Inductive Electrically Excited Synchronous Machine for Electrical Vehicles—Design, Optimization and Measurement
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Structure of This Article
1.2. Nomenclature
2. Modeling of EESMs
2.1. Modeling the EESM in dq-Frame
2.2. Determination of the Effective Turns Ratio
2.3. Rotor Winding Factor
3. Optimization for Field Weakening
3.1. Operation of EESMs in Field Weakening
3.1.1. Field Weakening by Reducing the Excitation Current
3.1.2. Field Weakening by Negative d-Axis Current
3.1.3. Conditions for Infinite Field Weakening
3.2. Rotor Design for Ld,abs < Lq,abs
4. Electromagnetic Optimization of the Machine Parts
4.1. Optimization Method
4.2. Applied Optimization
4.3. Electromagnetic Simulation of the Finalized Geometry
5. Design of the WPT System
6. Construction of the Prototype
6.1. Placement of the WPT
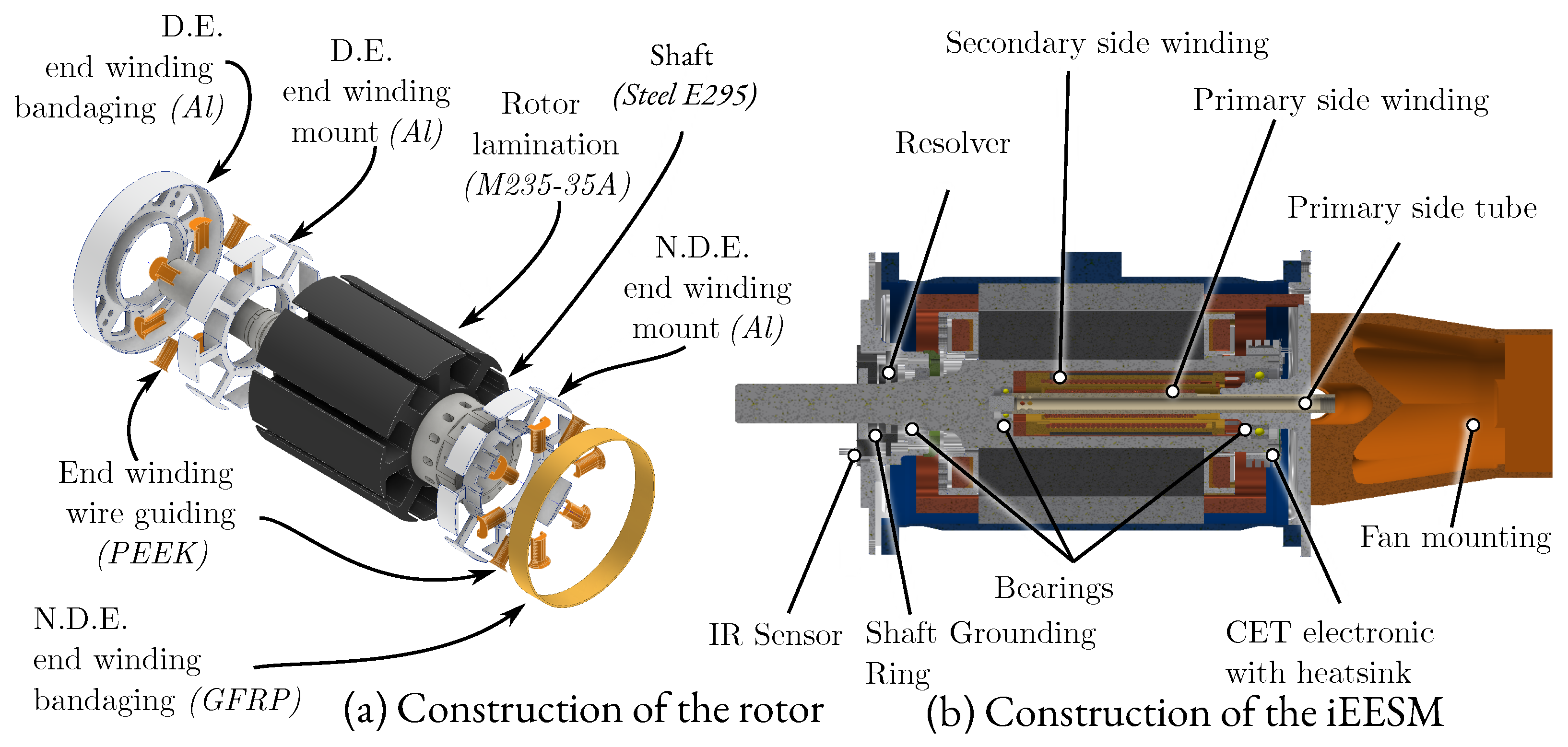
6.2. Rotor Construction
6.3. iEESM Construction
7. Prototype, Control and Measurement
7.1. Control
7.2. Test Bench Setup
7.3. Measurement Results
8. Conclusions
9. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BMW | Bayerische Motoren Werke AG |
| D.E. | Drive End |
| EC | Equivalent Circuit |
| EESM | Electrically Excited Synchronous Machine |
| EM | Electrical Machine |
| EV | Electrical Vehicle |
| FEA | Finite Element Analysis |
| GFRP | Glass-Fiber Reinforced Plastic |
| iEESM | Inductive Electrically Excited Synchronous Machine |
| IM | Induction Machine |
| IR | Infrared |
| LUT | LookUp Table |
| ME | Maximum Effciency |
| MTPA | Maximum Torque Per Ampere |
| N.D.E. | Non-Drive End |
| NSGA | Non-Dominated Sorting Genetic Algorithm |
| PLL | Phase-Locked Loop |
| PMASR | Permanent Magnet-Assisted Synchronous Reluctance Motor |
| PMSM | Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machine |
| PWM | Pulse Width Modulation |
| RP | Representative Point |
| WLTC | Worldwide Harmonized Light Vehicles Test Cycle |
| WPT | Wireless Power Transfer |
References
- Wayland, M. Auto Executives Say More than Half of U.S. Car Sales Will Be EVs by 2030, KPMG Survey Shows. Available online: https://www.cnbc.com/2021/11/30/auto-executives-say-more-than-half-of-us-car-sales-will-be-evs-by-2030-kpmg-survey-shows.html (accessed on 11 April 2022).
- Gül, T.; Tattini, J.; Pales, A.F. Global EV Outlook 2021. Available online: https://www.iea.org/reports/global-ev-outlook-2021/trends-and-developments-in-electric-vehicle-markets (accessed on 11 April 2022).
- Trading Economics. Price Trend of Neodymium. Available online: tradingeconomics.com/commodity/neodymium (accessed on 29 April 2022).
- Bailey, G.; Mancheri, N.; van Acker, K. Sustainability of Permanent Rare Earth Magnet Motors in (H)EV Industry. J. Sustain. Metall. 2017, 3, 611–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carraro, E.; Morandin, M.; Bianchi, N. Optimization of a traction PMASR motor according to a given driving cycle. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Transportation Electrification Conference and Expo (ITEC), Dearborn, MI, USA, 15–18 June 2014; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grundmann, D.; Gneiting, A.; Fischer, J.M.; Parspour, N. Design and Optimization of a Quadruple 3-Phase Permanent Magnet Assisted Synchronous Reluctance Machine. In Proceedings of the IECON 2021—47th Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Toronto, ON, Canada, 13–16 October 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mike Duff. BMW Brings the Electric HEAT: BMW EESM. Available online: https://www.caranddriver.com/news/a22656237/bmw-simplifies-ev-production/ (accessed on 4 February 2023).
- Tang, J.; Liu, Y.; Sharma, N. Modeling and Experimental Verification of High-Frequency Inductive Brushless Exciter for Electrically Excited Synchronous Machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2019, 55, 4613–4623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J. Design and Control of Electrically Excited Synchronous Machines for Vehicle Applications. Ph.D. Thesis, Chalmers University of Technology, Gothenburg, Sweden, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Illiano, E.M. Design of a Highly Efficient Brushless Current Excited Synchronous Motor for Automotive Purposes. Ph.D. Thesis, ETH Zurich, Zurich, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stancu, C.; Ward, T.; Rahman, K.M.; Dawsey, R.; Savagian, P. Separately Excited Synchronous Motor With Rotary Transformer for Hybrid Vehicle Application. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2018, 54, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krupp, H.; Mertens, A. Rotary Transformer Design for Brushless Electrically Excited Synchronous Machines. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Vehicle Power and Propulsion Conference (VPPC), Montreal, QC, Canada, 19–22 October 2015; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, J.N.; Rehfeldt, A.; Vip, S.A.; Ponick, B. Rotary transformer with electrical steel core for brushless excitation of synchronous machines. In Proceedings of the 2016 XXII International Conference on Electrical Machines (ICEM), Lausanne, Switzerland, 4–7 September 2016; pp. 884–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, M.; Parspour, N.; Kleemann, P.; Hagl, M. Construction and measurements of an electrical excited synchronous machine with inductive contactless energy transfer to the rotor. In Proceedings of the 2017 Brazilian Power Electronics Conference (COBEP), Juiz de Fora, Brazil, 19–22 November 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, D.; Kurz, J.; Parspour, N. Contactless Energy Transfer for Inductive Electrically Excited Synchronous Machines. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE PELS Workshop on Emerging Technologies: Wireless Power Transfer (WoW), London, UK, 18–21 June 2019; pp. 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, M. Betrieb Einer Elektrisch Erregten Synchronmaschine Mittels Kontaktloser, Induktiver Energieübertragung auf den Rotor, 1st ed.; Berichte aus dem Institut für Elektrische Energiewandlung; Shaker: Düren, Germany, 2020; Volume 11. [Google Scholar]
- Gunther, S.; Ulbrich, S.; Hofmann, W. Driving cycle-based design optimization of interior permanent magnet synchronous motor drives for electric vehicle application. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Power Electronics, Electrical Drives, Automation and Motion (SPEEDAM), Ischia, Italy, 18–20 June 2014; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2014; pp. 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinhal, D.B.; Gerling, D. Driving Cycle Simulation of Wound-Rotor Synchronous Machine with Hairpin Windings Considering AC-Losses. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Transportation Electrification Conference and Expo (ITEC), Detroit, MI, USA, 19–21 June 2019; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salameh, M.; Brown, I.P.; Krishnamurthy, M. Fundamental Evaluation of Data Clustering Approaches for Driving Cycle-Based Machine Design Optimization. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2019, 5, 1395–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazari, P.; Wang, J.; Chen, L. A Computationally Efficient Design Technique for Electric-Vehicle Traction Machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2014, 50, 3203–3213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarigiannidis, A.G.; Beniakar, M.E.; Kladas, A.G. Fast Adaptive Evolutionary PM Traction Motor Optimization Based on Electric Vehicle Drive Cycle. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2017, 66, 5762–5774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forster, D.; Inderka, R.B.; Gauterin, F. Data-Driven Identification of Characteristic Real-Driving Cycles Based on k-Means Clustering and Mixed-Integer Optimization. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2020, 69, 2398–2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, S.; Parspour, N. Applying a Measurement-Based Iron Loss Model to an Efficiency Optimized Torque Control of an Electrically Excited Synchronous Machine. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Electrical Machines (ICEM), Gothenburg, Sweden, 23–26 August 2020; pp. 779–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schröder, D. Elektrische Antriebe—Regelung von Antriebssystemen, 4. auflage ed.; Springer Vieweg: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grune, R. Verlustoptimaler Betrieb Einer Elektrisch Erregten Synchronmaschine für den Einsatz in Elektrofahrzeugen. Ph.D Thesis, Technische Universtität Berlin, Berlin, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Richter, R. Allgemeine Berechnungungselemente: Die Gleichstrommaschine; Julius Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1924; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Haala, O.; Wagner, B.; Hofmann, M.; März, M. Optimal current control of externally excited synchronous machines in automotive traction drive applications. Int. J. Electr. Comput. Energetic Electron. Commun. Eng. 2013, 7, 1133–1139. [Google Scholar]
- Bianchi, N. Electrical Machine Analysis Using Finite Elements; Power Electronics and Applications Series; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, E.; Susic, M. Parameter evaluation of permanent magnet synchronous machines with tooth coil windings using the frozen permeabilities method with the finite element analyses. In Proceedings of the 2012 25th IEEE Canadian Conference on Electrical and Computer Engineering (CCECE), Montreal, QC, Canada, 29 April–2 May 2012; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, D.; Heinrich, J.; Zimmer, M.; Maier, M.; Parspour, N. Contribution to the System Design of Contactless Energy Transfer Systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2019, 55, 316–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozpineci, B. FY2016 Electric Drive Technologies Annual Progress Report; EERE Publication and Product Library: Washington, DC, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MAHLE. MAHLE Develops Highly Efficient Magnet-Free Electric Motor. Available online: https://www.mahle.com/en/news-and-press/press-releases/mahle-develops-highly-efficient-magnet-free-electric-motor--82368 (accessed on 2 October 2021).
- Maier, D.; Müller, S.; Parspour, N. Elektrisch erregte Maschine und Anordnung für eine elektrisch erregte Maschine. German Pantent DE102020207000A1, 4 June 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Maier, D.; Müller, S.; Parspour, N. Elektrisch erregte Maschine und Anordnung für eine elektrisch erregte Maschine. European Union Patent EP3920385A1, 4 June 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Semikron. SKAI 45 A2 GD12-WDI. Available online: https://www.semikron-danfoss.com/de/produkte/produktklassen/systeme/detail/skai-45-a2-gd12-wdi-14282032.html (accessed on 30 January 2023).


















| Requirements | Operation Point Optimization | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Rated torque | 150 Nm | Speed | 9000 rpm |
| Maximum torque | >250 Nm | Torque | 40 Nm |
| Rated speed | 4800 rpm | Machine efficiency | maximize |
| Maximum speed | 11,400 rpm | Torque ripple | minimize |
| Prototype | BMW i3 [31] | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of pole pairs | p | 4 | 6 | ||
| Stator outer diameter | DS,out | 230 | mm | 242 | mm |
| Rotor outer diameter | DR,o | 179 | mm | 179 | mm |
| Stack length | lstack | 180 | mm | 132 | mm |
| Magnetic air-gap length | δ | 0.5 | mm | 0.5 | mm |
| Number of stator slots | QS | 48 | 72 | ||
| Tshaft for line peak current 530 A | 310 | Nm | 250 | Nm | |
| Torque density at maximum torque point | 41.4 | kNm/m3 | 41.1 | kNm/m3 | |
| Efficiency iEESM 50–75 Nm@2500–4000 rpm | 95% |
| Efficiency of reference PMSM for 50–75 Nm@2500–4000 rpm | 90–92% [31] |
| iEESM linearized inductance Ld,abs (ie) = 11 A | ≈300 mH |
| iEESM linearized inductance Lq,abs (ie) | ≈600 mH |
| iEESM effective turns ratio | = 0.0538 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Müller, S.; Maier, D.; Parspour, N. Inductive Electrically Excited Synchronous Machine for Electrical Vehicles—Design, Optimization and Measurement. Energies 2023, 16, 1657. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16041657
Müller S, Maier D, Parspour N. Inductive Electrically Excited Synchronous Machine for Electrical Vehicles—Design, Optimization and Measurement. Energies. 2023; 16(4):1657. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16041657
Chicago/Turabian StyleMüller, Samuel, David Maier, and Nejila Parspour. 2023. "Inductive Electrically Excited Synchronous Machine for Electrical Vehicles—Design, Optimization and Measurement" Energies 16, no. 4: 1657. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16041657
APA StyleMüller, S., Maier, D., & Parspour, N. (2023). Inductive Electrically Excited Synchronous Machine for Electrical Vehicles—Design, Optimization and Measurement. Energies, 16(4), 1657. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16041657








