A Grid-Wide Comprehensive Evaluation Method of Power Quality Based on Complex Network Theory
Abstract
1. Introduction
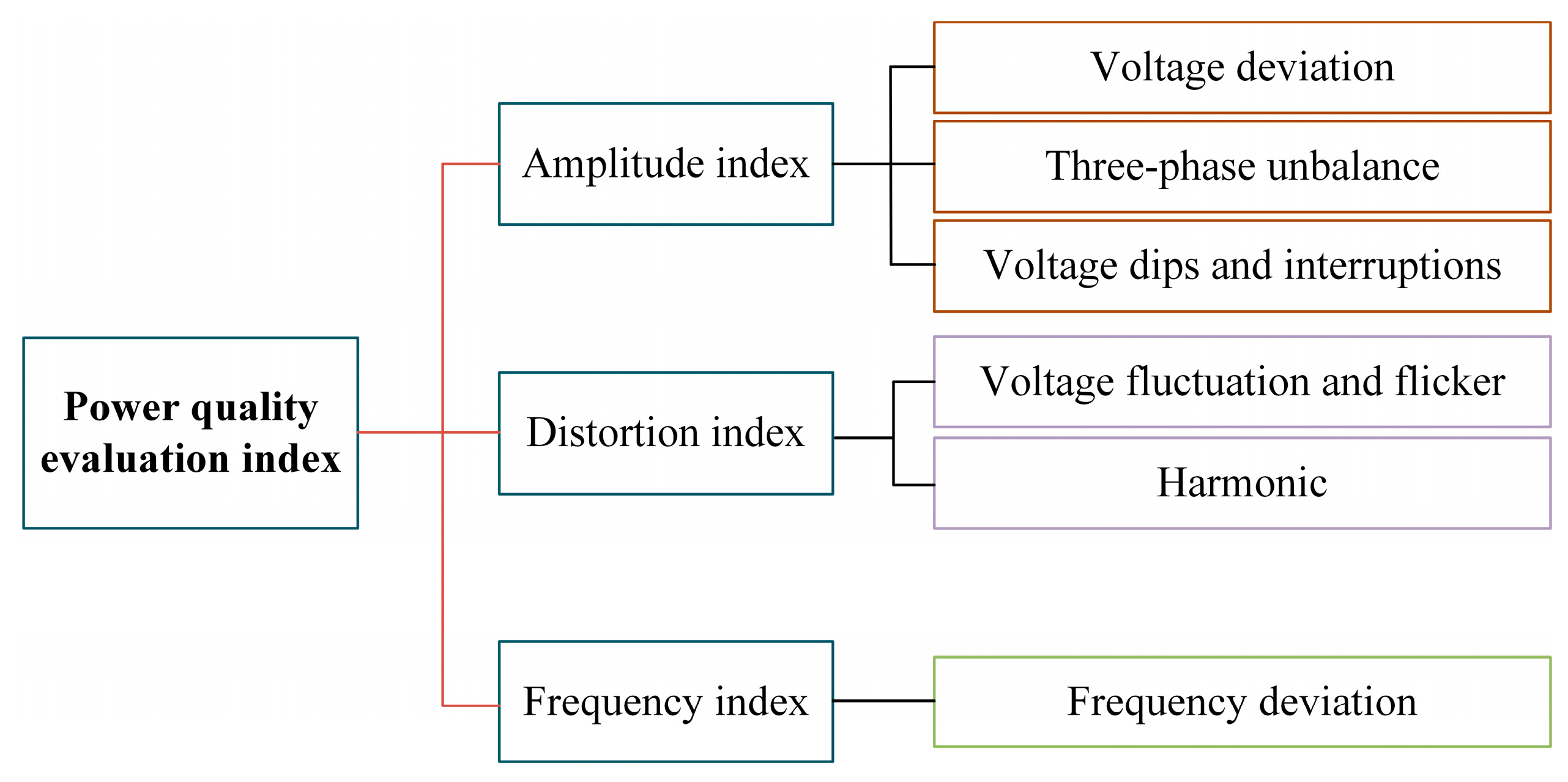
2. Analysis and Construction of the Power Quality Evaluation Index System
2.1. Power Quality Characteristic Analysis
2.2. Comprehensive Evaluation Index
3. Node Power Quality Influence Degree Based on Complex Network Theory
3.1. Improved Node Degree Index D1
3.2. Node Short-Circuit Ratio D2
3.3. Improved Node Electrical Betweenness Index D3
3.4. The Node Self-Healing Index D4
4. Comprehensive Power Quality Assessment Considering the Node Power Quality Impact at a Grid-Wide Level
4.1. Determining the Weighting of Power Quality Indicators
4.1.1. The GRA-ANP Method Determines Subjective Weights
- 1.
- Analyze and construct the ANP network structure
- 2.
- Construct the supermatrix and calculate the individual ANP weights
- 3.
- Improve the ANP weights using GRA
- (1)
- Determine the reference sequence and comparison sequenceAssuming that there are k power quality indicators and h decision-makers in each node, aly represents the ANP weight value of the l indicator given by the y decision-maker, and al0 = max(aly) is taken as the reference sequence X0 = {a10, a20, …, ak0}, then the comparison sequence is Xk = {ak1, ak2, …, akh}.
- (2)
- Obtain the sequence difference
- (3)
- Obtain the correlation coefficientwhere P is the resolution coefficient, P ∈ (0,1), usually set to 0.5.
- (4)
- Obtain the correlation degree qi [27]
- (5)
- Determine the subjective weight w1 of each power quality index of node i
4.1.2. Entropy Weight Method to Determine Objective Weights
- 1.
- Collect power quality monitoring data from the distribution network:
- 2.
- Standardize the collected data:
- 3.
- Solve the information entropy ej and information effective value dj:
- 4.
- Determine the objective weight w1 of each power quality index of node i:
4.1.3. Comprehensive Weights Based on Equalization Algorithm
- 1.
- Construct comprehensive weight w. Any comprehensive weight can be represented linearly by the subjective weight w1 and the objective weight w2:
- 2.
- Solve for the combination coefficients. To ensure that both weights are in a balanced state, use the principle of deviation minimization. Determine the optimization objective function and constraints based on the properties of matrix differentiation:
4.2. A Comprehensive Power Quality Evaluation Model for Nodes Based on the VIKOR Method
- (1)
- Sample data processing and establishment of an index standardization matrix.
- (2)
- Find the positive ideal solution A+ and the negative ideal solution A− of each index:
- (3)
- Determine the group benefit S and individual regret R of the evaluated objects:
- (4)
- Determine the benefit ratio Qj of the evaluated object j:
- (5)
- Rank the decisions based on the benefit ratio. According to the principle “the higher the benefit ratio Qj, the better the solution; conversely, the lower the ratio, the worse the solution”, this provides strong support for subsequent decision making and planning.
4.3. A Comprehensive Grid-Wide Power Quality Assessment Model
- (1)
- Establish a power quality assessment index system for the distribution system.
- (2)
- Consider the interdependence and coupling among various indicators, and use the GRA-ANP method to determine the subjective weights of each indicator. To reflect the disturbance of power quality under actual engineering operation, utilize the entropy weighting method to determine the objective weights of each indicator based on monitoring data.
- (3)
- To fully integrate the advantages of subjective and objective weights while avoiding the shortcomings of single-weight evaluation results, use game equilibrium algorithms to determine the comprehensive weights of each indicator.
- (4)
- To avoid errors in the evaluation results caused by large differences between positive and negative ideal solutions, use the VIKOR method to classify and evaluate the power quality of each node.
- (5)
- Based on complex network theory, construct node power quality impact indicators. The comprehensive power quality impact of node i is represented by Equation (23).
- (6)
- Integrating the classification assessment results of each node and the comprehensive electrical quality impact index of nodes, conduct a holistic electrical quality comprehensive assessment of the distribution system using Equation (24).
5. Case Study Verification
6. Conclusions
- This paper analyzes the mechanism characteristics of power quality disturbances in modern distribution networks and establishes a scientific power quality assessment system. To reflect the impact of power quality disturbances at each node on the overall power quality level of the distribution network, the power quality influence of nodes is determined based on improved node degree, short-circuit ratio, improved electrical betweenness, and node self-healing capability, laying the foundation for subsequent power quality assessments.
- By combining the GRA and ANP methods, the paper avoids the differences brought by different decision-makers, ensuring the rationality of subjective weights. The entropy weight method is used to determine objective weights, and a balanced algorithm is adopted to obtain comprehensive weights, eliminating the errors brought by a single weight and further improving the accuracy of the weight coefficients.
- Considering the correlation between various indicators and the impact of data integration, the VIKOR method is used to evaluate the power quality of each node. Based on the node power quality influence, the power quality level of the distribution network is determined, achieving a comprehensive and quantitative grid-wide power quality assessment. This assessment reflects the overall power quality level of the distribution network and provides a reference direction for subsequent optimization and management of power quality.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Branch | B01 | B02 | B03 | B04 | B05 | B06 | B07 | B08 | B09 | B10 | B11 | B12 | B13 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R/Ω | 0.092 | 0.493 | 0.366 | 0.381 | 0.819 | 0.187 | 0.711 | 1.030 | 1.044 | 0.197 | 0.374 | 1.468 | 0.542 |
| X/H | 0.047 | 0.251 | 0.186 | 0.194 | 0.707 | 0.619 | 0.235 | 0.740 | 0.740 | 0.065 | 0.124 | 1.155 | 0.713 |
| Branch | B14 | B15 | B16 | B17 | B18 | B19 | B20 | B21 | B22 | B23 | B24 | B25 | B26 |
| R/Ω | 5.910 | 7.463 | 3.289 | 7.320 | 0.164 | 1.504 | 0.410 | 0.709 | 4.512 | 0.898 | 0.896 | 0.203 | 0.284 |
| X/H | 5.260 | 5.450 | 4.721 | 5.740 | 0.157 | 1.355 | 0.478 | 0.937 | 3.083 | 0.709 | 0.701 | 0.103 | 0.145 |
| Branch | B27 | B28 | B29 | B30 | B31 | B32 | B33 | B34 | B35 | B36 | B37 | ||
| R/Ω | 1.059 | 0.804 | 0.508 | 0.974 | 0.311 | 0.341 | 2.000 | 2.000 | 2.000 | 0.500 | 0.500 | ||
| X/H | 0.934 | 0.701 | 0.259 | 0.963 | 0.362 | 0.530 | 2.000 | 2.000 | 2.000 | 0.500 | 0.500 |
| Node | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P/kW | 0 | 100 | 90 | 120 | 60 | 60 | 200 | 200 | 60 | 60 | 45 | 60 | 60 |
| Q/kW | 0 | 60 | 40 | 80 | 30 | 20 | 100 | 100 | 20 | 20 | 30 | 35 | 35 |
| Node | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 |
| P/kW | 120 | 60 | 60 | 60 | 90 | 90 | 90 | 90 | 90 | 90 | 420 | 420 | 60 |
| Q/kW | 80 | 10 | 20 | 20 | 40 | 40 | 40 | 40 | 40 | 50 | 200 | 200 | 25 |
| Node | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 | 32 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | ||
| P/kW | 60 | 60 | 120 | 200 | 150 | 210 | 60 | 60 | 60 | 120 | 200 | ||
| Q/kW | 25 | 20 | 10 | 600 | 70 | 100 | 40 | 25 | 20 | 10 | 600 |
| Node | 8 | 13 | 16 | 21 | 24 | 28 | 29 | 32 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type | ESS | V2G | PV | PV | PV | ESS | PV | V2G |
| Capacity/kW | 500 | 400 | 150 | 300 | 200 | 500 | 300 | 200 |
| Index | Voltage Deviation/% | Harmonic Wave/% | Three-Phase Unbalance/% | Voltage Fluctuation and Flicker/% | Voltage Dips and Interruptions/% | Frequency Deviation/% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Node | |||||||
| 0 | 0.514 | 2.070 | 1.273 | 0.815 | 0.156 | 0.131 | |
| 1 | 3.043 | 3.492 | 1.182 | 1.768 | 0.783 | 0.117 | |
| 2 | 5.802 | 2.146 | 0.723 | 1.096 | 2.287 | 0.124 | |
| 3 | 5.310 | 1.672 | 2.524 | 0.738 | 3.091 | 0.209 | |
| 4 | 2.012 | 2.983 | 1.572 | 0.417 | 3.661 | 0.130 | |
| 5 | 5.406 | 3.510 | 1.891 | 0.882 | 2.175 | 0.333 | |
| 6 | 2.320 | 4.510 | 1.467 | 1.912 | 1.477 | 0.324 | |
| 7 | 5.427 | 1.887 | 0.661 | 0.248 | 2.913 | 0.223 | |
| 8 | 2.568 | 3.675 | 0.679 | 0.942 | 0.914 | 0.105 | |
| 9 | 0.167 | 4.771 | 1.610 | 1.714 | 2.275 | 0.272 | |
| 10 | 4.009 | 2.714 | 1.286 | 0.087 | 1.174 | 0.093 | |
| 11 | 1.425 | 2.701 | 1.043 | 1.383 | 4.427 | 0.183 | |
| 12 | 4.785 | 1.556 | 1.384 | 1.958 | 2.039 | 0.154 | |
| 13 | 7.124 | 3.356 | 1.918 | 0.567 | 4.182 | 0.215 | |
| 14 | 3.691 | 0.910 | 2.752 | 0.268 | 3.731 | 0.397 | |
| 15 | 6.618 | 0.465 | 0.485 | 1.371 | 0.774 | 0.302 | |
| 16 | 1.696 | 4.317 | 2.147 | 1.819 | 3.720 | 0.392 | |
| 17 | 2.788 | 0.047 | 1.733 | 1.222 | 3.030 | 0.094 | |
| 18 | 1.982 | 4.575 | 1.300 | 1.800 | 1.272 | 0.211 | |
| 19 | 1.951 | 3.214 | 2.653 | 0.387 | 1.621 | 0.021 | |
| 20 | 4.268 | 4.007 | 1.179 | 1.509 | 2.009 | 0.303 | |
| 21 | 5.803 | 4.152 | 0.537 | 0.693 | 2.032 | 0.241 | |
| 22 | 4.711 | 1.042 | 1.900 | 0.837 | 1.931 | 0.343 | |
| 23 | 5.040 | 4.275 | 1.872 | 0.311 | 3.049 | 0.395 | |
| 24 | 2.792 | 5.636 | 0.984 | 1.638 | 5.834 | 0.372 | |
| 25 | 3.689 | 1.043 | 2.409 | 1.250 | 0.940 | 0.164 | |
| 26 | 4.075 | 3.635 | 2.998 | 1.477 | 0.473 | 0.000 | |
| 27 | 2.445 | 1.771 | 2.943 | 1.610 | 1.616 | 0.216 | |
| 28 | 3.153 | 2.902 | 0.381 | 0.134 | 3.848 | 0.083 | |
| 29 | 2.766 | 4.183 | 0.697 | 1.902 | 1.171 | 0.088 | |
| 30 | 3.772 | 2.183 | 0.071 | 0.995 | 3.702 | 0.130 | |
| 31 | 5.849 | 4.246 | 1.822 | 1.510 | 3.464 | 0.038 | |
| 32 | 6.650 | 0.248 | 0.332 | 1.485 | 4.120 | 0.299 | |
| Index | Voltage Deviation | Harmonic Wave | Three-Phase Unbalance | Voltage Fluctuation and Flicker | Voltage Dips and Interruptions | Frequency Deviation | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Node | |||||||
| 0 | 0.228 | 0.248 | 0.111 | 0.092 | 0.141 | 0.189 | |
| 1 | 0.196 | 0.174 | 0.153 | 0.164 | 0.126 | 0.184 | |
| 2 | 0.276 | 0.123 | 0.133 | 0.123 | 0.146 | 0.198 | |
| 3 | 0.281 | 0.130 | 0.126 | 0.119 | 0.163 | 0.174 | |
| 4 | 0.209 | 0.157 | 0.154 | 0.140 | 0.152 | 0.184 | |
| 5 | 0.142 | 0.179 | 0.159 | 0.170 | 0.122 | 0.226 | |
| 6 | 0.149 | 0.159 | 0.167 | 0.161 | 0.191 | 0.169 | |
| 7 | 0.158 | 0.141 | 0.163 | 0.189 | 0.195 | 0.154 | |
| 8 | 0.186 | 0.151 | 0.124 | 0.162 | 0.241 | 0.136 | |
| 9 | 0.165 | 0.130 | 0.118 | 0.185 | 0.279 | 0.120 | |
| 10 | 0.149 | 0.189 | 0.158 | 0.150 | 0.182 | 0.171 | |
| 11 | 0.153 | 0.147 | 0.127 | 0.207 | 0.216 | 0.149 | |
| 12 | 0.166 | 0.142 | 0.163 | 0.169 | 0.183 | 0.182 | |
| 13 | 0.153 | 0.162 | 0.128 | 0.204 | 0.173 | 0.180 | |
| 14 | 0.140 | 0.178 | 0.146 | 0.188 | 0.178 | 0.166 | |
| 15 | 0.117 | 0.236 | 0.133 | 0.224 | 0.137 | 0.150 | |
| 16 | 0.100 | 0.299 | 0.121 | 0.224 | 0.115 | 0.132 | |
| 17 | 0.123 | 0.241 | 0.135 | 0.163 | 0.128 | 0.200 | |
| 18 | 0.125 | 0.279 | 0.137 | 0.150 | 0.123 | 0.195 | |
| 19 | 0.160 | 0.149 | 0.136 | 0.184 | 0.134 | 0.234 | |
| 20 | 0.138 | 0.174 | 0.166 | 0.182 | 0.152 | 0.190 | |
| 21 | 0.147 | 0.161 | 0.153 | 0.190 | 0.122 | 0.223 | |
| 22 | 0.112 | 0.129 | 0.195 | 0.249 | 0.102 | 0.211 | |
| 23 | 0.098 | 0.122 | 0.215 | 0.282 | 0.112 | 0.172 | |
| 24 | 0.143 | 0.139 | 0.225 | 0.228 | 0.133 | 0.133 | |
| 25 | 0.131 | 0.176 | 0.198 | 0.154 | 0.185 | 0.161 | |
| 26 | 0.163 | 0.202 | 0.129 | 0.157 | 0.136 | 0.202 | |
| 27 | 0.136 | 0.198 | 0.104 | 0.198 | 0.195 | 0.169 | |
| 28 | 0.133 | 0.157 | 0.134 | 0.207 | 0.190 | 0.180 | |
| 29 | 0.159 | 0.164 | 0.115 | 0.172 | 0.222 | 0.174 | |
| 30 | 0.153 | 0.162 | 0.108 | 0.197 | 0.245 | 0.138 | |
| 31 | 0.158 | 0.172 | 0.118 | 0.192 | 0.220 | 0.140 | |
| 32 | 0.148 | 0.145 | 0.109 | 0.216 | 0.206 | 0.168 | |
| Index | D1 | D2 | D3 | D4 | D | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Node | ||||||
| 0 | 0.058 | 0.048 | 0.035 | 0.035 | 0.044 | |
| 1 | 0.064 | 0.033 | 0.026 | 0.030 | 0.038 | |
| 2 | 0.042 | 0.038 | 0.031 | 0.030 | 0.035 | |
| 3 | 0.029 | 0.036 | 0.027 | 0.021 | 0.028 | |
| 4 | 0.022 | 0.030 | 0.008 | 0.034 | 0.023 | |
| 5 | 0.025 | 0.029 | 0.030 | 0.017 | 0.025 | |
| 6 | 0.033 | 0.007 | 0.013 | 0.045 | 0.024 | |
| 7 | 0.052 | 0.018 | 0.032 | 0.021 | 0.031 | |
| 8 | 0.049 | 0.034 | 0.030 | 0.010 | 0.021 | |
| 9 | 0.038 | 0.023 | 0.026 | 0.030 | 0.029 | |
| 10 | 0.045 | 0.032 | 0.029 | 0.037 | 0.036 | |
| 11 | 0.014 | 0.040 | 0.050 | 0.035 | 0.035 | |
| 12 | 0.011 | 0.030 | 0.027 | 0.029 | 0.024 | |
| 13 | 0.008 | 0.015 | 0.037 | 0.057 | 0.029 | |
| 14 | 0.037 | 0.040 | 0.042 | 0.031 | 0.038 | |
| 15 | 0.002 | 0.030 | 0.020 | 0.037 | 0.022 | |
| 16 | 0.051 | 0.044 | 0.018 | 0.033 | 0.037 | |
| 17 | 0.016 | 0.022 | 0.029 | 0.036 | 0.016 | |
| 18 | 0.018 | 0.031 | 0.028 | 0.029 | 0.027 | |
| 19 | 0.037 | 0.042 | 0.043 | 0.029 | 0.038 | |
| 20 | 0.062 | 0.031 | 0.043 | 0.031 | 0.042 | |
| 21 | 0.009 | 0.041 | 0.033 | 0.022 | 0.016 | |
| 22 | 0.015 | 0.042 | 0.025 | 0.023 | 0.026 | |
| 23 | 0.046 | 0.008 | 0.040 | 0.020 | 0.028 | |
| 24 | 0.013 | 0.003 | 0.042 | 0.042 | 0.015 | |
| 25 | 0.034 | 0.040 | 0.037 | 0.037 | 0.037 | |
| 26 | 0.014 | 0.061 | 0.017 | 0.036 | 0.032 | |
| 27 | 0.054 | 0.056 | 0.018 | 0.011 | 0.026 | |
| 28 | 0.022 | 0.021 | 0.055 | 0.006 | 0.015 | |
| 29 | 0.025 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.047 | 0.019 | |
| 30 | 0.032 | 0.030 | 0.041 | 0.029 | 0.033 | |
| 31 | 0.017 | 0.009 | 0.032 | 0.029 | 0.022 | |
| 32 | 0.006 | 0.034 | 0.035 | 0.044 | 0.013 | |
References
- Li, B.; Chen, M.; Zhong, H.; Ma, Z.; Liu, D.; He, G. A Review of Long-term Planning of New Power Systems with Large Share of Renewable Energy. Proc. CSEE 2023, 43, 555–581. [Google Scholar]
- Denholm, P.; Arent, D.J.; Baldwin, S.F.; Bilello, D.E.; Brinkman, G.L.; Cochran, J.M.; Cole, W.J.; Frew, B.; Gevorgian, V.; Heeter, J.; et al. The challenges of achieving a 100% renewable electricity system in the United States. Joule 2021, 5, 1331–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gielen, D.; Boshell, F.; Saygin, D.; Bazilian, M.D.; Wagner, N.; Gorini, R. The role of renewable energy in the global energy transformation. Energy Strategy Rev. 2019, 24, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, M.; Goyal, S.K.; Saraswat, A.; Shekhawat, R.S.; Gangil, G. A Review on Power Quality Problems, Causes and Mitigation Techniques. In Proceedings of the Sustainable Technology for Power and Energy Systems (STPES), Srinagar, India, 4–6 July 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ding, R.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zha, X.; Cheng, X. Reactive voltage partitioning method for the power grid with comprehensive consideration of wind power fluctuation and uncertainty. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 124514–124525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, G.; Hu, R. Survey on the Power Quality Question Resultant from Connection of Distributed Power Generation to the Grid. Power Syst. Clean Energy 2015, 31, 38–46. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Guo, X.; Li, J.; Wang, X. Impact of Voltage Sags on Electric-Vehicle Charger and Critical Voltage Sag Determination. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2016, 31, 1397–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Ren, Z.; Li, Q.; Guo, Y.; Xu, Y. An Accommodation Strategy for Renewable Energy in Distribution Network Considering Coordinated Dispatching of Multi-Flexible Resources. Trans. China Electrotech. Soc. 2022, 37, 1820–1835. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Feng, D.; Lin, C.; Zhang, Y. Current status and development trend of power quality comprehensive assessment. Power Syst. Prot. Control. 2020, 48, 167–176. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, R.; Wang, R.; Liu, Q.; Yang, L.; Xi, C.; Wang, W.; Li, L.; Zhao, Z.; Zhou, Y. Review of Comprehensive Evaluation Methods for Power Quality and Its Trend in New Generation Energy System. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Advances in Energy Resources and Environment Engineering, Harbin, China, 8–10 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.; Zhang, J.; Liu, W.; Qiu, W.; Wu, X.; Jiang, C. Regional Power Grid Quality Evaluation Method Considering Index Characteristics. Proc. CSU-EPSA 2022, 34, 150–158. [Google Scholar]
- Elbasuony, G.S.; Aleem, S.H.A.; Ibrahim, A.M.; Sharaf, A.M. A unified index for power quality evaluation in distributed generation systems. Energy 2018, 149, 607–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.C.Y.; Lo, H.W.; Liou, J.J.H. A combination of DEMA-TEL and BWM-based ANP methods for exploring the system in Taiwan. Sustain. Green Build. Rat. 2020, 12, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, C.; Zhang, Y.; Shao, Z.; Liu, Y. Comprehensive Evaluation of Power Quality on Long-time Scale Based on Fuzzy DEA. High Volt. Eng. 2021, 47, 1751–1761. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Z.-Y.; Liu, D.; Wu, J.; Chen, L. Comprehensive Evaluation of Power Quality Based on Set Pair Analysis and Variable Fuzzy Sets. Power Syst. Technol. 2020, 44, 1950–1956. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, X.; Chen, H.; Liu, G.; Jin, X.M. Power Quality Comprehensive Evaluation Method for Distributed Generation. Proc. CSEE 2014, 34, 4270–4276. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J. Research on evaluation method of power quality based on cooperative game theory and improved TOPSIS. Power Syst. Prot. Control. 2018, 46, 109–115. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, Z.; Wu, M.; Song, Z.; Zhao, T.; Du, G. Comprehensive evaluation of power quality on CRITIC-TOPSIS method. Electr. Mach. Control. 2020, 24, 137–144. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, X.; Li, X.; Yan, S.; Wang, S.; Xu, S. Power Quality Assessment of SESN Power Supply Network Based on Deep Learning. Control. Eng. China 2021, 28, 2052–2059. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, N. An Analysis of the Influence of Grid-Connected Renewable Energy on Power Quality of Power Grids. Power Syst. Clean Energy 2022, 38, 108–114. [Google Scholar]
- Barros, J.; de Apraiz, M.; Diego, R.I. Power quality in DC distribution networks. Energies 2019, 12, 848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Huang, L.; Zhang, S.; Chen, H.; Tang, C. Effects of distributed photovoltaic generation and electric vehicle integrating into distribution network on line loss and voltage drift. Smart Power 2020, 48, 28–34. [Google Scholar]
- Chishti, F.; Murshid, S.; Singh, B. LMMN-based adaptive control for power quality improvement of grid intertie wind-PV system. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2019, 15, 4900–4912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Miao, S.; Guo, S.; Han, J.; Yin, H. Node vulnerability evaluation of distribution network considering randomness characteristic of distributed generation output. Electr. Power Autom. Equip. 2021, 41, 33–40. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.; Li, H.; Zhao, X.; Huang, Z. Assessment on Nodal Comprehensive Vulnerability Based on Operational State and Network Structure. Power Syst. Technol. 2014, 38, 731–735. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, Q.; Yang, H.; Yang, X.; Li, H. Comprehensive Evaluation on Power Quality Considering the Relevance of Indexes. Proc. CSU-EPSA 2016, 28, 73–78. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Q.; Chen, X.; Li, X.; Zhou, C.; Li, Z. Using Grey Target Theory for Power Quality Evaluation Based on Power Quality Monitoring Data. Energy Eng. J. Assoc. Energy Eng. 2022, 119, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, W.; Ge, Y.; Chen, B.; Ding, J.; Luo, X.; Lin, Z.; Qiu, W.; Lin, Z. Gaussian cloud and TOPSIS based power supply quality evaluation method. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Liu, Y.; Huang, T.; Wu, Z.; Liu, Y. Power Quality Evaluation Based on Extension Cloud Model and Fuzzy Proximity Degree. Smart Power 2022, 50, 23–29+52. [Google Scholar]




| Index | Voltage Deviation | Harmonic | Three-Phase Unbalance | Voltage Fluctuations and Flickers | Voltage Dip | Frequency Deviation | Weight Combination Coefficient |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Subjective weight | 0.191 | 0.159 | 0.168 | 0.170 | 0.122 | 0.190 | 0.717 |
| Objective weight | 0.215 | 0.213 | 0.110 | 0.153 | 0.135 | 0.174 | 0.283 |
| Comprehensive weight | 0.196 | 0.174 | 0.153 | 0.164 | 0.126 | 0.184 | / |
| Node | 16 | 15 | 5 | 12 | 22 | 18 | 20 | 27 | 13 | 23 | 28 | 25 | 14 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qj | 0.011 | 0.051 | 0.077 | 0.131 | 0.138 | 0.165 | 0.166 | 0.220 | 0.229 | 0.239 | 0.259 | 0.282 | 0.298 |
| Node | 17 | 19 | 31 | 11 | 6 | 29 | 24 | 9 | 32 | 26 | 30 | 7 | 10 |
| Qj | 0.313 | 0.318 | 0.348 | 0.353 | 0.365 | 0.390 | 0.391 | 0.410 | 0.413 | 0.482 | 0.487 | 0.494 | 0.506 |
| Node | 21 | 1 | 8 | 4 | 3 | 0 | 2 | ||||||
| Qj | 0.528 | 0.634 | 0.660 | 0.690 | 0.811 | 0.906 | 0.989 |
| Level | Qj Indicates the Value Range | Node |
|---|---|---|
| I | ≥0.780 | 3, 0, 2 |
| II | ≥0.476 | 26, 30, 7, 10, 21, 1, 8, 4 |
| III | ≥0.347 | 31, 11, 6, 29, 24, 9, 32 |
| IV | ≥0.153 | 18, 20, 27, 13, 23, 28, 25, 14, 17, 19 |
| V | ≥0 | 16, 15, 5, 12, 22 |
| Node | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Power quality level | Proposed method | I | II | I | I | II | V | IV | II | II | III | II | III | V | IV | IV | V | V |
| TOPSIS method | I | II | I | I | II | V | III | II | II | III | II | III | V | III | IV | V | IV | |
| Extension Cloud Theory | I | II | I | I | II | V | IV | II | II | III | II | III | IV | IV | IV | V | IV | |
| Node | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 | 32 | ||
| Power quality level | Proposed method | IV | IV | IV | IV | V | II | IV | III | IV | II | IV | III | III | II | III | III | |
| TOPSIS method | IV | IV | IV | IV | IV | II | IV | IV | IV | II | IV | III | III | II | III | III | ||
| Extension Cloud Theory | IV | IV | IV | IV | V | II | IV | III | IV | II | IV | III | IV | III | III | IV | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiang, Y.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Lan, J.; Hao, M.; Wang, L.; Wang, J.; Qin, L. A Grid-Wide Comprehensive Evaluation Method of Power Quality Based on Complex Network Theory. Energies 2024, 17, 3193. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17133193
Xiang Y, Lin Y, Zhang Y, Lan J, Hao M, Wang L, Wang J, Qin L. A Grid-Wide Comprehensive Evaluation Method of Power Quality Based on Complex Network Theory. Energies. 2024; 17(13):3193. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17133193
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiang, Yang, Yan Lin, Yan Zhang, Jinchen Lan, Meimei Hao, Lianhui Wang, Jiang Wang, and Liang Qin. 2024. "A Grid-Wide Comprehensive Evaluation Method of Power Quality Based on Complex Network Theory" Energies 17, no. 13: 3193. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17133193
APA StyleXiang, Y., Lin, Y., Zhang, Y., Lan, J., Hao, M., Wang, L., Wang, J., & Qin, L. (2024). A Grid-Wide Comprehensive Evaluation Method of Power Quality Based on Complex Network Theory. Energies, 17(13), 3193. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17133193






