Microbial Fuel Cell Equipped with Bipolar Membrane Using Iron (III) Hydroxide as Final Electron Acceptor
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strain and Seed-Culture
2.2. Fuel Solution
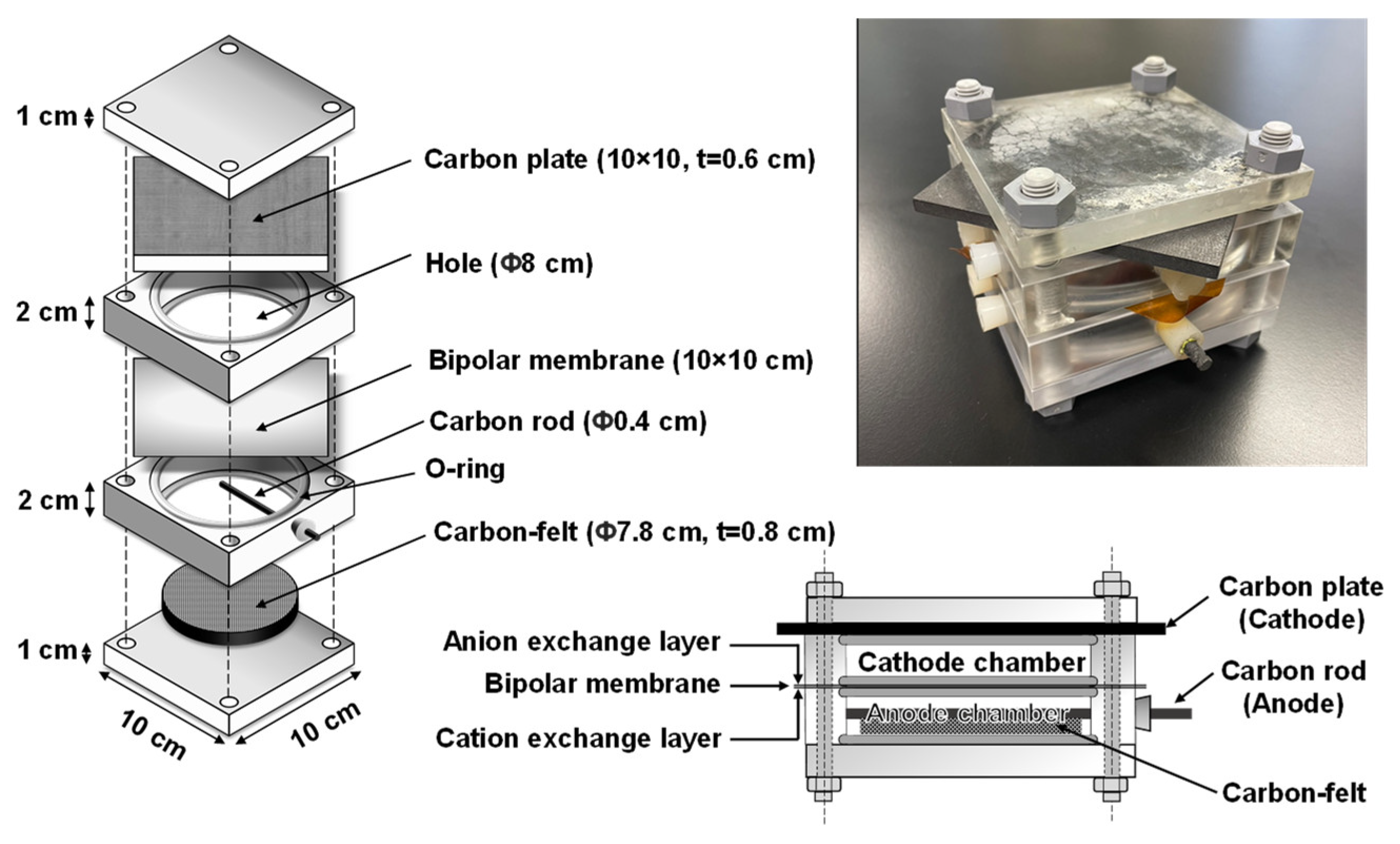
2.3. bMFC Configuration
2.4. bMFC Operation
2.5. Reference Experiments
2.6. Analysis of Lactic Acid
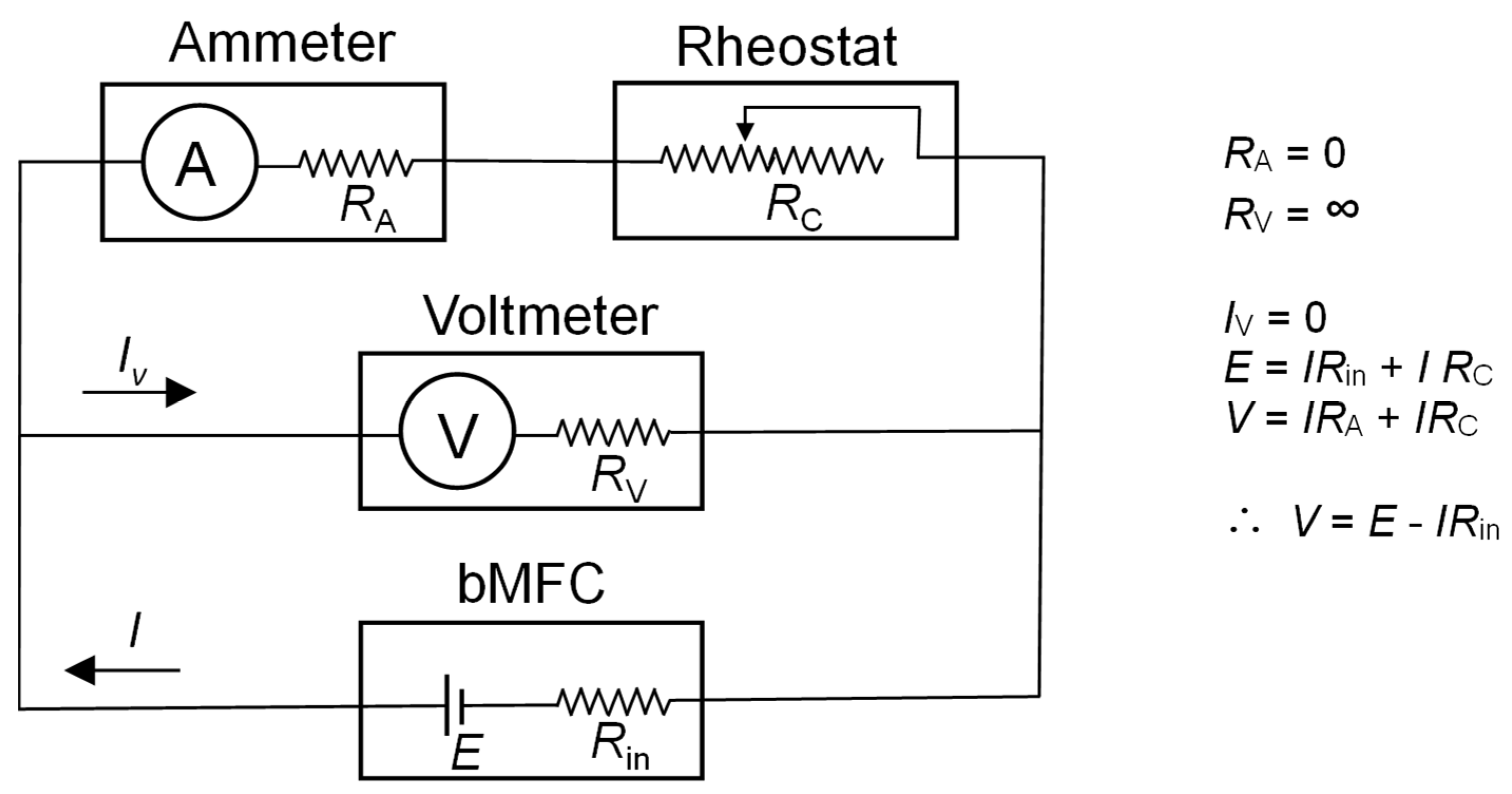
2.7. Ohmic Resistance
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. bMFC Operation
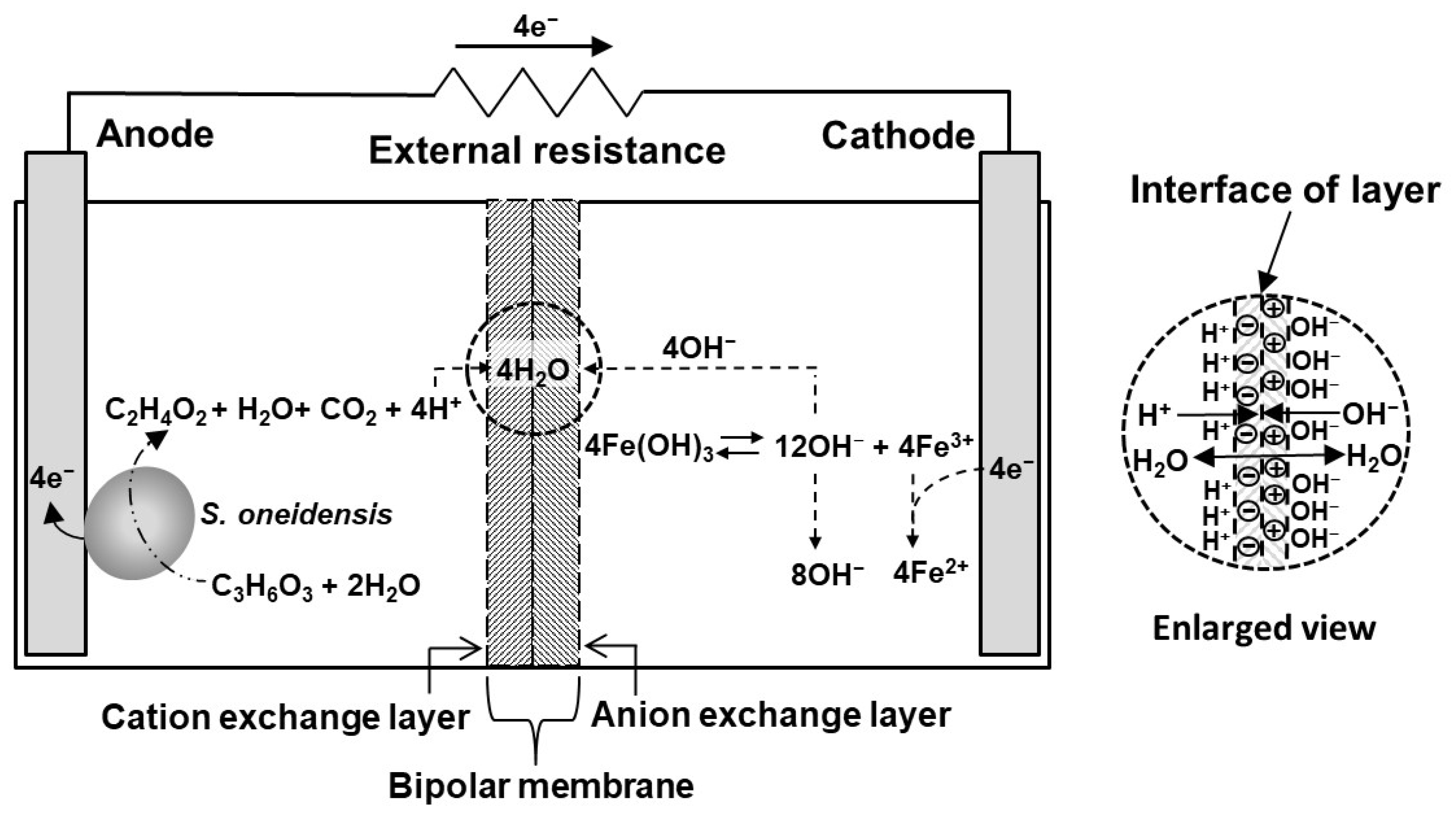
3.2. Mechanism of bMFC
3.3. Coulombic Efficiency
3.4. Ohmic Resistance
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Liu, H.; Ramnarayanan, R.; Logan, B.E. Production of Electricity during Wastewater Treatment Using a Single Chamber Microbial Fuel Cell. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 2281–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, S.; Min, B.; Logan, B.E. Cathode Performance as a Factor in Electricity Generation in Microbial Fuel Cells. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 4900–4904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Harnisch, F.; Schröder, U.; Scholz, F.; Bogdanoff, P.; Herrmann, I. Application of pyrolysed iron(II) phthalocyanine and CoTMPP based oxygen reduction catalysts as cathode materials in microbial fuel cells. Electrochem. Commun. 2005, 7, 1405–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Harnisch, F.; Schröder, U.; Scholz, F.; Bogdanoff, P.; Herrmann, I. Challenges and Constraints of Using Oxygen Cathodes in Microbial Fuel Cells. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 5193–5199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabaey, K.; Verstraete, W. Microbial fuel cells: Novel biotechnology for energy generation. Trends Biotechnol. 2005, 23, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabaey, K.; Lissens, G.; Siciliano, S.; Verstraete, W. A microbial fuel cell capable of converting glucose to electricity at high rate and efficiency. Biotechnol. Lett. 2003, 25, 1531–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabaey, K.; Clauwaert, P.; Aelterman, P.; Verstraete, W. Tubular Microbial Fuel Cells for Efficient Electricity Generation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 8077–8082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Logan, B.E. Electricity Generation Using an Air-Cathode Single Chamber Microbial Fuel Cell in the Presence and Absence of a Proton Exchange Membrane. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 4040–4046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Liu, H.; Logan, B.E. Power Densities Using Different Cathode Catalysts (Pt and CoTMPP) and Polymer Binders (Nafion and PTFE) in Single Chamber Microbial Fuel Cells. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 40, 364–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topcagic, S.; Minteer, S.D. Development of a membraneless ethanol/oxygen biofuel cell. Electrochim. Acta 2006, 51, 2168–2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmore, G.R.; Kim, H.-H. Electro-enzymatic reduction of dioxygen to water in the cathode compartment of a biofuel cell. J. Electroanal. Chem. 1999, 464, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simons, R.; Khanarian, G. Water dissociation in bipolar membranes: Experiments and theory. J. Membr. Biol. 1978, 38, 11–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurwitz, H.; Dibiani, R. Investigation of electrical properties of bipolar membranes at steady state and with transient methods. Electrochim. Acta 2001, 47, 759–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tongwen, X. Electrodialysis processes with bipolar membranes (EDBM) in environmental protection—A review. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2002, 37, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Jin, X.; Zhao, N.; Angelidaki, I.; Zhang, Y. Efficient treatment of aniline containing wastewater in bipolar membrane microbial electrolysis cell-Fenton system. Water Res. 2017, 119, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chacón-Carrera, R.; López-Ortiz, A.; Collins-Martínez, V.; Meléndez-Zaragoza, M.; Salinas-Gutiérrez, J.; Espinoza-Hicks, J.; Ramos-Sánchez, V. Assessment of two ionic exchange membranes in a bioelectrochemical system for wastewater treatment and hydrogen production. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 44, 12339–12345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ter Heijne, A.; Hamelers, H.V.M.; de Wilde, V.; Rozendal, R.A.; Buisman, C.J.N. A Bipolar Membrane Combined with Ferric Iron Reduction as an Efficient Cathode System in Microbial Fuel Cells. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 5200–5205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.; Lee, C.R.; Song, Y.E.; Heo, J.; Choi, S.M.; Lim, D.-H.; Cho, J.; Park, C.; Jang, M.; Kim, J.R. Hexavalent chromium as a cathodic electron acceptor in a bipolar membrane microbial fuel cell with the simultaneous treatment of electroplating wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 328, 703–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-H.; Wang, B.-S.; Liu, Y.-P.; Chen, Q.-Y. Electricity and hydrogen co-production from a bio-electrochemical cell with acetate substrate. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2013, 38, 6600–6606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oram, J.; Jeuken, L.J. Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 electron acceptor taxis and the perception of electrodes poised at oxidative potentials. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2017, 5, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, L.; Rosso, K.M.; Zachara, J.M.; Fredrickson, J.K. Mtr extracellular electron-transfer pathways in Fe(III)-reducing or Fe(II)-oxidizing bacteria: A genomic perspective. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2012, 40, 1261–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Xing, D.; Lu, L.; Wei, M.; Liu, B.; Ren, N. Ferric iron enhances electricity generation by Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 in MFCs. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 135, 630–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phansroy, N.; Aso, Y.; Sasaki, S.; Aoki, T.; Ohara, H. Immobilization of the iron on the surface of non-woven carbon fiber for use in a microbial fuel cell. Mater. Renew. Sustain. Energy 2016, 5, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takeuchi, Y.; Khawdas, W.; Aso, Y.; Ohara, H. Microbial fuel cells using Cellulomonas spp. with cellulose as fuel. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2017, 123, 358–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanthier, M.; Gregory, K.B.; Lovley, D.R. Growth with high planktonic biomass in Shewanella oneidensis fuel cells. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2008, 278, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tang, Y.J.; Hwang, J.S.; Wemmer, D.E.; Keasling, J.D. Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 Fluxome under Various Oxygen Conditions. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 718–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fan, Y.; Sharbrough, E.; Liu, H. Quantification of the Internal Resistance Distribution of Microbial Fuel Cells. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 8101–8107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logan, B.E.; Regan, J.M. Electricity-producing bacterial communities in microbial fuel cells. Trends Microbiol. 2006, 14, 512–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, P.; Huang, X.; Fan, M.-Z.; Cao, X.-X.; Wang, C. Composition and distribution of internal resistance in three types of microbial fuel cells. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2007, 77, 551–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

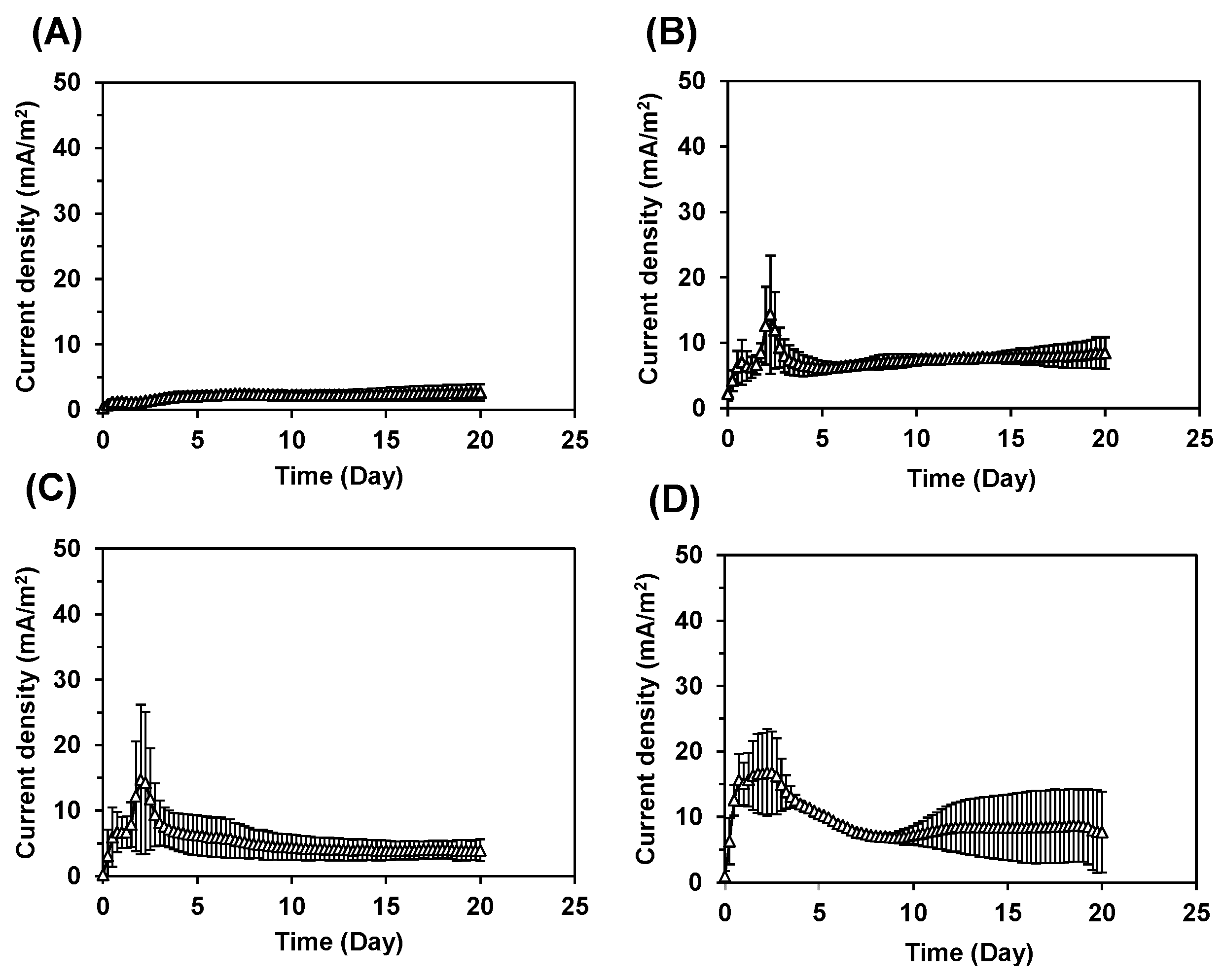
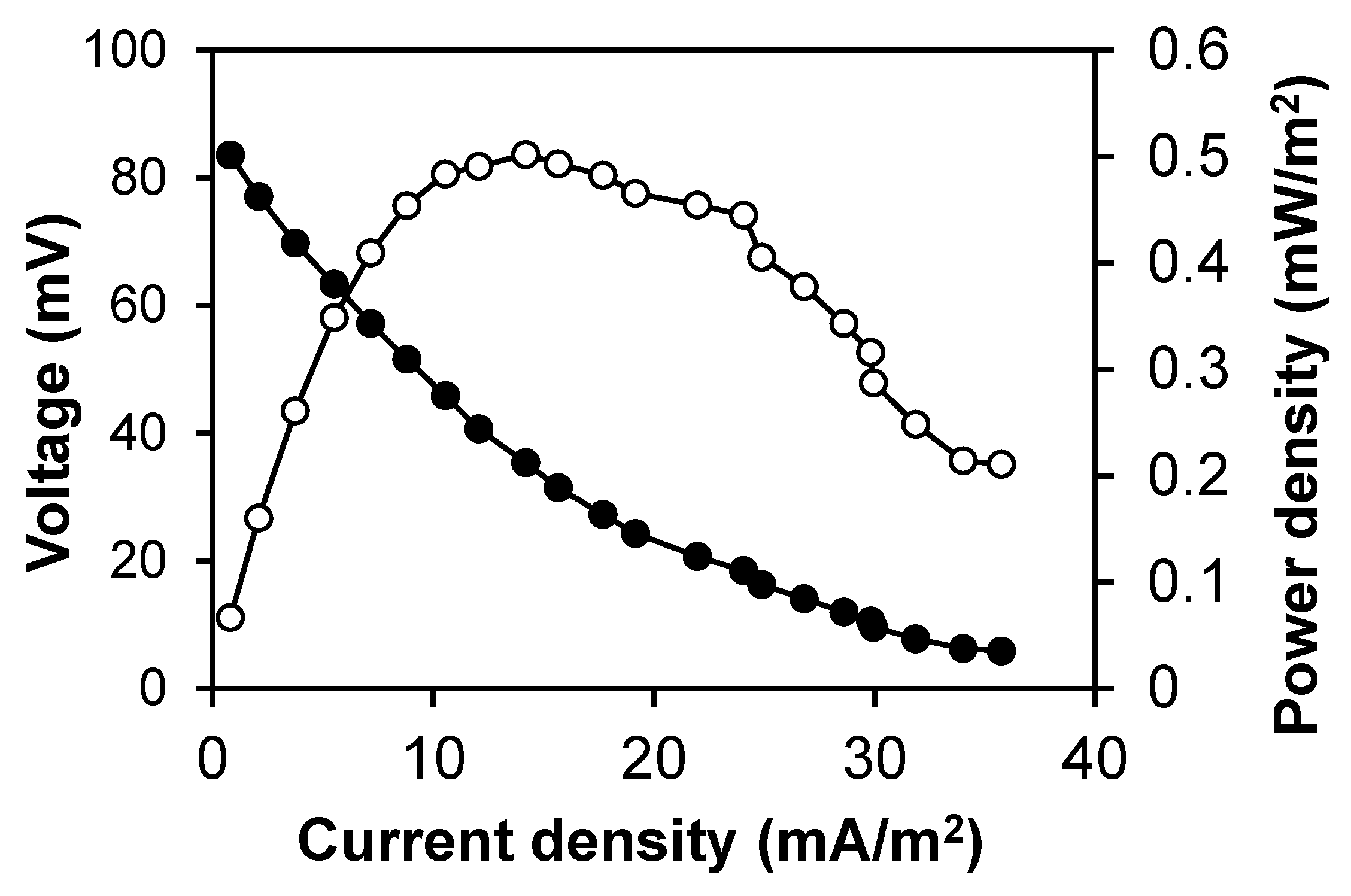
| Experiment | S. oneidensis | Iron (III) Hydroxide | Membrane | Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| bMFC | With | With | Bipolar | Figure 2 |
| First type | Without | With | Bipolar | Figure 3A |
| Second type | With | Without | Bipolar | Figure 3B |
| Third type | With | With | Cation exchange | Figure 3C |
| Fourth type | With | With | Bipolar (Opposite direction) | Figure 3D |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kazama, I.; Aso, Y.; Tanaka, T.; Ohara, H. Microbial Fuel Cell Equipped with Bipolar Membrane Using Iron (III) Hydroxide as Final Electron Acceptor. Energies 2023, 16, 2527. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16062527
Kazama I, Aso Y, Tanaka T, Ohara H. Microbial Fuel Cell Equipped with Bipolar Membrane Using Iron (III) Hydroxide as Final Electron Acceptor. Energies. 2023; 16(6):2527. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16062527
Chicago/Turabian StyleKazama, Iori, Yuji Aso, Tomonari Tanaka, and Hitomi Ohara. 2023. "Microbial Fuel Cell Equipped with Bipolar Membrane Using Iron (III) Hydroxide as Final Electron Acceptor" Energies 16, no. 6: 2527. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16062527
APA StyleKazama, I., Aso, Y., Tanaka, T., & Ohara, H. (2023). Microbial Fuel Cell Equipped with Bipolar Membrane Using Iron (III) Hydroxide as Final Electron Acceptor. Energies, 16(6), 2527. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16062527







