Accurate Modeling of CCS Combo Type 1 Cable and Its Communication Performance Analysis for High-Speed EV-EVSE Charging System
Abstract
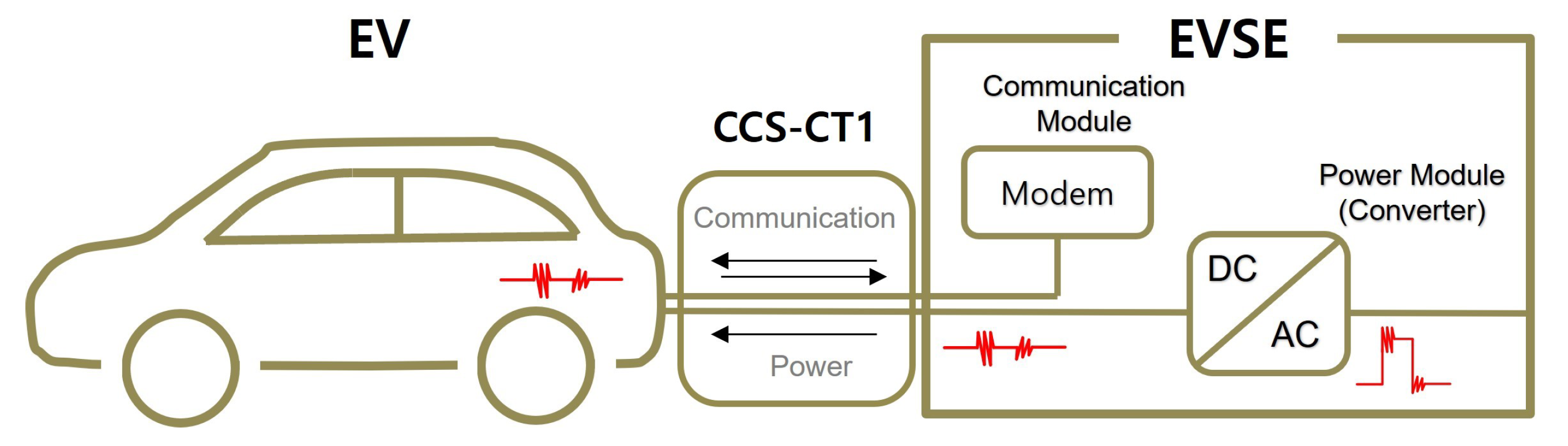
:1. Introduction
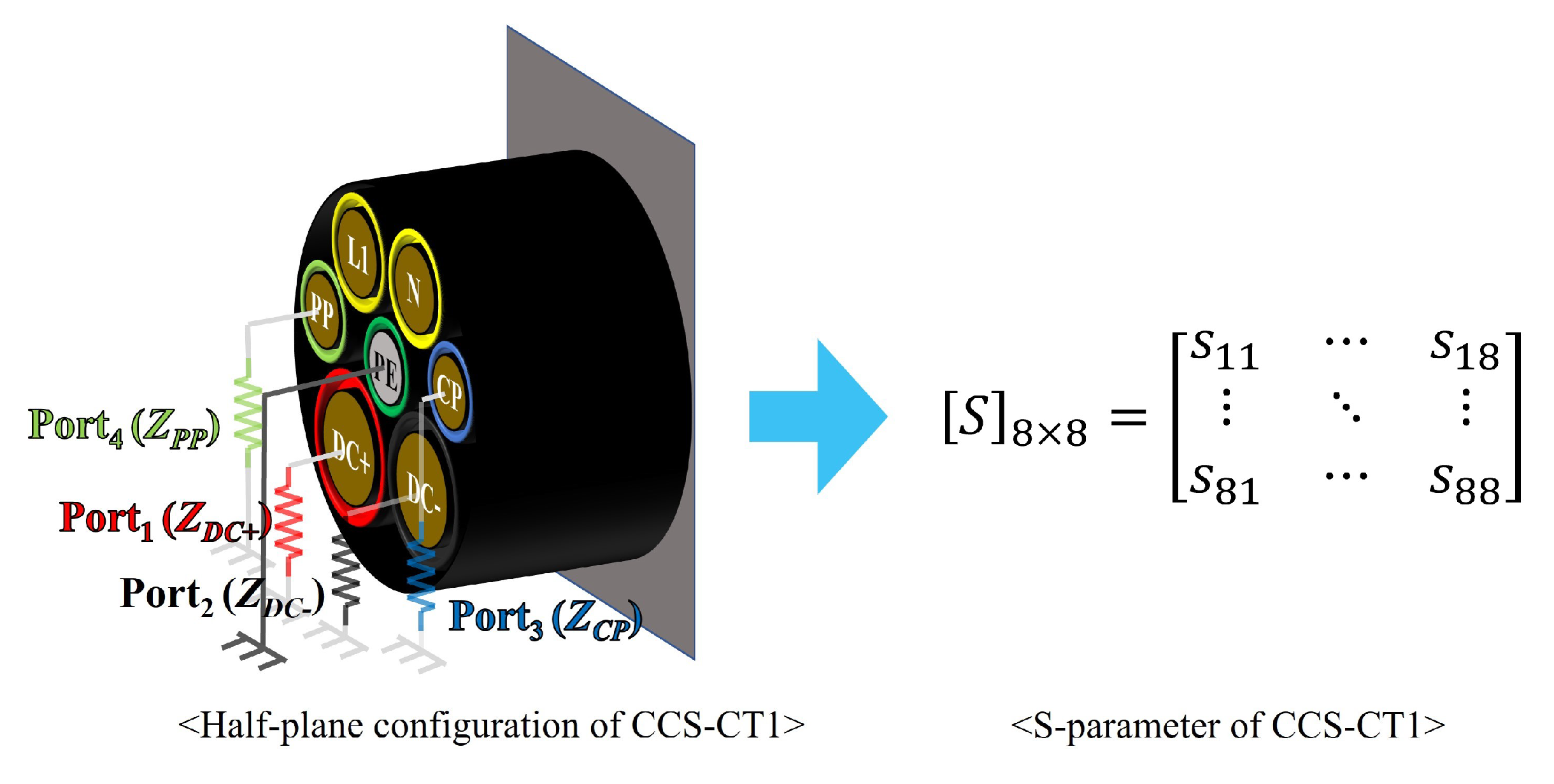
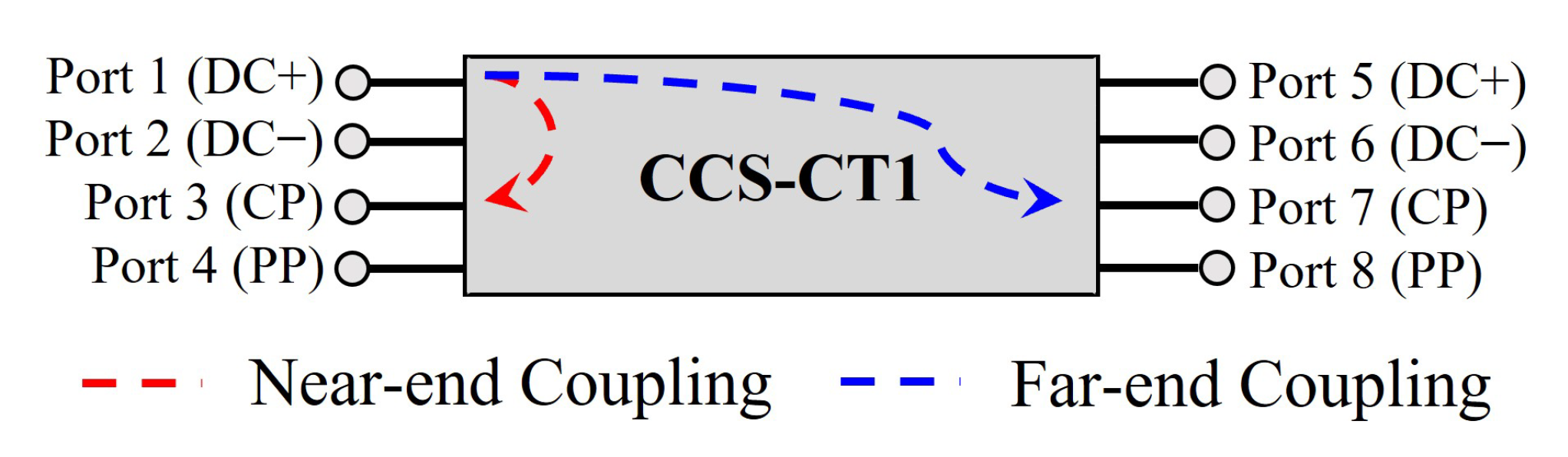
2. Measurement and Simulation Setup of CCS-CT1
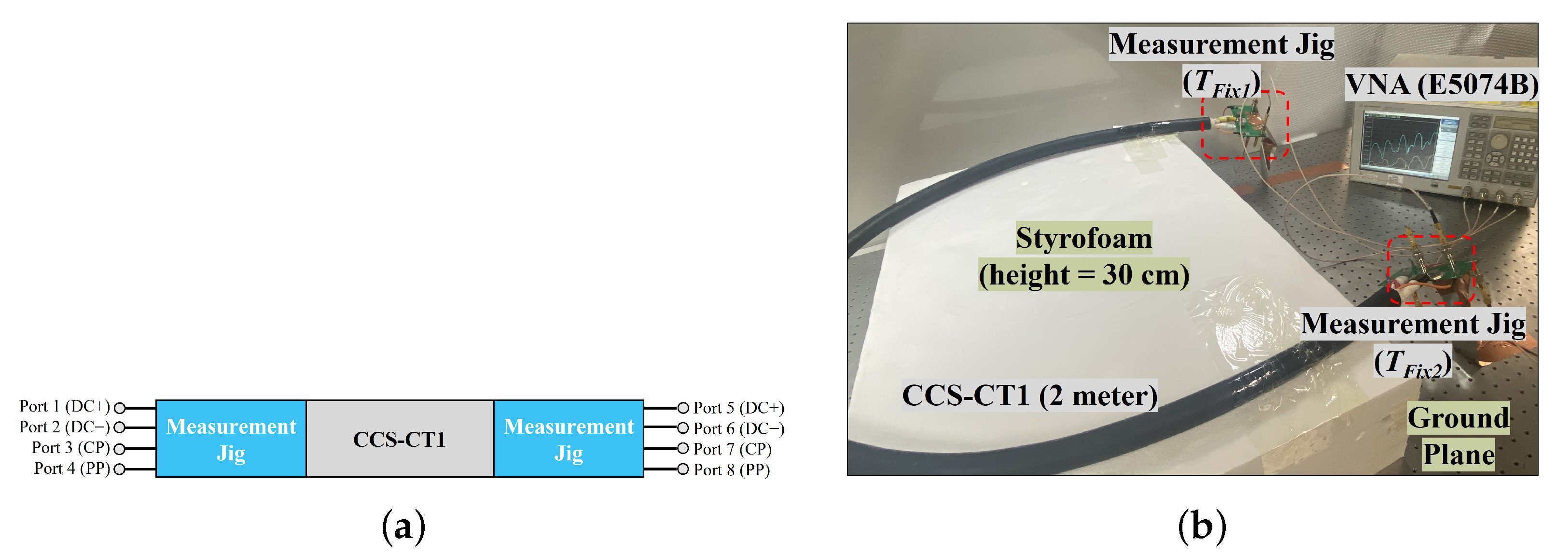
2.1. Fabrication of Measurement JIG for CCS-CT1
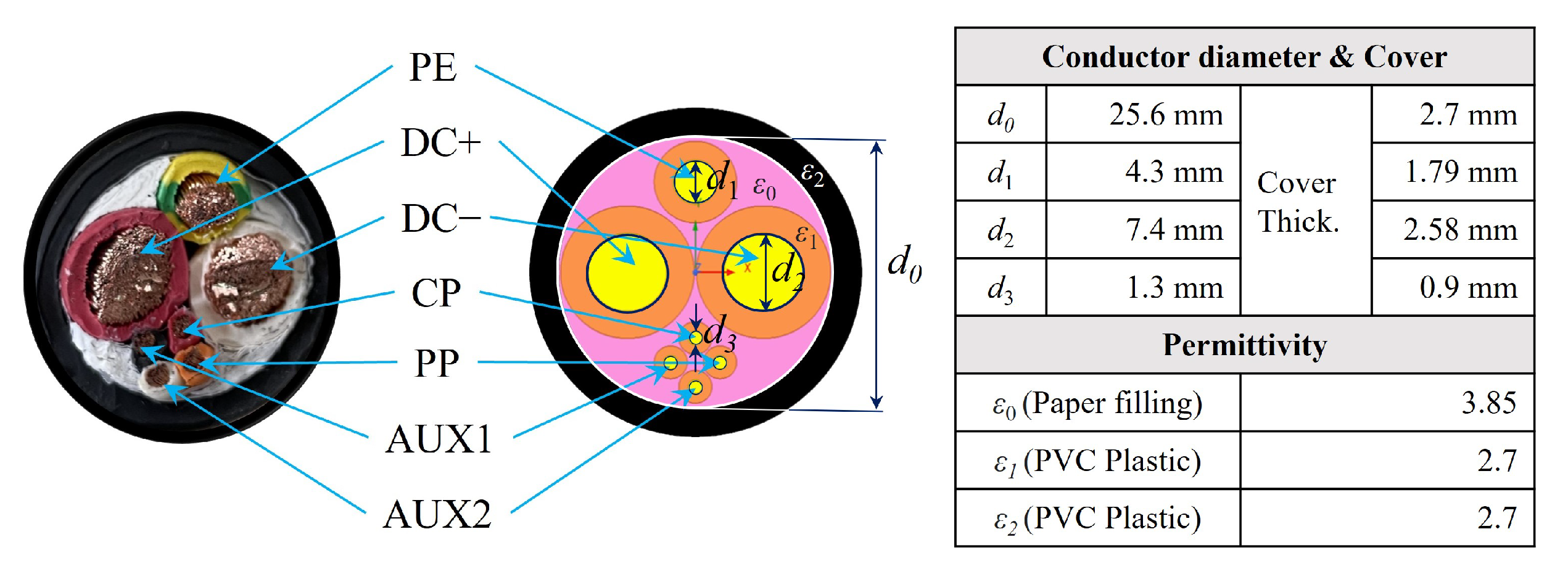
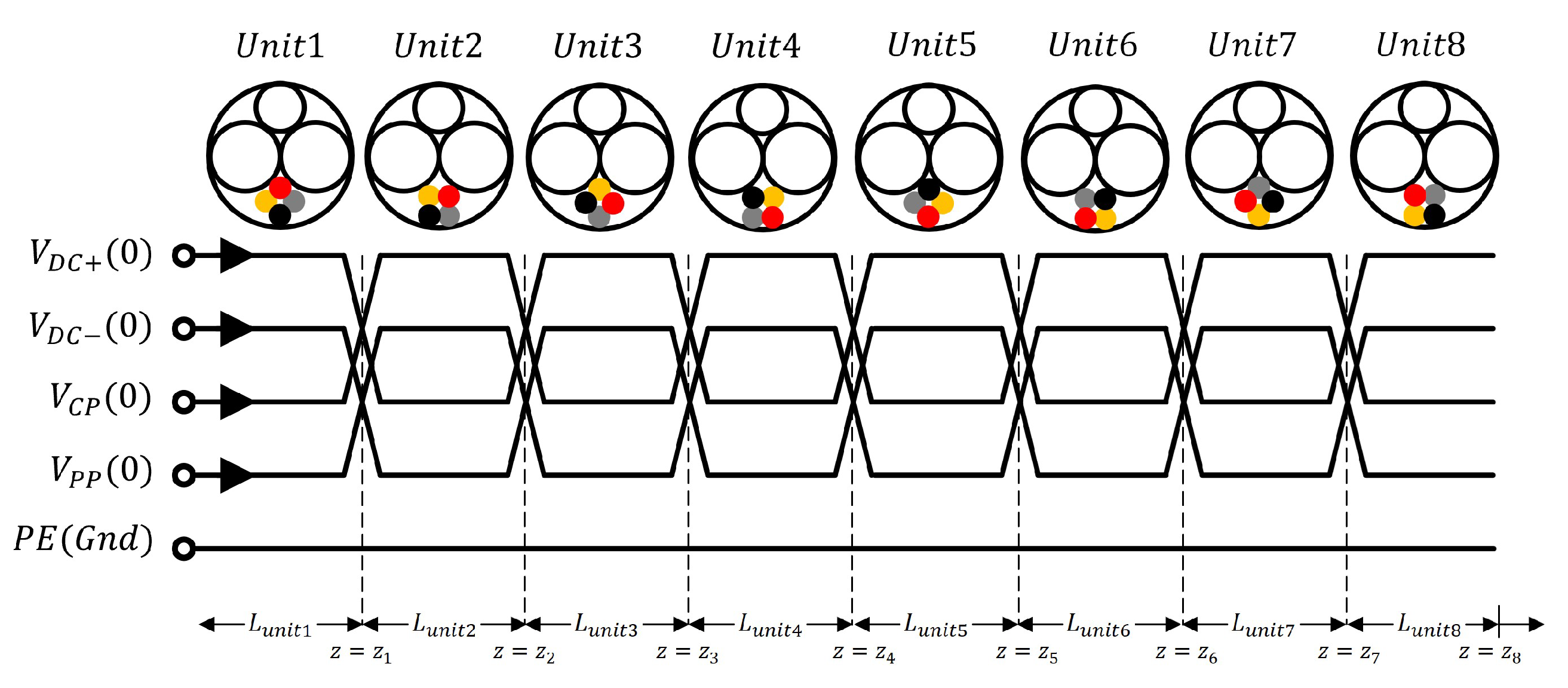
2.2. Simulation Modeling
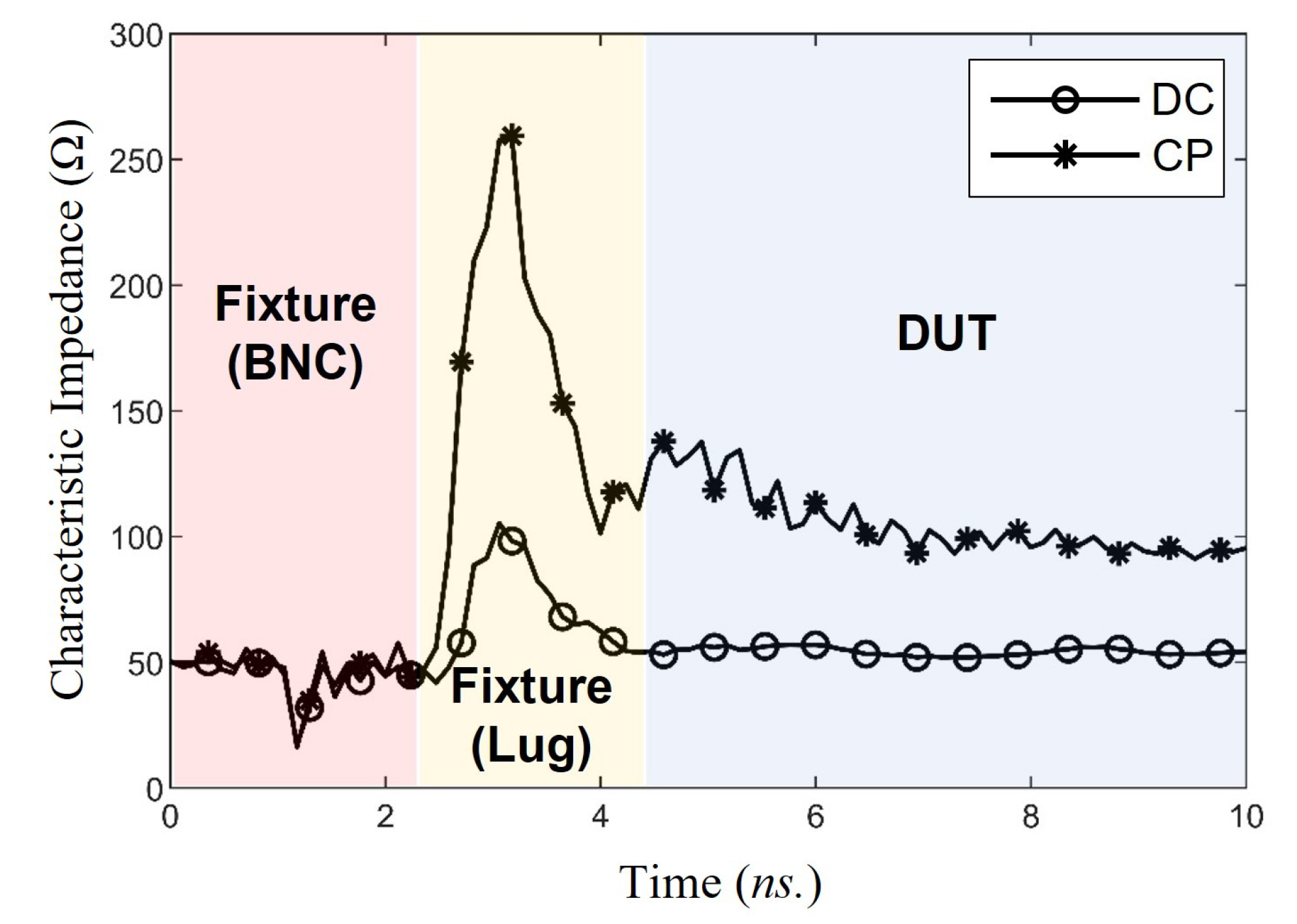
2.3. De-Embedding Process Using Impedance Peeling
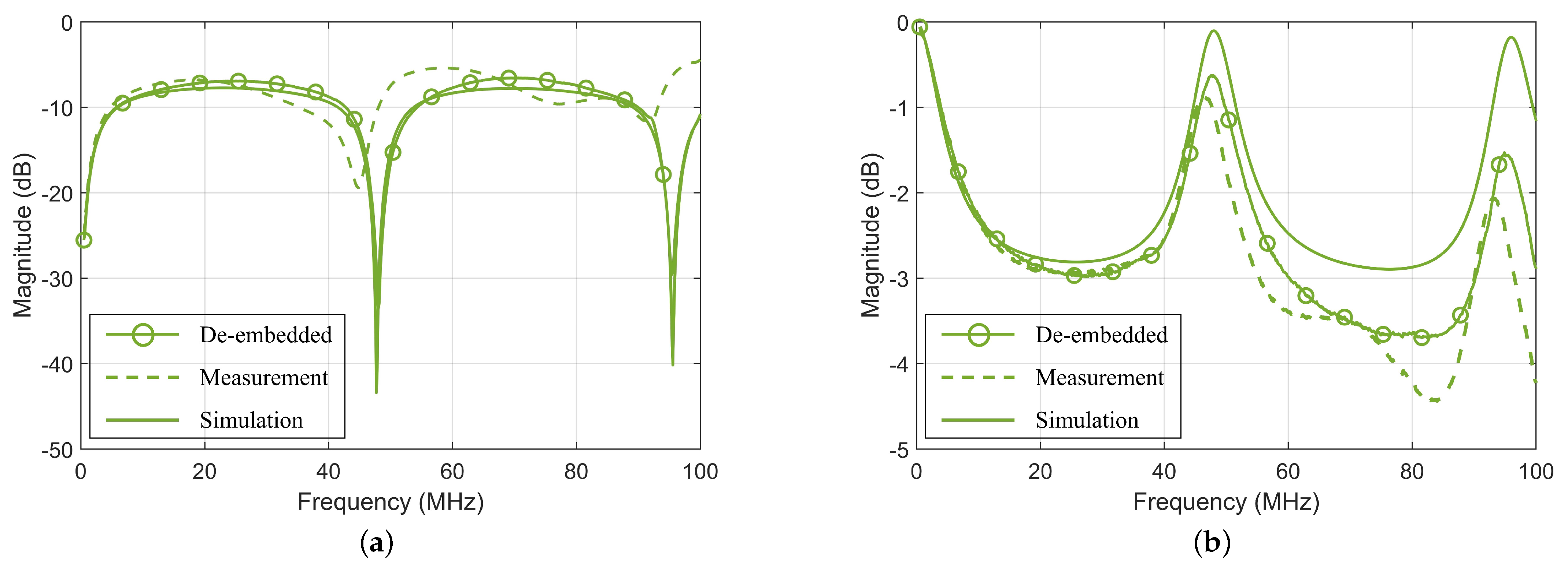
2.4. Comparison between De-Embedded Measurement and Simulation
3. Communication Simulation Using the Complete S-Parameter
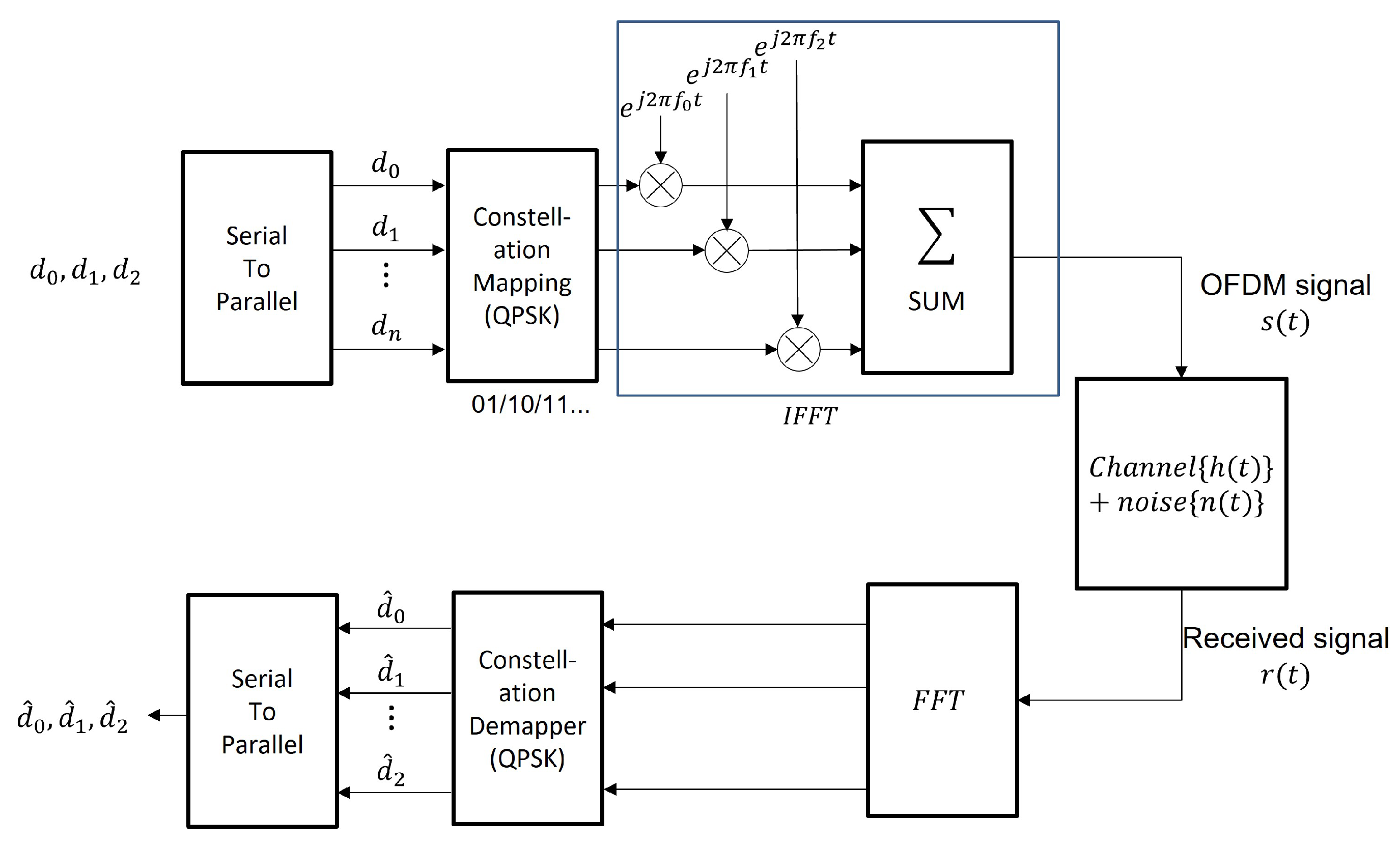
3.1. OFDM Communication Environment
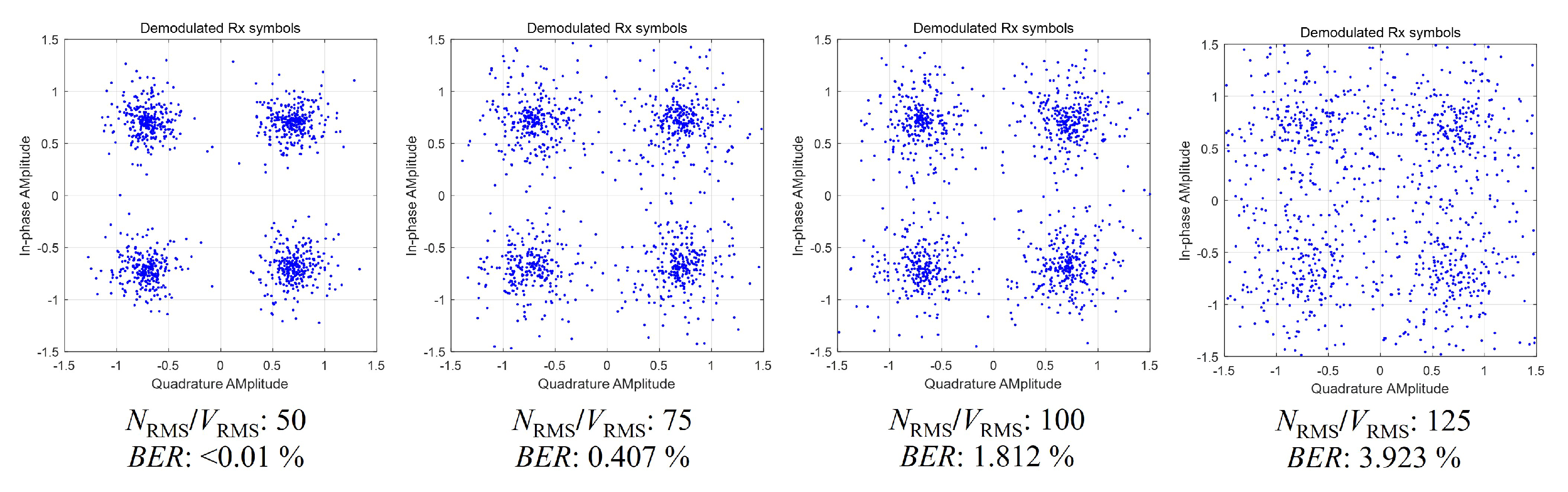
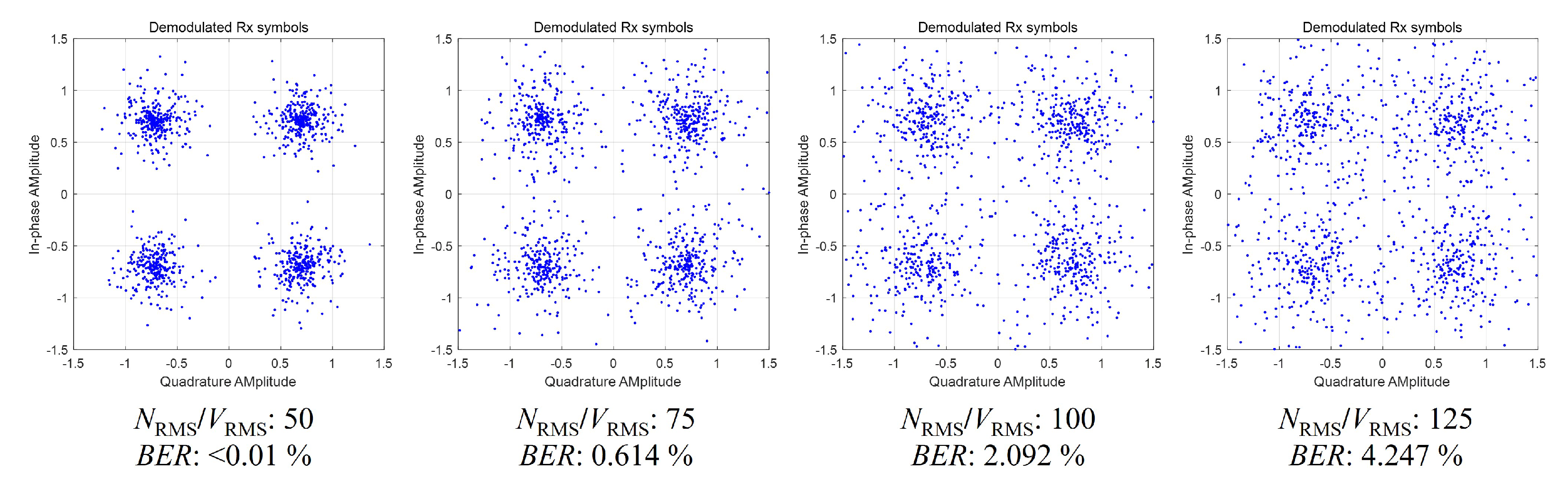
3.2. Error Threshold Analysis
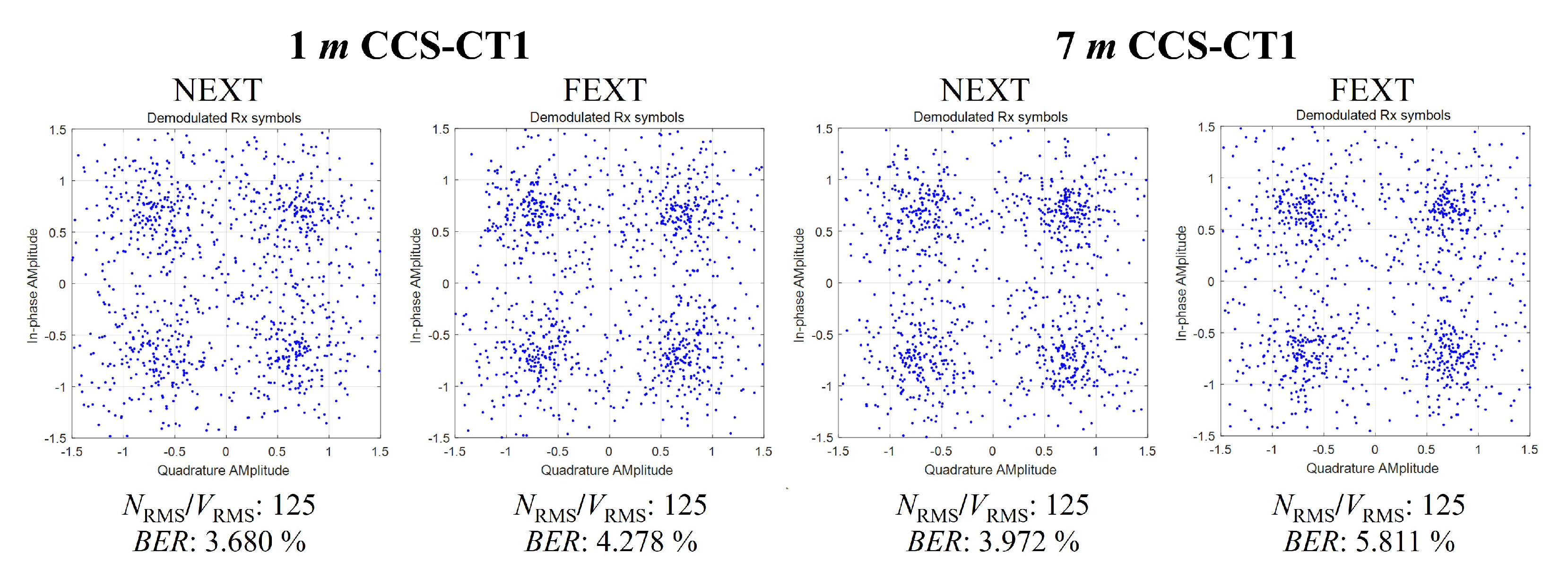
3.3. Error Scenario Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CCS-CT1 | Combined Charging System Combo Type 1 |
| SMPC | Switch-mode Power Conversion |
| EV | Electric Vehicle |
| EVSE | Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment |
| EMI | Electromagnetic Interference |
| TDR | Time-domain Reflectometer |
| OFDM | Orthogonal Frequency-division Multiplexing |
| DGS | Defected Ground Structure |
| GCPW | Grounded Co-planar Waveguide |
| IFT | Inverse Fourier Transformation |
| PE | Protectiv Earth |
| PWM | Pulse Width Modulation |
| HPGP | Homeplug GreenPHY |
| HLC | High-level Communicaiton |
| LLC | Low-level Communication |
| LS | Least Squre |
| MMSE | Minimum Mean-squre Error |
| CP | Control Pilot |
| NEXT | Near-end Crosstalk |
| FEXT | Far-end Crosstalk |
| EVM | Error Vector Magnitude |
References
- Wu, J.; Liao, H.; Wang, J.W.; Chen, T. The role of environmental concern in the public acceptance of autonomous electric vehicles: A survey from China. Transp. Res. Part F Traffic Psychol. Behav. 2019, 60, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, C.; McAndrews, G.; Byrnett, D.S. Electric Vehicles: Key Trends, Issues, and Considerations for State Regulators; National Association of Regulatory Utility Commissioners: Washington, DC, USA, 2019; pp. 1–44. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, J.; Xu, B.; Zhou, X.; Hou, J. A cloud-based energy management strategy for hybrid electric city bus considering real-time passenger load prediction. J. Energy Storage 2022, 45, 103749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, N.; Singh, R.; Brooks, R.R.; Bai, K. A review of extremely fast charging stations for electric vehicles. Energies 2021, 14, 7566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aretxabaleta, I.; De Alegria, I.M.; Andreu, J.; Kortabarria, I.; Robles, E. High-voltage stations for electric vehicle fast-charging: Trends, standards, charging modes and comparison of unity power-factor rectifiers. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 102177–102194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, M.; Krein, P.T. Review of Battery Charger Topologies, Charging Power Levels, and Infrastructure for Plug-In Electric and Hybrid Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2013, 28, 2151–2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Quan, Z.; Wu, J.; Li, Y.; Pou, J.; Zhong, H. Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient-DRL Enabled Multiphysics-Constrained Fast Charging of Lithium-Ion Battery. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2022, 69, 2588–2598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Wei, Z.; Liu, K.; Quan, Z.; Li, Y. Battery-Involved Energy Management for Hybrid Electric Bus Based on Expert-Assistance Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient Algorithm. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2020, 69, 12786–12796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasool, H.; Verbrugge, B.; Zhaksylyk, A.; Tran, T.M.; El Baghdadi, M.; Geury, T.; Hegazy, O. Design optimization and electro-thermal modeling of an off-board charging system for electric bus applications. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 84501–84519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.I.; Lee, J.G. Design of Smart Off-Board Charge System for Neighborhood Electric Vehicle. J. Korea Inst. Electron. Commun. Sci. 2013, 8, 1499–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shahir, F.M.; Gheisarnejad, M.; Sadabadi, M.S.; Khooban, M.H. A new off-board electrical vehicle battery charger: Topology, analysis and design. Designs 2021, 5, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Diao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, T. Review of the charging safety and charging safety protection of electric vehicles. World Electr. Veh. J. 2021, 12, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Dehghanian, P.; Wang, S.; Mitolo, M. Electrical safety considerations in large-scale electric vehicle charging stations. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2019, 55, 6603–6612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Electrotechnical Commission. Electric Vehicle Conductive Charging System—Part 24: Digital Communication between a d.c. EV Charging Station and an Electric Vehicle for Control of d.c. Charging; International Electrotechnical Commission: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Lewandowski, C.; Gröning, S.; Schmutzler, J.; Wietfeld, C. Performance evaluation of PLC over the IEC 61851 control pilot signal. In Proceedings of the 5th Workshop on Power Line Communications, Arnhem, The Netherlands, 22–23 September 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Chudy, A.; Stryczewska, H.D. Electromagnetic compatibility testing of electric vehicles and their chargers. Inform. Autom. Pomiary Gospod. Ochr. ŚRodowiska 2020, 10, 70–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, W.; Zhou, J.; Cai, J.; Ding, X.; Jiang, L. The Interoperability Test of Off-Board Charger for Electric Vehicle. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 4th Conference on Energy Internet and Energy System Integration (EI2), Wuhan, China, 31 October–1 November 2020; pp. 654–658. [Google Scholar]
- Martinez, W.; Lin, W.; Suarez, C. EMC implications of implementing WBG devices in battery charger modules for electric vehicles. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Power Electronics Conference (IPEC-Himeji 2022—ECCE Asia), Brasov, Romania, 25–28 September 2022; pp. 2516–2521. [Google Scholar]
- Alame, D.; Azzouz, M.; Kar, N. Assessing and mitigating impacts of electric vehicle harmonic currents on distribution systems. Energies 2020, 13, 3257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazurek, P.; Chudy, A. An Analysis of Electromagnetic Disturbances from an Electric Vehicle Charging Station. Energies 2022, 15, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slangen, T.M.H.; van Wijk, T.; Ćuk, V.; Cobben, J.F.G. The Harmonic and Supraharmonic Emission of Battery Electric Vehicles in The Netherlands. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Smart Energy Systems and Technologies (SEST), Istanbul, Turkey, 7–9 September 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Howe, W. Assessing the Harmonic and Supraharmonic Impact of Electric Vehicle Charging Facilities. In Proceedings of the 2022 20th International Conference on Harmonics & Quality of Power (ICHQP), Naples, Italy, 29 May–1 June 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karmaker, A.K.; Roy, S.; Ahmed, M.R. Analysis of the impact of electric vehicle charging station on power quality issues. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Electrical, Computer and Communication Engineering (ECCE), Cox’s Bazar, Bangladesh, 7–9 February 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Rajendran, G.; Vaithilingam, A.; Naidu, K.; Prakash, S.; Ahmed, R. Hard Switching Characteristics of SiC and GaN Devices for Future Electric Vehicle Charging Stations. MATEC Web Conf. 2021, 335, 02007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Organization for Standardization. Road Vehicles—Vehicle to Grid Communication Interface—Part 3: Physical and Data Link Layer Requirements; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Pallander, R. Implementation of HomePlug Green Phy standard (ISO15118) into Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment. 2021. Available online: https://ltu.diva-portal.org/smash/get/diva2:1546405/FULLTEXT01.pdf. (accessed on 17 July 2023).
- Jo, S.; Noh, Y.H.; Kim, C.g.; Park, Y.W.; Lee, D.H.; Jeong, K.S.; Yook, J.G. Analysis of HEMP Coupling Signal for a Coaxial Cable Considering Various Cable Parameters. J. Korean Inst. Electromagn. Eng. Sci. 2020, 31, 542–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, H.R.; Kim, W.B.; Kim, C.g.; Sohn, J.H.; Jeong, K.S.; Yook, J.G. Method for Approximated Analysis of HEMP Couplings to Cables in Reinforced Concrete. J. Korean Inst. Electromagn. Eng. Sci. 2020, 31, 623–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Noh, Y.H.; Lee, J.; Lee, J.; Choi, J.S.; Yook, J.G. Electromagnetic Signature of a Quadcopter Drone and Its Relationship With Coupling Mechanisms. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 174764–174773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SAE International. SAE Electric Vehicle and Plug in Hybrid Electric Vehicle Conductive Charge Coupler J1772_201710; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Paul, C.R. Analysis of Multiconductor Transmission Lines; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Rolfes, I.; Schiek, B. Multiport method for the measurement of the scattering parameters of N-ports. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2005, 53, 1990–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevanović, I.; Wunsch, B.; Madonna, G.L.; Skibin, S. High-frequency behavioral multiconductor cable modeling for EMI simulations in power electronics. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2014, 10, 1392–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pupalaikis, P.J. Time-domain techniques for de-embedding and impedance peeling. System 2020, 1, 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Stevanović, I.; Wunsch, B.; Madonna, G.L.; Vancu, M.F.; Skibin, S. Multiconductor cable modeling for EMI simulations in power electronics. In Proceedings of the IECON 2012—38th Annual Conference on IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Montreal, QC, Canada, 25–28 October 2012; pp. 5382–5387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L. Estimation of multi-conductor powerline cable parameters for the modelling of transfer characteristics. IET Sci. Meas. Technol. 2014, 8, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yonge, L.; Abad, J.; Afkhamie, K.; Guerrieri, L.; Katar, S.; Lioe, H.; Pagani, P.; Riva, R.; Schneider, D.M.; Schwager, A.; et al. An overview of the HomePlug AV2 technology. J. Electr. Comput. Eng. 2013, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homeplug Powerline Alliance. HomePlug Green PHY: The Standard For Inhome Smart Grid Powerline Communications—An Application and Technology Overview, 3rd ed.; 2012. Available online: https://content.codico.com/fileadmin/media/download/datasheets/powerline-communication/plc-homeplug-green-phy/homeplug_green_phy_whitepaper.pdf (accessed on 17 July 2023).
- SamWoo-Electronics. Electric Vehicle Charging Technology. Available online: http://scm.isamwoo.com/evalucon/pdf/EVT_Catalogue_C18_E01-ENG.PDF (accessed on 17 July 2023).
- Ye, X. De-embedding errors due to inaccurate test fixture characterization. IEEE Electromagn. Compat. Mag. 2012, 1, 75–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Fan, J.; Drewniak, J.L. New de-embedding techniques for PCB transmission-line characterization. In Proceedings of the DesignCon 2015, Santa Clara, CA, USA, 27–30 January 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Khandelwal, M.K.; Kanaujia, B.K.; Kumar, S. Defected ground structure: Fundamentals, analysis, and applications in modern wireless trends. Int. J. Antennas Propag. 2017, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadell, B.C. Transmission Line Design Handbook; Artech House: Norwood, MA, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Meyer, P. Multi-conductor transmission line analysis using the generalized multi-mode S-parameter transformation. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE 19th Workshop on Signal and Power Integrity (SPI), Berlin, Germany, 10–13 May 2015; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozar, D.M. Microwave Engineering, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Black, W.C. Power line S-parameter characterization using open-source tools. In Proceedings of the ISPLC2010, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 28–31 March 2010; pp. 62–66. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.W.; Wei, X.C.; Xv, C.X. A hybrid de-embedding method for low loss and reciprocal PCB fixtures. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2022, 71, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.S.; Mittra, R. Time-Domain Reflectometry Using Scattering Parameters and a De-Embedding Application; Technical Report; University of Illinois Urbana Electromagnetic Communication Laboratory: Champaign, IL, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Bordin, C.J., Jr.; dos Santos, K.M.G. Conversion of Scattering Parameters to Time-Domain for Imaging Applications: Rules and Examples. J. Commun. Inf. Syst. 2021, 36, 62–69. [Google Scholar]
- Frickey, D.A. Conversions between S, Z, Y, H, ABCD, and T parameters which are valid for complex source and load impedances. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 1994, 42, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frei, J.; Cai, X.D.; Muller, S. Multiport S-parameter and T-parameter conversion with symmetry extension. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2008, 56, 2493–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terzi, U.K.; Ilhan, H.E.; Kaymaz, H.; Erdal, H.; Çalik, H. A review of commercial electric vehicle charging methods. Promet-Traffic Transp. 2020, 32, 291–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kubel, M. Design Guide for Combined Charging System; CharIN eV: Berlin, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Sure, P.; Bhuma, C.M. A survey on OFDM channel estimation techniques based on denoising strategies. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 2017, 20, 629–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleri, S.; Ergen, M.; Puri, A.; Bahai, A. Channel estimation techniques based on pilot arrangement in OFDM systems. IEEE Trans. Broadcast. 2002, 48, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zimmermann, M.; Dostert, K. A multipath model for the powerline channel. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2002, 50, 553–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rautio, J. Techniques for Correcting Scattering Parameter Data of an Imperfectly Terminated Multiport When Measured with a Two-Port Network Analyzer. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 1983, 31, 407–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.S.; Lin, Y.S.; Chiu, H.W.; Chen, Y.C.; Meng, C.C. The determination of S-parameters from the poles of voltage-gain transfer function for RF IC design. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2005, 52, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.; Jiang, B.; Wei, X. Impedance characterization and modeling of lithium-ion batteries considering the internal temperature gradient. Energies 2018, 11, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hannan, M.A.; Lipu, M.H.; Hussain, A.; Mohamed, A. A review of lithium-ion battery state of charge estimation and management system in electric vehicle applications: Challenges and recommendations. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 78, 834–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voelker, K. Apply error vector measurements in communications design. Microwaves & RF 1995, 34, 143–144. [Google Scholar]
- Shafik, R.A.; Rahman, M.S.; Islam, A.R. On the Extended Relationships Among EVM, BER and SNR as Performance Metrics. In Proceedings of the 2006 International Conference on Electrical and Computer Engineering, Dhaka, Bangladesh, 19–21 December 2006; pp. 408–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anil, D.; Sivraj, P. Electric Vehicle Charging Communication Test-bed following CHAdeMO. In Proceedings of the 2020 11th International Conference on Computing, Communication and Networking Technologies (ICCCNT), Kharagpur, India, 1–3 July 2020; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lathika, A.; Nithin, S. Development of a Communication Test Bed for Electric Vehicle Charging. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Electronics and Sustainable Communication Systems (ICESC), Coimbatore, India, 2–4 July 2020; pp. 1127–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nia, M.S.S.; Shamsi, P.; Ferdowsi, M. EMC Modeling and Conducted EMI Analysis for a Pulsed Power Generator System Including an AC–DC–DC Power Supply. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2020, 48, 4250–4261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Kim, H.; He, J.; Erickson, N.; Cho, S.; Kim, D.; Hur, Y.; Pommerenke, D.J.; Fan, J. Analysis and Modeling of Conducted EMI from an AC–DC Power Supply in LED TV up to 1 MHz. IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 2019, 61, 2050–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
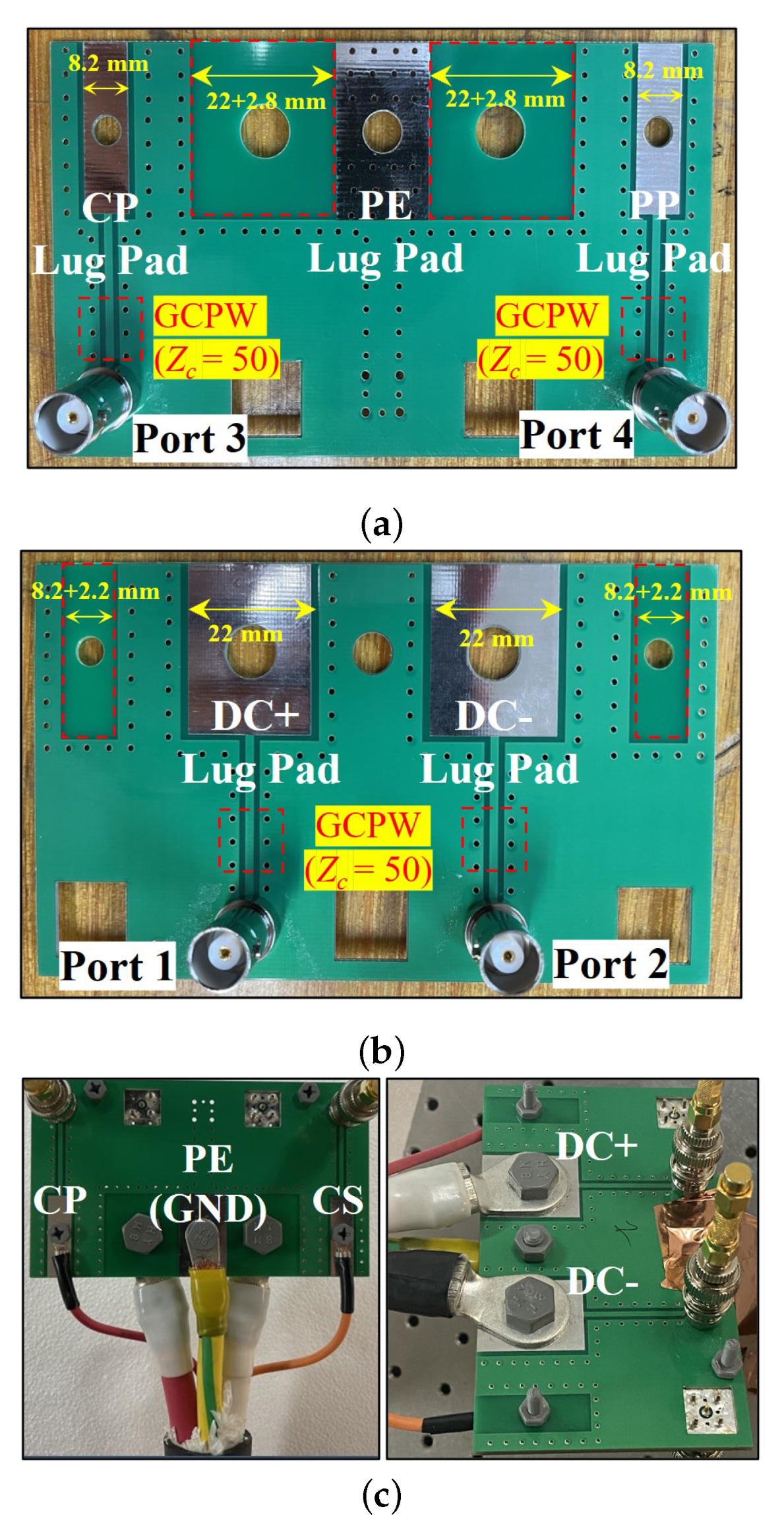


| Type | Height (Subs.) | Width (W) | Spacing (S) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CPWG (feed) | 0.8 mm | 1.5 mm | 1.08 mm |
| DGS (DC) | 0.8 mm | 22 mm | 1.4 mm |
| DGS (CP) | 0.8 mm | 8.2 mm | 1.1 mm |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, S.; Lee, E.; Noh, Y.-H.; Choi, D.-H.; Yook, J.-g. Accurate Modeling of CCS Combo Type 1 Cable and Its Communication Performance Analysis for High-Speed EV-EVSE Charging System. Energies 2023, 16, 5947. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16165947
Park S, Lee E, Noh Y-H, Choi D-H, Yook J-g. Accurate Modeling of CCS Combo Type 1 Cable and Its Communication Performance Analysis for High-Speed EV-EVSE Charging System. Energies. 2023; 16(16):5947. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16165947
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Sanghwa, Euibum Lee, Yeong-Hoon Noh, Dong-Hoon Choi, and Jong-gwan Yook. 2023. "Accurate Modeling of CCS Combo Type 1 Cable and Its Communication Performance Analysis for High-Speed EV-EVSE Charging System" Energies 16, no. 16: 5947. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16165947
APA StylePark, S., Lee, E., Noh, Y.-H., Choi, D.-H., & Yook, J.-g. (2023). Accurate Modeling of CCS Combo Type 1 Cable and Its Communication Performance Analysis for High-Speed EV-EVSE Charging System. Energies, 16(16), 5947. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16165947






