Factors and Kinetics Related to the Formation of Heavy Oil-in-Water Emulsions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Emulsification Experiments
2.3. Particle Size Analysis
3. Emulsification Rate and Kinetics Equation
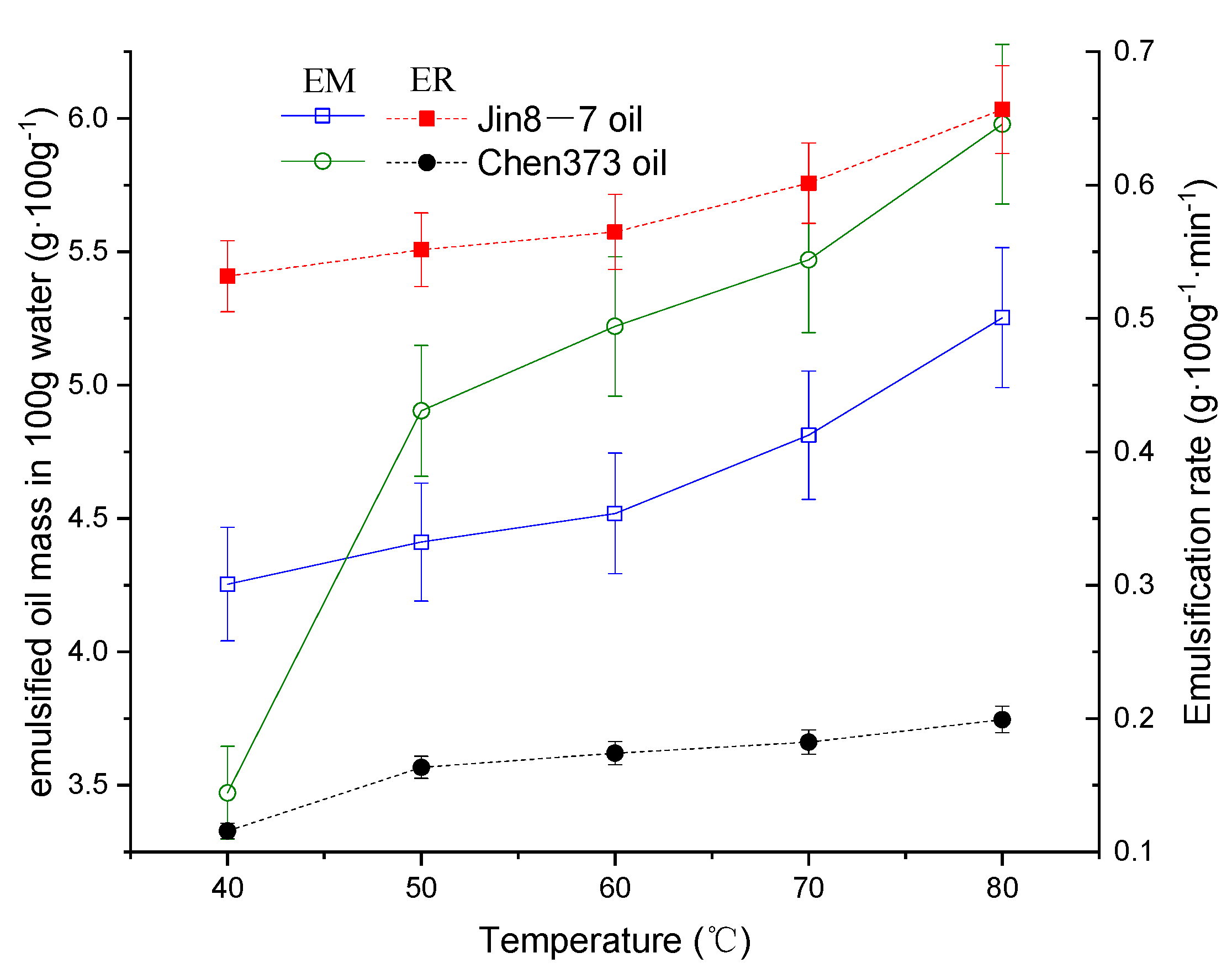
3.1. The Definition of Emulsification Rate
3.2. Kinetic Equation for the Emulsification Process
4. Results and Discussion
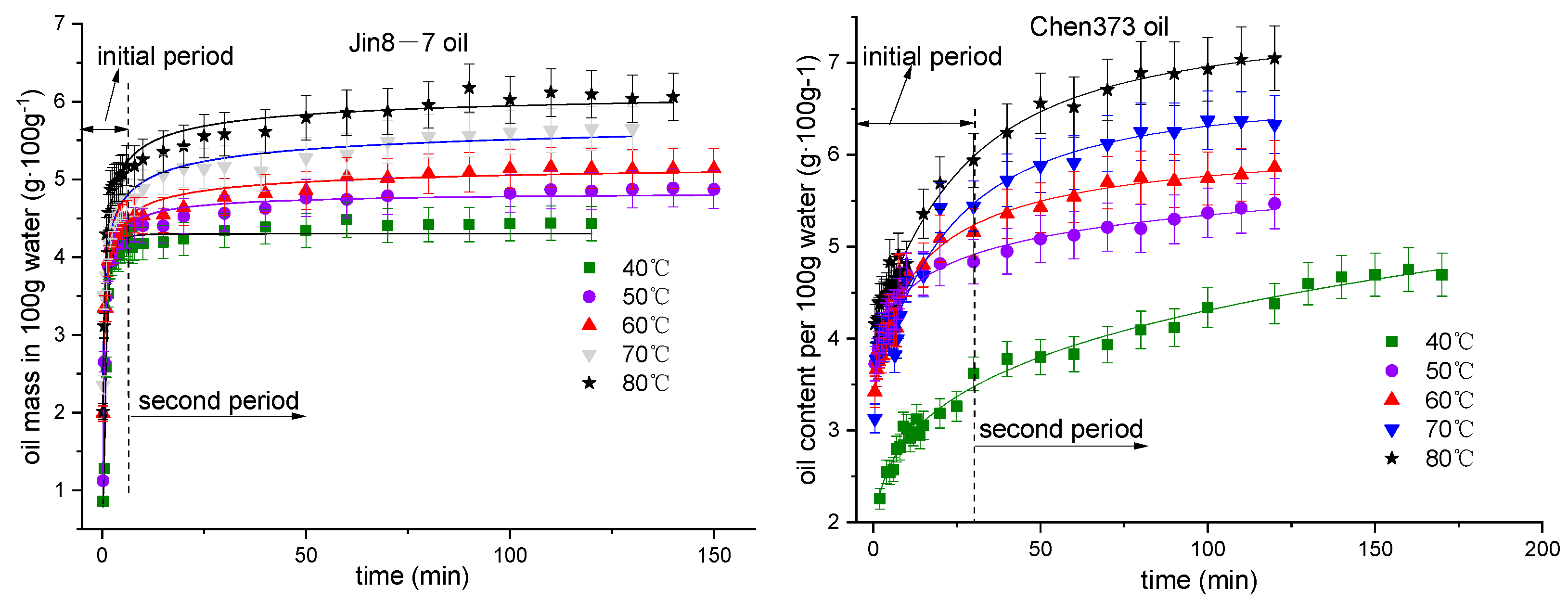
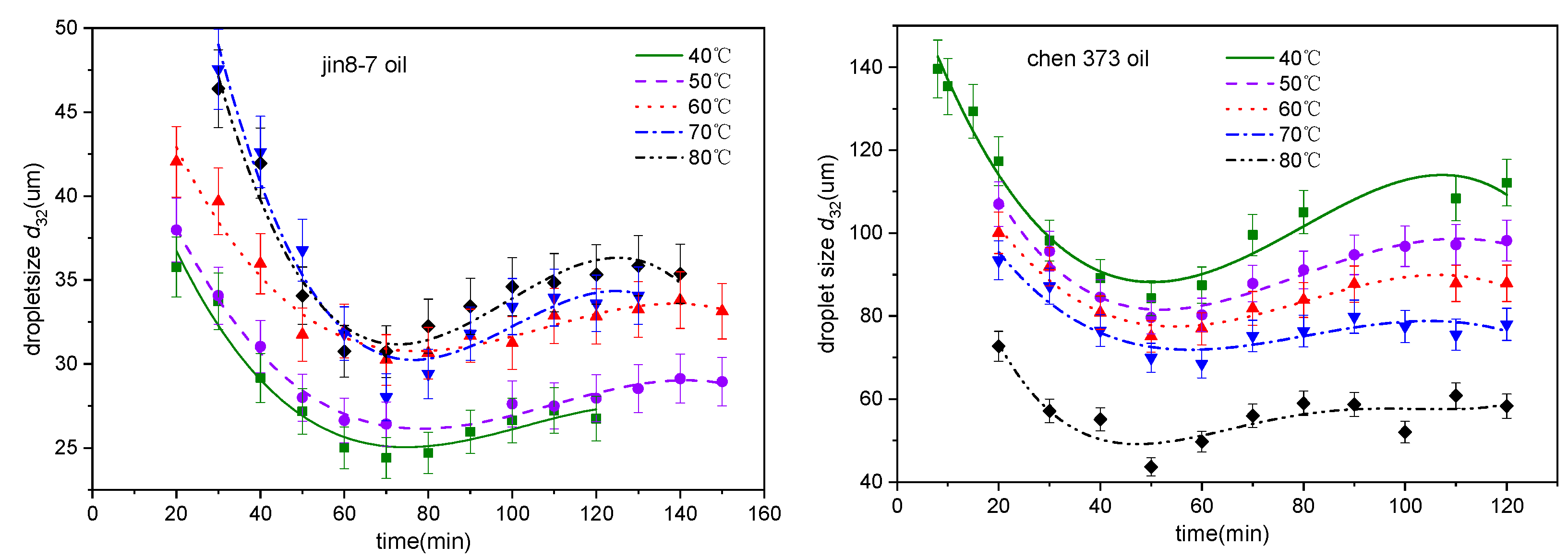
4.1. The Effect of Temperature on the Emulsification Process
4.2. The Effect of NaCl Concentration on the Emulsification Process
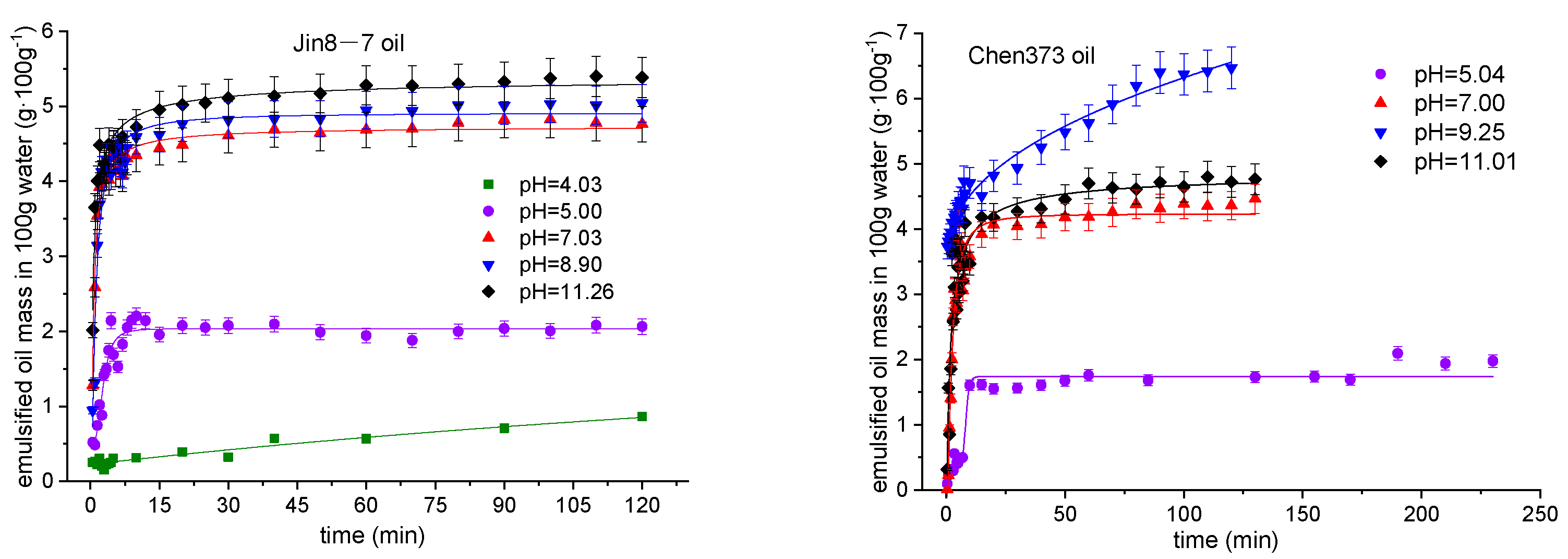
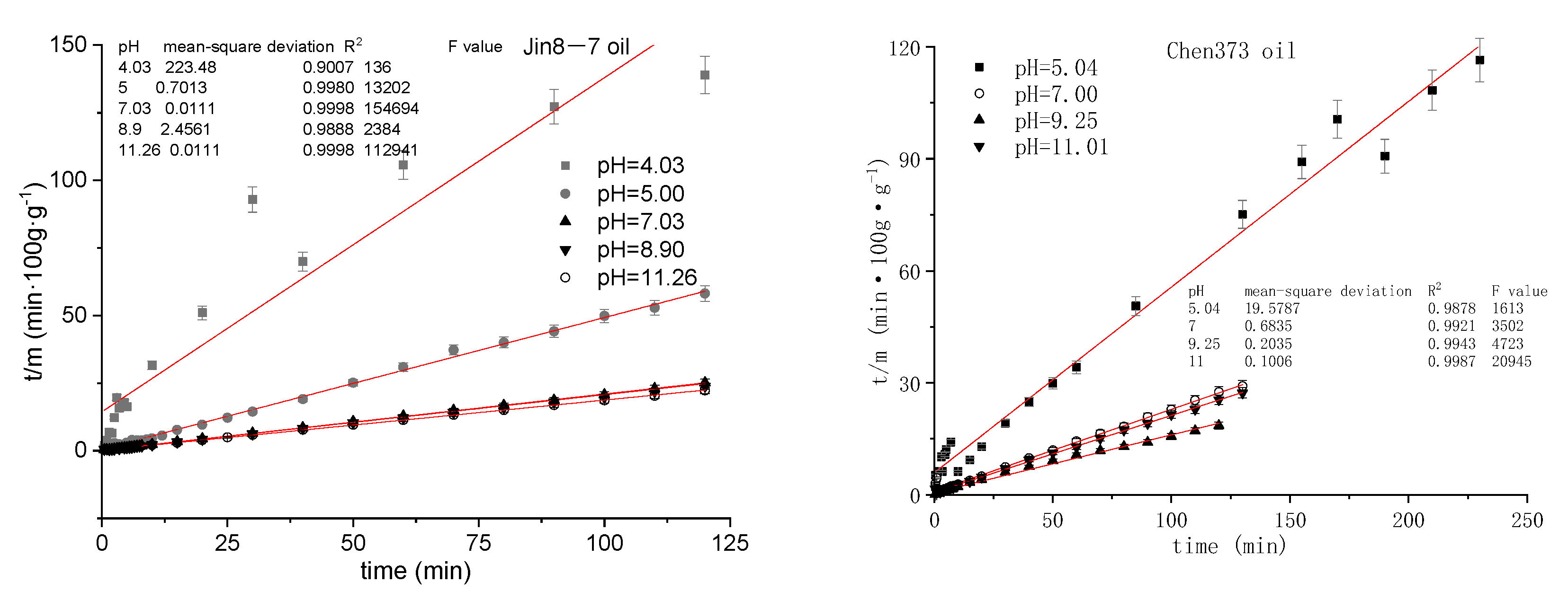
4.3. The Effect of pH on the Emulsification Process
4.4. Emulsification Mechanism
4.5. The Calculated Kinetic Equations for the Emulsification Process
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kang, W.; Xu, B.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Shan, X.; An, F.; Liu, J. Stability mechanism of W/O crude oil emulsion stabilized by polymer and surfactant. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2011, 384, 555–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, M.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, F.; Zhao, H.; Li, Z. A comparative study of the mechanism and performance of surfactant- and alkali-polymer flooding in heavy-oil recovery. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2020, 219, 115603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karambeigi, M.S.; Abbassi, R.; Roayaei, E.; Emadi, M.A. Emulsion flooding for enhanced oil recovery: Interactive optimization of phase behavior, microvisual and core-flood experiments. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 29, 382–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Dong, M.; Ding, B.; Yuan, Y. Experimental study on the effect of interfacial tension on the onformance control of oil-in-water emulsions in heterogeneous oil ands reservoirs. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2018, 89, 165–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryan, J.; Kantzas, A. Potential for Alkali-Surfactant Flooding in Heavy Oil Reservoirs Through Oil-in-Water Emulsification. J. Can. Pet. Technol. 2009, 48, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.; Zhu, T.; Huang, B.; Dai, T.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Liu, X. The efficiency of migration and profile control with emulsion systems in class III reservoirs. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2019, 6, 181634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Dong, M.; Yue, X.; Hou, J. Synergy of alkali and surfactant in emulsification of heavy oil in brine. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2006, 273, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Xue, S.; Zhang, J.; Han, Y.; Xia, S. Molecular Design of the Amphiphilic Polymer as a Viscosity Reducer for Heavy Crude Oil: From Mesoscopic to Atomic Scale. Energy Fuels 2021, 35, 1152–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.; Liu, J.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, J. Quadripolymers as Viscosity Reducers for Heavy Oil. Energy Fuels 2018, 32, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.; Fan, W.; Wang, Q.; Luo, H. Synthesis, Characterization, and Mechanism of Copolymer Viscosity Reducer for Heavy Oil. Energy Fuels 2019, 33, 4053–4061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Han, Y.; Yan, Z.; Chen, H.; Tan, Y. Fabricating a heavy oil viscosity reducer with weak interaction effect: Synthesis and viscosity reduction mechanism. Colloid Interface Sci. Commun. 2021, 42, 100426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, N.; Xia, S. Research progress and development trend of heavy oil emulsifying viscosity reducer: A review. Pet. Sci. Technol. 2021, 39, 550–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, W.; Shen, C.; Tang, X.; Pang, S.; Sun, D.; Mei, Z. Emulsification of acidic heavy oil for viscosity reduction and enhanced oil recovery. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2020, 41, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.; Balsamo, V. Emulsification of Heavy Oil in Aqueous Solutions of Poly(vinylalcohol): A Method for Reducing Apparent Viscosity of Production Fluids. Energy Fuels 2013, 27, 1736–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Jiang, H.; Fan, Z.; Xu, F.; Su, H.; Li, J. Formation and Flow Behaviors of in Situ Emulsions in Heavy Oil Reservoirs. Energy Fuels 2019, 33, 5961–5970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zheng, F.; Zhu, Y.; Han, S. Full and Partial Emulsification of Crude Oil−Water Systems as a Function of Shear Intensity, Water Fraction, and Temperature. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 9513–9520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yue, X.; Wang, Z.; Yan, R.; Guo, Y. Role of Emulsification and Interfacial Tension of a Surfactant for Oil Film Displacement. Energy Fuels 2021, 35, 3032–3041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Zhang, L.; Xie, L.; Lu, X.; Liu, Q.; Mantilla, C.A.; van den Berg, F.G.A.; Zeng, H. Interaction Mechanism of Oil-in-Water Emulsions with Asphaltenes Determined Using Droplet Probe AFM. Langmuir 2016, 32, 2302–2310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Babadagli, T. Comprehensive review on heavy-oil emulsions: Colloid science and practical applications. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2020, 228, 115962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, S. Interfacial chemistry in steam-based thermal recovery of oil sands bitumen with emphasis on steam-assisted gravity drainage and the role of chemical additives. Colloids Interf. 2018, 20, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y. Correlations between emulsification behaviors of crude oil-water systems and crude oil compositions. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2016, 146, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Li, C.; Zhang, X.; Yang, F.; Sun, G.; Yao, B.; Zhang, H. Polarity effects of asphaltene subfractions on the stability and interfacial properties of water-in-model oil emulsions. Fuel 2020, 269, 117450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourrel, M.; Passade-Boupat, N. Crude Oil Surface Active Species: Consequences for Enhanced Oil Recovery and Emulsion Stability. Energy Fuels 2018, 32, 2642–2652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Kang, W.; Yang, H.; Huang, Z.; Zhou, B.; Sarsenbekuly, B. Emulsification and stabilization mechanism of crude oil emulsion by surfactant synergistic amphiphilic polymer system. Colloids Surf. A 2021, 609, 125726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, Y.; Zhang, C.; Mahardika, M.A.; Patmonoaji, A.; Hu, Y.; Matsushita, S.; Suekane, T. Pore-scale study of in-situ surfactant flooding with strong oil emulsification in sandstone based on X-ray microtomography. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2021, 98, 247–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.; Tang, D. Effect of a type of spontaneous emulsification and viscosity reduction agent on the properties of heavy oil. Pet. Sci. Technol. 2018, 36, 781–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Lin, X.; Rui, Z.; Xu, M.; Zhan, S. The Role of Shearing Energy and Interfacial Gibbs Free Energy in the Emulsification Mechanism of Waxy Crude Oil. Energies 2017, 10, 721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alade, O.S.; Sasaki, K.; Sugai, Y.; Ademoji, B.; Kumasaka, J.; Ueda, R. Effect of Emulsification Process Conditions on the Properties of Water-in-Bitumen Emulsion. J. Jpn. Assoc. Pet. Technol. 2017, 82, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Luo, H.; Lon, Z. Emulsification behaviors of crude oil-water system and its quantitative relationship with exergy loss rate. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2019, 176, 502–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schalbart, P.; Kawaji, M. Comparison of paraffin nanoemulsions prepared by low-energy emulsification method for latent heat storage. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2013, 67, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, P.H.; Noïk, C.; Dalmazzone, C. Emulsion formation in a model choke-valve. In Proceedings of the SPE Annual Technical Conference—Society of Petroleum Engineering, New Orleans, LA, USA, 30 September–3 October 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Covis, R.; Marie, E.; Durand, A. Kinetics of Formation of Oil-in-Water Emulsions Using In Situ Rheo-Optical Measurements. AICHE J. 2015, 61, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadros, T.F. Emulsion Formation and Stability; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2013; p. 17. [Google Scholar]
- Morishita, R.; Matsuyama, R.; Ishiwata, T.; Tsuchiya, Y.; Giang, P.T.; Takahashi, S. Oil and Water Interactions during Low-Salinity Enhanced Oil Recovery in Water-Wet Porous Media. Energy Fuels 2020, 34, 5258–5266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, N.N.A.; Haber, A.; Graham, B.F.; Aman, Z.M.; May, E.F.; Fridjonsson, E.O.; Johns, M.L. Quantifying the Effect of Salinity on Oilfield Water-in-Oil Emulsion Stability. Energy Fuels 2018, 32, 10042–10049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarado, V.; Wang, X.; Moradi, M. Role of Acid Components and Asphaltenes in Wyoming Water-in-Crude Oil Emulsions. Energy Fuels 2011, 25, 4606–4613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eley, D.D.; Hey, M.J.; Symond, J.D. Emulsions of water in asphaltene-containing oils 1: Droplet size distribution and emulsification rates. Colloids Surf. 1988, 32, 87–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fingas, M. Water-in-Oil Emulsion Formation: A Review of Physics and Mathematical Modelling. Spill Sci. Technol. Bull. 1995, 2, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsuki, K.; Miyagawa, Y.; Matsuno, R.; Adachi, S. Evolution of the Size Distribution of Oil-droplets Over Time in Oil-in-water Emulsions. Jpn. J. Food Eng. 2015, 16, 231–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vankova, N.; Tcholakova, S.; Denkov, N.D.; Vulchev, V.D.; Danner, T. Emulsification in turbulent flow 2: Breakage rate constants. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2007, 313, 612–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tcholakova, S.; Denkov, N. Kinetics of drop breakage and drop-drop coalescence during emulsification in turbulent flow. In Proceedings of the Second International Conference “Advanced Functional Materials”, Nessebar, Bulgaria, 3–6 September 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, A.; Narsimhan, V.; Hatton, T.A.; Doyle, P.S. Kinetics of the Change in Droplet Size during Nanoemulsion Formation. Langmuir 2016, 32, 11551–11559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seekkuarachchi, I.N.; Tanaka, K.; Kumazawa, H. Formation and Charaterization of Submicrometer Oil-in-Water (O/W) Emulsions, Using High-Energy Emulsification. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2006, 45, 372–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covis, R.; Baravian, C.; Marie, E.; Durand, A. Kinetics of formation of polysaccharide-covered micrometric oildroplets under mechanical agitation. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2015, 466, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, M.C.; Berjano, M.; Guerrero, A.; Gallegos, C. Emulsification Rheokinetics of Nonionic Surfactant-Stabilized Oil-in-Water Emulsions. Langmuir 2001, 17, 5410–5416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mabille, C.; Leal-Calderon, F.; Bibette, J.; Schmitt, V. Monodisperse fragmentation in emulsions: Mechanisms and kinetics. Europhys. Lett. 2003, 5, 708–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caubet, S.; Le Guer, Y.; Grassl, B.; El Omari, K.; Normandin, E. A Low-Energy Emulsification Batch Mixer for Concentrated Oil-in-Water Emulsions. AICHE J. 2011, 57, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.-B.; Yue, X.-A.; Fu, J.Y.; Zhang, B. Relevance between Emulsification Capability and Interfacial Tension of Chemical Flooding Agents. Energy Fuels 2018, 32, 12345–12350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alotaibi, M.; Nasr-El-Din, H. Effect of brine salinity on reservoir fluids interfacial tension. In Proceedings of the SPE Europec featured at EAGE Conference and Exhibition? Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 8–11 June 2009; p. SPE-121569-MS. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, L.; Norton, I.T. Comparing droplet breakup for a high-pressure valve homogeniser and a Microfluidizer for the potential production of food-grade nanoemulsions. J. Food Eng. 2013, 114, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, L.L.; Niknafs, N.; Hancocks, R.D.; Norton, I.T. Emulsification: Mechanistic understanding. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 31, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Kang, W.; Wu, H.; Li, Z.; Chen, J.; Zhou, Q.; Bai, B. Study on the relationship between emulsion stability and droplet dynamics of a spontaneous emulsion for chemical enhanced oil recovery. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2018, 39, 1214–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, J.V.L.; Fryer, P.J.; Frith, W.J.; Norton, I.T. Emulsification mechanism and storage instabilities of hydrocarbon-in-water sub-micron emulsions stabilised with Tweens (20 and 80), Brij 96v and sucrose monoesters. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 338, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Wali, A. Effect of simple polar compounds and salinity on interfacial tension and wettability of rock/oil/brine system. J. King Saud. Univ. Eng. Sci. 1996, 8, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, H.H.; Zhang, G.C.; Ge, J.J.; Jin, L.C.; Liu, X.L. Analysis of microscopic displacement mechanisms of alkaline flooding for enhanced heavy-oil recovery. Energy Fuels 2011, 25, 4423–4429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wu, H.; Yang, M.; Jiang, J.; Xu, D.; Feng, H.; Lu, Y.; Kang, W.; Bai, B.; Hou, J. Spontaneous Emulsification via Once Bottom-Up Cycle for the Crude Oil in Low-Permeability Reservoirs. Energy Fuels 2018, 32, 3119–3126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashrafizadeh, S.N.; Kamran, M. Emulsification of heavy crude oil in water for pipeline transportation. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2010, 71, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, M.; Alvarado, V.; Huzurbazar, S. Effect of Salinity on Water-in-Crude Oil Emulsion: Evaluation through Drop-Size Distribution Proxy. Energy Fuels 2011, 25, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, M.; Zirrahi, M.; Hassanzadeh, H. An Analytical Model for Estimation of the Self-Diffusion Coefficient and Adsorption Kinetics of Surfactants Using Dynamic Interfacial Tension Measurements. J. Phys. Chem. B 2020, 124, 3206–3213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Dutcher, C.S. Size dependent droplet interfacial tension and surfactant transport in liquid–liquid systems, with applications in shipboard oily bilgewater emulsions. Soft Matter 2020, 16, 2994–3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nachtigall, S.; Zedel, D.; Kraume, M. Analysis of drop deformation dynamics in turbulent flow. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2016, 24, 264–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Politova, N.I.; Tcholakova, S.; Tsibranska, S.; Denkov, N.D.; Muelheims, K. Coalescence stability of water-in-oil drops: Effects of drop size and surfactant concentration. Colloids Surf. A 2017, 531, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudek, M.; Chicault, J.; Øye, G. Microfluidic Investigation of Crude Oil Droplet Coalescence: Effect of Oil/Water Composition and Droplet Aging. Energy Fuels 2020, 34, 5110–5120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Håkansson, A. Experimental methods for measuring coalescence during emulsification—A critical review. J. Food Eng. 2016, 178, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Oil Sample | Density /g·cm−3 | Petroleum Component Content/% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| w (Saturates) | w (Aromatics) | w (Resin) | w (Asphaltene) | ||
| Jin8-7 | 0.9523 | 45.18 | 28.68 | 25.36 | 0.63 |
| Chen373 | 1.0142 | 25.06 | 33.85 | 28.11 | 12.88 |
| Oil Sample | Components | w (H)/% | w (C)/% | w (N)/% | w (S)/% | w (O)/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jin8-7 | Resin | 10.97 | 86.06 | 0.82 | 0.48 | 1.67 |
| Asphaltene | 9.90 | 85.16 | 1.59 | 0.83 | 2.52 | |
| Chen373 | Resin | 9.27 | 80.18 | 1.20 | 6.61 | 2.74 |
| Asphaltene | 7.80 | 78.63 | 1.07 | 9.31 | 3.19 |
| Oil Sample | Temperature (℃) | pH | NaCl Content (wt%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| /(100 g · g−1 · min−1) | |||
| Jin8-7 | 0.2096 | 0.2170 | 0.2458 |
| Chen373 | 0.0642 | 0.0515 | 0.1209 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, J.; Zhao, W.; Lun, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, P.; Li, Y.; Sun, C. Factors and Kinetics Related to the Formation of Heavy Oil-in-Water Emulsions. Energies 2023, 16, 5499. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16145499
Liu J, Zhao W, Lun Z, Zhang Y, Zhang Q, Yang P, Li Y, Sun C. Factors and Kinetics Related to the Formation of Heavy Oil-in-Water Emulsions. Energies. 2023; 16(14):5499. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16145499
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Jinhe, Wei Zhao, Zengmin Lun, Yuhui Zhang, Qingxuan Zhang, Pujiang Yang, Yao Li, and Chengdi Sun. 2023. "Factors and Kinetics Related to the Formation of Heavy Oil-in-Water Emulsions" Energies 16, no. 14: 5499. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16145499
APA StyleLiu, J., Zhao, W., Lun, Z., Zhang, Y., Zhang, Q., Yang, P., Li, Y., & Sun, C. (2023). Factors and Kinetics Related to the Formation of Heavy Oil-in-Water Emulsions. Energies, 16(14), 5499. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16145499





