Abstract
This study is a systematic review of research on heat transfer analysis in cavities and aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of flow and heat transfer performance in various kinds of cavities with or without the presence of fins, obstacles, cylinders, and baffles. The study also examines the effects of different forces, such as magnetic force, buoyancy force, and thermophoresis effect on heat transfer in cavities. This study also focuses on different types of fluids, such as air, water, nanofluids, and hybrid nanofluids in cavities. Moreover, this review deals with aspects of flow and heat transfer phenomena for only single-phase flows. It discusses various validation techniques used in numerical studies and the different types and sizes of mesh used by researchers. The study is a comprehensive review of 297 research articles, mostly published since 2000, and covers the current progress in the area of heat transfer analysis in cavities. The literature review in this study shows that cavities with obstacles such as fins and rotating cylinders have a significant impact on enhancing heat transfer. Additionally, it is found that the use of nanofluids and hybrid nanofluids has a greater effect on enhancing heat transfer. Lastly, the study suggests future research directions in the field of heat transfer in cavities. This study’s findings have significant implications for a range of areas, including electronic cooling, energy storage systems, solar thermal technologies, and nuclear reactor systems.
1. Introduction
The study highlights that enclosed cavities have a broad area of uses, such as electronic cooling, energy storage systems, solar thermal technologies, and nuclear reactor systems. The study has considered various shapes of cavities, including square, rectangular, triangular, trapezoidal, semicircular, hexagonal, U-shaped, etc. Different types of boundary conditions are applied to the walls of the cavities, which affect the flow and thermal behavior inside the cavities. The study considers temperature, heat flux, adiabatic, and isothermal as thermal boundary conditions, such as. On the other hand, the hydraulic boundary conditions considered are fixed, moving, and elastic. Some authors have also applied magnetic field strength to enhance heat transfer or alter buoyancy effects. Different types of fluids have been used in the cavity, including pure water, air, nanofluids, phase change material, porous media, and non-Newtonian fluid.
The main mechanisms of heat transfer in enclosed cavities are natural, forced, or mixed convection. The driving force for natural convection is mainly the buoyancy force (according to Boussinesq approximation), which is caused by the change in fluid density resulting from the applied temperature difference [1,2]. Research has shown that the buoyancy force can destabilize the flow inside the enclosure, but the application of a magnetic field can stabilize it [3]. In addition, the addition of nanoparticles to the liquid inside the cavity can improve its thermal conductivity, heat capacity, and density [4]. Alqaed et al. [5] studied the use of Al2O3/H2O nanofluid with an applied magnetic field. They proved that the presence of nanoparticles contributed to the fluid properties and improved heat transfer. The magnetic field also imposed a specific force (Lorentz force), which opposes the flow inside the cavity and reduces the heat transfer rate. Hatami [6] demonstrated that the presence of fins inside the cavity leads to an increase in vortices (increased mixing) which in turn leads to an enhancement of the rate of heat transfer. The interplay between the magnetic and buoyancy of a hybrid nanofluid Cu-Al2O3 inside a cavity leads to a decrease in flow velocity and reduced heat transfer rate [7]. Similar trends in the effect of nanofluid have been observed in different-shaped enclosures such as hexagonal [8], U-shaped [9], and trapezoidal cavities [10].
The moving boundary imposes a shear force on the fluid surface, which can lead to the generation of recirculating eddies that closes the wall of the cavity. The direction of the moving boundary can affect the strength of the shear force and the characteristics of the eddies that are formed. Additionally, for low values of Prandtl numbers, the effects of the moving boundary on the flow can be more pronounced [11]. Adding nanoparticles to a fluid can have a similar effect to that of fixed boundaries in that the fluid’s thermal conductivity enhances, and the rate of heat transfer rises. That’s because nanoparticles can enhance a fluid’s thermal conductivity and improve the rate of heat transfer. Additionally, if the fluid has been subjected to a magnetic field, the presence of the nanoparticles can lead to the generation of Lorentz force that acts in the vertical direction of the magnetic field. This force can suppress circulation and reduce the heat transfer rate. This effect is observed when the nanoparticles are magnetic nanoparticles and the intensity of the magnetic field is raised [12].
The main objective of this work is to conduct a comprehensive literature review of the hydraulic and thermal behaviors inside a cavity. The focus will be on studying the effects of different shapes of the cavity, various applied boundary conditions, and different types of working fluids. The study will compare the effects of using various types of fluids such as air, water, nanofluids, non-Newtonian fluid, etc. The study will also aim to predict correlations for the Nusselt number for different ranges of Rayleigh and Reynolds numbers at different imposed boundary conditions.
The primary conclusion of this literature review is that not many studies have been conducted on phase change materials (PCMs) in cavities, and it is not the focus of our review. Additionally, few studies have considered the use of LES and DNS models to model turbulent flow in cavities. It is also suggested that optimization should be conducted to predict the optimum shape of the cavity. Finally, more studies are needed to investigate the behavior of cavities filled with different types of fluids, such as two immiscible fluids, which can include the interaction between two different regions inside the same enclosure, such as the development of a couple of thermal boundary layer with different fluids separated by different types of partition.
Aim of the Study
A configurative systematic review process is adopted for this study to review the following:
- Model geometry, flow domain, type, CFD modeling, parameters, and meshing.
- Different types of validations are used by researchers.
- Heat transfer behavior for different flow conditions, geometries, boundary conditions, and the presence of different obstacles inside cavities.
2. Methodology
The present review employs a configurative systematic review approach to report on the heat transfer analysis inside different shapes of cavities. A flow chart of the process is provided in Figure 1. The study used various databases such as ScienceDirect, SAGE, ResearchGate, Google Scholar, and Web of Science to conduct the literature search. The search was conducted using key terms such as “Heat transfer”, “Rectangular cavity”, “Square cavity”, “Trapezoidal cavity”, “Triangular cavity”, “Hexagonal cavity”, “Octagonal cavity”, “T-shaped cavity”, “U-shaped cavity”, “C-shaped cavity”, “V-shaped cavity”, “H-shaped cavity”, “Arc-shaped cavity”, “L-shaped cavity”, “M-shaped cavity”, and “Cavity or enclosure”. The article-searching process began on 1 March 2022 and ended on 30 November 2022. One restriction was imposed during the search process, which was that the articles must be written in English.
Figure 1.
Flow chart of the study selection process.
In addition to the language restriction, the review also excluded articles that were published in ArXiv and Preprints, including conference and review articles. Book chapters, editorials, duplicate articles, articles with no data on heat transfer, articles with no full text available, and other irrelevant articles were also excluded. The authors also reviewed all the references that are connected to their research. Eligible articles were selected by two authors (G.S. & A.A.) who worked independently, screened all the articles, checked the title and abstract as well as assessed the full text. If there was any disagreement regarding the selection, a third author (S.C.S.) discussed the issues that occurred between the first two authors and then resolved the problem. Two authors (G.S. & A.A.) collected some information from the appropriate studies: author’s last name, published year, CFD tools, flow domain or shape of the domain, dimension of the study, algorithms used to solve the problem, parameters and their ranges, type of flow, name of nanofluids or hybrid nanofluids, nanofluids thermo-physical properties, validation data, and results on heat transfer analysis. A total of 2732 articles were considered, 1257 articles were removed because of duplication, 905 articles were removed for other exclusion criteria, and 570 articles were considered which were related to heat transfer analysis inside cavities. After careful screening of the title and abstract, a total of 315 articles were considered for screening of the full text. Finally, 297 articles were selected for the present review study.
The word cloud map in Figure 2 shows the most frequently used words in the abstracts of the selected articles. It appears that the main topics of these articles are natural convection and mixed convection, steady flow, and heat transfer. These articles also focus on numerical experiments, using air and nanofluids as working fluids and utilizing FVM and FEM as numerical methods. The average rate of heat transfer is often presented as a function of the Nusselt number in relation to the Richardson number and Rayleigh number.

Figure 2.
Word Cloud Map.
Figure 3 shows that square cavities are the most studied among the different types of cavities, accounting for 47.5% of the total number of articles. The second most studied are triangular cavities, with 14.1% of the articles. Rectangular cavities (12.5%), trapezoidal cavities (7.4%), and cubical cavities (6.1%) are also studied in a significant number of articles. The other types of cavities are studied at much lower percentages, with T-shaped (0.7%) and U-shaped (1%) cavities being the least studied. 2.5% of articles deal with other types of cavities. Square cavities have a wide range of practical applications in various fields, such as aerospace, mechanical engineering, energy, and electronics. They have many advantages, for example, in heat transfer, fluid flow, and electromagnetic waves, and therefore are widely used in many engineering systems and devices. The high percentage of research articles focused on square cavities suggests that they are an important area of study in the field.
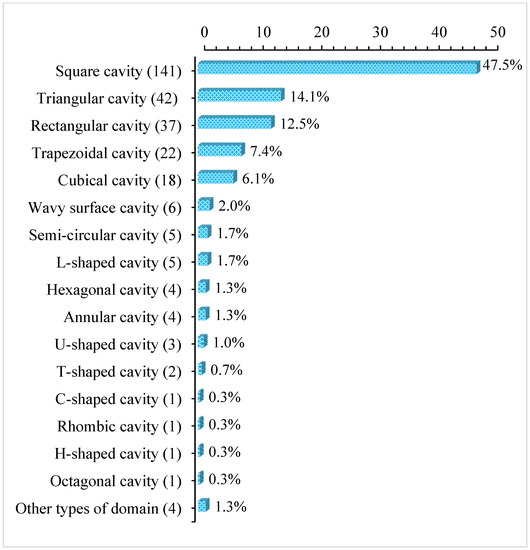
Figure 3.
Percentage of different types of cavities.
3. Physical Domain and Mathematical Modelling
3.1. Physical Domain
Many researchers have published a large number of articles over the years to study the hydraulic and thermal performances inside enclosures with various shapes such as square, rectangular, triangular, hexagonal, octagonal, trapezoidal, T-shaped, U-shaped, L-shaped, M-shaped, V-shaped, H-shaped, I-shaped, C-shaped, arc-shaped, and other modified geometries. These studies often introduce obstacles such as fins, cylinders, blocks, rotating blades, etc., inside these physical domains to further complicate the flow patterns and potentially enhance or degrade heat transfer rates Table 1 provides more information about this research.
3.2. Governing Equations
The Navier-Stokes equations describe the motion of a fluid and are widely used in engineering and physics to model different fluid flow phenomena. The equations consist of three main components: the continuity equation, which describes the conservation of mass, the momentum equation, which describes the forces that were applied to the fluid; and the energy equation, which describes the transfer of thermal energy. These equations can be applied to a wide range of fluid types and flow conditions, including incompressible, steady and unsteady flows, Newtonian and non-Newtonian fluids, laminar and turbulent flows, and fluids with different physical properties, such as air, water, and nanofluids. The geometry of the system can also be two or three-dimensional. Solving the Navier-Stokes equations is a challenging task and requires advanced mathematical techniques. In addition to the commonly studied body forces such as gravity and electromagnetic forces, other types of body forces can also play a role in various physical systems. These can include buoyancy forces, Brownian motion of particles, thermophoresis effect, heat generation or absorption, radiation, and the porous medium effect described by the Forchheimer-Brinkman model. These forces can have significant effects on the behavior of the system and must be taken into account when studying and modeling the system. Considering all the assumptions, the three-dimensional Navier-Stokes equation can be presented in the dimensional form (Versteeg [13]):
Continuity equation:
-momentum equation:
-momentum equation:
-momentum equation:
Energy equation:
Here, are the velocities, is the pressure, and t is the time. are the Cartesian coordinate systems, is the temperature, is density, is dynamic viscosity, is gravitational acceleration, is the angle, and is the thermal expansion coefficient respectively.
Complex geometries are often encountered in physical systems, and numerical methods are often used to solve the system of equations that govern these systems. Some common numerical techniques used include the finite difference method, finite volume method, finite element method, lattice Boltzmann method, wavelet-based methods such as Coiflet wavelet-homotopy method, fourth-order compact formulation, dual reciprocity boundary element method, spectral element method, large eddy simulation, direct numerical simulation, radial basis function-based partition of unity method, and Improved element-free Galerkin–reduced integration penalty method. These methods can be used to solve a wide range of problems and have been applied in various fields, such as fluid dynamics, heat transfer, and solid mechanics. The problem of heat transfer analysis inside cavities can also be solved using commercial and open-source computational fluid dynamics (CFD) codes or software. Some examples of commonly used commercial CFD codes include COMSOL Multiphysics, ANSYS Fluent, and ADINA Multiphysics. There are also open-source options, such as FlexPDE and OpenFOAM that can be used to solve such problems. These codes and software can be used to perform a wide range of simulations, including heat transfer, fluid flow, and solid mechanics. They are widely used in various fields such as aerospace, automotive, and mechanical engineering and often include a range of features and capabilities such as pre-processing, solving, and post-processing.
3.3. Meshing
In order to solve the system of equations that govern a physical system, the physical domain must be discretized into a smaller number of elements or cells. This process is known as meshing. The Navier-Stokes equations are then solved on these elements or cells to determine the complex flow and thermal field nature. The accuracy of the results largely relies on the number of cells used in the mesh, and smaller cells are preferred to obtain higher accuracy. However, there is a trade-off between the accuracy and computational resources required. It is necessary to find a balance between the computational time and cost and the desired accuracy of the solution.
Researchers have used a variety of meshing techniques to discretize the physical domain and solve the Navier-Stokes equations. These include uniform or non-uniform meshing with rectangular or orthogonal grids, tetrahedral meshing, and non-uniform meshing with triangular grids or clustered grids. The choice of meshing technique depends on the complexity of the geometry, the level of accuracy required, and the computational resources available. It is observed that many researchers have used structured meshes as opposed to unstructured meshes. This is because structured meshes are typically less computationally expensive and require less time for simulation. Additionally, most of the researchers carry out grid-independent tests (GIT) to ensure that the solution does not depend on the grid size. GIT is a vital part of numerical simulations, and it is important that researchers present a clear and detailed discussion of GIT. However, it is also seen that some researchers did not present a clear and detailed discussion on GIT.
A lack of comparison between the performance of uniform meshes and dense non-uniform or fine meshes on flow and temperature fields is often missing in the literature. This can make it difficult for readers to understand the effects of mesh resolution on the solution and the accuracy of the simulation. Comparing the results of simulations using different meshes is an important part of any numerical study, and it is known as a mesh independence study. This is particularly important for complex flow features and can help readers to understand or revisit the study. By comparing the performance of uniform meshes and dense non-uniform or fine meshes, one can determine the optimal mesh resolution for a specific problem and also identify the errors and uncertainties associated with the simulation. Therefore, a clear presentation of the mesh independence study is important for future readers to understand the study and to replicate the simulations.

Table 1.
(a): Research performed from 1989 to 2013. (b) The research was performed from 2014 to 2019. (c): Research performed from 2020 to 2023.
Table 1.
(a): Research performed from 1989 to 2013. (b) The research was performed from 2014 to 2019. (c): Research performed from 2020 to 2023.
| (a) | |||||
| Ref. | CFD Methods and Algorithms | Flow Domain | Dimension, Type of Flow | Parameters and Ranges | Meshing |
| Wee et al. [2] | Experimental, FDM, DADI | Rectangular cavity | 2D, unsteady, laminar | 2 105 ≤ GrT ≤ 2 106, 10 ≤ GrC ≤ 2 105, 2 104 ≤ Ra ≤ 1.47 106 | - |
| Moallemi & Jjang [11] | FVM, SIMPLIER | Lid-driven square cavity | 2D, steady, laminar, non-Newtonian | 102 ≤ Re ≤ 2200, 0.01 ≤ Pr ≤ 50, 0.01 ≤ Ri ≤ 10 | Non-uniform grid, 42 42 |
| Sasaguchi et al. [14] | Grid generation | Rectangular cavity with cylinders | 2D, unsteady, laminar | N/A | Uniform mesh, 31 101, 31 121 |
| Al-Amiri et al. [15] | FEM | Lid-driven cavity with wavy wall | 2D, steady, laminar, mixed convection | Pr = 0.71, 1, Gr = 104, 0.1 ≤ Ri ≤ 10, 0 ≤ Am ≤ 0.075, 0 ≤ ≤ 3, Re = 500 | - |
| Saha et al. [16] | FEM | Inclined rectangular enclosure | 2D, natural convection, steady, laminar | Pr = 0.71, 103 ≤ Gr ≤ 106, 0.5 ≤ A ≤ 1.0, 0 ≤ ≤ 30 | Non-uniform, six nodded 6394 elements |
| Saha et al. [17] | FVM | Triangular cavity | 2D, natural convection | Pr = 0.71, Gr = 1.33 106, 0.5 ≤ A ≤ 1.0 | 360 90, 720 160, 270 90 for A = 0.2, 0.5, 1.0 |
| Tiwari & Das [18] | FVM, SIMPLE, QUICK, TDMA | Double lid-driven square cavity | 2D, unsteady | Pr = 6.2, 0.1 ≤ Ri ≤ 10, 103 ≤ Ra ≤ 106, 0 ≤ ≤ 0.2, Cu-water nanofluid | Uniform grid, 61 61 |
| Saha et al. [19] | FEM | Inclined sinusoidal enclosure | 2D, steady, natural convection, laminar | Pr = 0.71, 103 ≤ Gr ≤ 106, 0 ≤ ≤ 45 | Non-uniform grid, 5240 elements |
| Varol et al. [20] | FDM | Triangular cavity | 2D, natural convection | 0.25 ≤ A ≤ 1.0, 102 ≤ Ra ≤ 103 | Uniform grid, 61 61 |
| Chen & Cheng [21] | FVM, SOR | Lid-driven triangular cavity | 2D, mixed convection, unsteady, laminar | Pr = 0.71, Re = 100, Gr = 5 105 | 41 41 |
| Noor et al. [22] | FDM, QUICK, RK-4, SOLA | Double lid-driven square cavity | 2D, unsteady, laminar | Pr = 0.71, 10 ≤ Re ≤ 103, 1 ≤ ≤ 5 | Clustered grid, 125 125 |
| Ouertatani et al. [23] | FVM, QUICK. CDS, RBSOR | Double lid-driven cubic cavity | 3D, mixed convection, unsteady, laminar | Pr = 0.71, 102 ≤ Re ≤ 103, 10−3 Ri ≤ 10 | 64 64 64 |
| Basak et al. [24] | FEM | Triangular porous cavities | 2D, natural convection, steady | 10−5 ≤ Da ≤ 10−1, 0.015 ≤ Pr ≤ 103, 103 ≤ Ra ≤ 5105 | 20 20–28 28 bi-quadratic elements |
| Lei & O’Neill [25] | FVM, SIMPLE, CDS, SUR | Square cavity with different corners | 2D, unsteady, natural convection | Pr = 6.62, 0 ≤ Ra ≤ 108 | 16,000 cells |
| Saha [26] | FEM | Sinusoidal corrugated enclosure | 2D, steady | Pr = 0.71, 103 ≤ Gr ≤ 106, 0 ≤ Ha ≤ 102 | Non-uniform grid, 4928 elements |
| Saha et al. [27] | FEM | Octagonal enclosure | 2D, natural convection, steady, laminar | Pr = 0.71, 7, 20, 50, 103 ≤ Ra ≤ 106 | Non-uniform, 10,466 elements |
| Saha et al. [28] | FVM, QUICK, SIMPLE | Triangular enclosure | 2D, natural convection, unsteady | Pr = 0.72, 104 ≤ Ra ≤ 7.2 106, A = 0.2, 0.5, 1.0 | 270 90, 320 80, 360 90 for A = 1, 0.5 & 0.2 |
| Saha et al. [29] | FVM, QUICK, SIMPLE | Triangular enclosure | 2D, natural convection, unsteady | Pr = 0.72, 7.2 103 ≤ Ra ≤ 1.5 106, A = 0.2, 0.5, 1.0 | 270 90, 320 80, 360 90 for A = 1, 0.5 & 0.2 |
| Saha et al. [30] | FVM, QUICK, SIMPLE | Triangular enclosure | 2D, natural convection, unsteady | Pr = 0.72, 5 ≤ Ra ≤ 1.5 107, A = 0.2, 0.5, 1.0 | 360 120, 320 90, 360 90 for A = 1, 0.5 & 0.2 |
| Sivasankaran et al. [31] | FVM, UDS, CDS, SOR | Lid-driven square cavity | 2D, unsteady, laminar, mixed convection | Pr = 0.71, 0 ≤ Am ≤ 1, 0 ≤ ≤ , 0.1 ≤ Ri ≤ 102, 102 ≤ Re ≤ 103 | Uniform grid, 81 81 |
| Sivakumar et al. [32] | FVM, SIMPLE, QUICK. CDS | Lid-driven square cavity | 2D, mixed convection, unsteady, laminar | Pr = 0.71, 102 ≤ Re ≤ 103, 102 ≤ Gr ≤ 106, 10−2 ≤ Ri ≤ 102 | Uniform grid, 81 81 |
| Al-Amiri & Khanafer [33] | ADINA, FSI, FEM, ALE | Lid-driven square cavity | 2D, steady, laminar | Pr = 0.71, 102 ≤ Re, Gr ≤ 103 | Non-uniform mesh, 120 120 |
| Cheng [34] | Compact formulation, SOR, ADI | Lid-driven square cavity | 2D, mixed convection | 10 ≤ Re ≤ 2200, 100 ≤ Gr ≤ 4.86 106, 10−2 ≤ Pr ≤ 50, 10−2 ≤ Ri ≤ 102 | 256 256 |
| Nasrin & Parvin [35] | FEM, TFM | Lid-driven square cavity with wavy wall | 2D, laminar, steady, mixed convection | 30 ≤ Re ≤ 300, 0 ≤ Ha ≤ 50, Pr = 0.71, Ra = 104 | Non-uniform, 37,123 nodes, 5604 elements |
| Saha [36] | FVM, QUICK | Triangular cavity | 2D, unsteady, natural convection | 0.2 ≤ A ≤ 1.0, 5 ≤ Pr ≤ 100, Ra = 107 | - |
| Saha [37] | FVM, SIMPLE, QUICK | Triangular cavity | 2D, unsteady, natural convection | 0.2 ≤ A ≤ 1.0, 5 ≤ Pr ≤ 100, 5 106 ≤ Ra ≤ 108 | - |
| Yu et al. [38] | Fluent, FVM, QUICK, SIMPLE | Square cavity | 2D, unsteady, natural convection | 104 ≤ Ra ≤ 106, 0 ≤ ≤ 0.04, CuO–H2O nanofluid | 100 100 |
| Al-Farhany & Turan [39] | FVM, SIMPLER | Inclined rectangular porous cavity | 2D, unsteady, natural convection | 0 ≤ ϕ ≤ 85, 0.1 ≤ Le ≤ 10, −5 ≤ N ≤ 5, Pr = 4.5, Ra = 5 × 106 | - |
| Arani et al. [40] | FVM, SIMPLIER, TDMA, CDS, UDS | Lid-driven square cavity | 2D, mixed convection, laminar, steady | 10−3 ≤ Ri ≤ 10, 0 ≤ ≤ 0.1, Gr = 102, Re = 102 Cu–H2O nanofluid | Uniform grid. 80 80 |
| Basak et al. [41] | FEM | Porous triangular cavities | 2D, natural convection, steady | Pr = 0.025, 1000, 10−5 ≤ Da ≤ 10−3, Ra = 5 105 | 28 28 bi-quadratic elements |
| Chamkha & Abu-Nada [42] | FVM, CDS, UDS, SOR, SUR | Double lid-driven square cavity | 2D, mixed convection, steady, laminar | 0.001 ≤ Ri ≤ 10, 0 ≤ ≤ 0.1, H2O-Al2O3 nanofluid | Uniform grid, 81 81 |
| Nasrin & Parvin [43] | FEM | Trapezoidal cavity | 2D, free convection, steady, laminar | Ra = 105, = 0.05, 0.65 ≤ A ≤ 2, 1.47 ≤ Pr ≤ 8.81, Cu–H2O nanofluid | 40,295 nodes, 10,936 elements |
| Raji et al. [44] | FVM, SIMPLIER | Square cavity with blocks | 2D, natural convection, laminar, steady | 103 ≤ Ra ≤ 108, Pr = 0.71 | 254 254 |
| Saha & Gu [45] | FVM | Triangular enclosure | 2D, natural convection, unsteady | Pr = 0.7, Ra = 105, A = 0.5 | Triangular grid, 8143 nodes |
| Saha & Gu [46] | FVM | Triangular enclosure | 2D, natural convection, unsteady | Pr = 0.72, 5.0 104 ≤ Ra ≤ 106, A = 0.5 | - |
| Teamah & El-Maghlany [47] | FVM, CDS, GS, TDMA | Square cavity | 2D, steady, laminar | 103 ≤ Ra ≤ 107, 0 ≤ Ha ≤ 60, 0 ≤ ≤ 0.06, −10 ≤ q ≤ 10, Pr = 6.2, H2O based Al2O, Cu, TiO2 nanofluids | 60 60 |
| Ahmed et al. [48] | Collocated FVM, UDS, CDS, TDMA | Inclined lid-driven square cavity | 2D, mixed convection, laminar, steady | 10−2 ≤ Ri ≤ 102, 0 ≤ ≤ 1.0, 0 ≤ Ha ≤ 100, 0 ≤ ≤ 90 | Uniform grid. 81 81 |
| Bhardwaj & Dalal [49] | FDM, QUICK, SOR, CDS | Porous triangular cavity | 2D, natural convection, laminar | 103 ≤ Ra ≤ 106, 10−4 ≤ Da ≤ 10−2, Am = 0.05 | Orthogonal mesh, 41 41 |
| Cho et al. [50] | FVM, SIMPLEC, TDMA | Lid-driven cavity with wavy surfaces | 2D, mixed convection, laminar, steady | 0 ≤ ≤ 0.1, 10−2 ≤ Ri ≤ 103, 101 ≤ Gr ≤ 104, 0 ≤ ≤ 0.2, Pr = 6.2, H2O based Cu, Al2O3, TiO2 nanofluids | 101 201 |
| Elsherbiny & Ragab [51] | - | Inclined rectangular cavities | 2D, laminar, natural convection | 102 ≤ Ra ≤ 106, 0.5 ≤ A ≤ 5, 0 ≤ ≤ 180 | Uniform mesh, 42 42 |
| Huelsz & Rechtman [52] | LBM | Inclined square cavity | 2D, natural convection, laminar, unsteady | Pr = 0.71, −180 ≤ ≤ 180, 103 ≤ Ra ≤ 106 | 103 103 |
| Khanafer & Aithal [53] | ADINA, FEM, NR | Lid-driven square cavity with cylinder | 2D, steady, laminar, mixed convection | Pr = 0.7, 104 ≤ Gr ≤ 106, 0.01 ≤ Ri ≤ 10, Re = 102 | Non-uniform grid, 19,520 nodes |
| Ramakrishna et al. [54] | FEM | Trapezoidal cavities | 2D, free convection, laminar | 30 ≤ ≤ 90, Pr = 0.015, 7.2, 103 ≤ Ra ≤ 105 | 28 28 bi-quadratic elements |
| Sivasankaran et al. [55] | FVM, UDS, CDS | Inclined lid-driven square cavity | 2D, unsteady, laminar, mixed convection | Pr = 0.71, 0.01 ≤ Ri ≤ 102, 0 ≤ ≤ 90 | 81 81 |
| (b) | |||||
| Ref. | CFD Methods and Algorithms | Flow Domain | Dimension, Type of Flow | Parameters and Ranges | Meshing |
| Sathitamoorthy & Chamkha [56] | FEM | Square cavity with thin partition | 2D, natural convection, steady | Pr = 0.7, 100, 103 ≤ Rah ≤ 105 | 20 20 elements, 41 41 grid points |
| Abu-Nada & Chamkha [57] | FVM, SOR, SUR, UDS | Lid-driven square cavity with wavy wall | 2D, mixed convection, laminar, steady | Pr = 6.57, 0.01 ≤ Ri ≤ 102, 0 ≤ ≤ 0.09, H2O-CuO nanofluid | Uniform grid, 81 81 |
| Ait-Taleb et al. [58] | FDM, SIMPLE, TDMA | Rectangular cavities with tiles | 2D, steady, laminar | 8.7 103 ≤ Rah ≤ 1.8 105, 4.1 105 ≤ RaH ≤ 1.23 107, Pr = 0.71 | Non-uniform mesh, 80 40 |
| Cheng & Liu [59] | Ansys Fluent, FVM, SOR, ADI | Lid-driven square and rectangular cavities | 2D, unsteady | Pr = 0.71, 10−2 ≤ Ri ≤ 102, 0.2 ≤ A ≤ 5, 0 ≤ ≤ 90, Re = 102 | Uniform grid, 640 128, 128 128, 128 640 |
| Cho [60] | FVM, SIMPLE, TDMA | Square cavity with wavy wall | 2D, natural convection, laminar, steady | 103 ≤ Ra ≤ 106, 0 ≤ ≤ 0.04, Pr = 6.2, H2O-Al2O3 nanofluid | 101 201 |
| Kalteh et al. [61] | FDM, CDS, SUR | Lid-driven square cavity with block | 2D, steady, mixed convection | Gr = 102, 0.000625 ≤ Ri ≤ 4, 0 ≤ ≤ 0.05, H2O based Al2O3, TiO2, Ag, CuO nanofluids | Regular grid, 80 80 |
| Khanafer [62] | ADINA, FEM, FSI, ALE | Lid-driven square cavity | 2D, steady, laminar, mixed convection | Pr = 0.7, 102 ≤ Gr ≤ 104, 10−4 ≤ Ri ≤ 1.0, 102 ≤ Re ≤ 103 | Non-uniform, 120 120 |
| Muthtamilselvan & Doh [63] | FVM, SIMPLE, QUICK, TDMA | Lid-driven square cavity | 2D, steady, mixed convection | 0 ≤ Rai ≤ 105, Pr = 6.2, 10−2 ≤ Ri ≤ 10, 0 ≤ ≤ 0.06, Cu-H2O nanofluid | Uniform grid, 41 41 |
| Ramakrishna et al. [64] | FEM | Porous trapezoidal cavity | 2D, natural convection, laminar, steady | 10−5 ≤ Da ≤ 10−3, 30 ≤ ≤ 90, Pr = 0.015, 103 | 28 28 bi-quadratic elements |
| Ray & Chatterjee [65] | Fluent, FVM | Lid-driven square cavity | 2D, steady, mixed convection | 0.1 ≤ Ri ≤ 10, 0 ≤ Ha ≤ 50, 0 ≤ J ≤ 5, Re = 102, Pr = 0.71 | Non-uniform, 56,126 mixed elements |
| Saha & Gu [66] | Fluent, FVM | Triangular cavity | 2D, unsteady, natural convection | Pr = 0.72, 105 ≤ Ra ≤ 108, A = 0.2, 0.5, 1.0 | Non-uniform grid, 400 100 |
| Xu & Saha [67] | FVM, SIMPLE, QUICK | Square cavity with fin | 2D, unsteady, natural convection | Pr = 0.71, 105 ≤ Ra ≤ 109 | Non-uniform grid, 198 198 |
| Cui et al. [68] | Fluent, FVM, SIMPLE, QUICK | Triangular cavity | 3D, natural convection, unsteady | A = 0.5, Pr = 6.98, Ra = 2.08 106 | Non-uniform grid, 100 66 45 |
| Elsherbiny & Ismail [69] | FDM, TDMA, CDS | Inclined rectangular cavities | 2D, laminar, steady | Pr = 0.71, 0 ≤ ≤ 180, 103 ≤ Ra ≤ 106, A = 1, 5, 10 | Uniform grid, 42 42 |
| Elsherbiny & Ragab [51] | - | Inclined rectangular cavities | 2D, laminar, natural convection | Pr = 0.71, 0 ≤ ≤ 180, 102 ≤ Ra ≤ 106 | Uniform mesh, 42 42 |
| Groşan et al. [70] | FDM, CDS | Porous square cavity | 2D, steady, natural convection | Ra = 10, 100, Le = 1, 10, H2O, aluminum foam, carbon nanotubes | 227 227 |
| Moumni et al. [71] | FVM, AB, QUICK, CDS, Euler, RBSOR | Double lid-driven square cavity | 2D, unsteady, laminar | 1 ≤ Re ≤ 102, Pr = 6.2, 10−2 ≤ Ri ≤ 20, 0 ≤ ≤ 0.2, H2O based Cu, Ag, Al2O3, TiO2 nanofluids | Uniform grid, 120 120 |
| Saha & Gu [72] | Fluent, FVM, QUICK | Triangular enclosure | 2D, natural convection, steady, unsteady | 105 ≤ Ra ≤ 106, Pr = 0.72, A = 0.2, 0.5, 1.0 | Non-uniform grid |
| Sheremet & Pop [73] | FDM, CDS, SOR | Lid-driven square cavity | 2D, unsteady, laminar, mixed convection | Re = 102, Pr = 6.26, 10 ≤ Gr ≤ 105, 10 ≤ Le ≤ 104, N, Nb, Nt = 0.1 to 0.4 | Uniform grid, 400 400 |
| Sojoudi et al. [74] | Fluent, FVM | Triangular cavity | 2D, natural convection, unsteady | 103 ≤ Ra ≤ 106, 0.2 ≤ A ≤ 1, Pr = 0.72 | 15,700 triangular elements |
| Armaghani et al. [75] | FVM, SIMPLE | L-shaped cavity with baffle | 2D, steady, natural convection | Pr = 0.71, 104 ≤ Ra ≤ 106, 0.1 ≤ A ≤ 0.7, 0 ≤ Bf ≤ 0.3, 0 ≤ ≤ 0.04, Al2O3-H2O nanofluid | Uniform grid, 100 100 |
| Jmai et al. [76] | FVM, QUICK, SOR, multigrid | Double lid-driven square cavity | 2D, unsteady, laminar, mixed convection | 10−2 ≤ Ri ≤ 102, 0 ≤ ≤ 0.1, Cu–H2O nanofluid | Non-uniform grid, 64 64 |
| Kareem et al. [77] | Fluent, URANS, LES, FVM, SIMPLE | Cubic lid-driven cavity | 3D, unsteady, mixed convection, turbulent | Re = 5000, 10,000, 15,000 and 30,000 | Structured, non-uniform, 1,699,200 grids |
| Kareem et al. [78] | FVM, UDS, SIMPLE | Lid-driven trapezoidal cavity | 2D, mixed convection | 0 ≤ ≤ 0.04, 0.1 ≤ Ri ≤ 10, 102 ≤ Re ≤ 1200, 0 ≤ ≤ 60, 0.5 ≤ A ≤ 2, H2O based Al2O3, CuO, SiO2, TiO2 nanofluids | Unstructured, non-uniform 5470 grids |
| Mamourian et al. [79] | FVM, SIMPLE | Lid-driven square cavity | 2D, steady, laminar, Mixed convection | 10−2 ≤ Ri ≤ 102, 0 ≤ ≤ 0.1, Gr = 102, Am = 0.25, Cu–H2O nanofluid | Structured non-uniform, 101 201 |
| Mejri et al. [80] | LBM | Triangular cavity | 2D, natural convection, laminar | 103 ≤ Ra ≤ 106, 0 ≤ ≤ 315, Ma = 0.1 | - |
| Rahmati et al. [81] | LBM | Double lid-driven cavity | 2D, mixed convection, laminar, steady | Gr = 100, Pr = 6.57, 10−2 ≤ Ri ≤ 102, 0 ≤ ≤ 0.06, Cu-H2O nanofluid | 100 100 |
| Rashad et al. [12] | FVM, ADI, SIMPLE, UDS, CDS | Lid-driven square cavity | 2D, mixed convection, laminar | 0 ≤ Ha ≤ 100, 10−3 ≤ Ri ≤ 10, 0 ≤ ≤ 0.01, Cu-H2O nanofluid | Uniform grid, 81 81 |
| Selimefendigil & Öztop [82] | FEM, ALE | Lid-driven inclined square cavity | 2D, steady | 10−2 ≤ Ri ≤ 102, 0 ≤ ≤ 0.05, 103 ≤ Rai ≤ 106, 0 ≤ Ha ≤ 50, 0 ≤ ≤ 90, 5 102 ≤ E ≤ 106, CuO-H2O nanofluid | Non-uniform mesh, 10,916 nodes |
| Selimefendigil & Öztop [83] | FEM, FSI, ALE | Triangular cavity | 2D, natural convection, steady | 104 ≤ Ra ≤ 106, 104 ≤ Rai ≤ 107, 0 ≤ Ha ≤ 40, 0 ≤ ≤ 90, Pr = 7.1, 5 102 ≤ E ≤ 105 | - |
| Selimefendigil et al. [84] | FEM, NR | Lid-driven square cavity | 2D, Mixed convection | 10−2 ≤ Ri ≤ 102, 0 ≤ Ha ≤ 50, 0 ≤ ≤ 90, 0 ≤ ≤ 0.05, CuO-H2O nanofluid | Non-uniform,. 17,408 elements |
| Sojoudi et al. [85] | FVM, QUICK, SIMPLE | Triangular cavity | 2D, unsteady, natural convection | 103 ≤ Ra ≤ 106, 0.2 ≤ A ≤ 1.0, Pr = 0.72 | 15,600 triangular elements |
| Sojoudi et al. [86] | FVM, QUICK, SIMPLE | Triangular cavity | 2D, unsteady, natural convection | 103 ≤ Ra ≤ 106, 0.2 ≤ A ≤ 1.0, Pr = 0.71 | 360 75, 360 90, 360 120 for A = 0.2, 0.5, 1 |
| Aparna & Seetharamu [87] | FEM | Porous trapezoidal cavity | 2D, natural convection | 100 ≤ Ra ≤ 2000 | 41 41 |
| Alsabery et al. [88] | COMSOL, FEM | Trapezoidal cavity | 2D, unsteady, non-Newtonian, laminar | 104 ≤ Ra ≤ 106, 0 ≤ ≤ 0.2, 0.1 ≤ Pr ≤ 103, 0 ≤ ≤ 21.8, H2O based TiO2, Cu, Al2O3, Ag nanofluids | Non-uniform, 4690 elements |
| Al-Weheibi et al. [89] | COMSOL, FEM | Trapezoidal enclosure | 2D, natural convection, unsteady, laminar | 103 ≤ Ra ≤ 106, 0 ≤ ≤ 0.1, 0.25 ≤ A ≤ 1.0 | 6-noded 403,388 elements, 204,436 grids |
| Balla et al. [90] | FEM | Inclined porous square cavity | 2D, free convection, laminar | 0.01 ≤ ≤ 0.3, 101 ≤ Ra ≤ 103, 0 ≤ M ≤ 10, 0 ≤ ≤ 90, H2O based TiO2, Cu, Al2O3, SiO2 nanofluids | 6-noded triangular grid, 5000 elements, 2601 nodes |
| Cui et al. [91] | FVM | Prismatic enclosure | 3D, unsteady, natural convection | 100 ≤ Ra ≤ 106, Pr = 0.71 | Non-uniform grid, 100 66 45 |
| Das et al. [92] | FEM | Square & triangular cavities | 2D, steady, laminar | Pr = 0.7, 103 ≤ Ra ≤ 105 | 34 34 biquadratic elements |
| Gangawane [93] | Fluent, FVM, SIMPLE, QUICK | Lid-driven cavity with triangular block | 2D, steady, laminar, mixed convection | 1 ≤ Re ≤ 103, 0 ≤ Gr ≤ 105, Pr = 1, 50, 102, b = 10%, 20%, 30% | Unstructured, non-uniform, 26,318 nodes, 9126 elements |
| Ghalambaz et al. [94] | FEM, FSI, ALE | Square cavity with oscillating elastic fin | 2D, natural convection, laminar, unsteady | Pr = 0.7, 104 ≤ Ra ≤ 107, 10−3 ≤ Am ≤ 0.1, 1 ≤ Tr ≤ 103, 108 ≤ E ≤ 1013 | 27,131 domain elements, 1022 boundary elements |
| Gibanov et al. [95] | FDM | Lid-driven square cavity with block | 2D, steady, laminar, mixed convection | 10−2 ≤ Ri ≤ 10, 0 ≤ ≤ 0.05, Re = 102, Pr = 6.82, Al2O3-H2O nanofluid | Uniform grid, 200 200 |
| Gibanov et al. [96] | FDM | Lid-driven inclined square cavity | 2D, unsteady, mixed convection | Ri =1, Re = 102, Pr = 6.26, Da = 10−7, 10−3, 0 ≤ Ha ≤ 102, 0 ≤ ≤ 0.05, 0 ≤ ≤ , ferrofluid | Uniform grid, 200 200 |
| Hammami et al. [97] | FVM, QUICK, RBSOR | Double lid-driven cubic cavity with cylinder | 3D, unsteady | 102 ≤ Re ≤ 1500, Pr | Staggered grid non-uniform, 80 80 80 |
| Hatami [6] | FEM, FlexPDE | Rectangular cavity with heated fins | 2D, steady | 0.03 ≤ ≤ 0.09, H2O based TiO2, Al2O3 nanofluids | - |
| Hatami et al. [98] | FEM, RSM, FlexPDE | Lid-driven T-shaped porous cavity | 2D, steady, mixed convection | Ri = 0.1, Re = 50, Da = 0.001, H2O based TiO2, Cu, Al2O3 nanofluids | - |
| Hussain et al. [99] | FEM, GE, CN | Double lid-driven square cavity | 2D, steady, mixed convection | 1 ≤ Re102, 0 ≤ ≤ 45, 0.01 ≤ Ri ≤ 10, 0 ≤ ≤ 0.04, Al2O3-H2O nanofluid | Uniform grid, 65,536 elements |
| Javed et al. [100] | FEM | Trapezoidal porous cavities | 2D, free convection, steady | Pr = 6.2, 10−5 ≤ Da ≤ 10−3, 105 ≤ Ra ≤ 107, 0 ≤ Ha ≤ 60, 0 ≤ ≤ 0.03, Cu-H2O nanofluid | 6 noded 704 elements, 1000 grids |
| Kareem & Gao [101] | Fluent, LES, URANS, SIMPLEC, QUICK | Lid-driven cubic cavity with cylinder | 3D, unsteady, mixed convection, turbulent | Pr, Re = 5000, 10,000, 15,000, 30,000, 0 ≤ ≤ 10 | Structured, non-uniform cells, 929,160 elements |
| Khanafer & Aithal [102] | ADINA, FEM | Lid-driven square cavity with cylinder | 2D, steady, laminar, mixed convection | 0.01 ≤ Ri ≤ 10, Re = 100, −10 ≤ ≤ 10 | 150 150 |
| Khatamifar et al. [103] | DNS, SIMPLE, QUICK | Rectangular cavity with partition | 2D, natural convection, unsteady | 105 ≤ Ra ≤ 109, Pr = 0.71, 0.05 ≤ Tp ≤ 0.2 | Non-uniform mesh, 300 250 |
| Mojumder et al. [104] | FEM | Lid-driven L-shaped cavity | 2D, mixed convection, laminar, steady | 1 ≤ Re ≤ 100, 103 ≤ Gr ≤ 105, 10−5 ≤ Da ≤ 10−3, Pr = 6.2 | Triangular mesh, 4452 elements |
| Selimefendigil et al. [105] | FEM, ALE, FSI | Lid-driven square cavity | 2D, steady | 0.01 ≤ Ri ≤ 5, 0 ≤ Ha ≤ 50, 102 ≤ Re ≤ 103, CuO-H2O nanofluid | Triangular elements, 17,224 grids |
| Selimefendigil et al. [106] | FEM, ALE, NR | Lid-driven Trapezoidal cavity with cylinder | 3D, steady, laminar, mixed convection | 0.5 ≤ Ri ≤ 50, 0 ≤ ≤ 20, 0 ≤ ≤ 0.04, 103 ≤ E ≤ 105, CuO-H2O nanofluid | Tetrahedral elements |
| Selimefendigil & Öztop [107] | FEM, FSI, ALE | Lid-driven triangular cavity | 2D, mixed convection, steady | 0.05 ≤ Ri ≤ 50, 0 ≤ ≤ 0.04, Pr = 6.8, 104 ≤ RaI ≤ 108, 500 ≤ E ≤ 105, H2O–CuO nanofluid | Non-uniform grid, 26,306 elements |
| Sheremet et al. [108] | FDM | Triangular cavities | 2D, natural convection | Pr = 0.7, 104 ≤ Ra ≤ 2 105, 102 ≤ Le ≤ 104, 0 ≤ N ≤ 5, Nb = Nt = 0.1 | Uniform grid, 300 150 |
| Yu et al. [3] | FDM, UCS, TVD, RK | Rectangular cavity | 2D, unsteady, laminar | Pr = 0.025, A = 2, 0 ≤ Ha ≤ 50, 0 ≤ Le ≤ 20 | Uniform grid, 41 81 |
| Aghakhani et al. [109] | FDLBM | C-shaped cavity | 2D, laminar, non-Newtonian | 103 ≤ Ra ≤ 105, 0 ≤ Ha ≤ 40, 0.2 ≤ A ≤ 0.6 | 160 160 |
| Astanina et al. [110] | FDM | Lid-driven square porous cavity | 2D, steady, mixed convection | 0.01 ≤ Ri ≤ 10, 0 ≤ ≤ 0.04, 10−7 ≤ Da ≤ 10−3, Da2 = 10−5, Re = 102, Pr = 6.82, H2O–Al2O3 nanofluid | Uniform grid, 200 200 |
| Alsabery et al. [111] | FEM, FEA, NR | Double lid-driven square cavity with block | 2D, steady, laminar, mixed convection | 1 ≤ Re ≤ 500, 10−2 ≤ Ri ≤ 102, 0 ≤ ≤ 0.04, Pr = 4.623, Le = 3.5 105, Sc = 3.55 104, H2O–Al2O3 nanofluid | Uniform triangular grid, 12,232 grids |
| Balootaki et al. [112] | LBM-BGK | Lid-driven rectangular cavity with block | 2D, mixed convection | 10−2 ≤ Ri ≤ 50, Re = 100, Pr = 0.7 | 450 150 |
| Bhowmick et al. [113] | FEM, SIMPLE, QUICK | V-shaped cavity | 2D, natural convection | 2.26 105 ≤ Ra ≤ 2.26 109, 0.1 ≤ A ≤ 1.0, Pr = 6.63 | Non-uniform, 800 150 |
| Cho [114] | FVM, TDMA, SIMPLE | Lid-driven cavity with wavy surface | 2D, steady, laminar, mixed convection | 10−2 ≤ Ri ≤ 102, 0 ≤ ≤ 0.04, 1 ≤ Re ≤ 200, Pr = 6.2, 0 ≤ Am ≤ 0.6, H2O–Cu nanofluid | 101 1001 |
| Gangawane et al. [115] | Fluent, FVM, SIMPLE, QUICK | Lid-driven square cavity with block | 2D, steady, laminar, mixed convection | Ri= 0.01, 1, 10, Pr= 1, 1 ≤ Re ≤ 103 | Unstructured, 17,874 nodes, 17,598 elements |
| Gibanov et al. [116] | FDM | Lid-driven square cavity | 2D, mixed convection, laminar, unsteady | 10−2 ≤ Ri ≤ 10, 0 ≤ ≤ 0.05, 1.0 ≤ K ≤ 20.0, Re = 100, Pr = 6.82, H2O–Al2O3 nanofluid | Uniform grid, 100 100 |
| Hussain et al. [117] | FEM, CN, GE | Double lid-driven square cavity | 2D, laminar, unsteady, mixed convection | 0 ≤ ≤ 0.04, 10−2 ≤ Ri ≤ 10, 0 ≤ Ha ≤ 102, 0 ≤ ≤ 90, H2O–Al2O3 nanofluid | Non-uniform triangular grid, 65,536 elements |
| Javed & Siddiqui [118] | FEM | Square cavity with square blockage | 2D, free convection, steady, laminar | 105 ≤ Ra ≤ 107, Pr = 0.062, 0 ≤ ≤ 0.06, 0 ≤ Ha ≤ 60, H2O–Cobalt ferrofluid | Non-uniform, 6-noded 1776 elements |
| Karbasifar et al. [119] | SIMPLEC | Lid-driven cubic cavity with cylinder | 3D, laminar, steady, mixed convection | 10−2 ≤ Ri ≤ 102, = 0, 0.1%, 0.2%, = 0, 15, 45, H2O–Al2O3 nanofluid | - |
| Kareem & Gao [120] | Fluent, URANS, SIMPLEC, QUICK | Lid-driven Cubical cavity with cylinder | 3D, mixed convection, unsteady, turbulent | 5000 ≤ Re ≤ 104, −5 ≤ Ω ≤ 5, SiO2-H2O nanofluid | 929,160 grids |
| Mikhailenko et al. [121] | FDM, CDS, Thomas, SOR | Rotating square cavity with obstacle | 2D, laminar, unsteady | Pr = 0.7, Ra = 105, 0 ≤ ≤ 180, 0 ≤ Ta ≤ 106, 0.1 ≤ Os ≤ 1.0, 0.0 ≤ ε ≤ 0.9 | 101 101 |
| Oglakkaya & Bozkaya [122] | DRBEM | Lid-driven square cavity | 2D, mixed convection, unsteady, laminar | Pr = 0.71, Re = 102, Am = 0.05, Ha = 0, 25, 50, 0 ≤ ≤ 90, J = 0, 1, 3, 5, 103 ≤ Ra ≤ 105 | 400 grids |
| Razera et al. [123] | Fluent, FVM, SIMPLEC | Lid-driven square cavity | 2D, steady, laminar, mixed convection | 101 ≤ Re ≤ 103, 103 ≤ Ra ≤ 106, Pr = 0.71 | Non-uniform, 33,248 volumes |
| Selimefendigil & Öztop [124] | FEM, COBYLA | Lid-driven trapezoidal cavity | 2D, mixed convection | 0.01 ≤ Ri ≤ 25, 0 ≤ Ha ≤ 40, 0 ≤ ≤ 90, 0 ≤ ≤ 0.03, H2O–Al2O3 nanofluid | 6282, 4685 and 3691 elements for different |
| Sheikholeslami [125] | LBM | Lid-driven square cavity with hot sphere | 3D, forced convection | 10−3 ≤ Da ≤ 102, 30 ≤ Re ≤ 180, 0 ≤ Ha ≤ 40, H2O–Al2O3 nanofluid | 81 81 81 |
| Sheremet et al. [126] | FDM | Porous square vented cavity | 2D, mixed convection, unsteady | 104 ≤ Ra ≤ 106, Nb = Nt = 10−6, 10−5 ≤ Da ≤ 10−2, 50 ≤ Re ≤ 300, Pr = 6.82, Le = 103, N = 1, H2O–Al2O3 nanofluid | Uniform grid, 201 201 |
| Taghizadeh & Asaditaheri [127] | OpenFOAM, FVM. SIMPLE | Lid-driven square cavity with cylinder | 2D, laminar, mixed convection | 0.01 ≤ Ri ≤ 10, 10−5 ≤ Da ≤ 10−2, 0 ≤ ≤ 90, Re = 100, Pr = 0.7 | Non-uniform, 11,200 |
| Zhai et al. [128] | FVM, SIMPLE, QUICK | Triangular Roof | 2D, unsteady, natural convection | 104 ≤ Ra ≤ 107, 0.1 ≤ A ≤ 1.0, Pr = 0.71 | Non-uniform mesh, 600 600 |
| Zhou et al. [129] | LBM, OpenMP | Double lid-driven cubic cavity | 3D, mixed convection, laminar, unsteady | 0.1 ≤ Ri ≤ 102, 0 ≤ ≤ 0.04, H2O–Al2O3 nanofluid | 101 101 101 |
| Alnaqi et al. [130] | FDM | Square cavity with a fin | 2D, laminar, steady | 0 ≤ Ha ≤ 60, 103 ≤ Ra ≤ 106, 0 ≤ Rd ≤ 3, 0 ≤ ≤ 0.06, H2O–Al2O3 nanofluid | Uniform grid. 120 120 |
| Al-Rashed et al. [131] | FVM, SIMPLEC | Inclined lid-driven cubical cavity | 3D, steady, mixed convection, laminar | Re, Gr, Pr, 1 ≤ Ri ≤ 102, 0 ≤ ≤ 45, H2O–Al2O3 nanofluid | - |
| Barnoon et al. [132] | FVM, SIMPLE | Lid-driven square cavity with cylinders | 2D, steady, laminar, mixed convection | 0 ≤ Ha ≤ 30, 1 ≤ Ri ≤ 102, 0 ≤ ≤ 90, 0.01 ≤ ≤ 0.03, H2O–Al2O3 nanofluid | Non-uniform grid, 19,297 elements |
| Bhowmick et al. [133] | Fluent, FVM, SIMPLE | V-shaped triangular cavity | 2D, natural convection, unsteady | 1 ≤ Ra ≤ 108, A = 0.5, Pr = 0.71 | 800 150 |
| Cho [134] | FVM, SIMPLE, TDMA | Lid-driven cavity with wavy wall | 2D, laminar, mixed convection | 1 ≤ Re ≤ 300, 0 ≤ Ha ≤ 50, 10−2 ≤ Re ≤ 102, 0 ≤ Am ≤ 0.7, 0 ≤ ≤ 0.04, 0 ≤ ≤ 360, Cu-H2O nanofluid | Non-uniform grid, 101 1001 |
| Cui et al. [135] | FVM | Prismatic enclosure | 3D, unsteady, natural convection | 100 ≤ Ra ≤ 107, Pr = 0.71, 0.1 ≤ A ≤ 1.5 | Non-uniform mesh, 138 42 51 |
| Hadavand et al. [136] | FVM, SIMPLEC | Lid-driven sim-circular cavity | 2D, mixed convection, laminar, steady | 1 ≤ Ri ≤ 10, = −90 to 90, 0 ≤ ≤ 0.06, Ag-H2O nanofluid | Unorganized triangular grid, 44,896 grids |
| Hamid et al. [137] | FEM | Trapezoidal cavity | 2D, steady, non-Newtonian, natural convection, laminar | 104 ≤ Ra ≤ 105.5, Pr = 20 | - |
| Jiang & Zhou [4] | FVM, QUICK, CDS, PISO | Rectangular cavity | 2D, steady, laminar | 0 ≤ ≤ 0.25, dp = 13, 36, 50 nm, distilled H2O-Al2O3, PGW-ZnO nanofluids | Non-uniform orthogonal grid, 200 50 |
| Karatas & Derbentli [138] | Experimental research | Rectangular cavity | 3D, unsteady | 4.5 103 ≤ Rai ≤ 1.13 108, A = 1, 2.09, 3, 4, 5, 6 | - |
| Lamarti et al. [139] | LBM | Lid-driven square cavity | 2D, mixed convection, laminar | Pr = 0.71, 102 ≤ Re ≤ 103, 102 ≤ Gr ≤ 106, 1 ≤ ≤ 5 | 100 100 |
| Louaraychi et al. [140] | FVM, SIMPLER, TDMA | Double lid-driven rectangular cavity | 2D, unsteady, mixed convection | 1 ≤ Ra ≤ 107, 0.1 ≤ Pe ≤ 500, A = 24 | Uniform grid, 381 121 |
| Mohebbi et al. [141] | LBM | Γ-shaped enclosure with obstacle | 2D, natural convection, steady, laminar | 103 ≤ Ra ≤ 106, 0 ≤ ≤ 0.05, 0.2 ≤ A ≤ 0.6, Al2O3-H2O nanofluid | 100 100 |
| Selimefendigil & Öztop [142] | FEM, ALE, NR | Lid-driven L-shaped cavity | 2D, steady, mixed convection | 0.03 ≤ Ri ≤ 30, 0 ≤ ≤ 180, 104 ≤ RaI ≤ 106, 0 ≤ Ha ≤ 50, CuO-H2O nanofluid | Non-uniform, 19,112 elements |
| (c) | |||||
| Ref. | CFD Methods and Algorithms | Flow Domain | Dimension, Type of Flow | Parameters and Ranges | Meshing |
| Abu-Hamdeh et al. [143] | FVM, SIMPLE, CDS, UDS, TDMA | Lid-driven porous square open cavity | 2D, mixed convection, steady | 102 ≤ Re ≤ 103, 10−3 ≤ Da ≤ 0.1, 103 ≤ Gr ≤ 105 | Staggered grid, 48 48 |
| Afrand et al. [144] | SIMPLE | Triangular cavity | 2D, free convection, laminar, steady | 104 ≤ Ra ≤ 106, 0 ≤ Ha ≤ 40, 0 ≤ ≤ 90, 0 ≤ ≤ 0.06, Al2O3-H2O nanofluid | Staggered grid |
| Alsabery et al. [145] | FEM | Lid-driven square cavity | 2D, mixed convection, steady, laminar | 1 ≤ Re ≤ 500, 0.01 ≤ Ri ≤ 100, 0 ≤ Ha ≤ 50, 0 ≤ ≤ 0.04, Al2O3-H2O nanofluid | Triangular grid, 6402 elements |
| Alsabery et al. [146] | FEM | Lid-driven cubic cavity with cylinder | 3D, mixed convection, steady | Re = 10, 100, Pr = 4.623, 10−2 ≤ Ri ≤ 102, 0 ≤ ≤ 0.04, Le = 3.5 105, Sc = 3.55 104, Al2O3-H2O nanofluid | Non-uniform triangular grid, 175,778 elements |
| Bilal et al. [147] | FEM | Triangular cavity with cylinder | 2D, laminar, steady, free convection | 103 ≤ Ra ≤ 106, 0.2 ≤ Pr ≤ 7 | Hybrid grid |
| Cho [148] | FVM, SIMPLE, TDMA | Square cavity with wavy walls | 2D, natural convection, steady, laminar | Pr = 6.2, 102 ≤ Ra ≤ 106, 10−6 ≤ Da ≤ 10−2, 0 ≤ ≤ 0.04, Cu-H2O nanofluid | 101 1001 |
| Ganesh et al. [149] | FEM | Square Cavity with different obstacles | 2D, steady, laminar | 103 ≤ Ra ≤ 106, 0 ≤ ≤ 0.08, 103 ≤ RaE ≤ 106, 103 ≤ RaI ≤ 105 Al2O3-H2O/Ethylene Glycol nanofluid | Circular: 6979 elements, Square: 21,916 elements, Triangular: 19,431 elements |
| Haq et al. [150] | FEM | Lid-driven hexagonal cavity with obstacle | 2D, steady | 200 ≤ Re ≤ 500, Pr = 6.2, 10−6 ≤ Ri ≤ 1, 0 ≤ Ha ≤ 20, SWCNT-H2O nanofluid | Non-uniform triangular elements |
| Khan et al. [151] | FEM | Porous trapezoidal cavity | 2D | Pr = 6.2, 102 ≤ Ha ≤ 104, 104 ≤ Ra ≤ 105, 0 ≤ ≤ 0.2%, Fe3O4-H2O ferrofluid | - |
| Li et al. [152] | FDLBM | Triangular enclosure | 2D, laminar, non-Newtonian, steady | 103 ≤ Ra ≤ 105, 0 ≤ Ha ≤ 60, 0 ≤ ≤ 90 | 160 160 or 19,600 nodes |
| Liu & Huang [153] | DNS, QUICK, SIMPLE, CDS | Rectangular cavities with or without fins | 2D, unsteady, turbulent | 1.15 108 ≤ Ra ≤ 3.68 109 | Non-uniform grid, 400 360 cells |
| Rammane et al. [154] | TS, MLS, NR, HO-MFA | Lid-driven square cavity | 2D, steady | 102 ≤ Re ≤ 2 104 | Mesh free |
| Saha et al. [155] | FVM, SIMPLE, QUICK | Triangular enclosure | 2D, unsteady, natural convection | Pr = 0.72, 105 ≤ Ra ≤ 109, 0.2 ≤ A ≤ 1.0 | 380 80, 380 100, 380 160 for A = 0.2, 0.5, 1 |
| Selimefendigil & Öztop [156] | FVM, QUICK, SIMPLE | U-shaped corrugated cavity | 2D, forced convection, laminar, steady | 102 ≤ Re ≤ 103, 0 ≤ Ha ≤ 50, 10−4 ≤ Da ≤ 5 10−2, CNT-H2O nanofluid | Non-uniform grid, 38,874 grids |
| Soomro et al. [157] | FEM | Lid-driven Triangular cavity with obstacle | 2D, mixed convection, laminar, steady | 200 ≤ Re ≤ 600, 0.01 ≤ Ri ≤ 1, 0 ≤ Ha ≤ 20, Pr = 6.2 | Around 5000 nodes |
| Thiers et al. [158] | SEM, NeK5000, GMRES | Rectangular cavity | 2D, unsteady | A = 4, Pr = 0.71, Ra = 9 107 | 183 169 |
| Aljabair et al. [159] | FDM, CDS, UDS, SOR | Sinusoidal lid-driven cavity | 2D, mixed convection, laminar | 1 ≤ Re ≤ 1000, 0 ≤ Ra ≤ 107, 0 ≤ ≤ 0.07, Cu-H2O nanofluid | 41 41 |
| Alsabery et al. [160] | FEM | Wavy lid-driven square cavity | 2D, laminar, steady, mixed convection | 0.01 ≤ Ri ≤ 10, Re = 100, 0 ≤ ≤ 0.04, H2O/Cu-Al2O3 hybrid nanofluid | - |
| Çolak et al. [161] | OpenFOAM, FVM, SIMPLE | Lid-driven cavity with porous block | 2D, mixed convection, steady | 10−1 ≤ Ri ≤ 10, Gr = 105, 10−7 ≤ Da ≤ 10−1, Pr = 6.2 | Uniform grid, 201 201 |
| Eshaghi et al. [162] | FEM | H-shaped cavity with a baffle inside | 2D, natural convection, laminar | 104 ≤ Ra ≤ 106, 2 ≤ Le ≤ 8, 1 ≤ N ≤ 3, −60 ≤ . ≤ 60, Cu-Al2O3-H2O hybrid nanofluid | - |
| Fayz-Al-Asad et al. [163] | FEM | Triangular cavity | 2D, natural convection, steady | Pr = 0.71, 104 ≤ Ra ≤ 106 | 6718 elements, 13,112 nodes |
| Hasnaoui et al. [164] | LBM, MRT, BGK | Rectangular cavity | 2D, biry mixture | Sr = −0.5, 0, 0.5, 0 ≤ Ra ≤ 80, Pr = 0.71, A = 2, Le = 2 | 120 240 |
| Hussain et al. [165] | FEM | Double lid-driven cavity with fins | 2D, laminar, steady | 0 ≤ Ha ≤ 100, 0 ≤ ≤ 90, 0.01 ≤ Ri ≤ 1, Pr = 6.2, Re = 100, = 0.02, Cu-H2O nanofluid | 33,177 grids |
| Hoston et al. [166] | IEFG–RIPM | Lid-driven square cavity | 2D, steady | Re = 10,000, 15,000, 20,000, 25,000, 30,000 and 35,000 | 150 150 (Refined at cavity walls) |
| Ibrahim & Hirpho [167] | COMSOL, FEM | Trapezoidal cavity | 2D, mixed convection, laminar | Ha = 0, 50, Ri = 0.1, 1, 10, Re = 100, Am = 0.25, 0.5, 1 | 91 91 |
| Ikram et al. [168] | FEM, ALE | Hexagonal cavity with rotating modulator | 2D, forced convection, unsteady, laminar | Pr = 0.71, 102 ≤ Re ≤ 103, 103 ≤ Bi ≤ 104, 103 ≤ Ra ≤ 107 | Non-uniform, 48,548 elements |
| Joe & Perumal [169] | OpenFOAM, FVM | Rectangular cavity containing cylinders | 2D, unsteady | Pr = 0.72, Re = 1600 | Unstructured triangular cells |
| Mondal & Mahapatra [170] | FDM, BiCGStab | Trapezoidal cavity | 2D, mixed convection, steady, laminar | Pr = 6.2, N = 5, 0.5 ≤ A ≤ 2, 10−2 ≤ Ri ≤ 102, 102 ≤ Re ≤ 103, 45 ≤ ≤ 90, 0 ≤ ≤ 0.5, 20 ≤ Ha ≤ 40, 1 ≤ Le ≤ 2, Al2O3-H2O nanofluid | 81 81 |
| Mebarek-Oudina et al. [171] | FEM | Trapezoidal porous cavity with zigzag wall | 2D, laminar, steady | 0 ≤ Ha ≤ 100, 0 ≤ ≤ 90, 103 ≤ Ra ≤ 105, 0 ≤ ≤ 0.08, Cu-Al2O3/H2O hybrid nanofluid | Triangular grid, 20,296 elements |
| Saha et al. [172] | FVM | Rectangular cavity with baffles | 2D, laminar, steady | 50 ≤ Re ≤ 250 Ri = 0, 2, 4 | 45 51 |
| Saha et al. [173] | FVM, SIMPLE, QUICK | Triangular cavity | 2D, natural convection | Pr = 0.72, 103 ≤ Ra ≤ 106, A = 0.2, 0.5, 1.0 | 360 75, 360 90, 360 120 for A = 0.2, 0.5, 1 |
| Shah et al. [174] | FEM, NR | Lid-driven trapezoidal cavity with obstacle | 2D, mixed convection, steady, laminar | 10−2 ≤ Ri ≤ 10, 0.1 ≤ Le ≤ 10, 300 ≤ Re ≤ 500, −10 ≤ N ≤ 10, Pr = 0.71 | Non-uniform, approx. 3200 elements |
| Shahid et al. [175] | MRT-LBM | Triangular lid driven cavity | 2D, mixed convection, unsteady | Pr = 0.71, 1, 7, 10−2 ≤ Ri ≤ 102, 104 ≤ Gr ≤ 107 | - |
| Shahid et al. [176] | MRT-LBM | Lid-driven rectangular cavity with obtacles | 2D, mixed convection, laminar | Pr = 0.71, 1, 7, 10−2 ≤ Ri ≤ 102, 103 ≤ Gr ≤ 106, A = 0.2, 0.5, 2, 5 | Not clearly mentioned for different A |
| Shekaramiz et al. [177] | OpenFOAM, FVM, SIMPLE | Wavy triangular cavity | 2D, free convection, steady | 5 103 ≤ Ra ≤ 2 105, Pr = 4.6, 0 ≤ Ha ≤ 50, 0 ≤ ≤ 90, = 2%, H2O-Fe3O4 nanofluid | 16,000 and 12,000 nodes |
| Tizakast et al. [178] | FVM, SIMPLER | Lid-driven rectangular cavity | 2D, laminar, unsteady, non-Newtonian | RaT ≤ 5 106, Pe ≤ 103, 10−3 ≤ Le ≤ 103, 10−3 ≤ N ≤ 103, 0.6 ≤ n ≤ 1.4 | Uniform grid, A = 24:381 121 |
| Velkennedy et al. [179] | FDM, ADI, CDS | Rectangular vented cavity | 2D, laminar, unsteady | 103 ≤ Ra ≤ 106, Pr = 0.71 | 181 121 |
| Xiong et al. [180] | FEM | Lid-driven triangular cavity | 2D, mixed convection | Pr = 6.2, 0 ≤ Ha ≤ 40, 0 ≤ Re ≤ 103, 0.01 ≤ Ri ≤ 2 | Uniform triangular mesh |
| Abbas et al. [181] | FEM | Square cavity with obstacles | 2D, steady, laminar | 0 ≤ ≤ 0.04, 10 ≤ Ha ≤ 40, 103 ≤ Ra ≤ 107, Cu-H2O nanofluid | 59,173 elements |
| Ahmed et al. [182] | Coiflet wavelet-homotopy method | Lid-driven square porous cavity | 2D, unsteady | Pr = 6.2, 10 ≤ Ri ≤ 102, 10−4 ≤ Da ≤ 10−1, 3 ≤ Le ≤ 106, Al2O3-Cu/H2O hybrid nanofluid | - |
| Alam et al. [8] | FEM | Semi-circular cavity | 2D, unsteady, semi-circular cavity, free convection | Pr = 23.0, 6.84, 1 ≤ dp ≤ 10, 0 ≤ ≤ 0.05, 0 ≤ Ha ≤ 100, 104 ≤ RaT ≤ 106, ZnO, Fe3O4, Co, Al2O3, Ag nanoparticles, H2O & kerosene as base fluids | 15,817 elements |
| Ali et al. [183] | Comsol, FEM | Lid-driven square cavity | 2D, mixed convection, steady | Re = 1, 10, 102, Ha = 0, 10, 25, = 0, 1%, 5%, Pr = 6.2, Gr = 102, Al2O3-H2O nanofluid | Non-uniform, 30,550 nodes, 60,036 elements |
| Alqaed et al. [5] | FVM, SIMPLE | Rectangular cavity with triangular blades | 2D, steady, laminar | 103 ≤ Ra ≤ 105, 0 ≤ Ha ≤ 30, = 0.3, Al2O3-H2O nanofluid | 150 450 |
| Acharya & Chamkha [184] | FEM | Hexagonal cavity with parallel fins | 2D, laminar, steady | 103 ≤ Ra ≤ 105, 0 ≤ Ha ≤ 100, 0 ≤ ≤ 0.04, Pr = 6.2, Al2O3-H2O nanofluid | Non-uniform, 34,502 elements |
| Batool et al. [185] | FVM, SIMPLE | Lid-driven square cavity | 2D, steady, laminar | 100 ≤ Re ≤ 400, micropolar nanofluids | Staggered grid |
| Charqui et al. [186] | FVM, SIMPLE, TDMA | Tall partitioned cavity | 2D, natural convection, laminar | Pr = 0.71, 7, A = 40 | Uniform mesh, 80 200 |
| Cui et al. [187] | FVM, SIMPLE | Triangular cavity | 3D, natural convection, unsteady | Pr = 0.7, 102 ≤ Ra ≤ 107, 0.1 ≤ A ≤ 1.5 | Non-uniform mesh, 141 41 51 |
| Dahani et al. [188] | LBM, MRT, BGK operator | Double lid-driven square cavity | 2D, unsteady | 0 ≤ ≤ 180, Re = 102, 10−2 ≤ Ri ≤ 102, 102 ≤ Gr ≤ 106, Pr = 0.71 | Uniform grid, 160 160 |
| Esfe et al. [9] | Fluent, FVM, SIMPLE | U-shaped porous enclosure | 2D, steady | 103 ≤ Ra ≤ 105, 0 ≤ ≤ 0.03, Al2O3-H2O nanofluid | Approx 1600 cells |
| Geridonmez & Oztop [10] | Rbf-Pum | Right Isosceles triangular cavity | 2D, natural convection, steady, laminar | 0 ≤ Ha ≤ 100, 0.25 ≤ A ≤ 1, Pr = 6.07, Ra = 105, 0 ≤ ≤ 0.02, Al2O3-Cu/H2O nanofluid | 1,842,025 & 1,741,596 nodes |
| Hirpho & Ibrahim [189] | FEM | Trapezoidal enclosure | 2D, mixed convection, non-Newtonian, steady, laminar | 10−1 ≤ Ri ≤ 102, Re = 100, Pr = 20, 0 ≤ ≤ 0.02, Al2O3-Cu/H2O hybrid nanofluid | 201 201 |
| Khalil et al. [190] | Fluent, FVM, RSM | Porous trapezoidal cavity with wavy wall | 2D, steady | 0 ≤ Ha ≤ 40, 0 ≤ Am ≤ 20, 5 102 ≤ Ra ≤ 2.4 104 | 320 320 |
| Liu [191] | CDS, SIMPLE, QUICK | Rectangular cavity with fins | 2D, free convection, unsteady | 0 ≤ ≤ 40, Ra = 1.84 109 | 360 400 |
| Noor et al. [192] | FEM | Lid-driven trapezoidal cavity with obstacle | 2D, forced convection, steady | 102 ≤ Re ≤ 700, 10−3 ≤ Ri ≤ 10, 0 ≤ Ha ≤ 102 | Trangular grid, 4622 nodes. 8929 elements |
| Nouraei et al. [193] | FVM, SIMPLE | Semi-circular vented cavity | 2D, mixed convection, laminar, steady | 10 ≤ Re ≤ 100, 0 ≤ ≤ 0.06, Cu-H2O nanofluid | 52,000 grids |
| Polasanapalli & Anupindi [194] | LBM | Concentric circular annular cavity | 2D, mixed convection, unsteady | 104 ≤ Ra ≤ 106, 0 ≤ Re ≤ 104, Pr = 0.71, 0 ≤ ≤ 360, 10−3 ≤ Ri ≤ 103 | 120 120, 180 180 |
| Prince et al. [195] | COMSOL, FEM | Trapezoidal cavity with different surface | 2D, natural convection | Pr = 0.716, 103 ≤ Ra ≤ 106, Materials: Pinewood, plexiglas, dry concrete, glass fiber | Rectangle: 6112, Triangle: 10,191, Sinusoidal: 5993 elements |
| Rahaman et al. [196] | Fluent, FVM, CDS, SIMPLE | Trapezoidal cavity | 2D, unsteady, natural convection | Pr = 0.71, 100 ≤ Ra ≤ 108, A = 0.5 | Non-uniform, 300 100 |
| Roy et al. [197] | FEM | Square enclosure with blocks | 2D, unsteady, natural convection | Pr = 6.2, 0 ≤ Rd ≤ 3, 0 ≤ ≤ 0.09, 104 ≤ Ra ≤ 106, 0 ≤ Ha ≤ 60, Cu- Al2O3/H2O hybrid nanofluid | Triangular 65,740 elements |
| Shah et al. [198] | FEM, NR | Lid-driven corrugated porous cavity | 2D, mixed convection, laminar, steady | 102 ≤ Re ≤ 400, 0 ≤ ≤ 0.05, 10−5 ≤ Da ≤ 10−1, Pr = 6.2, 10−2 ≤ Ri ≤ 100, CuO-H2O nanofluid | Approx 8000 elements |
| Tizakast et al. [199] | FVM, SIMPLE | Lid-driven Rectangular cavity | 2D, unsteady non-Newtonian, laminar | 2 ≤ A ≤ 30, 102 ≤ RaT ≤ 107, 10−3 ≤ Le ≤ 103, 0.1 ≤ Pe ≤ 104 | - |
| Xia et al. [200] | UPWIND | T-shaped lid-driven cavity | 2D, mixed convection | 0 ≤ ≤ 0.03, 0.1 ≤ Re ≤ 10, 0.2 ≤ A ≤ 0.4, Al2O3-H2O nanofluid | Uniform mesh, 250,000 cells |
| Zarei et al. [201] | FVM, SIMPLE | Square cavity with wavy walls | 2D, steady | Ra = 104, 0 ≤ Am ≤ 0.15, 0 ≤ ≤ 0.04, Cu-H2O nanofluid | 135,008 triangular cells |
| Zhang et al. [202] | FVM, SIMPLE | Semi-elliptic lid-driven cavity | 2D, mixed convection, steady, laminar | 0 ≤ ≤ 0.06, Gr = 5 104, 15 104, 25 104, 4 105, 10−1 ≤ Ri ≤ 10, Pr = 6.2, Ag-H2O nanofluid | 43,905 triangular grids |
| Akhter et al. [7] | FEM | square cavity with cylinder | 2D, steady | 104 ≤ Ra ≤ 5 106, Pr = 6.2, 0 ≤ ≤ 0.05, 0 ≤ Ha ≤ 102, Cu-Al2O3/H2O hybrid nanofluid | 24,961 nodes, 49,188 elements |
| He et al. [203] | Experimental, FVM, SIMPLE | Cubic cavity | 3D | 0 ≤ B ≤ 133, 0 ≤ ≤ 0.03, 6.9 105 ≤ Ram ≤ 11.6 105, Fe3O4-Paraffin nanofluid | 50 50 50 |
| Ikram et al. [204] | FEM, ALE | Hexagonal cavity with rotating modulator | 2D, forced convection, unsteady, laminar | Pr = 0.71, 102 ≤ Re ≤ 103, 104 ≤ Ra ≤ 106, Bi = 104 | 49,874, 50,672 and 52,601 elements |
| Ouri et al. [205] | Comsol, FEM, ANFIS | L-shaped cavity with rotating cylinder | 2D, unsteady | 200 ≤ Re ≤ 103, 102 ≤ Rew ≤ 103, 0 ≤ Ha ≤ 40, 0 ≤ ≤ 0.02, Ag-MgO/H2O hybrid nanofluid | Non-uniform triangular 65,216 elements |
| Sayed et al. [206] | FVM, LES, URANS | Cubical cavity | 3D, unsteady | Ra = 109, Pr = 0.71, Prt = 0.9 | 166,375 cells |
4. Validations
In computational fluid dynamics (CFD), validation is an important aspect of research. It is the process of comparing the numerical results with experimental, benchmark, or numerical results to assess the accuracy of the simulation. Validation is important for several reasons: it helps to ensure that the numerical model is implemented correctly and that the solution is not affected by any errors or bugs in the code; it also allows researchers to compare their results with other studies, and it gives an idea about the accuracy of the numerical model compared with real-world data. One common way to validate CFD simulations is to compare the numerical results with experimental data. This can be conducted by comparing the velocity, temperature, and pressure fields obtained from the simulation with measurements taken in a laboratory experiment. The percentage difference between the numerical and experimental results is used as a measure of the accuracy of the simulation. A percentage difference of less than 5% is generally considered to be a good match between the numerical and experimental results. The above-mentioned studies used different types of validations, and details of some of these are presented below. Providing detailed information about the validation process in a study is important for ensuring the accuracy of the numerical results and for providing a useful resource for future research. Moreover, according to the authors’ knowledge, no such details are available in previous studies. By presenting the details of their validation studies, the authors are providing a valuable resource for future researchers. This information can be used to compare the results of new studies with previous work and to assess the accuracy of new simulations. Additionally, the figures (Figure 4, Figure 5, Figure 6, Figure 7, Figure 8, Figure 9 and Figure 10) likely provide a visual representation of the validation results, making it easier for readers to understand and interpret the data.
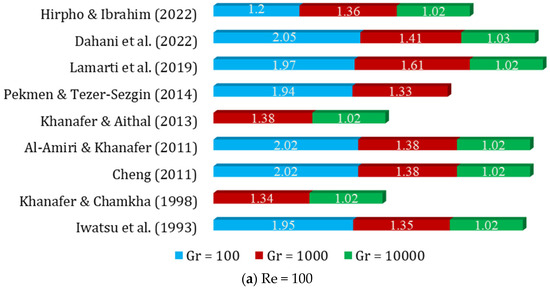
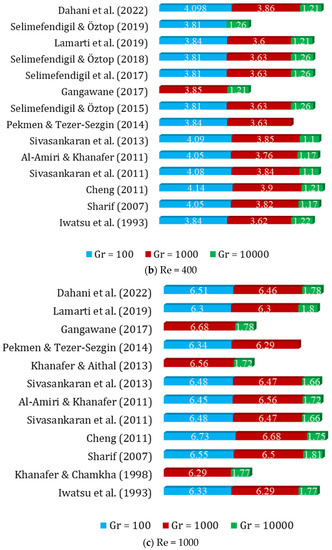
Figure 4.
Variation of Nuavg with different Gr for Pr = 0.71 (Case: Mixed convection flow inside a square lid-driven cavity) [31,33,34,53,55,93,105,106,124,139,142,188,189,207,208,209,210,211].
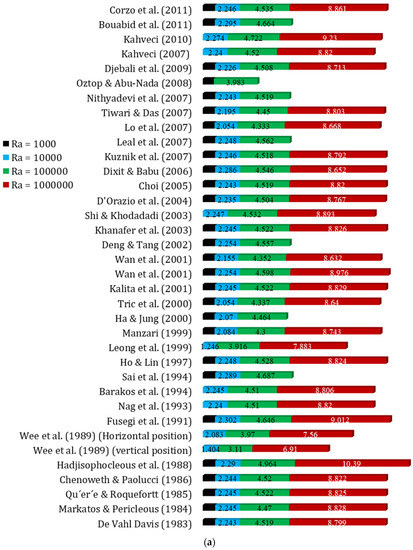
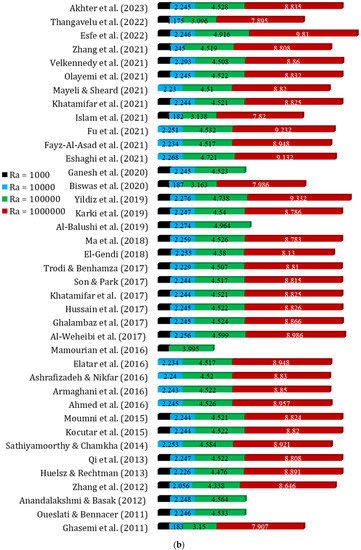
Figure 5.
(a,b): Variation of Nuavg with different Ra for Pr = 0.71 (Case: Natural convection flow in a square cavity) [2,7,9,18,52,71,75,79,89,94,99,103,149,162,163,179,212,213,214,215,216,217,218,219,220,221,222,223,224,225,226,227,228,229,230,231,232,233,234,235,236,237,238,239,240,241,242,243,244,245,246,247,248,249,250,251,252,253,254,255,256,257,258,259,260,261,262,263,264,265,266,267].
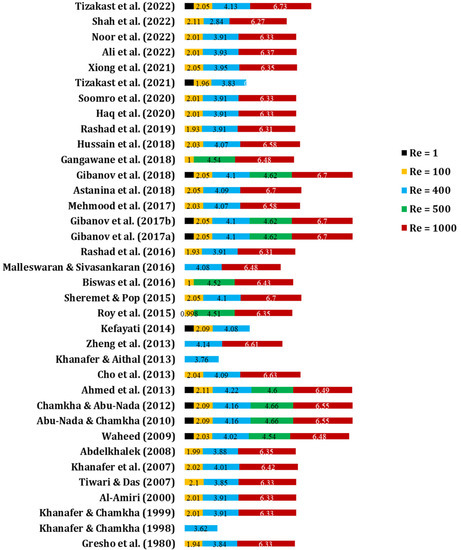
Figure 6.
Variation of Nuavg with different Re for Pr = 0.71 and Gr = 102 (Case: Mixed convection flow in a square lid-driven cavity) [12,18,42,48,50,53,73,95,96,110,115,116,117,150,157,178,180,183,192,198,199,208,268,269,270,271,272,273,274,275,276,277,278].
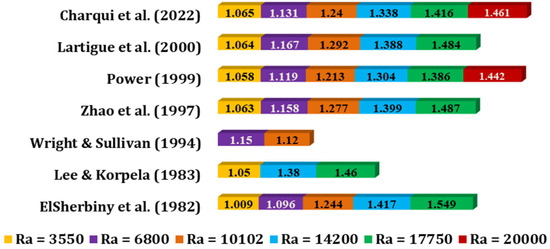
Figure 7.
Variation of Nuavg with different Ra for A = 40 [186,279,280,281,282,283,284].
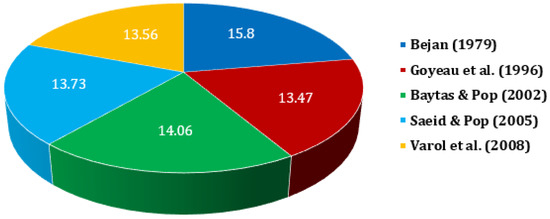
Figure 8.
Variation of for Ra = 103 (Case: Porous square cavity) [20,285,286,287,288].
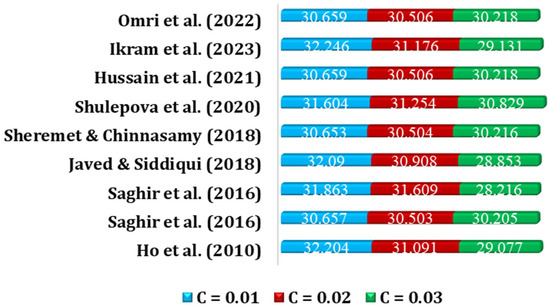
Figure 9.
Variation of for different nanoparticles concentration (C) of Al2O3 nanofluid [118,165,204,289,290,291,292,293].
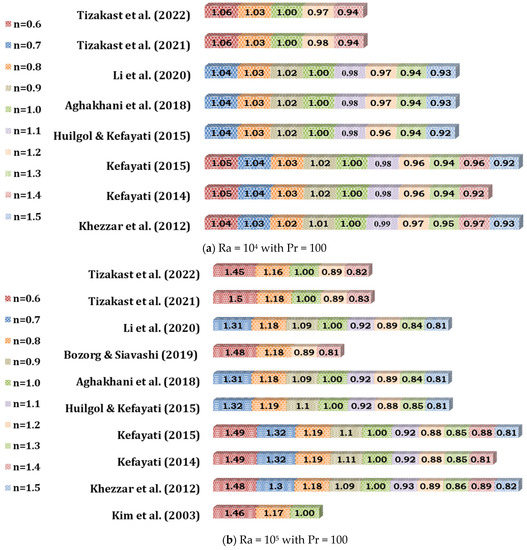

Figure 10.
Variation of relative average Nusselt number for different Ra (Case: Non-Newtonian Power-law Fluids) with Pr = 100 [109,152,178,199,218,273,294,295,296,297].
For a square lid-driven cavity with mixed convection flow, the variation of the average Nusselt number with different Gr for a fixed Pr of 0.71 was studied through numerical simulations or experiments. In the case of mixed convection, as the Gr increases, the Nuavg is expected to decrease. This is due to the lid-driven motion of the cavity. Details of the results are presented in Figure 4.
Based on the validation data presented in Figure 4a–c, the following correlations (Equations (6)–(8)) are proposed. It is worth noting that all these correlations exhibit a maximum percentage error of less than 10%, which indicates a strong relationship between the provided data and the proposed equations.
In a square cavity with natural convection flow, the variation of Nuavg with different Ra for a fixed Pr of 0.71 is studied throughout the literature. We know as Ra increases, the strength of natural convection increases, and the Nuavg increases. However, the relationship between Nuavg and Ra can be complex, as the flow pattern and heat transfer mechanisms in the cavity can vary with changing Ra. In general, for a square cavity with natural convection flow and Pr = 0.71, the variation of the Nuavg with Ra can be explained by different values of Ra. For low Ra < 104, the heat transfer is dominated by conductive heat transfer, and Nuavg is relatively constant and low. However, for intermediate Ra (104 < Ra < 108), the heat transfer is dominated by a combination of conduction and convection, and Nuavg increases rapidly with Ra due to the onset of natural convection. Such findings are explained in Figure 5.
Based on the results displayed in Figure 5a,b, a novel correlation is introduced for the computation of Nuavg, which is presented below. The correlation (Equation (9)) exhibits a high level of consistency with the aforementioned findings, with an error range of 1.4% to less than 10%. In a few instances, the maximum error is found to be approximately 13%, but this is attributed to the researcher’s recording of low Nuavg values.
As shown in Figure 6, for a fixed Pr = 0.71 and low Gr = 100 in mixed convection flow in a square lid-driven cavity, Nuavg always increases with increasing Re. This is because at low Gr, the buoyancy forces are weak, and the flow is dominated by the lid-driven motion. As Re increases, the flow becomes more vigorous, resulting in increased mixing and enhanced heat transfer.
Based on the findings depicted in Figure 6, a novel correlation for computing Nuavg is introduced and presented below. The proposed correlation (Equation (10)) exhibits a strong association with the provided data, with a minimum and maximum error of 0.01% and 7.30%, respectively. However, for some of the given data, a higher percentage of error is observed, which is not attributable to the correlation, but rather is due to poorly recorded research data obtained by the researcher.
We know that an increase in the aspect ratio leads to an increase in the heat transfer rate. This is because an increase in the aspect ratio leads to an increase in the surface area available for heat transfer. As a result, there is more area for the fluid to exchange heat with the solid surfaces, leading to a higher heat transfer rate. Additionally, an increase in the aspect ratio can also promote greater fluid mixing and circulation, which further enhances the heat transfer rate. We also know that Nuavg increases with increasing Ra for a porous square cavity case. At low Ra, the flow is dominated by conduction, and the heat transfer is primarily governed by thermal conduction. As Ra increases, the buoyancy forces become more significant, resulting in increased flow circulation and mixing. This enhanced mixing leads to an increase in the heat transfer rate and Nuavg. Such findings are presented in Figure 7 and Figure 8, that is observed by a different researcher.
Based on the results depicted in Figure 7, a new correlation for determining Nuavg is proposed and put forward. The correlation (Equation (11)) demonstrates a high level of accuracy, with a minimum error of 0.08% and a maximum error of 9.93%. These findings suggest that the correlation has significant potential for future use.
Figure 9 presents the variation of Nuavg with different nanoparticle concentrations (C) for Al2O3 nanofluid. It is observed that Nuavg slightly decreases with the increase in C. The decrease in Nuavg with increasing C may be due to several factors, such as the nanoparticles may aggregate at high concentrations, leading to a decrease in effective surface area and, thus, a decrease in convective heat transfer.
Based on the outcomes presented in Figure 9, a new correlation is suggested for computing Nuavg. This correlation (Equation (12)) demonstrates a robust concurrence with the results of earlier studies, with an error range of 0.01% to a maximum of 5.41%.
Figure 10 shows that the Nuavg increases with increasing Ra for a fixed Pr = 100, which indicates an enhancement of convective heat transfer. However, the rate of increase depends on the power-law index n. It is also seen that Nuavg slightly increases with the increase in n. It indicates that the non-Newtonian behavior of the fluid has a small effect on the convective heat transfer in the fluid.
Based on the data depicted in Figure 10, two correlations (Equations (13) and (14)) are proposed with minimum and maximum errors of 0.06% and 3.41%, and 0.01% and 7.69%, respectively. These correlations demonstrate excellent agreement with the provided data.
5. Heat Transfer Analysis
According to the above-mentioned literature, the flow behavior inside the cavities can be classified into the following categories: effect of the applied boundary conditions to walls such as temperature difference, localized heat sources, magnetic field, or inlet flow to the cavity through a specific port(s). The other types of cavities use internal fins or cylinders to drive the flow inside the cavity. Some of the above-mentioned references (Given in Table 1) are discussed below:
5.1. Square Cavity
In the study by Abbas et al. [181], the effect of using Cu-water nanofluid on heat transfer enhancement was investigated inside a square cavity, using two circular heated obstacles and applying a constant magnetic field. They found that Nuavg improved with the rise of Ra up to a certain point and then showed a negligible variation. However, for lower values of Ra, Nu decreased with Ha. Additionally, the increase in nanoparticle concentration resulted in a decrease in the heat transfer rate for each value of Ha. The study also found that the increase in magnetic field intensity led to a decrease in the rate of heat transfer because of the high sensitivity of Cu nanoparticles to the applied magnetic field. In the study by Roy et al. [197], the flow behavior inside a square cavity filled with MHD hybrid Cu-Al2O3/H2O nanofluid was investigated. A cold elliptical block and a hot square block were inserted inside the cavity, and all four walls were set at the same temperature as the elliptical object. The results of the study confirmed that the local Nu increased with Ra and decreased with an applied magnetic field. Additionally, the presence of nanoparticles enhanced the heat transfer rate. The study also found that Ha had a stronger effect on local and average Nu at high values of Ra. Furthermore, high Rd led to an improvement in the rate of heat transfer. In the study by Zarei et al. [201], the flow of a Cu-H2O nanofluid inside a square cavity with a wavy left wall and straight other walls was investigated, with a uniform heat flux applied to the left vertical wall and a constant temperature on the right vertical wall, while the other boundaries were adiabatic. They found that increasing the nanoparticles concentration and decreasing the wavelength and amplitude of the wavy wall led to an increase in Nuavg. In the study by Akhter et al. [7], the flow of a hybrid nanofluid Cu-Al2O3/H2O inside a square cavity was investigated. A heat-conductive circular solid was placed at the center of the cavity. The bottom and top boundaries of the cavity were partially heated and cooled, respectively. Their results confirmed that the heat transfer was enhanced with the Ra and decreased with the Ha. They also found that the thermal performance increased linearly with an increase in χ. For the nanoparticles volume fraction of 1% and 5%, there was an increase in heat transfer by 47.74% and 106.78%, respectively, as compared to the base fluid.
5.2. Rectangular Cavity
The study by Wee et al. [2] found that the rate of heat transfer in a rectangular cavity full of air is significantly higher when the cavity is in a vertical position with upwards transfer compared to a horizontal position with the downward transfer. Al-Farhany & Turan [39] found that using a rectangular porous cavity with left and right boundaries at various temperatures and insulated top and bottom walls, the flow inside the cavity was driven by buoyancy, and the results showed that the highest Nuavg occurred at zero inclination for high Ra, while for low Ra, the maximum Nuavg was found at 60 degrees inclination. Additionally, the results showed that as the aspect ratio and Le increase, Nuavg decreases and Sh increases. Elsherbiny & Ragab [51] studied an inclined rectangular cavity with a hot spot at the bottom wall and insulated surfaces. They found that as the aspect ratio increases, Nuavg decreases, and when the local heat source position was at the middle or quarter position of the bottom wall, the maximum Nuavg occurred at specific aspect ratio values. Moreover, they found that Nuavg increases with increasing tilt angle (φ) from 0 to 75 degrees, then starts to decrease until 150 degrees and remains constant up to 180 degrees. Elsherbiny & Ismail [69] studied an oblique rectangular cavity with two local heat sources at the bottom wall and insulated surfaces. They found that Nuavg increases until φ’s reaches 60 degrees and then starts to decrease until it reaches a minimum value at 180 degrees. They also found that at a tilt angle of 150 degrees, the effect of Ra on Nuavg is very low, and at 180 degrees, Nuavg becomes independent of Ra. Additionally, they observed that Nuavg decreases by 23% when the aspect ratio reaches 10. Hatami [6] numerically investigated the free convection and flow of nanofluids in a rectangular cavity with two heated fins installed on the cold lower and upper walls while the vertical walls were insulated. They found that Nuavg was higher for higher volume fractions of Al2O3 and similarly for lower volume fractions of TiO2. Additionally, they observed that Nuavg increases as the height of the fins increases. Yu et al. [3] studied numerically the effect of the magnetic field and electric source on the flow characteristics and heat and mass transfer of electrically conducting fluid inside a rectangular cavity. It was found that with the increase in the density of the magnetic field, the oscillatory flow became more stable, and heat transfer by convection and mass transfer was reduced. Moreover, it was also found that the magnetic field had no effect on Nuavg, which only varied with dimensionless heat generation or absorption coefficient, while Sh remained equal to one.
Jiang and Zhou’s [4] study examined the impact of nanofluids on surface tension in a rectangular cavity. They applied a temperature difference across the vertical walls and a free surface on the upper surface. They found that for distilled water-Al2O3 nanofluid, a rise in nanoparticles volume fraction led to convective flow being dominated by the fluid’s thermophysical properties and the surface tension temperature coefficient. For PGW-ZnO nanofluid, an increase in nanoparticle concentration resulted in convective flow being mainly controlled by the surface tension temperature coefficient. Karatas and Derbentli’s [138] study investigated free convection flow in a partially heated rectangular cavity with various aspect ratios. They kept the temperature of the vertical cold boundary constant, and the temperature of the hot boundary was a time-periodic temperature. They observed that Nuavg increased from 2.64 to 16.44 as the aspect ratio decreased from 6 to 1. Thiers et al. [158] explored the impact of local thermal disturbances (one on the cold side and the other on the hot side) on the flow instability in a rectangular enclosure with an aspect ratio of 4.0. They considered the left boundary as a hot boundary, while right boundary as a cold boundary, and the top and bottom walls as adiabatic. Their research showed that the highest heat transfer enhancement occurred when the local disturbance area was located at Lh= 0.7 and/or Lc = 0.3. Hasnaoui et al. [164] studied thermo-solutal convection in a rectangular cavity. They found that the flow became unstable for Sr = 0 and −0.5 and remained unstable until R = 20. They also observed that the rate of heat transfer was strongly impacted by thermo-diffusion in the range of R, leading to instabilities. Alqaed et al. [5] performed a numerical simulation to study the natural convection heat transfer and entropy generation of alumina-water nanofluid flow in a rectangular cavity. They installed two hot triangular blades on the bottom wall, and the two sidewalls were adiabatic, whereas the upper wall was set at a low temperature and the bottom wall was set at a high temperature. They found that a rise in Ra led to an increase in Nuavg and entropy generation, but it decreased Be, and the increment in Ha also led to reducing Be for higher Ra. They reported that the maximum values of Nuavg, entropy generation, and Be occurred at a cavity inclination of 30 degrees. Liu [191] examined the convection heat transfer behavior inside a rectangular cavity with an adiabatic fin fixed on each of the side walls. The top and bottom boundaries were adiabatic, while the left boundary was cold, and the right boundary was hot. The study found that Nuavg increased by 5% for the finned cavity as compared to the non-finned one. Additionally, Nuavg for both cases increased with the angle of inclination until 5 degrees and then decreased.
Sasaguchi et al. [14] studied the heat transfer analysis numerically in a rectangular cavity containing water. All boundaries were insulated and cold (−10 °C), including the internal presence of single or double cylinder inside the cavity. The study found that the solidification speed for a single cylinder was faster than double cylinders for a temperature equal to 0 °C, while the solidification was faster for the double cylinders for a temperature higher than 4 °C. Liu & Huang [153] investigated the effect of adding thin fins to the middle of the high and low-temperature walls of a rectangular cavity, with the top and bottom walls being considered as insulated walls. They applied a linear temperature distribution to the hot and cold side walls. The study found that the effect of the adiabatic horizontal thin fin led to a change in the convective flow attached to the middle of the sidewall. Nuavg correlated well with Ra0.25 for all three thermal heating conditions examined. However, when the slope of the applied linear temperature distribution was negative to both the right and left walls, Nuavg was lower than the other two heating conditions.
Joe and Perumal [169] studied the influences of rotating cylinders on the mixing and distribution of temperature within a rectangular cavity. They found that the best results were obtained when the cylinders were close to the middle line and rotated in the same direction. This resulted in improved mixing and a more uniform temperature distribution. Saha et al. [172] studied free convection flow inside a rectangular cavity with isothermally heated baffles. They concluded that the flow velocity and heat transfer interaction efficiency were highest for the case of plane baffles, where fluid was blended more effectively as the length of the baffles increased. They also found that the maximum value of Nuavg was achieved at Re = 250 for plane baffles. Additionally, they found that the heating efficiency increased with Re and Ri and decreased as the length of the baffles increased. Velkennedy et al. [179] investigated the air-flow behavior inside a ventilated rectangular cavity with two outlets and one inlet. The inlet vent was positioned on the bottom of the right wall, and the outlets were put on the top wall. Both vertical walls were considered hot walls, and the bottom wall was adiabatic. They found that the rate of heat transfer to the right wall was reduced at the upper part of the cavity due to the introduction of a cold partition. However, they also found that the heat transfer rate increased significantly with the introduction of the cold partition for lower Ra, and this difference was reduced for higher Ra. Ait-Taleb et al. [58] studied the flow behavior inside a building block that generally contains three air cavities in the horizontal orientation and two in the vertical orientation. They found that by keeping the temperatures of the upper and lower walls the cold outside and hot inside, respectively, the hollow block with two air cells deep in the vertical direction allowed for a significant reduction in heat transfer between the inside and outside of the building. Charqui et al. [186] numerically investigated the heat transfer and free convection flow inside a tall thin partitioned cavity, where the left and right parts were filled with air and water, respectively. They found that even though the partition was thin, air and water behaved differently. The temperature of the inside wall had less effect by solar flux than the heat flux through the partition. The wall opposite to sunlight was kept at 20 degrees Celsius, and the temperature of the other surface was varied between 0 degrees Celsius to 50 degrees Celsius. The other surfaces were assumed to be adiabatic.
5.3. Other Cavity Types
Alam et al. [8] investigated the effect of various types of nanofluids on thermal behavior inside a semicircular cavity that was exposed to a periodic magnetic field. They used nanoparticles such as ZnO, Fe3O4, Co, Al2O3, and Ag and base fluids such as water and kerosene. The bottom surface was exposed to non-uniform parabolic heating, while the circular surface was set at a fixed cold temperature. They found that the highest value of Nuavg was obtained for Co-kerosene nanofluid by 588.197% for χ = 5%. They also found that for a specific value of χ, there was a slight rise in Nu with the augmentation of Ra. The study also revealed that the variable magnetic field and the Brownian motion of nanoparticles had a significant effect on heat transmission enhancement. Additionally, the findings indicated that a non-uniform magnetic field showed higher heat transmission than a uniform case. Acharya & Chamkha [184] studied the thermal and fluid flow behavior of Al2O3-H2O nanofluid inside a hexagonal enclosure. The enclosure had three parallel fins inside, with the right and left fins being cooled and the middle one being heated. The top lid was partially heated, while the bottom boundary was fully heated, and the other boundaries were assumed to be adiabatic. The study also applied a horizontal magnetic field to the cavity. The results presented that the local Nu and Nuavg increased with the increase in Ra, and the u-shaped fins gave the highest outcomes. Additionally, local Nu and Nuavg decreased with Ha. The study found that the increase in the fin’s height led to an increase in the rate of heat transfer, and the central position of the fins was the optimized position that gave the highest rate of heat transfer. Esfe et al. [9] studied the effect of using Al2O3-H2O nanofluid in a U-shaped porous cavity on heat transfer and fluid flow. They found that Nuavg reduced with the increase in Ra and χ. However, Nuavg decreased when Da increased from 0 to 60, indicating that the porous structure had an impact on the heat transfer enhancement. Overall, the study provided insights into the utilization of nanofluids and porous structures to improve heat transfer in U-shaped cavities. Geridonmez & Oztop [10] studied the influence of an oblique partial periodic magnetic field on the free convection of hybrid Al2O3-Cu/H2O nanofluid inside an isosceles triangular cavity. They considered three cases with different wall temperatures and magnetic field orientations and found that the heat transfer rate was reduced with an increase in Ha and that a horizontal magnetic field provided a higher rate of heat transfer than the other cases. Hirpho and Ibrahim [189] studied the mixed convection of a hybrid nanofluid (Al2O3-Cu/H2O) in a trapezoidal cavity with a partially heated bottom wall, cold left and right walls, and an adiabatic top lid. They found that the local Nu number increased with the rise of χ, the Casson fluid parameter, and Ri. This indicates that the rate of heat transfer in the cavity is improved by the presence of nanoparticles, the non-Newtonian behavior of the fluid, and the buoyancy forces.
Khalil et al. [190] examined the free convection in a trapezoidal cavity with a wavy bottom wall filled with pure water and saturated metal foam as a porous medium. The top and side boundaries were kept at a cold temperature while the bottom surface was heated. The study found that Nuavg increased as the number of waves and amplitude of the bottom wall’s waves increased. Additionally, Nuavg improved when the cold temperature of the sides and top walls was decreased. Furthermore, an increase in Ha resulted in an increase in Nuavg. Nouraei et al. [193] explored mixed convection of an H2O-Cu nanofluid in an open semicircular cavity. The circular section was partially heated along 45 degrees at four different angles, and all other positions were insulated. The study found that the local Nu number increased from the inlet to the outlet along the curved surface for a Re of 100. Additionally, the results showed that the maximum Nulocal was obtained for χ = 0.06 for all cases. Prince et al. [195] investigated the conjugate natural convection inside a trapezoidal cavity with a thick base and different surface corrugations, such as flat, sinusoidal, and triangular surfaces. The base was made of different materials, such as pinewood, plexiglas, dry concrete, and glass fiber. The base was set isothermally hot while the top wall was kept isothermally cold, and the side walls were adiabatic. The study found that there was a considerable improvement in convection heat transfer for high Ra up to the value of Ra > 104. Moreover, the glass fiber showed the highest Nuavg and the lowest dimensionless fluid temperature. For Ra ≤ 104, the conduction heat transfer mode would be dominant. This suggests that the corrugated surface of the cavity base and the material of the base can significantly enhance the heat transfer rate, but the effect becomes less significant for lower Ra. Rahaman et al. [196] studied the natural convection of air inside a valley-shaped trapezoidal cavity, where the top and bottom walls were considered hot and cold, respectively, and both the side walls were adiabatic. The study found that Nu was small at the beginning for stratified air and gradually increased in the transitional phase when the stratification was broken and became fixed for Ra ≤ 106. After that, Nu exhibited oscillatory behavior for Ra ≥ 107.
He et al. [203] discussed the effect of a magnetic field on a phase change nanocomposite inside a cubical cavity filled with. The nanocomposites were obtained by adding Fe3O4 nanoparticles into paraffin. The left wall was set as a hot boundary while the other walls were insulated. The study found that, without applying a magnetic field and with a uniform distribution of the nanoparticles in the paraffin, the rate of heat transfer was increased. However, when a magnetic field was applied, the melting rate of paraffin was reduced. Ikram et al. [204] studied the heat transfer behavior inside a hexagonal enclosure equipped with different types of rotating modulators. A uniform heat flux was applied to the bottom inclined wall while the top was exposed to ambient temperature. The other two vertical walls were insulated. The results presented that the increase in Re from 100 to 1000 improved heat transfer by 57.1%. An inverse relationship between thermal storage capacity and thermal effectiveness was also observed, which means that as the thermal storage capacity increases, the thermal effectiveness decreases. Ouri et al. [205] studied the effect of convective heat transfer in an L-shaped vented cavity that contained an inner rotating cylinder. The cold fluid entered the cavity through the top lid, while the lower wall was hot, and the remaining boundaries were adiabatic. Their findings showed that Nuavg, the average Nusselt number, increased by 180% for the highest Re and 19% and 8% for cylinder rotational speeds of 1000 and −1000, respectively. In addition, the spatial Nuavg, which is the Nusselt number at different points within the cavity, showed an increase by varying the cylinder size up to 86% and 33.5% at cylinder rotational speeds of 1000 and −1000, respectively.
5.4. Lid-Driven Cavity
5.4.1. Square Cavity
In a study by Moallemi & Jang [11], the hydraulic and thermal behaviors in a square cavity were examined when a shearing force was applied by moving a glass sheet on the top wall and combined with the buoyancy force from heating the bottom wall. The results showed that the influence of buoyancy was clearer on heat transfer for higher values of Pr with constant Re and Gr. Additionally, for a minimum level of buoyancy, forced convection heat transfer was dominant and independent of Ri. The study also found that as buoyancy increased, the heat transfer mechanism transitioned from forced convection to mixed convection, with Nuavg being a function of Pr. In a study by Chamkha & Abu-Nada [42], the mixed convection of a water-Al2O3 nanofluid flow in single and double lid-driven square cavities was examined using different nanofluid viscosity approaches. The top lid-driven wall was kept at a constant hot temperature, while the bottom lid-driven wall was set at a cold temperature. The results showed that at moderate and large Ri, the increase in χ led to an improvement in the rate of heat transfer for single and double-lid-driven cavities for both the Pak and Cho correlation and the Brinkman model. Additionally, in the single lid-driven cavity and for small Ri, Pak and Cho’s correlation predicted a reduction in Nuavg. However, for other conditions, an increase in Nuavg was predicted by the Pak and Cho correlation, which was larger than the Brinkman model for all values of χ. In a study by Ahmed et al. [48], a numerical examination of MHD mixed convection flow in an oblique lid-driven square enclosure with an opposite temperature gradient was conducted. The sinusoidal temperature distribution was applied to the right and left walls, the top wall was considered as a moving boundary, and a zero velocity was considered for the bottom wall. The results showed that the increase in Ha had no effect on heat transfer on both vertical walls. Additionally, the rate of heat transfer enhanced with Ha and ϕ increased in the case of opposing buoyancy-driven convection. For forced convection, Nulocal increased on the left wall while it decreased on the right wall when the amplitude ratio of the sinusoidal temperature increased. In the study by Muthtamilselvan & Doh [63], the authors numerically investigated the heat transfer behavior of a Cu-H2O nanofluid flowing in a lid-driven square cavity. They found that Ri had a small effect on heat transfer except for Ri = 4, where a non-linear relationship between the Nusselt number and the volumetric solid fraction was observed. They also found that for non-uniform heating, a sinusoidal behavior of local heat transfer was attained, and a maximum heat transfer occurred in the middle of the bottom wall. In the study by Pekmen & Tezer-Sezgin [209], the authors investigated the mixed convection flow behavior inside a lid-driven square cavity filled with porous media with the application of a magnetic field. The top wall was hot and moving, the bottom wall was cold and fixed, and the vertical walls were adiabatic. They found that as Ha increased, Nuavg decreased due to the retarding effect of the Lorentz force. Additionally, they observed that as Da decreased, the heat transfer became more conductive even as Re increased.
In the study by Ray & Chatterjee [65], the authors discussed the influences of an external magnetic field on an electrically conducting fluid inside a lid-driven square cavity with a conducting cylindrical body inserted. The top wall was moving and fixed at a cold temperature. They found that a rise in Ri led to an enhancement in the rate of heat transfer and fluid temperature, while the presence of a magnetic field reduced the heat transfer rate. Moumni et al. [71] conducted a study on heat transfer and mixed convection flow and behavior in a square cavity with double lid-driven filled with different types of nanofluids. They found that adding nanoparticles to the fluid led to an improvement in the heat transfer rate, with copper and silver nanoparticles showing the highest heat transfer rate due to their high thermal conductivity. They also found that the rate of heat transfer raised with the increase in Ri and Re for constant nanoparticles concentration. Selimefendigil and Öztop [210] conducted a study on the effect of two rotating cylinders on mixed convection of ferrofluid flow inside a square cavity. They found that the enhancement of the Nuavg was 181.5% for a negative angular speed ratio (Ω = −400) and 181.6% for a positive angular speed ratio (Ω = 400). They also found that the rise in the angular speed ratio caused an increase of 91.7% in Nuavg and that an 88.9% enhancement in Nuavg was achieved when the diameter ratio of the cylinders was changed from 2 to 0. Sheremet and Pop [73] conducted a numerical analysis on the mixed convection of a nanofluid flow inside a lid-driven square cavity where both the top and bottom walls were moving in opposite directions. The top and bottom walls were considered hot and cold walls, respectively. Their results showed that the heat transfer mechanism depends strongly on Ri and the moving parameter. They also found that Nu slightly increased with Le except in the counter-direction of moving horizontal walls, where Nu decreased with Le. Jmai et al. [76] conducted research on the effect of a partially heated wall on mixed convection Cu/H2O nanofluid flow inside a lid-driven square cavity. Each vertical side wall contains a heat source of high temperature, and both the upper and lower boundaries can move in the same and opposite directions and are considered cold. Their results showed that for all speed ratios, Nu increased as Ri decreased. The maximum value of Nu = 54.41 was observed when the speed ratio = −2 and Ri = 0.01.
Rashad et al. [12] conducted a study on MHD mixed convection Cu–water nanofluid flow in a lid-driven square cavity. The upper and lower walls were moving opposite to each other and were considered adiabatic. The right vertical wall was partially heated, and the left wall was partially cold; the other parts of the vertical boundaries were adiabatic. Their results revealed that the highest heat transfer occurred when the size of the heat source was as small as possible and placed at the middle position of the walls. They also concluded that heat transfer decreased with the increase in Ri. The presence of a magnetic field was found to reduce the convective heat transfer, and the presence of nanoparticles led to a decrease in the Nu. Selimefendigil et al. [84] conducted a numerical analysis to study the effect of Ri, Ha, magnetic field inclination angles, and the combination of upper and lower diagonal domains on the hydraulic and thermal behavior inside a lid-driven square cavity. They found that Nuavg decreased by 80.14% when Ri increased from 0.01 to 100 for inclinations angles of 90 and 0 degrees. They also found that increasing the magnetic inclination angle of the upper triangular domain led to a higher average heat transfer compared to increasing the magnetic field in the lower triangular domain. Selimefendigil & Öztop [82] studied the mixed convection inside a lid-driven square cavity with nanofluid. The cavity had elastic side walls, where the left boundary was moving upward and fixed at a constant temperature, while the right wall was a hot one. They concluded that the rate of heat transfer is increased with increasing Ri, Ha, and nanoparticles concentration. However, the rate of heat transfer is decreased with the increasing inclined angle of the magnetic field. Additionally, the study found that the influence of elasticity on the heat transfer rate is considerable, where it increased with increasing elasticity. In the study by Gangawane [93], mixed convection heat transfer was numerically explored in a top lid-driven square cavity with a triangular heated block and constant heat flux. The top wall was moving while the other walls were kept stationary, and the upper and lower boundaries were adiabatic while the vertical boundaries were at ambient temperature. Nuavg increased up to a Recr between 190–220 and then began to decrease, particularly for Gr greater than 50. In the study by Gibanov et al. [95], Al2O3-H2O nanofluid flow was numerically studied in a lid-driven square cavity. The upper wall was hot and moving, while the bottom wall was fixed and cold. Nuavg was found to decrease with an increase in Ri and the backward step ratio.
The study by Khanafer and Aithal [102] investigated the effects of a rotating cylinder on mixed convection flow in a lid-driven square cavity. Their results demonstrated that the presence of the cylinder led to an increase in Nuavg and that clockwise rotation led to an increase in Nuavg, while counter-clockwise rotation led to a decrease in Nuavg with an increase in rotational speed. The study by Selimefendigil et al. [105] examined the effects of the magnetic field, Ri, E, Ha, nanoparticle concentration, and the presence of a flexible wall on the MHD flow of a nanofluid inside a square cavity. They found that Nuavg increased with the increase in Ri and observed 74.35% of heat transfer enhancement for Ri = 5. They also found that 66.5% heat transfer enhancement was obtained for E = 104 N/m2 as compared to the case E = 2.5 × 105 N/m2. Additionally, if Ha is reduced from 50 to 0, there will be an improvement in the rate of heat transfer by 54.55%. If the nanoparticles concentration increased from 0 to 0.04, there would be an improvement in heat transfer by 33.87%. The existence of a flexible wall led to an enhancement in heat transfer by 13.2%. Gibanov et al. [96] investigated mixed convection ferrofluid flow in a square cavity with a lid-driven with a moving, cold upper wall and a hot bottom wall and found that Nuavg at the heated wall increases with the increase in Ha and the thickness of porous media. Hussain et al. [99] examined the effect of an inclination angle on the heat transfer in a double lid-driven square cavity filled with Al2O3-H2O nanofluid, with two fixed heat sources at the bottom wall. They confirmed that heat transfer is improved with the increase in nanoparticles concentration and Ri. Additionally, an increase in inclination angle caused an increase in Nuavg because of the left heat source, but the inverse behavior was noticed for the right heat source. Alsabery et al. [111] studied the conjugate mixed convection of H2O-Al2O3 nanofluid flow inside a square cavity with a double lid driven containing a solid inner object. The top wall was kept at a constant cold temperature and moved to the right, while the bottom wall moved to the left and was kept at a fixed high temperature. The vertical walls were insulated. The study found that the presence of nanofluid enhanced the rate of heat transfer, but at low Re and high Ri, it had an inverse effect on the Nu.
Astanina et al. [110] studied mixed convection of Al2O3-H2O nanofluid flow in a square cavity with a lid-driven, including two layers of porous media at the bottom with different thermal properties, permeability, and porosity. The lower wall was kept at a hot temperature, and the top moving wall was considered cold. The other walls were adiabatic. The study found that heat transfer enhanced with an increase in Ri for constant Re. It also found that Nuavg reduced for different ranges of porous layer thicknesses when Ri > 1. Gangawane et al. [115] studied mixed convection flow in a square cavity containing a heated triangular block placed at the center of the cavity. The top wall was moving and insulated, while the lower wall was fixed and insulated as well, and the vertical wall was exposed to ambient temperature. The triangular block was considered isothermal and at a higher temperature than the ambient temperature. The results showed that there was a 50% increase in heat transfer when the size of the block increased from 10% to 30%. Gibanov et al. [116] studied the effect of Ri, the thickness of the lower wall, thermal conductivity ratio, and nanoparticle concentrations of Al2O3-H2O nanofluid flow inside a lid-driven square cavity. The top lid was moving and hot, while the bottom wall was considered cold. The other vertical walls were insulated. The study found that the increase in thermal conductivity ratio and nanoparticle ratio led to an increase in heat transfer rate, while the increase in Ri and thickness of the bottom wall reduced heat transfer. Razera et al. [123] studied the effect of a fin on mixed convection flow inside a lid-driven square cavity. A lower wall was considered as the first position for the fin and then located on the side walls. The fin surface was considered a hot spot with high temperature, while the vertical and lower walls were set to be adiabatic. The upper moving surface was considered to be cold. The results showed that the fins on the right wall gave the highest Nusselt number while the fins on the lower wall gave an intermediate performance between the three cases. Hussain et al. [117] investigated the influence of an inclined magnetic field on the mixed convection H2O-Al2O3 nanofluid flow inside a double-lid driven square cavity. The top and bottom walls were moving in opposite directions, and both walls were insulated. The left vertical wall was at a hot temperature, and the right one was considered to be cold. The results presented that Nuavg increased with the increase in χ and decreased with the increase in Ri. Furthermore, Nuavg reduced with the increase in Ha and the inclination angle of the magnetic field.
Taghizadeh & Asaditaheri [127] studied heat transfer by convection through an inclined lid-driven square cavity containing a circular porous cylinder placed at the center of the cavity. The lower and upper walls were considered hot and cold walls, respectively, and the vertical walls were considered adiabatic. The upper wall was moving at a steady speed, and the other walls remained fixed. They found that for all inclination angles, the increase in Da enhanced heat transfer when Ri = 0.01. For Ri ≥ 1, the rate of heat transfer decreased. For Ri = 5 and 10, heat transfer was more affected by the angle of inclination of the cavity, which weakens buoyancy forces and decreases the Nusselt number. Barnoon et al. [132] studied entropy generation and mixed convection of nanofluid flow in a lid-driven square cavity. The cavity was subjected to a magnetic field from the bottom wall, and a velocity was applied to the upper lid. They examined the effect of insulated and isothermal two rotating cylinders inside the cavity. They found that the increase in Ha led to reducing the heat transfer rate. The presence of an isothermal cylinder gave a higher rate of heat transfer than the existence of an insulated cylinder. However, in general, the cylinders inside the cavity-enhanced the rate of heat transfer, and the increase in angular speed of the cylinder led to a rise in the rate of heat transfer. Additionally, the fraction of nanofluid equal to 3% with a tilt angle of 0 of the cavity produces a higher rate of heat transfer. Lamarti et al. [139] explored mixed convection flow inside a square cavity with a periodically oscillating top lid. They discovered that the local Nusselt number starts high for high Re and drops rapidly. They also found that for a constant Gr, Re had a large effect on Nuavg and that forced convection became dominant. Alsabery et al. [145] investigated the influence of a magnetic field on mixed convection of nanofluid flow in a square cavity with a lid driven with a thick triangular wall placed in the lower left corner. They found that the rate of heat transfer increased with the increase in Re and Ri. The maximum Nu occurred at Re = 500 and χ = 0.02. Alsabery et al. [160] studied the influence of hybrid nanofluid H2O-Cu-Al2O3 flow inside a square lid-driven cavity with two vertical wavy walls containing a square block. The left wall was kept at a high temperature, the right wall was cold, and the top and bottom walls were adiabatic. They found that Nuavg increased with the increase in Ri and that Nu increased with the increase in χ.
Hussain et al. [165] explored the effect of fins and inclined magnetic fields on square cavities filled with H2O-Cu nanofluid with single and double-lid driven. The upper lid had a hot temperature, and the lower wall had a cold temperature, while the other walls were insulated. Two adiabatic vertical fins were installed on the upper wall, and an inclined magnetic field was applied to both cavities. They found that with the presence of fins, the convective heat transfer decreased with an increase in Ha and Ri. Additionally, Nuavg decreased with an increase in the number of fins. Ahmed et al. [182] studied the flow and heat transfer behavior in a porous lid-driven square cavity filled with Al2O3-Cu/water hybrid nanofluid. The horizontal walls were moving at a constant speed, considered adiabatic, and the vertical walls were stationary. The left wall was hot, and the right one was cold. They found that the thermophoresis parameters had a very small effect on Nuavg. Furthermore, Le had no effect on heat transfer enhancement, and Da had very little effect on the variation of Nuavg. Ali et al. [183] examined mixed convection nanofluid flow inside a square cavity with lid-driven. The top wall was cold and moving horizontally in both directions, while the hot bottom wall was fixed and partially heated. A rotating flat plate was inserted in the cavity, and a magnetic field was subjected to the cavity. The other remaining parts of the walls were set to be adiabatic. The results confirmed that the highest rate of heat transfer occurred when the flat plate length was a quarter of the length of the cavity side (L). The improvement is more than 137.04% as compared to the case of 0.15 L, and it will be 208.89% for the case without the plate. It was also discovered that the heat transfer rate increased by 123.02% for rotational speed = 100, plate length 0.25 L, and nanoparticles concentration = 0.05, as compared with base fluid water. Batool et al. [185] studied heat and mass transfer analysis of a square cavity with lid-driven containing micropolar nanofluids under the influence of magnetic field and buoyancy force. A speed was applied to the upper wall, and the bottom wall was considered hot. The rate of heat transfer became faster at the maximum vortex viscosity parameter. Moreover, an optimized heat transfer mechanism was noticed from the bottom to the top wall, reducing the Brownian motion parameter. Dahani et al. [188] studied mixed convection and surface radiation in a square cavity with double lid-driven. One of the moving walls was considered hot, and the other was set to be cold, while the stationary walls were considered adiabatic. At Ri = 100, the contribution of radiation to the total Nu far outweighs that of convection. To minimize heat transfer, a combined effect of large Ri and angle of inclination close to 180° and non-emissive walls should be considered.
5.4.2. Rectangular Cavity
The study by Balootaki et al. [112] investigated the influence of mixed convection flow in a lid-driven rectangular cavity with a hot-moving upper surface and insulated other surfaces. The presence of a cold obstacle inside the cavity was also considered. The results demonstrated that rising the cavity inclination improves the heat transfer rate under forced convection, and the Nusselt number increases with increasing Rayleigh number for different inclination angles. The study by Louaraychi et al. [140] examined mixed convection flow in horizontal rectangular cavities with single- and double-lid driven using both numerical and analytical methods. It was found that the mixed convection parameter Ra/Pe3 can be used to distinguish between three convection regimes: natural, mixed, and forced convection. The results showed that when forced convection is dominant, Nuavg remained constant for small values of Ra and slightly increased during mixed convection heat transfer. Beyond this range, a fast linear increase in Nuavg was observed for dominant natural convection heat transfer. Additionally, Nuavg increased with the Peclet number (Pe) due to the shear effect. Tizakast et al. [178] conducted a numerical and analytical study on the double-diffusive mixed convection of a non-Newtonian power-law fluid in a closed rectangular cavity. The study found that the flow intensity and heat and mass transfer were insensitive to an increase in the parameter A for values of A greater than or equal to 24. The results also showed that non-Newtonian double-diffusive mixed convection is controlled by the parameters RaT, Pe, Le, and power-law index n. Additionally, the study found that an increase in Le had no effect on heat transfer, while a high buoyancy ratio increased both heat and mass transfer. Tizakast et al. [199] conducted a numerical and analytical study on the Rayleigh-Bénard double-diffusive mixed convection flow inside horizontal rectangular cavities subjected to uniform heat and mass fluxes along the sliding horizontal walls, with the other walls fixed and insulated. They confirmed that the heat and mass transfer and flow intensity became insensitive to the aspect ratio, A, for values of A greater than or equal to 28. For a Prandtl number greater than or equal to 10, the flow behavior became independent of Pr. The study concluded that Newtonian Rayleigh–Bénard double-diffusive mixed convection is controlled by the parameters Pe, RaT, Le, buoyancy ratio N, and power-law index n.
5.4.3. Triangular Cavity
Selimefendigil & Öztop [107] conducted research on the mixed convection of nanofluid flow in a triangular cavity with lid-driven. They found that for negative and positive x-direction motion, Nuavg decreased by 41.02% and 38.77% for Ri, equal to 50 and 0.05, respectively. Additionally, Nuavg decreased by 55% when Ra increased from 104 to 107. Furthermore, the study found that an enhancement of 22.95% was obtained for Nuavg for the highest nanoparticle concentration. Soomro et al. [157] conducted a study on the convection heat transfer inside a lid-driven triangular cavity subjected to a horizontal constant magnetic field. The upper moving wall was set as hot, while the side inclined walls were adiabatic, and a cold temperature cylinder was placed at the center of the cavity. The study found that Nuavg increased with the increase in Ri at a high flow shear rate. Additionally, Nuavg increased with the increase in Re when high viscous forces were present. Shahid et al. [175] conducted a study on the mixed convection flow inside a heated lid-driven right-angle isosceles triangular cavity. The horizontal top side of the cavity was moving horizontally and kept adiabatic, the vertical wall was hot, and the inclined wall was cold. The results of the study showed that natural convection became more dominant than forced convection as Gr increased, and this led to an increase in Nuavg. Additionally, for small values of Ri, the forced convection was more dominant due to the effect of shear forces generated by the moving lid. Xiong et al. [180] studied mixed convective heat transfer of MHD fluid flow in a lid-driven triangular cavity subjected to heating by a thick triangular wall. The top wall was moving to the right with a high temperature, while the inclined sidewalls were adiabatic. Cold obstacles were placed near the side walls and along the left and right side inclined walls with a temperature lower than the top wall temperature. The results showed that the expansion of Ha led to a reduction in heat transfer. Additionally, for higher Ri, the heat transfer was enhanced due to the increase in shear rate. The study also found that for the left side obstacle, the heat transfer rate increased due to an increase in Re, while the opposite behavior was observed for Ha and Ri. For the right obstacle, the heat transfer rate was strengthened along the upper wall due to the emergence of Re, while a reverse process was followed for Ha and Ri.
5.4.4. Cubical Cavity
The study by Karbasifar et al. [119] focused on the heat transfer process of mixed convection Al2O3-H2O nanofluid flow in a lid-driven cubical cavity containing a hot elliptical centric cylinder. The results showed that Nuavg decreased as Ri increased for fixed χ and ϕ. Additionally, Nuavg raised with the increase in χ for constant Ri and ϕ. It was also found that Nuavg increased slightly when ϕ increased for constant Ri. The study also found that Nuavg increased with the increase in Re and χ. In the study by Kareem & Gao [120], they explored the effect of a SiO2-H2O nanofluid on turbulent mixed convection inside a cubical cavity with a heated top wall and a cold bottom wall. They found that the presence of the nanofluid improved the heat transfer effectiveness, with the highest Nuavg being observed for a rotational speed of −5. Additionally, the rotational velocity of the cylinder had a stronger effect on the bottom wall than on the top wall. Al-Rashed et al. [131] studied the flow of H2O-Al2O3 nanofluid in an oblique lid-driven cubical cavity, including a hot elliptical centric cylinder. They found that raising the concentration of nanoparticles led to an increase in heat transfer coefficients, and Nu decreased with the increase in Ri for constant χ and inclination angle. Additionally, increasing the inclination angle slightly increased Nu for constant Ri. Alsabery et al. [146] investigated the mixed convection H2O-Al2O3 nanofluid flow inside a cubical chamber containing a heat-conducting cylinder. The right vertical wall was partially heated, the left vertical wall was considered cold, and the other walls were insulated. They found that increasing χ led to an improvement in heat transfer for a fixed Re = 10.
5.4.5. Other Types of Cavities
Abu-Nada and Chamkha [57] numerically investigated the mixed convection flow of CuO-H2O nanofluid in a cavity with a wavy wall with a lid-driven. The top wall was hot and moving, while the cold bottom wall was wavy. They found that for all values of Ri, Nu was maximum at the left top corner of the cavity and then decreased along the heated lid until it reached zero at the middle position of the lid. After that, Nu increased slightly at the second half of the wall and then vanished at the right side of the cavity. Hatami et al. [98] investigated the behavior of nanofluid flow inside a T-shaped lid-driven porous cavity. The top moving wall was cold, while the bottom wall was hot, and the other walls were insulated. They found that both Nulocal and Nuavg increased with the increase in Ri and Re. Additionally, they observed that increasing Da and χ led to an increase in Nuavg. Selimefendigil et al. [106] studied mixed convection nanofluid flow inside a trapezoidal cavity with an adiabatic stationary cylinder. Both the left and right walls were flexible walls. The top wall was moving and considered cold, while the bottom was stationary and considered hot. The other walls were considered adiabatic. They found that heat transfer increased by 9.8% when the value of elastic modulus was raised from 103 to 105 when the elastic wall inclination was equal to 0 degrees. Additionally, they observed that Nuavg increased linearly with the increase in χ, and the heat transfer was enhanced by 25.30% at the highest χ as compared to the base fluid. Cho [134] analyzed heat transfer and entropy generation of Cu-H2O nanofluid in a lid-driven cavity and subjected it to an oblique magnetic field. The left wall was a hot moving wall, the right wavy wall was cold, and the other walls were insulated. Their results showed that Nu increased with the increase in χ or wave amplitude of the wavy surface. Additionally, during the natural convection-dominated regime, Nu had a higher value for the magnetic field inclination of 90° and 270°, while the opposite behavior was observed for the inclination of 0° and 180°. During the forced convection-dominated regime, Nu had a higher value for the magnetic field inclination of 135° and 315°, while the opposite behavior was observed for the inclination of 90° and 270°. Hadavand et al. [136] studied mixed convection H2O-Ag nanofluid flow inside a semi-circular cavity with a lid-driven. The left side of the cavity was heated by injecting hot water, while the upper lid was cold and moving. Other surfaces were considered adiabatic. Their results showed that the best heat transfer behavior was observed for Ri = 1, χ = 0.06, and ϕ = −45°, 0°, −90°, 45°, and 90°.
Selimefendigil and Öztop [142] conducted a study on the influence of a magnetic field on mixed convection nanofluid flow in an oblique L-shaped cavity. They found that Nuavg increased by 42.2% and 39.9% for water and nanofluid, respectively, when the cavity inclination angle was changed from 180° to 150°. They also found that Nuavg was reduced by 11% when an elastic wall was used instead of a solid wall at a specific Ri = 0.03. Additionally, Nuavg was reduced by approximately 42% for both fluid and nanofluid for the lowest and highest Ra. Haq et al. [150] examined the heat transfer behavior in a hexagonal cavity filled with water and subjected to a magnetic field. They discovered that the heat transfer could be improved by using a cylinder with variable thermal conditions in the middle of the cavity and by increasing Ha. The Nusselt number at the heated surface decreased as Ri decreased for a specific Re = 300 and Ha = 10. Noor et al. [192] studied the forced convection of MHD flow inside a trapezoidal cavity with a circular object inside. They found that Nu decreased near the heated top lid and remained constant along the horizontal direction of the top lid. Additionally, they found that at low Ri, Nu had a higher value at the top hot-moving wall. Conversely, at high Ri, Nu decreased abruptly along the heated part of the top lid for both heated and cold conditions of the circular object. Polasanapalli and Anupindi [194] studied the mixed heat transfer behavior in an air-filled concentric annular cavity with the inner surface being hot and the outer surface being cold. They considered four different rotational conditions of cylinders: counter-rotating cylinders, co-rotating cylinders, outer rotating cylinders, and inner rotating cylinders. They found that the rate of heat transfer is lower for the differentially heated cavity, regardless of the rotational velocity of the cylinders. Shah et al. [198] studied the mixed convection flow of CuO-H2O nanofluid in a lid-driven corrugated porous cavity with a cylindrical object inside. The object had three different surface conditions: adiabatic, cold, and hot. Internal heat generation/absorption and uniform heat were applied to the vertical wall, and the bottom was insulated. They found that Nu increased as Re increased. The highest Nu was attained for χ = 0.05. Xia et al. [200] studied the mixed convection flow of H2O-Al2O3 nanofluid inside a T-shaped lid-driven cavity with a hot obstacle at different positions. The top lid was moving to the right and had a cold temperature, while all the other walls were adiabatic except the hot obstacle, which was considered hot. Their results showed that as Ri increased, the heat transfer decreased. Additionally, they found that an increase in χ helped to increase the rate of heat transfer. Furthermore, an increase in aspect ratio caused a reduction in the rate of heat transfer. Zhang et al. [202] investigated Ag-water nanofluid flow inside a semi-elliptic lid-driven cavity. The top moving lid was cold, while the curved bottom wall was hot. Their results showed that the presence of nanoparticles with high circulation led to an increase in the rate of heat transfer. Additionally, the heat transfer rate enhanced with the increase in Gr for lower Ri.
6. Conclusions
Heat transfer analysis inside cavities has been investigated by many authors. Different geometries have been adopted for the enclosed cavity in order to enhance heat transfer and improve the flow behavior inside the cavity. A high percentage of published articles worked on rectangular and square cavities, while the other geometries were triangular, trapezoidal, semi-circular, etc. Furthermore, some articles discussed the flow behavior of two adjacent rectangular domains that are used in building blocks or some types of windows. Two main hydraulic boundary conditions are applied: fixed and moving boundaries (lid-driven), while several thermal boundary conditions are applied, starting with temperature difference, heat flux, cold and hot fins, and other types of objects, etc. Moreover, the effect of sinusoidal and triangular surfaces and flexible boundaries are also considered. In addition, several articles have studied the influence of magnetic fields and different fluids types on heat transfer.
Through the review of natural convection, the findings revealed that Nu increased with the rise of Ra and nanoparticles concentration. Moreover, Nu decreased with the increase in Ha. The effect of objects inside the cavity varied with the boundary conditions applied to the surface of the object and conditions of it whether it was fixed or moving. Moreover, Nu decreased with the increase in Da considering porous material inside the cavity. The cavity with forced convection is discussed by many authors. In addition to the previous mentioned boundary conditions and types of cavities, a moving boundary is applied (lid-driven cavity). This type of condition will move the flow inside the cavity from natural convection to forced convection or mixed convection between two types.
During the lid-driven cavity, there will be an interchange relationship between forced, and natural convection depending on the applied boundary conditions and types of fluids that have been used. Some results demonstrate that buoyancy will be dominant for high values of Pr while forced convection controls the flow process inside the cavity. The influence of adding different nanoparticles led to an increase in Nu and rate of heat transfer with the rise in nanoparticles concentration. In a few cases, nanofluid had an inverse effect on Nu at low Re when Ri is high. The majority of published articles demonstrated that the increase in Ri led to a decrease in Nu and the rate of heat transfer. In the case of elastic boundaries, some results presented that the heat transfer raised with an increase in Ri. In most cases, the rate of heat transfer improved with the increase in Ha. Some articles referred to a rise in Nu with the increase in Ha, with some boundaries being elastic and the cavity being filled with porous media. The existence of some objects inside the cavity had helped to increase in heat transfer rate. For example, rotating cylinders, flat plates, triangular blocks, rectangular blades, etc., led to an increase in Nu.
Finally, this configurative systematic review focuses on the importance of heat transfer enhancement or degeneration in relation to various factors such as the shape of the cavity, the presence of fins/cylinders/blocks/blades, and the use of fluids/nanofluids/hybrid-nanofluids and/or porous media. The review also proposes future research directions based on an extensive literature review. The review includes details of the flow domain, dimensions, type of flow, parameters and their ranges, meshing, CFD methods, and algorithms, which are presented in tabular form. Additionally, the review provides extensive details on CFD validation. The authors believe that this is the first time such detailed information has been presented in a review and that it will be valuable for future researchers.
7. Future Work
In conclusion, research on heat transfer behavior in cavities has been highlighted since around 1965, and much research is still being carried out by researchers. However, several key points are not highlighted yet and can be considered as future research, and such key points are mentioned below:
- Most of the studies focused on laminar natural/mixed/forced convection flow, but very few studies considered turbulent flow regimes.
- Most recently, rotating blades or plates inside the cavity received attention from researchers. Still, no work is conducted considering the design, shape, and aerodynamic behavior of blades.
- Will it be possible to develop a general form of correlation for the average Nusselt number?
- Very little research is found considering the LES and DNS modeling in cavities for transient/turbulent flow regimes. This area should be considered a high-interest area in the future.
- The choice of turbulence models has not been highlighted yet by researchers. It can be an important study.
- Different types of shapes are considered in the literature, but more research is suggested to find an optimum design of the physical domain that can give maximum heat transfer enhancement.
- Very little or limited research work is conducted considering the presence of nanoplastic or microplastic in fluids inside a cavity. It is highly considered research for future studies.
- Study the hydraulic and thermal behavior of two immiscible fluids (for example, air and water) inside a cavity.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.C.S.; methodology, G.S.; data curation, G.S. and A.A.Y.A.-W.; writing—original draft preparation, G.S. and A.A.Y.A.-W.; writing—review and editing, S.C.S. and M.C.P.; supervision, S.C.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
All data are available in the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing interests.
Nomenclature
| A | Aspect ratio |
| AB | Adams-Bashforth method |
| ADI | Alternate Direct Implicit scheme |
| ALE | Arbitrary-Lagrangian–Eulerian approach |
| Am | Amplitude |
| ANFIS | Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Interface System |
| b | Size of blocage (%) |
| B | Dimensionless magnetic induction |
| BGK | Bhatnagar–Gross–Krook |
| BiCGStab | Biconjugate gradient stabilized method |
| C | Concentration |
| CDS | Central differencing schemes |
| CN | Crank-Nicolson |
| COBYLA | Constrained Optimization BY Linear Approximations |
| Cp | Specific heat |
| DADI | Dynamic alternating direction implicit scheme |
| DRBEM | Dual reciprocity boundary element method |
| DNS | Direct numerical simulation |
| dp | Nanoparticles diameter |
| E | Young’s modulus |
| f | Fluid |
| FDM | Finite difference method |
| FEM | Finite element method |
| FVM | Finite volume method |
| FSI | Fluid-structure interaction |
| GE | Gaussian Elimination method |
| Gr | Grashof number |
| GrC | Mass transfer Grashof number |
| GrT | Heat transfer Grashof number |
| GS | Gauss-Seidel method |
| h | Cavity height |
| Ha | Hartmann number |
| HO-MFA | High-order mesh-free approach |
| IEFG–RIPM | Improved element-free Galerkin–reduced integration penalty method |
| J | Joul heating parameter |
| K | Thermal conductivity ratio |
| Kl | Low conductivity material |
| LB | lattice Boltzmann method |
| LES | Large Eddy Simulation |
| Le | Lewis number |
| Lh | Vertical distance between bottom of the cavity and the hot disturbance area |
| Lc | Vertical distance between bottom of the cavity and the cold disturbance area |
| M | Magnetic parameter |
| Ma | Mach number |
| MLS | Moving least squares |
| MRT | Multiple-Relaxation-Time |
| MWCNT | Multi wall carbon nanotubes |
| n | Flow behavior index for a power-law fluid |
| nf | Nanofluid |
| N | Buoyancy ratio |
| Nb | Brownian motion |
| Nt | Thermophoresis parameter |
| NR | Newton-Raphson method |
| Nu | Local Nusselt number |
| Average Nusselt number (Nuavg) | |
| NuL | Average Nusselt number based on the cavity length |
| NuymL | The mean of the local Nusselt numbers |
| Os | Ostrogradsky number |
| Pe | Peclet number |
| PCM | Phase change material |
| Pr | Prandtl number |
| Prt | Turbulent Prandtl number |
| q | Heat generation or absorption |
| QUICK | Quadratic upstream interpolation for convective kinematics |
| R | Internal to external Rayleigh numbers ratio |
| Ra | Rayleigh number |
| RaT | Generalized thermal Rayleigh number |
| RaI | Internal Rayleigh number |
| RaE | External Rayleigh number |
| Ram | Magnetic Rayleigh number |
| RaL | Average Rayleigh number based on the cavity length |
| Rayml | The mean of the local Rayleigh numbers |
| Rbf-Pum | Radial basis function-based partition of unity method |
| RBSOR | Red and black SOR method |
| Rd | Radiation parameter |
| Re | Reynolds number |
| Rew | Rotational Reynolds number |
| Ri | Richardson number |
| RK | Runge-Kutta method |
| RSM | Response surface methodology |
| s, np | Solid or nanoparticles |
| Sc | Schemidt number |
| SEM | Spectral element method |
| Sh | Sherwood number |
| SIMPLE | Semi-implicit method for pressure-linked equations |
| SOR | Successive over-relaxation |
| SUR | Successive under relaxation |
| Sr | Soret parameter |
| Ta | Taylor number |
| TDMA | Tri-diagonal matrix algorithm |
| TFM | Triangular factorization method |
| Tp | Partition thickness |
| Tr | Thermal conductivity ratio, |
| TS | Taylor series |
| UCS | Upwind compact Scheme |
| UDS | Upwind difference Scheme |
| URANS | Averaged Navier–Stokes |
| x | Horizontal coordinate |
| y | Vertical coordinate |
| Inclination angle | |
| Nanoparticles volume fraction | |
| Emissivity | |
| Number of undulation | |
| Thermal conductivity | |
| Phase deviation | |
| Density | |
| Rotational speed | |
| Oscillation frequency | |
| Angular frequency | |
| Dynamic viscosity |
References
- Holman, J.P. Heat Transfer, 10th ed.; Mcgraw-Hill Higher Education: Boston, MA, USA, 2010; ISBN 0073529362. [Google Scholar]
- Wee, H.K.; Keey, R.B.; Cunningam, M.J. Heat and moisture transfer by natural convection in a rectangular cavity. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 1989, 32, 1765–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.X.; Xiao, Z.; Wub, S.; Tian, Z.F.; Cheng, X. High accuracy numerical investigation of double-diffusive convection in a rectangular cavity under a uniform horizontal magnetic field and heat source. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2017, 110, 613–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Zhou, X. Analysis of flow and heat transfer characteristics of nanofluids surface tension driven convection in a rectangular cavity. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2019, 153–154, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqaed, S.; Mustafa, J.; Sharifpur, M. Numerical investigation and optimization of natural convection and entropy generation of alumina/H2O nanofluid in a rectangular cavity in the presence of a magnetic field with artificial neural networks. Eng. Anal. Bound. Elem. 2022, 140, 507–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatami, M. Numerical study of nanofluids natural convection in a rectangular cavity including heated fins. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 233, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhter, R.; Ali, M.M.; Alim, M.A. Entropy generation due to hydromagnetic buoyancy-driven hybrid-nanofluid flow in partially heated porous cavity containing heat conductive obstacle. Alex. Eng. J. 2023, 62, 17–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.S.; Billah, M.M.; Hossain, S.M.C.; Keya, S.S.; Haque, M.M. MHD influence on convective heat transfer in a semi-circular cavity using nonhomogeneous nanofluid model. Int. J. 2022, 16, 100197. [Google Scholar]
- Esfe, M.H.; Rostamian, H.; Toghraie, D.; Hekmatifar, M.; Abad, A.T.K. Numerical study of heat transfer of U-shaped enclosure containing nanofluids in a porous medium using two-phase mixture method. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2022, 38, 102150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geridonmez, B.P.; Oztop, H.F. The effect of inclined periodic magnetic field on natural convection flow of Al2O3-Cu/water nanofluid inside right isosceles triangular closed spaces. Eng. Anal. Bound. Elem. 2022, 141, 222–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moallemi, M.K.; Jjang, K.S. Prandtl number effects on laminar mixed convection heat transfer in a lid-driven cavity. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 1992, 35, 1881–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashad, A.M.; Ismael, M.A.; Chamkha, A.J.; Mansour, M.A. MHD mixed convection of localized heat source/sink in a nanofluid-filled lid-driven square cavity with partial slip. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2016, 68, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Versteeg, H.K. An Introduction to Computational Fluid Dynamics: The Finite Volume Method, 2nd ed.; Henk, K., Malalasekera, W., Malalasekera, W., Eds.; Pearson Education Ltd.: Harlow, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Sasaguchi, K.; Kusano, K.; Viskanta, R. A numerical analysis of solid-liquid phase change heat transfer around a single and two horizontal. vertically spaced cylinders in a rectangular cavity. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 1997, 40, 1349–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Amiri, A.; Khanafer, K.; Bull, J.; Pop, I. Effect of sinusoidal wavy bottom surface on mixed convection heat transfer in a lid-driven cavity. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2007, 50, 1771–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, G.; Saha, S.; Islam, M.Q.; Akhanda, M.A.R. Natural convection in enclosure with discrete isothermal heating from below. J. Nav. Archit. Mar. Eng. 2007, 4, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.C.; Lei, C.; Patterson, J.C. Effect of aspect ratio on natural convection in attics subject to periodic thermal forcing. ANZIAM J. 2007, 48, C677–C691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, R.K.; Das, M.K. Heat transfer augmentation in a two-sided lid-driven differentially heated square cavity utilizing nanofluids. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2007, 50, 2002–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Sultana, T.; Saha, G.; Rahman, M.M. Effects of discrete isoflux heat source size and angle of inclination on natural convection heat transfer flow inside a sinusoidal corrugated enclosure. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2008, 35, 1288–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varol, Y.; Oztop, H.F.; Mobedi, M.; Pop, I. Visualization of natural convection heat transport using heatline method in porous non-isothermally heated triangular cavity. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2008, 51, 5040–5051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-L.; Cheng, C.-H. Numerical study of the effects of lid oscillation on the periodic flow pattern and convection heat transfer in a triangular cavity. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2009, 36, 590–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noor, D.Z.; Kanna, P.R.; Chern, M.-J. Flow and heat transfer in a driven square cavity with double-sided oscillating lids in anti-phase. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2009, 52, 3009–3023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouertatani, N.; Cheikh, N.B.; Beya, B.B.; Lili, T.; Campo, A. Mixed convection in a double lid-driven cubic cavity. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2009, 48, 1265–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basak, T.; Roy, S.; Ramakrishna, D.; Pandey, B.D. Analysis of heat recovery and heat transfer within entrapped porous triangular cavities via heatline approach. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2010, 53, 3655–3669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, C.; O’Neill, A. Effects of adiabatic extensions on heat transfer through a differentially heated square cavity. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2010, 37, 1221–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, G. Finite element simulation of magnetoconvection inside a sinusoidal corrugated enclosure with discrete isoflux heating from below. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2010, 37, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, G.; Saha, S.; Hasan, M.N.; Islam, M.Q. Natural convection heat transfer within octagonal enclosure. IJE Trans. A Basics 2010, 23, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Saha, S.C.; Patterson, J.C.; Lei, C. Natural convection in attics subject to instantaneous and ramp cooling boundary conditions. Energy Build. 2010, 42, 1192–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.C.; Patterson, J.C.; Lei, C. Natural convection and heat transfer in attics subject to periodic thermal forcing. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2010, 49, 1899–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.C.; Patterson, J.C.; Lei, C. Natural convection in attic-shaped spaces subject to sudden and ramp heating boundary conditions. Heat Mass Transf. 2010, 46, 621–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivasankaran, S.; Sivakumar, V.; Prakash, P. Numerical study on mixed convection in a lid-driven cavity with non-uniform heating on both sidewalls. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2010, 53, 4304–4315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivakumar, V.; Sivasankaran, S.; Prakash, P.; Lee, J. Effect of heating location and size on mixed convection in lid-driven cavities. Comput. Math. Appl. 2010, 59, 3053–3065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Amiri, A.; Khanafer, K. Fluid–structure interaction analysis of mixed convection heat transfer in a lid-driven cavity with a flexible bottom wall. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2011, 54, 3826–3836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, T.S. Characteristics of mixed convection heat transfer in a lid-driven square cavity with various Richardson and Prandtl numbers. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2011, 50, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasrin, R.; Parvin, S. Hydromagnetic effect on mixed convection in a lid-driven cavity with sinusoidal corrugated bottom surface. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2011, 38, 781–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.C. Unsteady natural convection in a triangular enclosure under isothermal heating. Energy Build. 2011, 43, 695–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.C. Scaling of free convection heat transfer in a triangular cavity for Pr > 1. Energy Build. 2011, 43, 2908–2917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.-T.; Wang, W.; Xu, X.; Fan, L.-W.; Hu, Y.-C.; Cen, K.-F. A numerical investigation of transient natural convection heat transfer of aqueous nanofluids in a differentially heated square cavity. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2011, 38, 585–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Farhany, K.; Turan, A. Numerical study of double-diffusive natural convective heat and mass transfer in an inclined rectangular cavity filled with porous medium. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2012, 39, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arani, A.A.A.; Sebdani, S.M.; Mahmoodi, M.; Ardeshiri, A.; Aliakbari, M. Numerical study of mixed convection flow in a lid-driven cavity with sinusoidal heating on sidewalls using nanofluid. Superlattices Microstruct. 2012, 51, 893–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basak, T.; Gunda, P.; Anandalakshmi, R. Analysis of entropy generation during natural convection in porous right-angled triangular cavities with various thermal boundary conditions. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2012, 55, 4521–4535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamkha, A.J.; Abu-Nada, E. Mixed convection flow in single- and double-lid driven square cavities filled with water–Al2O3 nanofluid: Effect of viscosity models. Eur. J. Mech. B Fluid. 2012, 36, 82–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasrin, R.; Parvin, S. Investigation of buoyancy-driven flow and heat transfer in a trapezoidal cavity filled with water–Cu nanofluid. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2012, 39, 270–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raji, A.; Hasnaoui, M.; Naïmi, M.; Slimani, K.; Ouazzani, M.T. Effect of the subdivision of an obstacle on the natural convection heat transfer in a square cavity. Comput. Fluid. 2012, 68, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.C.; Gu, Y.T. Free convection in a triangular enclosure with fluid-saturated porous medium and internal heat generation. ANZIAM J. 2012, 53, C127–C141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.C.; Gu, Y.T. Natural convection in a triangular enclosure due to non-uniform cooling on top. ANZIAM J. 2012, 53, C53–C68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teamah, M.A.; El-Maghlany, W.M. Augmentation of natural convective heat transfer in square cavity by utilizing nanofluids in the presence of magnetic field and uniform heat generation/absorption. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2012, 58, 130–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.E.; Mansour, M.A.; Mahdy, A. MHD mixed convection in an inclined lid-driven cavity with opposing thermal buoyancy force: Effect of non-uniform heating on both side walls. Nucl. Eng. Des. 2013, 265, 938–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, S.; Dalal, A. Analysis of natural convection heat transfer and entropy generation inside porous right-angled triangular enclosure. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2013, 65, 500–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, C.-C.; Chen, C.-L.; Chen, C.-K. Mixed convection heat transfer performance of water-based nanofluids in lid-driven cavity with wavy surfaces. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2013, 68, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsherbiny, S.M.; Ragab, E.H. Laminar natural convection in inclined rectangular cavities with a localized heat source. Alex. Eng. J. 2013, 52, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huelsz, G.; Rechtman, R. Heat transfer due to natural convection in an inclined square cavity using the lattice Boltzmann equation method. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2013, 65, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanafer, K.; Aithal, S.M. Laminar mixed convection flow and heat transfer characteristics in a lid-driven cavity with a circular cylinder. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2013, 66, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakrishna, D.; Basak, T.; Roy, S. Analysis of heatlines and entropy generation during free convection within trapezoidal cavities. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2013, 45, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivasankaran, S.; Sivakumar, V.; Hussein, A.K. Numerical study on mixed convection in an inclined lid-driven cavity with discrete heating. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2013, 46, 112–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathiyamoorthy, M.; Chamkha, J. Analysis of natural convection in a square cavity with a thin partition for linearly heated side walls. Int. J. Numer. Method. Heat Fluid Flow 2014, 24, 1057–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Nada, E.; Chamkha, A.J. Mixed convection flow of a nanofluid in a lid-driven cavity with a wavy wall. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2014, 57, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ait-Taleb, T.; Abdelbaki, A.; Zrikem, Z. Simulation of coupled heat transfers in a hollow tile with two vertical and three horizontal uniform rectangular cavities heated from below or above. Energy Build. 2014, 84, 628–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, T.S.; Liu, W.-H. Effects of cavity inclination on mixed convection heat transfer in lid-driven cavity flows. Comput. Fluid. 2014, 100, 108–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, C.-C. Heat transfer and entropy generation of natural convection in nanofluid-filled square cavity with partially-heated wavy surface. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2014, 77, 818–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalteh, M.; Javaherdeh, K.; Toraj Azarbarzin, T. Numerical solution of nanofluid mixed convection heat transfer in a lid-driven square cavity with a triangular heat source. Powder Technol. 2014, 253, 780–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanafer, K. Comparison of flow and heat transfer characteristics in a lid-driven cavity between flexible and modified geometry of a heated bottom wall. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2014, 78, 1032–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthtamilselvan, M.; Doh, D.H. Mixed convection of heat generating nanofluid in a lid-driven cavity with uniform and non-uniform heating of bottom wall. Appl. Math. Model. 2014, 38, 3164–3174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakrishna, D.; Basak, T.; Roy, S.; Momoniat, E. Analysis of thermal efficiency via analysis of heat flow and entropy generation during natural convection within porous trapezoidal cavities. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2014, 77, 98–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, S.; Chatterjee, D. MHD mixed convection in a lid-driven cavity including heat conducting circular solid object and corner heaters with Joule heating. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2014, 57, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.C.; Gu, Y.T. Transient air flow and heat transfer in a triangular enclosure with a conducting partition. Appl. Math. Model. 2014, 38, 3879–3887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Saha, S.C. Transition to an unsteady flow induced by a fin on the sidewall of a differentially heated air-filled square cavity and heat transfer. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2014, 71, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Xu, F.; Saha, S.C. A three-dimensional simulation of transient natural convection in a triangular cavity. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2015, 85, 1012–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsherbiny, S.M.; Ismail, O.I. Heat transfer in inclined air rectangular cavities with two localized heat sources. Alex. Eng. J. 2015, 54, 917–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groşan, T.; Revnic, C.; Pop, I.; Ingham, D.B. Free convection heat transfer in a square cavity filled with a porous medium saturated by a nanofluid. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2015, 87, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moumni, H.; Welhezi, H.; Djebali, R.; Sediki, E. Accurate finite volume investigation of nanofluid mixed convection in two-sided lid-driven cavity including discrete heat sources. Appl. Math. Model. 2015, 39, 4164–4179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.C.; Gu, Y.T. Natural convection in a triangular enclosure heated from below and non-uniformly cooled from top. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2015, 80, 529–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheremet, M.A.; Pop, I. Mixed convection in a lid-driven square cavity filled by a nanofluid: Buongiorno’s mathematical model. Appl. Math. Comput. 2015, 266, 792–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sojoudi, A.; Saha, S.C.; Gu, Y.T. Natural convection due to differential heating of inclined walls and heat source placed on bottom wall of an attic shaped space. Energy Build. 2015, 89, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armaghani, T.; Kasaeipoor, A.; Alavi, N.; Rashidi, M.M. Numerical investigation of water-alumina nanofluid natural convection heat transfer and entropy generation in a baffled L-shaped cavity. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 223, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jmai, R.; Ben-Beya, B.; Lili, T. Numerical analysis of mixed convection at various walls speed ratios in two-sided lid-driven cavity partially heated and filled with nanofluid. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 221, 691–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kareem, A.K.; Gao, S.; Ahmed, A.Q. Unsteady simulations of mixed convection heat transfer in a 3D closed lid-driven cavity. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2016, 100, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kareem, A.K.; Mohammed, H.A.; Hussein, A.K.; Gao, S. Numerical investigation of mixed convection heat transfer of nanofluids in a lid-driven trapezoidal cavity. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2016, 77, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamourian, M.; Shirvan, K.M.; Ellahi, R.; Rahimi, A.B. Optimization of mixed convection heat transfer with entropy generation in a wavy surface square lid-driven cavity by means of Taguchi approach. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2016, 102, 544–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mejri, I.; Mahmoudi, A.; Abbassi, M.A.; Omri, A. LBM simulation of natural convection in an inclined triangular cavity filled with water. Alex. Eng. J. 2016, 55, 1385–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmati, A.R.; Roknabadi, A.R.; Abbaszadeh, M. Numerical simulation of mixed convection heat transfer of nanofluid in a double lid-driven cavity using lattice Boltzmann method. Alex. Eng. J. 2016, 55, 3101–3114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selimefendigil, F.; Öztop, H.F. Analysis of MHD mixed convection in a flexible walled and nanofluids filled lid-driven cavity with volumetric heat generation. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2016, 118, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selimefendigil, F.; Öztop, H.F. Natural convection in a flexible sided triangular cavity with internal heat generation under the effect of inclined magnetic field. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2016, 417, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selimefendigil, F.; Öztop, H.F.; Chamkha, A.J. MHD mixed convection and entropy generation of nanofluid filled lid driven cavity under the influence of inclined magnetic fields imposed to its upper and lower diagonal triangular domains. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2016, 406, 266–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sojoudi, A.; Saha, S.C.; Sefidan, A.M.; Gu, Y.T. Natural convection subject to sinusoidal thermal forcing on inclined walls and heat source located on bottom wall of an attic-shaped space. Energy Build. 2016, 128, 845–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sojoudi, A.; Saha, S.C.; Xu, F.; Gu, Y.T. Transient air flow and heat transfer due to differential heating on inclined walls and heat source placed on the bottom wall in a partitioned attic shaped space. Energy Build. 2016, 113, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aparna, K.; Seetharamu, K.N. Investigations on the effect of non-uniform temperature on fluid flow and heat transfer in a trapezoidal cavity filled with porous media. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2017, 108, 63–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsabery, A.I.; Chamkha, A.J.; Saleh, H.; Hashim, I. Transient natural convective heat transfer in a trapezoidal cavity filled with non-Newtonian nanofluid with sinusoidal boundary conditions on both sidewalls. Powder Technol. 2017, 308, 214–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Weheibi, S.M.; Rahman, M.M.; Alam, M.S.; Vajravelu, K. Numerical simulation of natural convection heat transfer in a trapezoidal enclosure filled with nanoparticles. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2017, 131–132, 599–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balla, C.S.; Kishan, N.; Gorla, R.S.R.; Gireesha, B.J. MHD boundary layer flow and heat transfer in an inclined porous square cavity filled with nanofluids. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2017, 8, 237–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Xu, F.; Saha, S.C. Transition to unsteady natural convection flow in a prismatic enclosure of triangular section. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2017, 111, 330–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, D.; Lukose, L.; Basak, T. Role of finite element based grids and simulations on evaluation of Nusselt numbers for heatfunctions within square and triangular cavities involving multiple discrete heaters. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2017, 89, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangawane, K.M. Computational analysis of mixed convection heat transfer characteristics in lid-driven cavity containing triangular block with constant heat flux: Effect of Prandtl and Grashof numbers. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2017, 105, 34–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghalambaz, M.; Jamesahar, E.; Ismael, M.A.; Chamkha, A.J. Fluid-structure interaction study of natural convection heat transfer over a flexible oscillating fin in a square cavity. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2017, 111, 256–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibanov, N.S.; Sheremet, M.A.; Oztop, H.F.; Al-Salem, K. Convective heat transfer in a lid-driven cavity with a heat-conducting solid backward step under the effect of buoyancy force. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2017, 112, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibanov, N.S.; Sheremet, M.A.; Oztop, H.F.; Abu-Hamdeh, N. Effect of uniform inclined magnetic field on mixed convection in a lid-driven cavity having a horizontal porous layer saturated with a ferrofluid. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2017, 114, 1086–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammami, F.; Souayeh, B.; Ben-Cheikh, N.; Ben-Beya, B. Computational analysis of fluid flow due to a two-sided lid driven cavity with a circular cylinder. Comput. Fluids 2017, 156, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatami, M.; Zhou, J.; Geng, J.; Song, D.; Jing, D. Optimization of a lid-driven T-shaped porous cavity to improve the nanofluids mixed convection heat transfer. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 231, 620–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.; Ahmad, S.; Mehmood, K.; Sagheer, M. Effects of inclination angle on mixed convective nanofluid flow in a double lid-driven cavity with discrete heat sources. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2017, 106, 847–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, T.; Mehmood, Z.; Siddiqui, M.A.; Pop, I. Study of heat transfer in water-Cu nanofluid saturated porous medium through two entrapped trapezoidal cavities under the influence of magnetic field. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 240, 402–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kareem, A.K.; Gao, S. Mixed convection heat transfer of turbulent flow in a three-dimensional lid-driven cavity with a rotating cylinder. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2017, 112, 185–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanafer, K.; Aithal, S.M. Mixed convection heat transfer in a lid-driven cavity with a rotating circular cylinder. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2017, 86, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatamifar, M.; Lin, W.; Armfield, S.W.; Holmes, D.; Kirkpatrick, M.P. Conjugate natural convection heat transfer in a partitioned differentially-heated square cavity. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2017, 81, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mojumder, S.; Saha, S.; Rahman, M.R.; Rahman, M.M.; Rabbi, K.M.; Ibrahim, T.A. Numerical study on mixed convection heat transfer in a porous L-shaped cavity. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 2017, 20, 272–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selimefendigil, F.; Öztop, H.F.; Chamkha, A.J. Fluid–structure-magnetic field interaction in a nanofluid filled lid-driven cavity with flexible side wall. Eur. J. Mech. B Fluid. 2017, 61, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selimefendigil, F.; Öztop, H.F.; Chamkha, A.J. Analysis of mixed convection of nanofluid in a 3D lid-driven trapezoidal cavity with flexible side surfaces and inner cylinder. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2017, 87, 40–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selimefendigil, F.; Öztop, H.F. Mixed convection in a partially heated triangular cavity filled with nanofluid having a partially flexible wall and internal heat generation. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2017, 70, 168–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheremet, M.A.; Revnic, C.; Pop, I. Natural convective heat transfer through two entrapped triangular cavities filled with a nanofluid: Buongiorno’s mathematical model. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2017, 133, 484–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghakhani, S.; Pordanjani, A.H.; Karimipour, A.; Abdollahi, A.; Afrand, M. Numerical investigation of heat transfer in a power-law non-Newtonian fluid in a C-Shaped cavity with magnetic field effect using finite difference lattice Boltzmann method. Comput. Fluid. 2018, 176, 51–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astanina, M.S.; Sheremet, M.A.; Oztop, H.F. MHD natural convection and entropy generation of ferrofluid in an open trapezoidal cavity partially filled with a porous medium. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2018, 48, 326–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsabery, A.I.; Ismael, M.A.; Chamkha, A.J.; Hashim, I. Mixed convection of Al2O3-water nanofluid in a double lid-driven square cavity with a solid inner insert using Buongiorno’s two-phase model. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2018, 119, 939–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balootaki, A.; Karimipour, A.; Toghraie, D. Nano scale lattice Boltzmann method to simulate the mixed convection heat transfer of air in a lid-driven cavity with an endothermic obstacle inside. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2018, 508, 681–701. [Google Scholar]
- Bhowmick, S.; Xu, F.; Zhang, X.; Saha, S.C. Natural convection and heat transfer in a valley shaped cavity filled with initially stratified water. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2018, 128, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, C.-C. Heat transfer and entropy generation of mixed convection flow in Cu-water nanofluid-filled lid-driven cavity with wavy surface. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2018, 119, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangawane, K.M.; Oztop, H.F.; Abu-Hamdeh, N. Mixed convection characteristic in a lid-driven cavity containing heated triangular block: Effect of location and size of block. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2018, 124, 860–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibanov, N.S.; Sheremet, M.A.; Oztop, H.F.; Abu-Hamdeh, N. Mixed convection with entropy generation of nanofluid in a lid-driven cavity under the effects of a heat-conducting solid wall and vertical temperature gradient. Eur. J. Mech. B Fluid. 2018, 70, 148–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.; Öztop, H.F.; Mehmood, K.; Abu-Hamdeh, N. Effects of inclined magnetic field on mixed convection in a nanofluid filled double lid-driven cavity with volumetric heat generation or absorption using finite element method. Chin. J. Phys. 2018, 56, 484–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, T.; Siddiqui, M.A. Effect of MHD on heat transfer through ferrofluid inside a square cavity containing obstacle/heat source. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2018, 125, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karbasifar, B.; Akbari, M.; Toghraie, D. Mixed convection of Water-Aluminum oxide nanofluid in an inclined lid-driven cavity containing a hot elliptical centric cylinder. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2018, 116, 1237–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kareem, A.K.; Gao, S. A comparison study of mixed convection heat transfer of turbulent nanofluid flow in a three-dimensional lid-driven enclosure with a clockwise versus an anticlockwise rotating cylinder. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2018, 90, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhailenko, S.A.; Sheremet, M.A.; Mohamad, A.A. Convective-radiative heat transfer in a rotating square cavity with a local heat-generating source. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2018, 142–143, 530–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oglakkaya, F.S.; Bozkaya, C. Unsteady MHD mixed convection flow in a lid-driven cavity with a heated wavy wall. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2018, 148, 231–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razera, A.L.; da Fonseca, R.J.C.; Isoldi, L.A.; dos Santos, E.D.; Rocha, L.A.O.; Biserni, C. Constructal design of a semi-elliptical fin inserted in a lid-driven square cavity with mixed convection. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2018, 126, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selimefendigil, F.; Öztop, H.F. Modeling and optimization of MHD mixed convection in a lid-driven trapezoidal cavity filled with alumina–water nanofluid: Effects of electrical conductivity models. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2018, 136, 264–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikholeslami, M. Influence of magnetic field on Al2O3-H2O nanofluid forced convection heat transfer in a porous lid-driven cavity with hot sphere obstacle by means of LBM. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 263, 472–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheremet, M.A.; Roşca, N.C.; Roşca, A.V.; Pop, I. Mixed convection heat transfer in a square porous cavity filled with a nanofluid with suction/injection effect. Comput. Math. Appl. 2018, 76, 2665–2677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghizadeh, S.; Asaditaheri, A. Heat transfer and entropy generation of laminar mixed convection in an inclined lid-driven enclosure with a circular porous cylinder. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2018, 134, 242–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, H.; Xu, F.; Hou, Y.; Saha, S.C. Natural Convection and Heat Transfer on a Section-Triangular Roof. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2018, 92, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Yan, Y.; Liu, X.; Chen, H.; Liu, B. Lattice Boltzmann simulation of mixed convection of nanofluid with different heat sources in a double lid-driven cavity. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2018, 97, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alnaqi, A.A.; Aghakhani, S.; Pordanjani, A.H.; Bakhtiari, R.; Asadi, A.; Minh-Duc Tran, M.-D. Effects of magnetic field on the convective heat transfer rate and entropy generation of a nanofluid in an inclined square cavity equipped with a conductor fin: Considering the radiation effect. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2019, 133, 256–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Rashed, A.A.A.A.; Shahsavar, A.; Akbari, M.; Toghraie, D.; Akbari, M.; Afrand, M. Finite Volume Simulation of mixed convection in an inclined lid-driven cavity filled with nanofluids: Effects of a hot elliptical centric cylinder cavity angle and volume fraction of nanoparticles. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2019, 527, 121122. [Google Scholar]
- Barnoon, P.; Toghraie, D.; Dehkordi, R.B.; Abed, H. MHD mixed convection and entropy generation in a lid-driven cavity with rotating cylinders filled by a nanofluid using two phase mixture model. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2019, 483, 224–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhowmick, S.; Saha, S.C.; Qiao, M.; Xu, F. Transition to a chaotic flow in a V-shaped triangular cavity heated from below. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2019, 128, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, C.-C. Mixed convection heat transfer and entropy generation of Cu-water nanofluid in wavy-wall lid-driven cavity in presence of inclined magnetic field. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2019, 151, 703–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Xu, F.; Saha, S.C.; Liu, Q. Transient free convection heat transfer in a section-triangular prismatic enclosure with different aspect ratios. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2019, 139, 282–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadavand, M.; Yousefzadeh, S.; Akbari, O.A.; Pourfattah, F.; Nguyen, H.M.; Asadi, A. A numerical investigation on the effects of mixed convection of Ag-water nanofluid inside a sim-circular lid-driven cavity on the temperature of an electronic silicon chip. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2019, 162, 114298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamid, M.; Usman, M.; Khan, Z.H.; Haq, R.U.; Wang, W. Heat transfer and flow analysis of Casson fluid enclosed in a partially heated trapezoidal cavity. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2019, 108, 104284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karatas, H.; Derbentli, T. Natural convection in differentially heated rectangular cavities with time-periodic boundary condition on one side. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2019, 129, 224–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamarti, H.; Mahdaoui, M.; Bennacer, R.; Chahboun, A. Numerical simulation of mixed convection heat transfer of fluid in a cavity driven by an oscillating lid using lattice Boltzmann method. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2019, 137, 615–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louaraychi, A.; Lamsaadi, M.; Naïmi, M.; Harfi, H.E.; Kaddiri, M.; Raji, A.; Hasnaoui, M. Mixed convection heat transfer correlations in shallow rectangular cavities with single and double-lid driven boundaries. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2019, 132, 394–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohebbi, R.; Izadi, M.; Sajjadi, H.; Delouei, A.A.; Sheremet, M.A. Examining of nanofluid natural convection heat transfer in a Γ-shaped enclosure including a rectangular hot obstacle using the lattice Boltzmann method. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2019, 526, 120831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selimefendigil, F.; Öztop, H.F. MHD mixed convection of nanofluid in a flexible walled inclined lid-driven L-shaped cavity under the effect of internal heat generation. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2019, 534, 122144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Hamdeh, N.H.; Oztop, H.F.; Alnefaie, K.A. A computational study on mixed convection in a porous media filled and partially heated lid-driven cavity with an open side. Alex. Eng. J. 2020, 59, 1735–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afrand, M.; Pordanjani, A.H.; Aghakhani, S.; Oztop, H.F.; Abu-Hamdeh, N. Free convection and entropy generation of a nanofluid in a tilted triangular cavity exposed to a magnetic field with sinusoidal wall temperature distribution considering radiation effects. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2020, 112, 104507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsabery, A.I.; Armaghani, T.; Chamkha, A.J.; Hashim, I. Two-phase nanofluid model and magnetic field effects on mixed convection in a lid-driven cavity containing heated triangular wall. Alex. Eng. J. 2020, 59, 129–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsabery, A.I.; Sheremet, M.A.; Chamkha, A.J.; Hashim, I. Energy transport of two-phase nanofluid approach inside a three-dimensional lid-driven cubic cavity containing solid cylinder and heat source. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2020, 154, 108010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilal, S.; Mahmood, R.; Majeed, A.H.; Khan, I.; Nisar, K.S. Finite element method visualization about heat transfer analysis of Newtonian material in triangular cavity with square cylinder. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 4904–4918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, C.-C. Effects of porous medium and wavy surface on heat transfer and entropy generation of Cu-water nanofluid natural convection in square cavity containing partially-heated surface. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2020, 119, 104925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesh, N.V.; Javed, S.; Al-Mdallal, Q.M.; Kalaivanan, R.; Chamkha, A.J. Numerical study of heat generating γ Al2O3–H2O nanofluid inside a square cavity with multiple obstacles of different shapes. Heliyon 2020, 6, e05752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haq, R.U.; Soomro, F.A.; Wang, X.; Tlili, I. Partially heated lid-driven flow in a hexagonal cavity with inner circular obstacle via FEM. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2020, 117, 104732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Z.H.; Makinde, O.D.; Hamid, M.; Haq, R.U.; Khan, W.A. Hydromagnetic flow of ferrofluid in an enclosed partially heated trapezoidal cavity filled with a porous medium. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2020, 499, 166241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Shahsavar, A.; Niazi, K.; Al-Rashed, A.A.A.A.; Talebizadehsardari, P. The effects of vertical and horizontal sources on heat transfer and entropy generation in an inclined triangular enclosure filled with non-Newtonian fluid and subjected to magnetic field. Powder Technol. 2020, 364, 924–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Huang, H. Effect of three modes of linear thermal forcing on convective flow and heat transfer in rectangular cavities. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2020, 147, 118951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rammane, M.; Mesmoudi, S.; Tri, A.; Braikat, B.; Damil, N. Solving the incompressible fluid flows by a high-order mesh-free approach. Int. J. Numer. Method. Fluid. 2020, 92, 422–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.C.; Sefidan, A.M.; Sojoudi, A. Unsteady natural convection within an attic-shaped space subject to sinusoidal heat flux on inclined walls. Energy Eng. 2020, 117, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Selimefendigil, F.; Öztop, H.F. Magnetohydrodynamics forced convection of nanofluid in multi-layered U-shaped vented cavity with a porous region considering wall corrugation effects. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2020, 113, 104551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soomro, F.A.; Haq, R.U.; Algehyne, E.A.; Tlili, I. Thermal performance due to magnetohydrodynamics mixed convection flow in a triangular cavity with circular obstacle. J. Energy Storage 2020, 31, 101702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiers, N.; Gers, R.; Skurtys, O. Heat transfer enhancement by localised time varying thermal perturbations at hot and cold walls in a rectangular differentially heated cavity. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2020, 151, 106245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljabair, S.; Ekaid, A.L.; Ibrahim, S.H.; Alesbe, I. Mixed convection in sinusoidal lid-driven cavity with non-uniform temperature distribution on the wall utilizing nanofluid. Heliyon 2021, 7, e06907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsabery, A.I.; Tayebi, T.; Kadhim, H.T.; Ghalambaz, M.; Hashim, I.; Chamkha, A.J. Impact of two-phase hybrid nanofluid approach on mixed convection inside wavy lid-driven cavity having localized solid block. J. Adv. Res. 2021, 30, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Çolak, E.; Ekici, O.; Öztop, H.F. Mixed convection in a lid-driven cavity with partially heated porous block. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2021, 126, 105450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eshaghi, S.; Izadpanah, F.; Dogonchi, A.S.; Chamkha, A.J.; Hamida, M.B.B.; Alhumade, H. The optimum double-diffusive natural convection heat transfer in H-Shaped cavity with a baffle inside and a corrugated wall. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2021, 28, 101541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayz-Al-Asad, M.; Alam, M.N.; Ahmad, H.; Sarker, M.M.A.; Alsulami, M.D.; Gepreel, K.A. Impact of a closed space rectangular heat source on natural convective flow through the triangular cavity. Results Phys. 2021, 23, 104011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasnaoui, S.; Amahmid, A.; Raji, A.; Beji, H.; Mansouri, A.E.; Hasnaoui, M. LBM simulation of stabilizing/destabilizing effects of thermodiffusion and heat generation in a rectangular cavity filled with a binary mixture. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2021, 126, 105417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.; Jamal, M.; Geridonmez, B.P. Impact of fins and inclined magnetic field in double lid-driven cavity with Cu–water nanofluid. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2021, 61, 106707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hostos, J.C.A.; Bove, J.C.S.; Cruchaga, M.A.; Fachinotti, V.D.; Agelvis, R.A.M. Solving steady-state lid-driven square cavity flows at high Reynolds numbers via a coupled improved element-free Galerkin–reduced integration penalty method. Comput. Math. Appl. 2021, 99, 211–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, W.; Hirpho, M. Finite element analysis of mixed convection flow in a trapezoidal cavity with non-uniform temperature. Heliyon 2021, 7, e05933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikram, M.M.; Saha, G.; Saha, S.C. Conjugate forced convection transient flow and heat transfer analysis in a hexagonal partitioned, air filled cavity with dynamic modulator. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2021, 167, 120786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joe, E.S.; Perumal, D.A. Computational analysis of nonhomogeneous fluid flow in a two-cylinder-driven rectangular cavity. Appl. Eng. Sci. 2021, 7, 100064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, P.; Mahapatra, T.R. MHD double-diffusive mixed convection and entropy generation of nanofluid in a trapezoidal cavity. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2021, 208, 106665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mebarek-Oudina, F.; Fares, R.; Aissa, A.; Lewis, R.W.; Abu-Hamdeh, N.H. Entropy and convection effect on magnetized hybrid nano-liquid flow inside a trapezoidal cavity with zigzagged wall. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2021, 125, 105279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Biswas, P.; Das, A.N.; Raut, S. Analysis of heat transfer characteristics through an rectangular enclosure. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 47, 2905–2911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.C.; Sefidan, A.M.; Sojoudi, A.; Molla, M.M. Transient free convection and heat transfer in a partitioned attic-shaped space under diurnal thermal forcing. Energy Eng. 2021, 118, 487–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.S.; Haq, R.U.; Al-Kouz, W. Mixed convection analysis in a split lid-driven trapezoidal cavity having elliptic shaped obstacle. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2021, 126, 105448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, H.; Yaqoob, I.; Khan, W.A.; Rafique, A. Mixed convection in an isosceles right triangular lid driven cavity using multi relaxation time lattice Boltzmann method. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2021, 128, 105552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, H.; Yaqoob, I.; Khan, W.A.; Aslam, M. Multi relaxation time Lattice Boltzmann analysis of lid-driven rectangular cavity subject to various obstacle configurations. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2021, 129, 105658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shekaramiz, M.; Fathi, S.; Ataabadi, H.A.; Kazemi-Varnamkhasti, H.; Toghraie, D. MHD nanofluid free convection inside the wavy triangular cavity considering periodic temperature boundary condition and velocity slip mechanisms. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2021, 170, 107179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tizakast, Y.; Kaddiri, M.; Lamsaadi, M. Double-diffusive mixed convection in rectangular cavities filled with non-Newtonian fluids. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2021, 208, 106667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velkennedy, R.; Nisrin, J.J.; Kalidasan, K.; Rajeshkanna, P. Numerical investigation of convective heat transfer in a rectangular vented cavity with two outlets and cold partitions. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2021, 129, 105659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, P.-Y.; Hamid, A.; Iqbal, K.; Irfan, M.; Khan, M. Numerical simulation of mixed convection flow and heat transfer in the lid-driven triangular cavity with different obstacle configurations. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2021, 123, 105202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, S.Z.; Wang, X.; Khan, W.A.; Hobiny, A.; Iqbal, K. Finite element analysis of nanofluid flow and heat transfer in a square cavity with two circular obstacles at different positions in the presence of magnetic field. J. Energy Storage 2022, 51, 104462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Xu, H.; Zhou, Y.; Qiang Yu, Q. Modelling convective transport of hybrid nanofluid in a lid-driven square cavity with consideration of Brownian diffusion and thermophoresis. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2022, 137, 106226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.M.; Akhter, R.; Alim, M.A. Magneto-mixed convection in a lid driven partially heated cavity equipped with nanofluid and rotating flat plate. Alex. Eng. J. 2022, 61, 257–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, N.; Chamkha, A.J. On the magnetohydrodynamic Al2O3-water nanofluid flow through parallel fins enclosed inside a partially heated hexagonal cavity. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2022, 132, 105885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batool, S.; Rasool, G.; Alshammari, N.; Khan, I.; Kaneez, H.; Hamadneh, N. Numerical analysis of heat and mass transfer in micropolar nanofluids flow through lid-driven cavity: Finite volume approach. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2022, 37, 102233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charqui, Z.; Moutaouakil, L.E.; Boukendil, M.; Hidki, R. Numerical study of heat transfer in a tall, partitioned cavity confining two different fluids: Application to the water Trombe wall. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2022, 171, 107266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Wang, W.; Xu, F.; Saha, S.C.; Liu, Q. Transitional free convection flow and heat transfer within attics in cold climate. Therm. Sci. 2022, 26, 4699–4709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahani, Y.; Hasnaoui, M.; Amahmid, A.; Hasnaoui, S. A Multiple-Relaxation-Time lattice Boltzmann analysis of coupled mixed convection and radiation effect in a tilted two-sided lid-driven enclosure. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2022, 791, 139386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirpho, M.; Ibrahim, W. Modeling and simulation of hybrid Casson nanofluid mixed convection in a partly heated trapezoidal enclosure. Int. J. 2022, 15, 100166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, W.H.; Azzawi, I.D.J.; Al-damook, A. The optimisation of MHD free convection inside porous trapezoidal cavity with the wavy bottom wall using response surface method. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2022, 134, 106035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y. Free convection and heat transfer characteristics in differentially heated finned cavities with inclination. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2022, 182, 107729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noor, N.F.M.; Haq, R.U.; Wong, H.F.; Alzahrani, A.K.; Ullah, M.Z. Flow and heat transfer due to partially heated moving lid in a trapezoidal cavity with different constraints at inner circular obstacle. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2022, 135, 106111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouraei, S.; Anvari, A.; Abed, A.M.; Akbari, O.A.; Montazerifar, F.; Baghaei, S.; Fatholahi, M. Heat transfer and entropy analysis for nanofluid flow in a semi-circular open cavity under mixed convection. Alex. Eng. J. 2022, 64, 309–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polasanapalli, S.R.G.; Anupindi, K. Mixed convection heat transfer in a two-dimensional annular cavity using an off-lattice Boltzmann method. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2022, 179, 107677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prince, H.A.; Rozin, E.H.; Sagor, M.J.H.; Saha, S. Evaluation of overall thermal performance for conjugate natural convection in a trapezoidal cavity with different surface corrugations. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2022, 130, 105772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahaman, M.M.; Bhowmick, S.; Mondal, R.N.; Saha, S.C. Unsteady natural convection in an initially stratified air-filled trapezoidal enclosure heated from below. Processes 2022, 10, 1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, N.C.; Amin, R.; Ishak, A. Magnetohydrodynamic Natural Convective Hybrid Nanofluid Flow in a Square Enclosure with Different Blocks. Iran. J. Sci. Technol. Trans. Mech. Eng. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.S.; Haq, R.U.; McCash, L.B.; Bahaidarah, H.M.S.; Aziz, T. Numerical simulation of lid driven flow in a curved corrugated porous cavity filled with CuO-water in the presence of heat generation/absorption. Alex. Eng. J. 2022, 61, 2749–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tizakast, Y.; Kaddiri, M.; Lamsaadi, M. Rayleigh-Bénard double-diffusive mixed convection in two-dimensional rectangular cavities filled with non-Newtonian fluids. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2022, 227, 107448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, S.; Mostafavi, M.; Alghazali, T.; Sadi, S.; Guerrero, J.W.G.; Suksatan, W.; Toghraie, D.; Khan, A. Numerical investigation of nanofluid mixed convection in a T-shaped cavity by considering a thermal barrier. Alex. Eng. J. 2022, 61, 7393–7415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarei, M.S.; Abad, A.T.K.; Hekmatifar, M.; Toghraie, D. Heat transfer in a square cavity filled by nanofluid with sinusoidal wavy walls at different wavelengths and amplitudes. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2022, 34, 101970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Nie, X.; Bokov, D.O.; Toghraie, D.; Akbari, O.A.; Montazerifar, F.; Pourfattah, F.; Esmaeili, Y.; Khodaparast, R. Numerical study of mixed convection and entropy generation of Water-Ag nanofluid filled semi-elliptic lid-driven cavity. Alex. Eng. J. 2022, 61, 8875–8896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Zhuang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, C. Experimental and numerical investigations on the melting behavior of Fe3O4 nanoparticles composited paraffin wax in a cubic cavity under a magnetic-field. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2023, 184, 107961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikram, M.M.; Saha, G.; Saha, S.C. Unsteady Conjugate Heat Transfer Characteristics in Hexagonal Cavity Equipped with a Multi-Blade Dynamic Modulator. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2023, 200C, 123527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouri, H.; Selimefendigil, F.; Bouterra, M.; Omri, M.; Alshammari, B.M.; Kolsi, L. MHD hybrid nanofluid convection and phase change process in an L-shaped vented cavity equipped with an inner rotating cylinder and PCM-packed bed system. Alex. Eng. J. 2023, 63, 563–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayed, M.A.; Hadžiabdić, M.; Dehbi, A.; Ničeno, B.; Mikityuk, K. Simulation of flow and heat transfer in a differentially heated cubical cavity using coarse Large Eddy Simulation. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2023, 183, 107892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwatsu, R.; Hyun, J.M.; Kuwahara, K. Mixed convection in a driven cavity with a stable vertical temperature gradient. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 1993, 36, 1601–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanafer, K.M.; Chamkha, A.J. Mixed convection flow in a lid-driven enclosure filled with a fluid-saturated porous medium. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 1999, 42, 2465–2481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pekmen, B.; Tezer-Sezgin, M. MHD flow and heat transfer in a lid-driven porous enclosure. Comput. Fluid. 2014, 89, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selimefendigil, F.; Öztop, H.F. Mixed convection of ferrofluids in a lid driven cavity with two rotating cylinders. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 2015, 18, 439–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharif, M.A.R. Laminar mixed convection in shallow inclined driven cavities with hot moving lid on top and cooled from bottom. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2007, 27, 1036–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Balushi, L.M.; Uddin, M.J.; Rahman, M.M. Natural convective heat transfer in a square enclosure utilizing magnetic nanoparticles. Propuls. Power Res. 2019, 8, 194–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anandalakshmi, R.; Basak, T. Heat flow visualization for natural convection in rhombic enclosures due to isothermal and non-isothermal heating at the bottom wall. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2012, 55, 1325–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashrafizadeh, A.; Nikfar, M. On the numerical solution of generalized convection heat transfer problems via the method of proper closure equations–Part II: Application to test problems. Numerical Heat Transfer. Part B 2016, 70, 204–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barakos, G.; Mitsoulis, E.; Assimacopoulos, D. Natural convection flow in a square cavity revisited: Laminar and turbulent models with wall functions. Numer. Method. Fluid. 1994, 18, 695–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, N.; Chamkha, A.J.; Manna, N.K. Energy-saving method of heat transfer enhancement during magneto-thermal convection in typical thermal cavities adopting aspiration. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouabid, M.; Hidouri, N.; Magherbi, M.; Brahim, A.B. Analysis of the magnetic field effect on entropy generation at thermosolutal convection in a square cavity. Entropy 2011, 13, 1034–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.J. A Numerical Study on a Lumped-Parameter Model and a CFD Code Coupling for the Analysis of the Loss of Coolant Accident in a Reactor Containment. Ph.D. Thesis, Universit’e de Marne-la-Vall´ee, Paris, France, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Chenoweth, D.R.; Paolucci, S. Natural convection in an enclosed vertical air layer with large horizontal temperature differences. J. Fluid Mech. 1986, 169, 173–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corzo, S.F.; Damian, S.M.; Ramajo, D.; Nigro, N.M. Numerical simulation of natural convection phenomena. Mec. Comput. 2011, 30, 277–296. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, Q.H.; Tang, G.F. Numerical visualization of mass and heat transport for conjugate natural convection/heat conduction by streamline and heatline. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2002, 45, 2373–2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vahl Davis, G. Natural convection of air in a square cavity: A benchmark numerical solutions. Int. J. Numer. Method. Fluid. 1983, 3, 249–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Orazio, A.; Corcione, M.; Celata, G.P. Application to natural convection enclosed flows of a lattice Boltzmann BGK model coupled with a general purpose thermal boundary condition. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2004, 43, 575–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixit, H.N.; Babu, V. Simulation of high Rayleigh number natural convection in a square cavity using the lattice Boltzmann method. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2006, 49, 727–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djebali, R.; Ganaoui, M.E.l.; Sammouda, H.; Bennacer, R. Some benchmarks of a side wall heated cavity using Lattice Boltzmann approach. Fluid Dyn. Mater. Process. 2009, 5, 261–282. [Google Scholar]
- Elatar, A.; Teamah, M.A.; Hassab, M.A. Numerical study of laminar natural convection inside square enclosure with single horizontal fin. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2016, 99, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Gendi, M.M. Numerical simulation of unsteady natural convection flow inside a pattern of connected open square cavities. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2018, 127, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.; Rahmani, A.; Suksatan, W.; Alizadeh, S.M.; Zarringhalam, M.; Chupradit, S.; Toghraie, D. Comprehensive investigations of mixed convection of Fe–ethylene-glycol nanofluid inside an enclosure with different obstacles using lattice Boltzmann method. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 20710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fusegi, T.; Kuwahara, K.; Farouk, B. A numerical study of three-dimensional natural convection in a differentially heated cubic enclosure. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 1991, 34, 1543–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, B.; Aminossadati, S.M.; Raisi, A. Magnetic field effect on natural convection in a nanofluid-filled square enclosure. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2011, 50, 1748–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, M.Y.; Jung, M.J. A numerical study of three-dimensional conjugate heat transfer of natural convection and conduction in a differentially heated cubic enclosure with a heat-generating cubic conducting body. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2000, 43, 4229–4248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjisophocleous, G.V.; Sousa, A.C.M.; Venart, J.E.S. Prediction of the transient natural convection in enclosures of arbitrary geometry using a nonorthogonal numerical model. Numer. Heat Transf. Part A 1988, 13, 373–392. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, C.J.; Lin, F.H. Simulation of natural convection in a vertical enclosure by using a new incompressible flow formulation-pseudovorticity-velocity formulation. Numer. Heat Transf. Part A Appl. 1997, 31, 881–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, T.; Alam, M.N.; Asjad, M.I.; Parveen, N.; Chu, Y.-M. Heatline visualization of MHD natural convection heat transfer of nanofluid in a prismatic enclosure. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 10972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalita, J.C.; Dalal, D.C.; Dass, A.K. Fully compact higher-order computation of steady-state natural convection in a square cavity. Phys. Rev. E 2001, 64, 066703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karki, P.; Yadav, A.K.; Perumal, D.A. Study of adiabatic obstacles on natural convection in a square cavity using Lattice Boltzmann method. J. Therm. Sci. Eng. Appl. 2019, 11, 034502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahveci, K. A differential quadrature solution of natural convection in an enclosure with a finite-thickness partition. Numer. Heat Transf. Part A Appl. 2007, 51, 979–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahveci, K. Buoyancy driven heat transfer of nanofluids in a tilted enclosure. ASME J. Heat Transf. 2010, 132, 062501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanafer, K.; Vafai, K.; Lightstone, M. Buoyancy-driven heat transfer enhancement in a two-dimensional enclosure utilizing nanofluids. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2003, 46, 3639–3653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatamifar, M.; Lin, W.W.; Dong, L. Transient conjugate natural convection heat transfer in a differentially-heated square cavity with a partition of finite thickness and thermal conductivity. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2021, 25, 100952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocutar, P.; Skerget, L.; Ravnik, J. Hybrid les/urans simulation of turbulent natural convection by bem. Eng. Anal. Bound. Elem. 2015, 61, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznik, F.; Vareilles, J.; Rusaouen, G.; Krauss, G. A double-population lattice Boltzmann method with non-uniform mesh for the simulation of natural convection in a square cavity. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 2007, 28, 862–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, M.A.; Machado, H.A.; Cotta, R.M. Integral transform solutions of transient natural convection in enclosures with variable fluid properties. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2007, 43, 3977–3990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, W.H.; Hollands, K.G.T.; Brunger, A.P. Experimental Nusselt numbers for a cubical-cavity benchmark problem in natural convection. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 1999, 42, 1979–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, D.C.; Young, D.L.; Murugesan, K.; Tsai, C.C.; Gou, M.H. Velocity-vorticity Formulation for 3-D Natural Convection in an Inclined Cavity by DQ Method. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2007, 50, 479–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Mohebbi, R.; Rashidi, M.M.; Yang, Z. Simulation of nanofluid natural convection in a U-shaped cavity equipped by a heating obstacle: Effect of cavity’s aspect ratio. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2018, 93, 263–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamourian, M.; Shirvan, K.M.; Pop, I. Sensitivity analysis for MHD effects and inclination angles on natural convection heat transfer and entropy generation of Al2O3-water nanofluid in square cavity by Response Surface Methodology. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2016, 79, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzari, M.T. An explicit finite element algorithm for convection heat transfer problems. Int. J. Numer. Method. Heat Fluid Flow 1999, 9, 860–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markatos, N.C.; Pericleous, K.A. Laminar and turbulent natural convection in an enclosed cavity. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 1984, 27, 755–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayeli, P.; Sheard, G.J. Natural convection and entropy generation in square and skew cavities due to large temperature differences: A Gay–Lussac-type vorticity stream-function approach. Int. J. Numer. Method. Fluid. 2021, 93, 2396–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nag, A.; Sarkar, A.; Sastri, V.M.K. Natural convection in a differentially heated square cavity with a horizontal partition plate on the hot wall. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 1993, 110, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nithyadevi, N.; Sivasankaran, S.; Kandaswamy, P. Buoyancy-driven convection of water near its density maximum with time-periodic partially active vertical walls. Meccanica 2007, 42, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olayemi, O.A.; Khaled, A.-F.; Temitope, O.J.; Victor, O.O.; Odetunde, C.B.; Adegun, I.K. Parametric study of natural convection heat transfer from an inclined rectangular cylinder embedded in a square enclosure. Aust. J. Mech. Eng. 2021, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oueslati, F.S.; Bennacer, R. Heterogeneous nanofluids: Natural convection heat transfer enhancement. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2011, 6, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oztop, H.; Abu-Nada, E. Numerical study of natural convection in partially heated rectangular enclosures filled with nanofluids. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 2008, 29, 1326–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, C.; He, Y.; Yan, S.; Tian, F.; Hu, Y. Numerical simulation of natural convection in a square enclosure filled with nanofluid using the two-phase Lattice Boltzmann method. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu´er´e, P.L.; Roquefortt, T.A.D. Computation of natural convection in two- dimensional cavities with Chebyshev polynomials. J. Comput. Phys. 1985, 57, 210–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sai, B.V.K.S.; Seetharamu, K.N.; Narayana, P.A.A. Solution of transient laminar natural convection in a square cavity by an explicit finite element scheme. Numer. Heat Transf. Part A Appl. 1994, 25, 412–422. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, X.; Khodadadi, J.M. Laminar natural convection heat transfer in a differentially heated square cavity due to a thin fin on the hot wall. J. Heat Transf. 2003, 125, 624–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, J.H.; Park, I.S. Numerical study of MHD natural convection in a rectangular enclosure with an insulated block. Numer. Heat Transf. Part A Appl. 2017, 71, 1004–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thangavelu, M.; Nagarajan, N.; Yang, R.-J. Magnetohydrodynamic effect on thermal transport by silver nanofluid flow in enclosure with central and lower heat sources. Heat Transf. Eng. 2022, 43, 1755–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tric, E.; Labrosse, G.; Betrouni, M. A First Incursion into the 3-D Structure of Natural Convection of Air in a Differentially Heated Cubic Cavity from Accurate Numerical Solutions. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2000, 43, 4043–4056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trodi, A.; Benhamza, M.E.H.B. Particle shape and aspect ratio effect of Al2O3–water nanofluid on natural convective heat transfer enhancement in differentially heated square enclosures. Chem. Eng. Commun. 2017, 204, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, C.; Patnaik, B.S.V.; Wei, D.G.W. A new benchmark quality solution for the buoyancy-driven cavity by discrete singular convolution. Numer. Heat Transf. Part B Fundam. 2001, 40, 199–228. [Google Scholar]
- Yıldız, C.; Arıcı, M.; Karabay, H. Comparison of a theoretical and experimental thermal conductivity model on the heat transfer performance of Al2O3-SiO2/water hybrid-nanofluid. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2019, 140, 598–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, C.; Xi, G. Conjugate wall conduction-fluid natural convection in a three-dimensional inclined enclosure. Numer. Heat Transf. Part A Appl. 2012, 61, 122–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.H.; Saeed, T.; Algehyne, E.A.; El-Shorbagy, M.A.; El-Refaey, A.M.; Ibrahim, M. Effect of L-shaped heat source and magnetic field on heat transfer and irreversibilities in nanofluid-filled oblique complex enclosure. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 16458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelkhalek, M.M. Mixed convection in a square cavity by a perturbation technique. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2008, 42, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Nada, E.; Chamkha, A.J. Mixed convection flow in a lid-driven inclined square enclosure filled with a nanofluid. Eur. J. Mech. B Fluid. 2010, 29, 472–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Amiri, A.M. Analysis of momentum and energy transfer in a lid-driven cavity filled with a porous medium. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2000, 43, 3513–3527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, N.; Manna, N.K.; Mahapatra, P.S. Enhanced thermal energy transport using adiabatic block inside lid-driven cavity. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2016, 100, 407–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gresho, P.M.; Lee, R.L.; Sani, R.L. On the time-dependent solution of the incompressible Navier–Stokes equations in two and three dimensions. In Recent Adv. Numerical Methods in Fluids; Pineridge: Swansea, UK, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Kefayati, G.R. Double-diffusive mixed convection of pseudoplastic fluids in a two-sided lid-driven cavity using FDLBM. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2014, 45, 2122–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanafer, K.M.; Al-Amiri, A.M.; Pop, I. Numerical simulation of unsteady mixed convection in a driven cavity. Using an externally excited sliding lid. Eur. J. Mech. B Fluid. 2007, 26, 669–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehmood, K.; Hussain, S.; Sagheer, M. Mixed convection in alumina-water nanofluid filled lid driven square cavity with an isothermally heated square blockage inside with magnetic field effect. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2017, 109, 397–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashad, A.M.; Mansour, M.A.; Armaghani, T.; Chamkha, A.J. MHD mixed convection and entropy generation of nanofluid in a lid-driven U-shaped cavity with internal heat and partial slip. Phys. Fluid. 2019, 31, 042006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, M.; Roy, S.; Basak, T. Role of various moving walls on energy transfer rates via heat flow visualization during mixed convection in square cavities. Energy 2015, 82, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waheed, M.A. Mixed convective heat transfer in rectangular enclosures driven by a continuously moving horizontal plate. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2009, 52, 5055–5063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ElSherbiny, S.M.; Raithby, G.D.; Hollands, K.G.T. Heat transfer by natural convection across vertical and inclined air layers. J. Heat Transf. Trans. ASME 1982, 104, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lartigue, B.; Lorente, S.; Bourret, B. Multicellular natural convection in a high aspect ratio cavity: Experimental and numerical results. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2000, 43, 3157–3170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Korpela, S.A. Multicellular natural convection in a vertical slot. J. Fluid Mech. 1983, 126, 91–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Power, J.P. Finite Element Model of Turbulent Flow and Heat Transfer in a Fenestration System. Ph.D. Thesis, The University of Massachusetts Amherst, Amherst, MA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Wright, J.L.; Sullivan, H.F. A two-dimensional numerical model for natural convection in a vertical. rectangular window cavity. ASHRAE Trans. 1994, 100, 1193–1206. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Goss, W.P.; Curcija, D. Prediction of the multicellular flow regime of natural convection in fenestration glazing cavities. ASHRAE Trans. 1997, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Baytas, A.C.; Pop, I. Free convection in a square porous cavity using a thermal non-equilibrium model. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2002, 41, 861–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bejan, A. On the boundary layer regime in a vertical enclosure filled with a porous medium. Lett. Heat Mass Transf. 1979, 6, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyeau, B.; Songbe, J.P.; Gobin, D. Numerical study of double-diffusive natural convection in a porous cavity using the Darcy-Brinkman formulation. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 1996, 39, 1363–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeid, N.H.; Pop, I. Natural convection from a discrete heater in a square cavity filled with a porous medium. J. Porous Media 2005, 8, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, C.J.; Liu, W.K.; Chang, Y.S.; Lin, C.C. Natural convection heat transfer of alumina-water nanofluid in vertical square enclosures: An experimental study. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2010, 49, 1345–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omri, M.; Jamal, M.; Hussain, S.; Kolsi, L.; Maatki, C. Conjugate natural convection of a hybrid nanofluid in a cavity filled with porous and non-newtonian layers: The impact of the power law index. Mathematics 2022, 10, 2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saghir, M.Z.; Ahadi, A.; Mohamad, A.; Srinivasan, S. Water aluminum oxide nanofluid benchmark model. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2016, 109, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheremet, M.; Chinnasamy, S. Convective–radiative heat transfer in a cavity filled with a nanofluid under the effect of a nonuniformly heated plate. Int. J. Numer. Method. Heat Fluid Flow 2018, 28, 1392–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shulepova, E.V.; Sheremet, M.A.; Oztop, H.F.; Abu-Hamdeh, N. Mixed convection of Al2O3–H2O nanoliquid in a square chamber with complicated fin. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2020, 165, 105192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huilgol, R.R.; Kefayati, G.H.R. Natural convection problem in a Bingham fluid using the operator-splitting method. J. Non Newton. Fluid Mech. 2015, 220, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kefayati, G.R. Mesoscopic simulation of magnetic field effect on natural convection of power-law fluids in a partially heated cavity. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2015, 94, 337–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khezzar, L.; Siginer, D.; Vinogradov, I. Natural convection of power law fluids in inclined cavities. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2012, 53, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.B.; Hyun, J.M.; Kwak, H.S. Transient buoyant convection of a power-law non-Newtonian fluid in an enclosure. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2003, 46, 3605–3617. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).