Design and Analysis of 15 MW SPM Vernier Generator for Direct-Drive Wind Turbine Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
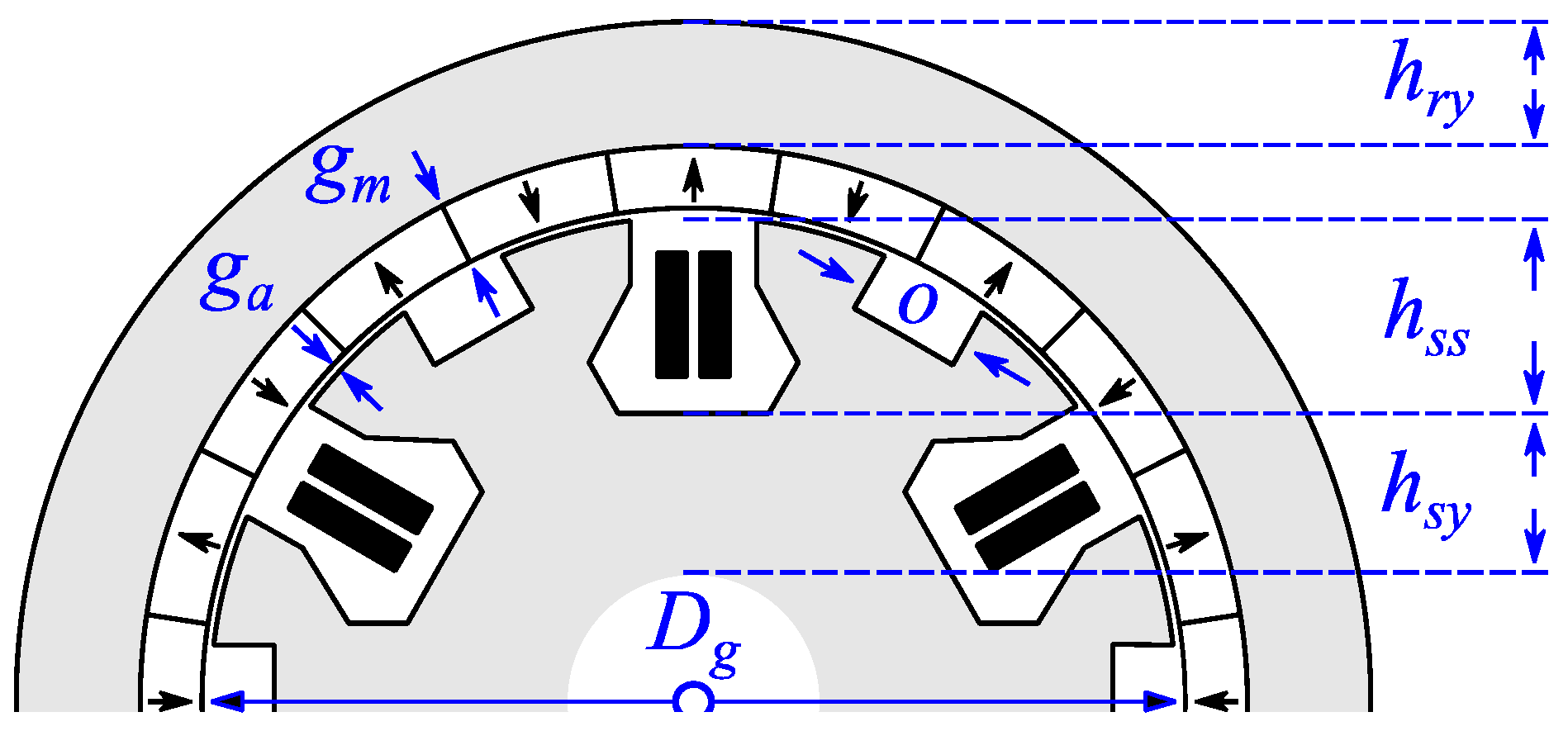
2. Basic Operation Principle and Analytical Modeling
2.1. Air-Gap Flux Density and Back EMF
2.2. Specfic Electric Loading and Torque Density
2.3. Flux Densities of Teeth and Back Yoke
2.4. Inductance and Power Factor
3. Nature of the Design Problem and Design Criteria
3.1. Back EMF Perofrmance and Slection of Optimal PM Thickness
3.2. Available Surface Current Density
3.3. Torque Density and Power Factor
4. FEM Modeling and Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Global Wind Energy Council (GWEC). GWEC Global Wind Report 2022; GWEC: Brussels, Belgium, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Bortolotti, P.; Tarres, H.; Dykes, K.; Merz, K.; Sethuraman, L.; Verelst, D.; Zahle, F. IEA Wind Task 37 on Systems Engineering in Wind Energy WP2.1 Reference Wind Turbines; National Renewable Energy Laboratory: Golden, CO, USA, 2019.
- Gaertner, E.; Rinker, J.; Sethuraman, L.; Zahle, F.; Anderson, B.; Barter, G.E.; Abbas, N.J.; Meng, F.; Bortolotti, P.; Skrzypinski, W.; et al. IEA Wind TCP Task 37: Definition of the IEA 15-Megawatt Offshore Reference Wind Turbine; National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL): Golden, CO, USA, 2020.
- Polinder, H.; Ferreira, J.A.; Jensen, B.B.; Abrahamsen, A.B.; Atallah, K.; McMahon, R.A. Trends in Wind Turbine Generator Systems. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2013, 1, 174–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.; Lipo, T.A. Operation and design principles of a PM vernier motor. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2014, 50, 3656–3663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Qu, R.; Li, J.; Xiao, L.; Wu, L.; Xu, W. Analysis of torque capability and quality in vernier permanent-magnet machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2016, 52, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B. Design method of a direct-drive permanent magnet vernier generator for a wind turbine system. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2019, 55, 4665–4675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, A.; Kim, B. Characteristics analysis of consequent pole ferrite magnet vernier machine using novel equivalent magnetic circuit. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2021, 10, 1823–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tlali, P.M.; Wang, R.-J.; Gerber, S.; Botha, C.D.; Kamper, M.J. Design and performance comparison of vernier and conventional PM synchronous wind generators. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2020, 56, 2570–2579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.; Lipo, T.A. Analysis of a PM Vernier Motor with Spoke Structure. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2016, 52, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padinharu, D.K.K.; Li, G.J.; Zhu, Z.Q.; Foster, M.P.; Stone, D.A.; Griffo, A.; Clark, R.; Thomas, A.S. Scaling effect on electromagnetic performance of surface-mounted permanent-magnet vernier machine. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2020, 56, 8100715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atallah, K.; Rens, J.; Mezani, S.; Howe, D. A novel “pseudo” direct-drive brushless permanent magnet machine. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2008, 44, 4349–4352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padinharu, D.K.K.; Li, G.J.; Zhu, Z.Q.; Clark, R.; Thomas, A.S.; Azar, Z. System-level investigation of multi-MW direct-drive wind power PM vernier generators. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 191433–191446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padinharu, D.K.K.; Li, G.J.; Zhu, Z.Q.; Clark, R.; Thomas, A.; Azar, Z.; Duke, A. Permanent magnet vernier machines for direct-drive offshore wind power: Benefits and challenges. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 20652–20668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tlali, P.; Wang, R.-J. Prospect of PM Vernier Machine for Wind Power Application. Energies 2022, 15, 4912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]













| Parameters | Reference Model [3] | SPM Vernier Machine | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rated Power/Rated Speed | Prated/ωrated | 15 MW/7.56 rpm | |
| Air-gap diameter | Dg | 10.16 m | |
| Air-gap length | ga | 10.16 mm | |
| Stack length | lstk | 2.17 m | 1.30 m |
| PM thickness | gm | 58.39 mm | 58.75 mm |
| Slots/PM pole pairs | Zs/Zr | 240/100 | 78/65 |
| Modulation pole pairs | ------- | 13 | |
| Surface current density | Ks | 92.46 kA/m | 85.52 kA/m |
| Volume current density | Js | 3.39 A/mm2 | |
| Coil turns per phase | Nph | 320 | |
| Parameters | Reference Model | SPM Vernier Machine |
|---|---|---|
| Back EMF (RMS) | 3.99 kV | 3.92 kV |
| Average Torque | 19.42 MNm | |
| Torque/Volume (TRV) | 110.38 kPa | 184.26 kPa |
| Torque Ripple | 1.61% | 8.57% |
| Power Factor | 66.68% | 37.14% |
| Efficiency | 96.55% | 96.40% |
| Parameters | Reference Model | SPM Vernier Machine |
|---|---|---|
| Permanent Magnet | 26.54 | 20.06 |
| Copper Winding | 9.01 | 5.08 |
| Stator Core | 153.00 | 107.32 |
| Rotor Core | 38.91 | 75.62 |
| Total Generator Mass | 227.46 | 208.08 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rehman, A.; Kim, B. Design and Analysis of 15 MW SPM Vernier Generator for Direct-Drive Wind Turbine Applications. Energies 2023, 16, 1094. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16031094
Rehman A, Kim B. Design and Analysis of 15 MW SPM Vernier Generator for Direct-Drive Wind Turbine Applications. Energies. 2023; 16(3):1094. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16031094
Chicago/Turabian StyleRehman, Abdur, and Byungtaek Kim. 2023. "Design and Analysis of 15 MW SPM Vernier Generator for Direct-Drive Wind Turbine Applications" Energies 16, no. 3: 1094. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16031094
APA StyleRehman, A., & Kim, B. (2023). Design and Analysis of 15 MW SPM Vernier Generator for Direct-Drive Wind Turbine Applications. Energies, 16(3), 1094. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16031094






