Resonant DC/DC Converters: Investigating Phase-Shift Control
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Related Work
1.2. Research Contribution
- Elucidate the operating principle of an LCL-T-type resonant converter employing a PSG strategy for control.
- Analyze the converter using the Fourier series approach, taking into account multiple harmonic components of voltages and current waveforms to enhance performance prediction accuracy.
- Present a systematic design procedure for the converter.
- Assess and verify the converter’s operational characteristics through simulations using the PSIM 2021a software.
- Conduct loss calculations for power to determine the efficiency of the converter.
- Develop an experimental prototype to validate the theoretical and simulation results.
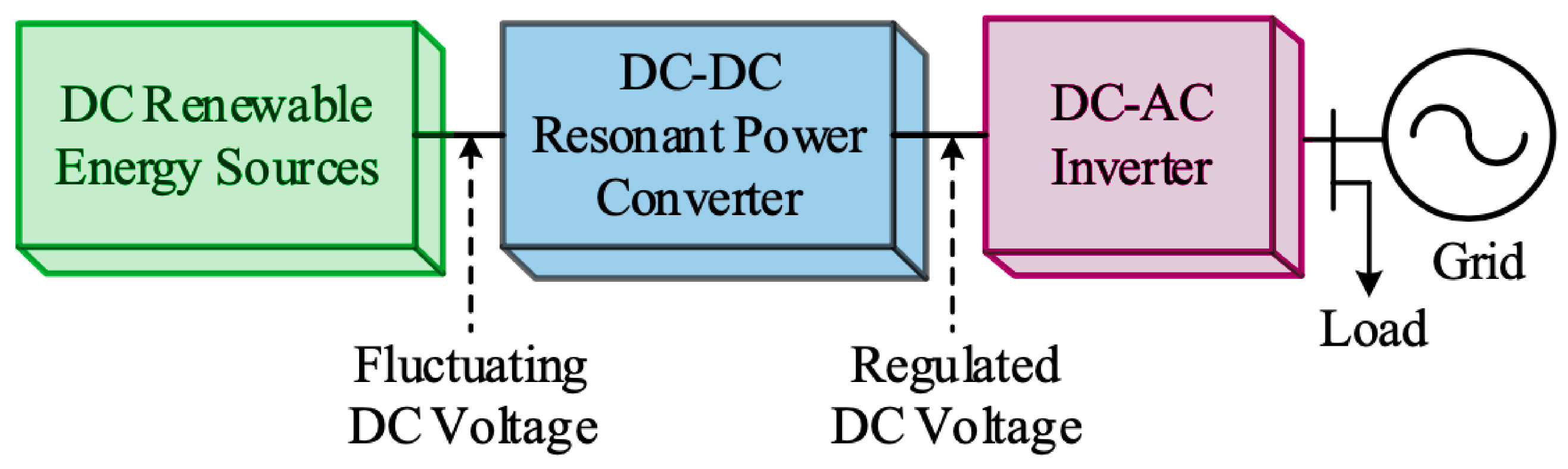
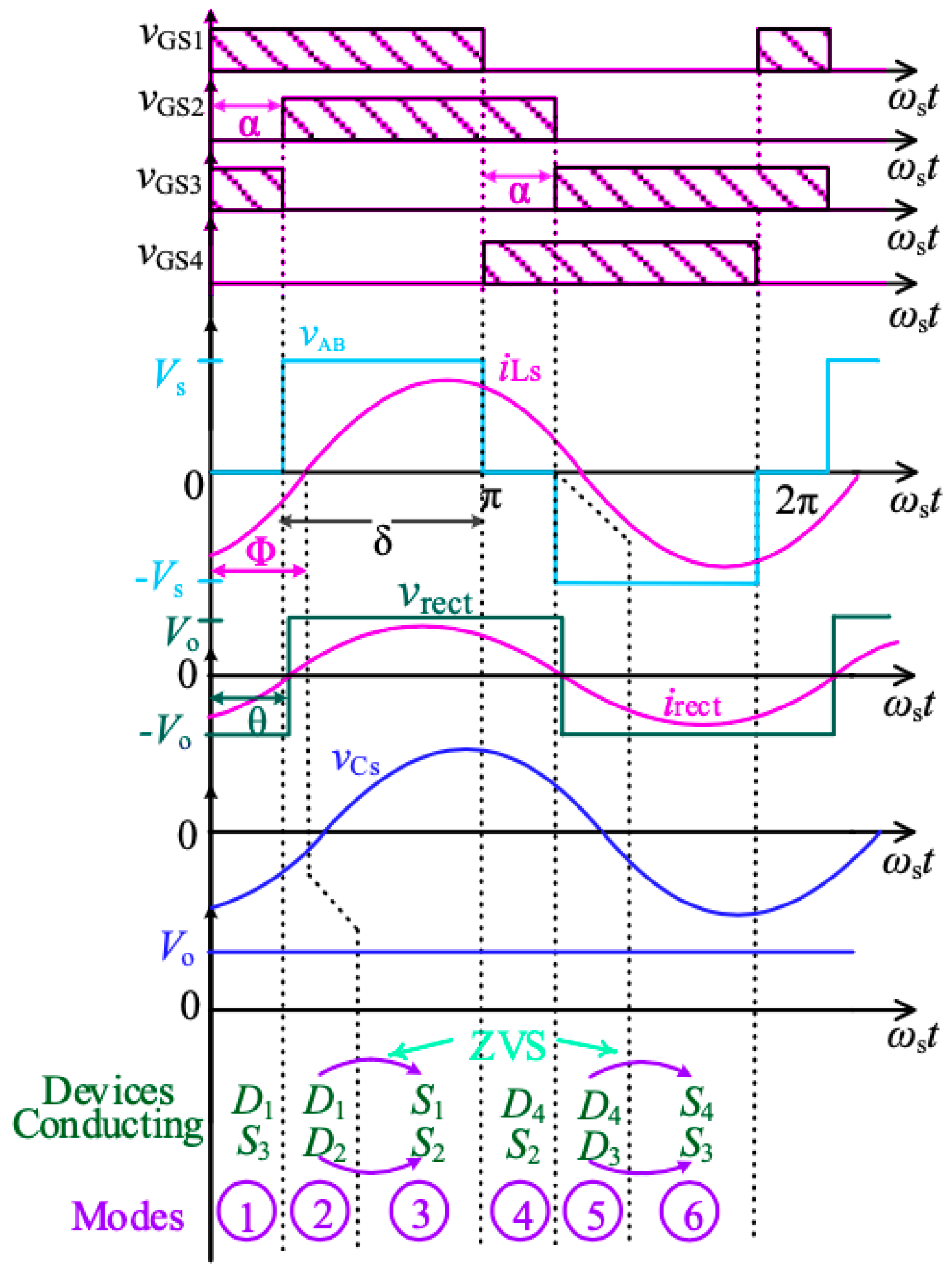
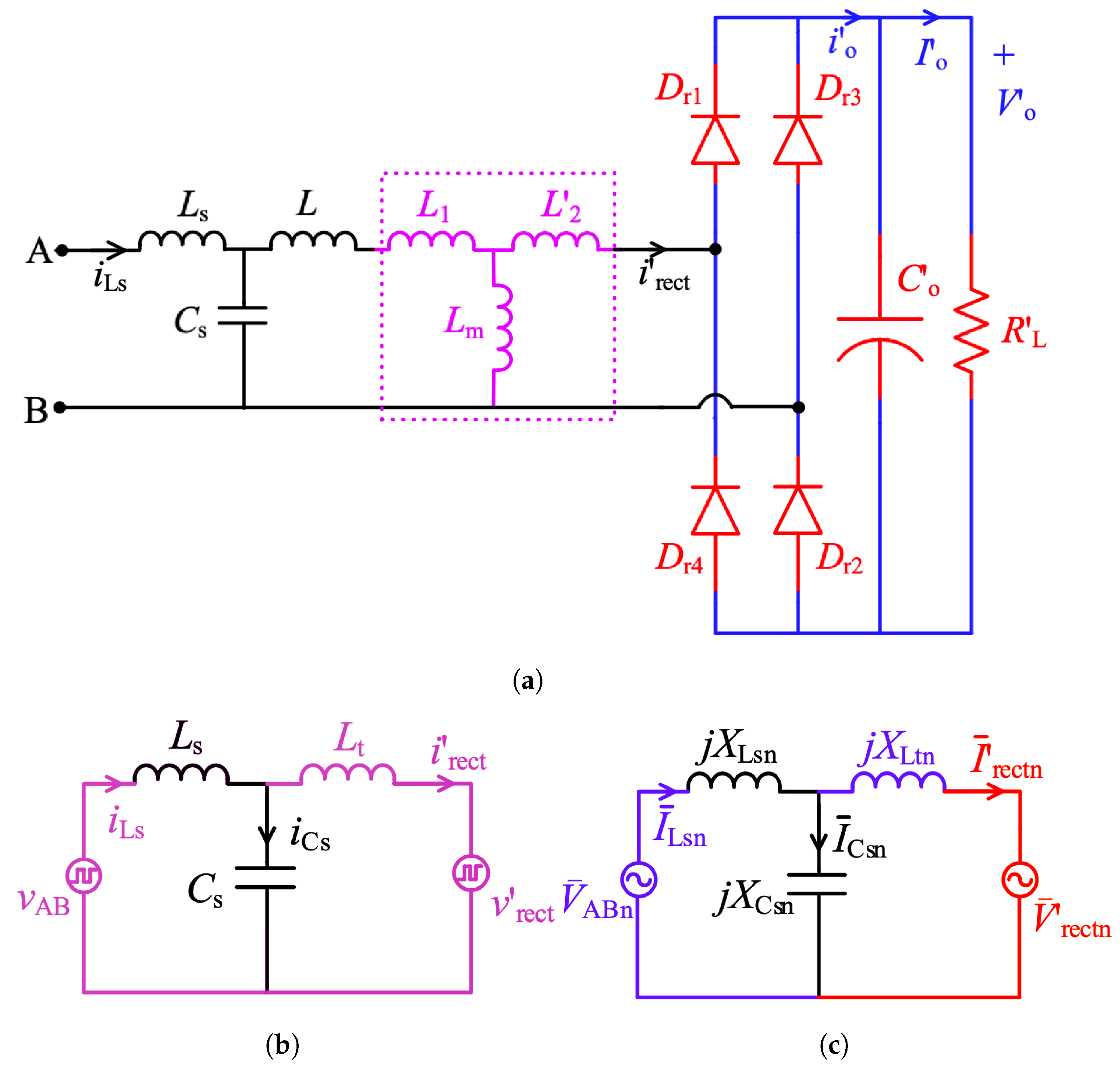
2. Power Circuit and Operations
3. Steady-State Analysis Using Fourier series
3.1. Converter Modelling
3.2. Normalization
3.3. Investigation of the Converter
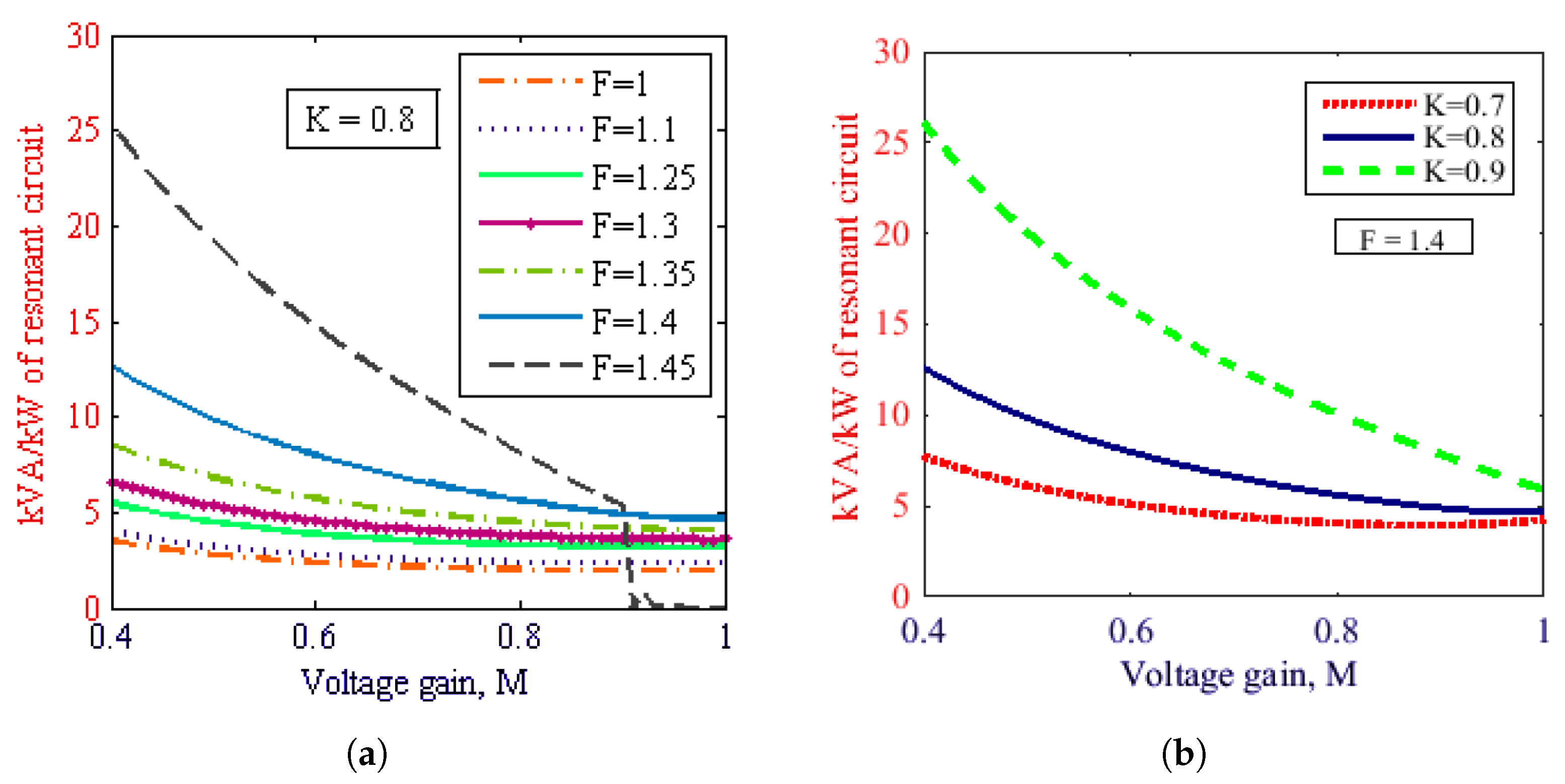
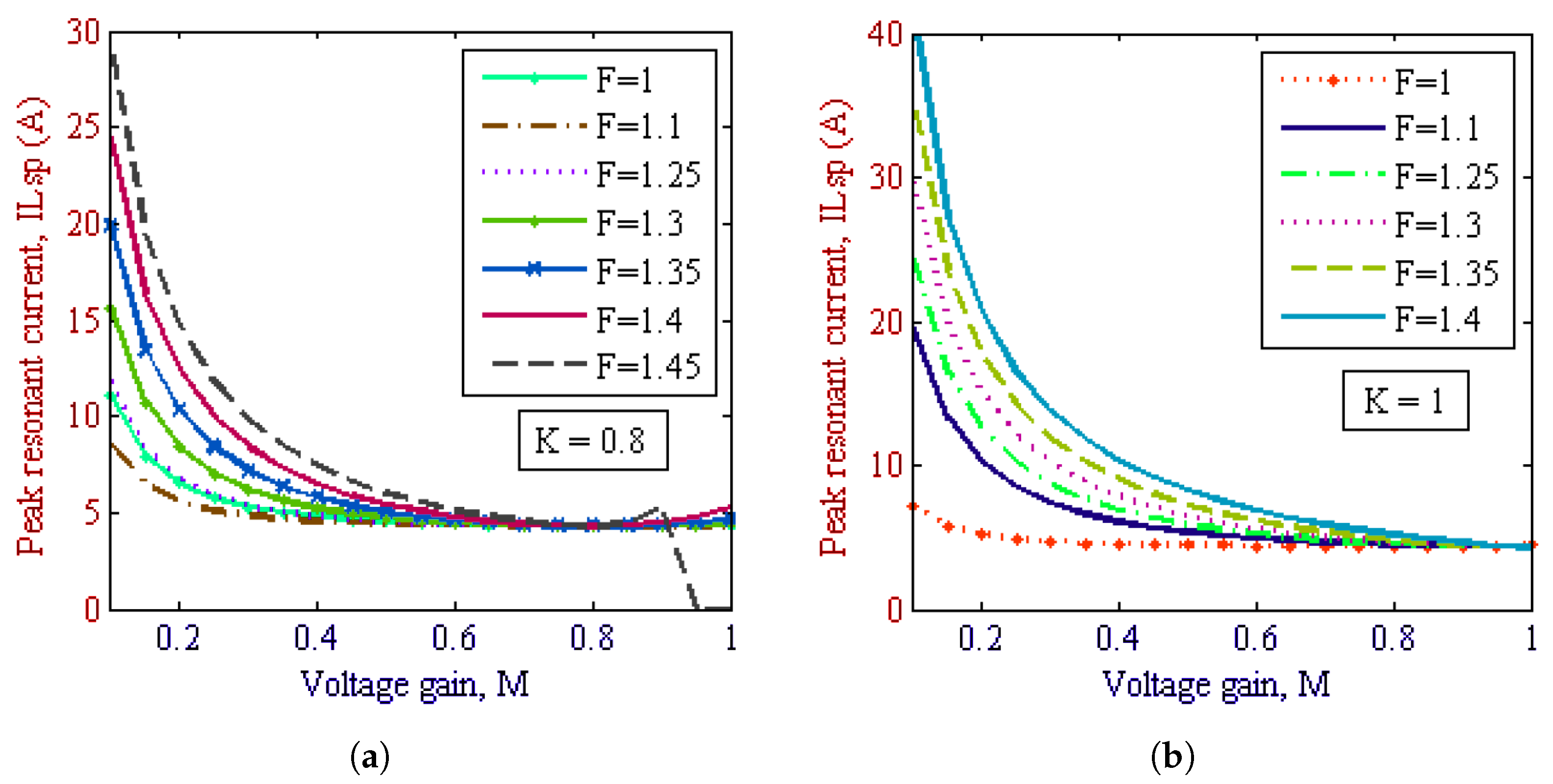
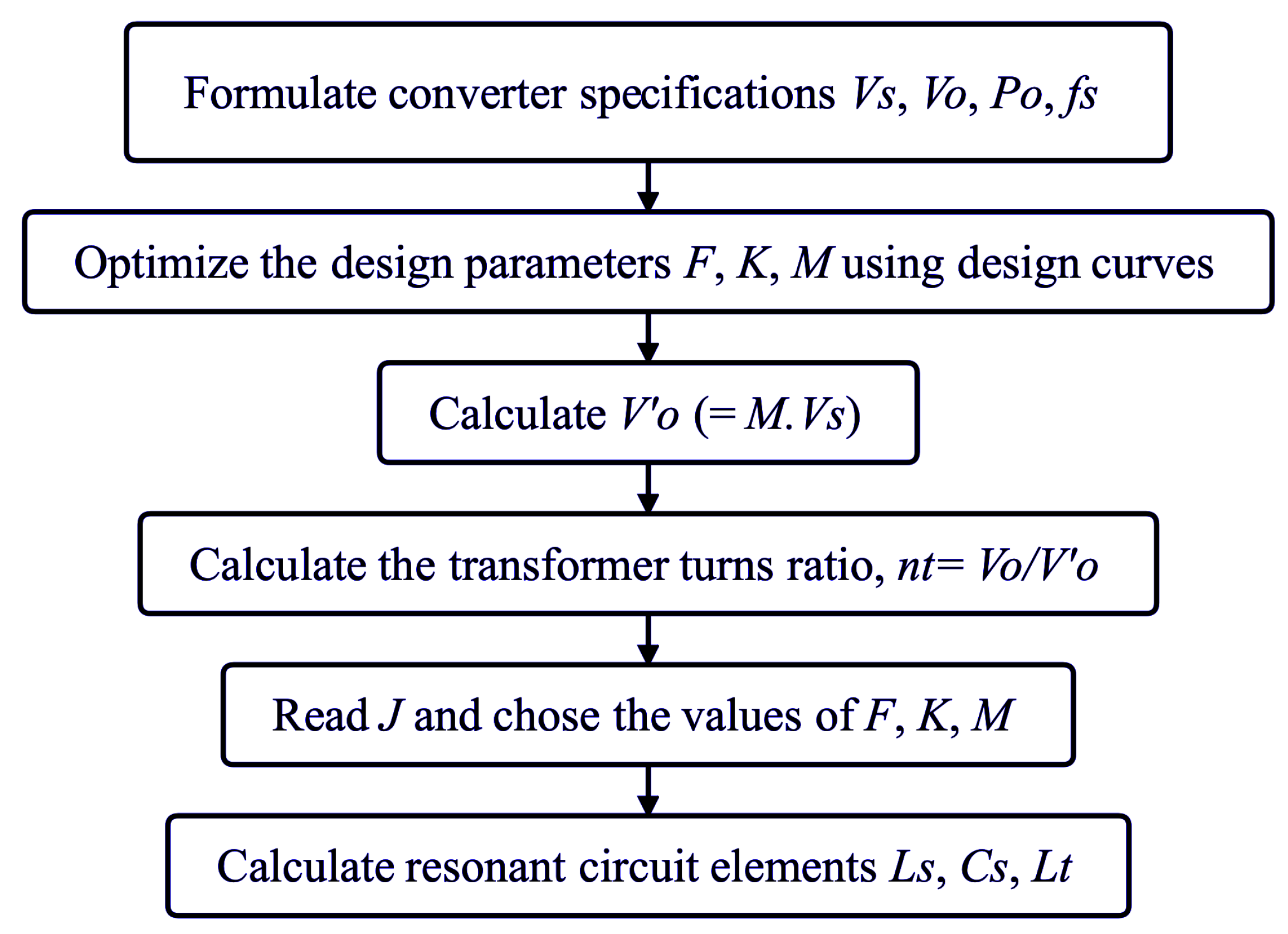
4. Design Consideration
Design Trade-Offs
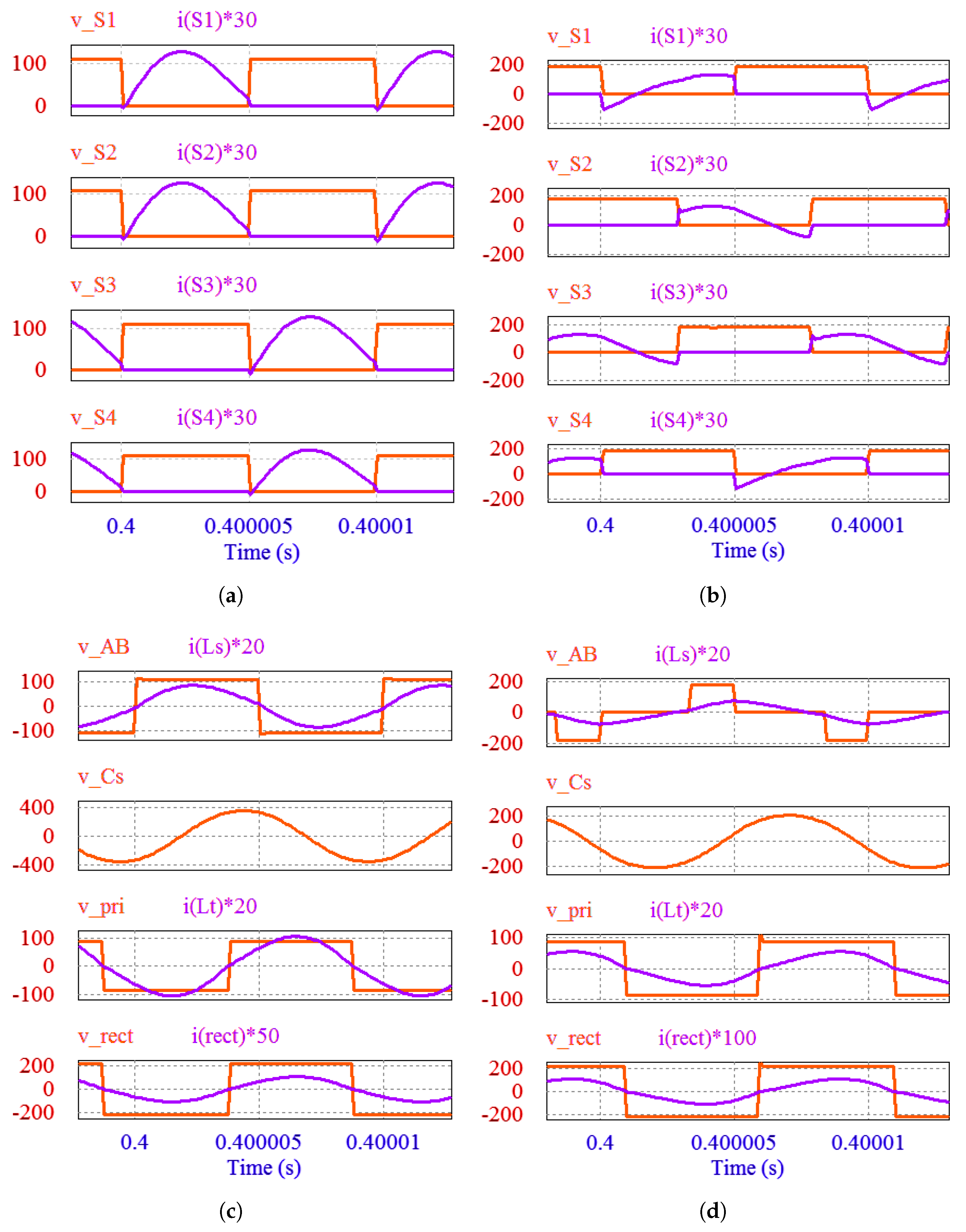
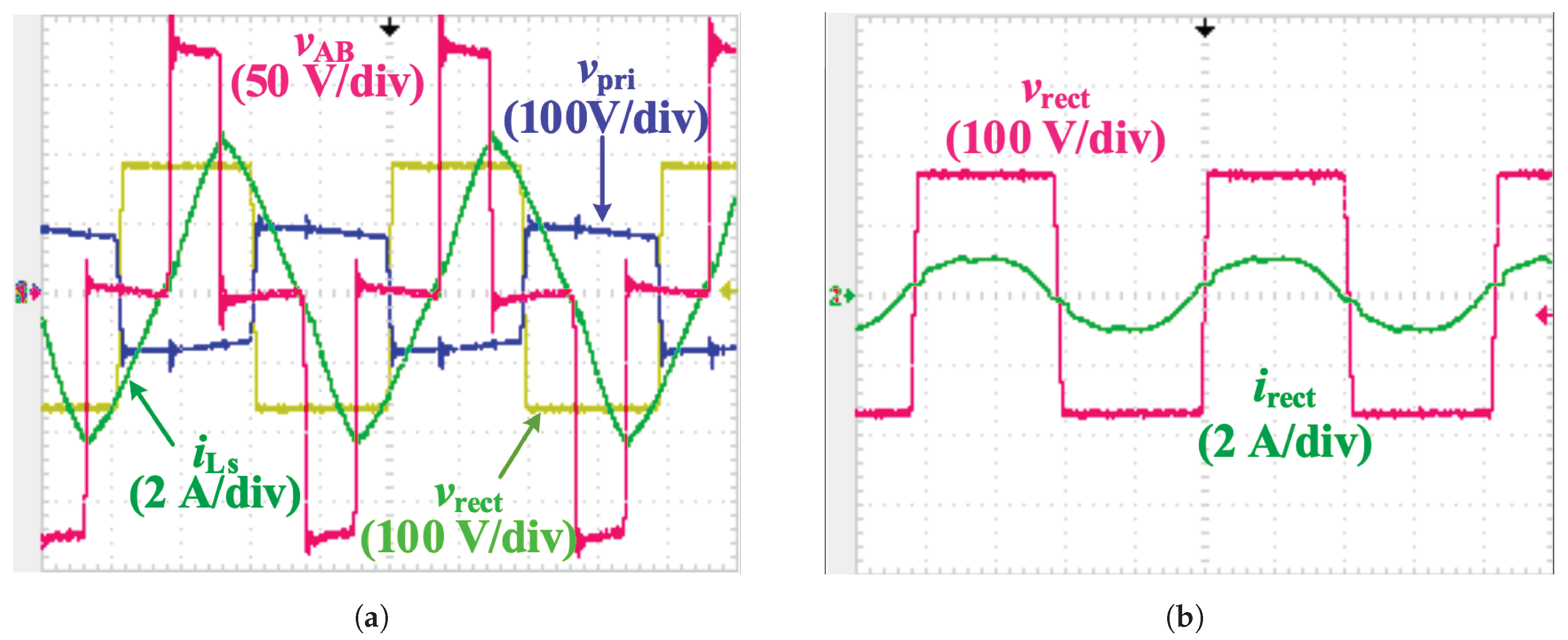
5. Simulation Results
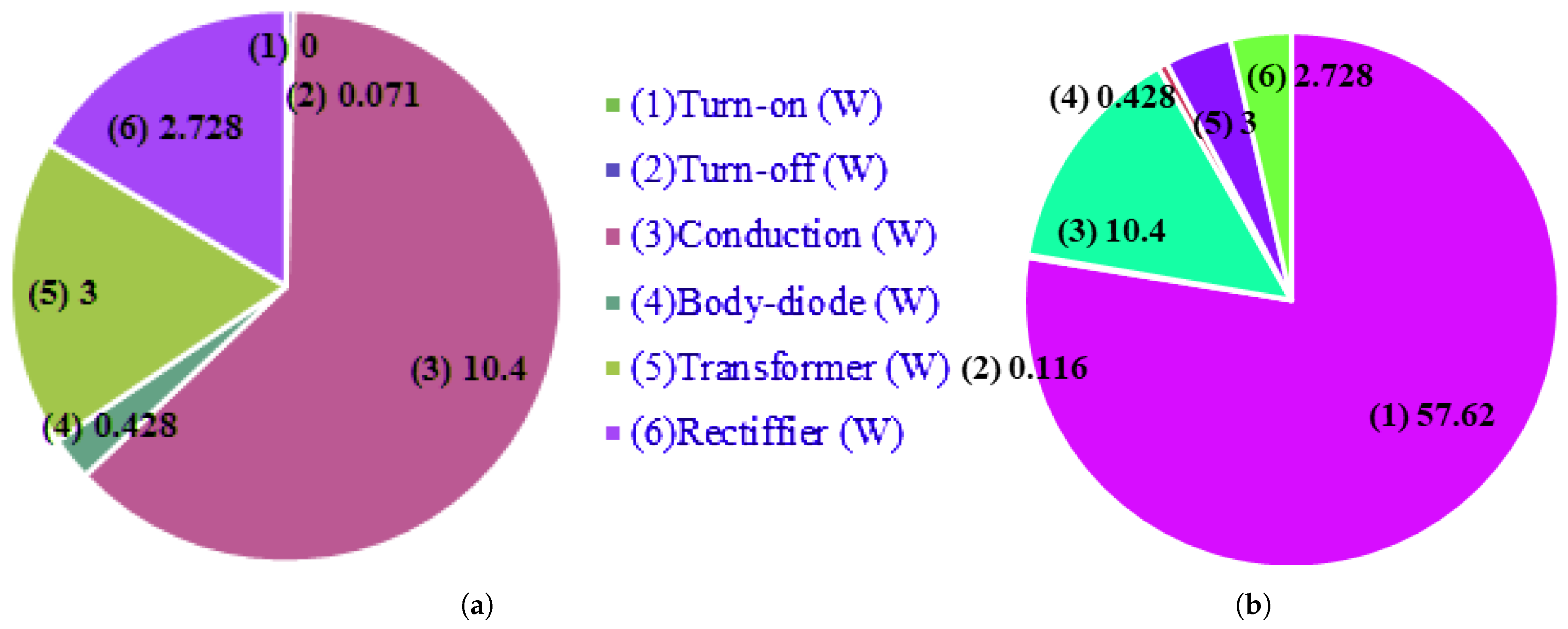
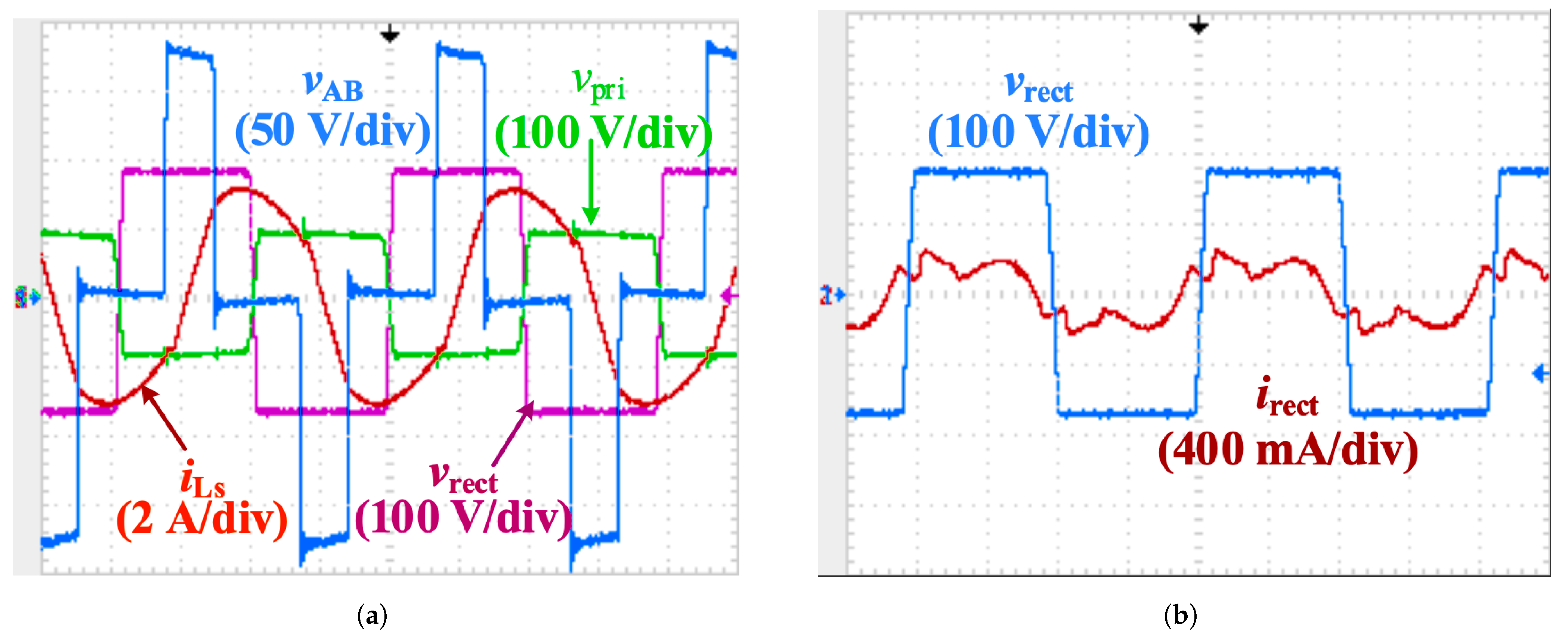
6. Experimental Results
- (i)
- In theoretical calculations, all components such as switches, diodes, inductors, capacitors, and HF transformers are assumed to be ideal. However, in simulations, the resistance in MOSFETs (IRF 740) and a 1V voltage drop in UF5404 are taken into account, while all other elements are still considered ideal. In the prototype, components experience voltage and power losses.
- (ii)
- The theoretical calculations assumed 1% power loss for the utilized transformer, while in prototype testing, the copper loss changes according to load, and the core losses remain constant.
- (iii)
- In the practical circuit, a small deviation in component values is inevitable due to the challenges in constructing accurate values of components.
- (iv)
- The theoretical calculations do not take into account any dead gap whereas, in the experiment, a dead gap of approximately 150 ns is introduced.
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rezvanyvardom, M.; Mirzaei, A.; Heydari, S. Fully Soft-Switching Nonisolated Quasi-Z-Source DC-DC Converter with High-Voltage Gain. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2021, 9, 1854–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanamarlapudi, V.R.K.; Wang, B.; Kandasamy, N.K.; So, P.L. A New ZVS Full-Bridge DC–DC Converter for Battery Charging With Reduced Losses Over Full-Load Range. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2018, 54, 571–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Xu, D. Review of Soft-Switching Topologies for Single-Phase Photovoltaic Inverters. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2022, 37, 1926–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, N.A.; Madouh, J.Y. High-frequency full-bridge isolated DC–DC converter for fuel cell power generation systems. Electr. Eng. 2018, 100, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.F.; Liu, C.; Wang, D.; Zhang, Y. State-of-the-Art Review on Soft-Switching Technologies for Non-Isolated DC-DC Converters. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 119235–119249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Wang, L.; Fang, J.; Li, R.; Han, R.; Wang, Y. A High-Efficiency ZVS Wireless Power Transfer System for Electric Vehicle Charging with Variable Angle Phase Shift Control. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2020, 9, 2356–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Liu, Z.; Du, J.; Yu, B. Research on Zero Voltage Switching Non-inductive Current Circulation Control of Bidirectional DC/DC Converter for Hybrid Energy Source System of Electric Vehicle. J. Electr. Eng. Technol. 2021, 16, 873–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elizondo, D.; Barrios, E.L.; Larequi, I.; Ursua, A.; Sanchis, P. Zero-Loss Switching in LLC Resonant Converters under Discontinuous Conduction Mode: Analysis and Design Methodology. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2023, 59, 3576–3592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, J.; Smedley, K.M.; Cheng, H. Full-Range Regulation Method for Half-Bridge Series Resonant Converter. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2023, 70, 1905–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.; Guan, M.; Lin, Z.; Fang, Q.; Wu, W.; Chen, W. Series-Series/Series Compensated Inductive Power Transmission System with Symmetrical Half-Bridge Resonant Converter: Design, Analysis, and Experimental Assessment. Energies 2019, 12, 2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Xu, Y.; Lu, H.; Yan, Z.; Yu, Z.; Li, Q.; Tan, Y. Fixed Frequency LCC Resonant Converter Modeling and Optimal Design for High-Voltage Capacitor Charging Power Supply in Constant Power Control. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2023; 1–12, early access. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, I.O. Hybrid DC-DC Converter with Phase-Shift or Frequency Modulation for NEV Battery Charger. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 884–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Luo, Q.; Woldegiorgis, D.; Mhiesan, H.; Mantooth, A. Characteristics Analysis of LLC and LCL-T Resonant Tank. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Transportation Electrification Conference and Expo, ITEC 2020, Chicago, IL, USA, 23–26 June 2020; pp. 427–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Ruan, X. Equivalence Relations of Resonant Tanks: A New Perspective for Selection and Design of Resonant Converters. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 2111–2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patarau, T.M.; Petreus, D.M.; Ferencz, I.; Orban, Z. Comparison between LLC and Phase-Shift Converter with Synchronous Rectification for High Power, High Current Applications. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 26th International Symposium for Design and Technology in Electronic Packaging, SIITME 2020, Pitesti, Romania, 21–24 October 2020; pp. 398–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosrogorji, S.; Soori, S.; Torkaman, H. A new design strategy for DC/DC LLC resonant converter: Concept, modeling, and fabrication. Int. J. Circuit Theory Appl. 2019, 47, 1645–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.; Yang, X.; Liu, Y.; Yan, C.; Zheng, T.Q.; Igarashi, S.; Chen, Q. Short-Circuit Protection for Resonant Switched-Capacitor Converter. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2022, 59, 1956–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Jin, X.; Hu, H.; Xing, Y. Multielement Resonant Converters With a Notch Filter on Secondary Side. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2016, 31, 3999–4004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, H.; Guan, J.; Zhang, C.; Li, Z. Optimal Control Strategy of CLLC Bidirectional Resonant Converter under Light Load. In Proceedings of the 2022 9th International Forum on Electrical Engineering and Automation, IFEEA 2022, Zhuhai, China, 4–6 November 2022; pp. 921–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, C.; Lee, F.C.; Li, Q. Digital Implementation of Soft Start-Up and Short-Circuit Protection for High-Frequency LLC Converters With Optimal Trajectory Control (OTC). IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2017, 32, 8008–8017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwu, K.I.; Guo, Y.S. Efficiency improvement for LLC converter based on automatic tuning of blanking time. Int. J. Circuit Theory Appl. 2019, 47, 1477–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Yang, Z.; Cui, S.; Doncker, R.W.D. Closed-Form Asymmetrical Duty-Cycle Control to Extend the Soft-Switching Range of Three-Phase Dual-Active-Bridge Converters. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2021, 36, 9609–9622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Soltau, N.; Doncker, R.W.D. Asymmetrical duty-cycle control of three-phase dual-active bridge converter for soft-switching range extension. In Proceedings of the ECCE 2016—IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition, Milwaukee, WI, USA, 18–22 September 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veeramallu, V.K.; Porpandiselvi, S.; Narasimharaju, B.L. A Nonisolated Wide Input Series Resonant Converter for Automotive LED Lighting System. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2021, 36, 5686–5699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, C.; Han, B.; Kwon, B.H.; Kim, M. Highly Efficient Bidirectional Series-Resonant DC/DC Converter over Wide Range of Battery Voltages. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2020, 35, 3636–3650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Wang, H.; Al-Durra, A.; Qin, Z.; Blaabjerg, F. A Bidirectional Resonant DC-DC Converter Suitable for Wide Voltage Gain Range. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2018, 33, 2957–2975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, M.; Emamalipour, R.; Cheema, M.A.M.; Lam, J. A Constant-Frequency High-Voltage Gain Resonant Converter Module With Semiactive Phase-Shifted Voltage Multiplier for MVdc Distribution. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2022, 10, 3603–3616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Wang, P.; Bi, H.; Wang, Z. A Bidirectional LLCL Resonant DC-DC Converter with Reduced Resonant Tank Currents and Reduced Voltage Stress of the Resonant Capacitor. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 125549–125564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wei, Y.; Cheng, X.; Yang, H.; Xue, H.; Wang, X. Univesal Design of LLC Resonant Converter with Fixed Switching Frequency. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Information Technology, Big Data and Artificial Intelligence, ICIBA 2020, Chongqing, China, 6–8 November 2020; pp. 1323–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinnikov, D.; Chub, A.; Kosenko, R.; Zakis, J.; Liivik, E. Comparison of Performance of Phase-Shift and Asymmetrical Pulsewidth Modulation Techniques for the Novel Galvanically Isolated Buck–Boost DC–DC Converter for Photovoltaic Applications. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2017, 5, 624–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakib, S.M.S.I.; Mekhilef, S. A Frequency Adaptive Phase Shift Modulation Control Based LLC Series Resonant Converter for Wide Input Voltage Applications. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2017, 32, 8360–8370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, G.V.B.; Nagendrappa, H. Fixed frequency control of LCL-T resonant power converter with capacitive output filter. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Computer Applications In Electrical Engineering-Recent Advances (CERA), Roorkee, India, 5–7 October 2017; pp. 568–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harischandrappa, N.; Bhat, A.K.S. A Fixed-Frequency LCL-Type Series Resonant Converter With a Capacitive Output Filter Using a Modified Gating Scheme. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2014, 50, 4056–4064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy G., V.B.; Nagendrappa, H. Modified Gating Signal Controlled High-Frequency Transformer Isolated LCL-T Type DC-DC Resonant Power Converter. In Proceedings of the 2018 8th IEEE India International Conference on Power Electronics (IICPE), Jaipur, India, 13–15 December 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Bhat, A.K.S. A bidirectional dual-bridge LCL-type series resonant converter controlled with modified gating scheme. In Proceedings of the IEEE 8th International Power Electronics and Motion Control Conference (IPEMC-ECCE Asia), Hefei, China, 22–26 May 2016; pp. 3036–3042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


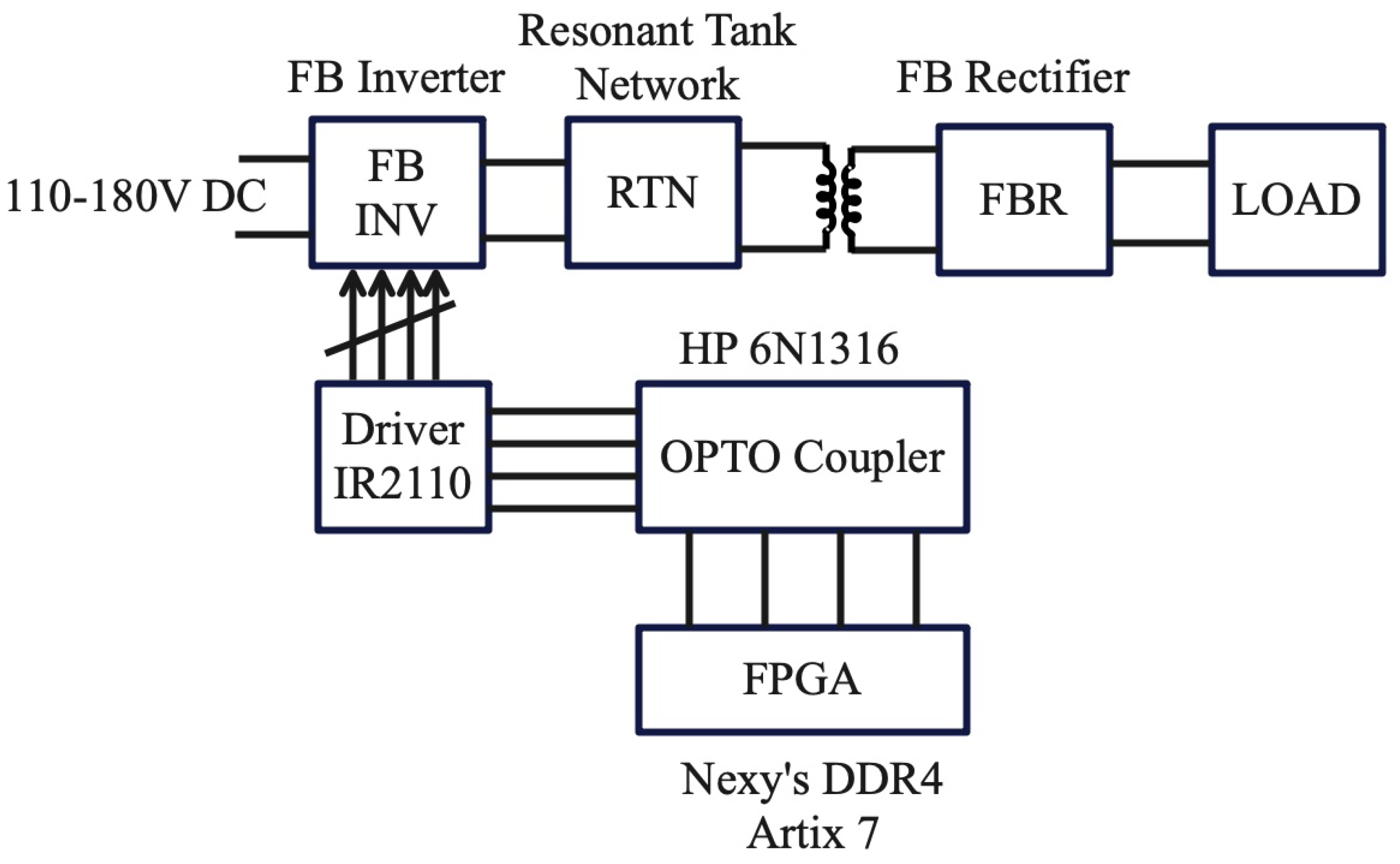
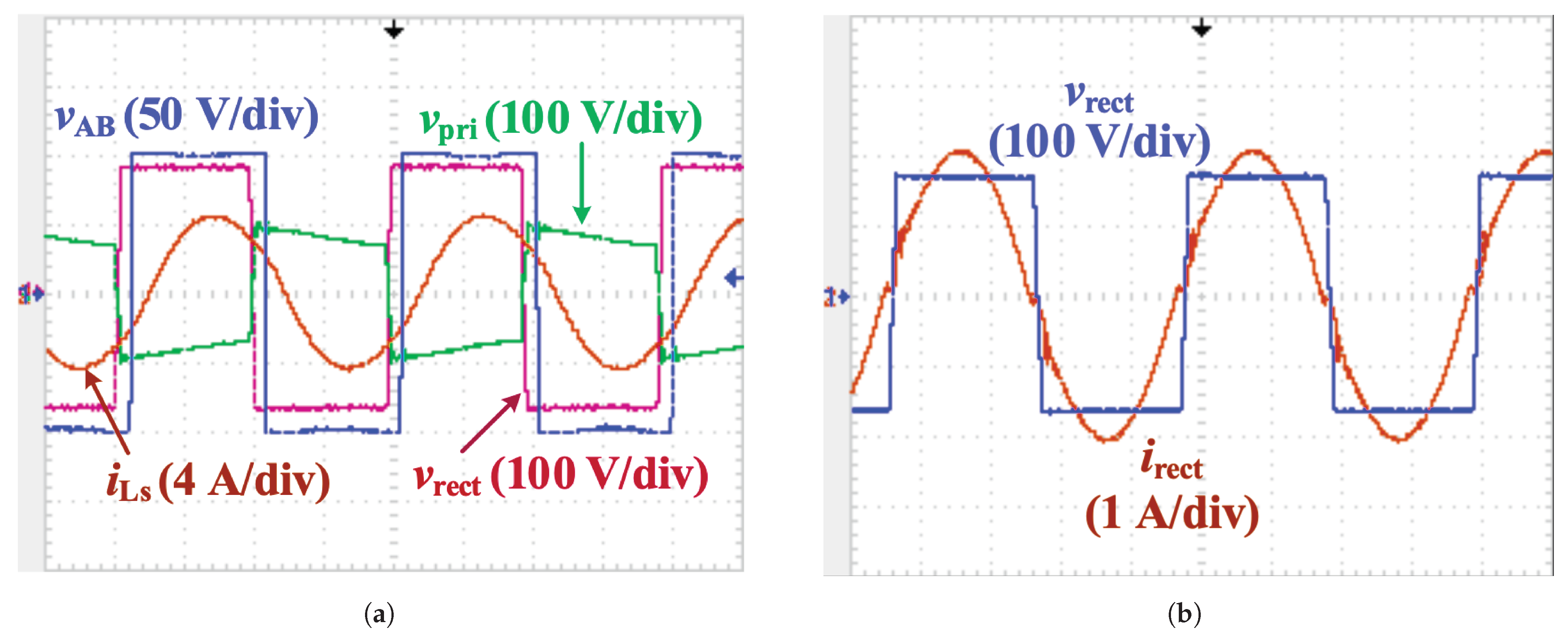
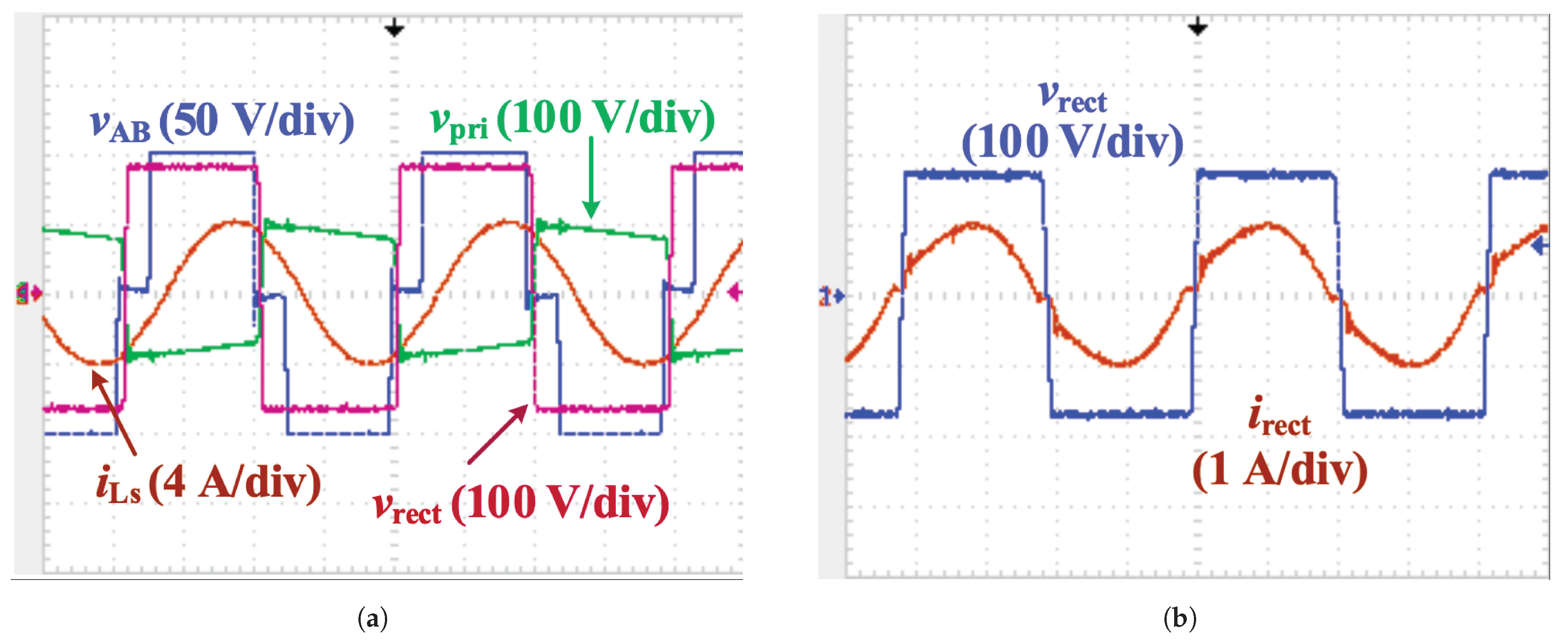
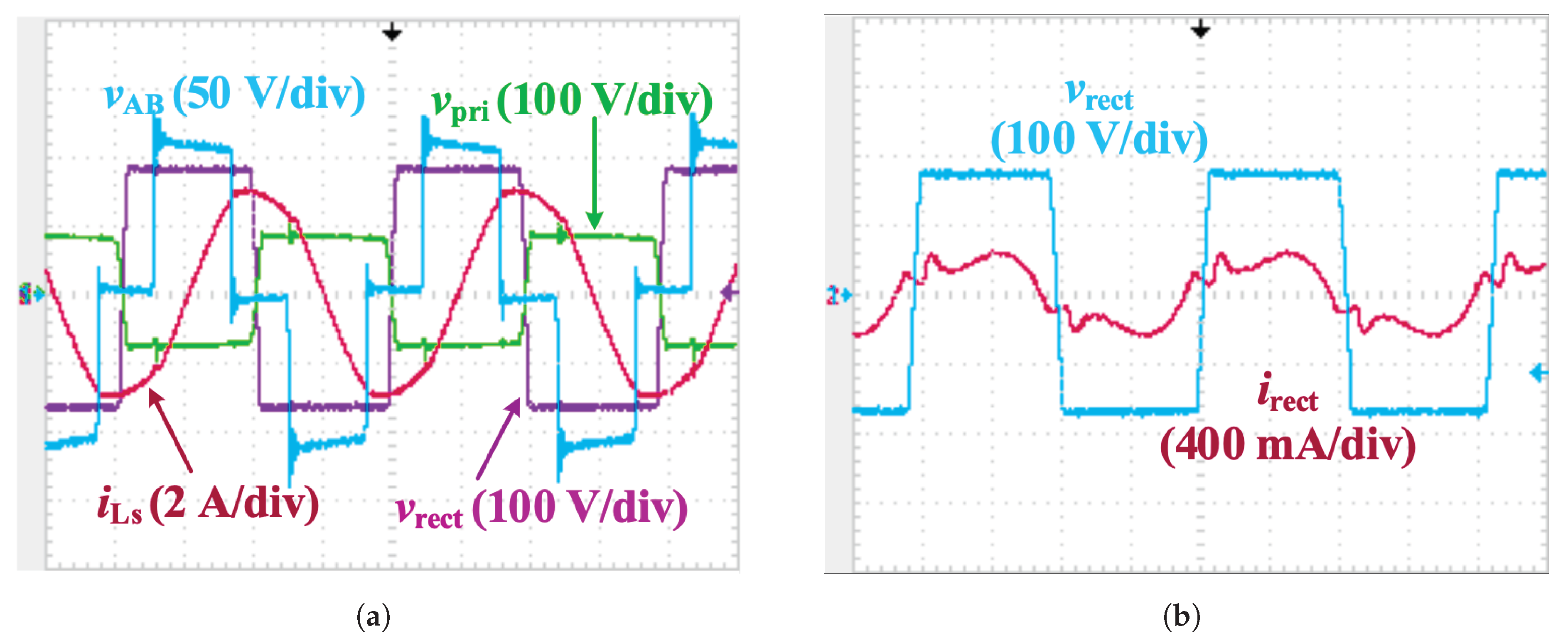

| Indicators | Value |
|---|---|
| (min.), (max.) | 110.00 V, 180.00 V |
| , | 220.00 V, 300.00 W |
| 100.00 kHz |
| Component | Details |
|---|---|
| MOSFET switches (–) | IRF740 (400 V, 10 A) |
| , , , | 122.83 µH, 94.6 µH, 470 µF (400 V), 38.15 nF |
| HF transformer, turns ratio | Core: EE4215, 16:40 |
| to | UF5404 (voltage = 400 V, current = 3 A) |
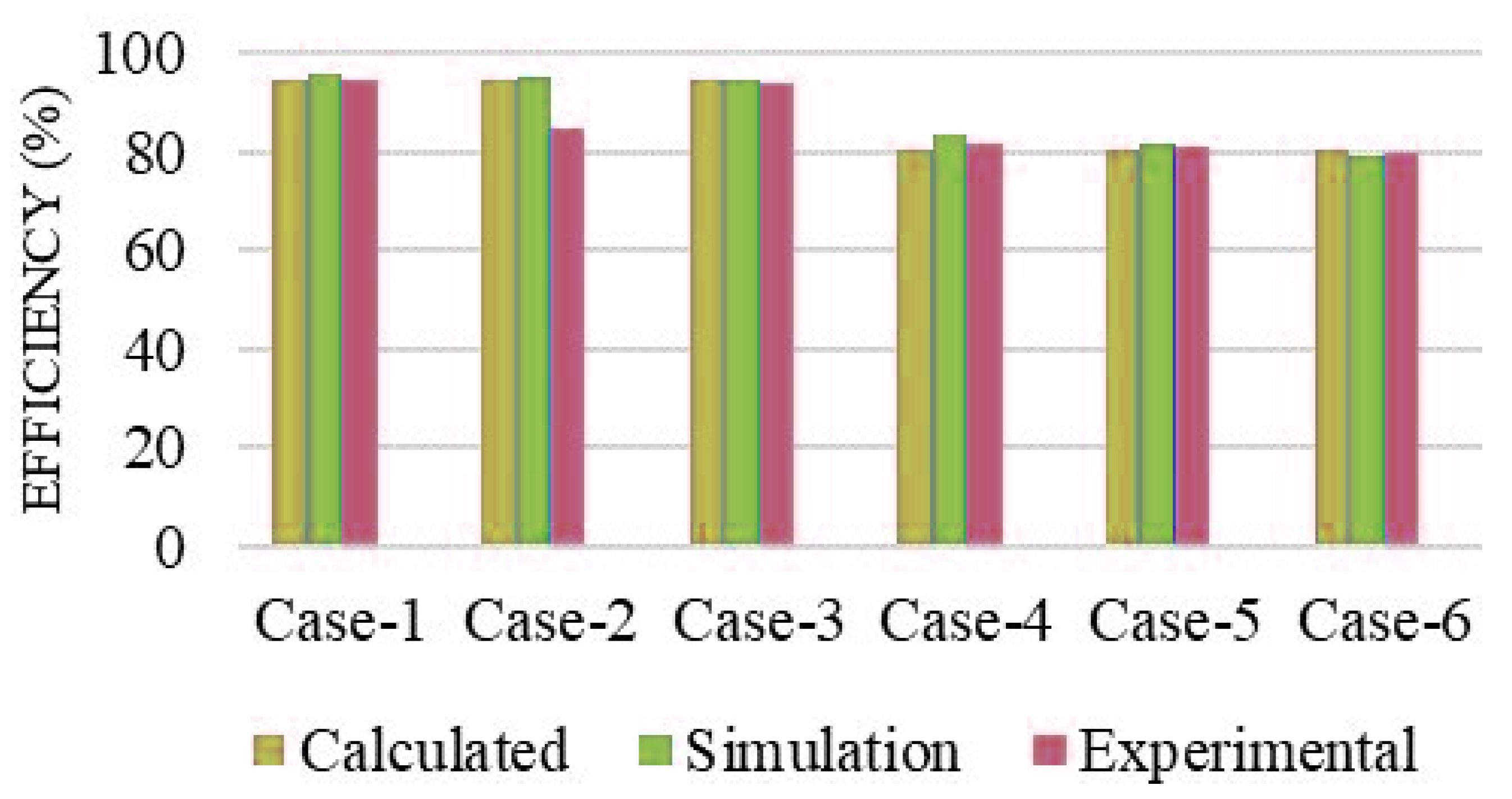
| Parameters | Calculation | Simulation | Experimental |
|---|---|---|---|
| (V) | 220 | 214.62 | 206 |
| (A) | 1.36 | 1.33 | 1.31 |
| (o) | 180 | 180 | 176.3 |
| (A) | 3.04 | 2.99 | 3.04 |
| (A) | 3.80 | 3.70 | 3.425 |
| (V) | 260 | 253 | 254 |
| (A) | 2.72 | 2.703 | 2.6 |
| (%) | 94.74 | 96 | 94.35 |
| Parameter | ADC Control | Phase-Shift Control | Modified Gating Control |
|---|---|---|---|
| Switch utilization | Underutilized | Well utilized | Well utilized |
| DC blocking capacitor for full-bridge operation | Required | Not required | Not required |
| Possibilities of transformer core saturation | Maximal | Minimal | Minimal |
| Range of duty cycle | Broad | Limited | Very Limited |
| Loss of ZVS with maximum input voltage | Two switches | Two switches | 1 switch |
| Circuits | Factors | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pulse Width Angle () Change | Component Stresses | Protection for Short-Circuit Load | Soft-Switching | ||
SRC | 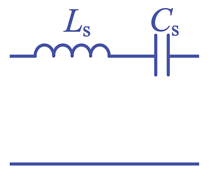 | Broad | Minimal | Absent | ZVS |
PRC | 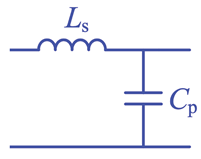 | Broad | Maximal | Present | ZVS |
LCC |  | Limited | Maximal | Absent | ZVS |
LCL |  | Moderate | Minimal | Absent | ZVS, ZCS |
LCL-T | 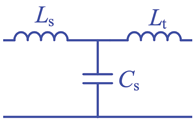 | Limited | Minimal | Present | ZVS |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Reddy, V.B.; Bhaskar, M.S.; Subramaniam, U. Resonant DC/DC Converters: Investigating Phase-Shift Control. Energies 2023, 16, 6012. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16166012
Reddy VB, Bhaskar MS, Subramaniam U. Resonant DC/DC Converters: Investigating Phase-Shift Control. Energies. 2023; 16(16):6012. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16166012
Chicago/Turabian StyleReddy, Vijaya Bhaskar, Mahajan Sagar Bhaskar, and Umashankar Subramaniam. 2023. "Resonant DC/DC Converters: Investigating Phase-Shift Control" Energies 16, no. 16: 6012. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16166012
APA StyleReddy, V. B., Bhaskar, M. S., & Subramaniam, U. (2023). Resonant DC/DC Converters: Investigating Phase-Shift Control. Energies, 16(16), 6012. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16166012








