A Practical Hybrid Hysteresis Model for Calculating Iron Core Losses in Soft Magnetic Materials
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Bertotti Empirical Method
3. Hysteresis Model
3.1. Static J–A Hysteresis Model
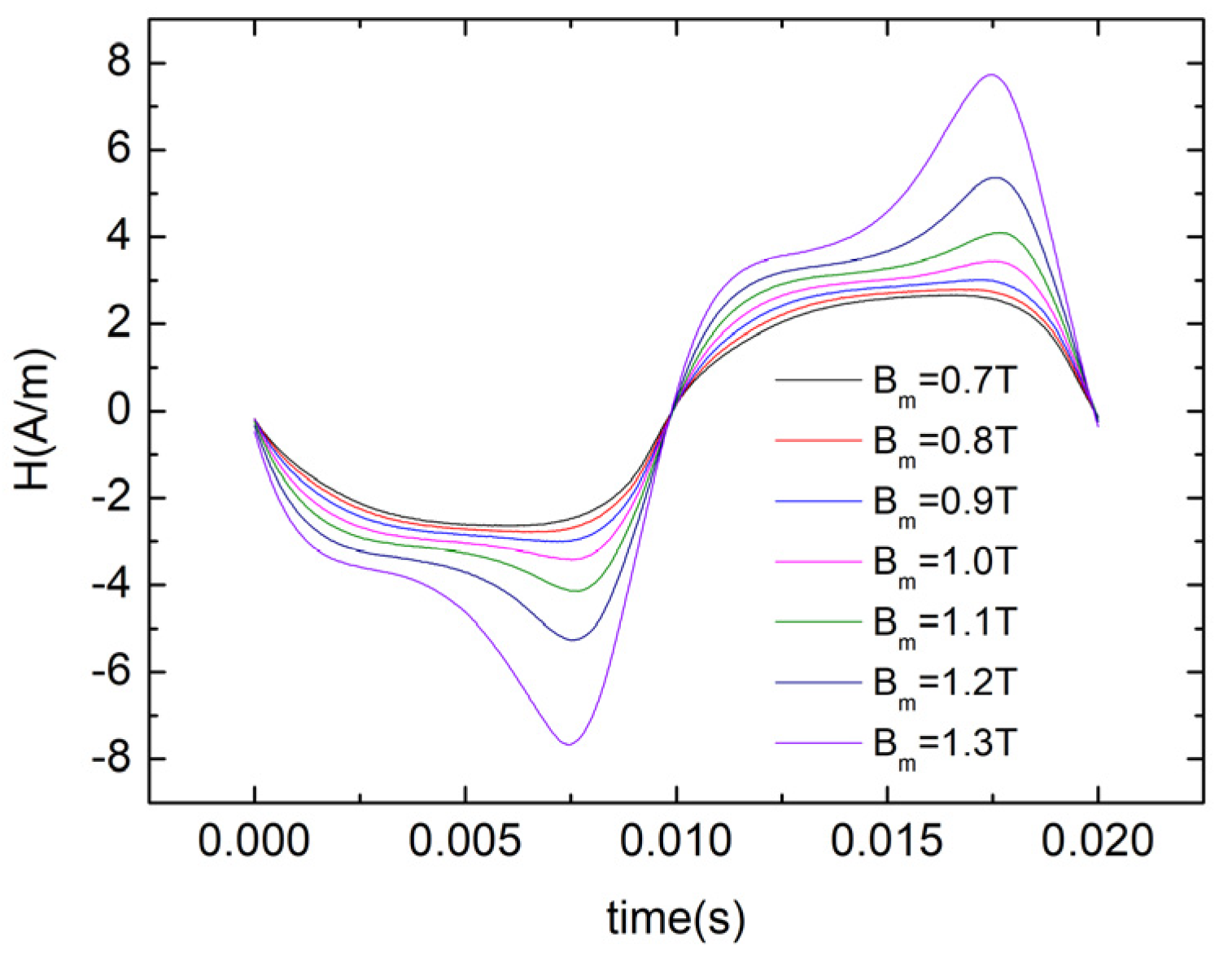
3.2. Dynamic J–A Hysteresis Model
3.3. Fourier Hysteresis Model
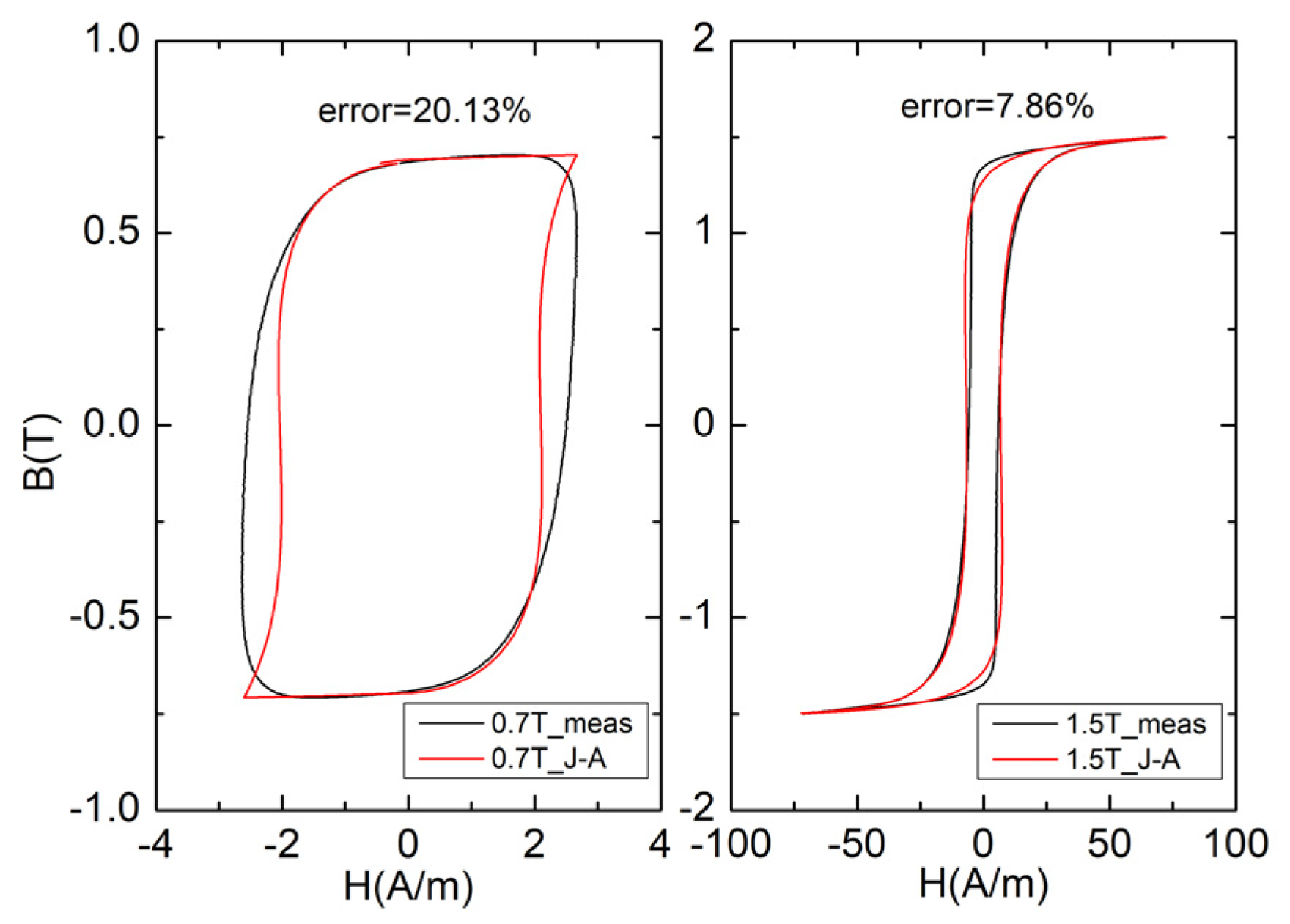
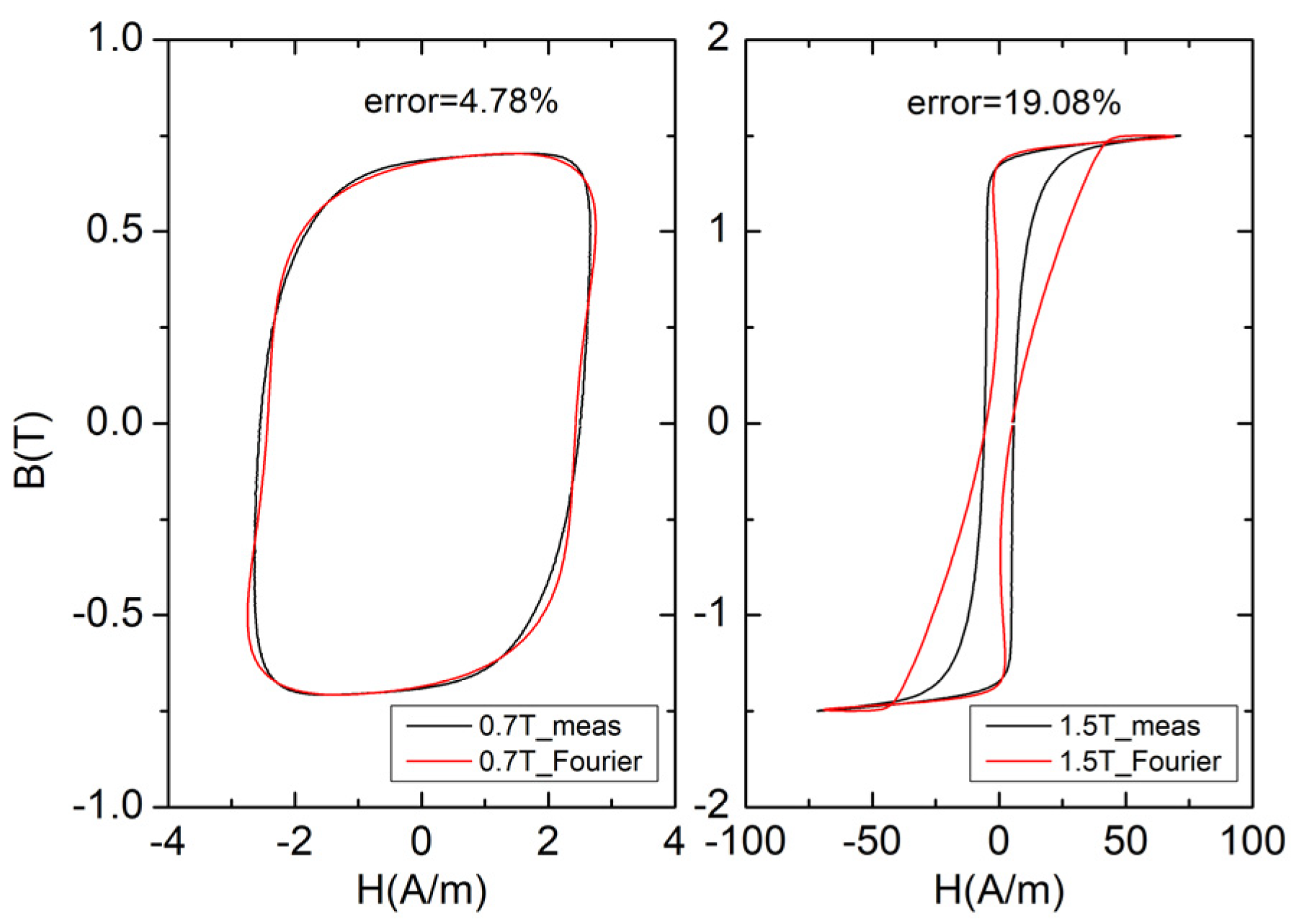
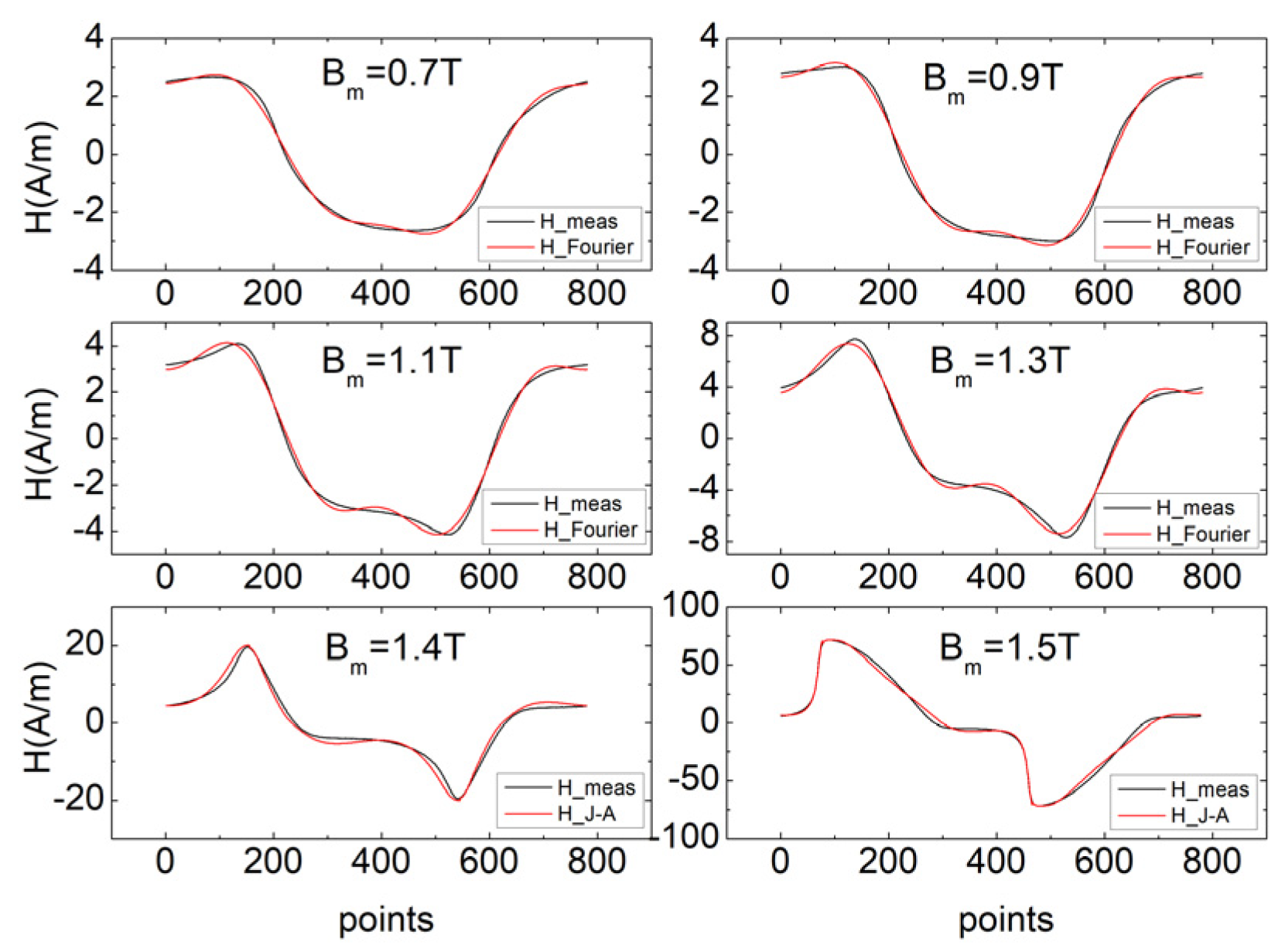
3.4. Comparison of J–A Model and Fourier Model
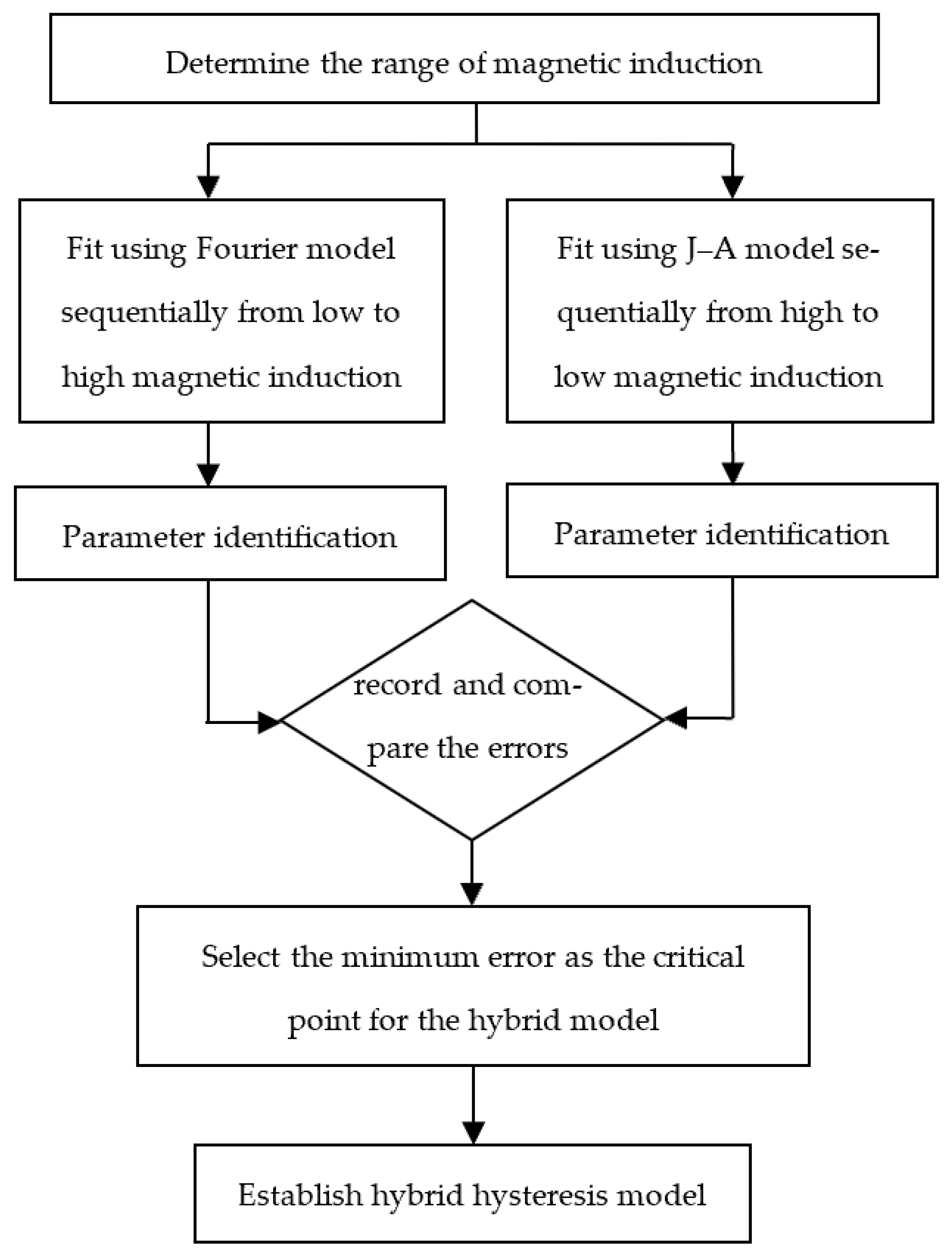
4. Hybrid Hysteresis Model
4.1. Hybrid Hysteresis Model
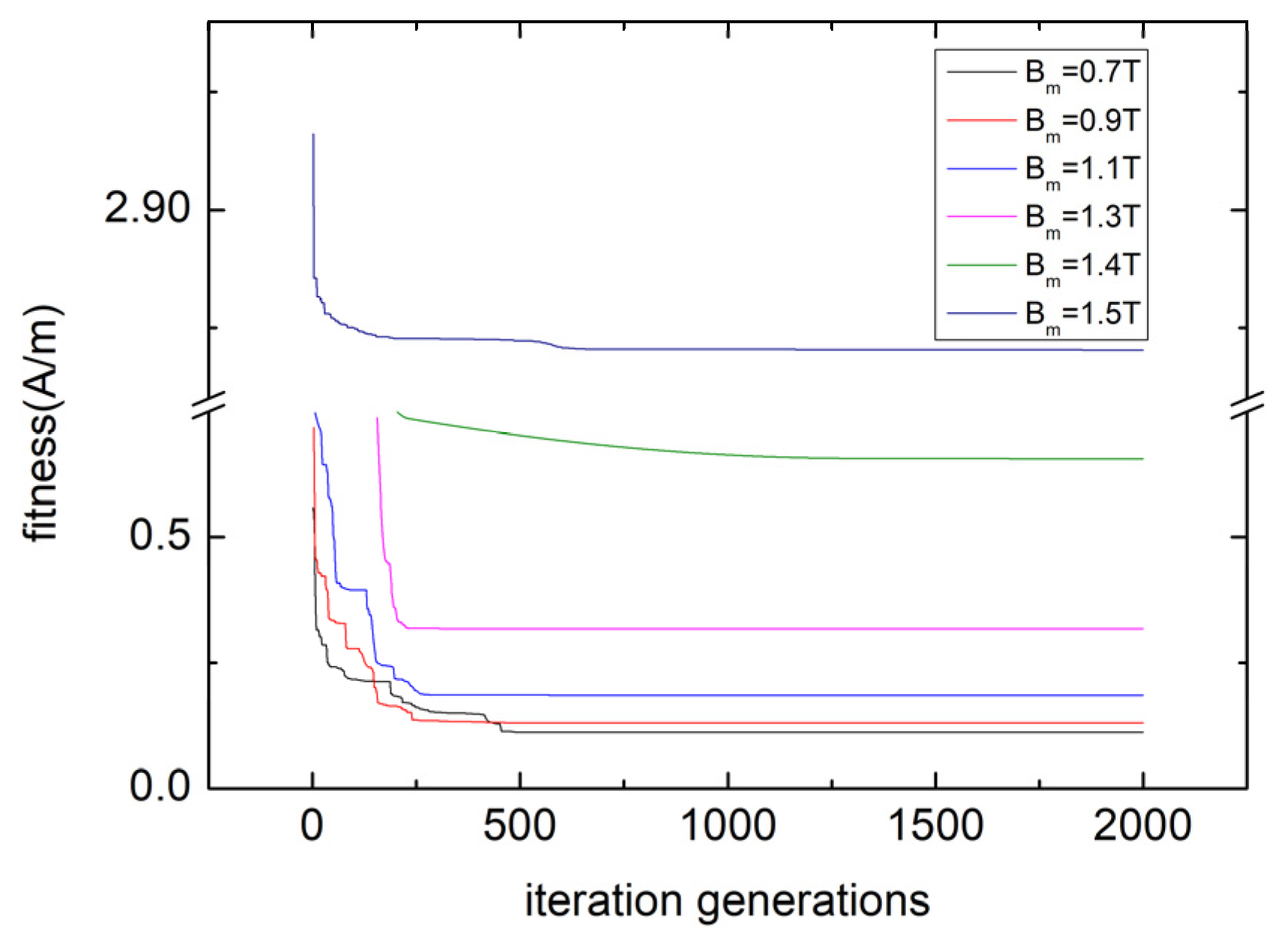
4.2. Calculation Time of Hybrid Hysteresis Model
4.3. Critical Point of Hybrid Hysteresis Model
5. Experimental Results
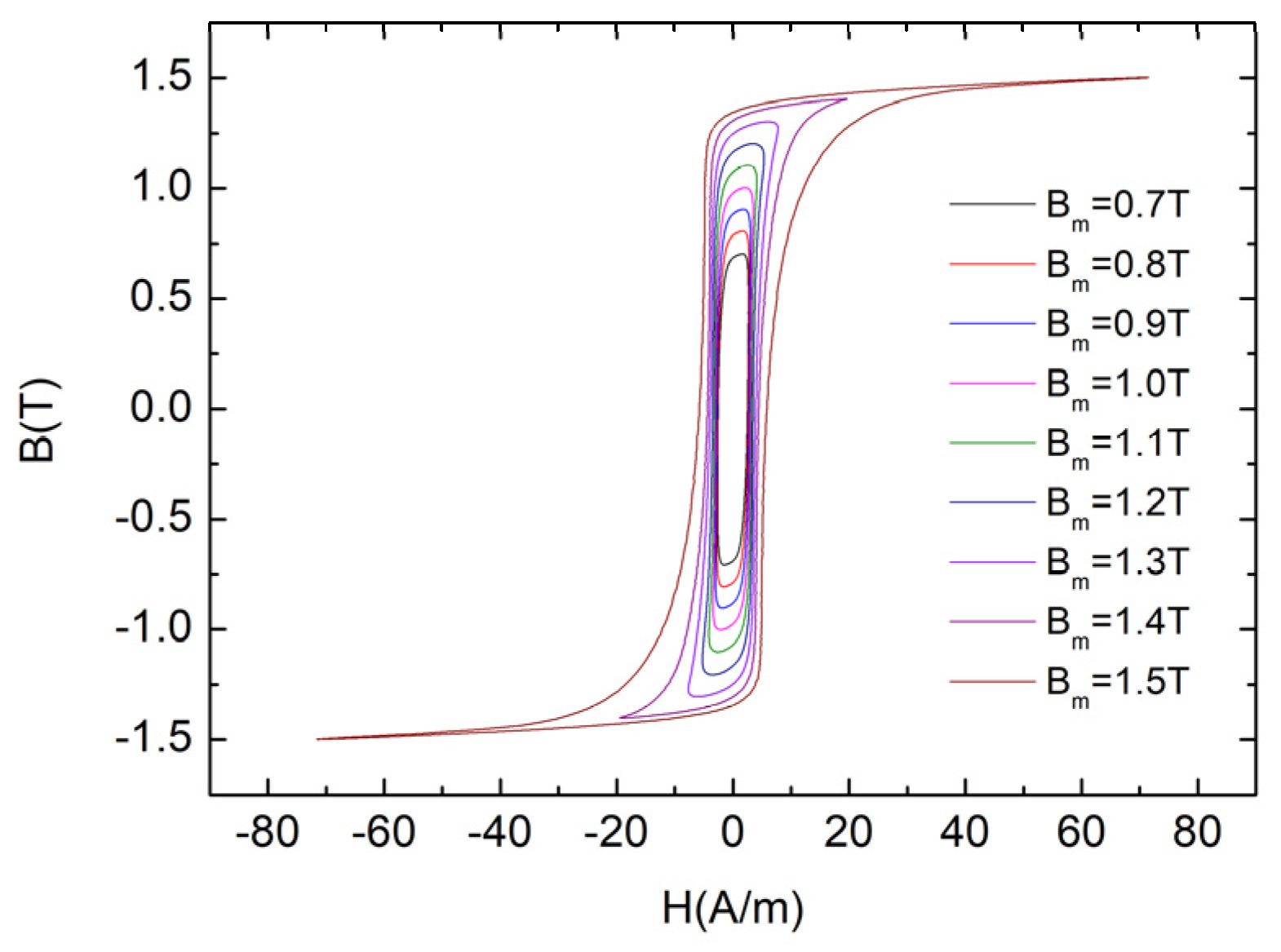
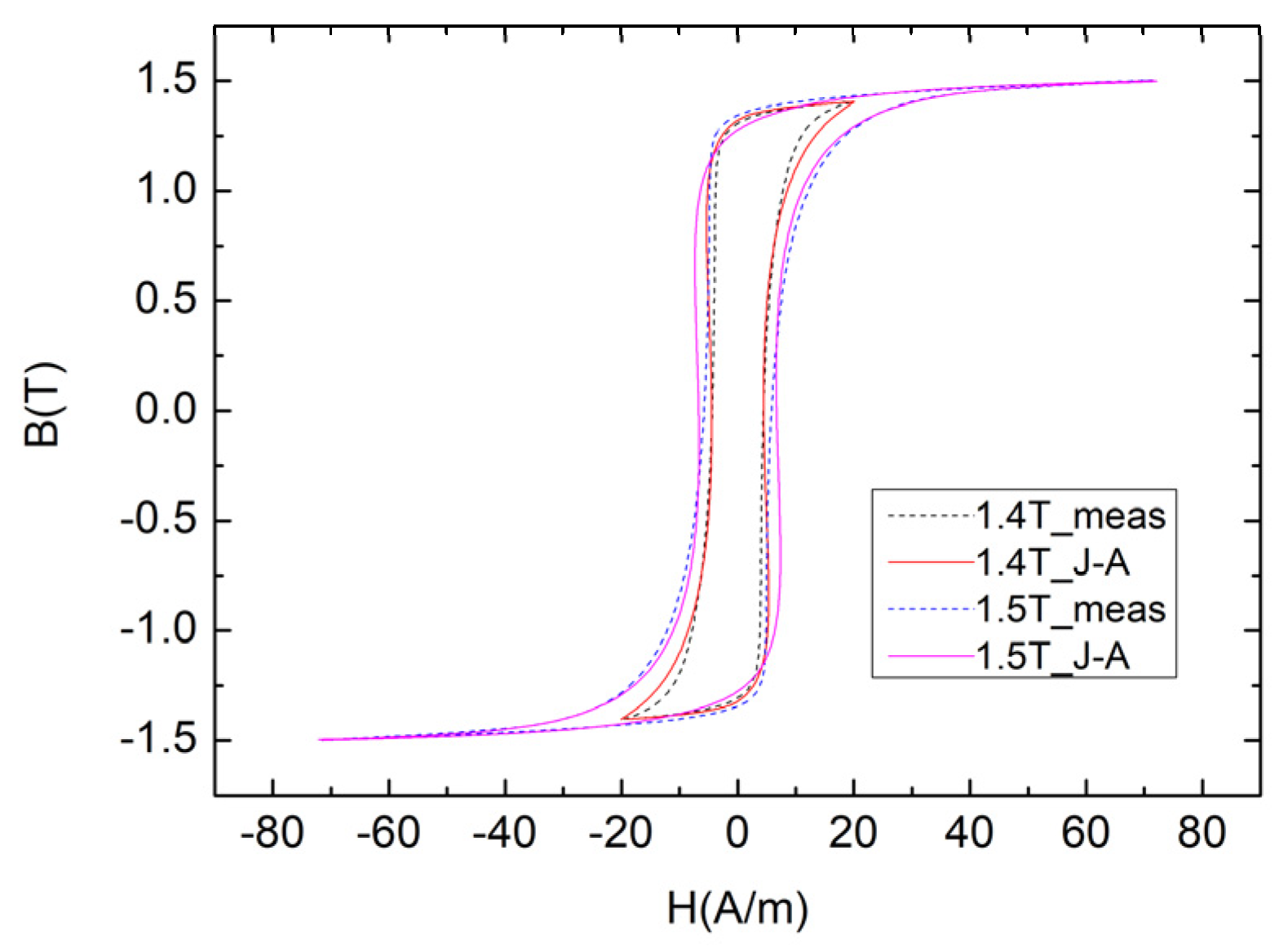
5.1. Testing and Fitting Results of Hysteresis Loop Families
5.2. Calculation Results of Losses
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix A.1. Derivation of Static J–A Model Equation
Appendix A.2. Derivation of Dynamic J–A Model Equation
References
- Liu, R.; Gu, C.; Sun, J.; Shu, F.; Tang, B. Analytical Inverse Preisach Model and Its Comparison with Inverse Jiles-Atherton Model in Terms of Accuracy and Computational Speed. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2023, 59, 7300605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zou, J.; Li, Y.; Zhu, J. Prediction of Core Loss in Transformer Laminated Core under DC Bias Based on Generalized Preisach Model. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2023, 60, 8400405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinmetz, C. On the law of hysteresis (originally published in 1892). Proc. IEEE 1984, 72, 197–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinert, J.; Brockmeyer, A.; De Doncker, R. Calculation of losses in ferro and ferrimagnetic materials based on the modified Steinmetz equation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2001, 37, 1055–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertotti, G. Physical interpretation of eddy current losses in ferromagnetic materials. I. theoretical considerations. J. Appl. Phys. 1985, 57, 2110–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertotti, G. Physical interpretation of eddy current losses in ferromagnetic materials. II. analysis of experimental results. J. Appl. Phys. 1985, 57, 2118–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertotti, G.; Di Schino, G.; Milone, A.F.; Fiorillo, F. On the effect of grain size on magnetic losses of 3% non-oriented SiFe. J. Phys. Colloq. 1985, 46, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorillo, F.; Novikov, A. An improved approach to power losses in magnetic laminations under nonsinusoidal induction waveform. IEEE Trans. Magn 1990, 26, 2904–2910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, H. Die ferromagnetischen konstanten für schwache wechselfelder. Elektr. Nachrichtentechnik 1924, 1, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Preisach, F. Über die magnetische Nachwirkung. Z. Phys. 1935, 94, 277–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayergoyz, I.D. Mathematical Models of Hysteresis and their Applications, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2003; ISBN 9780124808735. [Google Scholar]
- Jiles, D.; Atherton, D. Theory of ferromagnetic hysteresis. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1986, 61, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiles, D.C.; Thoelke, J.B.; Devine, M.K. Numerical Determination of Hysteresis Parameters for the Modeling of Magnetic Properties using the Theory of Ferromagnetic Hysteresis. IEEE Trans. Magn. 1992, 28, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiles, D.C. Frequency dependence of hysteresis curves in conducting magnetic materials. J. Appl. Phys. 1994, 76, 5849–5855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenbaum, S.; Ruderman, M.; Strohla, T.; Bertram, T. Use of Jiles–Atherton and Preisach hysteresis models for inverse feedforward control. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2010, 46, 3984–3989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leite, J.V.; Benabou, A.; Sadowski, N. Accurate minor loops calculation with a modified Jiles-Atherton hysteresis model. COMPEL-Int. J. Comput. Math. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2009, 28, 741–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Yang, X.; Chen, Y.; Zheng, H.; Su, L. Prediction of Magnetic Losses in Giant Magnetostrictive Materials Under Different Sinusoidal Excitation Magnetic Fields. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2022, 58, 7300909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamimid, M.; Mimoune, S.M.; Feliachi, M. Minor hysteresis loops model based on exponential parameters scaling of the modified Jiles–Atherton model. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2012, 407, 2438–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mörée, G.; Leijon, M. Review of hysteresis models for magnetic materials. Energies 2023, 16, 3980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krings, A.; Soulard, J. Overview and Comparison of Iron Loss Models for Electrical Machines. J. Electr. Eng. 2010, 10, 162–169. [Google Scholar]
- Schutte, J.F.; Groenwold, A.A. A Study of Global Optimization Using Particle Swarms. J. Glob. Optim. 2005, 31, 93–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadowski, N.; Batistela, N.; Bastos, J.; Lajoie-Mazenc, M. An inverse Jiles-Atherton model to take into account hysteresis in time-stepping finite-element calculations. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2002, 38, 797–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chwastek, K. Modeling of dynamic hysteresis loops using the Jiles-Atherton approach. Math. Comput. Model. Dyn. Syst. 2009, 15, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z. Study on the Mathematical Model of Hysteresis Loop for Ferromagnetic Materials; Guangxi University: Nanning, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- IEC 60404-6:2018; Methods of Measurement of the Magnetic Properties of Magnetically Soft Metallic and Powder Materials at Frequencies in the Range 20 Hz to 100 kHz by the Use of Ring Specimens. 2018. Available online: https://webstore.iec.ch/publication/27825 (accessed on 13 April 2024).



| Model | 500 Iterations | 1000 Iterations | Computer Configuration |
|---|---|---|---|
| J–A | 212.80 s | 423.44 s | 8 GB |
| Fourier | 13.38 s | 23.80 |
| Density (g/cm3) | Resistivity (μΩ·cm) | Crystallization Temperature (T) | Saturated Magnetic Flux Density (T) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 7.18 | 135 | 528 | 1.56 |
| Bm | μ1 | μ3 | θ1 | θ3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.7 T | 0.24 | −1.61 | 1.29 | 1.15 |
| 0.9 T | 0.39 | −2.21 | −5.05 | 0.88 |
| 1.1 T | 0.43 | −1.84 | −5.04 | −5.35 |
| 1.3 T | 0.21 | −0.64 | 1.04 | −5.08 |
| Bm (T) | Ms (A/m) | a (A/m) | α (A/m) | K (A/m) | c |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.4 | 1.24 × 106 | 1.85 | 9.88 × 10−5 | 3.74 | 0.56 |
| 1.5 | 1.24 × 106 | 3 | 1.33 × 10−5 | 0.18 | 0.78 |
| Bm (T) | Measure (W/kg) | Hybrid Model (W/kg) | Bertotti (W/kg) | Error of Hybrid Model | Error of Bertotti |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.7 | 0.04422 | 0.04429 | 0.04315 | 0.16% | −2.42% |
| 0.9 | 0.06443 | 0.0645 | 0.06309 | 0.11% | −2.08% |
| 1.1 | 0.09428 | 0.0945 | 0.0917 | 0.23% | −2.74% |
| 1.3 | 0.1515 | 0.1520 | 0.1496 | 0.33% | −1.27% |
| 1.4 | 0.2012 | 0.1950 | 0.2082 | −3.11% | 3.50% |
| 1.5 | 0.3141 | 0.3094 | 0.3087 | −1.50% | −1.72% |
| Bm (T) | J–A (W/kg) | Fourier (W/kg) | Error of J–A | Error of Fourier | |
| 0.7 | 0.03994 | 0.04429 | −9.67% | 0.16% | |
| 0.9 | 0.05701 | 0.0645 | −11.5% | 0.11% | |
| 1.1 | 0.08252 | 0.0945 | −12.5% | 0.23% | |
| 1.3 | 0.1264 | 0.1520 | −16.5% | 0.33% | |
| 1.4 | 0.1950 | 0.2075 | −3.11% | 3.13% | |
| 1.5 | 0.3094 | 0.4247 | −1.50% | 35.2% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fu, X.; Yan, S.; Chen, Z.; Xu, X.; Ren, Z. A Practical Hybrid Hysteresis Model for Calculating Iron Core Losses in Soft Magnetic Materials. Energies 2024, 17, 2326. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17102326
Fu X, Yan S, Chen Z, Xu X, Ren Z. A Practical Hybrid Hysteresis Model for Calculating Iron Core Losses in Soft Magnetic Materials. Energies. 2024; 17(10):2326. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17102326
Chicago/Turabian StyleFu, Xiaotong, Shuai Yan, Zhifu Chen, Xiaoyu Xu, and Zhuoxiang Ren. 2024. "A Practical Hybrid Hysteresis Model for Calculating Iron Core Losses in Soft Magnetic Materials" Energies 17, no. 10: 2326. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17102326
APA StyleFu, X., Yan, S., Chen, Z., Xu, X., & Ren, Z. (2024). A Practical Hybrid Hysteresis Model for Calculating Iron Core Losses in Soft Magnetic Materials. Energies, 17(10), 2326. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17102326






