An Overview of the State of the Art and Challenges in the Use of Gelling and Thickening Agents to Create Stable Thermal Energy Storage Materials
Abstract
1. Introduction
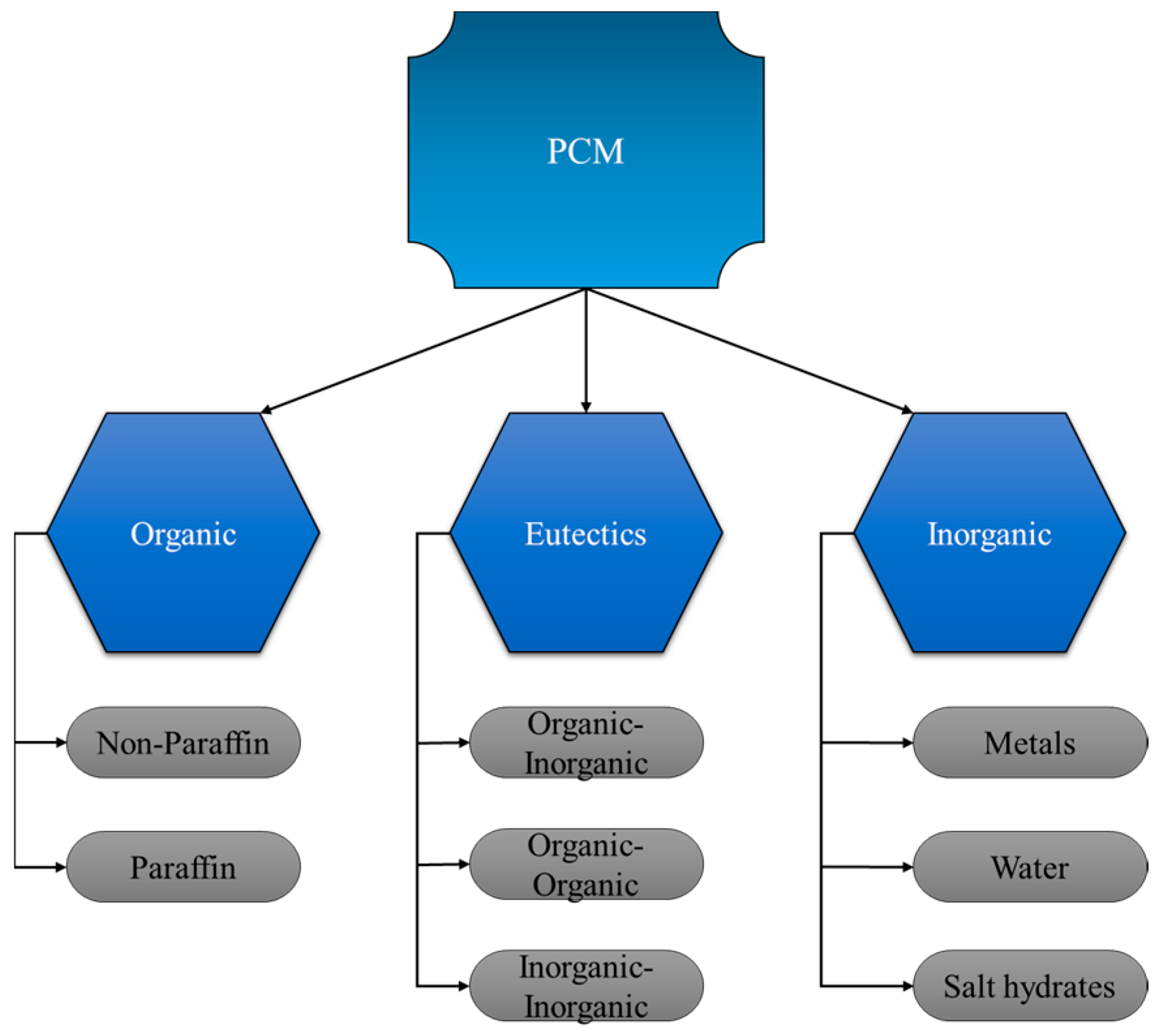
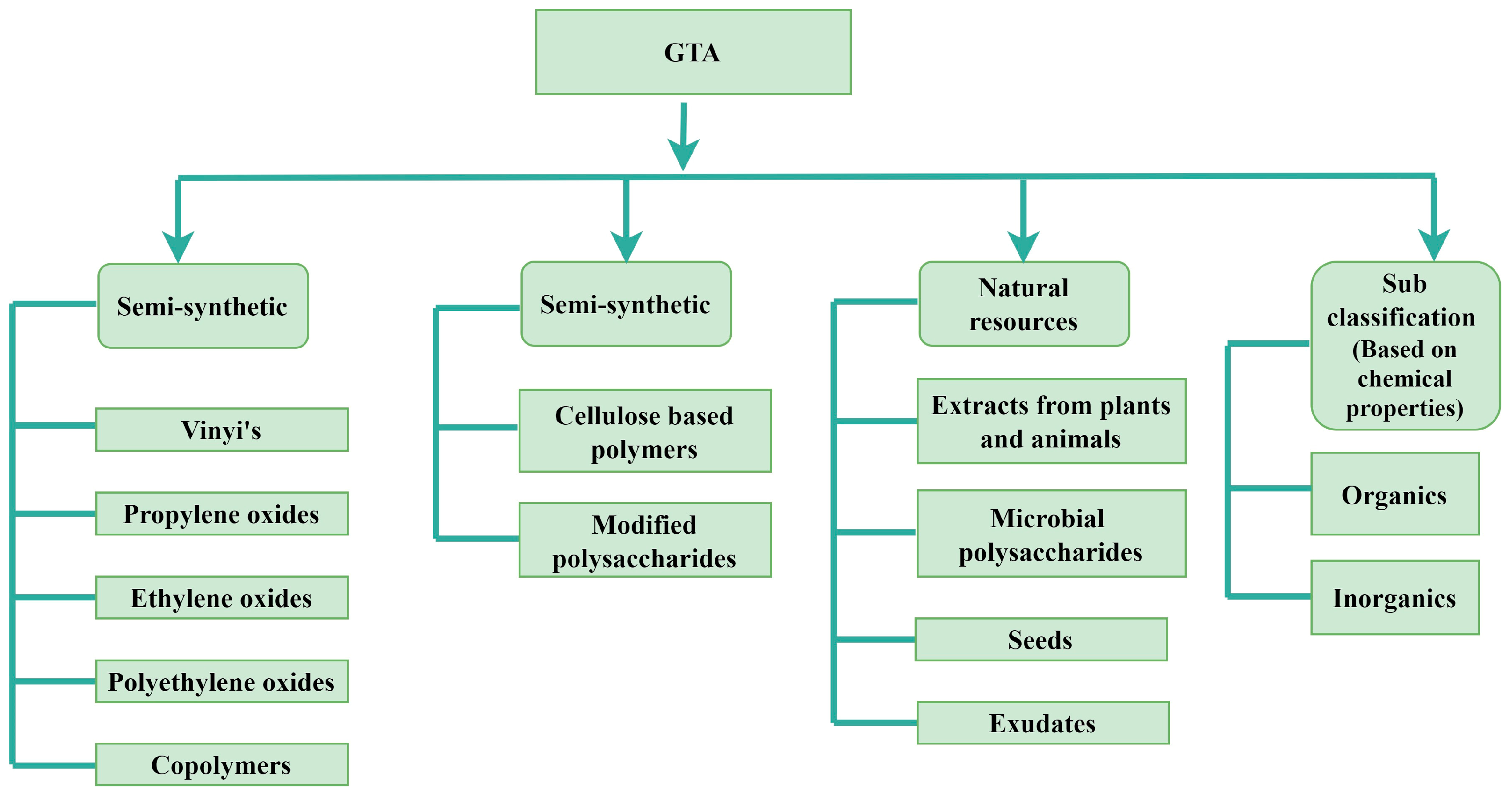
2. GTA Classifications
2.1. Natural GTAs
2.2. Synthetic GTAs
2.3. Semi-Synthetic GTAs
3. GTA Mechanism
- Interlace thickening: This mechanism is observed in natural GTAs and is characterized by a high elastic nature with pseudo-plastic behavior. The increase in viscosity during thickening occurs due to the entangling of heavy polymer molecules in the solution. The efficacy of the thickening process is determined by the molecular weight of the polymer [56].
- Physical thickening: This mechanism is observed in good water-soluble GTAs and light-molecular-weight molecules, which make an interconnection with one another to form a texture, resulting in an increase in viscosity [57]. Additionally, the interconnection strength depends on the GTA nature: if the strength is higher it leads to an increase in viscosity at a higher rate.
- Physical gelling: This mechanism is experienced in gel with reversible nature, and external conditions such as temperature, pressure, and pH significantly affect the physical gelling [58]. H2 bonding can be achieved by modulating the temperature or pH of the water-based solution. The repulsion effect between hydrophilic and hydrophobic components results in hydrophobic gelling. Similarly, the interfacing of anionic and ionic components leads to coacervation gelling.
- Chemical gelling: This mechanism occurs due to the reaction among the functional components, creating covalent chemical gelling. The type of chemical gelling varies based on the GTA’s nature and corresponding functionalization [58]. Redox reactions due to the formation of free radicals produce radical polymerization gelling, while click reaction gelling is mostly employed in biological fields because of its efficiency, strong gelling, and hastened reaction kinetics even at medium temperatures.
4. PCM + GTA Preparation
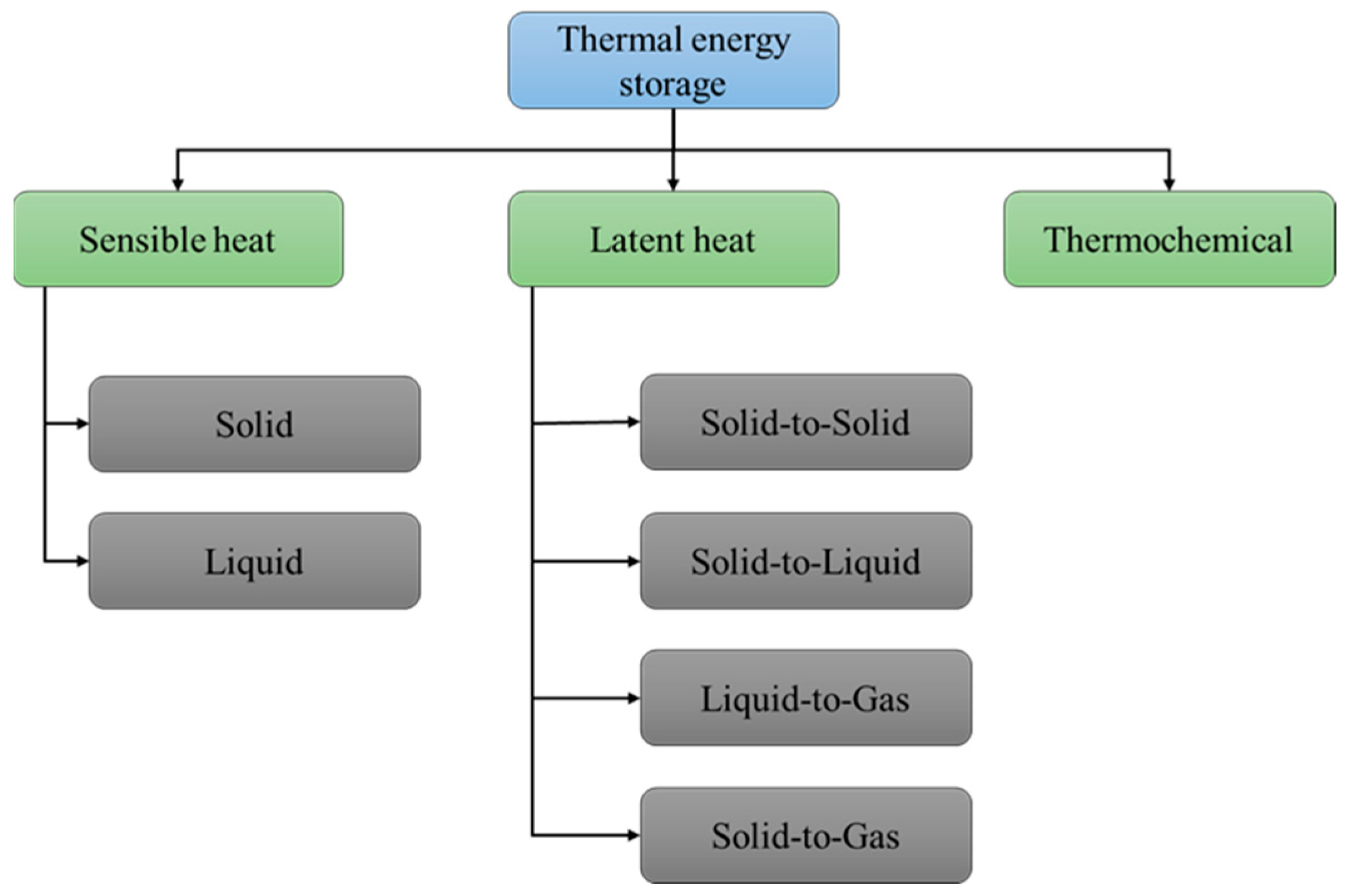
5. Application of GTA in LH-TES
5.1. PCM + GTA with NTs
5.2. PCM + GTA with NPs
6. Summary, Limitations, and Potential Scope of PCMs with GTA
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| CB | Cellulose-based |
| CCH | Calcium chloride hexahydrate |
| CNF | Cellulose nanofibrils |
| CNP | Carbon nanoparticle |
| DHPD | Disodium hydrogen phosphate dodecahydrate |
| DPM | Dry PCM mixing |
| GG | Guar gum |
| GNP | Graphene nanoplatelets |
| GS | Glauber’s salt |
| GTA | Gelling and thickening agents |
| HPEC | Hydroxypropyl ether cellulose |
| ITM | Inorganic thixotropic material |
| LH | Latent heat (J g−1 or kJ kg−1) |
| LNH | Lithium nitrate trihydrate |
| LPM | Liquid PCM mixing |
| MCH | Magnesium chloride hexahydrate |
| MNH | Magnesium nitrate hexahydrate |
| MNP | Metal nanoparticle |
| MWCNT | Multi-walled carbon nanotubes |
| NP | Nanoparticle |
| NT | Nucleating trigger |
| PAAM | Poly-acrylamide |
| PCM | Phase-change material |
| PCT | Phase-change temperature (°C) |
| PEG | Polyethylene glycol |
| PS | Potassium sulfates |
| PVA | Polyvinyl alcohol |
| PVP | Polyethylene pyrrolidone |
| SAT | Sodium acetate trihydrate |
| SCD | Supercooling degree (°C) |
| SM | Solution mixing |
| TC | Thermal conductivity (W m−1 K−1) |
| TES | Thermal energy storage |
| TMU | Thermal management unit |
| VB | Vinyl-based |
| XG | Xanthan gum |
References
- Prabakaran, R.; Sidney, S.; Lal, D.M.; Selvam, C.; Harish, S. Solidification of graphene-assisted phase change nanocomposites inside a sphere for cold storage applications. Energies 2019, 12, 3473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samykano, M. Role of phase change materials in thermal energy storage: Potential, recent progress and technical challenges. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2022, 52, 102234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purohit, B.K.; Sistla, V.S. Inorganic salt hydrate for thermal energy storage application: A review. Energy Storage 2021, 3, e212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, F.; Belusko, M.; Liu, M.; Tay, N.H.S. Using Solid-Liquid Phase Change Materials (PCMs) in Thermal Energy Storage Systems. In Advances in Thermal Energy Storage Systems; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2015; pp. 201–246. [Google Scholar]
- Prabakaran, R.; Kumar, J.P.N.; Lal, D.M.; Selvam, C.; Harish, S. Constrained melting of graphene-based phase change nanocomposites inside a sphere. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2020, 139, 941–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabeza, L.F.; Castell, A.; Barreneche, C.D.; De Gracia, A.; Fernández, A.I. Materials used as PCM in thermal energy storage in buildings: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2011, 15, 1675–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wu, C.; Wang, X.; Sun, S.; Cui, D.; Pan, S.; Sheng, H. A review of eutectic salts as phase change energy storage materials in the context of concentrated solar power. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2023, 205, 123904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feliński, P.; Sekret, R. Effect of a low cost parabolic reflector on the charging efficiency of an evacuated tube collector/storage system with a PCM. Solar Energy 2017, 144, 758–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, A.K.; Ahmed, M.S.; Kang, H.; Prabakaran, R.; Said, Z.; Rahman, S.; Sathyamurthy, R.; Kim, J.; Hwang, J.Y. Critical Review on Internal and External Battery Thermal Management Systems for Fast Charging Applications. Adv. Energy Mater. 2023, 13, 2202944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zare, M.; Mikkonen, K.S. Phase Change Materials for Life Science Applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2213455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenisarin, M.; Mahkamov, K. Salt hydrates as latent heat storage materials: Thermophysical properties and costs. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2016, 145, 255–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvnes, H.; Allouche, Y.; Manescu, R.I.; Hafner, A. Review on cold thermal energy storage applied to refrigeration systems using phase change materials. Therm. Sci. Eng. Prog. 2021, 22, 100807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feliński, P.; Sekret, R. Experimental study of evacuated tube collector/storage system containing paraffin as a PCM. Energy 2016, 114, 1063–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feliński, P.; Sekret, R. Effect of PCM application inside an evacuated tube collector on the thermal performance of a domestic hot water system. Energy Build. 2017, 152, 558–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pielichowska, K.; Pielichowski, K. Phase change materials for thermal energy storage. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2014, 65, 67–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathishkumar, A.; Cheralathan, M. Charging and discharging processes of low capacity nano-PCM based cool thermal energy storage system: An experimental study. Energy 2023, 263, 125700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alva, G.; Liu, L.; Huang, X.; Fang, G. Thermal energy storage materials and systems for solar energy applications. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 68, 693–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zsembinszki, G.; Fernández, A.G.; Cabeza, L.F. Selection of the appropriate phase change material for two innovative compact energy storage systems in residential buildings. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castell, A.; Sole, C. Design of latent heat storage systems using phase change materials (PCMs). In Advances in Thermal Energy Storage Systems; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2014; pp. 285–305. [Google Scholar]
- Salunkhe, P.B. Investigations on latent heat storage materials for solar water and space heating applications. J. Energy Storage 2017, 12, 243–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirbani, M.; Siavashi, M.; Bidabadi, M. Phase Change Materials Energy Storage Enhancement Schemes and Implementing the Lattice Boltzmann Method for Simulations: A Review. Energies 2023, 16, 1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathishkumar, A.; Cheralathan, M. Influence of thermal transport properties of NEPCM for cool thermal energy storage system. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2022, 147, 367–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Stonehouse, A.; Abeykoon, C. Encapsulation methods for phase change materials—A critical review. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2023, 200, 123458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, W.; Jamshideasli, D.; Khodadadi, J.M. Improved Performance of Latent Heat Energy Storage Systems in Response to Utilization of High Thermal Conductivity Fins. Energies 2023, 16, 1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesh Kumar, P.; Prabakaran, R.; Sakthivadivel, D.; Thangapandian, N.; Velraj, R.; Kim, S.C. Effect of shot blasting on droplet contact angle of carbon aided phase change nanocomposites. Surf. Eng. 2021, 37, 1002–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.C.; Prabakaran, R.; Sakthivadivel, D.; Thangapandian, N.; Bhatia, A.; Kumar, P.G. Thermal transport properties of carbon-assisted phase change nanocomposite. Fuller. Nanotub. Carb. Nanostruct. 2020, 28, 925–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nartowska, E.; Styś-Maniara, M.; Kozłowski, T. The Potential Environmental and Social Influence of the Inorganic Salt Hydrates Used as a Phase Change Material for Thermal Energy Storage in Solar Installations. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cong, L.; Zou, B.; Palacios, A.; Navarro, M.E.; Qiao, G.; Ding, Y. Thickening and gelling agents for formulation of thermal energy storage materials—A critical review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 155, 111906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, D.; Bhattacharya, S. Hydrocolloids as thickening and gelling agents in food: A critical review. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 47, 587–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raut, D.; Kalamkar, V.R. A review on latent heat energy storage for solar thermal water-lithium bromide vapor absorption refrigeration system. J. Energy Storage 2022, 55, 105828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, C.; Lan, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Ran, R.; Shi, L.Y. Shape-stable hydrated salts/polyacrylamide phase-change organohydrogels for smart temperature management. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 21810–21821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves, T.F.; Morsink, M.; Batain, F.; Chaud, M.V.; Almeida, T.; Fernandes, D.A.; da Silva, C.F.; Souto, E.B.; Severino, P. Applications of natural, semi-synthetic, and synthetic polymers in cosmetic formulations. Cosmetics 2020, 7, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Yang, H.; Zhu, C.; Xiao, J.; Cao, H.; Simal-Gandara, J.; Li, Y.; Fan, D.; Deng, J. A comprehensive review of food gels: Formation mechanisms, functions, applications, and challenges. Critic. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahim, S.A.; Hassabo, A.G.; Othman, H. Natural thickener in textile printing (A Mini Review). J. Text. Color. Polym. Sci. 2021, 18, 55–64. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, Y.B.; He, Y.L. A review of phase change material and performance enhancement method for latent heat storage system. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 93, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.K.; Lim, Y.Y.; Leow, A.T.; Namasivayam, P.; Abdullah, J.O.; Ho, C.L. Factors affecting yield and gelling properties of agar. J. Appl. Phycol. 2017, 29, 1527–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayakody, M.M.; Vanniarachchy, M.P.; Wijesekara, I. Seaweed derived alginate, agar, and carrageenan based edible coatings and films for the food industry: A review. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2022, 16, 1195–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramdhan, T.; Ching, S.H.; Prakash, S.; Bhandari, B. Physical and mechanical properties of alginate based composite gels. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 106, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafie, M.H.; Kamal, M.L.; Zulkiflee, F.F.; Hasan, S.; Uyop, N.H.; Abdullah, S.; Hussin, N.A.; Tan, Y.C.; Zafarina, Z. Application of Carrageenan extract from red seaweed (Rhodophyta) in cosmetic products: A review. J. Indian Chem. Soc. 2022, 28, 100613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aga, M.B.; Dar, A.H.; Nayik, G.A.; Panesar, P.S.; Allai, F.; Khan, S.A.; Shams, R.; Kennedy, J.F.; Altaf, A. Recent insights into carrageenan-based bio-nanocomposite polymers in food applications: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 192, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Hossen, M.A.; Zeng, Y.; Dai, J.; Li, S.; Qin, W.; Liu, Y. Gelatin-based composite films and their application in food packaging: A review. J. Food Eng. 2022, 313, 110762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thombare, N.; Jha, U.; Mishra, S.; Siddiqui, M.Z. Guar gum as a promising starting material for diverse applications: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 88, 361–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petri, D.F. Xanthan gum: A versatile biopolymer for biomedical and technological applications. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132, 42035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Villalobos, U.; Akhmetov, B.; Gil, A.; Khor, J.O.; Palacios, A.; Li, Y.; Ding, Y.; Cabeza, L.F.; Tan, W.L.; et al. A comprehensive review on sub-zero temperature cold thermal energy storage materials, technologies, and applications: State of the art and recent developments. Appl. Energy 2021, 288, 116555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, L.; Goswami, J. Poly (Vinyl Alcohol) as Sustainable and Eco-Friendly Packaging: A Review. J. Packag. Technol. Res. 2022, 7, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaikwad, K.K.; Singh, S.; Lee, Y.S. Oxygen scavenging films in food packaging. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2018, 16, 523–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, L.; Warkar, S.G.; Ahmad, S.I.; Kant, R.; Jain, M. A review on carboxylic acid cross-linked polyvinyl alcohol: Properties and applications. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2022, 62, 225–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundararajan, S.; Samui, A.B.; Kulkarni, P.S. Versatility of polyethylene glycol (PEG) in designing solid–solid phase change materials (PCMs) for thermal management and their application to innovative technologies. J. Mater. Chem A 2017, 5, 18379–18396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watcharakitti, J.; Win, E.E.; Nimnuan, J.; Smith, S.M. Modified starch-based adhesives: A review. Polymers 2022, 14, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurya, N.K.; Mandal, A. Studies on behavior of suspension of silica nanoparticle in aqueous polyacrylamide solution for application in enhanced oil recovery. Petr. Sci. Technol. 2016, 34, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Karsani, K.S.; Al-Muntasheri, G.A.; Sultan, A.S.; Hussein, I.A. Impact of salts on polyacrylamide hydrolysis and gelation: New insights. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2014, 131, 41185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Han, X.; Jiang, Y. Preparation and characterization of a form-stable phase change hydrogel for heat-protective clothing. New J. Chem. 2023, 47, 1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, A.; Sandewicz, R.W. Cosmetic science and polymer chemistry: Perfect together. In Polymers for Personal Care and Cosmetics, American Chemical Society; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2013; pp. 13–37. [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee, S.; Bhattacharya, S. Food gels: Gelling process and new applications. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2012, 52, 334–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Himashree, P.; Sengar, A.S.; Sunil, C.K. Food thickening agents: Sources, chemistry, properties and applications—A review. Int. J. Gastron. Food Sci. 2022, 27, 100468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohani, A.; Singh, G.; Bhattacharya, S.S.; Verma, A. Interpenetrating polymer networks as innovative drug delivery systems. J. Drug Deliv. 2014, 2014, 583612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadajji, V.G.; Betageri, G.V. Water soluble polymers for pharmaceutical applications. Polymers 2011, 3, 1972–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bearat, H.H.; Lee, B.H.; Vernon, B.L. Comparison of properties between NIPAAm-based simultaneously physically and chemically gelling polymer systems for use in vivo. Acta Biomater. 2012, 8, 3629–3642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, R.M.; Schlegel, J.P.; Castano, C.; Sawafta, R. Preparation and enhanced thermal performance of novel (solid to gel) form-stable eutectic PCM modified by nano-graphene platelets. J. Energy Storage 2018, 15, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yu, K.; Peng, H.; Ling, X. Preparation and thermal properties of sodium acetate trihydrate as a novel phase change material for energy storage. Energy 2019, 167, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marks, S. An investigation of the thermal energy storage capacity of Glauber’s salt with respect to thermal cycling. Solar Energy 1980, 25, 255–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telkes, M. Thermal energy storage in salt hydrates. Solar Energy Mater. 1980, 2, 381–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, H.W.; Woo, S.W.; Shin, B.C.; Kim, S.D. Prevention of supercooling and stabilization of inorganic salt hydrates as latent heat storage materials. Solar Energy Mater. Solar Cells 1992, 27, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, B.C.; Kim, S.D.; Won-Hoon, P. Phase separation and supercooling of a latent heat-storage material. Energy 1989, 14, 921–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabeza, L.F.; Svensson, G.; Hiebler, S.; Mehling, H. Thermal performance of sodium acetate trihydrate thickened with different materials as phase change energy storage material. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2003, 23, 1697–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, X.Z.; Tan, Z.C.; Yue, D.T.; Shi, Q.; Yang, C.G. Heat storage performance of disodium hydrogen phosphate dodecahydrate: Prevention of phase separation by thickening and gelling methods. Chin. J. Chem. 2007, 25, 921–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, X.Z.; Tan, Z.C.; Shi, Q.; Yang, C.G. A novel gelling method for stabilization of phase change material Na2HPO4·12H2O with sodium alginate grafted sodium acrylate. Thermochim. Acta 2007, 463, 18–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, X.Z.; Tan, Z.C.; Shi, Q.; Gao, Z.H. Gelled Na2HPO4·12H2O with amylose-g-sodium acrylate: Heat storage performance, heat capacity and heat of fusion. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2009, 96, 1035–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Q.; Luo, X.; Lin, X.; Zhang, H. Study of magnesium nitrate hexahydrate and magnesium chloride hexahydrate mixture as phase change material. In Proceedings of the 2012 Asia-Pacific Power and Energy Engineering Conference IEEE, Shanghai, China, 27–29 March 2012; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- El-Sebaii, A.A.; Al-Heniti, S.; Al-Agel, F.; Al-Ghamdi, A.A.; Al-Marzouki, F. One thousand thermal cycles of magnesium chloride hexahydrate as a promising PCM for indoor solar cooking. Energy Convers. Manag. 2011, 52, 1771–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, B.G.; Glorieux, C.; Martinez, E.S.; Cuautle, J.F. Tuning of thermal properties of sodium acetate trihydrate by blending with polymer and silver nanoparticles. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2014, 62, 838–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ushak, S.; Galazutdinova, Y.; Gutierrez, A.; Cabeza, L.F.; Farid, M.M.; Grágeda, M. Thermal management system of li-ion batteries using inorganic phase-change materials. In Proceedings of the EuroSun 2014: International Conference on Solar Energy and Buildings, Aix-les-Bains, France, 16–19 September 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkan, C.; Döğüşcü, D.K.; Gottschalk, A.; Ramamoorthi, U.; Kumar, A.; Yadav, S.K.; Yadav, A.S.; Adıgüzel, E.; Altıntaş, A.; Damlıoğlu, Y.; et al. Polyvinyl alcohol-salt hydrate mixtures as passive thermal energy storage systems. Energy Procedia. 2016, 91, 1012–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimineghlani, P.; Emmons, E.; Green, M.J.; Shamberger, P.; Sukhishvili, S.A. A temperature-responsive poly (vinyl alcohol) gel for controlling fluidity of an inorganic phase change material. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 12474–12482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Chen, X. Preparation and thermal properties of eutectic hydrate salt phase change thermal energy storage material. Int. J. Photoenergy 2018, 2018, 6432047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, C.Y. Experimental investigation of barium hydroxide octahydrate as latent heat storage materials. Solar Energy 2019, 177, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Huang, J.; Wang, T.; Zhu, P. Effect of fumed silica additive on supercooling, thermal reliability and thermal stability of Na2HPO4·12H2O as inorganic PCM. Thermochim. Acta 2019, 675, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dannemand, M.; Johansen, J.B.; Furbo, S. Solidification behavior and thermal conductivity of bulk sodium acetate trihydrate composites with thickening agents and graphite. Solar Energy Mater. Solar Cells 2016, 145, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Q.; Zhang, M.; Fan, J.; Li, L.; Xu, T.; Yuan, W. Thermal conductivity enhancement of hydrated salt phase change materials employing copper foam as the supporting material. Solar Energy Mater. Solar Cells 2019, 199, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasilyev, G.; Koifman, N.; Shuster, M.; Gishvoliner, M.; Cohen, Y.; Zussman, E. Synergistic Effect of Two Organogelators for the Creation of Bio-Based, Shape-Stable Phase-Change Materials. Langmuir 2020, 36, 15572–15582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, K.; Kwon, S.; Xu, W.; Wang, X.; Toivakka, M. Effect of micro-and nanofibrillated cellulose on the phase stability of sodium sulfate decahydrate based phase change material. Cellulose 2020, 27, 5003–5016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Yazdani, M.R.; Ajdary, R.; Rojas, O.J. Leakage-proof microencapsulation of phase change materials by emulsification with acetylated cellulose nanofibrils. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 254, 117279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabakaran, R.; Sidney, S.; Lal, D.M.; Harish, S.; Kim, S.C. Experimental performance of a mobile air conditioning unit with small thermal energy storage for idle stop/start vehicles. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2022, 147, 5117–5132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, A.K.; Prabakaran, R.; Elkadeem, M.R.; Sharshir, S.W.; Arıcı, M.; Wang, C.; Zhao, W.; Hwang, J.Y.; Saidur, R. A state of art review and future viewpoint on advance cooling techniques for Lithium–ion battery system of electric vehicles. J. Energy Storage 2020, 32, 101771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.G.; Sakthivadivel, D.; Prabakaran, R.; Vigneswaran, S.; SakthiPriya, M.; Thakur, A.K.; Sathyamurthy, R.; Kim, S.C. Exploring the thermo-physical characteristic of novel multi-wall carbon nanotube—Therminol-55-based nanofluids for solar-thermal applications. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 10717–10728. [Google Scholar]
- Eneren, P.; Aksoy, Y.T.; Vetrano, M.R. Experiments on Single-Phase Nanofluid Heat Transfer Mechanisms in Microchannel Heat Sinks: A Review. Energies 2022, 15, 2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modi, N.; Wang, X.; Negnevitsky, M. Solar Hot Water Systems Using Latent Heat Thermal Energy Storage: Perspectives and Challenges. Energies 2023, 16, 1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhou, Y.; Nian, H.; Zhu, F.; Ren, X.; Dong, O.; Hai, C.; Shen, Y.; Zeng, J. Preparation and thermal energy storage studies of CH3COONa3H2O–KCl composites salt system with enhanced phase change performance. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2016, 102, 708–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, W.; Yuan, Y.; Sun, L.; Cao, X.; Yang, X. Experimental studies on the supercooling and melting/freezing characteristics of nano-copper/sodium acetate trihydrate composite phase change materials. Renew. Energy 2016, 99, 1029–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhang, B.; Xie, B.; Zhao, X.; Chen, J. Tailored phase change behavior of Na2SO410H2O/expanded graphite composite for thermal energy storage. Energy Convers. Manag. 2020, 208, 112586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorbacheva, S.N.; Makarova, V.V.; Ilyin, S.O. Hydrophobic nanosilica-stabilized graphite particles for improving thermal conductivity of paraffin wax-based phase-change materials. J. Energy Storage 2021, 36, 102417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhang, N.; Zhou, J.; Pan, X. Photo-to-thermal conversion and energy storage of polyethylene glycol/copper sulfide composite PCMs. Solar Energy Mater. Solar Cells 2022, 238, 111583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.G.; Prabakaran, R.; Sakthivadivel, D.; Somasundaram, P.; Vigneswaran, V.S.; Kim, S.C. Ultrasonication time optimization for multi-walled carbon nanotube based Therminol-55 nanofluid: An experimental investigation. J. Therm. Analysis Calorim. 2022, 147, 10329–10336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, A.K.; Ahmed, M.S.; Park, J.; Prabakaran, R.; Sidney, S.; Sathyamurthy, R.; Kim, S.C.; Periasamy, S.; Kim, J.; Hwang, J.Y. A review on carbon nanomaterials for K-ion battery anode: Progress and perspectives. Int. J. Energy Res. 2022, 46, 4033–4070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Du, J.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Chen, L.; Chai, Y.; Li, Y. Preparation and Characterization of n-Octadecane@SiO2/GO and n-Octadecane@SiO2/Ag Nanoencapsulated Phase Change Material for Immersion Cooling of Li-Ion Battery. Energies 2023, 16, 1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mebarek-Oudina, F.; Chabani, I. Review on Nano Enhanced PCMs: Insight on nePCM Application in Thermal Management/Storage Systems. Energies 2023, 16, 1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalidasan, B.; Pandey, A.K.; Rahman, S.; Sharma, K.; Tyagi, V.V. Experimental Investigation of Graphene Nanoplatelets Enhanced Low Temperature Ternary Eutectic Salt Hydrate Phase Change Material. Energies 2023, 16, 1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olabi, A.G.; Wilberforce, T.; Elsaid, K.; Sayed, E.T.; Ramadan, M.; Rahman, S.A.; Abdelkareem, M.A. Recent progress on Carbon-based nanomaterial for phase change materials: Prospects and challenges. Therm. Sci. Eng. Prog. 2021, 23, 100920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yu, K.; Gao, X.; Ren, M.; Jia, M.; Yang, Y. Enhanced thermal properties of hydrate salt/poly (acrylate sodium) copolymer hydrogel as form-stable phase change material via incorporation of hydroxyl carbon nanotubes. Solar Energy Mater. Solar Cells 2020, 208, 110387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Jin, X.Z.; Zhang, N.; Qi, X.D.; Yang, J.H.; Zhou, Z.W.; Wang, Y. Constructing cellulose nanocrystal/graphene nanoplatelet networks in phase change materials toward intelligent thermal management. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 253, 117290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasilyev, G.; Koifman, N.; Shuster, M.; Gishvoliner, M.; Cohen, Y.; Zussman, E. Phase Change Material with Gelation Imparting Shape Stability. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 11887–11902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Liu, X.; Wang, Z.; Tie, S.; Wang, C.A. Hierarchically porous CMC/rGO/CNFs aerogels for leakage-proof mirabilite phase change materials with superior energy thermal storage. Front. Mater. Sci. 2022, 16, 220619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bott, C.; Dressel, I.; Bayer, P. State-of-technology review of water-based closed seasonal thermal energy storage systems. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 113, 109241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, R.; Ravindra, M.R. Cold thermal energy storage for milk chilling: A numerical and experimental study. J. Food Eng. 2023, 337, 111223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathishkumar, A.; Cheralathan, M. Influence of functionalized carbon flake on phase change characteristics of deionized (DI) water for cool thermal storage system. Fuller. Nanotub. Carb. Nanostruct. 2022, 30, 958–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeyaraman, P.N.; Prabakaran, R.; Dhasan, M.L. A novel solar operated DC compressor refrigerator with thermal energy storage. Energy Sour. Part A Recovery Utiliz. Environ. Eff. 2023, 45, 860–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidney, S.; Dhasan, M.L.; Harish, S. Experimental investigation of freezing and melting characteristics of graphene-based phase change nanocomposite for cold thermal energy storage applications. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidney, S.; Prabakaran, R.; Kim, S.C.; Dhasan, M.L. A novel solar-powered milk cooling refrigeration unit with cold thermal energy storage for rural application. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 16346–16370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundaram, P.; Kalaisselvane, A.; Sathishkumar, A.; Ganesh Kumar, P.; Kim, S.C.; Prabakaran, R. Synthesis, stability, and heat transfer behavior of water and graphene nanoplatelet-based nanofluid for cool thermal storage applications. J. Energy Storage 2023, 64, 107219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gracia, A.; Rincóna, L.; Castell, A.; Jiménez, M.; Boer, D.; Medranoa, M.; Cabeza, L.F. Life Cycle Assesment of the inclusion of phase change materials (PCM) in experimental buildings. Energybuild 2010, 2, 1517–1523. [Google Scholar]



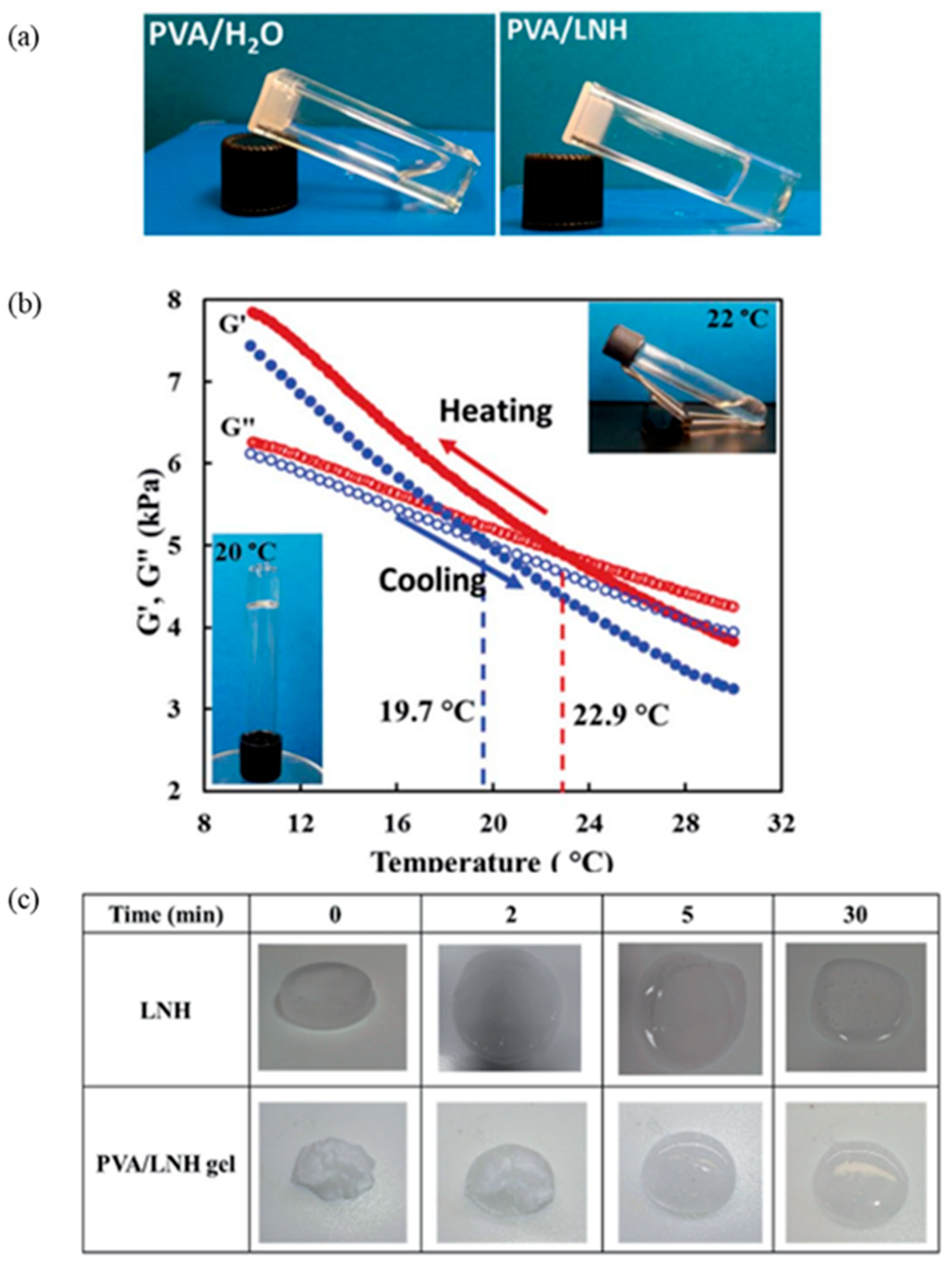


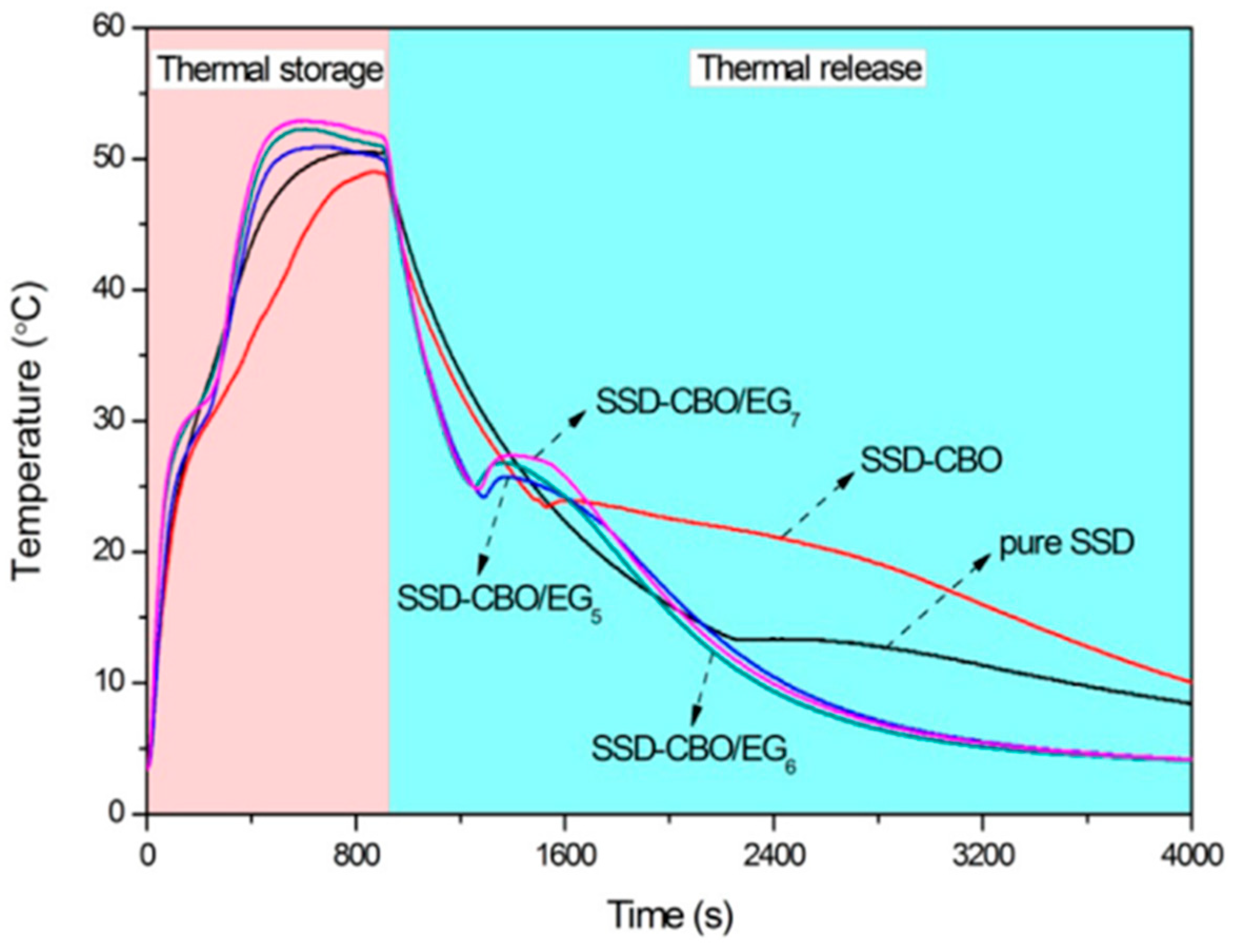

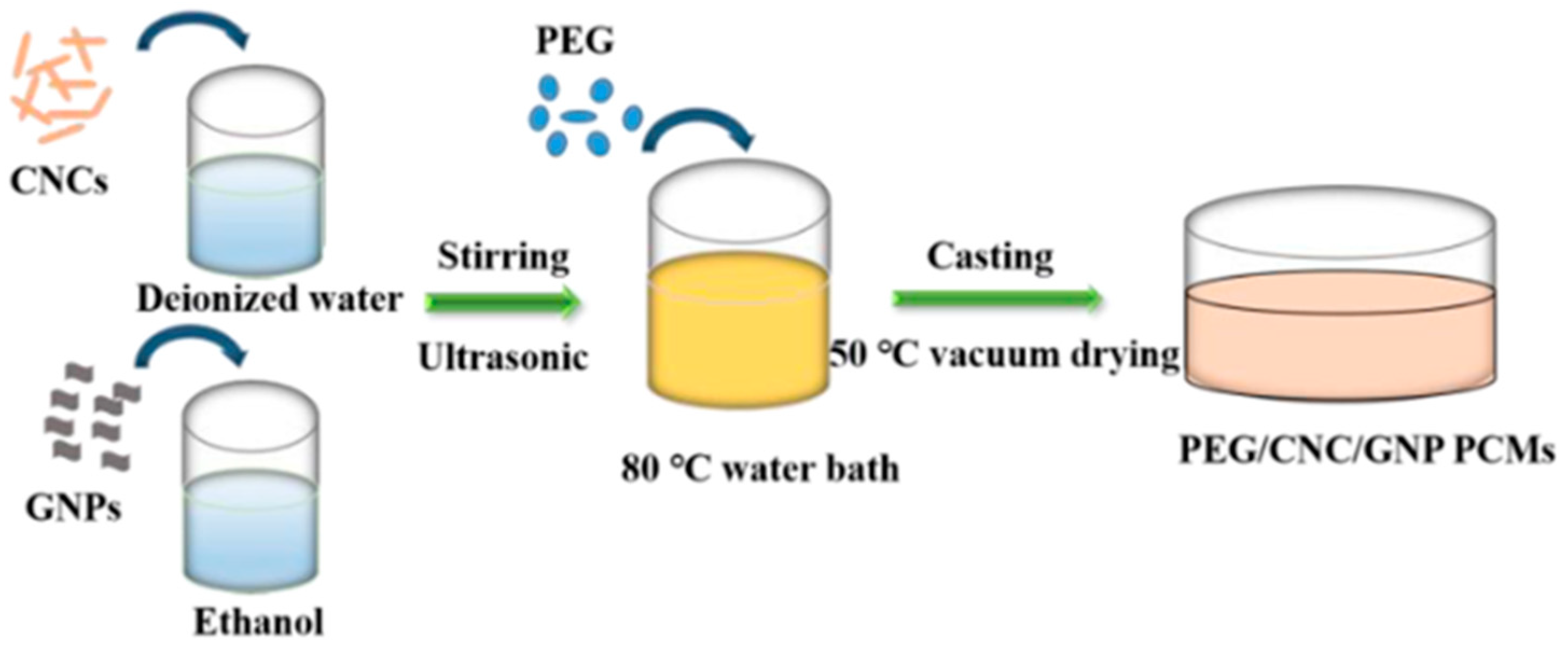
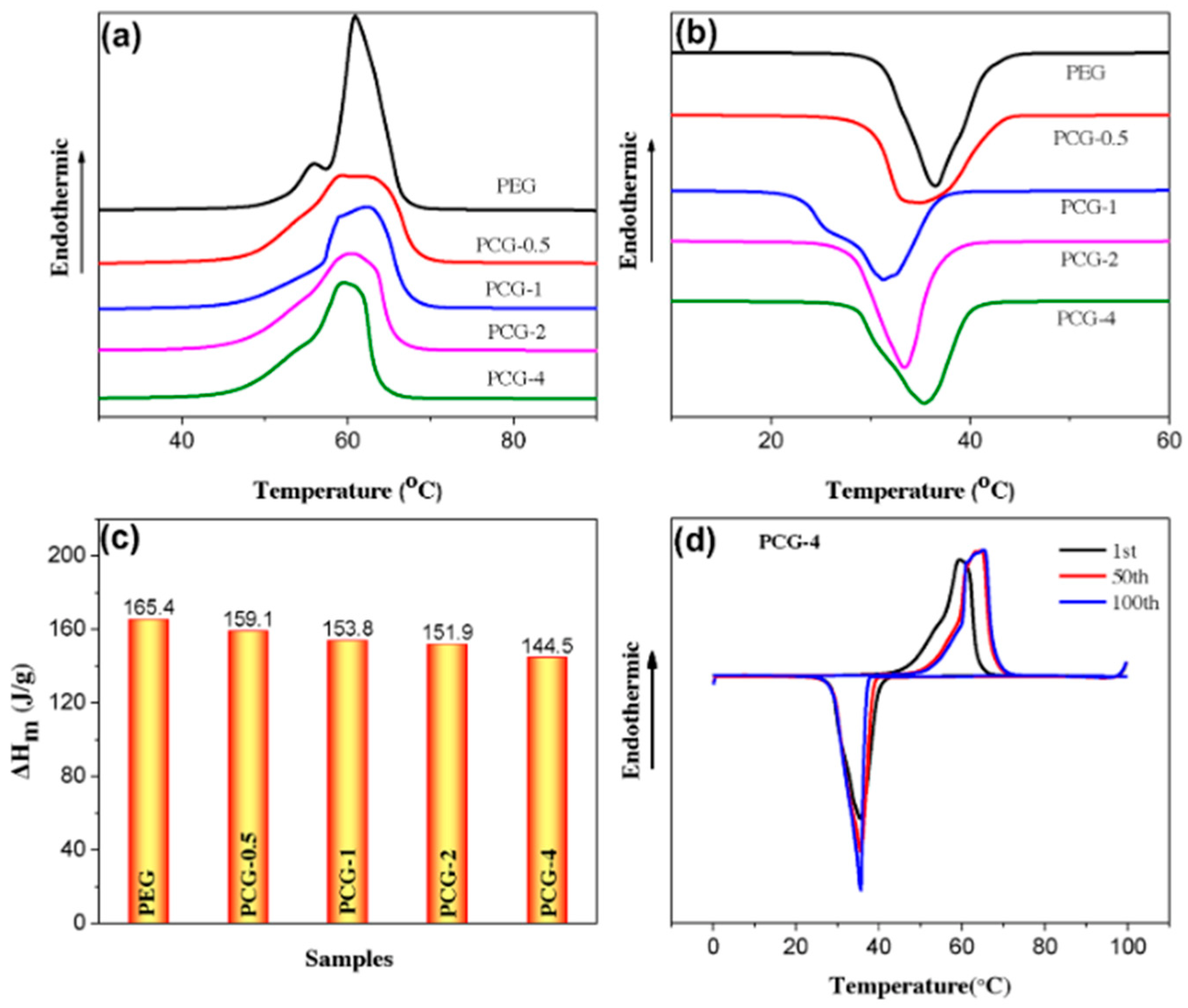

| GTA Type | Structure | Ionic Charge | Solubility | Limitation | Working Nature | Application (Industries) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Agar | Linear/hetero- polymers | Non-ionic | Only in hot water | Not recommended for acidic solutions (pH < 4) | Reversible | Food, medical, and leather |
| Alginates | Linear/hetero-/homo-polymers | Anionic | Water (except lambda in cold water) | Salt solution (base) might cause the gelling formation | Reversible | Food and medical |
| Gelatin | Protein-based biopolymer | Covalent compounds | Water soluble | Poor mechanical properties and short degradation times | Reversible | Food and medical |
| GG | Hydrophilic biopolymer | Non-ionic | Water soluble | Unstable nature at lower pH (<3.5) and higher temperatures (>90 °C) | Reversible | Food, cosmetics, paper, and medical |
| XG | Hetero-polymers | Anionic | Water soluble | Not recommended in heat-produced (>300 °C) process and (high) salt solvents | Shear-thinning/reversible pseudo-plasticity | Food |
| PVA | Linear aliphatic | Cationic | Water soluble | Poor permeability and moisture-absorbing nature | Shear-thinning/reversible | Food |
| PEG | Linear (semicrystalline polyether) | Non-ionic | Water soluble | May cause leakage at higher temperatures, poor loading capacity | Shear-thinning/reversible | Textile and medical |
| PAAM | Linear-chain or cross-linked | Cationic | Water soluble | Prone to microbial contamination and more difficult to prepare and handle than other GTAs | Shear-thinning/reversible | Medical, oil recovery, and waste-water treatment |
| CMC | Linear | Anionic | Water soluble | Poor antimicrobial properties | Shear-thinning/reversible | Medical |
| PCM | GTA/wt.% | NT/wt.% | Preparation Approach | Observations | Application | Ref. | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PCT Melting (°C) | SCD (°C) | TC (W m−1 K−1) | LH (kJ kg−1) (No. of Cycles) | ||||||
| GS | Attapulgite clay/9.3 | Borax/2.7 | SM | 32.4 | 7 | - | 105 (200) | Space heating | [61] |
| SAT | CMC/3 SAP/3 | PS/2 Borax/3 | LPM | 58 32 | 0–3 3–4 | 0.6 0.64 | 206 (200) 227 (200) | Solar heating | [63] |
| DHPD | Sodium alginate | - | SM | 35.4 | - | - | 260.9 (-) | - | [68] |
| MNH + MCH (60:40) | CMC/5 | - | LPM | 57 | - | - | 100 (100) | Solar heating and building | [69] |
| SAT | CMC + silica gel (85:15)/3 | Silver | - | 62.13 | - | - | 285.8 (10) | Solar heating | [71] |
| GS | PEG/5 | Boric acid/5 | - | 34.9 | - | - | 191.8 (-) | Battery | [72] |
| CCH GS | PVA | - | - | 42.1 34.2 | - - | 0.16–0.19 | 248.7 (-) 80.0 (-) | Green house and food preservation | [73] |
| SAT | XG/0.5 CMC/1 | - | LPM | - | - | 0.54 0.64 | - | Solar thermal | [78] |
| SAT | XG/2 | Disodium phosphate/- | LPM | 58.8 | - | - | 240.3 (200) | Solar thermal | [79] |
| Fatty acids | MT-800 (Mil)/3 | - | LPM | 58.1 | - | - | - | - | [80] |
| GS | Fibrillated cellulose (nano/micro-sized)/1 | Borax/5 | SM | 29 | 1.9 | - | - | - | [81] |
| Paraffin | Cellulose nanofibrils (CNF)/20 | - | SM | 54.8 | 9 | - | 171.4 | Building heating | [82] |
| PCM | GTA/wt.% | NP/wt.% | Preparation Approach | Observations | Application | Ref. | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PCT Melting (°C) | SCD (°C) | TC (W m−1 K−1) | LH (kJ kg−1) (No. of Cycles) | ||||||
| SAT + PC | CMC/4 | Al2O3/1 | Simple blending | 50.45 | 0.1 | - | 232.3 (50) | Building and water heating | [88] |
| SAT | CMC/3 | Cu/0.5 | Dispersion in liquid SAT | 57.8 | 0.5 | 0.936 | 231.4 (50) | - | [89] |
| GS | CMC/2 | EG/0.7 | - | 31.06 | 8.03 | 1.96 | 114 (50) | Building envelope | [90] |
| Paraffin | Silica/3 | Graphite/15 | LPM | 57.5 | - | - | 131.6 | - | [91] |
| PEG | PVP/2 | Cu Sulfide/10 | 56.23 | 13.37 | 0.247 | 151.8 (100) | Solar thermal | [92] | |
| GS | PAAS/7 | MWCNT/3 | Mechanical mixing | 38.5 | - | 1.38 | 180.4 (500) | Solar thermal | [99] |
| PEG | CNC/8 | GNP/4 | Physical compound | 59.6 | - | 2.018 | 145.2 (100) | Electronic devices | [100] |
| Bio-PCM | Mil + HAS (17:83 by mass)/15 | GNP/3 MWCNT/0.6 | LPM | 26.9–28.3 | 0.2–0.3 | 0.454 0.33 | - | Green house and water heating | [101] |
| Mirabilite-PCM | CMC/- | GO + CNF/- | - | - | 0.7–1 | - | 86.3 (1500) | Solar thermal | [102] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Prabakaran, R.; Dhamodharan, P.; Sathishkumar, A.; Gullo, P.; Vikram, M.P.; Pandiaraj, S.; Alodhayb, A.; Khouqeer, G.A.; Kim, S.-C. An Overview of the State of the Art and Challenges in the Use of Gelling and Thickening Agents to Create Stable Thermal Energy Storage Materials. Energies 2023, 16, 3306. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16083306
Prabakaran R, Dhamodharan P, Sathishkumar A, Gullo P, Vikram MP, Pandiaraj S, Alodhayb A, Khouqeer GA, Kim S-C. An Overview of the State of the Art and Challenges in the Use of Gelling and Thickening Agents to Create Stable Thermal Energy Storage Materials. Energies. 2023; 16(8):3306. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16083306
Chicago/Turabian StylePrabakaran, Rajendran, Palanisamy Dhamodharan, Anbalagan Sathishkumar, Paride Gullo, Muthuraman Ponrajan Vikram, Saravanan Pandiaraj, Abdullah Alodhayb, Ghada A. Khouqeer, and Sung-Chul Kim. 2023. "An Overview of the State of the Art and Challenges in the Use of Gelling and Thickening Agents to Create Stable Thermal Energy Storage Materials" Energies 16, no. 8: 3306. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16083306
APA StylePrabakaran, R., Dhamodharan, P., Sathishkumar, A., Gullo, P., Vikram, M. P., Pandiaraj, S., Alodhayb, A., Khouqeer, G. A., & Kim, S.-C. (2023). An Overview of the State of the Art and Challenges in the Use of Gelling and Thickening Agents to Create Stable Thermal Energy Storage Materials. Energies, 16(8), 3306. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16083306







