Biocatalyzed Transesterification of Waste Cooking Oil for Biodiesel Production Using Lipase from the Amazonian Fungus Endomelanconiopsis endophytica
Abstract
:1. Introduction
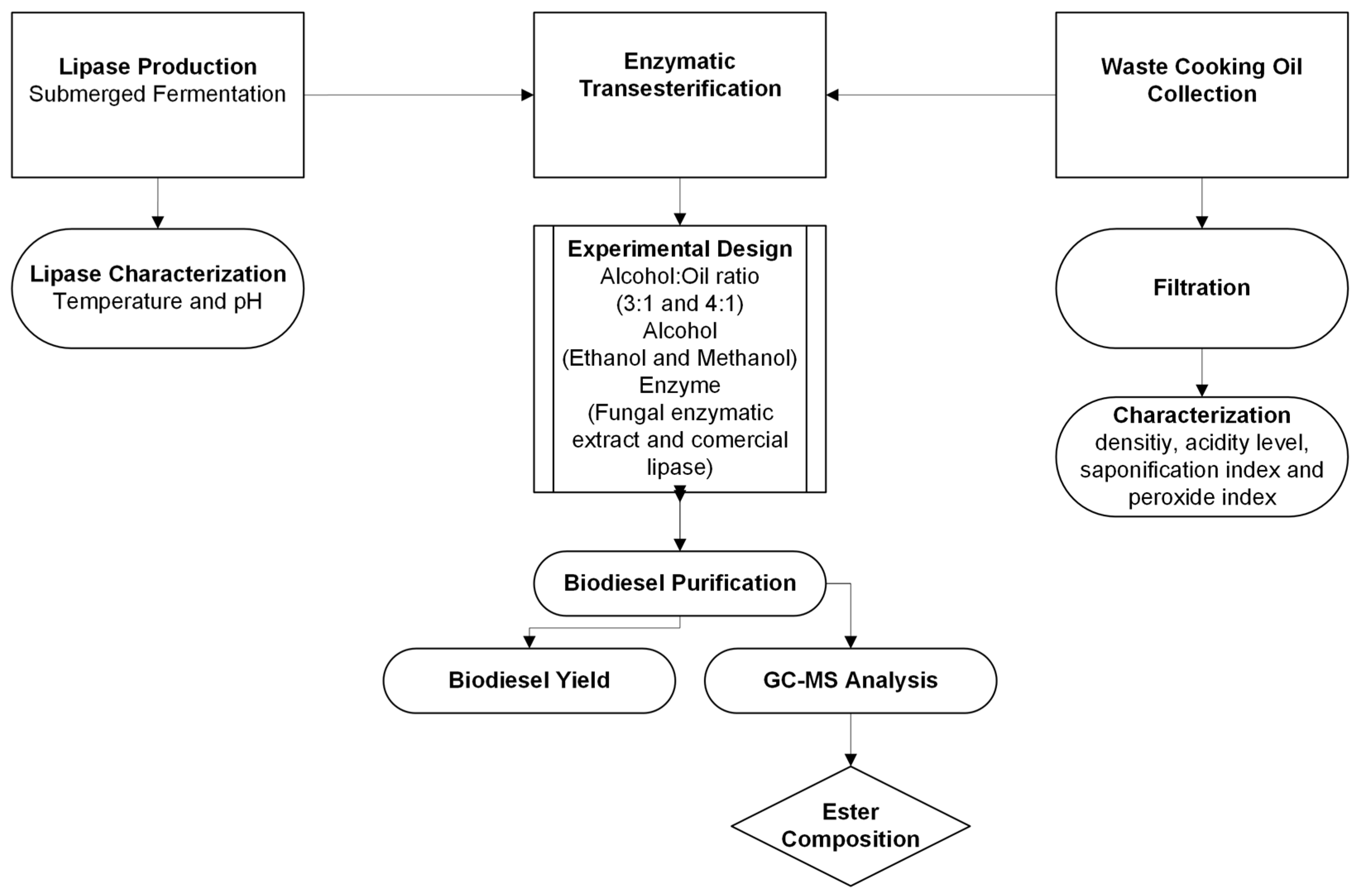
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Waste Cooking Oil and Soybean Oil
2.2. Physicochemical Characterization of Waste Cooking Oil
2.3. Microorganism
2.4. Lipase Production
2.5. Determination of Lipase Enzyme Activity
2.6. Characterization of Enzyme Extract
2.7. Determination of Protein Concentration
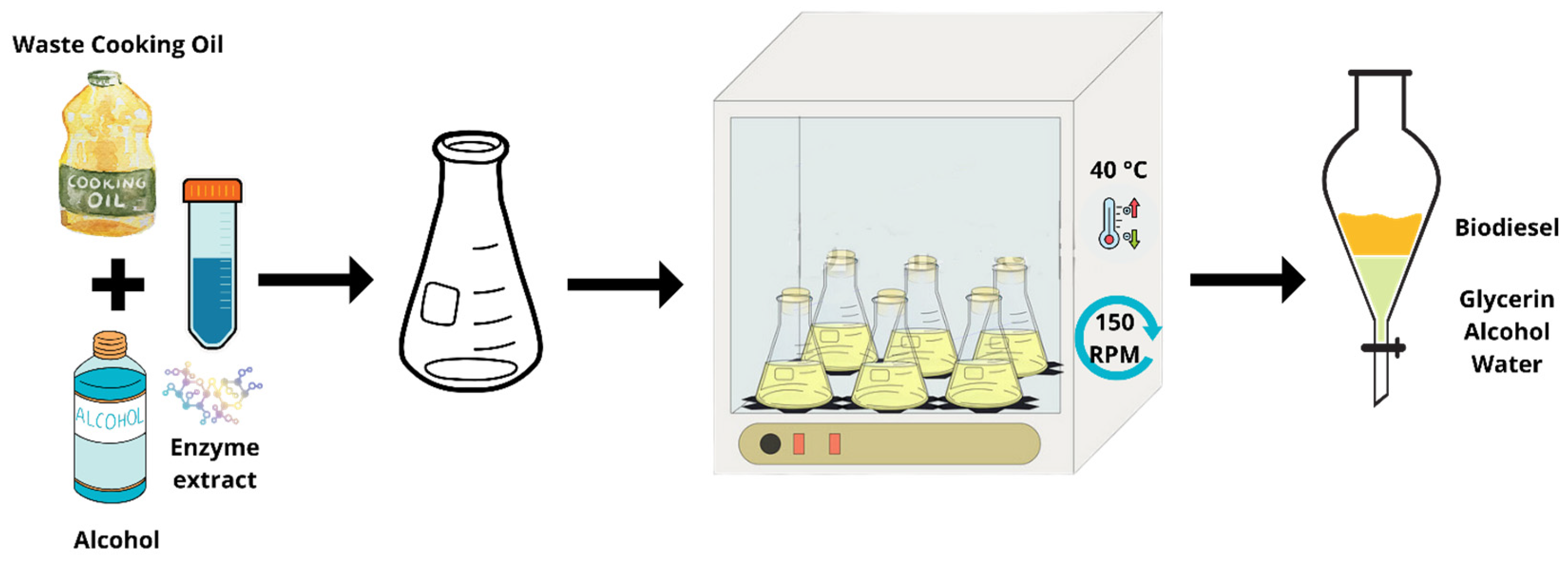
2.8. Enzymatic Transesterification—Biodiesel Production
2.9. Purification of the Biodiesel
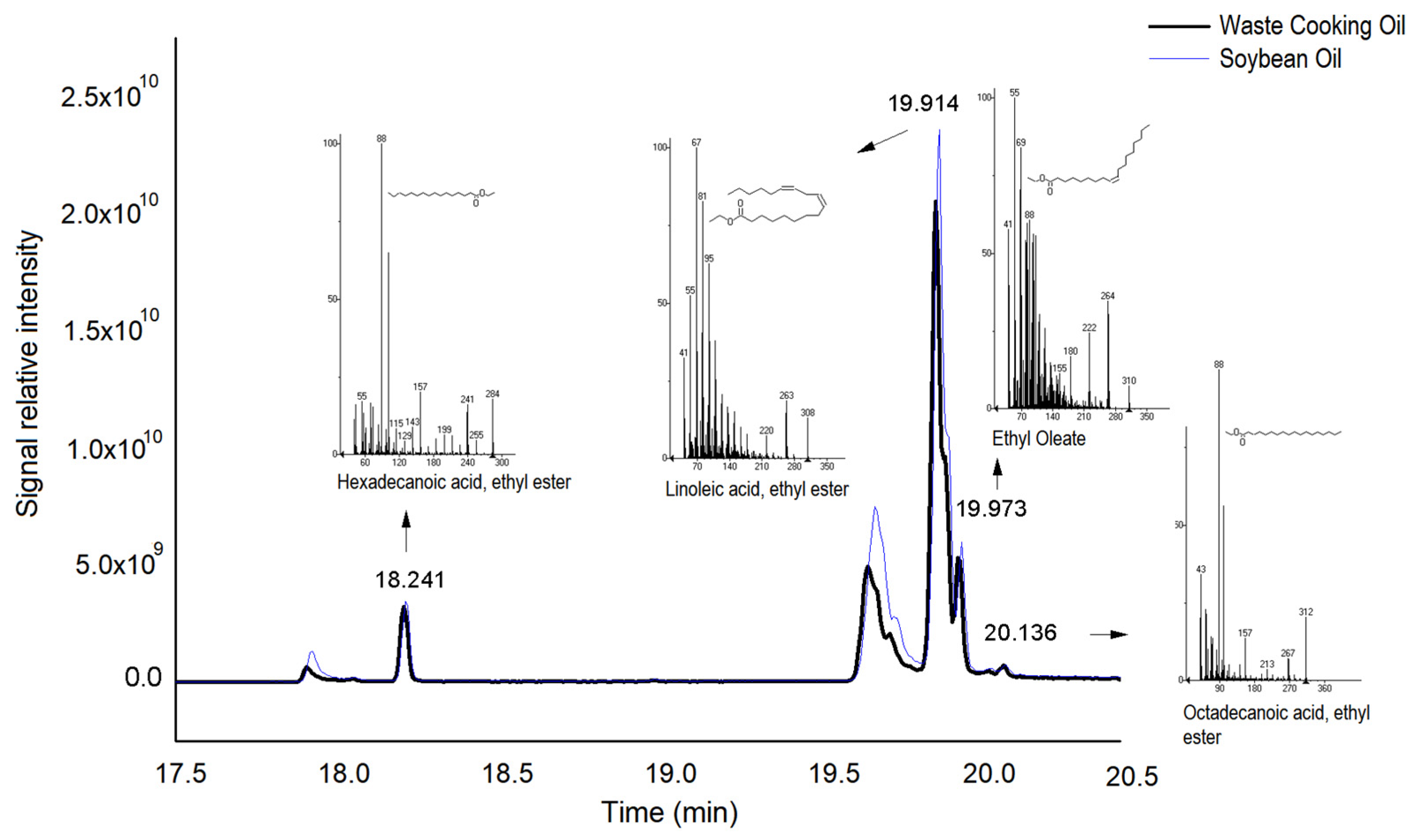
2.10. Chromatographic Analysis
2.11. Biodiesel Yield
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of the Waste Oil
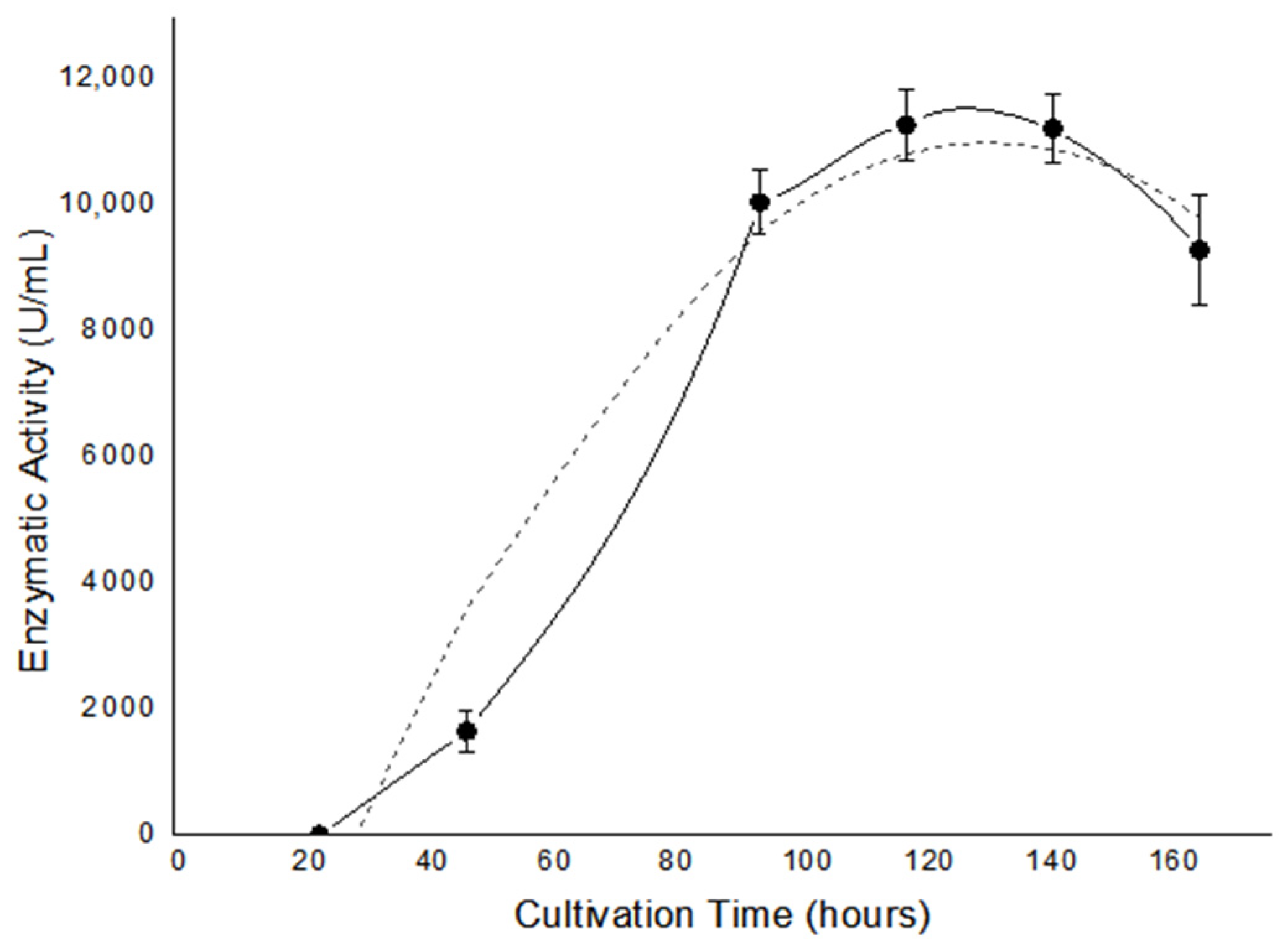
3.2. Enzyme Production
3.3. Characterization of the Enzyme Extract
3.4. Biodiesel Production
3.5. Biodiesel Production—Evaluation of the Parameters Involved in the Reaction
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aransiola, E.F.; Ojumu, T.V.; Oyekola, O.O.; Madzimbamuto, T.F.; Ikhu-Omoregbe, D.I.O. A review of current technology for biodiesel production: State of the art. Biomass Bioenergy 2014, 61, 276–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiong, A.N.T.; Khan, Z.; Chin, Z.; Wahid, O.A.; Wachira, R.M.; Kung, S.M. Plant design of biodiesel production from waste cooking oil in Malaysia. Biofuels 2023, 14, 353–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpio, L.G.T. Transmission of variations in the biodiesel mandate for Brazilian biodiesel market. Biofuels 2023, 14, 373–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grand View Research: Biodiesel Market Size, Share & Trends Analysis Report by Feedstock (Vegetable Oils, Animal Fats), By Application (Fuel, Power Generation), by Region (Europe, APAC), and Segment Forecasts, 2022–2030. Available online: https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/biodiesel-market (accessed on 4 May 2023).
- Naylor, R.L.; Higgins, M.M. The rise in global biodiesel production: Implications for food security. Glob. Food Secur. 2018, 16, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ávila, M.T.; Gazzoni, D.L. Biocombustível: Embrapa—Empresa Brasileira de Pesquisa Agropecuária: Soja. 8 December 2021. Available online: https://www.embrapa.br/agencia-de-informacao-tecnologica/cultivos/soja/pos-producao/agroenergia/biocombustiveis (accessed on 3 May 2022).
- Lin, Y.; Amesho, K.T.T.; Chen, C.; Cheng, P.; Chou, F. A cleaner process for green biodiesel synthesis from waste cooking oil using recycled waste oyster shells as a sustainable base heterogeneous catalyst under the microwave heating system. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2020, 17, 100310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahar, S.S.; Iqbal, J.; Ullah, I.; Bhatti, H.N.; Nouren, S.; Rehman, H.; Nisar, J.; Iqbal, M. Biodiesel production from waste cooking oil: An efficient Technique to convert waste into biodiesel. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2018, 41, 220–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tambor, J.H.M.; Cwejgorn, F.V.; Santos, A.G.; Lopes, G.C.; Lescano, V.P. Biodiesel production from the used kitchen oil: A sustainable alternative. Rev. Caleidosc. 2019, 11, 545–548. [Google Scholar]
- Sarno, B.; Iuliano, M. Biodiesel production from waste cooking oil. Green Process. Synth. 2019, 8, 828–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thilakarathne, D.; Miyuranga, K.A.V.; Arachchige, U.S.P.R.; Weerasekara, N.A.; Jayasinghe, R.A. Production of biodiesel from Waste Cooking Oil Laboratory Scale: A Review. Int. J. Sci. Eng. Sci. 2021, 5, 28–34. [Google Scholar]
- Fonseca, J.M.; Taleken, J.G.; Almeida, V.C.; Silva, C. Biodiesel from waste frying oils: Methods of production and purification. Energy Convers. Manag. 2019, 184, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasirajan, R. Biodiesel production by two step process from an energy source of Chrysophyllum albidum oil using homogeneous catalyst. S. Afr. J. Chem. Eng. 2021, 37, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.X.; Xia, W.; Wang, S. Biodiesel production from waste cooking oil using a waste diaper derived heterogeneous magnetic catalyst. Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 2022, 40, 511–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, H.M.; Iqbal, T.; Ali, C.H.; Yasin, S.; Jamil, F. Waste quail beaks as renewable source for synthesizing novel catalysts for biodiesel production. Renew. Energy 2020, 154, 1035–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.-P.; Amesho, K.T.T.; Chen, C.-E.; Jhang, S.-R.; Chou, F.-C.; Lin, Y.-C. Optimization of Biodiesel Production from Waste Cooking Oil Using Waste Eggshell as a Base Catalyst under a Microwave Heating System. Catalysts 2018, 8, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrusca, M.C.; Romero, r.; Martínez, S.L.; Remírez-Serrano, A.; Natividade, R. Biodiesel production from waste cooking oil: A pespective on catalytic processes. Processes 2023, 11, 1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husain, I.A.; Alkhatib, M.F.; Jammi, M.S.; Mirghani, M.E.; Bin Zainudin, Z.; Hoda, A. Problems, control and treatment of fat, oil and grease (FOG): A review. J. Oleo Sci. 2014, 36, 747–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaur, A.; Mishra, S.; Chowdhury, S.; Baredar, P.; Verma, P. A review on factor affecting biodiesel production from waste cooking oil: An Indian perspective. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 46, 5594–5600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Muhtaseb, A.H.; Osman, A.I.; Murphin Kumar, P.S.; Jamil, F.; Al-Haj, L.; Al Nabhani, A.; Kyaw, H.H.; Myint, M.T.Z.; Mehta, N.; Rooney, D.W. Circular economy approach of enhanced bifunctional catalytic system of CaO/CeO2 for biodiesel production from waste loquat seed oil with life cycle assessment study. Energy Convers. Manag. 2021, 236, 114040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corral-Bobadilla, M.; Lostado-Lorza, R.; Somovilla-Gómez, F.; Íñiguez-Macedo, S. Life cycle assessment multi-objective optimization for eco-efficient biodiesel production using waste cooking oil. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 359, 132113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claeys, C. Used Cooking Oil (UCO) feedstock now accounts for one-fifth of all european biofuels. In Proceedings of the ACI Oleofuels Conference, Marseille, France, 18–19 May 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Mandari, V.; Devarai, S.K. Biodiesel production using homogeneous, heterogeneous, and enzyme catalysts via transesterification and esterification reactions: A critical review. Bioenergy Res. 2021, 15, 935–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avhad, M.R.; Marchetti, J.M. Uses of Enzymes for Biodiesel Production. In Advanced Bioprocessing for Alternative Fuels, Biobased Chemicals, and Bioproducts; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2019; pp. 135–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, L.P.; Kothe, V.; Aparecida, M.; Muniz-Wypych, A.S.; Nakagaki, S.; Krieger, N.; Wypych, F.; Cordeira, C. Biodiesel: Raw materials, production technologies and fuel properties. Rev. Virtual Quím. 2017, 9, 317–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norjannah, B.; Ong, H.C.; Masjuki, H.H.; Juan, J.C.; Chong, W.T. Enzymatic transesterification for biodiesel production: A comprehensive review. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 60034–60055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, N.M.L.; Vieira-Almeida, E.C.; Silva, L.P.; Paula, C.B.C.; Bastos, A.C.M.; Santos, I.L.; Paula-Elias, F.C.; Almeida, A.F. Processos Químicos e Biotecnológicos—Lipases microbianas. In Bioprocessos e Aplicações Industriais, 1st ed.; Andrade, D.F., Souza, A.A., Andrade, D.E., Oliveira, E.J., Santos, F., Lopes, J.E.F., Neves, O.F., Lima, L.C., Ferreira Filho, N., Oliveira, V.A., Eds.; Poisson: Belo Horizonte, Brazil, 2020; Volume 5, pp. 2–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marotti, B.S.; Cortez, D.V.; Gonçalves, D.B.; Castro, H.F. Screening of species from the genus Penicillium producing cell bound lipases to be applied in the vegetable oil hydrolysis. Quím. Nova 2017, 40, 427–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, P.; Enespa, S.R.; Arora, P.K. Microbial lipases and their industrial applications: A comprehensive review. Microb. Cell Fact. 2020, 9, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambare, V.; Patankar, R.; Bhusare, B.; Christopher, L. Recents advances in feedstock and lipase research and development towards commecialization of enzymatic biodiesel. Processes 2021, 9, 1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Klimova, E.; Rodríguez-Peña, K.; Sánchez, S. Endophytes as sources of antibiotics. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2017, 134, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matias, R.R.; Sepúlveda, A.M.G.; Batista, B.N.; Lucena, J.M.V.M.; Albuquerque, P.M. Degradation of Staphylococcus aureus biofilm using hydrolytic enzymes produced by amazonian endophytic fungi. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2021, 193, 2145–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matias, R.R.; Rodrigues, J.G.C.; Procópio, R.E.L.; Matte, C.R.; Duvoisin Junior, S.; Soares, R.M.D.; Albuquerque, P.M. Lipase production from Aniba canelilla endophytic fungi, characterization, and application of the enzymatic extract. Res. Soc. Dev. 2022, 11, e180111234326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batista, B.N.; Matias, R.R.; Oliveira, R.L.; Albuquerque, P.M. Hydrolytic enzyme production from açai palm (Euterpe precatoria) endophytic fungi and characterization of the amylolytic and cellulolytic extracts. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 38, 30–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, Q.U.A.; Irfan, M.; Ahmed, S.; Hasan, F.; Shah, A.A.; Khan, S.; Rehman, F.U.; Khan, H.; Ju, M.; Li, W.; et al. Bio-catalytic transesterification of mustard oil for biodiesel production. Biofuels 2019, 13, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOCS: American Oil Chemists’ Society. A.O.C.S. Official Method Cc 10a-25. In Official Methods and Recommended Practices of the American Oil Chemists’ Society, 4th ed.; AOCS: Champaign, IL, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Instituto Adolfo Lutz. Métodos Físico-Químicos para Análise de Alimentos; Instituto Adolfo Lutz: São Paulo, Brazil, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- AOCS: American Oil Chemists’ Society. AOCS Official Method Cd 8-53. In Official Methods and Recommended Practices of the American Oil Chemists’ Society, 4th ed.; AOCS: Champaign, IL, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- AOCS: American Oil Chemists’ Society. A.O.C.S. Official Method Cd 3-25. In Official Methods and Recommended Practices of the American Oil Chemists’ Society, 4th ed.; AOCS: Champaign, IL, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Gurgel, R.S.; Rodrigues, J.G.C.; Matias, R.R.; Batista, B.N.; Oliveira, R.L.; Albuquerque, P.M. Biological activity and production of metabolites from Amazon endophytic fungi. Afr. J. Micrbiol. Res. 2020, 14, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, U.K.; Stuckmann, M. Glycogen, hyaluronate and some other polysaccharides greatly enhance the formation of exolipase by Serratia marcescens. J. Bacteriol. 1979, 138, 663–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tombini, J. Selection of Lipolytic Microorganisms and Lipase Production from Soy Processing by Products. Master’s Thesis, Federal Technological University of Paraná, Pato Branco, Brazil, 29 May 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Dantas, A. Imobilização e Caracterização da Lipase Ns-40116 em Poliestireno. Master’s Thesis, Federal University of Santa Catarina, Florianópolis, Brazil, 24 February 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz Junior, A. Imobilização de Lipase de Candida antarctica B em Quitosana para Obtenção de Biodiesel por Transesterificação do Óleo de Mamona. Master’s Thesis, Federal University of Santa Catarina, Florianópolis, Brazil, 18 July 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Marder, F.; Celin, M.M.; Mazuim, M.S.; Scneider, R.C.S.; Macganan, M.T.; Carbellini, V.A. Produção de biodiesel por biocatálise utilizando método alternativo de imobilização da lipase em hidrogel. Tecno-Lógica 2008, 12, 56–64. [Google Scholar]
- Parawira, W. Biotechnological production of biodiesel fuel using biocatalysed transesterification: A review. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2009, 29, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muanruksa, P.; Kaewkannetra, P. Combination of fatty acids extraction and enzymatic esterification for biodiesel production using sludge palm oil as a low-cost substrate. Renew. Energy 2020, 146, 901–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burmana, A.D.; Tambun, R.; Haarynato, B.; Alexander, V. Effect of reaction time on biodiesel production from palm fatty acid distillate by, using PTSA as a catalyst. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 1003, 12134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedro, K.C.N.R.; Parreira, J.M.; Correia, I.N.; Henriques, C.A.; Langone, M.A.P. Enzymatic biodiesel synthesis from acid oil using a lipase mixture. Quim. Nova 2018, 41, 284–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosset, D.V.; Wancura, J.H.C.; Mazutti, M.A.; Jahn, S.L. Produção de biodiesel catalisada por lipases solúveis: Influência do excesso de metanol e da concentração de água na reação. In Proceedings of the Anais do XII Congresso Brasileiro de Engenharia Química, São Carlos, Brazil, 16–19 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Aquino, I.P. Evaluation of Biodiesel Corrosiveness by Gravimetric and Eletrochemical Techniques. Doctoral Thesis, University of Sao Paulo, São Paulo, Brazil, 20 March 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Naser, J.; Avbenake, O.P.; Dabai, F.N.; Jibril, B.Y. Regeneration os spent bleaching earth and conversion of recovered oil to biodiesel. Waste Manag. 2021, 126, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parandi, E.; Safaripour, M.; Abdellatif, M.H.; Saidi, M.; Bozorgian, A.; Nodeh, H.R.; Rezania, S. Biodiesel production from waste cooking oil using a novel biocatalyst of lipase enzyme immobilized magnetic nanocomposite. Fuel 2022, 313, 123057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamil, N.; Zairi, M.N.M.; Nasim, N.A.M.; Pa’ee, F. Influences of Enviromental Conditions to Phytoconstituents in Clitoria ternatea (Butterfly Pea Flower)—A review. J. Sci.Technol. 2018, 10, 208–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, S.V.F.; Silva, C.V.; Previdi, D.; Portela, F.M.; Gomes, M.F. Caracterização Estrututral e físico-química de biodiesel produzido a partir de óleo residual do reifeitório do IF Goiano—Campus Urutaí. Multi-Sci. J. 2018, 1, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aworanti, O.A.; Ajani, A.O.; Agarry, S.E. Process parameter estimation of biodiesel production from waste frying oil (vegetable and palm oil) using homogeneous catalyst. J. Food Process. Technol. 2019, 10, 811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Saadi, A.; Mathan, B.; He, Y. Biodiesel production via simultaneous transesterification and esterification reactions over SrO–ZnO/Al2O3 as a bifunctional catalyst using high acidic waste cooking oil. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2020, 162, 238–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, M.; Ramli, A.; Naeem, A. Biodiesel production from low FFA waste cooking oil using geterogeneous catalyst derived from chicken bones. Renew. Energy 2015, 76, 362–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siqueira, A.F.; Vidigal, I.G.; Melo, M.P.; Giordani, D.S.; Batista, P.S.; Ferreira, A.L.G. assessing waste cooking oils for the production of quality biodiesel using na eletronic nose and a stochastic model. Energy Fuels 2019, 33, 3221–3226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agência Nacional de Vigilância Sanitária (ANVISA). Resolução RDC nº 270, de 22 de Setembro de 2005. 2005. Available online: http://www.anvisa.gov.br/e-legis/ (accessed on 12 December 2021).
- Plata, V.; Ferreira-Beltrán, D.; Gauthier-Maradei, P. Effect of cooking conditions on selected properties of biodiesel produced from Palm-Based waste cooking oil. Energies 2022, 15, 908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morais, V.S.; Castro, E.V.R.; Carneiro, M.T.W.D.; Brandão, G.P.; Fabri Junior, R.; Sena, D.R. ASTM color: A simple and fast method for determining quality of biodiesel produced from used cooking oils. Quim. Nova 2013, 36, 587–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, D.S.; Yoo, H.Y.; Park, C.; Kim, S.W. Biodiesel production by lipases co-immobilized on the functionalized activated carbon. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2019, 7, 100248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binhayeedung, N.; Lomklao, S.; Prasertsan, P.; Sangkharak, K. Improvement of biodiesel production using waste cooking oil and applying single and mixed immobilized lipases on polyhydroxyalkanoate. Renew. Energy 2020, 162, 1819–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovere, B.O.; Rodrigues, J.H.; Teleken, J.G. Reduction of the acidity index through neutralization and esterification for biodiesel production. Braz. J. Dev. 2020, 6, 24678–24686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu, M.L.; Nooh, H.M.; Oslan, S.N.; Salleh, A.B. Optimization of physical conditions for the production of thermostable T1 lipase in Pichia guilliermondii strain SO using response surface methodology. BMC Biotechnol. 2017, 17, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, B.; Shamekh, S.; Deska, J.; Bandopadhyay, R. Statistical optimization of media components for production of extracellular lipase from edible mushroom Cantharellus cibarius. Biol. Futur. 2022, 73, 315–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behera, A.R.; Veluppal, A.; Dutta, K. Optimization of physical parameters for enhanced production of lipase from Staphylococcus hominis using response surface methodology. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 34277–34284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho Neto, F.G.M.R. Isolamento e Clonagem do Gene que Codifica a Lipase do Fungo Endomelanconiopsis Endophytica. Master’s Thesis, Amazonas State University, Manaus, Brazil, 25 October 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Sopalun, K.; Laosripaiboon, W.; Wachirachaikarn, A.; Iamtham, S. Biological potential and chemical composition of bioactive compounds from endophytic fungi associated with thai mangrove plants. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2021, 141, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, G.F.; Silva, M.R.L.; Hirata, D.B. Production of new lipase from Preussia africana and a partial characterization. Prep. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2021, 52, 942–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, K.S.C.; Queiroz, M.S.R.; Gomes, B.S.; Dallago, R.; Souza, R.O.M.A.; Guimarães, D.O.; Itabaiana, I., Jr.; Leal, I.C.R. Lipases of Endophytic Fungi Stemphylium lycopersici and Sordaria sp.: Application in the synthesis of solketal derived monoacylglycerols. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2020, 142, 109664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sena, I.S.; Ferreira, A.M.; Marinho, V.H.; Holanda, F.H.; Borges, S.F.; Souza, A.A.; Koga, R.C.R.; Lima, A.L.; Florentino, A.C.; Ferreira, I.M. Euterpe oleracea Mart (Açaizeiro) from the Brazilian Amazon: A Novel Font of Fungi for Lipase Production. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szymczak, T.; Cybulska, J.; Podlesny, M.; Frac, M. Various Perspectives on Microbial Lipase Production Using Agri-Food Waste and Renewable Products. Agriculture 2021, 11, 540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colla, L.M.; Ficanha, A.M.M.; Rizzardi, J.; Bertolin, T.E.; Reinehr, C.O.; Costa, J.A.V. Production and Characterization of Lipases by Two New Isolates of Aspergillus through Solid-State and Submerged Fermentation. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 725959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsiao, M.C.; Liao, P.H.; Lan, N.V.; Hou, S.S. Enhancement of biodiesel production from high-acid-value waste cooking oil via a microwave reactor using a homogeneous alkaline catalyst. Energies 2021, 14, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talukder, M.M.R.; Wu, J.C.; Fen, N.M.; Melissa, Y.L.S. Two-step lipase catalysis for production of biodiesel. Biochem. Eng. J. 2010, 49, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lampi, A.M.; Yang, Z.; Mustonen, O.; Piironen, V. Potential of faba bean lipase and lipoxygenase to promote formation of volatile lipid oxidation products in food models. Food Chem. 2020, 311, 125982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, F.A. Estudo da Produção de Biodiesel Utilizando Etanol e Óleo de Soja ou De macaúba, Catalisada por Lipase de Mamona e de Thermomyces lanuginosus. Master’s Thesis, São Carlos Federal University, São Carlos, Brazil, 25 February 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Aguieiras, E.C.G.; Barros, D.S.N.; Sousa, H.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R.; Freire, D.M.G. Influence of the raw material on the final properties of biodiesel produced using lipase from Rhizomucor miehei grown on babassu cake as biocatalyst of esterification reactions. Renew. Energy 2017, 113, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguieiras, E.C.G.; Oliveira, E.D.C.; Castro, A.M.; Langone, M.A.P.; Freire, D.M.G. Biodiesel production from Acrocomia aculeata acid oil by (enzyme/enzyme) hydroesterification process: Use of vegetable lipase and fermented solid as low-cost biocatalysts. Fuel 2014, 135, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Chen, B.; Tan, T. Esterification synthesis of ethyl oleate in solvent-free system catalyzed by lipase mebrane from fermentation broth. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2011, 163, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raita, M.; Laothanachareon, T.; Champreda, V.; Laosiripojana, N. Biocatalytic esterification of palm oil fatty acids for biodiesel production using glycine-based cross-linked protein coated microcrystalline lipase. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2011, 73, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ávila Vázquez, V.; Aguilera Flores, M.M.; Hernández Casas, L.F.; Medellín Castillo, N.A.; Rocha Uribe, A.; Correa Aguado, H.C. Biodiesel production catalyzed by lipase extract powder of Leonotis nepetifolia (Christmas Candlestick) seed. Energies 2023, 16, 2848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalcanti, F.T.T.; Simao Neto, F.; Falcao, I.R.A.; Souza, J.E.S.; Moura Junior, L.S.; Sousa, P.S.; Rocha, T.G.; Sousa, I.G.; Gomes, P.H.L.; Souza, M.C.M.; et al. Opportunities for improving biodiesel production via lipase catalysis. Fuel 2020, 288, 119577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Yan, Y.; Liu, S.; Hu, L.J.; Wang, G. Praparation of cross-linked lipase-coated micro-crystals for biodiesel production from waste cooking oil. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 4755–4758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulla, R.; Derman, E.; Mathialagan, T.; Yaser, A.Z.; Samah, M.A.A.; Gansau, J.A.; Najmuddin, S.U.F.S. Biodiesel production from waste palm cooking oil using immobilized Candida rugosa lipase. Sustainability 2022, 14, 13632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taher, H.; Nashef, E.; Anvar, N.; Al-Zuhair, S. Enzymatic production of biodiesel from waste oil in ionic liquid medium. Biofuels 2017, 10, 463–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, H.; Gao, L.; Nie, K.; Wang, M.; Tan, T. A new reactor for enzymatic synthesis of biodiesel from waste cooking oil: A static-mixed reactor pilot study. Renew. Energy 2020, 15, 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geris, R.; Santos, N.A.C.; Amaral, B.A.; Maia, I.S.; Castro, V.D.; Carvalho, J.R.M. Biodiesel from soybean oil: Experimental procedure of transesterification for organic chemistry laboratories. Quím. Nova 2007, 30, 1369–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Li, Y.; Liu, D. Free lipase-catalyzed esterefication of oleic acid fatty acid ethyl ester preparation with response surface optimization. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2013, 90, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- José, C.; Bonetto, R.D.; Gambaro, L.A.; Torres, M.P.G.; Foresti, M.L.; Ferreira, M.J.; Birand, L.R. Investigation of the causes of deactivation degradation of the commercial biocatalyst Novozym 432 in ethanol and ethanol-aqueous media. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzymat. 2011, 71, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguieiras, E.C.G.; Souza, S.L.; Langone, M.P. Study of immobilized lipase Lipozyme RM IM esterification reactions for biodiesel synthesis. Quím. Nova 2013, 36, 646–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queiroz, D.S.; Parreira, J.M.; Bastos, C.M. Efeito do solvente na atividade enzimática de lipases comerciais imobilizadas. In Proceedings of the Anais do XX Congresso Brasileiro de Engenharia Química, Florianópolis, Brazil, 19–22 October 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen, M.; Brask, J.; Fjerbaek, L. Enzymatic biodiesel production: Technical and economical considerations. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2008, 100, 692–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.; Resende, R.J.; Costa, T.C.; Sousa, B.V.O.; Santos, A.K.; Marotti, B.S.; Silva, S.L.; Cancelier, A.; Gonçalves, D.B. Análise do potencial biocatalítico de lipase de Candida rugosa imobilizada em diferentes suportes. Rev. Acta Ambient. Catarin. 2021, 18, 10–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bessa, D.H.R.F.; Flumignan, D.L.; Souza, A.O.; Gonçalves, M.C.M.; Castro, C.F.S. Crude enzymatic broth from lipoliptic fungi for the production of metylic esters. Rev. Agronegócio Meio Ambiente 2022, 15, e9279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, T.S.; Erazo, R.G.T.P.; Ramos, R.A.V.; Dias Filho, N.L. Transesterificação de óleo de soja e de pinhão-manso por metanólise e etanólise empregando diversos catalisadores. In Proceedings of the 6th Congresso da Rede Brasileira de Tecnologia de Biodiesel, Natal, Brazil, 22–25 November 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Banchapattanasakda, W.; Asavatesanupap, C.; Santikunaporn, M. Conversion of waste cooking oil into bio-fuel via pyrolysis using activated carbon as a catalyst. Molecules 2023, 28, 3590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anwar, M.; Rasul, M.G.; Ashwath, N. A Systematic multivariate analysis of Carica papaya biodiesel blends and their interactive effect on performance. Energies 2018, 11, 2931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
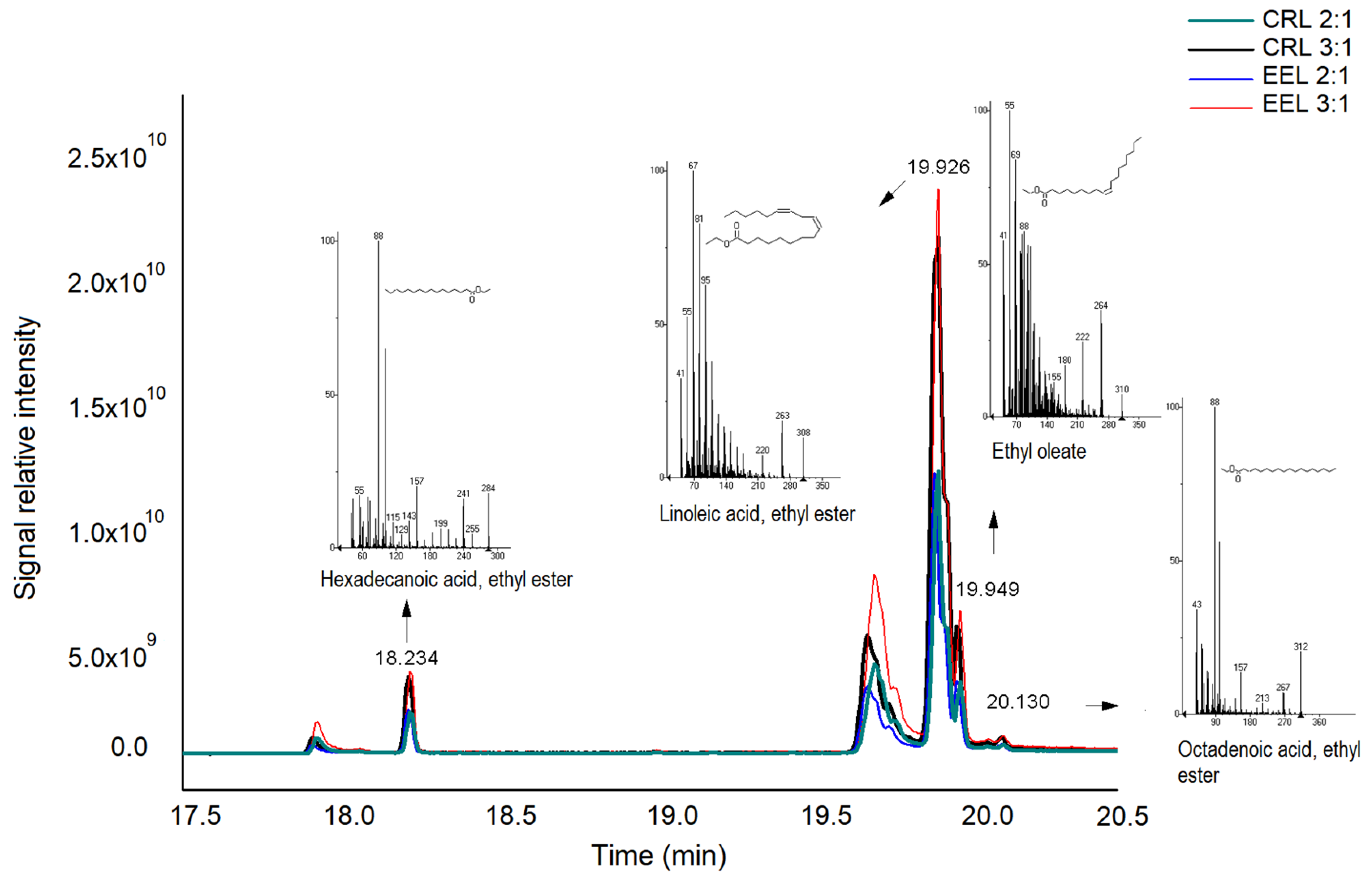
 ) 3:1. The reaction was carried out for 360 min at 40 °C. Experiments that do not share the same letter and symbol (*) are significantly different according to the Tukey test (p < 0.05).
) 3:1. The reaction was carried out for 360 min at 40 °C. Experiments that do not share the same letter and symbol (*) are significantly different according to the Tukey test (p < 0.05).
 ) 3:1. The reaction was carried out for 360 min at 40 °C. Experiments that do not share the same letter and symbol (*) are significantly different according to the Tukey test (p < 0.05).
) 3:1. The reaction was carried out for 360 min at 40 °C. Experiments that do not share the same letter and symbol (*) are significantly different according to the Tukey test (p < 0.05).

| Density at 25 °C (g/cm3) | Acidity Index (mgKOH/g) | Peroxide Index (meq/kg) | Saponification Index (mgKOH/g) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.922 | 1.45 | 25.98 | 172.77 | Castro et al., 2018 [56] |
| 0.908 | 28.50 | - | 175.87 | Aworanti et al., 2019 [57] |
| 0.916 | 35.40 | - | 234.71 | Al-Saadi et al., 2020 [58] |
| - | 1.86 | - | 181.25 | Farooq et al., 2015 [59] |
| 0.917 | 1.78 | 18.36 | - | Siqueira et al., 2019 [60] |
| 0.917 | 5.75 | 19.38 | 175.70 | This study |
| Temperature (°C) | EA (U/mL) | pH | EA (U/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 35 | 8611 c ± 29 | 5.5 | 8840 a ± 17 |
| 37 | 8559 c ± 10 | 6.0 | 8703 b ± 10 |
| 40 | 9100 a ± 6 | 7.0 | 8729 b ± 5 |
| 45 | 8445 c ± 4 | 8.0 | 8618 c ± 3 |
| 50 | 8849 b ± 5 | 8.5 | 8579 d ± 4 |
| Raw Material | Reaction Conditions (T; A:O; t; A) | Biocatalyst | Yield (%) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soybean oil | 37 °C; 1:1; 2 h; EtOH | Lipase from Thermomyces lanuginosus | 85.0 | Silva [80] |
| Macauba oil | 37 °C; 1:1; 2 h; EtOH | Lipase from Thermomyces lanuginosus | 71.0 | Silva [80] |
| Soybean oil | 45 °C; 3:1; 6 h; EtOH | Lipase from Rhizomucor miehei | 74.0 | Aguieras et al. [81] |
| Macauba oil | 40 °C; 2:1; 8 h; EtOH | Lipase from Rhizomucor miehei | 91.0 | Aguieras et al. [82] |
| Olive oil | 30 °C; 1:1; 3 h; EtOH | Candida Lipase sp. | 80.0 | Li et al. [83] |
| Palm oil | 50 °C; 4:1; 6 h; EtOH | Commercial lipase Novozyme® 435 | 87.2 | Raita et al. [84] |
| Soybean oil | 34 °C; 3:1; 8 h; MetOH | Lipase from Leonotis nepetifolia | 74.5 | Vazquez et al. [85] |
| Waste cooking oil | 40 °C; 3:1; 6 h; EtOH | Lipolytic extract of E. endophytica | 89.0 | This study |
| Soybean oil | 40 °C; 3:1; 6 h; EtOH | Lipolytic extract of E. endophytica | 92.0 | This study |
| Reaction Conditions (T; A:O; t; A) | Biocatalyst | Yield (%) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| 40 °C; 4:1; 30 h; MetOH | Lipase B from Candida antarctica immobilized | 96.0 | Parandi et al. [54] |
| 40 °C; 4:1; 4 h; MetOH | Lipase from Geotrichum sp. | 85.0 | Yan et al. [87] |
| 42.5 °C; 4:1; 36 h; MetOH | Lipase from Pseudomonas cepacia immobilized | 76.3 | Kuan et al. [88] |
| 40 °C; 10:1; 32 h; EtOH | Lipase from Candida rugosa immobilized | 85.7 | Abdulla et al. [89] |
| 50 °C; 6:1; 4 h; MetOH | Commercial lipase Novozyme® 435 | 72.0 | Taher et al. [90] |
| 40 °C; 6:1; 9 h, MetOH | Lipase from Candida sp. | 80.0 | Gong et al. [91] |
| 40 °C; 3:1; 6 h; EtOH | Lipolytic extract of E. endophytica | 90.0 | This study |
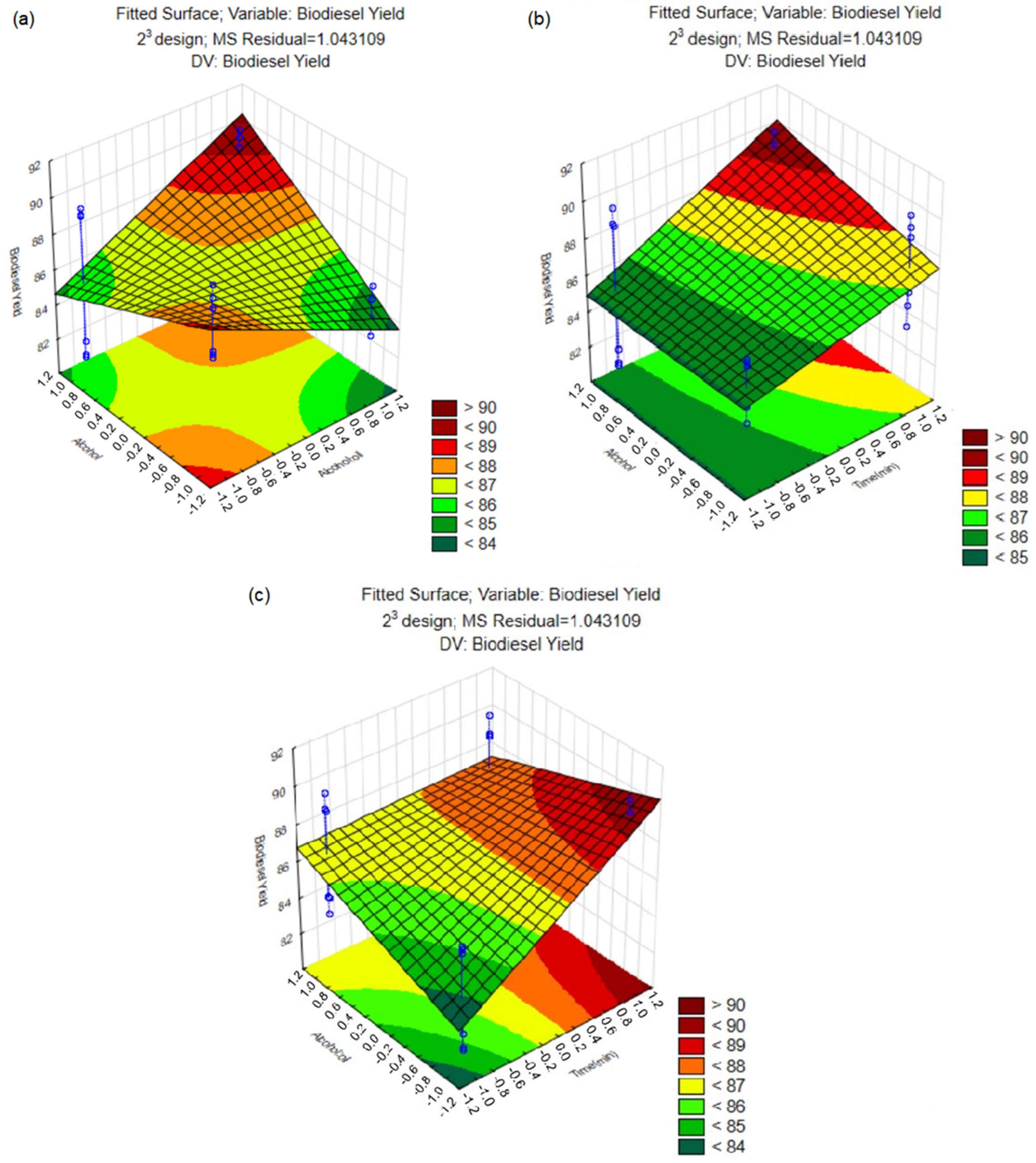
| Assay | Parameters * | Yield (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time (min) | Alcohol:Waste Cooking Oil | Alcohol | ||
| 1 | 120 (−1) | 3:1 (−1) | Methanol (−1) | 86.50 b ± 0.19 |
| 2 | 360 (+1) | 3:1 (−1) | Methanol (−1) | 89.57 a ± 0.60 |
| 3 | 120 (−1) | 4:1 (+1) | Methanol (−1) | 83.83 c ± 0.55 |
| 4 | 360 (+1) | 4:1 (+1) | Methanol (−1) | 81.43 d ± 0.49 |
| 5 | 120 (−1) | 3:1 (−1) | Ethanol (+1) | 85.15 b,c ± 0.95 |
| 6 | 360 (+1) | 3:1 (−1) | Ethanol (+1) | 89.29 a ± 0.22 |
| 7 | 120 (−1) | 4:1 (+1) | Ethanol (+1) | 89.19 a ± 0.53 |
| 8 | 360 (+1) | 4:1 (+1) | Ethanol (+1) | 89.50 a ± 0.60 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rodrigues, J.G.C.; Cardoso, F.V.; Santos, C.C.d.; Matias, R.R.; Machado, N.T.; Duvoisin Junior, S.; Albuquerque, P.M. Biocatalyzed Transesterification of Waste Cooking Oil for Biodiesel Production Using Lipase from the Amazonian Fungus Endomelanconiopsis endophytica. Energies 2023, 16, 6937. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16196937
Rodrigues JGC, Cardoso FV, Santos CCd, Matias RR, Machado NT, Duvoisin Junior S, Albuquerque PM. Biocatalyzed Transesterification of Waste Cooking Oil for Biodiesel Production Using Lipase from the Amazonian Fungus Endomelanconiopsis endophytica. Energies. 2023; 16(19):6937. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16196937
Chicago/Turabian StyleRodrigues, Juliana Gisele Corrêa, Fernanda Veras Cardoso, Celine Campos dos Santos, Rosiane Rodrigues Matias, Nélio Teixeira Machado, Sergio Duvoisin Junior, and Patrícia Melchionna Albuquerque. 2023. "Biocatalyzed Transesterification of Waste Cooking Oil for Biodiesel Production Using Lipase from the Amazonian Fungus Endomelanconiopsis endophytica" Energies 16, no. 19: 6937. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16196937
APA StyleRodrigues, J. G. C., Cardoso, F. V., Santos, C. C. d., Matias, R. R., Machado, N. T., Duvoisin Junior, S., & Albuquerque, P. M. (2023). Biocatalyzed Transesterification of Waste Cooking Oil for Biodiesel Production Using Lipase from the Amazonian Fungus Endomelanconiopsis endophytica. Energies, 16(19), 6937. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16196937








