Calorific Value Prediction Model Using Structure Composition of Heat-Treated Lignocellulosic Biomass
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
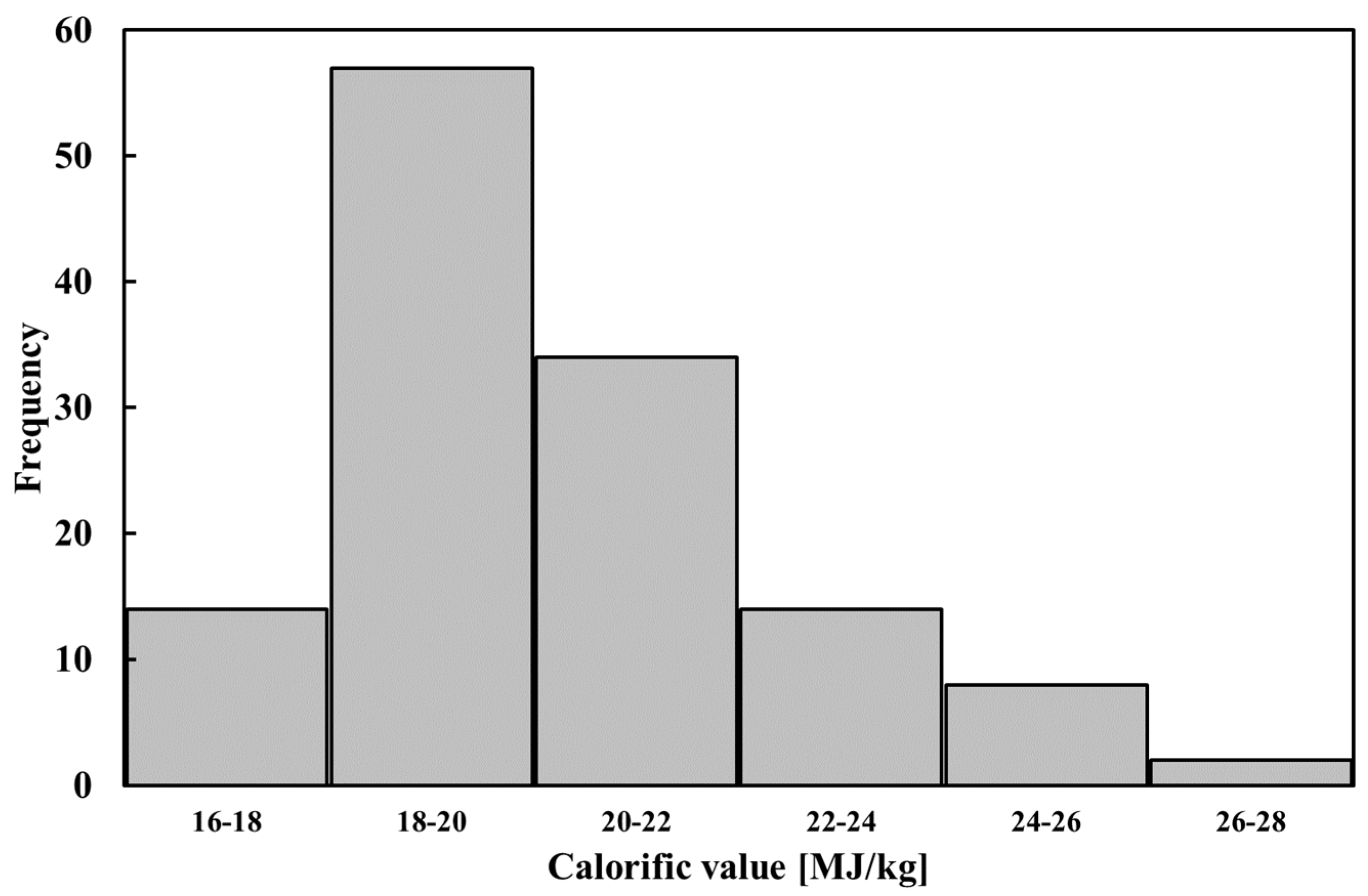
2.1. Collection of Data
2.2. Pearson Correlation Coefficient
2.2.1. Linear Regression
2.2.2. Polynomial Regression
2.3. Model Evaluation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Result of Pearson Correlation Coefficient
3.2. Prediction Model Using Total Biomass
3.3. Prediction Model Using Woody Biomass
3.4. Prediction Model for Herbaceous Biomass
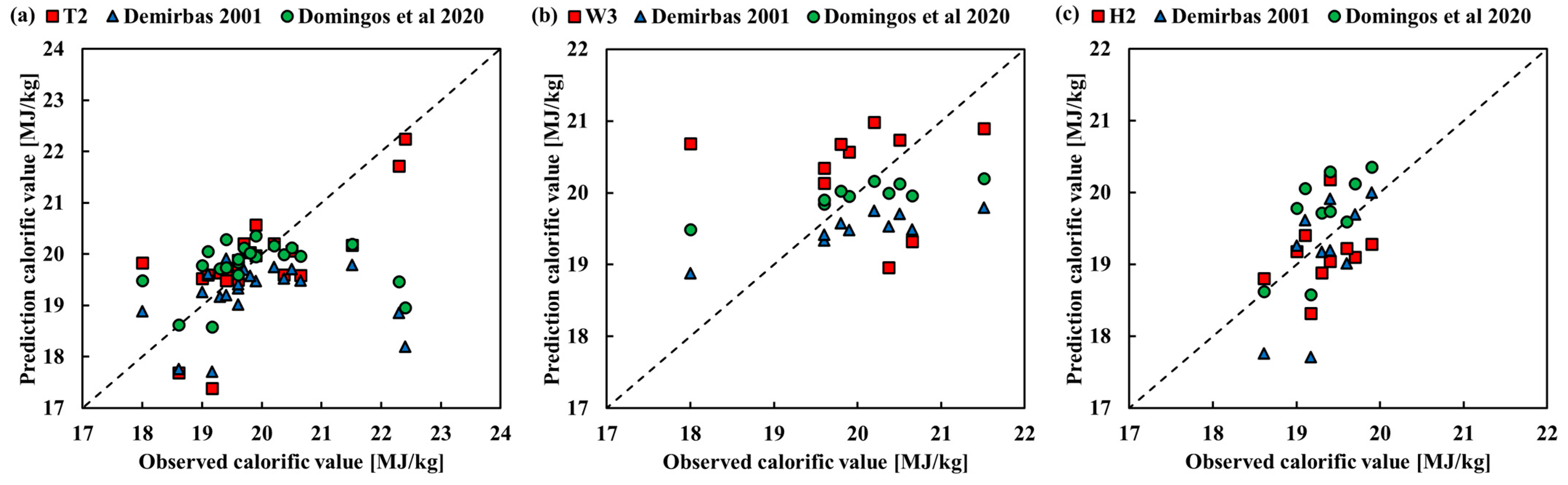
3.5. Validation of Calorific Value Prediction Models
3.6. Comparison of the Model with Previous Models
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Park, S.; Kim, S.J.; Oh, K.C.; Jeon, Y.K.; Kim, Y.; Cho, A.Y.; Lee, D.; Jang, C.S.; Kim, D.H. Biochar from Agro-Byproducts for Use as a Soil Amendment and Solid Biofuel. J. Biosyst. Eng. 2023, 48, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Cheng, P.; Yu, Y.; Chen, S.-H.; Wang, C.-X.; He, L.; Nie, H.-T.; Wang, J.-C.; Zhang, J.-C.; Fan, B.-G.; et al. Regeneration Mechanism of a Novel High-Performance Biochar Mercury Adsorbent Directionally Modified by Multimetal Multilayer Loading. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 326, 116790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Kim, S.J.; Cho, A.Y.; Kim, Y.; Lee, D.H.; Oh, K.C.; Jang, C.S.; Kim, D.H. Effect of Agro-byproduct Biochar Fertilization on Cherry Tomato Growth and Carbon Sequestration. J. Agric. Life Environ. Sci. 2022, 34, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motta, I.L.; Miranda, N.T.; Maciel Filho, R.; Wolf Maciel, M.R. Biomass Gasification in Fluidized Beds: A Review of Biomass Moisture Content and Operating Pressure Effects. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 94, 998–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, K.H.; Blackwell, J. The Structure of Native Cellulose. Biopolymers 1974, 13, 1975–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, J.Y.; Chin, B.L.F.; Tan, J.K.; Loh, Y.S. Comparative Studies on the Pyrolysis of Cellulose, Hemicellulose, and Lignin Based on Combined Kinetics. J. Energy Inst. 2019, 92, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ralph, J.; Lapierre, C.; Boerjan, W. Lignin Engineering-Special Issue for Lignin Structure and Its Engineering. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2019, 56, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanholme, R.; Morreel, K.; Ralph, J.; Boerjan, W. Lignin Engineering. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2008, 11, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, E.T. Heat of Combustion of Various Southern Pine Materials. Wood Sci. 1973, 5, 194–197. [Google Scholar]
- Tillman, D.A. Wood as an Energy Resource; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- White, R.H. Effect of lignin content and extractives on the higher heating value of wood. Wood Fiber. Sci. 1987, 19, 446–452. [Google Scholar]
- Callejón-Ferre, A.J.; Carreño-Sánchez, J.; Suárez-Medina, F.J.; Pérez-Alonso, J.; Velázquez-Martí, B. Prediction Models for Higher Heating Value Based on the Structural Analysis of the Biomass of Plant Remains from the Greenhouses of Almería (Spain). Fuel 2014, 116, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirbas, A. Relationships between Lignin Contents and Heating Values of Biomass. Energy Convers. Manag. 2001, 42, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirbaş, A. Biodiesel Fuels from Vegetable Oils via Catalytic and Non-Catalytic Supercritical Alcohol Transesterifications and Other Methods: A Survey. Energy Convers. Manag. 2003, 44, 2093–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acar, S.; Ayanoglu, A. Determination of Higher Heating Values (HHVs) of Biomass Fuels. Energy Educ. Sci. Technol. Part A Energy Sci. Res. 2012, 28, 749–758. [Google Scholar]
- Álvarez, A.; Pizarro, C.; García, R.; Bueno, J.L. Spanish Biofuels Heating Value Estimation Based on Structural Analysis. Ind. Crops Prod. 2015, 77, 983–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Aquino, F.; Ruiz-Ángel, S.; Feria-Reyes, R.; Santiago-García, W.; Suárez-Mota, M.E.; Rutiaga-Quiñones, J.G. Wood Chemical Composition of Five Tree Species from Oaxaca, Mexico. Bioresources 2019, 14, 9826–9839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingos, I.; Ayata, U.; Ferreira, J.; Cruz-Lopes, L.; Sen, A.; Sahin, S.; Esteves, B. Calorific Power Improvement of Wood by Heat Treatment and Its Relation to Chemical Composition. Energies 2020, 13, 5322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, C.; Li, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, X.; Hu, J.; Cao, W. Prediction of Higher Heating Values of Biochar from Proximate and Ultimate Analysis. Fuel 2020, 265, 116925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, K.C.; Kim, J.; Park, S.Y.; Kim, S.J.; Cho, L.H.; Lee, C.G.; Roh, J.; Kim, D.H. Development and Validation of Torrefaction Optimization Model Applied Element Content Prediction of Biomass. Energy 2021, 214, 119027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben, H.; Ragauskas, A.J. Torrefaction of Loblolly Pine. Green Chem. 2012, 14, 72–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahyanti, M.N.; Doddapaneni, T.R.K.C.; Madissoo, M.; Pärn, L.; Virro, I.; Kikas, T. Torrefaction of Agricultural and Wood Waste: Comparative Analysis of Selected Fuel Characteristics. Energies 2021, 14, 2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.Y.; Chen, W.H.; Colin, B.; Pétrissans, A.; Lopes Quirino, R.; Pétrissans, M. Thermodegradation Characterization of Hardwoods and Softwoods in Torrefaction and Transition Zone between Torrefaction and Pyrolysis. Fuel 2022, 310, 122281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reza, M.T.; Uddin, M.H.; Lynam, J.G.; Coronella, C.J. Engineered Pellets from Dry Torrefied and HTC Biochar Blends. Biomass Bioenergy 2014, 63, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arous, S.; Koubaa, A.; Bouafif, H.; Bouslimi, B.; Braghiroli, F.L.; Bradai, C. Effect of Pyrolysis Temperature and Wood Species on the Properties of Biochar Pellets. Energies 2021, 14, 6529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, K.L.; H’ng, P.S.; Go, W.Z.; Wong, W.Z.; Lim, T.W.; Maminski, M.; Paridah, M.T.; Luqman, A.C. Optimization of Torrefaction Conditions for High Energy Density Solid Biofuel from Oil Palm Biomass and Fast Growing Species Available in Malaysia. Ind. Crops Prod. 2013, 49, 768–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanovski, M.; Goricanec, D.; Krope, J.; Urbancl, D. Torrefaction Pretreatment of Lignocellulosic Biomass for Sustainable Solid Biofuel Production. Energy 2022, 240, 122483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.H.; Hsu, H.C.; Lu, K.M.; Lee, W.J.; Lin, T.C. Thermal Pretreatment of Wood (Lauan) Block by Torrefaction and Its Influence on the Properties of the Biomass. Energy 2011, 36, 3012–3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdez, E.; Tabil, L.G.; Mupondwa, E.; Cree, D.; Moazed, H. Microwave Torrefaction of Oat Hull: Effect of Temperature and Residence Time. Energies 2021, 14, 4298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granados, D.A.; Ruiz, R.A.; Vega, L.Y.; Chejne, F. Study of Reactivity Reduction in Sugarcane Bagasse as Consequence of a Torrefaction Process. Energy 2017, 139, 818–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, Y.; Wang, J.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Wang, S. Oxygen Migration Characteristics during Bamboo Torrefaction Process Based on the Properties of Torrefied Solid, Gaseous, and Liquid Products. Biomass Bioenergy 2019, 128, 105300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanwal, S.; Chaudhry, N.; Munir, S.; Sana, H. Effect of Torrefaction Conditions on the Physicochemical Characterization of Agricultural Waste (Sugarcane Bagasse). Waste Manag. 2019, 88, 280–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Linnebur, K.; Wang, D. Torrefaction of Conservation Reserve Program Biomass: A Techno-Economic Evaluation. Ind. Crops Prod. 2014, 61, 382–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, Y.; Di Marcello, M.; De Jong, W. Torrefaction: Mechanistic Study of Constituent Transformations in Herbaceous Biomass. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2015, 115, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Qu, B.; Wang, W.; Wang, W.; Ji, G.; Li, A. Rice Husk and Rice Straw Torrefaction: Properties and Pyrolysis Kinetics of Raw and Torrefied Biomass. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 24, 101872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chicco, D.; Warrens, M.J.; Jurman, G. The Coefficient of Determination R-Squared Is More Informative than SMAPE, MAE, MAPE, MSE and RMSE in Regression Analysis Evaluation. PeerJ Comput. Sci. 2021, 7, e623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumder, A.K.; Jain, R.; Banerjee, P.; Barnwal, J.P. Development of a New Proximate Analysis Based Correlation to Predict Calorific Value of Coal. Fuel 2008, 87, 3077–3081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmaz, F.; Yücel, Ö.; Mutlu, A.Y. Makine Öğrenmesi Ile Kısa ve Elemental Analiz Kullanarak Katı Yakıtların Üst Isı Değerinin Tahmin Edilmesi. Int. J. Adv. Eng. Pure Sci. 2020, 32, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Q. Model Detection for Functional Polynomial Regression. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 2014, 70, 183–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gendy, T.S.; El-Shiekh, T.M.; Zakhary, A.S. A Polynomial Regression Model for Stabilized Turbulent Confined Jet Diffusion Flames Using Bluff Body Burners. Egypt. J. Pet. 2015, 24, 445–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phanphanich, M.; Mani, S. Impact of Torrefaction on the Grindability and Fuel Characteristics of Forest Biomass. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 1246–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, J.; Imran, M.; Ali, A.M.; Nawaz, Z.; Muhammad, A.; Butt, R.K.; Jillani, M.S.; Naeem, H.A. Torrefaction and Thermochemical Properties of Agriculture Residues. Energies 2021, 14, 4218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.F.; Shen, Y.; Sun, J.K.; Bian, J.; Chen, C.Z.; Sun, R.C. Wet Torrefaction of Bamboo in Hydrochloric Acid Solution by Microwave Heating. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 2022–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Fan, X.; Zhang, H.; Ai, F.; Jiao, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Z. Pretreatment of Corn Stover by Torrefaction for Improving Reducing Sugar and Biohydrogen Production. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 351, 126905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.F.; Chen, C.Z.; Li, X.; Shen, Y.; Bian, J.; Sun, R.C. Torrefaction of Bamboo under Nitrogen Atmosphere: Influence of Temperature and Time on the Structure and Properties of the Solid Product. Fuel 2015, 161, 193–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strandberg, M.; Olofsson, I.; Pommer, L.; Wiklund-Lindström, S.; Åberg, K.; Nordin, A. Effects of Temperature and Residence Time on Continuous Torrefaction of Spruce Wood. Fuel Process. Technol. 2015, 134, 387–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mafu, L.D.; Neomagus, H.W.J.P.; Everson, R.C.; Carrier, M.; Strydom, C.A.; Bunt, J.R. Structural and Chemical Modifications of Typical South African Biomasses during Torrefaction. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 202, 192–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grams, J.; Kwapińska, M.; Jędrzejczyk, M.; Rzeźnicka, I.; Leahy, J.J.; Ruppert, A.M. Surface Characterization of Miscanthus × Giganteus and Willow Subjected to Torrefaction. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2019, 138, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Wu, S.; Wang, H.; Ma, P.; Shimanouchi, T.; Kimura, Y.; Zhou, J. Effect of Wet and Dry Torrefaction Process on Fuel Properties of Solid Fuels Derived from Bamboo and Japanese Cedar. Bioresources 2017, 12, 8629–8640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smit, A.; Huijgen, W. Effective Fractionation of Lignocellulose in Herbaceous Biomass and Hardwood Using a Mild Acetone Organosolv Process. Green Chem. 2017, 19, 5505–5514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thammasouk, K.; Tandjo, D.; Penner, M.H. Influence of Extractives on the Analysis of Herbaceous Biomass†. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1997, 45, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enes, T.; Aranha, J.; Fonseca, T.; Lopes, D.; Alves, A.; Lousada, J. Thermal Properties of Residual Agroforestry Biomass of Northern Portugal. Energies 2019, 12, 1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Model | Biomass | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Pine | [9] | |
| Extractive-free wood | [10] | |
| Unextracted wood, four softwoods and four hardwoods | [11] | |
| Extractive-free wood | ||
| Extractive-free softwood | ||
| Extractive-free hardwood | ||
| Extractive-free wood and non-wood | [13] | |
| Extractive-free lignocellulosic materials | ||
| Extractive-free non-wood | ||
| Extractive-free sunflower shells, almond shells, hazelnut shells, wood bark, olive husks, hazelnut kernel husks, and walnut shells | [14] | |
| Corn stover, corn cobs, sunflower shells, beech wood, Ailanthus wood, hazelnut shells, wood bark, olive husks, and walnut shells | [15] | |
| Greenhouse crops | [12] | |
| Twenty biomass samples of agro-forestry wastes and industrial wastes | [16] | |
| Tree species from Oaxaca, Mexico | [17] | |
| Mixture of eight untreated and heat-treated woods | [18] |
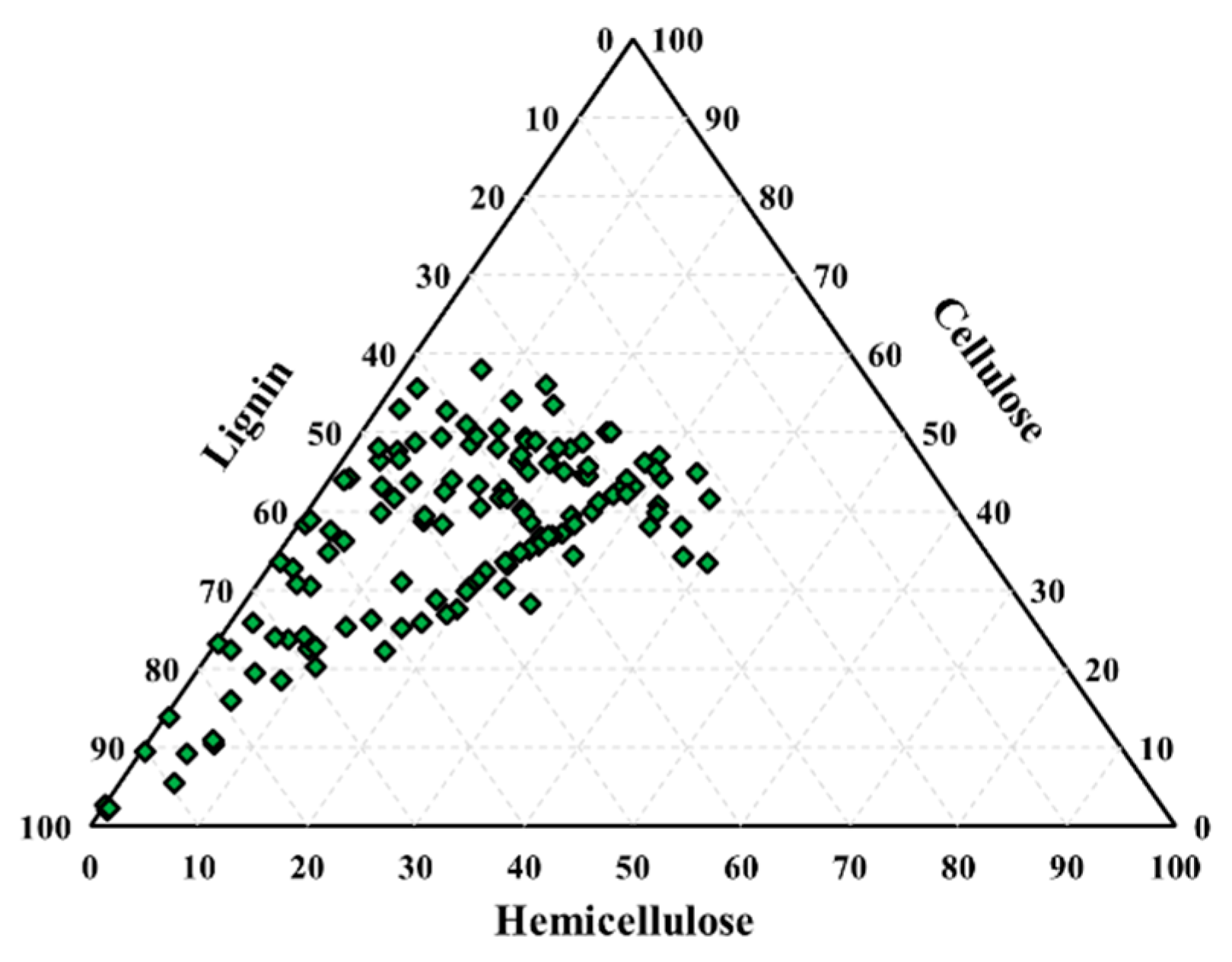
| Biomass | Type | Cell [%] | Hemi [%] | Lig [%] | HHV [MJ/kg] | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mixed waste wood | Woody | 38.30 | 25.50 | 22.00 | 17.50 | [27] |
| Torrefied mixed waste wood (200 °C) | Woody | 41.10 | 26.30 | 26.50 | 19.20 | |
| Torrefied mixed waste wood (250 °C) | Woody | 43.70 | 7.70 | 31.40 | 19.90 | |
| Torrefied mixed waste wood (300 °C) | Woody | 36.20 | 5.30 | 43.70 | 20.80 | |
| Oak waste wood | Woody | 38.30 | 25.50 | 22.00 | 18.60 | |
| Torrefied Oak waste wood (200 °C) | Woody | 41.10 | 26.30 | 26.50 | 19.10 | |
| Torrefied Oak waste wood (250 °C) | Woody | 43.70 | 7.70 | 31.40 | 21.20 | |
| Torrefied Oak waste wood (300 °C) | Woody | 36.20 | 5.30 | 43.70 | 22.50 | |
| Miscanthus | Herbaceous | 41.40 | 19.70 | 22.60 | 16.41 | |
| Torrefied miscanthus (200 °C) | Herbaceous | 41.90 | 21.20 | 23.10 | 19.15 | |
| Torrefied miscanthus (250 °C) | Herbaceous | 44.10 | 8.40 | 41.60 | 21.10 | |
| Torrefied miscanthus (300 °C) | Herbaceous | 35.00 | 3.20 | 52.30 | 21.28 | |
| Hops | Herbaceous | 42.2 | 0 | 26.20 | 16.59 | |
| Torrefied hops (200 °C) | Herbaceous | 42.9 | 0 | 26.80 | 18.80 | |
| Torrefied hops (250 °C) | Herbaceous | 47.00 | 0 | 35.10 | 18.90 | |
| Torrefied hops (300 °C) | Herbaceous | 39.90 | 0 | 38.70 | 20.70 | |
| Torrefied pine chip (225 °C) | Woody | 41.23 | 12.87 | 38.42 | 19.48 | [41] |
| Torrefied pine chip (250 °C) | Woody | 41.90 | 6.93 | 45.70 | 20.08 | |
| Torrefied pine chip (275 °C) | Woody | 39.54 | 0.99 | 53.30 | 21.82 | |
| Torrefied pine chip (300 °C) | Woody | 12.84 | 0.56 | 79.99 | 25.38 | |
| Logging residue chip | Woody | 37.49 | 13.26 | 26.15 | 18.79 | |
| Torrefied logging residue chip (225 °C) | Woody | 41.04 | 14.77 | 33.20 | 19.79 | |
| Torrefied logging residue chip (250 °C) | Woody | 38.57 | 5.87 | 42.49 | 21.21 | |
| Torrefied logging residue chip (275 °C) | Woody | 34.08 | 5.23 | 52.80 | 22.03 | |
| Torrefied logging residue chip (300 °C) | Woody | 6.10 | 1.04 | 85.06 | 26.41 | |
| Torrefied Cotton Balls | Herbaceous | 29.44 | 24.22 | 34.20 | 18.73 | [42] |
| Torrefied Sunflower | Herbaceous | 31.00 | 29.35 | 24.73 | 19.65 | |
| Wet torrefied bamboo (180 °C 30 min 0 M HCl) | Herbaceous | 42.61 | 25 | 23.18 | 17.79 | [43] |
| Wet torrefied bamboo (180 °C 15 min 0.2 M HCl) | Herbaceous | 34.97 | 0 | 33.94 | 24.19 | |
| Wet torrefied bamboo (180 °C 30 min 0.2 M HCl) | Herbaceous | 13.96 | 0 | 36.98 | 24.86 | |
| Corn straw | Herbaceous | 39.12 | 30.95 | 10.73 | 18.61 | [44] |
| Torrefied corn straw (160 °C) | Herbaceous | 38.03 | 28.86 | 10.12 | 19.17 | |
| Torrefied corn straw (180 °C) | Herbaceous | 37.11 | 28.12 | 9.87 | 19.79 | |
| Torrefied oat hull (285 °C) | Herbaceous | 33.52 | 0.72 | 45.65 | 22.45 | [29] |
| Torrefied bamboo (280 °C 10 min) | Herbaceous | 49.76 | 8.60 | 39.79 | 19.88 | [45] |
| Torrefied bamboo (280 °C 30 min) | Herbaceous | 49.40 | 5.56 | 43.12 | 20.11 | |
| Torrefied bamboo (280 °C 60 min) | Herbaceous | 47.40 | 2.03 | 50.40 | 20.42 | |
| Sweet sorghum bagasse | Herbaceous | 29.80 | 24.40 | 5.24 | 17.30 | [46] |
| Torrefaction sweet sorghum bagasse | Herbaceous | 19.90 | 4.80 | 16 | 23 |
| Biomass | Type | Cell [%] | Hemi [%] | Lig [%] | HHV [MJ/kg] | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Softwood | Woody | 47.40 | 13.80 | 23.50 | 18.00 | [47] |
| Torrefied softwood | Woody | 36.60 | 2.65 | 23.20 | 22.30 | |
| Torrefied hardwood | Woody | 46.70 | 1.20 | 15.70 | 22.40 | |
| Norway spruce | Woody | 41.70 | 26.00 | 30.90 | 20.37 | [46] |
| Torrefied Norway spruce (260 °C 8 min) | Woody | 42.30 | 23.20 | 30.40 | 20.65 | |
| Torrefied Norway spruce (260 °C 25 min) | Woody | 40.10 | 13.50 | 33.90 | 21.51 | |
| Corn straw | Herbaceous | 39.12 | 30.95 | 10.73 | 18.61 | [44] |
| Torrefied corn straw (160 °C) | Herbaceous | 38.03 | 28.86 | 10.12 | 19.17 | |
| Torrefied miscanthus (230 °C 15 min) | Herbaceous | 44.50 | 18.50 | 26.80 | 19.30 | [48] |
| Torrefied miscanthus (250 °C 15 min) | Herbaceous | 44.90 | 12.20 | 32.80 | 19.70 | |
| Torrefied miscanthus (250 °C 30 min) | Herbaceous | 43.30 | 9.90 | 36.20 | 19.90 | |
| Torrefied willow (230 °C 15 min) | Woody | 39.70 | 18.10 | 28.70 | 19.60 | |
| Torrefied willow (250 °C 15 min) | Woody | 40.50 | 15.30 | 30.30 | 19.90 | |
| Torrefied willow (270 °C 15 min) | Woody | 41.10 | 12.90 | 33.40 | 20.20 | |
| Torrefied willow (230 °C 30 min) | Woody | 39.30 | 16.80 | 29.60 | 19.60 | |
| Torrefied willow (250 °C 30 min) | Woody | 40.30 | 14.70 | 31.40 | 19.80 | |
| Torrefied willow (270 °C 30 min) | Woody | 41.60 | 14.20 | 32.90 | 20.50 | |
| Bamboo | Herbaceous | 48.03 | 24.13 | 27.83 | 19.00 | [49] |
| Wet torrefied bamboo (200 °C) | Herbaceous | 50.22 | 22.68 | 27.10 | 19.40 | |
| Wet torrefied bamboo (220 °C) | Herbaceous | 49.88 | 25.09 | 25.03 | 19.60 | |
| Dry torrefied bamboo (180 °C) | Herbaceous | 43.13 | 25.04 | 31.84 | 19.10 | |
| Dry torrefied bamboo (200 °C) | Herbaceous | 36.78 | 27.96 | 35.25 | 19.40 |
| No. | Equation | R2P [-] 1 | RMSEP [-] 2 | MAEP [%] 3 | AAEP [%] 4 | ABEP [%] 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | 0.5423 | 1.3858 | 1.1006 | 5.3455 | 0.4302 | |
| T2 | 0.5719 | 1.5215 | 1.1764 | 5. 7280 | 2.1895 | |
| T3 | 0.5814 | 1.5455 | 1.1924 | 5.8641 | 2.9964 |
| No. | Equation | R2P [-] | RMSEP [-] | MAEP [%] | AAEP [%] | ABEP [%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| W1 | 0.7811 | 1.2810 | 1.0860 | 5.3534 | 2.8879 | |
| W2 | 0.8222 | 1.1888 | 0.8724 | 4.0008 | −1.7930 | |
| W3 | 0.8392 | 0.9626 | 0.7238 | 3.5106 | 0.2286 |
| No. | Equation | R2P [-] | RMSEP [-] | MAEP [%] | AAEP [%] | ABEP [%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H1 | 0.8256 | 1.2958 | 1.1723 | 5.9563 | −5.8252 | |
| H2 | 0.8561 | 0.6294 | 0.5243 | 2.7030 | 1.8674 | |
| H3 | 0.8739 | 0.4836 | 0.3698 | 1.8929 | −0.2333 |
| R2CV [-] | RMSECV [-] | MAECV [%] | AAECV [%] | ABECV [%] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | 0.4920 | 1.9178 | 1.3871 | 6.6409 | 0.3278 |
| T2 | 0.7870 | 1.1258 | 0.9180 | 4.3728 | 0.3878 |
| T3 | 0.4902 | 1.9198 | 1.4490 | 7.0107 | 1.2695 |
| R2CV [-] | RMSECV [-] | MAECV [%] | AAECV [%] | ABECV [%] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| W1 | 0.6217 | 2.0387 | 1.8632 | 9.1077 | 7.6093 |
| W2 | 0.6933 | 1.4568 | 1.2382 | 5.9518 | 3.7659 |
| W3 | 0.8108 | 1.4423 | 1.2070 | 5.9422 | 5.2810 |
| R2CV [-] | RMSECV [-] | MAECV [%] | AAECV [%] | ABECV [%] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H1 | 0.8959 | 2.1312 | 1.9740 | 9.4032 | −9.3217 |
| H2 | 0.8528 | 1.3266 | 1.0707 | 5.0002 | −3.5535 |
| H3 | 0.8672 | 1.5457 | 1.3415 | 6.2997 | −5.3494 |
| Equation | R2 | RMSE | MAE | AAE | ABE | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T2 | 0.5171 | 0.7702 | 0.5768 | 2.9346 | −0.2742 | |
| Demirbaş [13] | 0.0058 | 1.3534 | 0.8719 | 4.2037 | −3.1029 | |
| Domingos et al. [18] | 0.0058 | 1.1299 | 0.7384 | 3.5927 | −0.4441 |
| Equation | R2 | RMSE | MAE | AAE | ABE | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| W3 | 0.4152 | 1.2668 | 1.0902 | 5.3992 | 2.7024 | |
| Demirbaş [13] | 0.0894 | 1.7427 | 1.2145 | 5.7017 | −4.8843 | |
| Domingos et al. [18] | 0.0894 | 1.4359 | 0.9479 | 4.4850 | −2.3996 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, S.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, H.E.; Oh, K.C.; Kim, S.J.; Cho, L.H.; Jeon, Y.K.; Kim, D. Calorific Value Prediction Model Using Structure Composition of Heat-Treated Lignocellulosic Biomass. Energies 2023, 16, 7896. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16237896
Park S, Kim SY, Kim HE, Oh KC, Kim SJ, Cho LH, Jeon YK, Kim D. Calorific Value Prediction Model Using Structure Composition of Heat-Treated Lignocellulosic Biomass. Energies. 2023; 16(23):7896. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16237896
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Sunyong, Seon Yeop Kim, Ha Eun Kim, Kwang Cheol Oh, Seok Jun Kim, La Hoon Cho, Young Kwang Jeon, and DaeHyun Kim. 2023. "Calorific Value Prediction Model Using Structure Composition of Heat-Treated Lignocellulosic Biomass" Energies 16, no. 23: 7896. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16237896
APA StylePark, S., Kim, S. Y., Kim, H. E., Oh, K. C., Kim, S. J., Cho, L. H., Jeon, Y. K., & Kim, D. (2023). Calorific Value Prediction Model Using Structure Composition of Heat-Treated Lignocellulosic Biomass. Energies, 16(23), 7896. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16237896






