Recent Development of Heat Sink and Related Design Methods
Abstract
:1. Introduction
Heat Transfer Principles in Heat Sinks
2. Literature Review of Heat Transfer Studies on Heat Sinks
2.1. Heat Conduction Solutions for Heat Sinks
2.2. Heat Convection Solutions for Heat Sinks
2.2.1. Natural Convection Heat Sinks
2.2.2. Forced Convection Heat Sinks
2.3. Radiation Solutions for Heat Sinks
2.4. Phase Change Heat Sinks
2.5. Nanofluid Heat Sinks
3. Literature Review of Structure Designs and Optimization Approaches
3.1. Surface Features
3.2. Fins
3.3. Microchannels
3.4. Latticework
3.5. Bionic Design
4. Recommendations
5. Conclusions
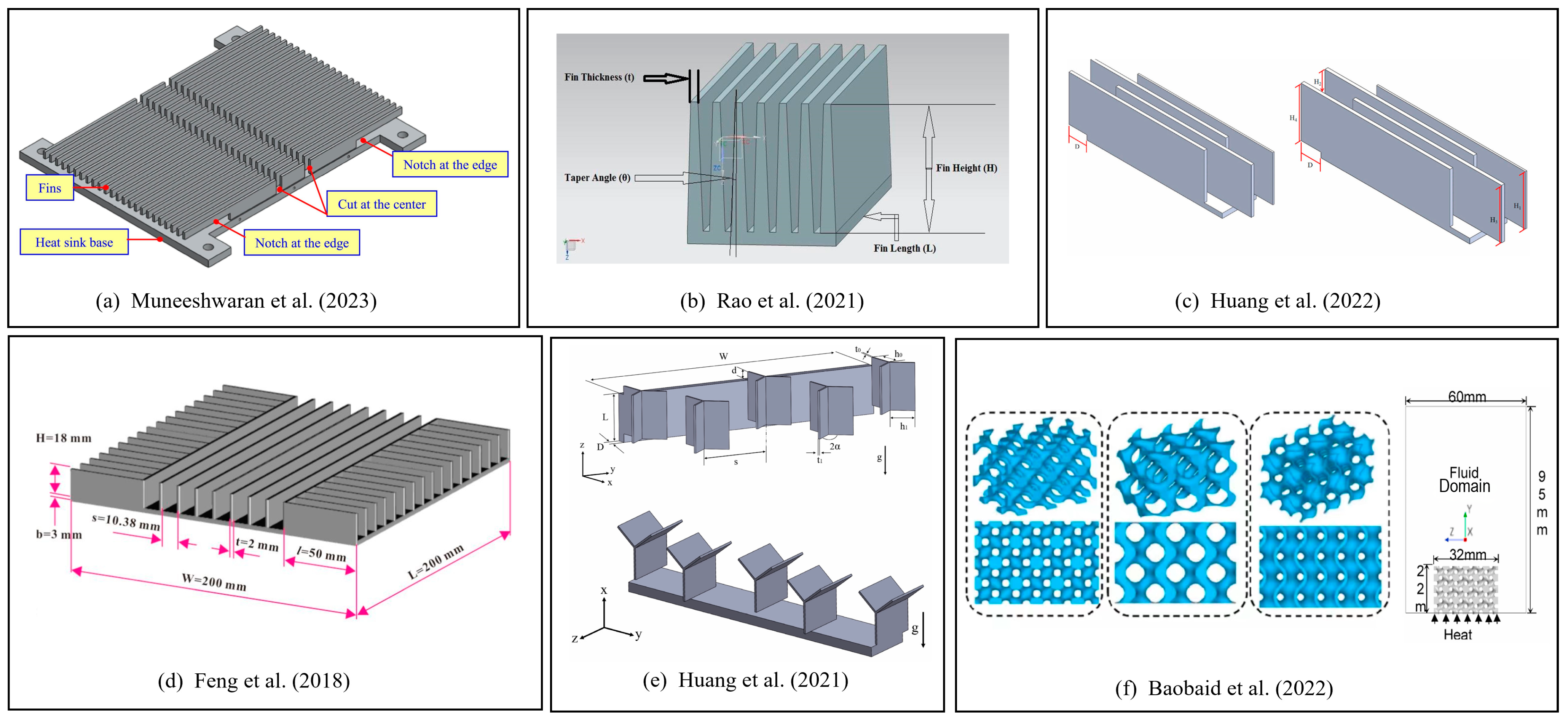
- The heat sinks following the principle of natural convection are mostly designed with a fin structure, since this kind of structure is a simple and effective method for passive cooling techniques. For heat sinks with pin fins, changing the pin-fin arrangement can increase the heat dissipation. For conventional heat sinks with straight ribs, adding miniature structures to the surface of the straight ribs or changing the straight ribs to curved ones exhibited a significant improvement in cooling temperature. Researchers combined empirical formulas and existing studies to optimize the parameters that have an influence on fluid flow when designing fins.
- Most heat sinks use positive cooling management, which obeys the rule of forced convection. Introducing TPMS to microchannel heat sinks and designing manifold microchannel heat sinks are promising techniques in terms of improving heat dissipation. The generation of TPMS is based on different optimized algorithms and formulas, and these core formulas can be the focus of further research in the future.
- Bionic structures accompanying topology optimization methods represented significant cooling effects, as well as the uniformity of temperature and low-pressure drops in heat sinks. This type of geometry could be a good research direction for the future.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| Heat flow density (W/m2) | |
| Heat transfer area (m2) | |
| Temperature (K) | |
| ,y,z | Coordinates axis (m) |
| Heat transfer coefficient (W/m2·K) | |
| Temperature on the wall (K) | |
| Temperature of the fluid (K) | |
| Thermal resistance (K/W) | |
| Area convection heat transfer coefficient (W/K) | |
| Nusselt number | |
| Reynolds number | |
| Greek symbols | |
| Heat transfer rate (W/m·K) | |
| Blackbody radiation constant (W/(m2·K4)) | |
| Emissivity | |
| Thermal efficiency index | |
| Abbreviations | |
| HS | Heat sinks |
| IGBT | Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor |
| MCHS | Microchannel heat sink |
| IMCHS | Interrupted Microchannel heat sink |
| MMCHS | Manifold microchannel heat sink |
| PCM | Phase change material |
| PV | Photovoltaic |
| IMCHS | Interrupted microchannel heat sinks |
| TPMS | Triply periodic minimal surfaces |
| MHD | Magnetohydrodynamics |
| GO | Graphene oxide |
| MWCNT | Multi-walled carbon nanotube |
| CNT | Carbon nanotube |
References
- Du, P.; Zhou, Z.Q. Research progress of microchannel cooling technology for high-density microsystems. Microelectron. Comput. 2023, 1, 87–96. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Holman, J.P.; Lloyd, J. Heat Transfer, 10th ed.; McGraw-Hill Higher Education: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y. Thermal Resistance Modeling and Heat Dissipation Improvement of Press-Pack IGBT. Master’s Thesis, Chong Qing University, Chongqing, China, 2021. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.; Liu, H.; Du, F.; Chen, X.; Li, B.; Hong, J. MMC-based heat sink topology optimization design for natural convection problems. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2023, 192, 108376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muneeshwaran, M.; Tsai, M.K.; Wang, C.C. Heat transfer augmentation of natural convection heat sink through notched fin design. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2023, 142, 106676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, A.K.; Somkuwar, V. Heat transfer of a tapered fin heat sink under natural convection. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 46, 7886–7891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-H.; Chen, W.-Y. A natural convection horizontal straight-fin heat sink design problem to enhance heat dissipation performance. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2022, 176, 107540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Shi, M.; Yan, H.; Sun, S.; Li, F.; Lu, T.J. Natural convection in a cross-fin heat sink. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2018, 132, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-H.; Chen, L. An optimized natural convection Y-shape-shifted heat sink design problem. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2021, 28, 101520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baobaid, N.; Ali, M.I.; Khan, K.A.; Al-Rub, R.K.A. Fluid flow and heat transfer of porous TPMS architected heat sinks in free convection environment. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2022, 33, 101944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krstic, M.; Pantic, L.; Djordjevic, S.; Radonjic, I.; Begovic, V.; Radovanovic, B.; Mancic, M. Passive cooling of photovoltaic panel by aluminum heat sinks and numerical simulation. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2023, 102330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obaid, A.J.; Hameed, V.M. An experimental and numerical comparison study on a heat sink thermal performance with new fin configuration under mixed convective conditions. South Afr. J. Chem. Eng. 2023, 44, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuşka, M.; Çorumlu, V. A comparative experimental thermal performance analysis of conical pin fin heat sink with staggered and modified staggered layout under forced convection. Therm. Sci. Eng. Prog. 2023, 37, 101560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathi, M.; Heyhat, M.M.; Targhi, M.Z.; Bigham, S. Porous-fin microchannel heat sinks for future micro-electronics cooling. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2023, 202, 123662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maheswari, A.; Prajapati, Y.K. Thermal performance enhancement and optimization of double-layer microchannel heat sink with intermediate perforated rectangular fins. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2023, 185, 108043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, K.; Lin, G.; Guo, Y.; Huang, J.; Zhang, H.; Miao, J. Simulation and optimization of thermal performance in diverging/converging manifold microchannel heat sink. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2023, 200, 123495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.H.; Zhao, R.; Nian, Y.L.; Cheng, W.L. Numerical study on heat transfer characteristics of a pin–fin staggered manifold microchannel heat sink. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2023, 219, 119436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
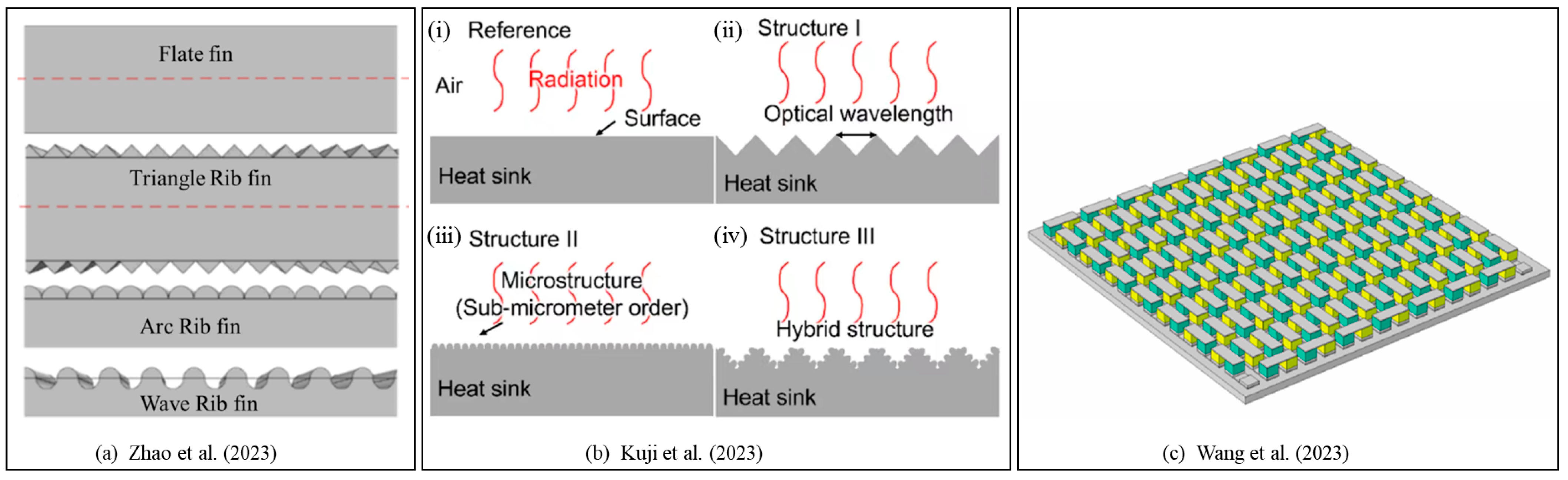
- Zhao, Y.; Song, Y.; Zhuang, N.; Zhao, H.; Tang, X. Optimization design of surface microstructure of high-efficiency space radiation heat dissipation fins. Ann. Nucl. Energy 2023, 182, 109590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuji, C.; Ishii, M.; Yoshikawa, R.; Mizutani, M.; Soyama, H. Fabrication of temperature-selective thermal radiation surfaces utilizing surface texturing. Precis. Eng. 2023, 82, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Deng, W.; Tang, X.; He, H. Experiment and simulation study on the specification parameters of finned heat sink for thermoelectric system in consideration of radiation among fins. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2023, 185, 108097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
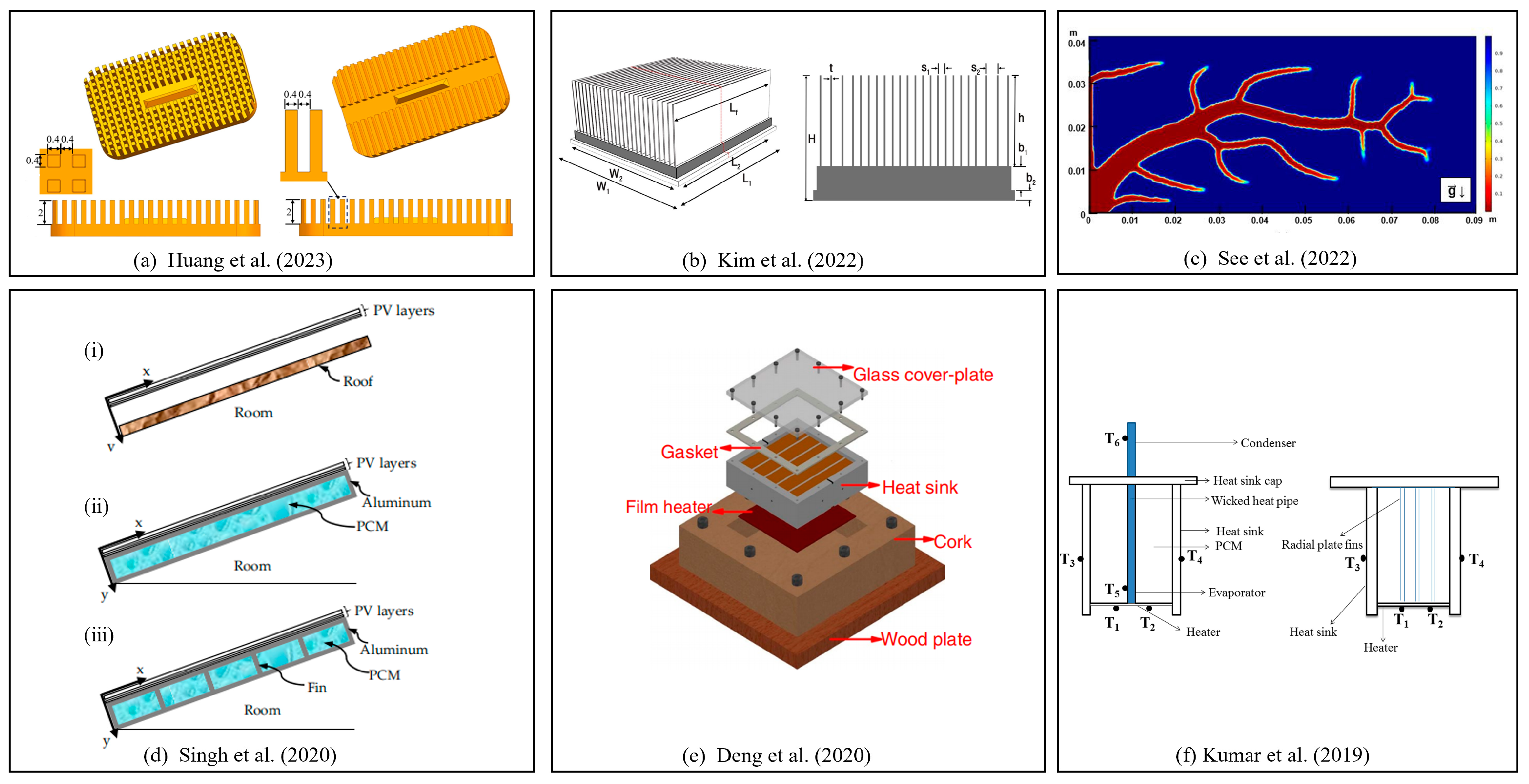
- Huang, Y.; Yang, Q.; Miao, J.; Tang, K.; Zhao, J.; Huang, J.; Guo, Y. Experimental investigation on flow boiling characteristics of a radial micro pin–fin heat sink for hotspot heat dissipation. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2023, 219, 119622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Heu, C.; Mok, J.; Kang, S.-W.; Kim, D.R. Enhanced thermal performance of phase change material-integrated fin-type heat sinks for high power electronics cooling. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2022, 184, 122257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- See, Y.; Ho, J.; Leong, K.; Wong, T. Experimental investigation of a topology-optimized phase change heat sink optimized for natural convection. Appl. Energy 2022, 314, 118984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Khanna, S.; Newar, S.; Sharma, V.; Reddy, K.S.; Mallick, T.K.; Becerra, V.; Radulovic, J.; Hutchinson, D.; Khusainov, R. Solar Photovoltaic Panels with Finned Phase Change Material Heat Sinks. Energies 2020, 13, 2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.; Zhang, C.; Sun, Q.; Wu, L.; Yao, F.; Xu, D. Experimental study on melting performance of phase change material-based finned heat sinks by a comprehensive evaluation. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2020, 144, 869–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar Marri, G.; Balaji, C. Experimental and Numerical Investigations on a Phase Change Material Based Heat Sink with Symbiotically Joined Heat Pipe. Heat Transf. Eng. 2019, 42, 23–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azodinia, M.; Mudabbir, M.; Karimipour, A. Numerical investigation of two-phase Al2O3 nanofluid in a microchannel equipped with bump through slip flow. Eng. Anal. Bound. Elem. 2023, 155, 1028–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Rashed, A.A.; Shahsavar, A.; Entezari, S.; Moghimi, M.A.; Adio, S.A.; Nguyen, T.K. Numerical investigation of non-Newtonian water-CMC/CuO nanofluid flow in an offset strip-fin microchannel heat sink: Thermal performance and thermodynamic considerations. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2019, 155, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Pang, M.; Diao, Y.; Zhao, Y. Heat transfer characteristics and flow features of nanofluids in parallel flat minichannels. Powder Technol. 2022, 402, 117321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansouri, R.; Pourrajab, R.; Behbahani, M.; Daneh-Dezfuli, A. Evaluating the convective heat transfer of graphene oxide–gold hybrid nanofluid flow in CPU. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2023, 148, 5765–5776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Sarkar, J. Particle ratio optimization of Al2O3-MWCNT hybrid nanofluid in minichannel heat sink for best hydrothermal performance. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2019, 165, 114546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, B.; Sundén, B. Analysis of laminar flow and heat transfer in an interrupted microchannel heat sink with different shaped ribs. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2019, 140, 1259–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, J.; Han, S.; Song, Y.; An, N.; Zhou, L.; Li, L.; Zhang, H.; Du, X. Improving internal cooling performance of turbine blade with steam in channel with rhombus-patterned biomimetic ribs: A numerical investigation. Therm. Sci. Eng. Prog. 2023, 40, 101789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, T.; Hou, Q.; Song, K.; Hu, W.; Wu, X. Thermal hydraulic performance augmentation by petal-shaped ribs in a two-pass cooling channel. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2022, 40, 102542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Zhang, W.; Xin, G.; Li, F.; Pu, J.H.; Du, M. Improved thermal–hydraulic performance of a microchannel with hierarchical honeycomb porous ribs. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2022, 101, 1083–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Zhao, J.; Rao, Z. Heat transfer performance enhancement of liquid cold plate based on mini V-shaped rib for battery thermal management. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2021, 189, 116729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinawa, M.L.; Chauhan, P.; Sharma, R.; Poonia, A.; Singh, H.K.; Sharma, A.K.; Subbiah, R. Numerical investigation of modified fin shapes for the improved heat transfer. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 62, 1854–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, H.-C.; Youh, M.-J.; Hsieh, R.-H.; Jang, J.-H.; Kumar, B. Numerical investigation on the temperature uniformity of micro-pin-fin heat sinks with variable density arrangement. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2023, 44, 102853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanan, V.; Umesh, C.K. Numerical comparison for thermo-hydraulic performance of pin fin heat sink with micro channel pin fin heat sink. Sadhana 2018, 43, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rath, S.; Siddhartha Dash, S.K. Thermal performance of a radial heat sink with longitudinal wavy fins for electronic cooling applications under natural convection. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2022, 147, 9119–9137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlapalem, V.; Dash, S.K. On the enhancement of natural convection heat transfer with multi-branching fins. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2023, 183, 107868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.B.; Gao, X.N. Status and Progress of Electronic Cooling Technologies. Guangdong Chem. Ind. 2013, 40, 67–68. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.-L.; An, D.; Yang, Y.-R.; Zheng, S.-F.; Wang, X.-D.; Lee, D.-J. Heat transfer and flow characteristics in symmetric and parallel wavy microchannel heat sinks with porous ribs. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2023, 185, 108080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.-L.; Fan, C.-C.; He, Y.-L.; Nobes, D.S. Heat transfer and flow characteristics in a rectangular channel with combined delta winglet inserts. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2019, 134, 149–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, D.; Yang, Y.; Ding, G.; Du, X.; Hu, Z. Optimization of Microchannel Heat Sink with Rhombus Fractal-like Units for Electronic Chip Cooling. Int. J. Refrig. 2020, 116, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memon, S.A.; Cheema, T.A.; Kim, G.M.; Park, C.W. Hydrothermal Investigation of a Microchannel Heat Sink Using Secondary Flows in Trapezoidal and Parallel Orientations. Energies 2020, 13, 5616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilmore, N.; Timchenko, V.; Menictas, C. Manifold microchannel heat sink topology optimisation. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2021, 170, 121025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Z.; Xie, G.; Shen, H.; Wang, C.C. Thermal performance and entropy generation of single-layer and double-layer constructal Y-shaped bionic microchannel heat sinks. Int. J. Energy Res. 2021, 45, 9449–9462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Yan, Y.; Feng, S.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Z. Multi-objective optimizations on thermal and hydraulic performance of symmetric and asymmetric bionic Y-shaped fractal networks by genetic algorithm coupled with CFD simulation. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2021, 124, 105261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, M.; Ali, M.I.H.; Khan, K.A.; Abu Al-Rub, R. Forced convection heat transfer in heat sinks with topologies based on triply periodic minimal surfaces. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2022, 38, 102313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Gao, R.; Liu, S. A novel battery thermal management system based on P type triply periodic minimal surface. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2022, 194, 123090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, S.; Yang, L.; Qiu, H.; Luan, Y.; Sun, H. Effect of sidewall slots and pin fins on the performance of latticework cooling channel for turbine blades. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2017, 117, 275–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, Z.A.; Elnajjar, E.; Al-Ketan, O.; Abu Al-Rub, R.; Al-Omari, S.B. Heat transfer performance of a finned metal foam-phase change material (FMF-PCM) system incorporating triply periodic minimal surfaces (TPMS). Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2021, 170, 121001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, D.; Shi, C.; Li, W.; Chen, W.; Chyu, M.K. Design, flow characteristics and performance evaluation of bioinspired heat exchangers based on triply periodic minimal surfaces. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2023, 201, 123620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navickaitė, K.; Mocerino, A.; Cattani, L.; Bozzoli, F.; Bahl, C.; Liltrop, K.; Zhang, X.; Engelbrecht, K. Enhanced heat transfer in tubes based on vascular heat exchangers in fish: Experimental investigation. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2019, 137, 192–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, K.; Lu, C.; Yu, B.; Yang, L.; Rao, Y. Optimization of bionic heat sinks with self-organized structures inspired by termite nest morphologies. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2023, 202, 123735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.-H.; Liu, H.-L.; Xie, G.; Sang, L.; Zhou, J. Topology optimization for spider web heat sinks for electronic cooling. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2021, 195, 117154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Zhou, F.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Y. Performance analysis of axial air cooling system with shark-skin bionic structure containing phase change material. Energy Convers. Manag. 2021, 250, 114921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, F.; Yang, N.; Liu, X.; Liu, H.; Li, W.; Liu, H.; Huang, B. Performance analysis of phase change material in battery thermal management with biomimetic honeycomb fin. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2021, 196, 117296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

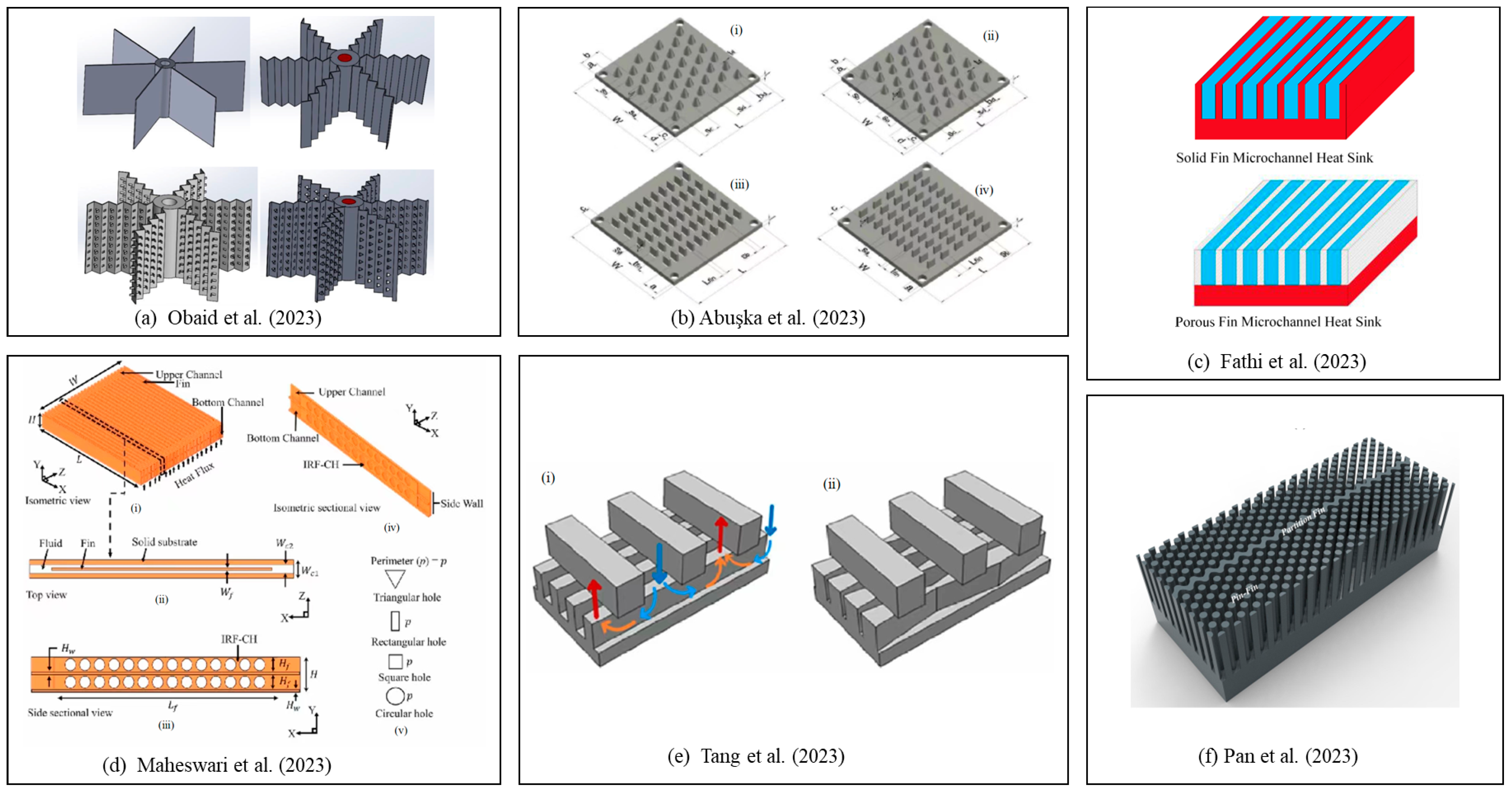
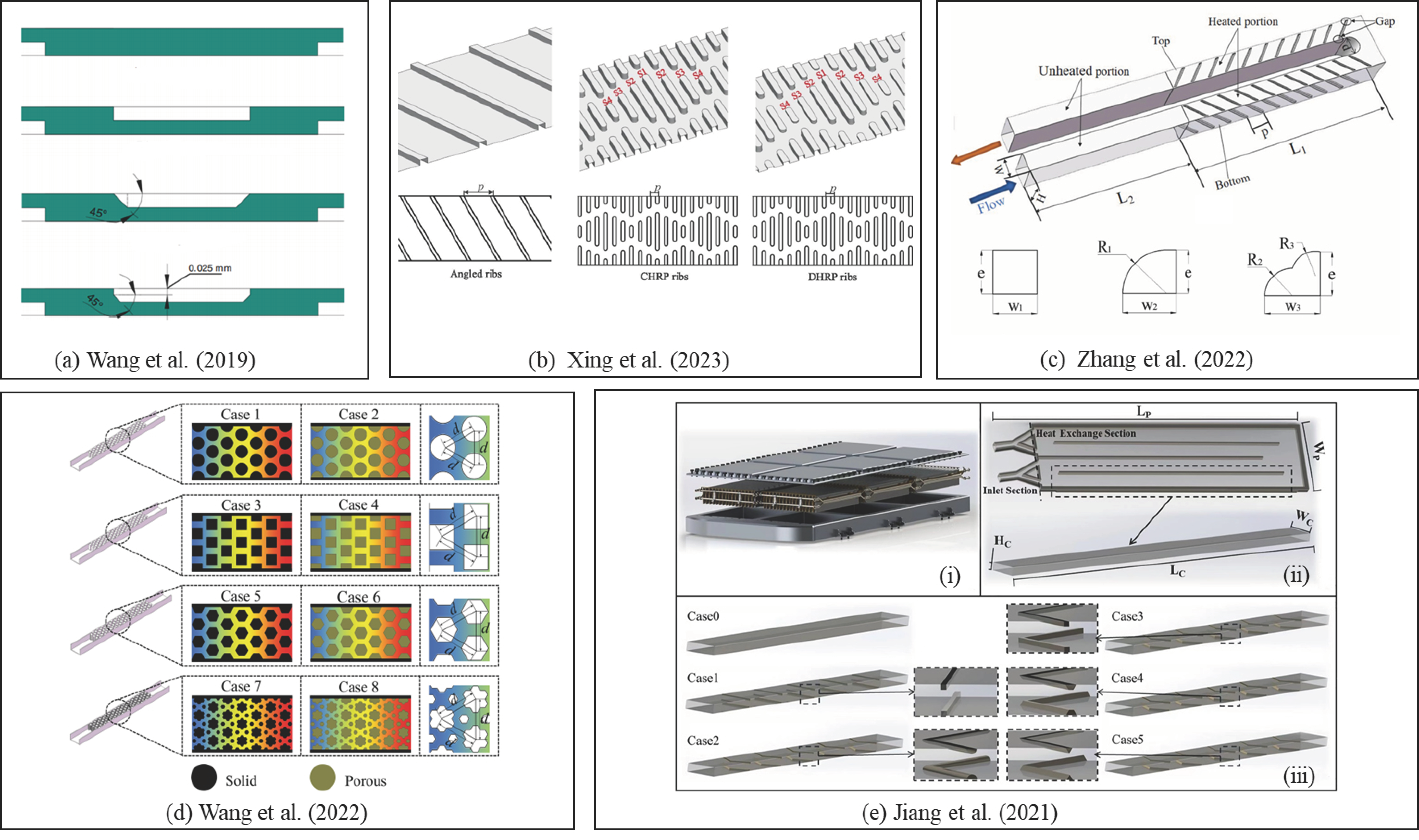

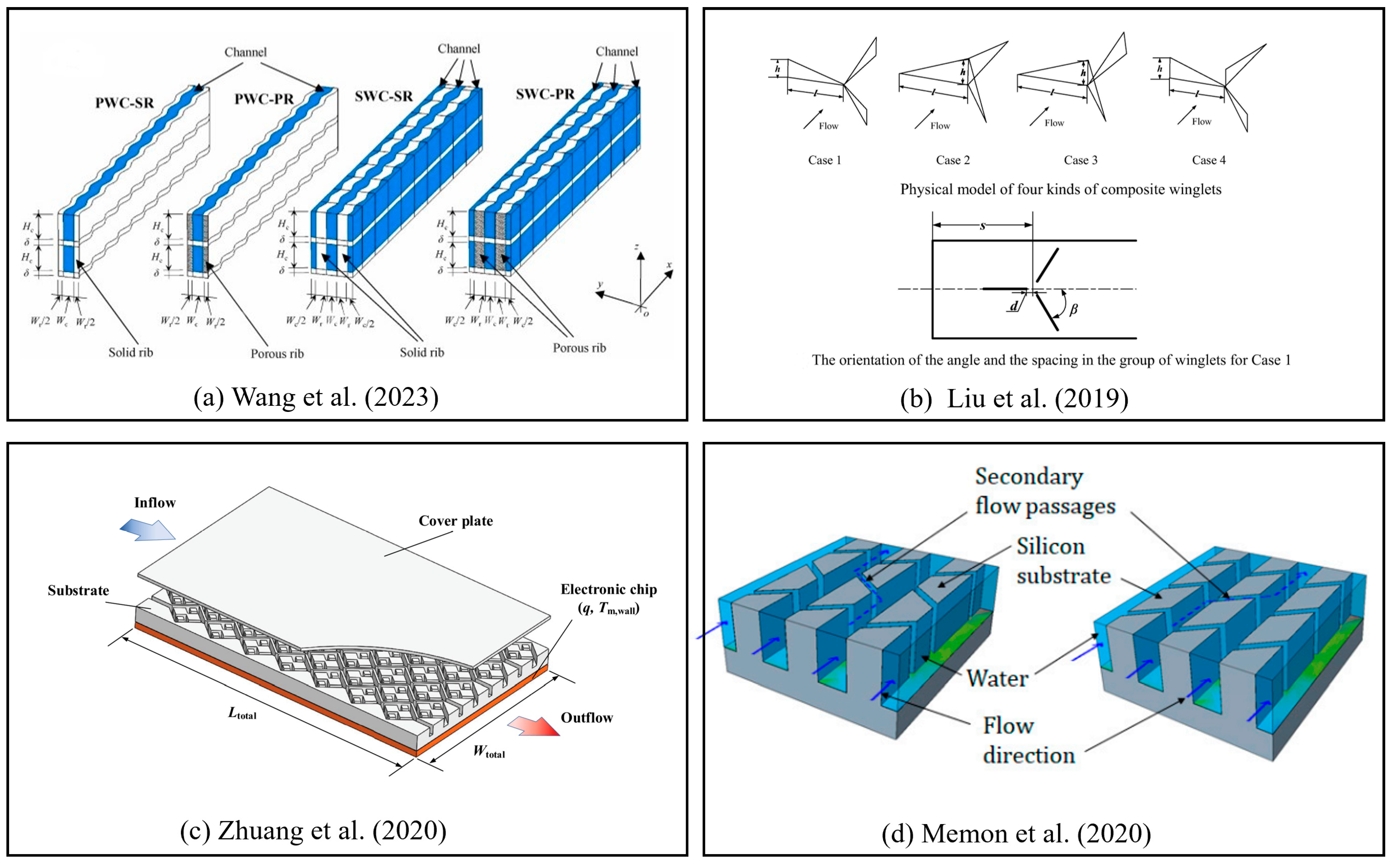
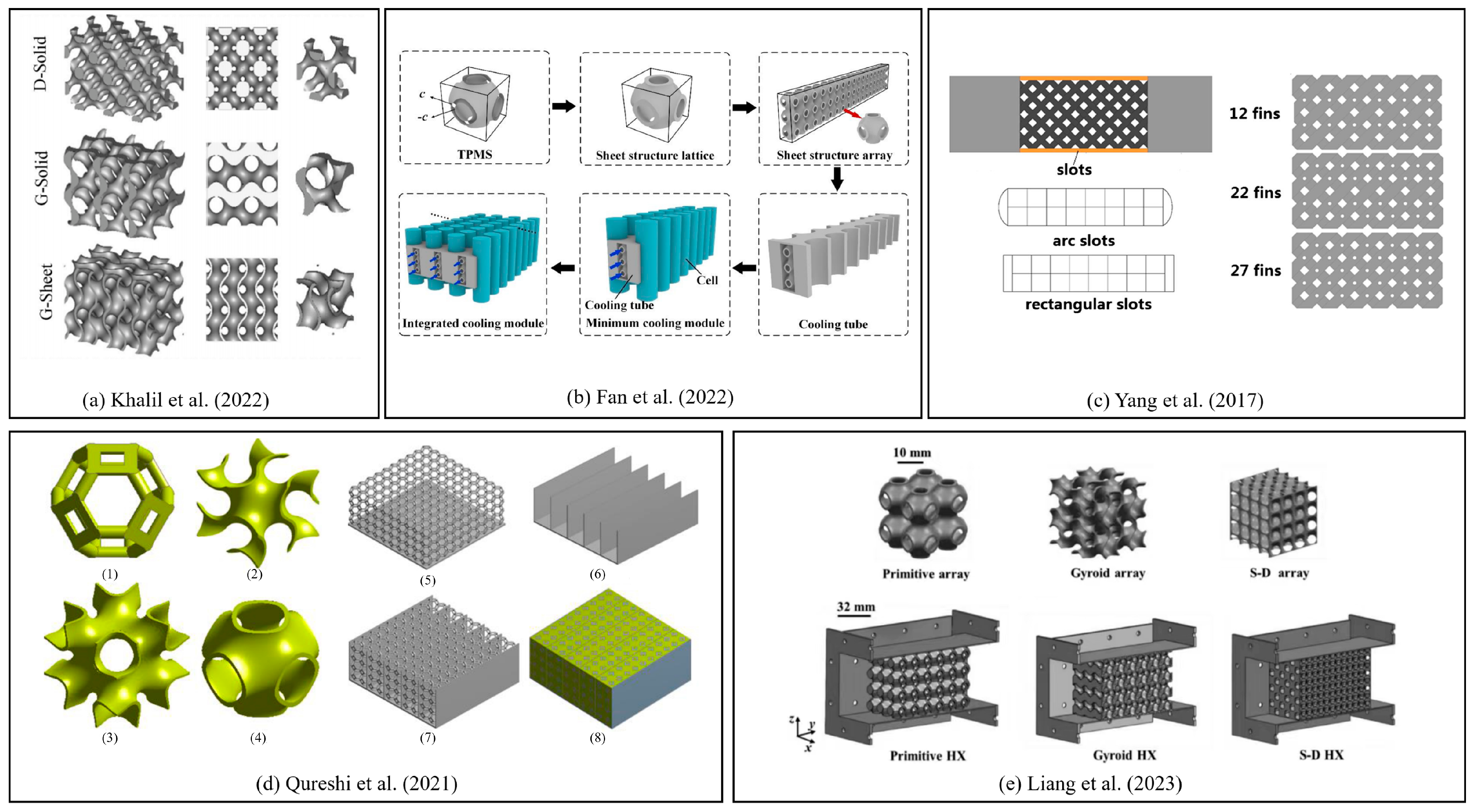
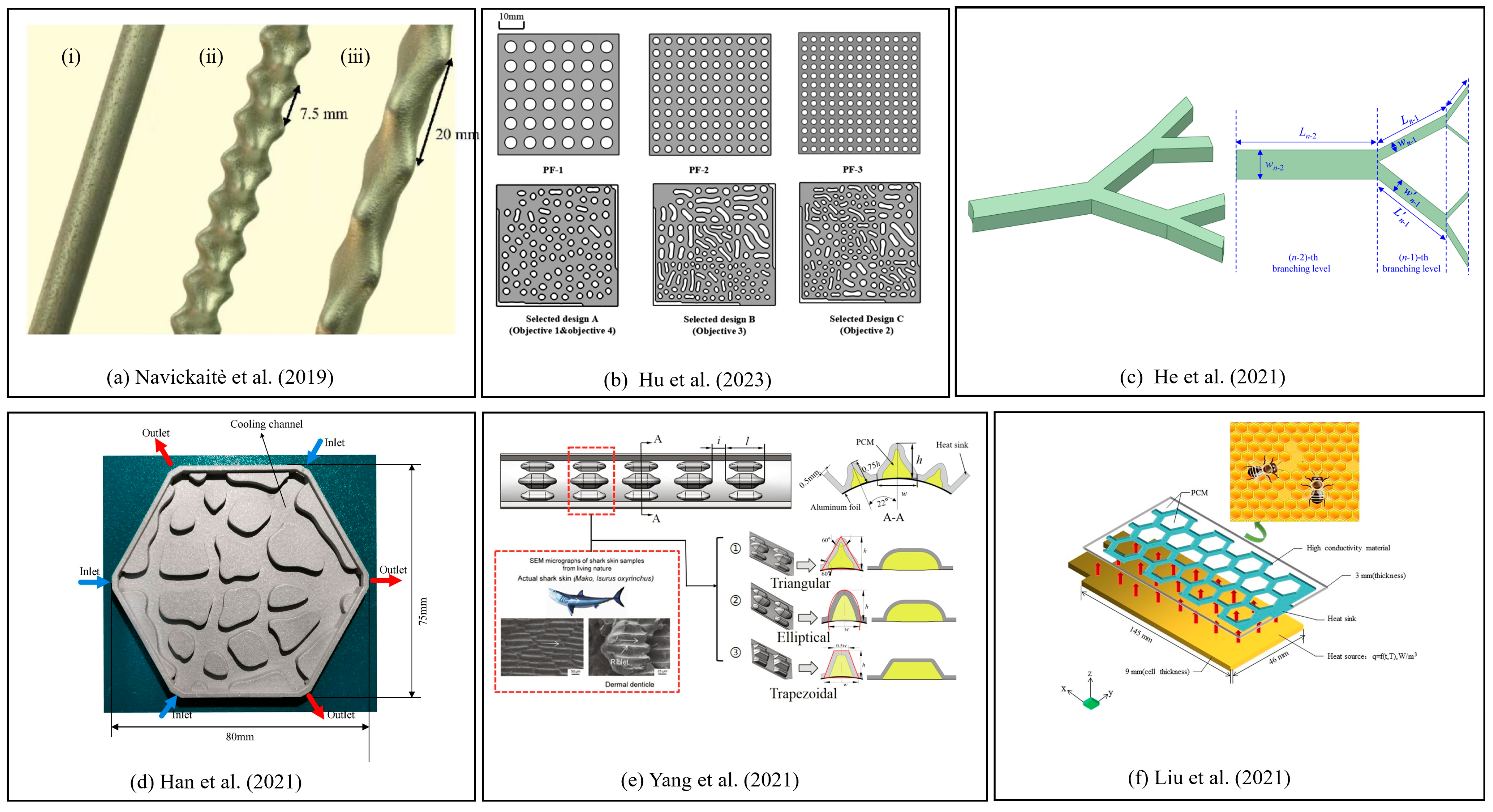
| The Author | Study Methods | Heat Sinks Design Features |
|---|---|---|
| Fathi et al. [14] | Simulation method | Heat sinks with parallel solid fins and porous fins. |
| Maheswari et al. [15] | Simulation method | Double-layer MCHS with different holes cut in the fins. |
| Tang et al. [16] | Simulation method | Applied diverging/converging channels to the typical microchannel structure. |
| Pan et al. [17] | Simulation method | A pin-fin staggered MMCHS. |
| Azodinia et al. [27] | Simulation method | Two-phase Al2O3 nanofluid flow in a microchannel. |
| Al-Rasheda et al. [28] | Simulation method | Non-Newtonian water-CMC/CuO nanofluid flow in an offset strip-fin microchannel heat sink. |
| Mansouri et al. [30] | Experimental method | Hybrid nanofluid containing graphene oxide (GO)-gold/water and GO/water nanofluid in cooling a computer’s CPU. |
| Saravanan et al. [39] | Simulation method | Combined the structure of square and circular pin fins to the MMCHS. |
| Wang et al. [43] | Simulation method | Double-layered MMCHS with parallel and symmetric wavy porous fins. |
| Liu et al. [44] | Simulation and experimental methods | Delta winglet generators inserted in a rectangular microchannel. |
| Zhuang et al. [45] | Simulation and experimental methods | A novel structure of MCHS with rhombus fractal-like units. |
| Memon et al. [46] | Simulation method | Introduced secondary flow channels to the walls between adjacent mainstream microchannels. |
| Gilmore et al. [47] | Simulation method | Applied topology optimization to design a multi-objective 3D conjugate heat transfer model. |
| Duan et al. [48] | Simulation method | A Y-shaped bionic MMCHS. |
| He et al. [49] | Simulation method | A bionic Y-shaped fractal heat sink obtained by the multi-objective optimization of the genetic algorithm. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, J.; Yang, L. Recent Development of Heat Sink and Related Design Methods. Energies 2023, 16, 7133. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16207133
Li J, Yang L. Recent Development of Heat Sink and Related Design Methods. Energies. 2023; 16(20):7133. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16207133
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Jingnan, and Li Yang. 2023. "Recent Development of Heat Sink and Related Design Methods" Energies 16, no. 20: 7133. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16207133
APA StyleLi, J., & Yang, L. (2023). Recent Development of Heat Sink and Related Design Methods. Energies, 16(20), 7133. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16207133







