Power Generation by Halophilic Bacteria and Assessment of the Effect of Salinity on Performance of a Denitrifying Microbial Fuel Cell
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and Enrichment of Halophilic Bacteria
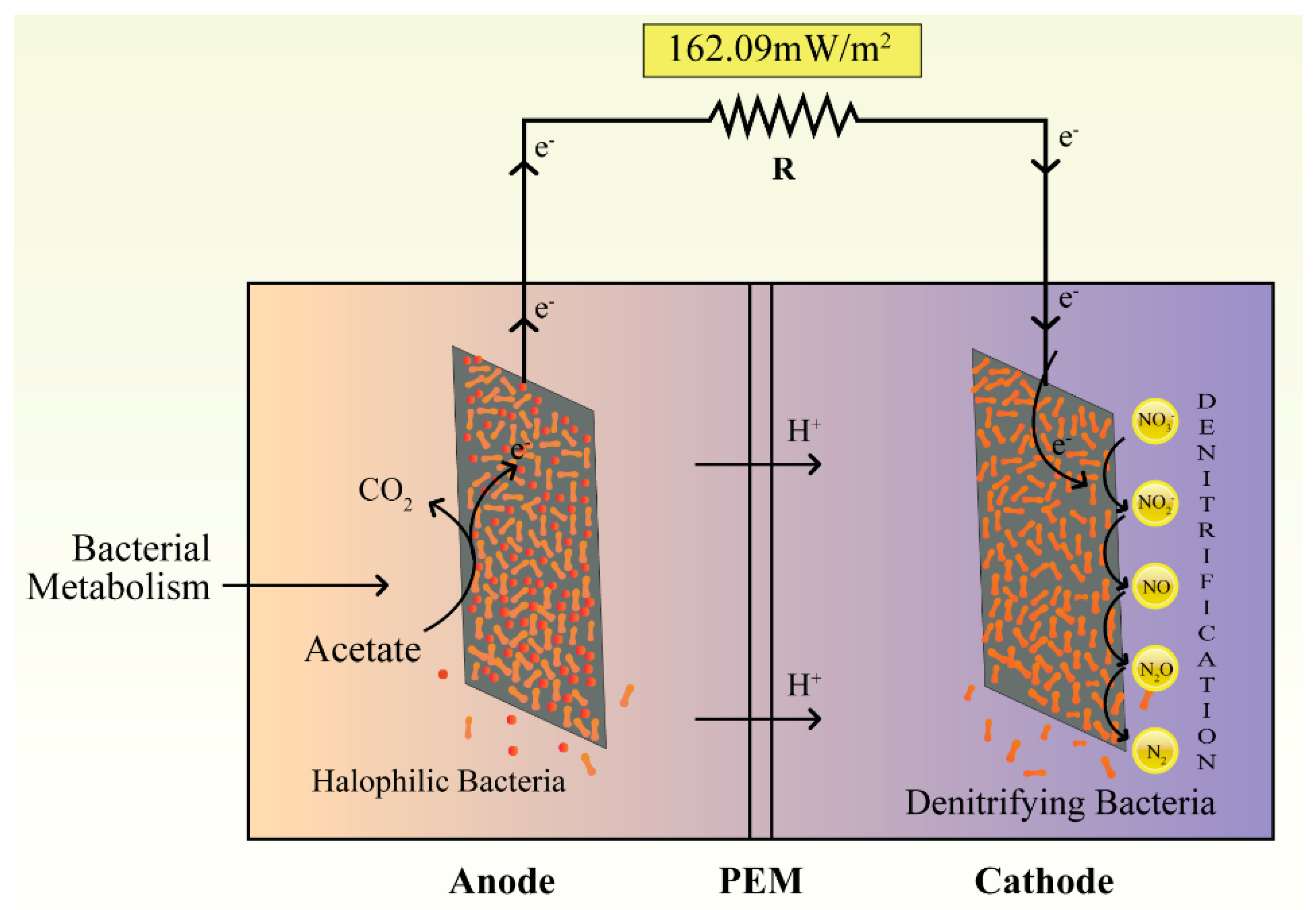
2.2. MFC Configuration and Operation
2.3. Analysis and Calculations
2.4. Electrochemical Analysis
2.5. Anodic Microbial Population Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Voltage Generation Profile with Time
3.2. Power Generation at Different Salinities
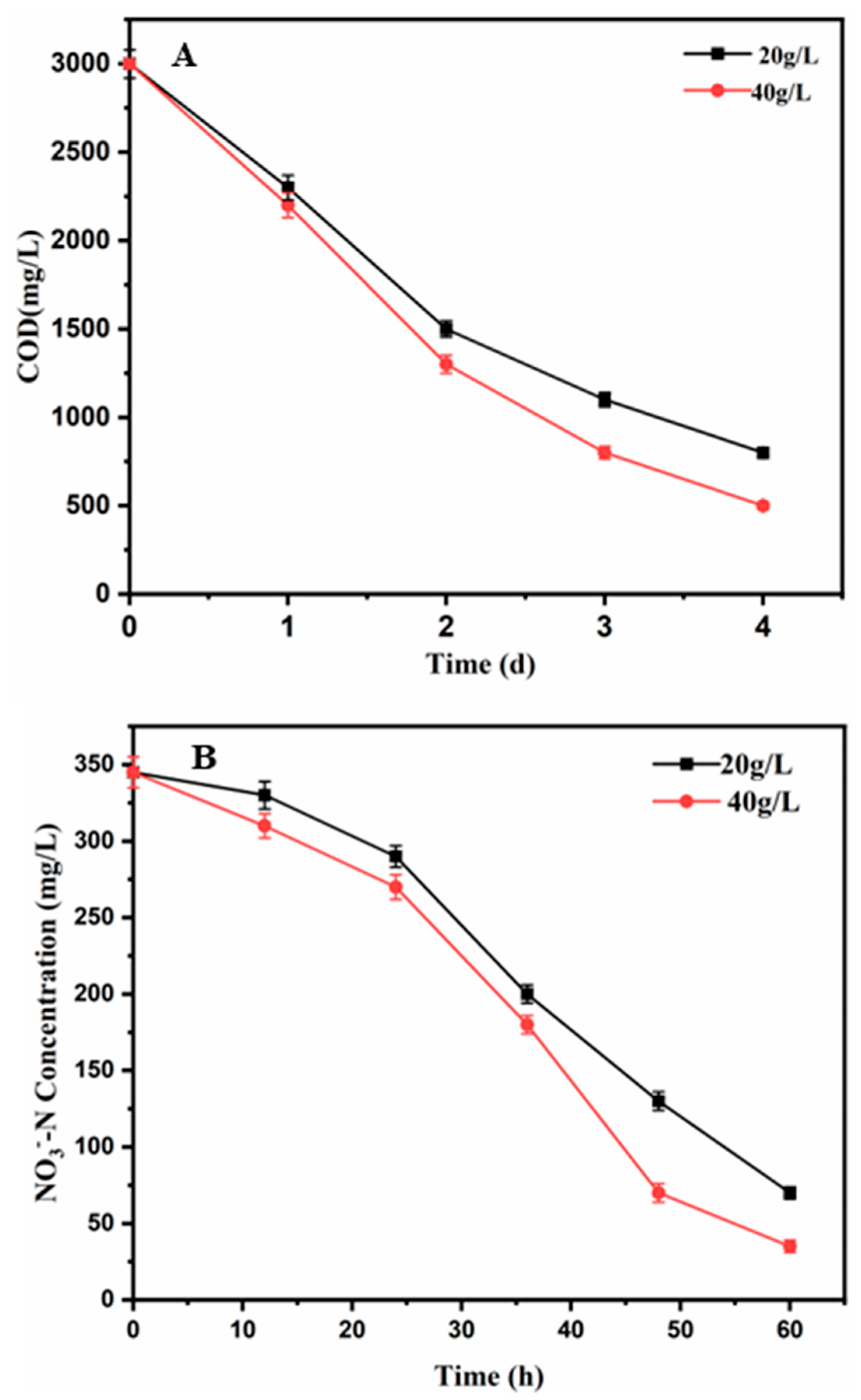
3.3. COD Removal Efficiency at Different Salinities
3.4. Nitrate Removal at Different Salinities
3.5. Cyclic Voltammetry (CV)
3.6. EIS Analysis
3.7. Microbial Community and Diversity Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lefebvre, O.; Tan, Z.; Kharkwal, S.; Ng, H.Y. Effect of increasing anodic NaCl concentration on microbial fuel cell performance. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 112, 336–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefebvre, O.; Moletta, R. Treatment of organic pollution in industrial saline wastewater: A literature review. Water Res. 2006, 40, 3671–3682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Logan, B.E.; Hamelers, B.; Rozendal, R.; Schröder, U.; Keller, J.; Freguia, S.; Aelterman, P.; Verstraete, W.; Rabaey, K. Microbial Fuel Cells: Methodology and Technology. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 5181–5192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Logan, B.E. Exoelectrogenic bacteria that power microbial fuel cells. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2009, 7, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Yates, M.D.; Cheng, S.; Call, D.F.; Sun, D.; Logan, B.E. Examination of microbial fuel cell start-up times with domestic wastewater and additional amendments. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 7301–7306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Logan, B.E.; Rabaey, K. Conversion of Wastes into Bioelectricity and Chemicals by Using Microbial Electrochemical Technologies. Science 2012, 337, 686–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozendal, R.A.; Hamelers, H.; Rabaey, K.; Keller, J.; Buisman, C.J. Towards practical implementation of bioelectrochemical wastewater treatment. Trends Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 450–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Cheng, S.; Logan, B.E. Power Generation in Fed-Batch Microbial Fuel Cells as a Function of Ionic Strength, Temperature, and Reactor Configuration. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 5488–5493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.S.; Kumar, V.; Gude, V.G.; Malyan, S.K.; Pugazhendhi, A. Alkalinity and salinity favor bioelectricity generation potential of Clostridium, Tetrathiobacter and Desulfovibrio consortium in Microbial Fuel Cells (MFC) treating sulfate-laden wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 306, 123110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Sun, B.; Zhang, X. Electricity generation at high ionic strength in microbial fuel cell by a newly isolated Shewanella marisflavi EP1. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 85, 1141–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monzon, O.; Yang, Y.; Yu, C.; Li, Q.; Alvarez, P.J.J. Microbial fuel cells under extreme salinity: Performance and microbial analysis. Environ. Chem. 2015, 12, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zheng, R.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhu, R.; Zhang, X.; Gao, D. A novel exoelectrogen from microbial fuel cell: Bioremediation of marine petroleum hydrocarbon pollutants. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 235, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijay, A.; Arora, S.; Gupta, S.; Chhabra, M. Halophilic starch degrading bacteria isolated from Sambhar Lake, India, as potential anode catalyst in microbial fuel cell: A promising process for saline water treatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 256, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adelaja, O.; Keshavarz, T.; Kyazze, G. The effect of salinity, redox mediators and temperature on anaerobic biodegradation of petroleum hydrocarbons in microbial fuel cells. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 283, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, F.X.; Zhang, L.H.; Liu, W.F.; Zhu, Y.M. Osmotic Pressure Compensated Solute Ectoine Improves Salt Tolerance of Microbial Cells in Microbial Fuel Cells. Fuel Cells 2019, 19, 616–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grattieri, M.; Minteer, S.D. Microbial fuel cells in saline and hypersaline environments: Advancements, challenges and future perspectives. Bioelectrochemistry 2018, 120, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Fu, G.; Zhang, Z. Simultaneous nutrient and carbon removal and electricity generation in self-buffered biocathode microbial fuel cell for high-salinity mustard tuber wastewater treatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 272, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monzon, O.; Yang, Y.; Kim, J.; Heldenbrand, A.; Li, Q.; Alvarez, P.J. Microbial fuel cell fed by Barnett Shale produced water: Power production by hypersaline autochthonous bacteria and coupling to a desalination unit. Biochem. Eng. J. 2017, 117, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pugazhendi, A.; Al-Mutairi, A.E.; Jamal, M.T.; Jeyakumar, R.B.; Palanisamy, K. Treatment of seafood industrial wastewater coupled with electricity production using air cathode microbial fuel cell under saline condition. Int. J. Energy Res. 2020, 44, 12535–12545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorab, R.E.A.; Pugazhendi, A.; Jamal, M.T.; Jeyakumar, R.B.; Godon, J.J.; Mathew, D.K. Tannery wastewater treatment coupled with bioenergy production in upflow microbial fuel cell under saline condition. Environ. Res. 2022, 212, 113304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pugazhendi, A.; Jamal, M.T.; Al-Mur, B.A.; Jeyakumar, R.B. Bioaugmentation of electrogenic halophiles in the treatment of pharmaceutical industrial wastewater and energy production in microbial fuel cell under saline condition. Chemosphere 2022, 288, 132515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijay, A.; Sonawane, J.M.; Chhabra, M. Denitrification process in microbial fuel cell: A comprehensive review. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2022, 17, 100991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijay, A.; Chhabra, M.; Vincent, T. Microbial community modulates electrochemical performance and denitrification rate in a biocathodic autotrophic and heterotrophic denitrifying microbial fuel cell. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 272, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khandelwal, A.; Vijay, A.; Dixit, A.; Chhabra, M. Microbial fuel cell powered by lipid extracted algae: A promising system for algal lipids and power generation. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 247, 520–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atlas, R.M. Handbook of Microbiological Media, 4th ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Clauwaert, P.; Rabaey, K.; Aelterman, P.; De Schamphelaire, L.; Pham, T.H.; Boeckx, P.; Boon, N.; Verstraete, W. Biological Denitrification in Microbial Fuel Cells. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 3354–3360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijay, A.; Vaishnava, M.; Chhabra, M. Microbial fuel cell assisted nitrate nitrogen removal using cow manure and soil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 7744–7756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APHA. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water & Wastewater, 21st ed.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijay, A.; Khandelwal, A.; Chhabra, M.; Vincent, T. Microbial fuel cell for simultaneous removal of uranium (VI) and nitrate. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 388, 124157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, L.G.; Oremland, R.S. Electricity generation by anaerobic bacteria and anoxic sediments from hypersaline soda lakes. Extremophiles 2008, 12, 837–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grattieri, M.; Suvira, M.; Hasan, K.; Minteer, S.D. Halotolerant extremophile bacteria from the Great Salt Lake for recycling pollutants in microbial fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2017, 356, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyahara, M.; Kouzuma, A.; Watanabe, K. Sodium chloride concentration determines exoelectrogens in anode biofilms occurring from mangrove-grown brackish sediment. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 218, 674–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L. Effects of electrolyte total dissolved solids (TDS) on performance and anodic microbes of microbial fuel cells. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2011, 10, 16897–16908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.K.; Pham, T.H.; Chang, I.S.; Kang, K.H.; Moon, H.; Cho, K.S.; Kim, B.H. Construction and operation of a novel mediator- and membrane-less microbial fuel cell. Process. Biochem. 2004, 39, 1007–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katuri, K.P.; Scott, K.; Head, I.M.; Picioreanu, C.; Curtis, T.P. Microbial fuel cells meet with external resistance. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 2758–2766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christwardana, M.; Kwon, Y. Yeast and carbon nanotube based biocatalyst developed by synergetic effects of covalent bonding and hydrophobic interaction for performance enhancement of membraneless microbial fuel cell. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 225, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabaey, K.; Boon, N.; Siciliano, S.D.; Verhaege, M.; Verstraete, W. Biofuel Cells Select for Microbial Consortia That Self-Mediate Electron Transfer. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 5373–5382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aaron, D.; Tsouris, C.; Hamilton, C.Y.; Borole, A.P. Assessment of the Effects of Flow Rate and Ionic Strength on the Performance of an Air-Cathode Microbial Fuel Cell Using Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy. Energies 2010, 3, 592–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Luo, H.; Shi, Z.; Wu, Y.; Liu, H. Substrate salinity: A critical factor regulating the performance of microbial fuel cells, a review. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 763, 143021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurav, R.; Bhatia, S.K.; Choi, T.-R.; Jung, H.-R.; Yang, S.-Y.; Song, H.-S.; Park, Y.-L.; Han, Y.-H.; Park, J.-Y.; Kim, Y.-G.; et al. Chitin biomass powered microbial fuel cell for electricity production using halophilic Bacillus circulans BBL03 isolated from sea salt harvesting area. Bioelectrochemistry 2019, 130, 107329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurav, R.; Bhatia, S.K.; Choi, T.-R.; Kim, H.J.; Song, H.-S.; Park, S.-L.; Lee, S.-M.; Lee, H.-S.; Kim, S.-H.; Yoon, J.-J.; et al. Utilization of different lignocellulosic hydrolysates as carbon source for electricity generation using novel Shewanella marisflavi BBL25. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 277, 124084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.S.; Kim, B.H.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, G.T.; Kim, M.; Chang, I.S.; Park, Y.K.; Chang, H.I. A Novel Electrochemically Active and Fe(III)-reducing Bacterium Phylogenetically Related to Clostridium butyricum Isolated from a Microbial Fuel Cell. Anaerobe 2001, 7, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Malyan, S.K.; Basu, S.; Bishnoi, N.R. Syntrophic association and performance of Clostridium, Desulfovibrio, Aeromonas and Tetrathiobacter as anodic biocatalysts for bioelectricity generation in dual chamber microbial fuel cell. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 16019–16030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Park, H.S.; Hyun, M.S.; Chang, I.S.; Kim, M.; Kim, B.H. A mediator-less microbial fuel cell using a metal reducing bacterium, Shewanella putrefaciens. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2002, 30, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.A.; Chen, X.H.; Xu, F.C.; Wang, W.; Xiong, X.J. Influence of Substrate and Salinity on Electricity Production by Deep-Sea Strain Shewanella sp DS1. Power Energy Eng. Conf. 2010, 2010, 259–262. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, D.; Zhang, X. Current Production by a Deep-Sea Strain Shewanella sp. DS1. Curr. Microbiol. 2007, 55, 497–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Cho, S.; Kim, S.; Cho, H.; Lee, T. Comparison of Exoelectrogenic Bacteria Detected Using Two Different Methods: U-tube Microbial Fuel Cell and Plating Method. Microbes Environ. 2011, 27, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, L.D.S. Clostridium oceanicum, sp. n., a sporeforming anaerobe isolated from marine sediments. J. Bacteriol. 1970, 103, 811–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, A.; Zhao, D.; Ding, F.; Du, S.; Lu, H.; Zhang, M.; Zheng, P. Effect of inocula on performance of bio-cathode denitrification and its microbial mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 343, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Sample | Salinity (ppt) | TDS (mg/L) | Conductivity (mS/cm) | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 69 ± 1.5 | 560 ± 3 | 89 ± 1.2 | 7.2 ± 0.1 |
| 2 | 55 ± 1.3 | 520 ± 2 | 82 ± 1 | 7.3 ± 0.1 |
| Parameters | NaCl (20 g/L) | NaCl (40 g/L) |
|---|---|---|
| Conductivity (mS/cm) | 49 ± 1.5 | 82 ± 2 |
| OCV (mV) | 435 ± 10 | 670 ± 12 |
| Voltage at 100 ohms (mV) | 240 ± 8 | 374 ± 7 |
| Highest current density (mA/m2) | 1908.60 ± 12 | 2161.29 ± 15 |
| Highest power density (mW/m2) | 96.77 ± 3 | 162.09 ± 3 |
| Nitrate removal (%) | 80 ± 3 | 89 ± 3.2 |
| COD removal (%) | 76 ± 3.8 | 83 ± 4 |
| Charge transfer resistance (Ohm) | 20 | 16 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vijay, A.; Ghosh, P.C.; Mukherji, S. Power Generation by Halophilic Bacteria and Assessment of the Effect of Salinity on Performance of a Denitrifying Microbial Fuel Cell. Energies 2023, 16, 877. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16020877
Vijay A, Ghosh PC, Mukherji S. Power Generation by Halophilic Bacteria and Assessment of the Effect of Salinity on Performance of a Denitrifying Microbial Fuel Cell. Energies. 2023; 16(2):877. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16020877
Chicago/Turabian StyleVijay, Ankisha, Prakash C. Ghosh, and Suparna Mukherji. 2023. "Power Generation by Halophilic Bacteria and Assessment of the Effect of Salinity on Performance of a Denitrifying Microbial Fuel Cell" Energies 16, no. 2: 877. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16020877
APA StyleVijay, A., Ghosh, P. C., & Mukherji, S. (2023). Power Generation by Halophilic Bacteria and Assessment of the Effect of Salinity on Performance of a Denitrifying Microbial Fuel Cell. Energies, 16(2), 877. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16020877







