan, C.; Farshadnia, M.; Fletcher, J.E. Postfault Zero-Sequence Current Injection for Open-Circuit Diode/Switch Failure in Open-End Winding PMSM Machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 66, 5124–5132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Y.; Zhu, X.; Si, X.; Lee, C.H.T. Fault-Tolerant Control for Multiple Open-Leg Faults in Open-End Winding Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor System Based on Winding Reconnection. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2021, 36, 6068–6078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Yang, T.; Giangrande, P.; Chowdhury, S.; Galea, M.; Wheeler, P. An Active Modulation Scheme to Boost Voltage Utilization of the Dual Converter With a Floating Bridge. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 66, 5623–5633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, S.; Wheeler, P.W.; Patel, C.; Gerada, C. A Multilevel Converter with a Floating Bridge for Open-End Winding Motor Drive Applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 5366–5375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oto, Y.; Noguchi, T.; Sasaya, T.; Yamada, T.; Kazaoka, R. Space Vector Modulation of Dual-Inverter System Focusing on Improvement of Multilevel Voltage Waveforms. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 66, 9139–9148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Wang, X.; Xiao, D.; Meng, X.; Mao, Y.; Wang, Z. A Novel Two-Mode Inverter Based Open-Winding PMSM Drive and Its Modulation Strategies. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2023, 38, 8762–8774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh Majumder, M.; Rakesh, R.; Gopakumar, K.; Umanand, L.; Al-Haddad, K.; Jarzyna, W. A Fault-Tolerant Five-Level Inverter Topology with Reduced Component Count for OEIM Drives. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2021, 9, 961–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Zhao, P.; Xu, D.; Chen, Z.; Zhu, J. Hybrid Modulation Fault-Tolerant Control of Open-End Windings Linear Vernier Permanent-Magnet Motor With Floating Capacitor Inverter. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2019, 34, 2563–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Nian, H. Current Zero-Crossing Duration Reduction of a Semicontrolled Open-Winding PMSG System Based on Third Harmonic Current Injection. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 750–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivas, S.; Kalaiselvi, J. Pulse width modulation schemes enabling single DC power source driven dual two-level voltage source inverter with single voltage source inverter switching. IET Power Electron. 2014, 7, 1181–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandulescu, P.; Meinguet, F.; Kestelyn, X.; Semail, E.; Bruyere, A. Control Strategies for Open-End Winding Drives Operating in the Flux-Weakening Region. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2014, 29, 4829–4842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rovere, L.; Formentini, A.; Calzo, G.L.; Zanchetta, P.; Cox, T. Zero-Sequence Voltage Elimination for Dual-Fed Common DC-Link Open-End Winding PMSM High-Speed Starter-Generator—Part II: Deadtime Hysteresis Control of Zero-Sequence Current. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2019, 55, 7813–7821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, L.; Zhu, Z. Modeling and compensation of inverter nonlinearity effects in carrier signal injection-based sensorless control methods from positive sequence carrier current distortion. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition, Atlanta, GA, USA, 12–16 September 2010; pp. 3434–3441. [Google Scholar]
- Somasekhar, V.T.; Srinivas, S.; Kumar, K.K. Effect of Zero-Vector Placement in a Dual-Inverter Fed Open-End Winding Induction Motor Drive with Alternate Sub-Hexagonal Center PWM Switching Scheme. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2008, 23, 1584–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somasekhar, V.T.; Srinivas, S.; Kumar, K.K. Effect of Zero-Vector Placement in a Dual-Inverter Fed Open-End Winding Induction-Motor Drive with a Decoupled Space-Vector PWM Strategy. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2008, 55, 2497–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somasekhar, V.; Gopakumar, K.; Pittet, A.; Ranganathan, V. PWM inverter switching strategy for a dual two-level inverter fed open-end winding induction motor drive with a switched neutral. IEE Proc.-Electr. Power Appl. 2002, 149, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Somasekhar, V.; Gopakumar, K.; Baiju, M. Dual two-level inverter scheme for an open-end winding induction motor drive with a single DC power supply and improved DC bus utilisation. IEE Proc.-Electr. Power Appl. 2004, 151, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Somasekhar, V.; Srinivas, S.; Gopakkumar, K. A space vector based PWM switching scheme for the reduction of common-mode voltages for a dual inverter fed open-end winding induction motor drive. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE 36th Power Electronics Specialists Conference, Recife, Brazil, 12–16 June 2005; pp. 816–821. [Google Scholar]
- Stemmler, H.; Guggenbach, P. Configurations of high-power voltage source inverter drives. In Proceedings of the 1993 Fifth European Conference on Power Electronics and Applications, Brighton, UK, 13–16 September 1993; pp. 7–14. [Google Scholar]
- Shivakumar, E.; Gopakumar, K.; Sinha, S.; Pittet, A.; Ranganathan, V. Space vector PWM control of dual inverter fed open-end winding induction motor drive. In Proceedings of the APEC 2001, Sixteenth Annual IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition (Cat. No. 01CH37181), Anaheim, CA, USA, 4–8 March 2001; pp. 399–405. [Google Scholar]
- Srinivas, S.; Somasekhar, V. Space-vector-based PWM switching strategies for a three-level dual-inverter-fed open-end winding induction motor drive and their comparative evaluation. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2008, 2, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, P.; Narasimharaju, B.L.; Srikanth, N.V. Space-vector pulse width modulation scheme for open-end winding induction motor drive configuration. IET Power Electron. 2015, 8, 1083–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Jiang, D.; Zhu, L.; Xu, Y.; Zou, T.; Liu, Z.; Qu, R. A Novel Zero-Sequence Current Elimination PWM Scheme for an Open-Winding PMSM With Common DC Bus. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2019, 34, 12476–12490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Nian, H.; Zheng, T. Torque ripple suppression method with reduced switching frequency for open-winding PMSM drives with common DC bus. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 66, 674–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darijević, M. Modulation and Control Strategies for Multilevel Five-Phase Open-End Winding Drives; Liverpool John Moores University: Merseyside, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Somani, A.; Gupta, R.K.; Mohapatra, K.K.; Mohan, N. On the Causes of Circulating Currents in PWM Drives with Open-End Winding AC Machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2013, 60, 3670–3678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; He, Y. A novel model predictive current control method for open-winding PMSG fed by dual inverter. In Proceedings of the 2018 21st International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (ICEMS), Jeju, Republic of Korea, 7–10 October 2018; pp. 1450–1454. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Y.; Sun, D.; Chen, W.; Nian, H. Model predictive current control for an open-winding PMSM system with a common DC bus in 3-D space. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2020, 35, 9597–9607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Shang, J. Three-dimension space vector based finite control set method for OW-PMSM with zero-sequence current suppression and switching frequency reduction. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2021, 36, 14074–14086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, S. Torque Ripple Suppression for Open-End Winding Permanent-Magnet Synchronous Machine Drives with Predictive Current Control. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020, 67, 1771–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, K. Current Prediction Based Zero Sequence Current Suppression Strategy for the Semicontrolled Open-Winding PMSM Generation System with a Common DC Bus. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 65, 6066–6076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, C.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, C. An Improved Deadbeat Predictive Current Control Scheme for Open-Winding Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors Drives with Disturbance Observer. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2021, 36, 4622–4632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Q.; Liu, J.; Peng, Z.; Sun, L.; Sun, L. Dual-space vector control of open-end winding permanent magnet synchronous motor drive fed by dual inverter. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2016, 31, 8329–8342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalaiselvi, J.; Srinivas, S. Bearing currents and shaft voltage reduction in dual-inverter-fed open-end winding induction motor with reduced CMV PWM methods. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 62, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muetze, A.; Tamminen, J.; Ahola, J. Influence of motor operating parameters on discharge bearing current activity. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2011, 47, 1767–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Song, Z.; Wang, W.; Liu, C. Improved Zero-Sequence Current Hysteresis Control Based-Space Vector Modulation for Open-End Winding PMSM Drives with Common DC Bus. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2022, 70, 10755–10760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, N.M.; Priestley, M.; Dutta, R.; Fletcher, J.E. Torque ripple minimization in dual inverter open-end winding PMSM drives with non-sinusoidal back-EMFs by harmonic current suppression. In Proceedings of the IECON 2016-42nd Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Florence, Italy, 23–26 October 2016; pp. 2975–2980. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, Y.; Zhu, Z.-Q. Reduction of both harmonic current and torque ripple for dual three-phase permanent-magnet synchronous machine using modified switching-table-based direct torque control. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 62, 6671–6683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.V.P.; Kumar, T.V. Improvised direct torque control strategies of open end winding PMSM fed with multi-level inversion. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Industrial Technology (ICIT), Lyon, France, 19–22 February 2018; pp. 425–430. [Google Scholar]
- Meesala, R.E.K.; Thippiripati, V.K. An improved direct torque control of three-level dual inverter fed open-ended winding induction motor drive based on modified look-up table. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2019, 35, 3906–3917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaramasu, V.; Wu, B. Model Predictive Control of Wind Energy Conversion Systems; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelrahem, M.; Hackl, C.M.; Kennel, R.; Rodriguez, J. Efficient Direct-Model Predictive Control with Discrete-Time Integral Action for PMSGs. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2019, 34, 1063–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravi Eswar, K.M.; Kumar, K.V.P.; Vinay Kumar, T. Modified predictive torque and flux control for open end winding induction motor drive based on ranking method. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2018, 12, 463–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodumur Meesala, R.E.; Kunisetti, V.P.K.; Kumar Thippiripati, V. Enhanced Predictive Torque Control for Open End Winding Induction Motor Drive Without Weighting Factor Assignment. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2019, 34, 503–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Liu, C. Model predictive torque control of an open-end winding PMSM with reduced computation time. In Proceedings of the 2017 20th International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (ICEMS), Sydney, Australia, 11–14 August 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Huang, L.; Xu, D.; Liu, J.; Jin, J. Performance evaluation of two-vector-based model predictive current control of PMSM drives. Chin. J. Electr. Eng. 2018, 4, 65–81. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, M.; Zhang, S.; Li, X.; Zhang, C.; Zhou, Y. Parameter Robust Deadbeat Predictive Current Control for Open-Winding Surface Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors Drives. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2023, 11, 3117–3126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhang, S.; Cui, X.; Zhang, C.; Li, X. An accurate torque output method for open-end winding permanent magnet synchronous motors drives. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2021, 36, 3470–3480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, C.; Li, X.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, S. An Improved Model-Free Predictive Current Control Scheme for Open-Winding PMSM with Common DC Bus. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2022, 2224, 012113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Liu, C.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, H. Model predictive two-target current control for OW-PMSM. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2020, 36, 3224–3235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, W. Model Predictive Full-Torque Control for the Open-Winding PMSM System Driven by Dual Inverter with a Common DC Bus. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2021, 9, 1541–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welchko, B.A.; Lipo, T.A.; Jahns, T.M.; Schulz, S.E. Fault Tolerant Three-Phase AC Motor Drive Topologies: A Comparison of Features, Cost, and Limitations. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2004, 19, 1108–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gandhi, A.; Corrigan, T.; Parsa, L. Recent Advances in Modeling and Online Detection of Stator Interturn Faults in Electrical Motors. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2011, 58, 1564–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Sun, J.; Li, H.; Lu, M.; Zeng, F. PMSM Open-Phase Fault-Tolerant Control Strategy Based on Four-Leg Inverter. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2020, 35, 2799–2808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Ruan, C.; Nian, H.; Sun, D. Simplified Modulation Scheme for Open-End Winding PMSM System with Common DC Bus under Open-Phase Fault Based on Circulating Current Suppression. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2020, 35, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Sun, D.; Wang, M.; Nian, H. Modeling and Control for Open-Winding PMSM under Open-Phase Fault Based on New Coordinate Transformations. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2021, 36, 6892–6902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Zhou, F.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, R.; Hu, S. Open-Phase Fault-Tolerant Predictive Control Strategy for Open-End-Winding Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machines Without Postfault Controller Reconfiguration. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2021, 68, 3770–3781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Gan, C.; Ni, K.; Yu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Shi, H.; Qu, R. Zero-Sequence Current Suppression Method for Fault-Tolerant OW-PMSM Drive with Asymmetric Zero-Sequence Voltage Injection. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2022, 70, 2351–2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xu, C. Second-time fault-tolerant topology and control strategy for the open-winding PMSM system based on shared bridge arm. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2020, 35, 12181–12193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muttalib, A.S.; Ferdous, S.; Saleque, A.M.; Hasan, N.M.A.; Chowdhury, M.M. Design and simulation of an inverter with high frequency sinusoidal PWM switching technique for harmonic reduction in a standalone/utility grid synchronized photovoltaic system. In Proceedings of the 2012 International Conference on Informatics, Electronics & Vision (ICIEV), Dhaka, Bangladesh, 18–19 May 2012; pp. 1168–1173. [Google Scholar]
- Na, R.; Wang, X. An improved vector-control system of PMSM based on fuzzy logic controller. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Symposium on Computer, Consumer and Control, Taichung, Taiwan, 10–12 June 2014; pp. 326–331. [Google Scholar]
- Bouzeria, H.; Fetha, C.; Bahi, T.; Abadlia, I.; Layate, Z.; Lekhchine, S. Fuzzy logic space vector direct torque control of PMSM for photovoltaic water pumping system. Energy Procedia 2015, 74, 760–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feng, G.; Lai, C.; Kar, N.C. A closed-loop fuzzy-logic-based current controller for PMSM torque ripple minimization using the magnitude of speed harmonic as the feedback control signal. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 64, 2642–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Gupta, R.; Bansal, A.K. Identification and control of PMSM using artificial neural network. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE International Symposium on Industrial Electronics, Vigo, Spain, 4–7 June 2007; pp. 30–35. [Google Scholar]
- Du, H.; Wen, G.; Cheng, Y.; Lü, J. Design and implementation of bounded finite-time control algorithm for speed regulation of permanent magnet synchronous motor. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020, 68, 2417–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Liu, H.; Ding, S. A speed control for a PMSM using finite-time feedback control and disturbance compensation. Trans. Inst. Meas. Control 2010, 32, 170–187. [Google Scholar]




| Methods | Paper | Num. of Candidate VVs | Number of Applied VVs | Calc. Time (µs) | Current THD | Torque Ripple |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MPCC | Conventional MPCC | 27 | 1 | Extremely high | high | high |
| [58] | 8 | 1 | Relatively low | high | high | |
| 8 | 3 | Moderate | low | low | ||
| [23] | 5–9 | 1 | Relatively low | high | high | |
| 5–9 | 3 | Moderate | low | low | ||
| [21] | (Offline calculation) | 1 | Lowest | Similar to conventional FCS-MPCC | Similar to conventional FCS-MPCC | |
| [24] (Semi-controlled) | 3 or 5 (Reduced from 49 VVs) | 2 | Relatively low | low | N/A | |
| [80] | 12 | 3 | Moderate | high (11.31% at rated speed) | High (23.5% At rated speed) | |
| MPTC | [22] | 6 | 3 | Moderate | low | low |
| [81] | 6 or 7 | 1 | Moderate (60.6 µs) | high | N/A |
| Methods | Swit. Freq. | Dyna- Mics | Param. Sensitivity | Calc. Time | SVPWM Modulator | Control Param. Tuning | Multi-Step Optimization | Paper | Current THD (Steady State) | Torque Ripple (Steady State) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SVPWM control | Fixed | Slower | Less sensitive | low | Required | PI and PR coefficient | Not supported | [10] | 4.39% | 1.79% |
| [14] | 7.75% | 10% | ||||||||
| [11] | 7.56% | N/A | ||||||||
| [54] | 54.8% | 1.15% | ||||||||
| [66] | 3.08% | N/A | ||||||||
| MPC | Variable | Faster | Sensitive | high | Not required | Not required for MPCC, required for MPTC if the cost function is related to both torque and flux | Supported | [60] | N/A | 2.5% |
| [58] | 8.06% | 10% | ||||||||
| [24] (Semi-Controlled) | 8.33% | N/A | ||||||||
| [81] | 30.31% | N/A | ||||||||
| [80] | 11.31% | 23.5% | ||||||||
| [61] (Semi-Controlled) | 9.28% | N/A | ||||||||
| [22] | 6.83% | 7.2% | ||||||||
| [23] | 13.38% | N/A | ||||||||
| DTC | Variable | Faster | Sensitive | low | May/may not require | Not required | Not supported | [19] | 7.04% | 5.0% |
| [20] | 16.3% | 14% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rahman, A.; Dutta, R.; Chu, G.; Xiao, D.; Thippiripati, V.K.; Rahman, M.F. Open-Winding Permanent Magnet Synchronous Generator for Renewable Energy—A Review. Energies 2023, 16, 5268. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16145268
Rahman A, Dutta R, Chu G, Xiao D, Thippiripati VK, Rahman MF. Open-Winding Permanent Magnet Synchronous Generator for Renewable Energy—A Review. Energies. 2023; 16(14):5268. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16145268
Chicago/Turabian StyleRahman, Abdur, Rukmi Dutta, Guoyu Chu, Dan Xiao, Vinay K. Thippiripati, and Muhammed F. Rahman. 2023. "Open-Winding Permanent Magnet Synchronous Generator for Renewable Energy—A Review" Energies 16, no. 14: 5268. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16145268
APA StyleRahman, A., Dutta, R., Chu, G., Xiao, D., Thippiripati, V. K., & Rahman, M. F. (2023). Open-Winding Permanent Magnet Synchronous Generator for Renewable Energy—A Review. Energies, 16(14), 5268. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16145268







