Wellbore and Reservoir Thermodynamic Appraisal in Acid Gas Injection for EOR Operations
Abstract
:1. Introduction
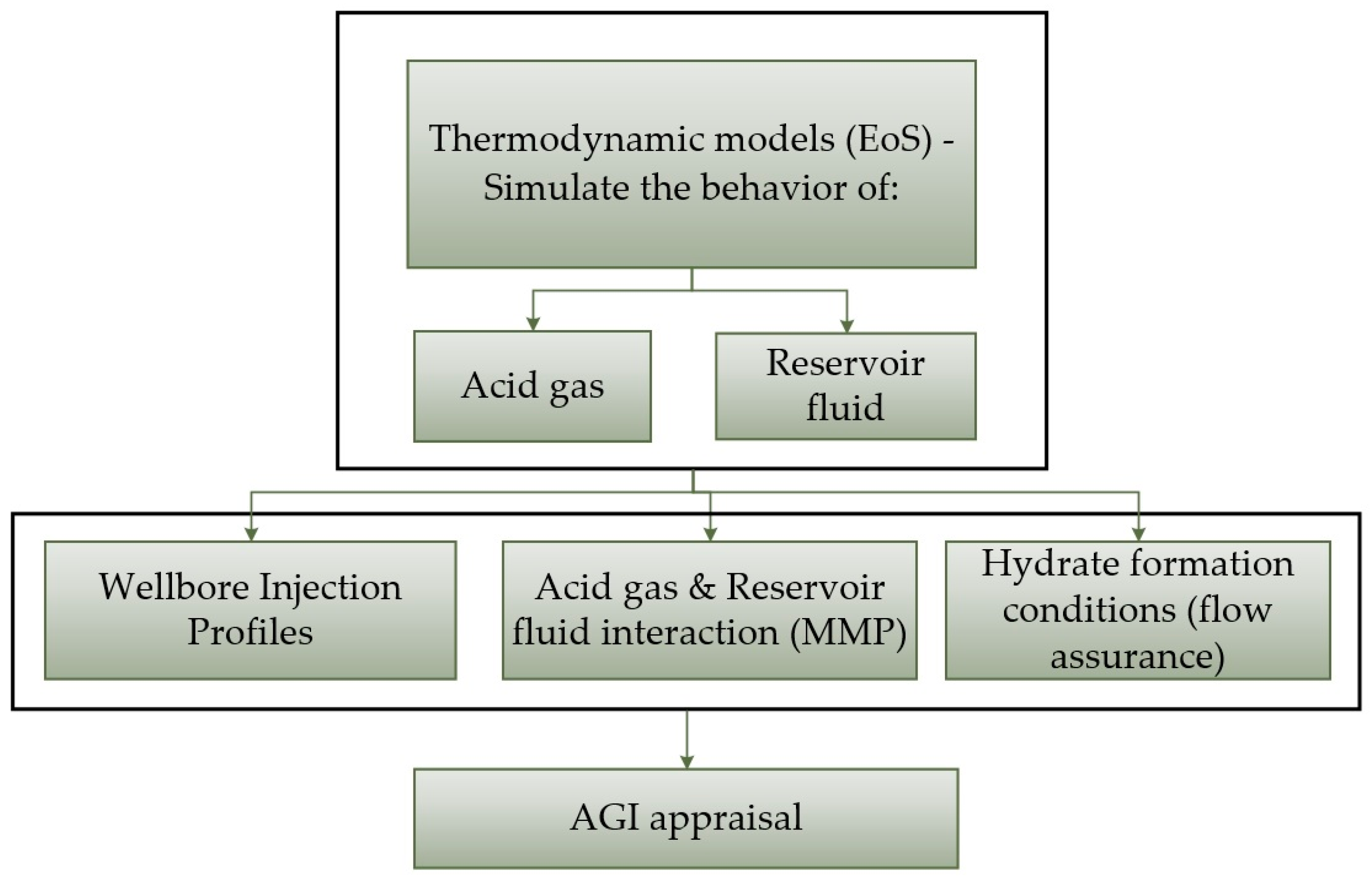
2. Acid Gas and Reservoir Oil Thermodynamic Models
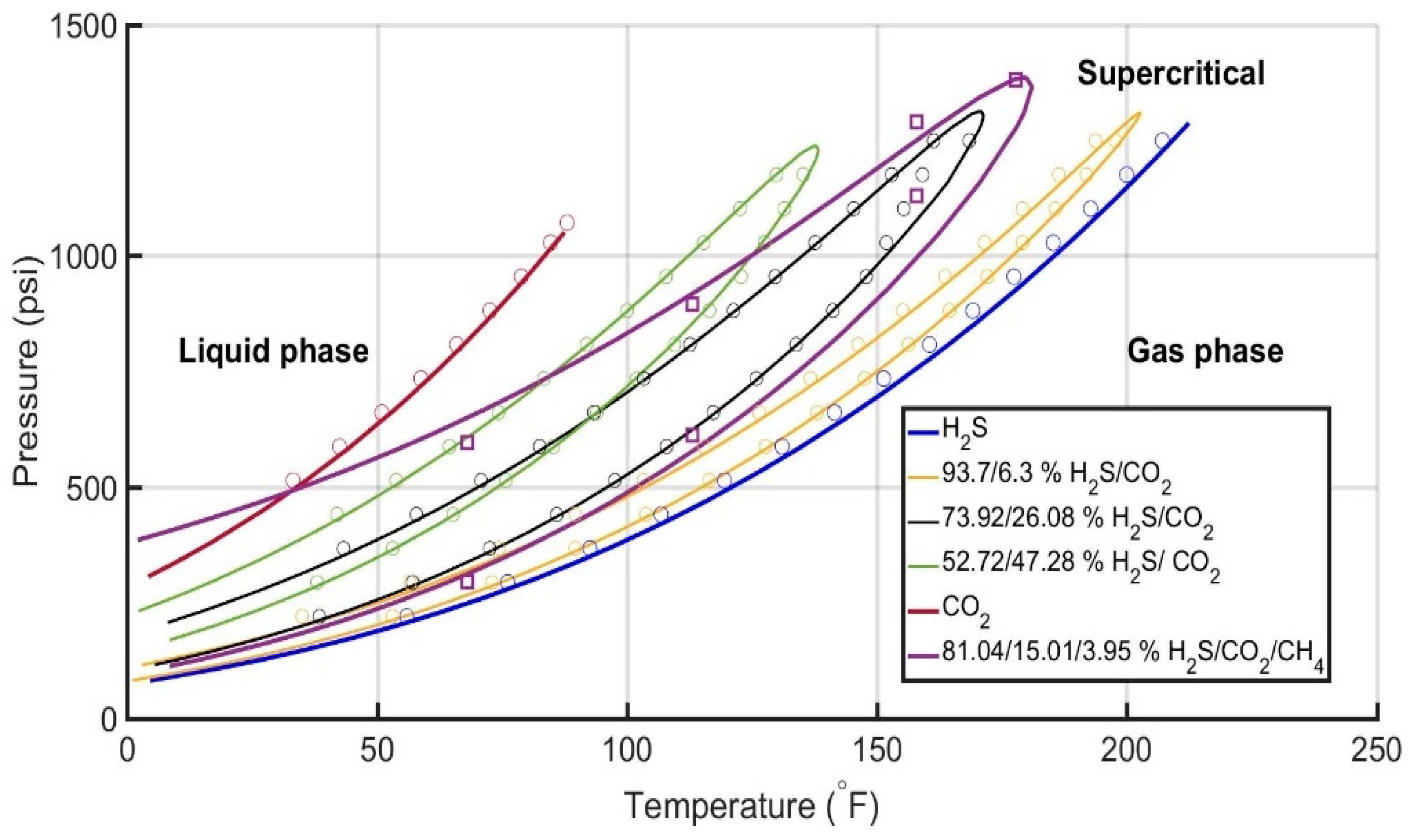
2.1. Acid Gas Thermodynamic Modelling
2.2. Reservoir Fluid Thermodynamic Modelling
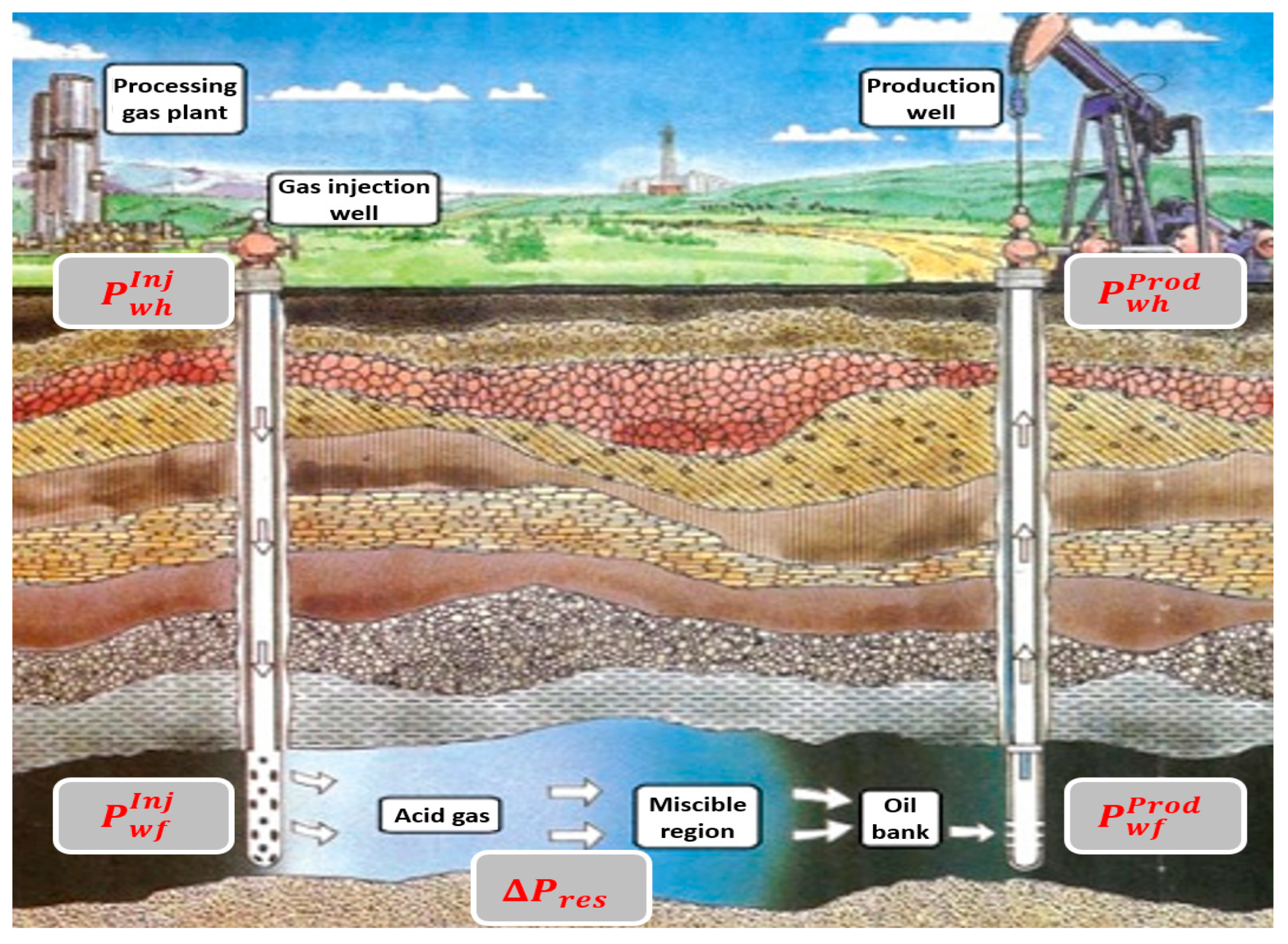
3. Specification of the Gas Injection Conditions
4. MMP Estimation Methodologies
5. Wellbore Flow Assurance
6. Results
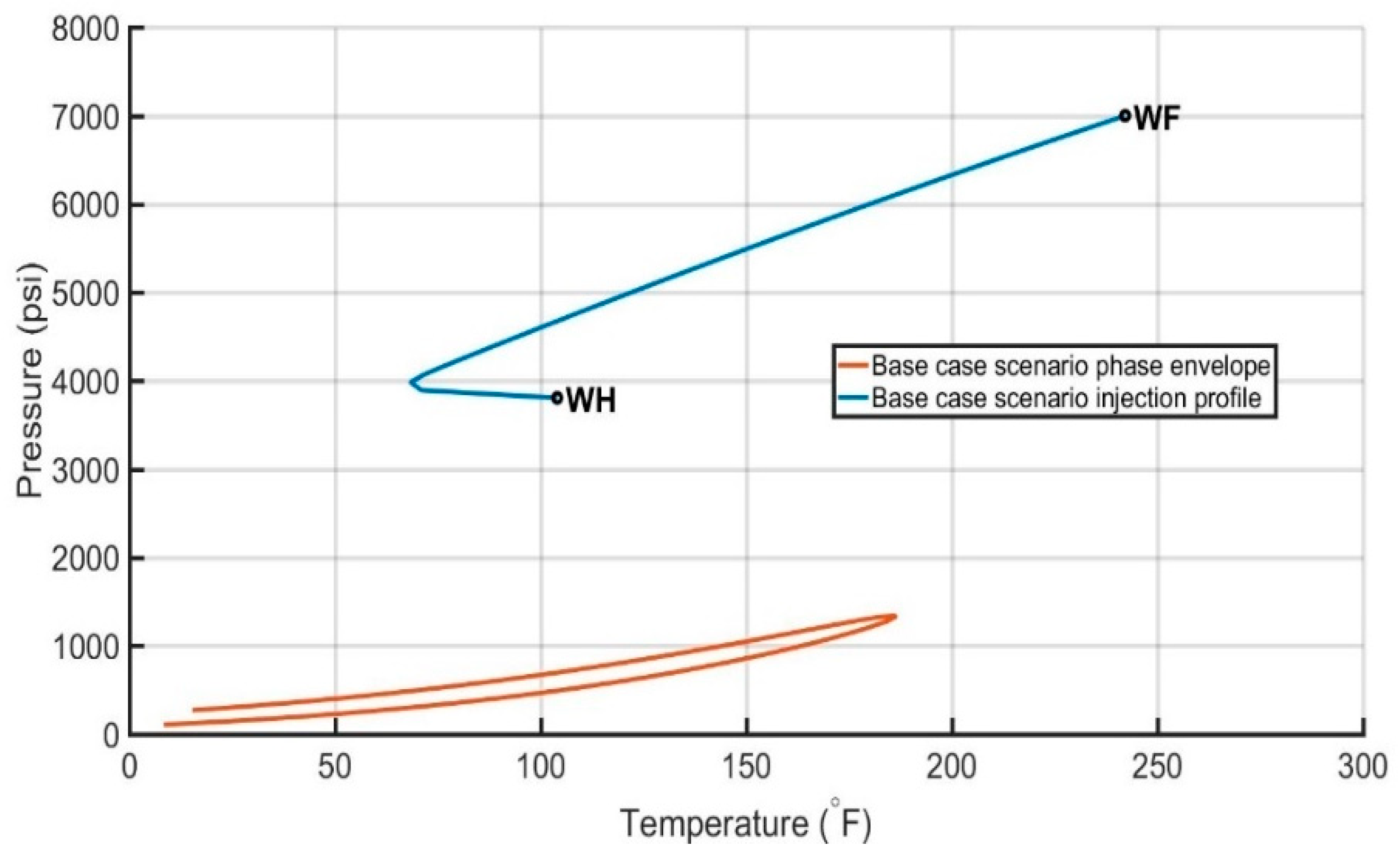
6.1. AGI in “Prinos” Reservoir
6.2. Evaluation of the Thermodynamic Tools
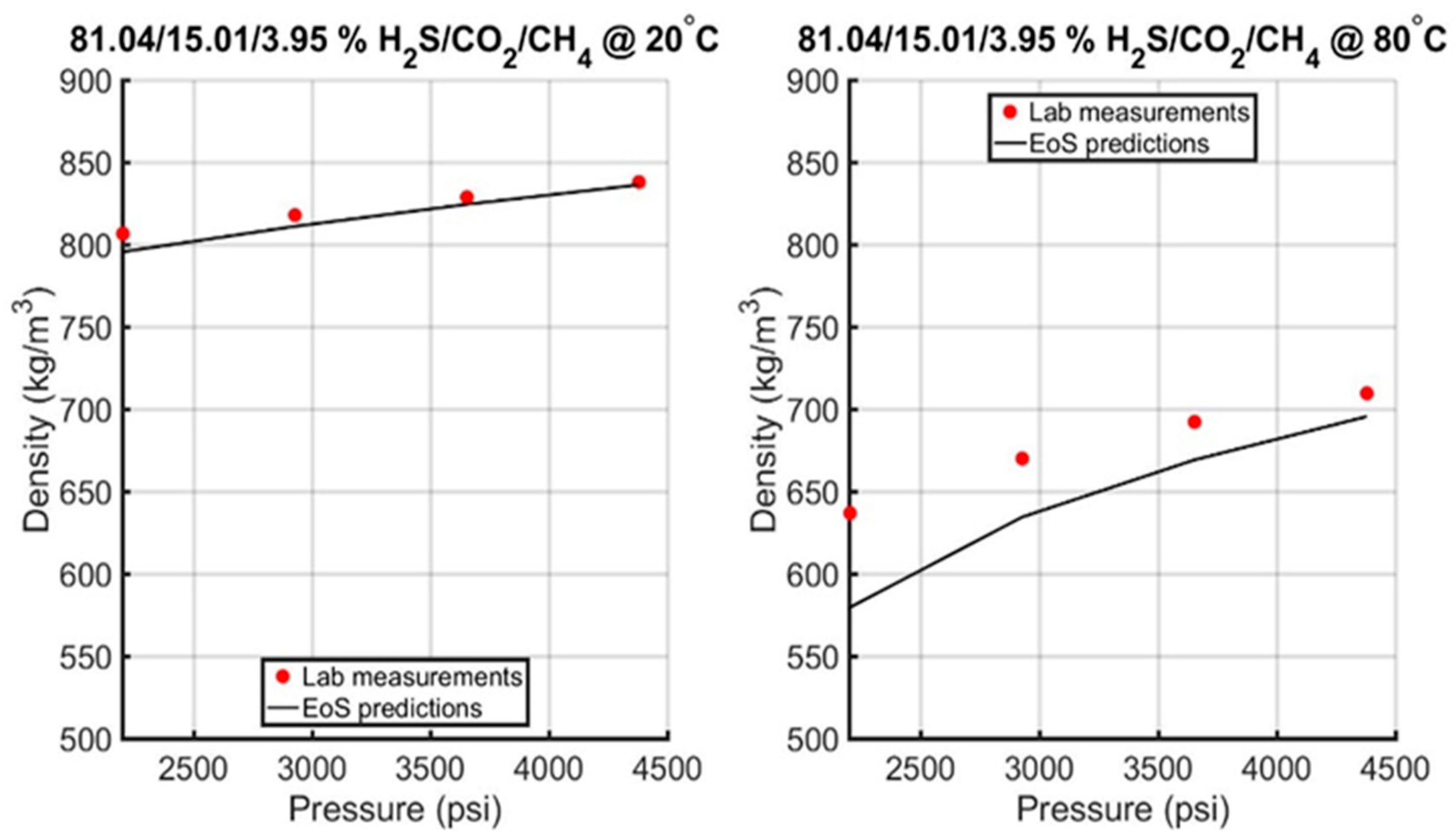
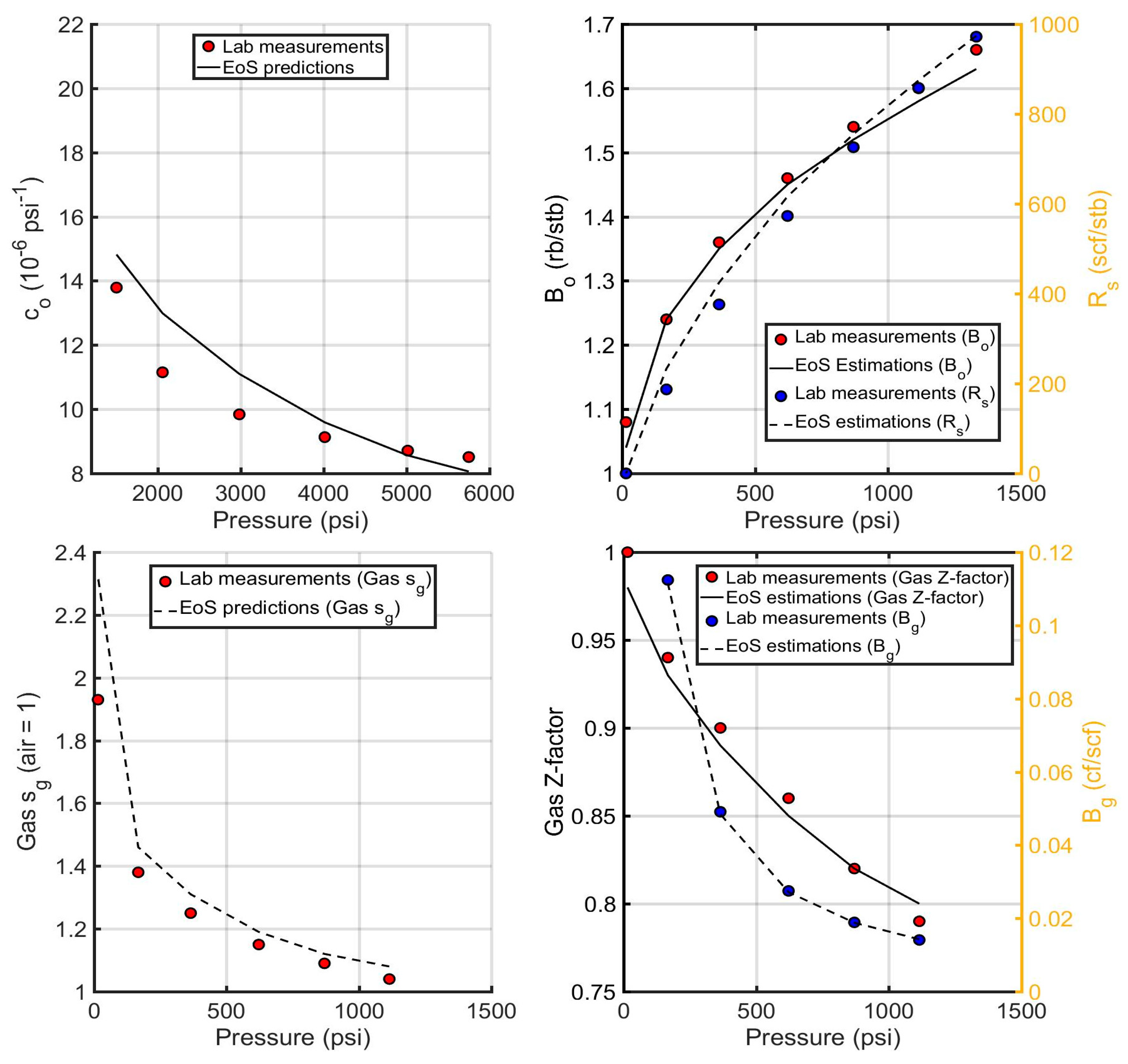
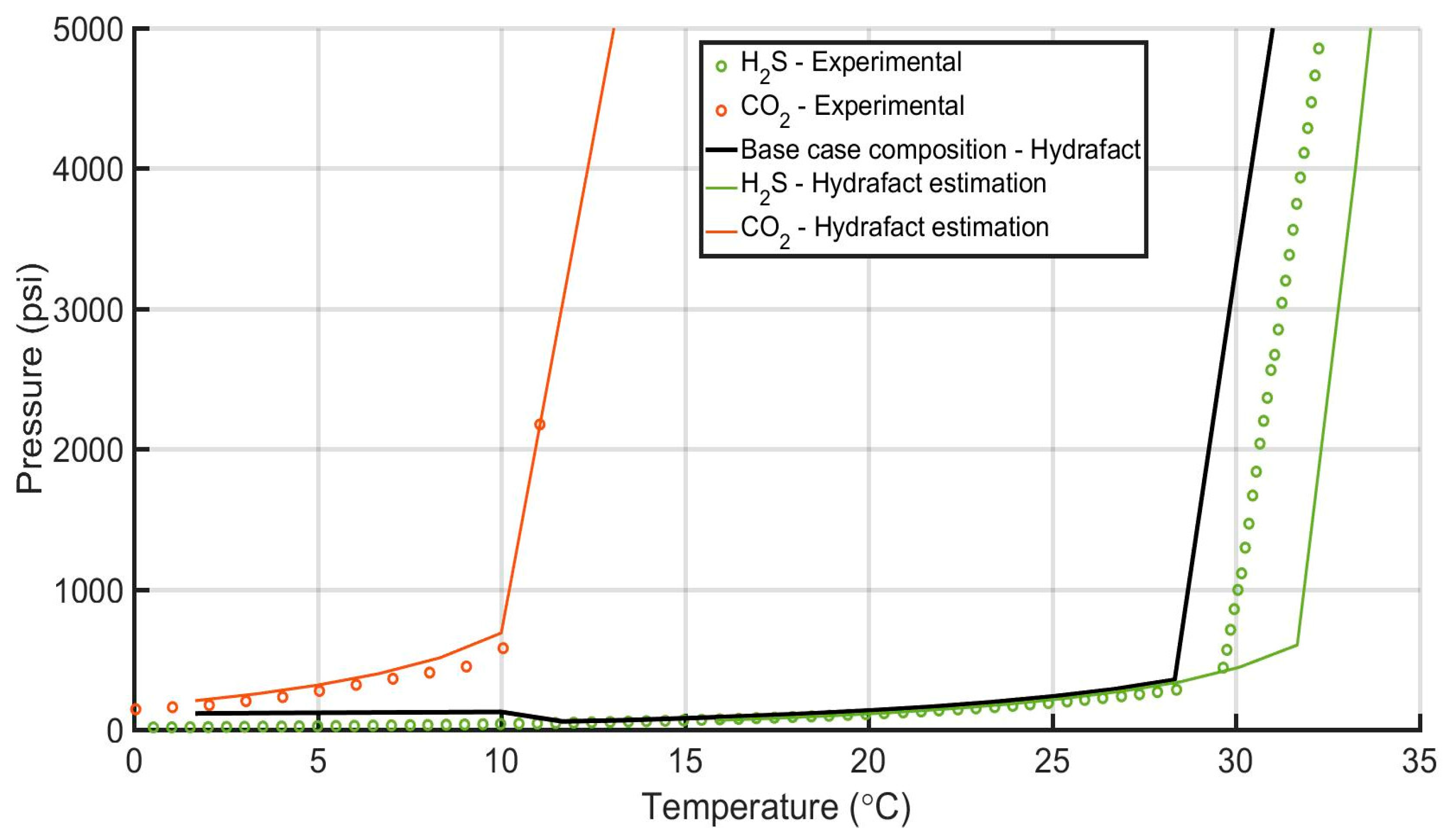
6.2.1. Evaluation of the Acid Gas EoS Model
6.2.2. Evaluation of the Reservoir oil EoS Model
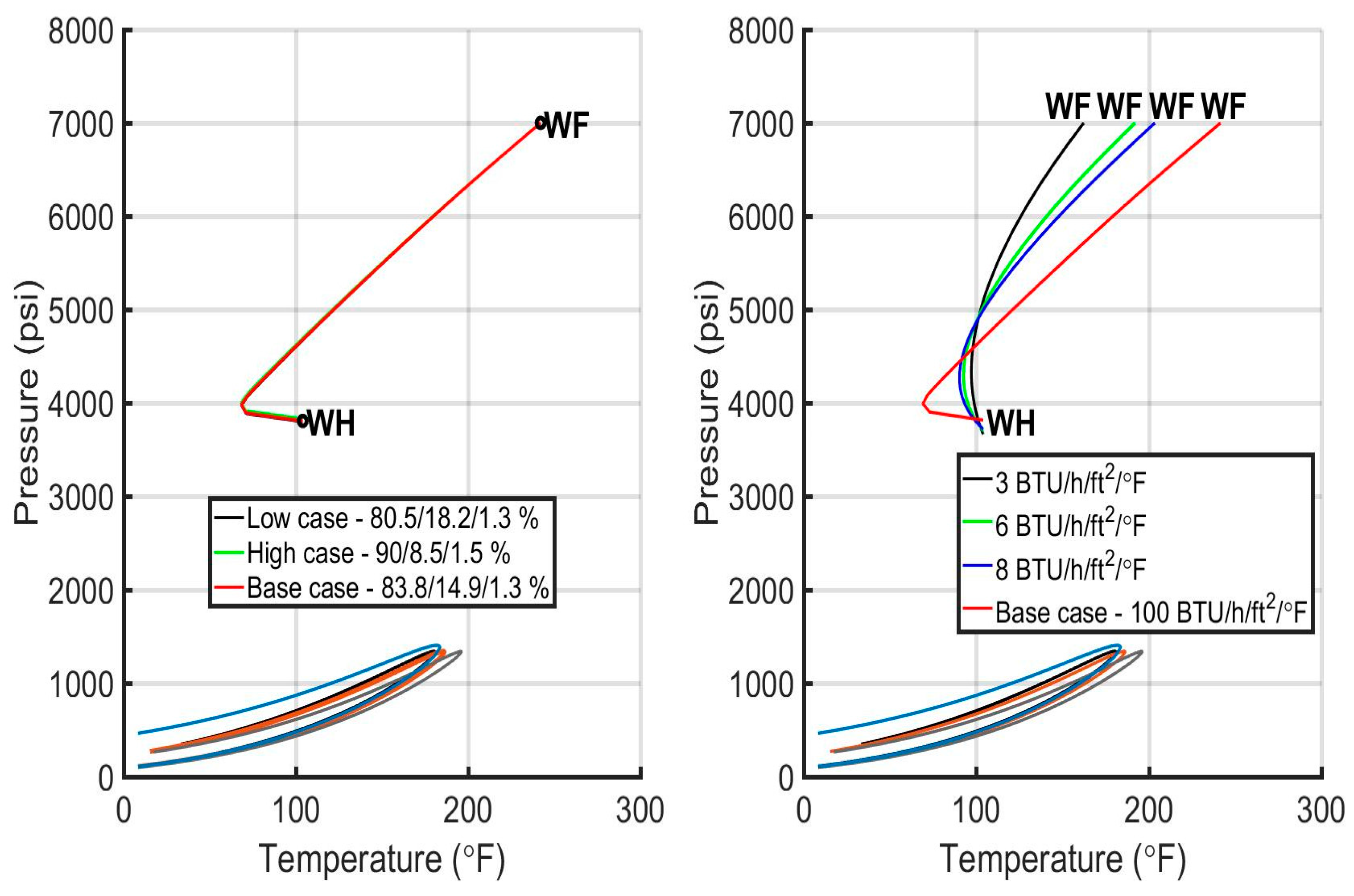
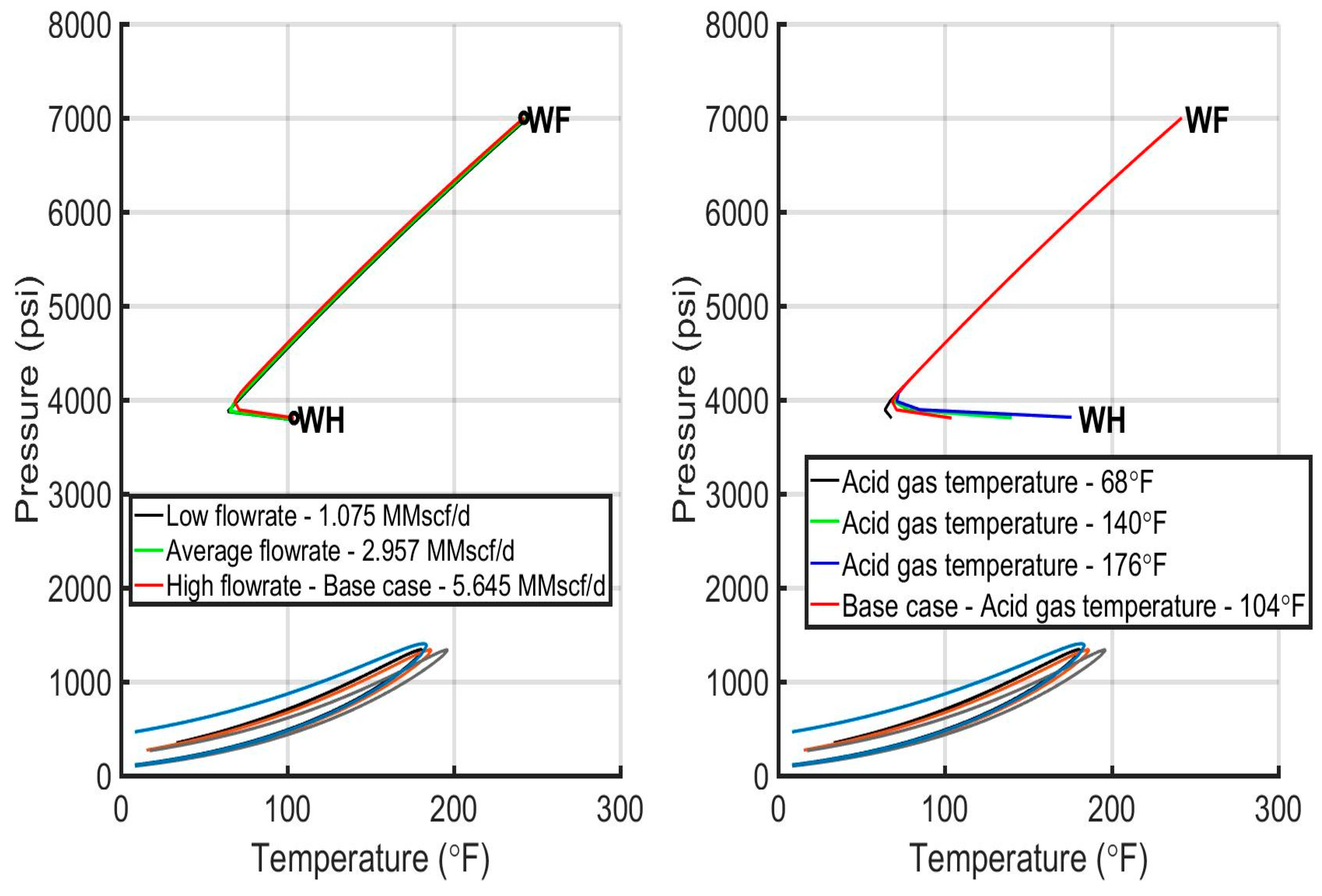
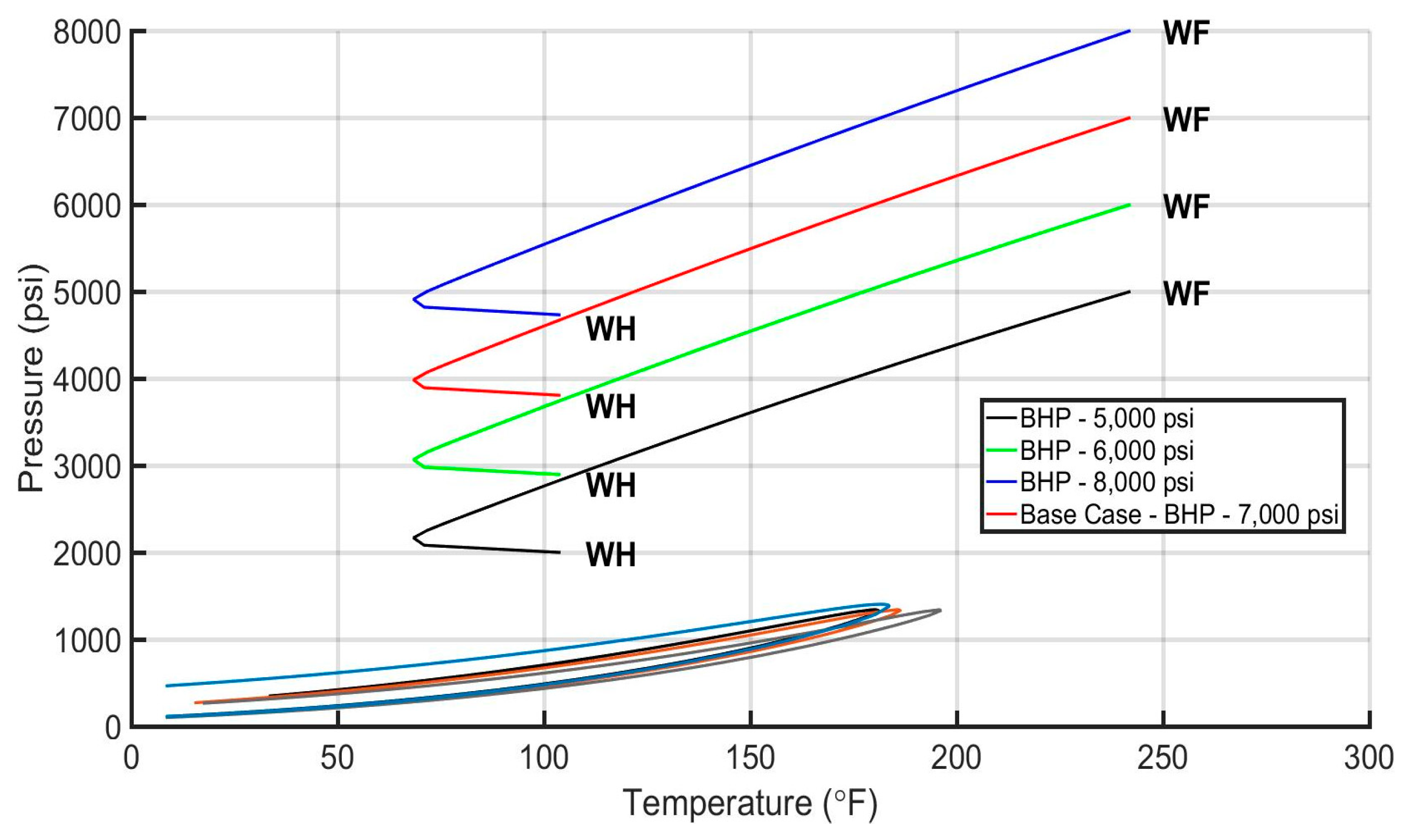
6.3. Evaluation of the Injection Profiles
6.4. MMP Evaluation
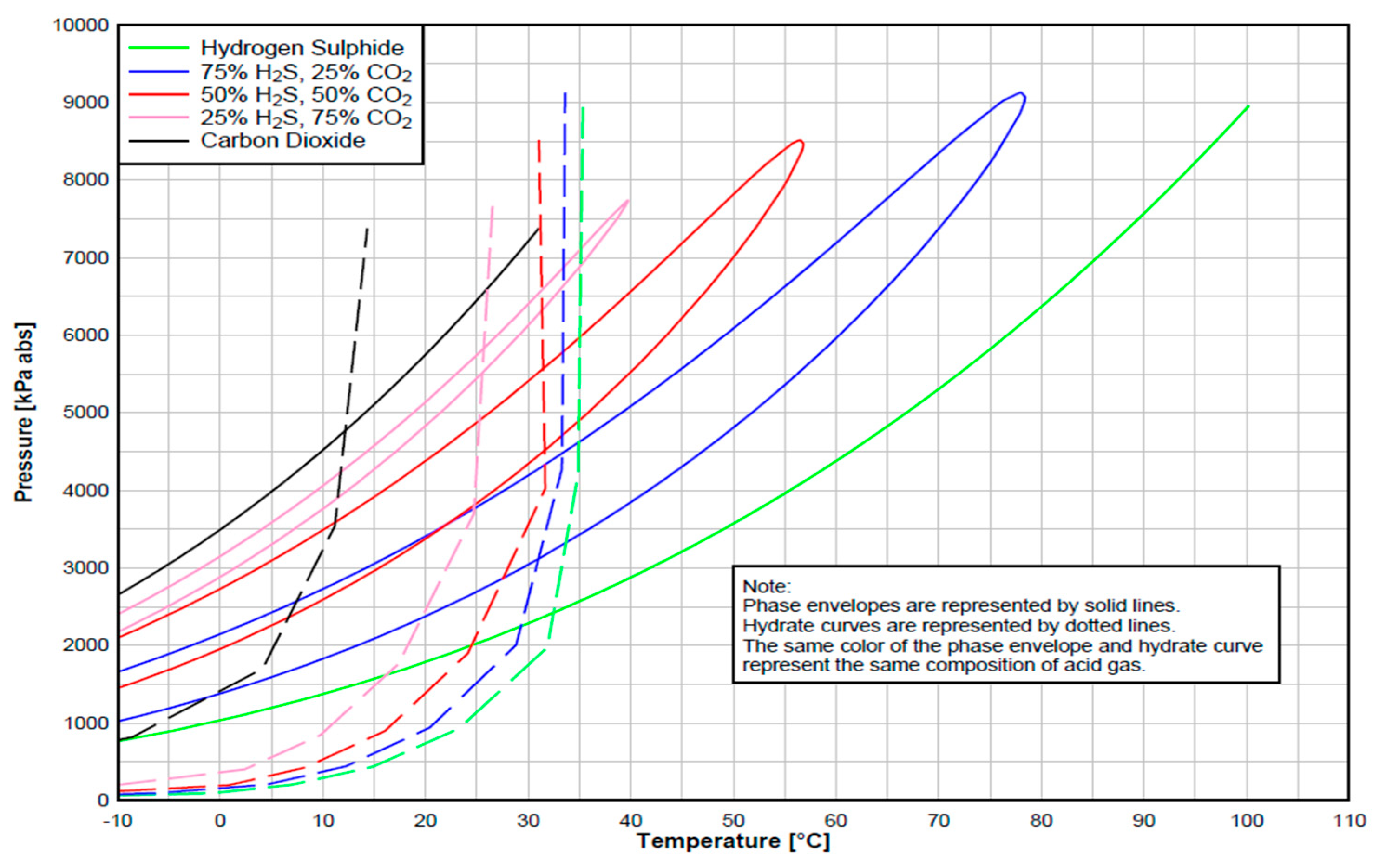
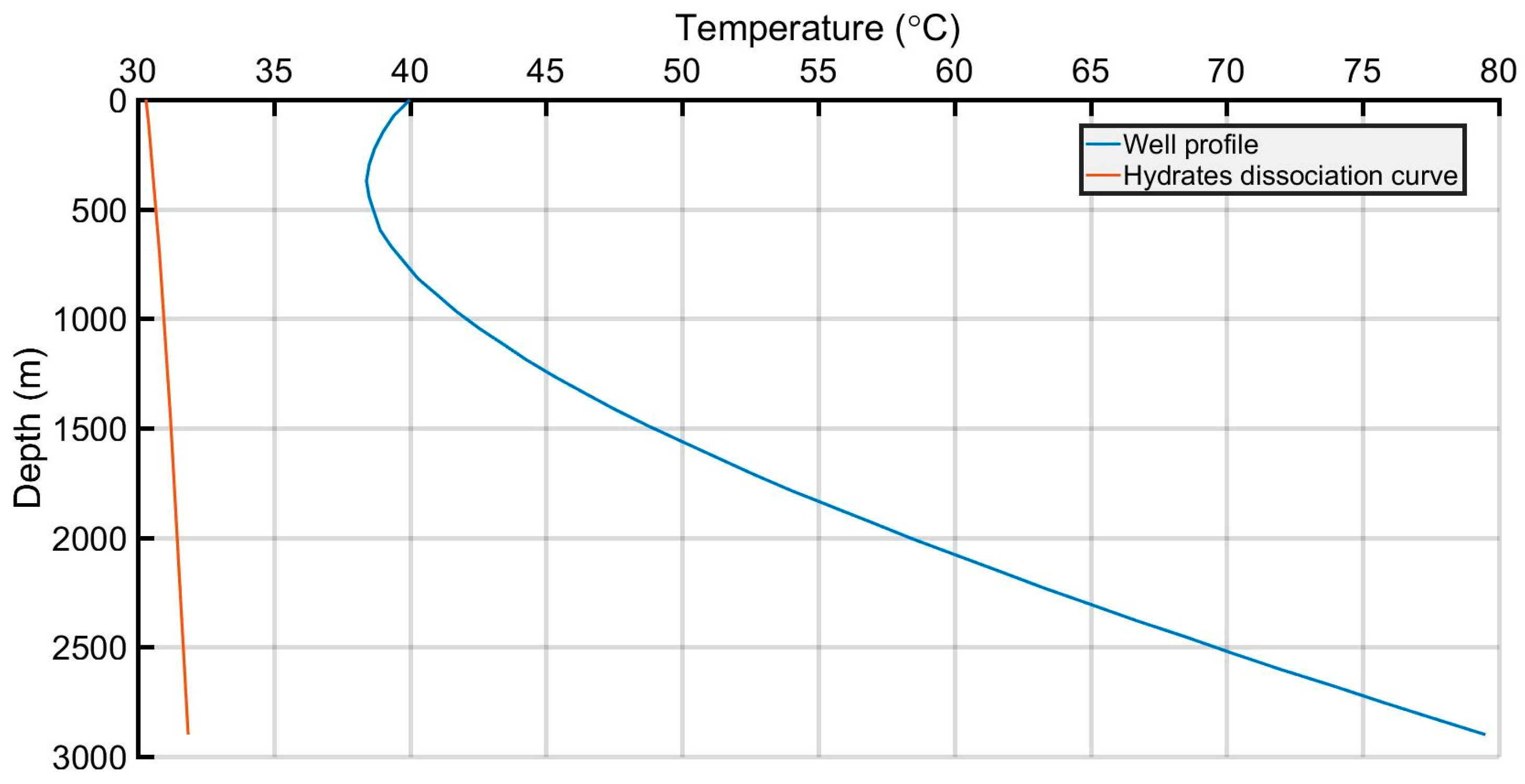
6.5. Hydrate Formation Conditions
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siddiqui, M.I.; Baber, S.; Saleem, W.A.; Jafri, M.O.; Hafeez, Q. Industry practices of sour gas management by reinjection: Benefits, methodologies, economic evaluation and case studies. In Proceedings of the SPE/PAPG Annual Technical Conference, Islamabad, Pakistan, 26–27 November 2013; p. SPE-169645-MS. [Google Scholar]
- Kokal, S.L.; Al-Utaibi, A. Sulfur Disposal by Acid Gas Injection: A Road Map and A Feasibility Study. In Proceedings of the SPE Middle East Oil and Gas Show and Conference, Al Manama, Bahrain, 12–15 March 2005; p. SPE-93387-MS. [Google Scholar]
- Burgers, W.F.J.; Northrop, P.S.; Kheshgi, H.S.; Valencia, J.A. Worldwide development potential for sour gas. Energy Procedia 2011, 4, 2178–2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maddocks, J. Capacity Control Considerations for Acid Gas Injection Systems; Gas Liquids Engineering Ltd.: Calgary, AB, Canada, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Bachu, S.; Gunter, W.D. Overview of acid-gas injection operations in Western Canada. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Greenhouse Gas Control Technologies, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 5 September 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Mokhatab, S.; Poe, W.A.; Mak, J.W. Handbook of Natural Gas Transmission and Processing, 4th ed.; Gulf Professional Publishing: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; ISBN 978-0-12-815817-3. [Google Scholar]
- Carroll, J.J. Acid gas injection: Past, present, and future. In Proceedings of the International Acid Gas Injection Symposium, Calgary, AB, Canada, 5–6 October 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Chen, J.-Y.; Gao, P.-C.; Tang, H.-J. Wellbore flow model of acid gas reinjection. Nat. Gas Ind. 2005, 25, 76–78. [Google Scholar]
- Mireault, R.A.; Stocker, R.; Dunn, D.W.; Pooladi-Darvish, M. Wellbore dynamics of acid gas injection well operation. In Proceedings of the Canadian Unconventional Resources and International Petroleum Conference, Calgary, AB, Canada, 19–21 October 2010; p. SPE-135455-MS. [Google Scholar]
- Carroll, J.J. Acid Gas Injection—The Next Generation; Gas Liquids Engineering Ltd.: Calgary, AB, Canada, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- International Energy Agency Greenhouse Gas R&D Program. Acid Gas Injection: A Study of Existing Operations, Phase I: Final Report, PH4/18; IEAG: Cheltenham, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Bachu, S.; Gunter, W. Acid-gas injection in the Alberta basin, Canada: A CO2-storage experience. Geol. Soc. 2004, 233, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, Z.; Charfeddine, M.; Moore, S.; Francia, L.; Denby, P. The Supergiant Kashagan Field: Making a Sweet Development Out of Sour Crude. In Proceedings of the International Petroleum Technology Conference, Doha, Qatar, 21–23 November 2005; p. IPTC-10636-MS. [Google Scholar]
- Abou-Sayed, A.S.; Summers, C.; Zaki, K.S. An Assessment of Engineering Economical and Environmental Drivers of Sour Gas Management by Injection. In Proceedings of the SPE International Improved Oil Recovery Conference in Asia Pacific, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 5–6 December 2005; p. SPE-97628-MS. [Google Scholar]
- Urazgaliyeva, G.; King, G.R.; Darmentaev, S.; Tursinbayeva, D.; Dunger, D.; Howery, R.; Zalan, T.; Lindsell, K.; Iskakov, E.; Turymova, A.; et al. Tengiz Sour Gas Injection Project: An Update. In Proceedings of the SPE Annual Caspian Technical Conference and Exhibition, Astana, Kazakhstan, 12–14 November 2014; p. SPE-172284-MS. [Google Scholar]
- Miwa, M.; Shiozawa, Y.; Saito, Y.; Tarmoom, I.O. Sour Gas Injection Project. In Proceedings of the Abu Dhabi International Petroleum Exhibition and Conference, Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 13–16 October 2002; p. SPE-78547-MS. [Google Scholar]
- Haynes, B.; Kaura, N.C.; Faulkner, A. Life Cycle of a depletion drive and sour gas injection development: Birba A4C Reservoir, South Oman. In Proceedings of the International Petroleum Technology Conference, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 3–5 December 2008; p. IPTC-12175-MS. [Google Scholar]
- Battistelli, A.; Ceragioli, P.; Marcolini, M. Injection of Acid Gas Mixtures in Sour Oil Reservoirs: Analysis of Near-Wellbore Processes with Coupled Modelling of Well and Reservoir Flow. Transp. Porous Media 2011, 90, 233–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adewumi, M. Phase Relations in Reservoir Engineering; Pennsylvania State University: State College, PA, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Chapoy, A.; Coquelet, C.; Liu, H.; Valtz, A.; Tohidi, B. Vapor-liquid equilibrium data for the hydrogen sulfide (H2S) + carbon dioxide (CO2) system at temperatures from 258 to 313 K. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2013, 356, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamataki, S.; Magoulas, K. Predictions of Phase Equilibria and Volumetric Behavior of Fluids with High Concentration of Hydrogen Sulfide. Oil Gas Sci. Technol. 2000, 55, 511–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmed, T. Reservoir Engineering Handbook, 4th ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2010; ISBN 9780080966670. [Google Scholar]
- Tsivintzelis, I.; Kontogeorgis, G.M.; Michelsen, M.L.; Stenby, E.H. Modeling phase equilibria for acid gas mixtures using the CPA equation of state. I. Mixtures with H2S. AIChE J. 2010, 56, 2965–2982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Computer Modelling Group Ltd. WinProp User Guide. Phase Property Program; Version 2010; Computer Modelling Group Ltd.: Calgary, AB, Canada, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Gaganis, V.; Kourlianski, E.; Varotsis, N. An accurate method to generate composite PVT data for Black Oil Simulation. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2007, 157, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, K.S.; Blilie, A.L.; Meisingset, K.K. PVT Calculations on petroleum reservoir fluid using measured and estimated composition data for the plus fraction. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1992, 31, 1378–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitson, C.H. Characterizing hydrocarbon plus fractions. SPE J. 1983, 23, 683–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chueh, P.L.; Prausnitz, J.M. Vapor-liquid equilibria at high pressures: Calculation of partial molar volumes in nonpolar liquid mixtures. AIChE J. 1967, 13, 1099–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kordas, A.; Tsoutsouras, K.; Stamataki, S.; Tassios, D. A generalized correlation for the interaction coefficients of CO2—Hydrocarbon binary mixtures. Fluid Phase Equilibria 1994, 93, 141–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jhaveri, B.S.; Youngren, G.K. Three parameters modification of the Peng-Robinson Equation of State to improve volume predictions. SPE Reserv. Eng. 1988, 3, 1033–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastasiadou, V.; Samnioti, A.; Kanakaki, R.; Gaganis, V. Acid gas re-injection system design using machine learning. Clean Technol. 2022, 4, 1001–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tureyen, O.I.; Karaalioglu, H.; Satman, A. Effect of the Wellbore Conditions on the Performance of Underground Gas-Storage Reservoirs. In Proceedings of the SPE/CERI Gas Technology Symposium, Calgary, AB, Canada, 3–5 April 2000; p. SPE-59737-MS. [Google Scholar]
- Rigzone. How Does Gas Injection Work? Available online: https://www.rigzone.com/training/insight?insight_id=345&c_id= (accessed on 15 September 2022).
- Green, D.W.; Willhite, G.P. Enhanced Oil Recovery, 2nd ed.; Society of Petroleum Engineers: Richardson, TX, USA, 2018; ISBN 978-1-61399-494-8. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Wu, J. Factors affecting the lower limit of the safe mud weight window for drilling operation in hydrate-bearing sediments in the Northern South China Sea. Geomech. Geophys. Geo-Energy Geo-Resour. 2022, 8, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.N.; Li, B.; Gan, Q.; Li, Y.L. Research progress of natural gas hydrate exploitation with CO2 replacement: A review. Fuel 2022, 312, 122873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wang, F.; Forson, K.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, C.; Chen, J.; Xu, N.; Wang, Y. Affecting analysis of the rheological characteristic and reservoir damage of CO2 fracturing fluid in low permeability shale reservoir. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 7815–37826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodera, M.; Matsueda, T.; Belosludov, R.V.; Zhdanov, R.K.; Belosludov, V.R.; Takeya, S.; Alavi, S.; Ohmura, R. Physical properties and characterization of the binary clathrate hydrate with methane + 1,1,1,3,3-Pentafluoropropane (HFC-245fa) + Water. J. Phys. Chem. C 2020, 124, 20736–20745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ripmeester, J.A.; Tse, J.S.; Ratcliffe, C.I.; Powell, B.M. A new clathrate hydrate structure. Nature 1987, 325, 135–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, C.A.; Sloan Jr, E.D. Clathrate Hydrates of Natural Gases; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007; ISBN 9780849390784. [Google Scholar]
- Zatsepina, O.Y.; Buffett, B.A. Thermodynamic conditions for the stability of gas hydrate in the seafloor. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1998, 103, 24127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, D.W.; Garg, S.K.; Gough, S.R.; Handa, Y.P.; Ratcliffe, C.I.; Ripmeester, J.A.; Tse, J.S.; Lawson, W.F. Laboratory analysis of a naturally occurring gas hydrate from sediment of the Gulf of Mexico. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1986, 50, 619–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharathi, A.; Nashed, O.; Lal, B.; Foo, K.S. Experimental and modelling studies on enhancing the thermodynamic hydrate inhibition performance of monoethylene glycol via synergistic green material. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elgibaly, A.A.; Elkamel, A.M. A new correlation for predicting hydrate formation conditions for various gas mixtures and inhibitors. Fluid Phase Equilibria 1998, 152, 23–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Waals, J.H.; Platteeuw, J.C. Clathrate solutions. In Advances in Chemical Physics; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1959; ISBN 9780470143483. [Google Scholar]
- Hydrafact PVT and Flow Assurance. HydraFLASHTM PVT and Flow Assurance Prediction Software. Available online: https://www.hydrafact.com/products/hydraflash/ (accessed on 1 November 2022).
- KBC Global. A Yokogawa Company. Gas Hydrates Modeling with CPA. Available online: https://www.kbc.global/resources/whitepapers/gas-hydrates-modeling-with-cpa/ (accessed on 1 November 2022).
- Offshore Technology. Prinos Offshore Development Project, North Aegean Sea, Gulf of Kavala. Available online: https://www.offshore-technology.com/projects/prinos-offshore-development-project-north-aegean-sea-gulf-of-kavala/ (accessed on 1 October 2022).
- Proedrou, P.; Papaconstantinou, C.M. Prinos basin—A model for oil exploration. Bull. Geol. Soc. Greece 2004, 36, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiomourtzi, P.; Pasadakis, N.; Zelilidis, A. Source Rock and Depositional Environment Study of Three Hydrocarbon Fields in Prinos—Kavala Basin (North Aegean). Open Pet. Eng. J. 2008, 1, 16–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bierlein, J.A.; Kay, W.B. Phase Equilibrium Properties of System Carbon Dioxide Hydrogen Sulfide. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1953, 45, 618–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellerman, S.J.; Stouffer, C.E.; Eubank, P.T.; Holste, J.C.; Hall, K.R. Thermodynamic Properties of CO2 + H2S Mixtures: Project 842; Gas Processors Assoc.: Tulsa, OK, USA, 1995; ISBN 1567000495. [Google Scholar]
- Bennion, D.B.; Thomas, F.B.; Schulmeister, B.E.; Imer, D.; Shtepani, E.; Becker, L. The Phase Behavior of Acid Disposal Gases and the Potential Adverse Impact on Injection or Disposal Operations. J. Can. Pet. Technol. 2004, 43, PETSOC-04-05-01. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodwin, R.D. Hydrogen Sulfide Provisional Thermophysical Properties From 188 to 700 K at Pressure to 75 MPa; National Bureau of Standards, Chemical Engineering Science Division, U.S. Department of Commerce: Boulder, CO, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Commodore, J.A.; Deering, C.E.; Bernard, F.; Marriott, R.A. High-pressure densities and excess molar volumes for the binary mixture of carbon dioxide and hydrogen sulfide at T = 343 to 397 K. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2021, 66, 4236–4247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petroleum Experts Ltd. Prosper User Manual; Version 12; Petroleum Experts Ltd.: Edinburgh, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Sayegh, S.; Huang, S.; Zhang, Y.P.; Lavoie, R. Effect of H2S and pressure depletion on the CO2 MMP of Zama oils. J. Can. Pet. Technol. 2007, 46, PETSOC-07-08-03. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, S.; Liao, X.; Chen, H.; Chen, Z.; Lv, X.; Zhou, X. Predicting the Effects of Acid Gas on Enhanced Oil Recovery in Hydrocarbon Gas Injection. In Proceedings of the SPE Western Regional Meeting, Anchorage, AK, USA, 23–26 May 2016; p. SPE-180434-MS. [Google Scholar]
- He, C.; Mu, L.; Xu, A.; Zhao, L.; He, J.; Zhang, A.; Shan, F.; Luo, E. Phase behavior and miscible mechanism in the displacement of crude oil with associated sour gas. Oil Gas Sci. Technol. 2019, 74, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Emera, M.; Sarma, H. A reliable correlation to predict the change in minimum miscibility pressure when CO2 is diluted with other gases. SPE Reserv. Eval. Eng. 2006, 9, 366–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokir, E.M.E.M. Precise model for estimating CO2-oil minimum miscibility pressure. Pet. Chem 2007, 47, 368–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petroleum Experts Ltd. PVTP User Manual; Version 10; Petroleum Experts Ltd.: Edinburgh, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, L.; Pekot, L.G.; Hawthorne, S.B.; Gobran, B.; Greeves, A.; Bosshart, N.W.; Jiang, T.; Hamling, J.A.; Gorecki, C.D. Impact of CO2 impurity on MMP and oil recovery performance of the Bell Creek oil field. Energy Procedia 2017, 114, 6997–7008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michelsen, M.L. Multiphase isenthalpic and isentropic flash algorithms. Fluid Phase Equilibria 1987, 33, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma, A.M.; Queimada, A.J.; Coutinho, J. Modelling Hydrate Dissociation Curves in the presence of hydrate inhibitors with a modified CPA EoS. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 19239–19250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, I.; Gaganis, V.; Marinakis, D.; Mousavi, R.; Tohidi, B. Accuracy of different thermodynamic software packages in predicting hydrate dissociation conditions. Chem. Thermodyn. Therm. Anal. 2022, 9, 100103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Xin, Y.; Chou, I.-M.; Sun, R.; Jiang, L. Hydrate stability in the H2S-H2O system—Visual observations and measurements in a high-pressure optical cell and thermodynamic models. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2020, 65, 3884–3892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selleck, F.T.; Carmichael, L.T.; Sage, B.H. Phase Behavior in the Hydrogen Sulfide-Water System. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1952, 44, 2219–2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wikipedia. The Free Encyclopedia. Carbon Dioxide Clathrate. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Carbon_dioxide_clathrate (accessed on 1 December 2022).
- Wu, Y.; Carroll, J.J. The research on experiments and theories about hydrates in high-sulfur gas reservoirs. In Acid Gas Injection and Related Technologies; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011; ISBN 978-1-118-09426-6. [Google Scholar]
- Gas Liquids Engineering. AQUAlibrium Software. Available online: https://www.gasliquids.com/software-library/ (accessed on 15 September 2022).
- Grynia, E.W.; Carroll, J.J.; Griffin, P.J. Dehydration of acid gas prior to injection. In Proceedings of the 2nd Annual Gas Processing Symposium, Doha, Qatar, 10–14 January 2010; pp. 177–185. [Google Scholar]



| Acid Gas Composition (%) H2S/CO2/C1 | Heat Transfer Coef. (BTU/h/ft2/°F) | AGI Rate (MMscf/d) | AGI Temperature (°F/°C) | Bottomhole Pressure (psi) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Base case scenario | 83.8/14.9/1.5 | 100 | 5.645 | 104/40 | 7000 |
| Low H2S | Average H2S | High H2S | High C1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Composition H2S/CO2/C1 (%) | 80.5/18.2/1.3 | 83.8/14.9/1.3 | 90/8.5/1.5 | 83/12/5 |
| Parameters | Case 1 | Case 2 | Case 3 | Case 4 | Case 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acid gas composition (%) H2S/CO2/C1 | 90/8.5/1.5 | 83.8/14.9/1.3 | 83.8/14.9/1.3 | 83.8/14.9/1.3 | 83.8/14.9/1.3 |
| 80.5/18.2/1.3 | |||||
| Heat transfer coefficient (BTU/h/ft2/F) | 100 | 3 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| 6 | |||||
| 8 | |||||
| 100 | |||||
| AGI rate (MMscf/d) | 5.645 | 5.645 | 1.075 | 5.645 | 5.645 |
| 2.957 | |||||
| 5.645 | |||||
| AGI temperature (°F/°C) | 104/40 | 104/40 | 104/40 | 68/20 | 104/40 |
| 104/40 | |||||
| 140/60 | |||||
| 176/80 | |||||
| Required bottomhole pressure (psi) | 7000 | 7000 | 7000 | 7000 | 5000 |
| 6000 | |||||
| 7000 | |||||
| 8000 |
| Field | MMP (psi) |
|---|---|
| KR-G2G (Zama field) (extrapolation) | 1900 |
| K oil field (extrapolation) | 1960 |
| Field in Kazakhstan (pure H2S) | 3000 |
| Author | Fluid Context | MMP (psi) |
|---|---|---|
| Emera & Sarma | MMP using CO2 stream with impurities | 2606 |
| Shokir | MMP using CO2 stream with impurities | 2629 |
| Emera & Sarma | MMP using pure CO2 | 3345 |
| Parameter | Scenarios | MMP (psi) |
|---|---|---|
| - | Base case scenario (10 cells) | 2400 |
| Cell Size | Increased cells number (40 cells) | 2400 |
| Rel. perm. curves | Brooks and Corey (λ = 0.5) | 2400 |
| Brooks and Corey (λ = 3.7) | 2400 | |
| Injected gas composition | 78% H2S—20% CO2—2% CH4 | 2500 |
| 83% H2S—15% CO2—2% CH4 | 2400 | |
| 88% H2S—10% CO2—2% CH4 | 2250 | |
| 70% H2S—20% CO2—10% CH4 | 3300 |
| Injected Gas Composition (%): H2S/CO2/C1 | MMP (psi) |
|---|---|
| 78/20/2 | 2238 |
| 83/15/2 | 2225 |
| 88/10/2 | 2200 |
| 70/20/10 | 2363 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Samnioti, A.; Kanakaki, E.M.; Koffa, E.; Dimitrellou, I.; Tomos, C.; Kiomourtzi, P.; Gaganis, V.; Stamataki, S. Wellbore and Reservoir Thermodynamic Appraisal in Acid Gas Injection for EOR Operations. Energies 2023, 16, 2392. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16052392
Samnioti A, Kanakaki EM, Koffa E, Dimitrellou I, Tomos C, Kiomourtzi P, Gaganis V, Stamataki S. Wellbore and Reservoir Thermodynamic Appraisal in Acid Gas Injection for EOR Operations. Energies. 2023; 16(5):2392. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16052392
Chicago/Turabian StyleSamnioti, Anna, Eirini Maria Kanakaki, Evangelia Koffa, Irene Dimitrellou, Christos Tomos, Paschalia Kiomourtzi, Vassilis Gaganis, and Sofia Stamataki. 2023. "Wellbore and Reservoir Thermodynamic Appraisal in Acid Gas Injection for EOR Operations" Energies 16, no. 5: 2392. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16052392
APA StyleSamnioti, A., Kanakaki, E. M., Koffa, E., Dimitrellou, I., Tomos, C., Kiomourtzi, P., Gaganis, V., & Stamataki, S. (2023). Wellbore and Reservoir Thermodynamic Appraisal in Acid Gas Injection for EOR Operations. Energies, 16(5), 2392. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16052392







