Abstract
The application of 5G-based communication for pilot protection in a distribution network with distributed generators is becoming increasingly widespread, but the existence of a 5G communication transmission data delay adversely affects the rapidity and reliability of the pilot protection based on the principle of the traditional dynamic time warping distance (DTW) algorithm. Therefore, to address this problem, and according to the difference in fault currents between distributed generators and synchronous machines, a new scheme of pilot protection based on the principle of an improved DTW is proposed. The scheme firstly performs cosine transform on the fault current sequence, and then it normalizes the DTW value. Finally, the proposed scheme is verified via simulation. The simulation results show that, compared with the traditional DTW, the proposed algorithm has better anti-delay characteristics and a stronger anti-interference ability, and the scheme can quickly and reliably identify in-zone and out-of-area faults with strong noise resistance. Further, the action times for a single-phase ground fault, two-phase ground fault, two-phase-to-phase fault, and three-phase short-circuit fault were reduced by 2.9 ms, 4.54 ms, 5.81 ms, and 5.89 ms, respectively. In addition, it is also sui for a distribution network with a high wind and photovoltaic penetration rate.
1. Introduction
With the depletion of fossil energy sources and the proposal of environmental protection policies, distributed generators (DGs) represented by wind power and photovoltaics play a key role in the new power system. However, DG access has transformed the traditional single-source radial distribution network into a multi-source network, and the current distribution has been significantly changed during faults [1,2]. Simultaneously, power outputs from distributed generators exhibit fluctuations and intermittency [3,4,5]. These factors present significant challenges to the traditional three-stage protection that is reliant on fault current settings [6,7], leading to notable decreases in rapidity and reliability. Considering the fault characteristics and current distribution patterns of distributed generators, it is undeniable that differential protection is the optimal solution to address these issues. However, in distribution networks, inflexible and expensive fiber-optic networks no longer meet the high communication requirements of pilot protection [8], and this is becoming a major bottleneck in their widespread adoption. Compared to the fourth-generation mobile network (4G), the fifth-generation mobile network (5G) offers significant improvements in transmission rate, latency, and stability. The performance characteristics of 5G, known as “three highs and one low”, align well with the requirements of distribution network protection [9,10], providing a new solution for the application and promotion of current differential protection in a distribution network.
Traditional current pilot protection has very high requirements for data synchronization, and 5G networks are prone to jitter, packet loss, and disorder during data transmission [11]. This will lead to difficulties in maintaining consistency in transceiver routing, and the traditional timing method based on ping-pong timing is no longer applicable [12]. Therefore, if 5G communication is used as a longitudinal channel to transmit real-time data, the reliability of the traditional current differential protection will be greatly reduced.
In response to the latency challenges posed by 5G, the dynamic time warping (DTW) algorithm, known for its strong anti-latency performance and excellent tolerance characteristics, can be employed in longitudinal differential protection for 5G. Researchers [13,14,15] have studied DTW-based differential protection. Reference [13] calculated the similarity between waveforms at both ends of the contact line using the DTW algorithm to realize the discrimination of in-zone and out-of-area faults, which improved the reliability of the protection. Reference [14] utilized DTW to compute the similarity between fault currents for the purpose of identifying fault types. Furthermore, the study took into consideration the impact of external interference factors on DTW-based protection and proposed a faster and more reliable protection scheme. In reference [15], which addressed the fault current characteristics in distributed generators, a protection scheme suitable for high-proportion new energy systems was introduced by combining the DTW differential principle with the ratio-constrained differential principle. This presented a novel approach for a distribution network with a large proportion of distributed generators. It is evident that DTW has a wide range of applications, and if a differential protection system is established based on the principle of DTW, it would be highly suitable for protection research in the context of 5G communication.
For this reason, related scholars have improved DTW. Reference [16] proposed improving the DTW differential protection scheme, which would solve the time delay problem existing in 5G communication, allow it to operate reliably under different types of faults, and exert the advantages of the 5G longitudinal channel. Reference [17] provided a practical solution for the application of 5G communication technology to the differential protection of a distribution network by improving DTW, which improved the reliability of the protection while at the same time maintaining good adaptability to the delay jitter and asynchronous errors. Reference [18] proposed a novel DTW protection scheme through a relaxation search and derivative estimation that minimized the impact of data synchronization errors and data loss on protection, and it was applicable in a distribution network containing distributed generators. Reference [19] introduced a weighted DTW algorithm that optimized the output values of DTW, mitigating the influence of edge effects and enhancing the algorithm’s resilience to synchronization errors.
By improving DTW, the above scholars have realized the advantages of DTW in 5G scenarios, but they have neglected the problem of the “singularity” that occurs when DTW is matched, which leads to the low efficiency of DTW algorithm metrics and poor anti-interference ability. Based on the original DTW differential protection scheme, under the influence of the 5G delay, its rapidity and reliability cannot be guaranteed, and its protection has the potential for false activations and refusals to operate.
Novelty and Contribution
Aiming at solving the above problems, this paper proposes a pilot protection scheme for a distribution network containing distributed generators with improved DTW. Compared with traditional DTW, the improved DTW firstly performs the cosine transform on the fault current sequence and then normalizes the DTW value, which effectively mitigates the impact of the 5G delay problem on DTW protection and improves the anti-delay characteristics and anti-interference ability of the algorithm. The simulation results of this study showed that during the in-zone fault, the action times for a single-phase ground fault, two-phase ground fault, two-phase-to-phase fault, and three-phase short-circuit fault were reduced by 2.9 ms, 4.54 ms, 5.81 ms, and 5.89 ms, respectively. During the out-of-area fault, there was no refusal of action or false action. In addition, it is also suitable for use in scenarios with noise, high wind and photovoltaic penetration rate. The distribution network model containing the distributed generators was constructed in PSCAD/EMTDC, and the algorithm was processed in MATLAB. Scenarios under noise, high wind and photovoltaic penetration rate, as well as in-zone and out-of-area faults, were simulated to verify the superiority of the proposed scheme.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Characterization of the Fault Current in a Distribution Network Containing Distributed Generators
Current distributed generators mainly consist of wind turbines and photovoltaics. The fault characteristics of the different distributed generators are similar during a fault, and a fault current is mainly related to the control strategy [20,21]. The expressions for a short-circuit current of a distributed generator are as follows [22]:
where is the fault phase current of a distributed generator, is the cutoff frequency, is the angular frequency, is the time constant, R and L are the equivalent resistance and equivalent inductance, respectively, and K is a constant. From Equation (1), it can be seen that the fault is influenced by the control strategy, the short-circuit current contains harmonic components, the angular frequency will deviate from the industrial frequency, and a distributed generator’s short-circuit current has obvious weak feed characteristics, and this presents the amplitude of the non-industrial frequency characteristics.
The synchronous generator fault current can be expressed as follows [23]:
where represents the fault current of the synchronous machine; is the synchronous machine potential; , , and are the synchronizing reactance, transient reactance, and sub-transient reactance of the synchronous machine, respectively; , , and are the DC component, transient AC component, and sub-transient AC component wailing time constants; is the industrial angular frequency; and is the fault initial angle. The short-circuit current of the synchronous generator during the fault consists of the attenuation of the industrial frequency component, steady-state industrial frequency component, and attenuation of the DC component. The waveform under the fault is an exponentially decaying industrial frequency sine wave.
By analyzing Equations (1) and (3), it can be concluded that there are significant differences between the fault characteristics on the distributed generators’ side and those on the synchronous machine’s side. According to Kirchhoff’s current law, during an in-zone fault, there is a substantial difference between the fault currents on the two sides. During an out-of-area fault, the presence of through-currents results in a small difference between the fault currents on the two sides. Based on the significant difference in the fault currents between the in-zone and out-of-area situations, this provides a theoretical foundation for developing a new pilot protection scheme for a distribution network with distributed generators.
2.2. 5G-Based Pilot Protection for Distribution Network
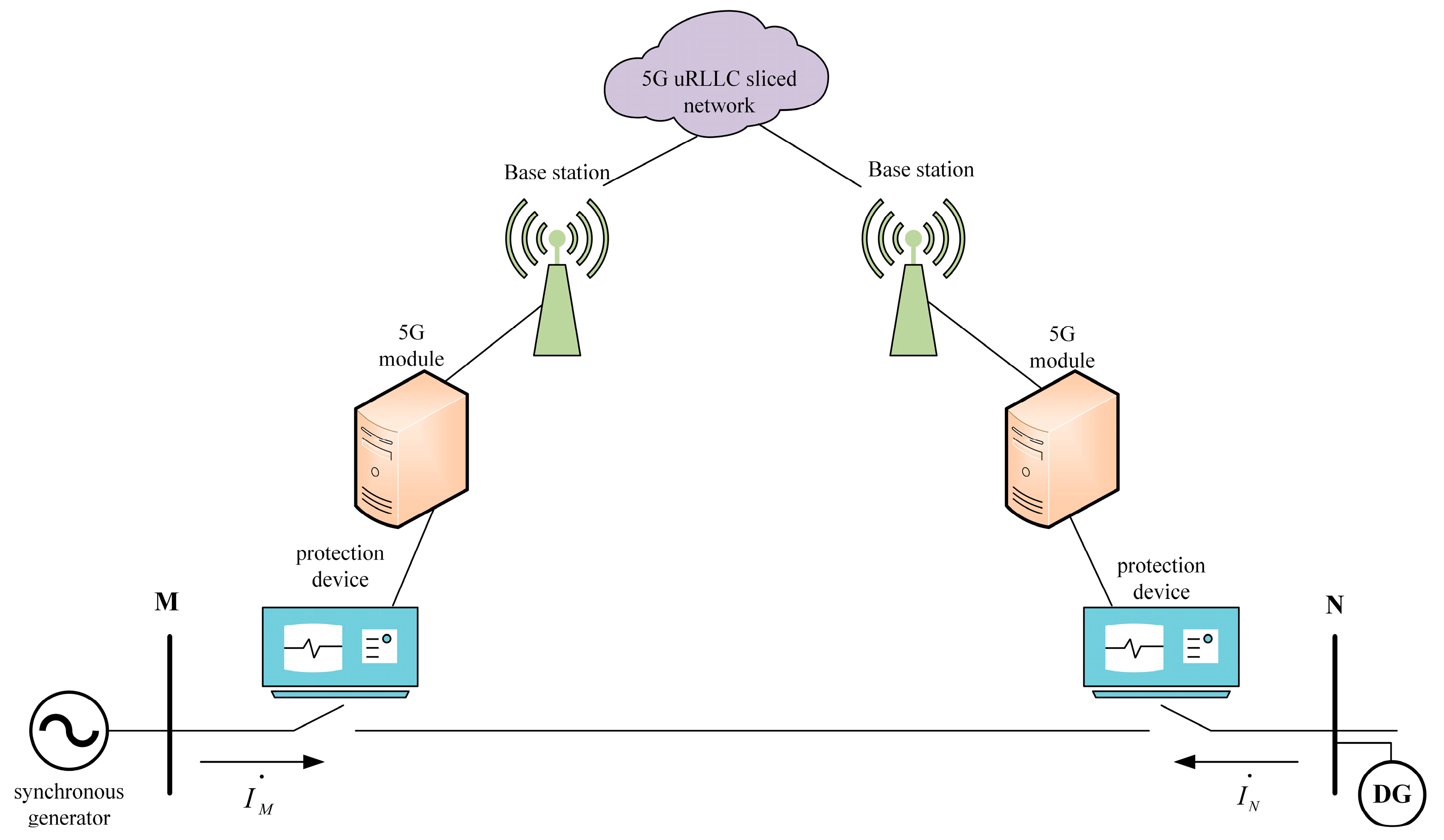
With the commercialization of 5G and its development in vertical industries, one of the three major scenarios of 5G, ultra-reliable and low-latency communications (URLLC), can be applied in the field of distribution network differential protection [24,25]. A schematic diagram of URLLC is shown in Figure 1. By introducing network slicing within the 5G architecture and combining it with mobile edge computing (MEC) [26], the sinking of user-facing functions, and network function virtualization technology [27,28], the data processing capabilities of base stations and data centers can be significantly enhanced. Additionally, the reliability of data transmission can also be guaranteed. Consequently, data transmission in a 5G URLLC network scenario becomes faster, more secure, and more confidential.
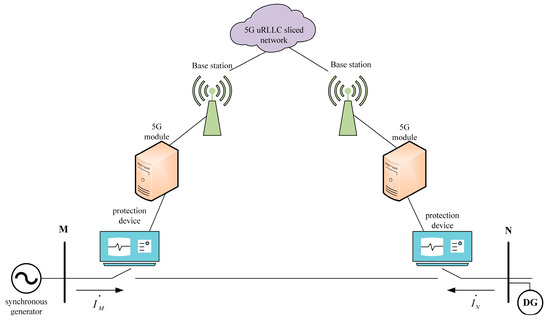
Figure 1.
Pilot protection based on a 5G URLLC scenario.
Given the above analysis, a 5G URLLC network can provide a new alternative to optical fibers for the distribution network current differential protection. Such a network aims to address the communication challenges in the “last mile” of a distribution network. At the same time, it compensates for the drawbacks of traditional optical fiber channels, such as high costs, limited flexibility, and long construction periods.
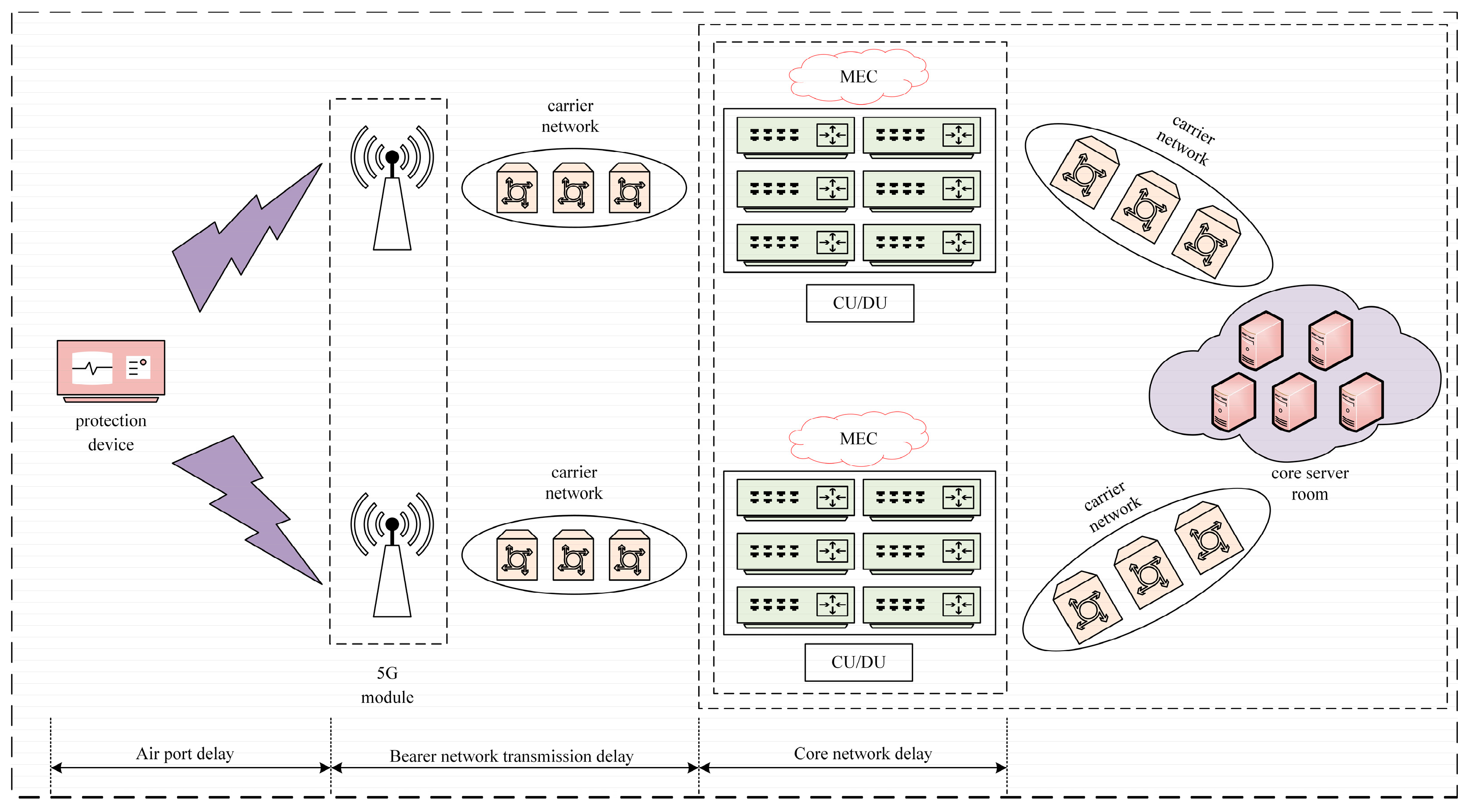
In a 5G URLLC (ultra-reliable and low-latency communication) scenario, the total latency is primarily composed of the following three components: an airport delay, a bearer network transmission delay, and a core network delay, as illustrated in Figure 2. If we denote the total latency as , it can be expressed by the following formula:
where the airport delay is , the bearer network transmission delay is , and the core network delay is .
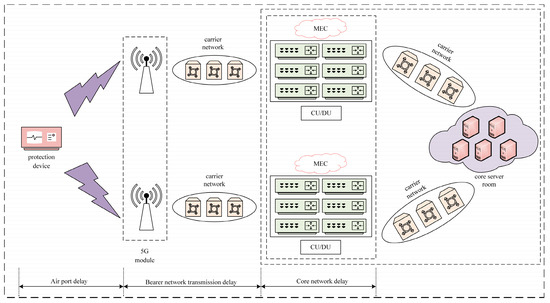
Figure 2.
A 5G URLLC network slicing total delay.
Regarding the airport delay, in the domestic context of using a TDD (time division duplex) network with a dual-frame structure, the maximum delay generated during a data downlink is 3 ms. A bearer network transmission delay consists of data transmission delay and a delay introduced by the routing equipment forwarding. With existing technologies, a bearer network transmission delay can be controlled to approximately 0.05 ms [29]. A core network delay primarily encompasses the time required for data processing, transmission, and scheduling, and it can typically be controlled to approximately 5 ms [30,31]. However, due to the presence of latency variations in actual operational scenarios, when considering a certain margin for latency tolerance, the end-to-end latency in a 5G network can extend to approximately 10 ms [32,33].
2.3. Principle of the DTW Algorithm
The dynamic time warping (DTW) distance algorithm is used to measure the similarity between time sequences [34], and its core idea is to minimize the distance from one sequence to another by stretching or compressing one of the sequences on its time axis, which can solve the problem of the temporal offset in the time sequences due to the 5G delay. It is very suitable for researching 5G pilot protection.
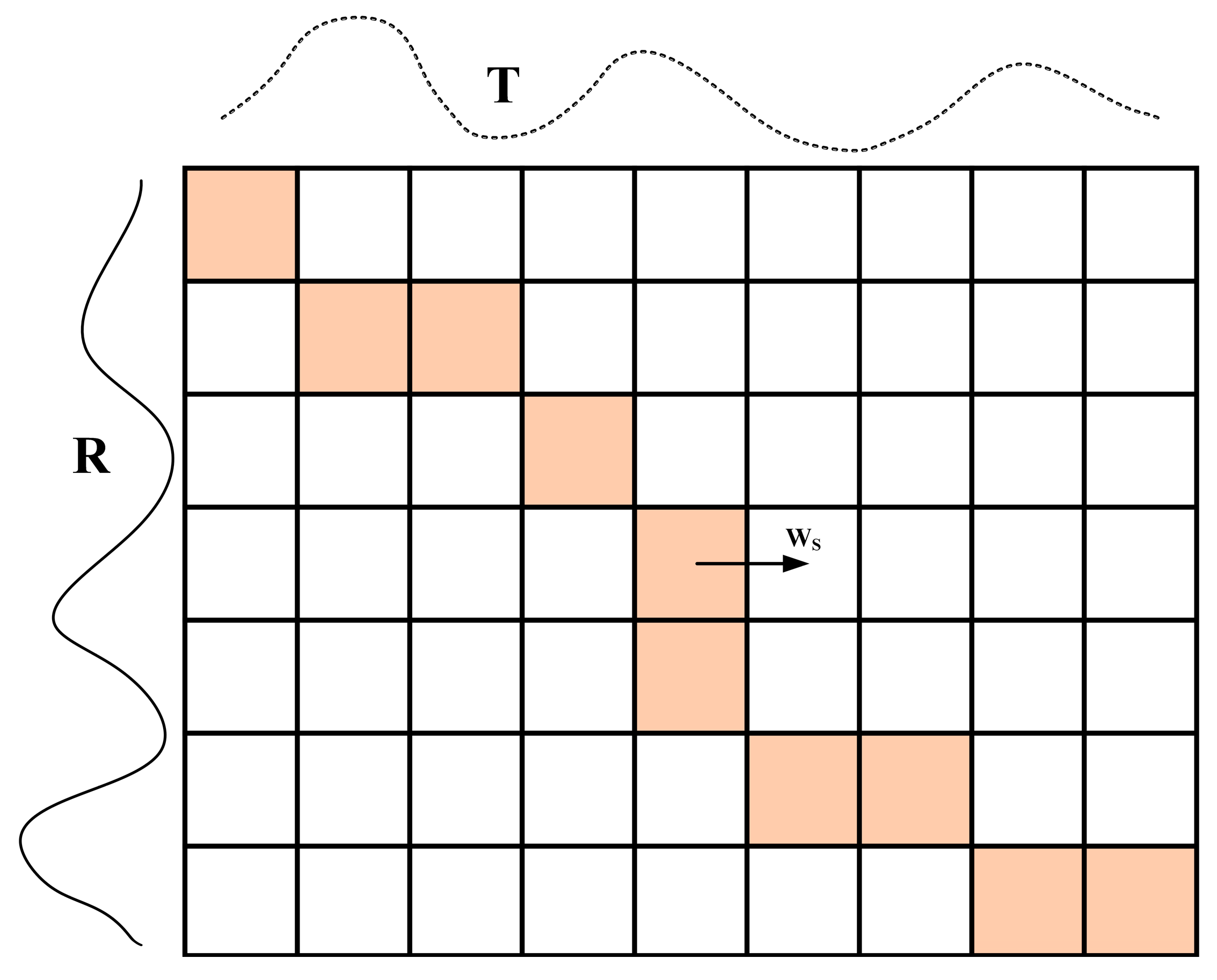
In the two current sequences, and , m and n denote the number of currents in the R and T sequences, respectively, and the matching path of the current sequences R and T is indicated by the colored square elements shown in Figure 3.
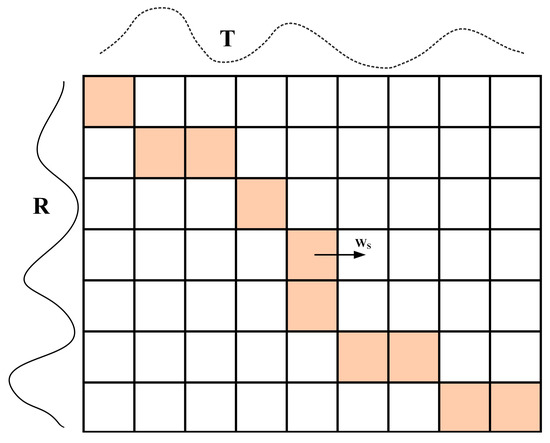
Figure 3.
The warping path.
There exists an optimal path in the two current series, R and T, and the shortest path of and must be satisfied to find the shortest distance from , , and and three points to , whose DTW distance is calculated as follows:
We solved using dynamic programming, and the distance d between every two points of the two sequences defined the cumulative distance matrix D, which is given by:
where i = 1, 2, …, m; j = 1, 2, …, n; D(0,0) = 0; and D(i,0) = D(0,j) = +∞.
2.4. Improved DTW Algorithm
The problem of the DTW pathological matching phenomenon has always existed. Pathological matching refers to the phenomenon where one point in a sequence map leads to multiple points in another sequence (the singularity phenomenon) [35]. This phenomenon will reduce the accuracy of a sequence evaluation, and the uncertainty of the 5G delay makes the singularity phenomenon even more prominent while the differential protection based on the principle of the traditional DTW may face failure and the protection of the rapidity and reliability will be greatly affected.
The singularity issue can be resolved by introducing a non-uniform transformation called the cosine transform. This method can add new information that is effective for measuring the distance between time series, reducing the probability of singularity matching and improving the tolerance characteristics of DTW. It helps solve the asynchronization problem between the data at both ends of the pilot protection caused by 5G latency and enhances the protection’s resilience to latency and interference. The specific improvement approach is as follows:
Sequence , the cosine transform is , and the formula is as follows:
The distance between the points R and T can be replaced with and , and then the new distance between the points R and T can be calculated as follows:
Then the shortest path of the improved DTW is , and the formula is as follows:
According to Equations (9) and (10), it can be seen that the Euclidean distance of the original DTW is replaced by calculating the distance after the cosine transform, which makes up for the defects of the original DTW matching at the singularities, and the shortest paths and the distances between the two points are updated after the improvement, which improves the matching accuracy of the two different time sequences of R and T. The anti-delay characteristics and anti-interference capability of the algorithm are strengthened, but increases in the numbers of matching times and matching paths result in the calculated DTW distance amplitude also increasing, and the existence of the amplitude error makes the protection performance worrying, and so the DTW value after the cosine transform is normalized so as to reduce the impact of the amplitude error on the algorithm. The normalized DTW value can be recorded as D, as shown in Equation (11) below:
After normalization, the problems caused by DTW after the cosine transform can be circumvented, and the fault tolerance of DTW can be further improved. The longitudinal current differential protection based on the principle of the improved DTW, in combination with the 5G URLLC slicing network scenario, can provide a more reliable protection scheme in the distribution network containing distributed generators. This also contributes to the popularization of the application of 5G communication in the longitudinal differential protection in distribution networks.
2.5. Cosine Transform Based Action Criteria for DTW Protection
From Equation (11), it is evident that the value of D falls within the range [0–1]. It is defined that the positive direction of the bus current flows in the direction of the line. For internal faults, the currents on the synchronous machine’s side and the distributed generator’s side are in the same direction during the fault, and thus, D approaches a value of one. For normal and external faults, the currents on the synchronous machine’s side and those on the distributed generator’s side are in an opposite direction during the fault, and the value of D approaches zero.
Therefore, it is possible to construct protection criteria based on the differences in the values of D for internal and external faults. By finding an appropriate threshold value, it becomes possible to effectively identify internal and external faults. If we let represent the calibration value, then when an internal fault occurs, the value of D should satisfy the following condition:
2.6. Protection Value Calibration
The main purpose of protection calibration is to ensure that the protection can still accurately and quickly recognize faults in a zone under the interference of external unfavorable factors. Usually, the protection value needs to be multiplied by a reliability coefficient, K, to complete the calibration, as follows:
where the value of D lies in [0–1], and for the sensitive, fast, and reliable operation of the protection, D in Equation (13) takes a value of one. In order to escape errors during normal operations as well as out-of-area faults, the value of K can be determined by Equation (14) as follows:
In Equation (14), K is the reliability coefficient, K1 is the time delay reliability coefficient, K2 is the data transmission reliability coefficient, K3 is the amplitude reliability coefficient, and Kmar is the margin reliability coefficient. After a large number of experiments for verification, we assigned a delay reliability coefficient of 0.8, a data transmission reliability coefficient of 0.8, an amplitude reliability coefficient of 0.7, and a margin reliability coefficient of 0.9. Through an analysis of Equations (13) and (14), the protection calibration value could be obtained as follows:
In order to make it easier to apply in engineering practice and with reference to the calculated calibration value, the actual calibration value of the protection could be set to 0.4, and then the new protection action criterion was as follows:
when the value of D was greater than 0.4 for in-zone faults, there was protection, and when the value was less than 0.4 for out-of-area faults, there was no protection.
2.7. Protection Realization
Based on the analysis provided in the previous five sections, the discriminative steps for the proposed protection principle were established as follows:
- Sample the currents on both sides using the protection device to obtain the fault waveform sequences for both sides.
- Transmit a one-side fault current sequence through a 5G longitudinal communication channel to the opposite side and calculate the value of D based on Equation (11).
- If the value of D is greater than 0.4, this indicates that there is an internal fault within the specified area, and the protection system takes action.
- If the value of D is less than 0.4, this indicates that there is an external fault or a normal operation status, and the protection system does not take action.
3. Results and Discussion
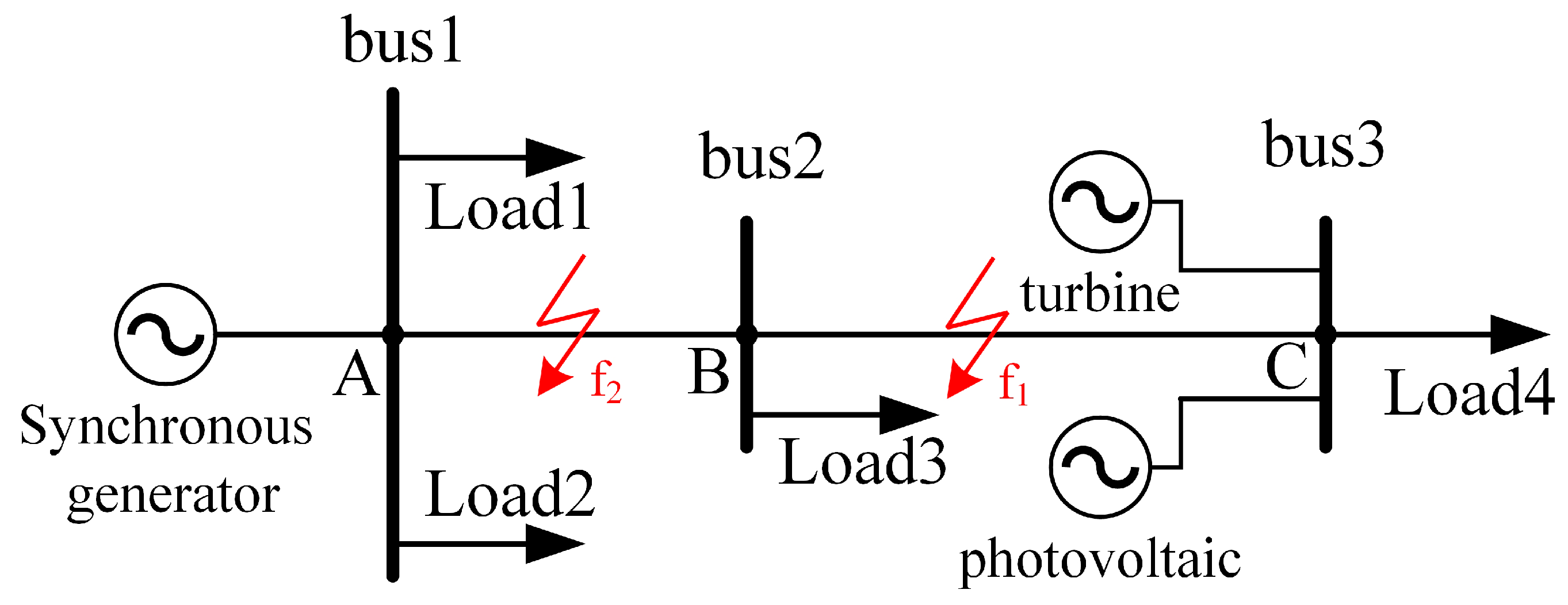
In order to validate the effectiveness of the proposed scheme, a distribution network model, as shown in Figure 4, was created in PSCAD/EMTDC, and the proposed protection scheme was validated in conjunction with MATLAB.
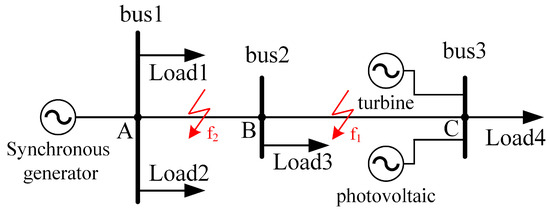
Figure 4.
The distribution network model with distributed generators.
The distribution network had a voltage level of 10 kV, with lengths of AB and BC measuring 2 km and 4 km, respectively. Load 1, Load 2, Load 3, and Load 4 were all rated at 2 MV·A. The wind and the photovoltaic capacity were each rated at 1 MV·A. The line impedance for a positive sequence and a zero sequence was 0.069 + j0.009 Ω/km. The fault occurrence time was set at 1 s. We employed 5G communication as the longitudinal data transmission channel, introducing a maximum end-to-end delay of 10 ms for the fault current on the synchronous machine’s side. This was then compared with the fault current on the distributed generator’s side. The computer configuration used for the simulations was as follows: the CPU was an Intel Core i5-7300H (made in Beijing, China), 8 GB of RAM was used, and the graphics card was a GeForce 1050Ti (made in Beijing, China). The operating system was Windows 10 64 bit. The simulation platform included PSCAD 4.6.2 and MATLAB 2022a.
In order to verify the effectiveness of the proposed scheme, as discussed in Section 3.1, the simulation of an in-zone fault was carried out for a scenario with a wind and photovoltaic penetration rate of 25%; as discussed in Section 3.2, the simulation of an out-of-area fault was conducted for a scenario with a wind and photovoltaic penetration rate of 25%; as discussed in Section 3.3, the simulation of both an in-zone fault and an out-of-area fault was performed for a scenario with a wind and photovoltaic penetration rate of 25%, considering the effect of noise; and as discussed in Section 3.4, the simulation of both an in-zone fault and an out-of-area fault was conducted for a scenario with a wind and photovoltaic penetration rate of 50%. The specific simulation results are shown below.
3.1. Failure Analysis in the Zone
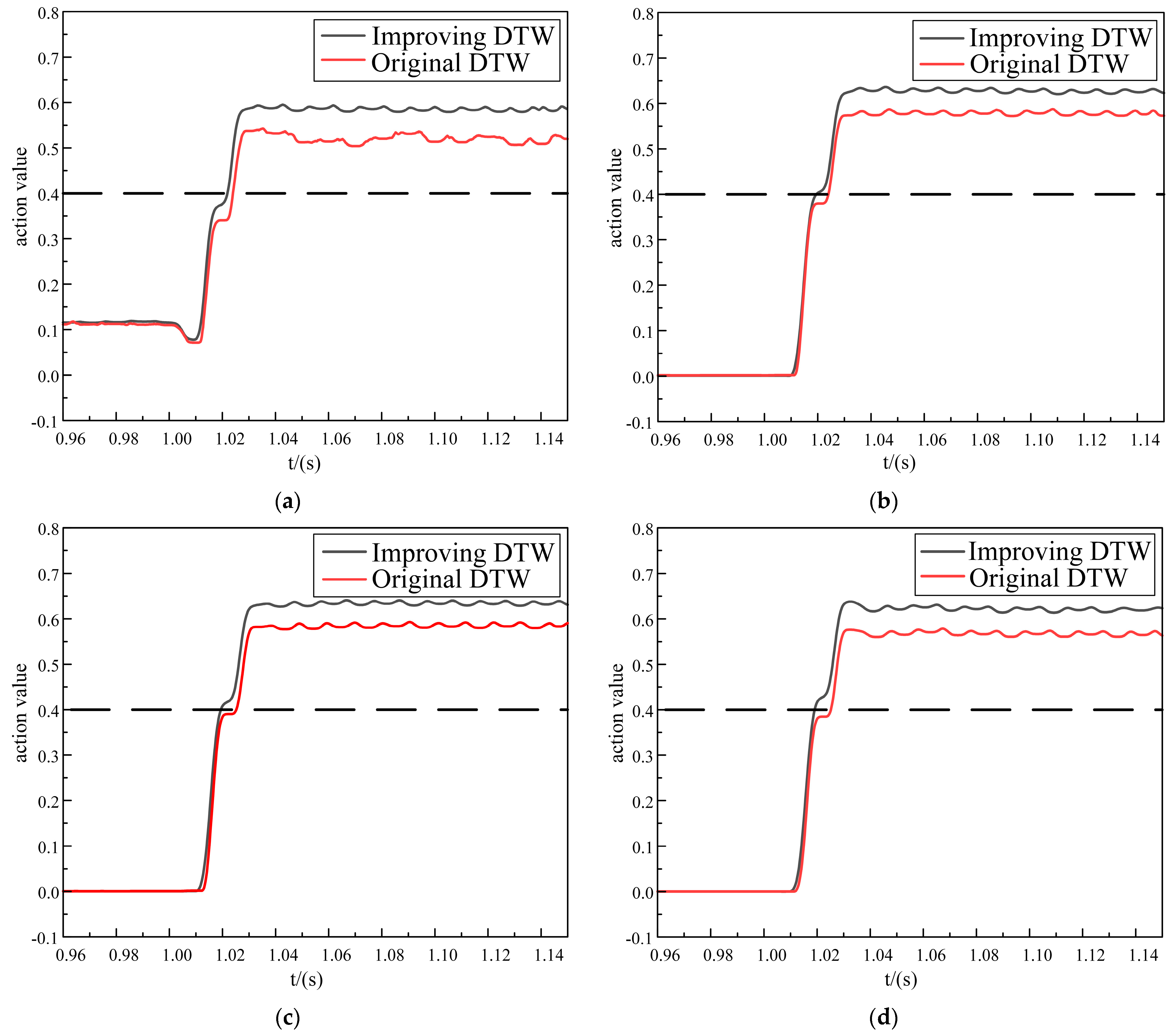
Fault location f1 was set between the bus2 and bus3 buses, and the fault occurred as an in-zone fault. Different fault types in the area were simulated and analyzed, and the specific simulation results are shown in Figure 5 and Table 1.
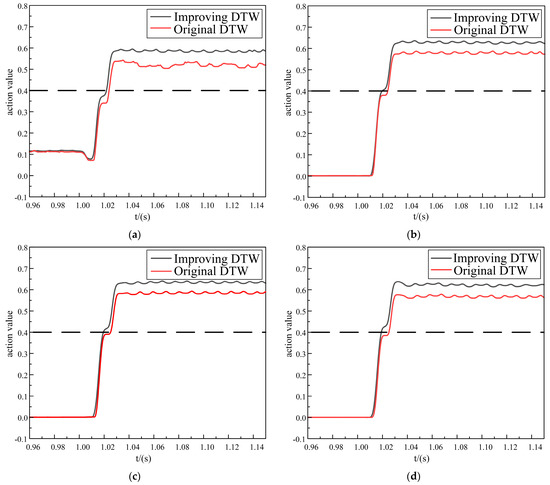
Figure 5.
The simulation analysis of the in-zone faults. (a) Internal single-phase ground fault. (b) Internal two-phase ground fault. (c) Internal two-phase-to-phase fault. (d) Internal three-phase short-circuit fault.

Table 1.
In-zone fault action times.
The fault action times in the zone are shown below in Table 1.
Based on Figure 5 and Table 1, it can be observed that the protection principle based on the improved DTW exhibited better latency tolerance characteristics compared to the original DTW method, the action change curve increased preferentially and reached the protection value quickly, and the action times for the single-phase ground fault, two-phase ground fault, two-phase-to-phase fault, and three-phase short-circuit fault were reduced by 2.9 ms, 4.54 ms, 5.81 ms, and 5.89 ms, respectively. Therefore, the new protection scheme based on the improved DTW offered excellent latency tolerance, a rapid response, and superior high-speed operation characteristics.
3.2. Out-of-Area Failure Analysis
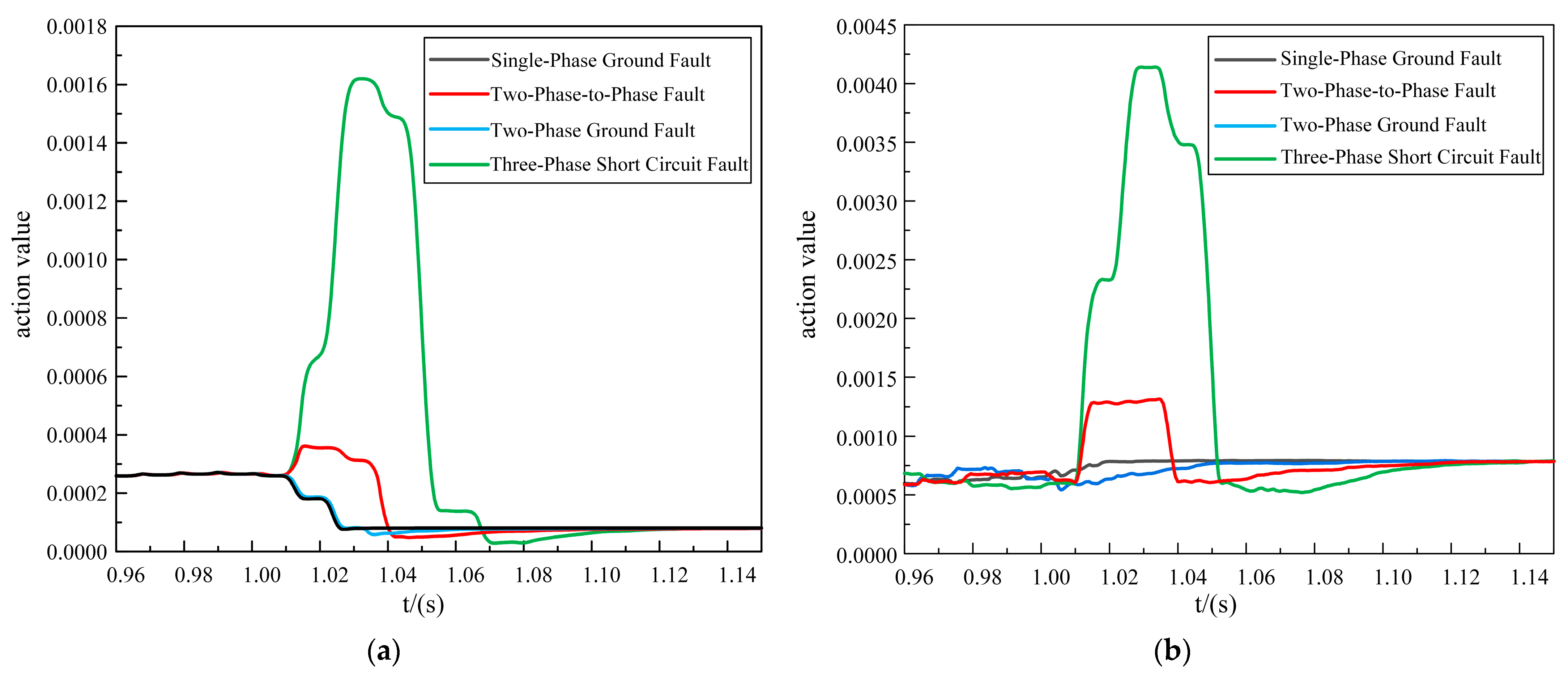
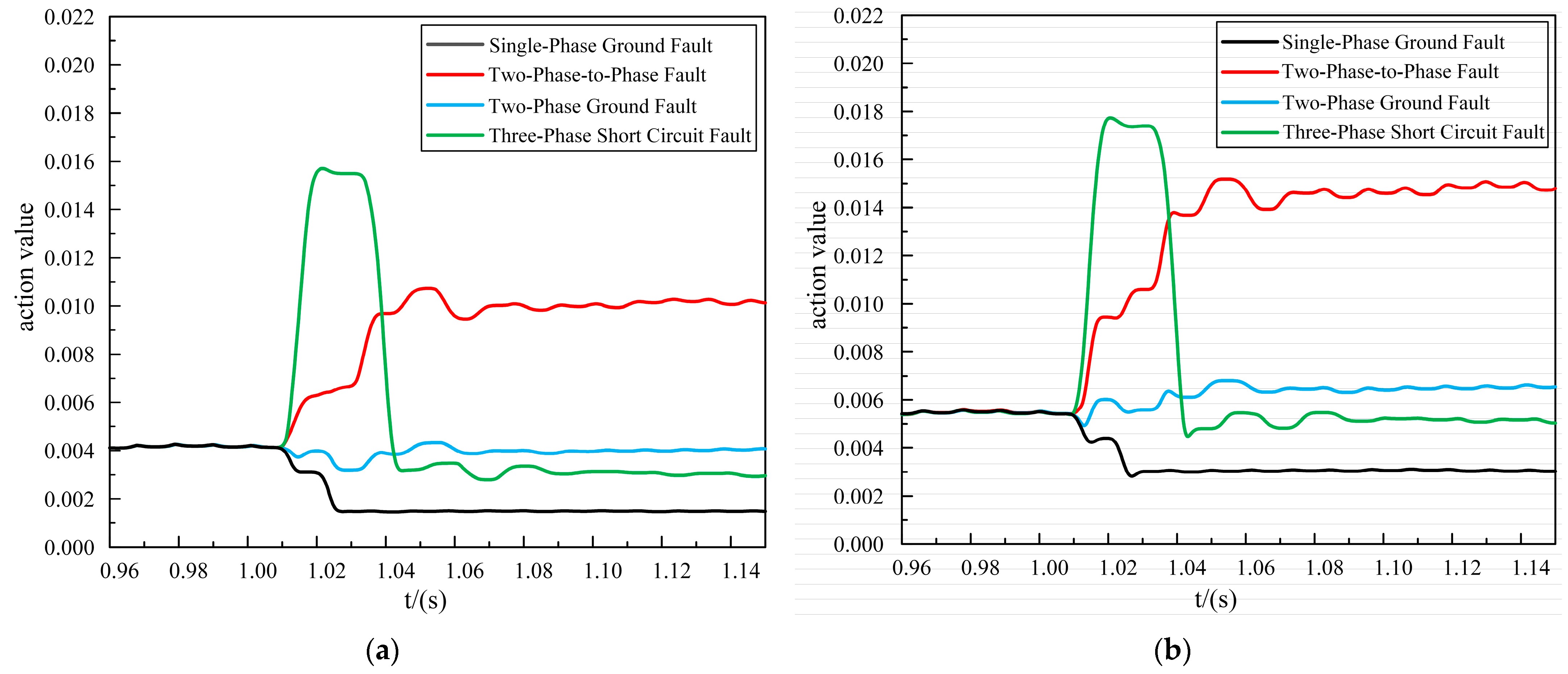
Fault location f2 was set between the bus1 and bus2 buses, and the fault occurred as an out-of-area fault. Different fault types in the out-of-area were simulated and analyzed, and the specific simulation results are shown in Figure 6.
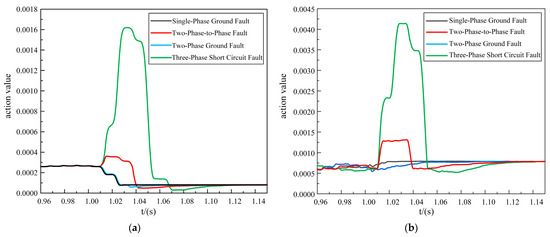
Figure 6.
The out-of-area fault simulation analysis. (a) Improved DTW action value. (b) Original DTW action value.
According to Figure 6, it can be seen that the action values of the two schemes under the out-of-area fault were much smaller than the protection calibration value, and there was no false activation. However, the action values of the proposed scheme ranged from 0 to 0.0017, and they tended to be closer to 0. In contrast, the action values of the original DTW ranged from 0.0005 to 0.00425. Therefore, the proposed scheme demonstrated a comparative advantage, particularly in the context of out-of-area faults, and it exhibited superior reliability.
3.3. Noise Impact Analysis
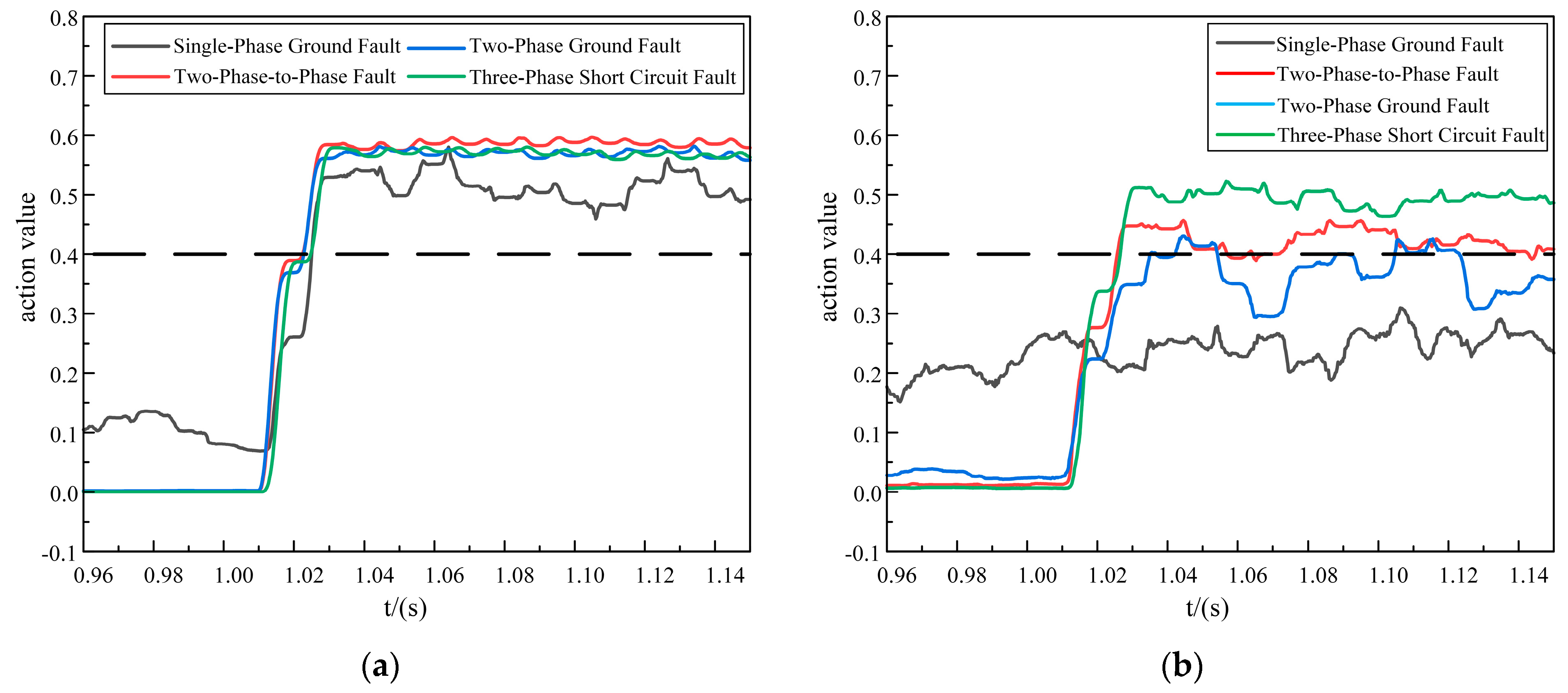
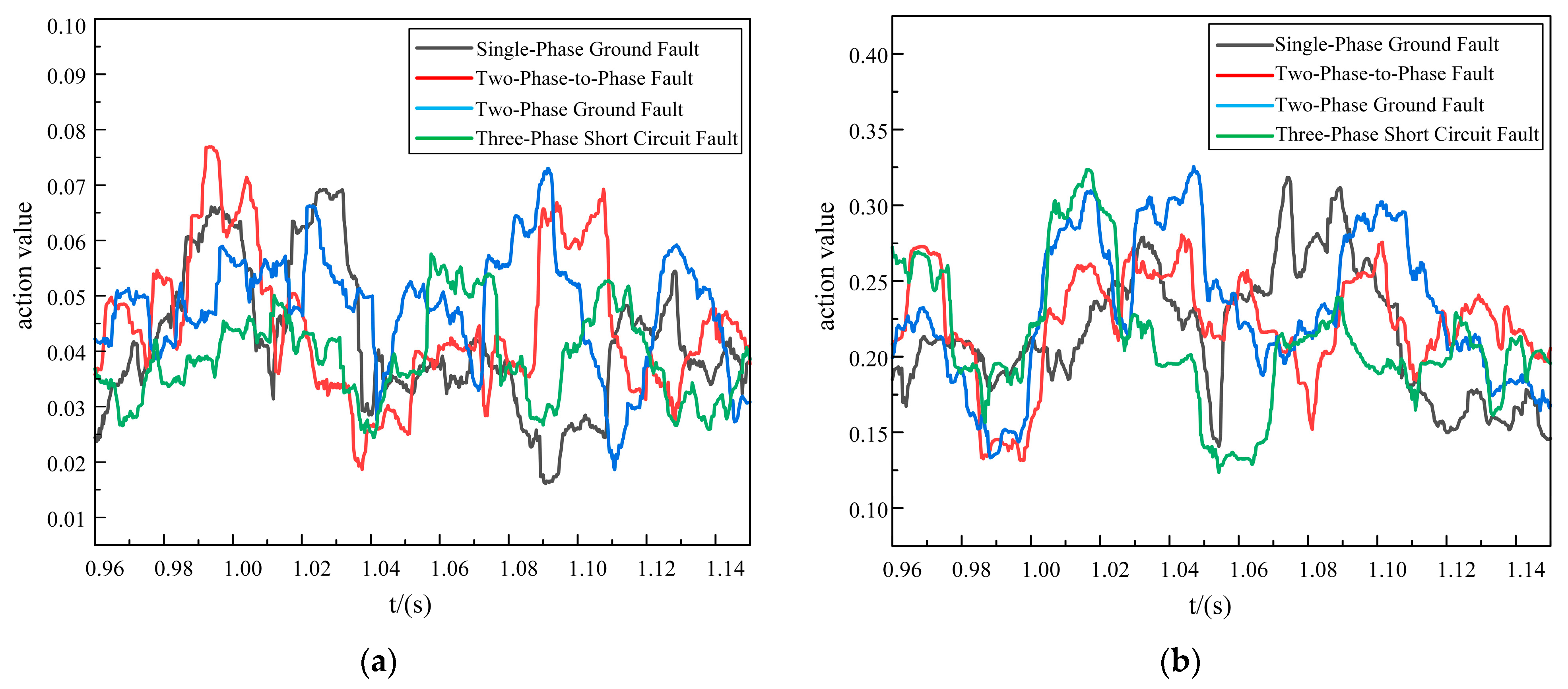
Considering the noisy electromagnetic environment of the distribution network, noise was bound to interfere with the use of 5G communication as the longitudinal transmission channel, and the protection would be exposed to a risk of false activation or even a refusal to activate, and so it was necessary to analyze the impact of noise on the protection. In the current simulation process, we simulated a high-noise environment by adding Gaussian white noise with a high signal-to-noise ratio of 10 dB to the sampled fault current values on both sides. We conducted separate simulations for in-zone and out-of-area faults under noisy conditions for the two proposed schemes. The specific simulation results are shown in Figure 7, Figure 8 and Figure 9.
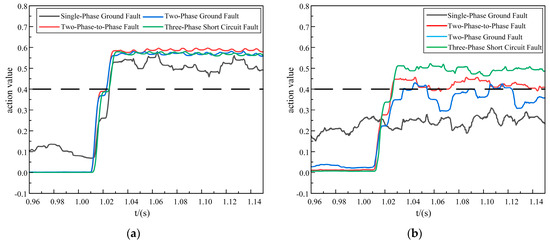
Figure 7.
In-zone fault action values. (a) Improved DTW action value. (b) Original DTW action value.
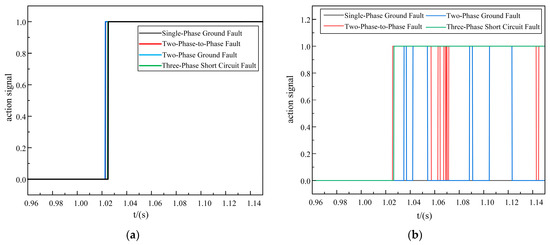
Figure 8.
In-zone fault action times. (a) Improved DTW action time. (b) Original DTW action time.
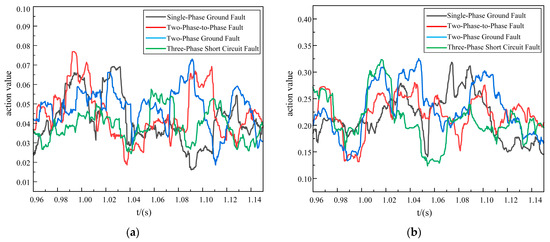
Figure 9.
Out-of-area fault action values. (a) Improved DTW action value. (b) Original DTW action value.
As shown in Figure 7, Figure 8 and Figure 9, it was evident that in a strong 10 dB noise environment, under in-zone fault conditions, the improved DTW protection scheme exhibited operation times of 25.25 ms for a single-phase ground fault, 23 ms for a two-phase-to-phase fault, 22.75 ms for a two-phase ground fault, and 24.75 ms for a three-phase short-circuit fault. These times met the relay protection operation time requirements.
Although the protection scheme of the original DTW presented the phenomenon of refusing to operate on a single-phase ground fault, the two-phase-to-phase fault and the two-phase ground fault exhibited false activations, and the action time of the three-phase short-circuit fault was 2 ms slower compared to the proposed scheme, and so the action time of the proposed new scheme was faster.
Under out-of-area fault conditions, although the action values of both schemes were less than 0.4, the action values of the proposed scheme ranged from 0.015 to 0.08, whereas the action values of the original DTW ranged from 0.125 to 0.35. Thus, the original DTW scheme was less noise-tolerant and less fault-tolerant than the proposed new scheme.
In summary, the proposed scheme was able to adapt to the strong noise environment, it had a strong anti-interference ability, and it retained certain anti-delay characteristics. Further, it could quickly and reliably identify the faults inside and outside the area, and the transmission of data in the 5G longitudinal channel was also strongly guaranteed.
3.4. Analysis of the Impact of High Wind and a High Solar Penetration Rate
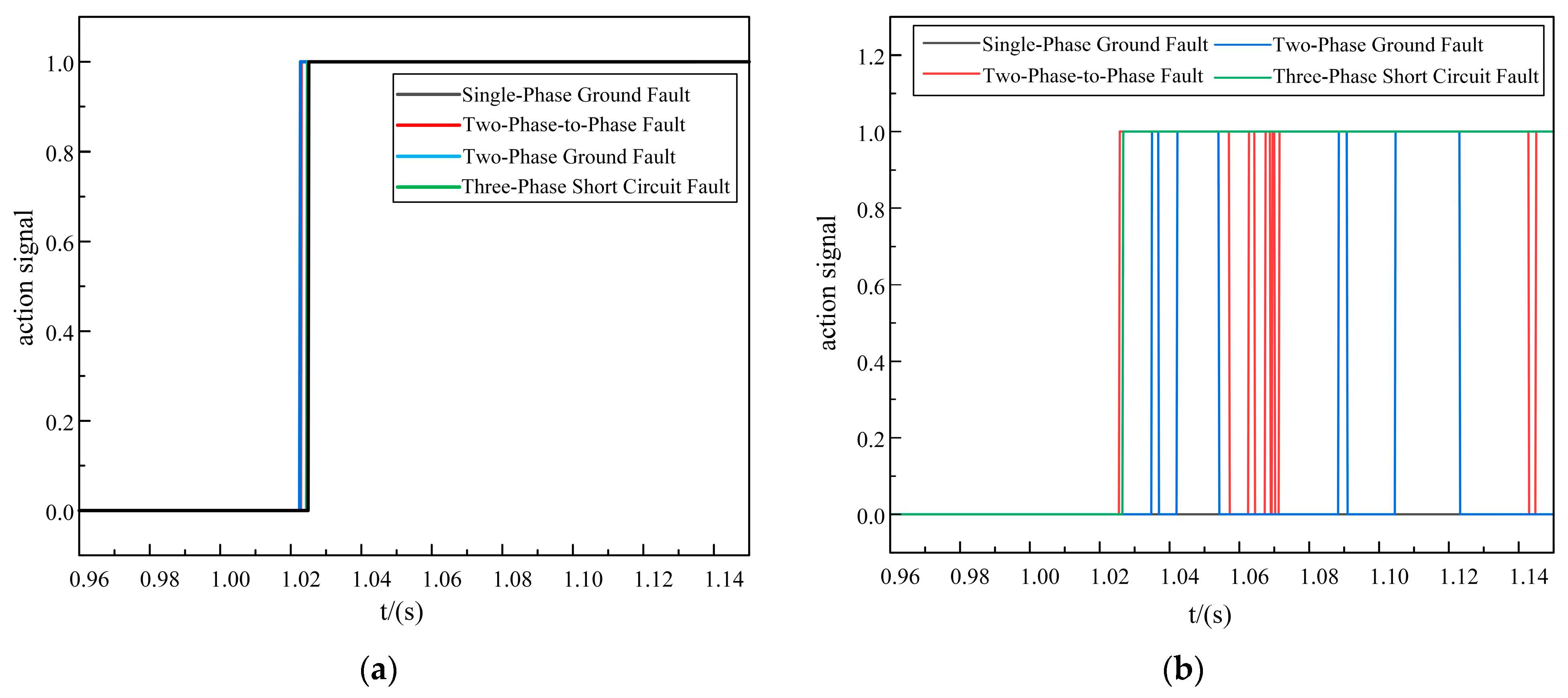
As discussed in Section 3.1 and Section 3.2, when the penetration rate of the distributed generators was 25%, the proposed protection scheme could correctly recognize the faults inside and outside the zone and act reliably. However, under the access of the distributed generators with high penetration rates, it was difficult to maintain the original structural characteristics of the distribution network, and the protection could be ineffective due to the complexity of and variability in the currents during the faults. Therefore, we simulated scenarios where the distributed generators had a high penetration rate (50%) and verified whether the proposed scheme could act stably and reliably. The specific simulation results are shown in Table 2 and Figure 10.

Table 2.
Action times for the faults in the zone at different permeabilities.
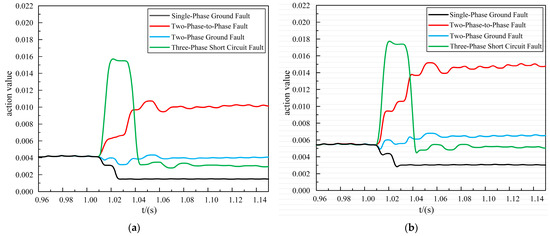
Figure 10.
Out-of-area fault action value at 50% permeability. (a) Improved DTW action value. (b) Original DTW action value.
As shown in Table 2, when in-zone faults occurred, compared with the scenario where the penetration rate of the distributed generators was 25%, the action time improvement was small, and this was mainly due to the fact that in the high-penetration scenario, the fault current was complex, the algorithm-matching was difficult, and the optimization time was increased, all of which resulted in a small improvement time for the protection. However, the action time of the proposed protection scheme still met the requirements of the relay protection action time, and so the proposed protection scheme was also applicable to the distribution network with distributed generators under a high penetration rate.
In Figure 10, it can be seen that in the scenario with a 50% penetration rate for the distributed generators, when an out-of-area fault occurred, the action values of the improved DTW were smaller than those of the original DTW. The action values of the proposed scheme ranged from 0.001 to 0.016, whereas the action values of the original DTW ranged from 0.002 to 0.018, and thus, the proposed scheme was more reliable under out-of-area fault conditions.
4. Conclusions
The latency of 5G has resulted in decreases in the rapidity and reliability of longitudinal current differential protections based on the DTW principle. To address this issue, we proposed a new 5G pilot protection scheme for distribution networks with distributed generators, and it was based on an improved DTW approach. We conducted simulation and validation experiments using the proposed scheme, and we arrived at the following conclusions:
- By cosine-transforming the fault current sequences, the anti-delay and anti-interference abilities of DTW were enhanced, and at the same time, after normalization, the reliability of the algorithm was improved. The scheme based on the principle of an improved DTW was very suitable for researching pilot protection for 5G communications.
- The simulation showed that, compared with the traditional DTW pilot protection, the 5G pilot protection scheme based on the principle of an improved DTW could quickly and accurately distinguish in-zone and out-of-area faults, and the action times for a single-phase ground fault, a two-phase ground fault, a two-phase-to-phase fault, and a three-phase short-circuit fault were reduced by 2.9 ms, 4.54 ms, 5.81 ms, and 5.89 ms, respectively. Meanwhile, the scheme demonstrated strong noise resistance, and it could continue to act stably and reliably in scenarios with a high wind and photovoltaic penetration rate, with a good protection performance. Therefore, the proposed protection scheme has strong applicability in distribution networks containing distributed generators.
- The new scheme in this paper was based on a 5G URLLC scenario, and it provides a new idea for 5G pilot protection that can take advantage of 5G communication in pilot protection and is conducive to the application and promotion of 5G communication in the protection of distribution networks containing distributed generators. Currently, other scholars have conducted relevant research on information security, data loss, and the self-synchronization of fault information in 5G pilot protection. Therefore, in future research, it will be essential to integrate and align with the research directions of other scholars to propose a more reliable and effective pilot protection scheme that maximizes the advantages of 5G.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.W. and Z.Y.; methodology, D.W., Z.Y. and K.Z.; validation, D.W. and Z.Y.; data curation, D.W. and K.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, D.W.; writing—review and editing, D.W., Z.Y. and K.Z.; supervision, Z.Y. and W.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The Major Science and Technology Project of the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region—Fast Protection Technology for Energy Network Based on 5G provided funding for this study under project number 2022A01001-4. This project was also funded by the Department of Science and Technology of the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Acknowledgments
The authors express their gratitude for the support provided by the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region’s major science and technology special program.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Zang, L.D.; Zou, G.B.; Zhou, C.H.; Zheng, M.R.; Du, T. A D-Axis Based Current Differential Protection Scheme for an Active Distribution Network. Prot. Control Mod. Power Syst. 2022, 7, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.X.; Wan, J.L.; Wang, P.F.; Weng, H.L.; Li, Z.H. A Novel Fault Section Locating Method Based on Distance Matching Degree in Distribution Network. Prot. Control Mod. Power Syst. 2021, 6, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Ouyang, J.X.; Xiong, X.F.; Wang, Y.T.; Luo, Y.J. Fault Protection Method of Single-Phase Break for Distribution Network Considering the Influence of Neutral Grounding Modes. Prot. Control Mod. Power Syst. 2020, 5, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, T.; Roy, R.; Mandal, K.K. Impact of the Penetration of Distributed Generation on Optimal Reactive Power Dispatch. Prot. Control Mod. Power Syst. 2020, 5, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Pradhan, A.K. A Local Measurement Based Protection Technique for Distribution System with Photovoltaic Plants. IET Renew. Power Gener 2020, 14, 996–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheta, A.N.; Abdulsalam, G.M.; Sedhom, B.E.; Eladl, A.A. Comparative framework for AC-microgrid protection schemes: Challenges, solutions, real applications, and future trends. Prot. Control Mod. Power Syst. 2023, 8, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quispe, J.C.; Orduna, E. Transmission line protection challenges influenced by inverter-based resources: A review. Prot. Control Mod. Power Syst. 2022, 7, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.M.; Guo, J.H.; Shi, M.M.; Zhao, J.P.; Wu, Y.F.; Wu, Y. A Novel Longitudinal Differential Protection Method for DC Microgrid. In Proceedings of the 2022 China International Conference on Electricity Distribution (CICED), Changsha, China, 7–8 September 2022; pp. 845–851. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.R.; Dai, J.; Chen, K.; Zhu, X.R.; Xie, J.H.; Fang, T.Y. Differential Protection of Active Distribution Network Based on 5G Communication Technology. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 5th International Electrical and Energy Conference (CIEEC), Nanjing, China, 27–29 May 2022; pp. 4639–4644. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.T.; Guo, X.R.; Shi, Y.Y.; Li, Y.P.; Li, F.; Duan, X.W. Research on Distribution Network Differentiated Protection Technology Based on Power 5G Virtual Private Network. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 10th Joint International Information Technology and Artificial Intelligence Conference (ITAIC), Chongqing, China, 17–19 June 2022; pp. 2607–2610. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Chen, L.; Chen, J.J. Enabling Technologies for Low-Latency Service Migration in 5G Transport Network [Invited]. J. Opt. Commun. Netw. 2021, 13, A200–A210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.R.; Hu, J.; Sun, B.; Gui, H.; Tong, J.; Jiang, X.C.; Yuan, H.T.; Dong, J. Research on Self Synchronization Method of Line Differential Protection Based on 5G Communication. In Proceedings of the 2022 China International Conference on Electricity Distribution (CICED), Changsha, China, 7–8 September 2022; pp. 1400–1404. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, C.; Zhang, H.Z.; Kong, H.; Chen, M.; Wei, Z. Longitudinal Protection Method Based on Voltage Wave Comparison in AC/DC Hybrid System. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2022, 58, 1564–1572. [Google Scholar]
- Manassero, G.; Tiferes, R.R. Dynamic Time Warping Based Pilot Protection Algorithm for AC and HVDC Transmission Lines. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 56846–56857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.N.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, D.; Fan, X.; Luo, B.; Wen, M.H. A Novel Pilot Protection Scheme for AC Power Grid with Energy Router Interconnection. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/IAS Industrial and Commercial Power System Asia (I&CPS Asia), Shanghai, China, 8–11 July 2022; pp. 67–75. [Google Scholar]
- Pu, H.F.; Wu, T.H.; Yao, G.; Hong, F.; Zheng, X.J.; Wang, W.W.; Li, X.D. A New Differential Protection Scheme of Distribution Network Line Based on Improved DTW Algorithm and 5G Communication. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Top-Level Forum on Engineering Science and Technology Development Strategy, Singapore, 22 March 2022; pp. 183–200. [Google Scholar]
- Long, W.; Pan, S.; Wu, H. Distribution Network Differential Protection Method Based on Dynamic Time Warping Algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Top-Level Forum on Engineering Science and Technology Development Strategy, Singapore, 22 March 2022; pp. 29–42. [Google Scholar]
- Miao, X.R.; Zhao, D.; Lin, B.Q.; Jiang, H.; Chen, J. A Differential Protection Scheme Based on Improved DTW Algorithm for Distribution Network with Highly-Penetrated Distributed Generation. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 40399–40411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, Q.S.; Zhang, Z.; Han, J.X. Pilot Protection Scheme for DC Distribution Network Based on Improved Dynamic Time Warping Distance Algorithm. Electr. Power Autom. Equip. 2022, 12, 157–164. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.H.; Ruan, X.B.; Liu, S.W.; Chi, K.T. Full Feedforward of Grid Voltage for Grid-Connected Inverter with LCL Filter To Suppress Current Distortion Due to Grid Voltage Harmonics. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2010, 25, 3119–3127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmud, R.; Narang, D.; Hoke, A. Reduced-Order Parameterized Short-Circuit Current Model of Inverter- Interfaced Distributed Generators. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2021, 36, 3671–3680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Liu, D.; Liu, Z.; Chen, Z. Fault Modeling and Analysis of Grid-Connected Inverters with Decoupled Sequence Control. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2021, 69, 5782–5792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.Q. Transient Analysis of Power System, 3rd ed.; China Electric Power Press: Beijing, China, 2007; pp. 49–50. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, Y.; Liu, L.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Z. A Survey: Several Technologies of Non-Orthogonal Transmission for 5G. China Commun. 2015, 12, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demestichas, P.; Georgakopoulos, A.; Karvounas, D.; Tsagkaris, K.; Stavroulaki, V.; Lu, J.; Yao, J. 5G on the Horizon: Key Challenges for the Radio-Access Network. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2013, 8, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.X.; Hajisami, A.; Pandey, P.; Pompili, D. Collaborative Mobile Edge Computing in 5G Network: New Paradigms, Scenarios, and Challenges. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2017, 5, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casellas, R.; Vilalta, R.; Martínez, R.; Muñoz, R. Highly Available SDN Control of Flexi-grid Network with Network Function Virtualization-Enabled Replication. J. Opt. Commun. Netw. 2017, 9, A207–A215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Nguyen, L.; Hu, Q. Network Function Virtualization in Elastic Optical Network. J. Light. Technol. 2023, 41, 5183–5192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masmoudi, A.; Bellili, F.; Affes, S.; Ghrayeb, A. Maximum Likelihood Time Delay Estimation from Single- and Multi-Carrier DSSS Multipath MIMO Transmissions for Future 5G Network. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2017, 16, 4851–4865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvez, I.; Rahmati, A.; Guvenc, I.; Sarwat, A.I.; Dai, H.Y. A Survey on Low Latency Towards 5G: RAN, Core Network and Caching Solutions. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor 2018, 20, 3098–3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, M.; Lin, Y.K.; Mao, Z.M.; Sen, S.; Spatscheck, O. A Customizable, Low-Latency, and Scalable 5G Core Network Architecture. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2018, 36, 438–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rischke, J.; Sossalla, P.; Itting, S.; Fitzek, F.H.P.; Reisslein, M. 5G Campus Network: A First Measurement Study. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 121786–121803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.C.; Xiao, Y.Q.; Zhang, S.S.; Wang, J.Z. Adaptive Finite Blocklength for Ultra-Low Latency in Wireless Communications. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2022, 21, 4450–4463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.L.; Liang, Y.; Wang, S.C. Review on Dynamic Time Warping in Time Series Data Mining. Control Decis. 2018, 33, 1345–1353. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.H.; Liu, J.X.; Yang, Z.L.; Liu, R.W.; Wu, K.F.; Wan, Y. Adaptively Constrained Dynamic Time Warping for Time Series Classification and Clustering. Inf. Sci. 2020, 534, 97–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).