Hydrogen Refueling Stations: A Review of the Technology Involved from Key Energy Consumption Processes to Related Energy Management Strategies
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Hydrogen as an Alternative Fuel
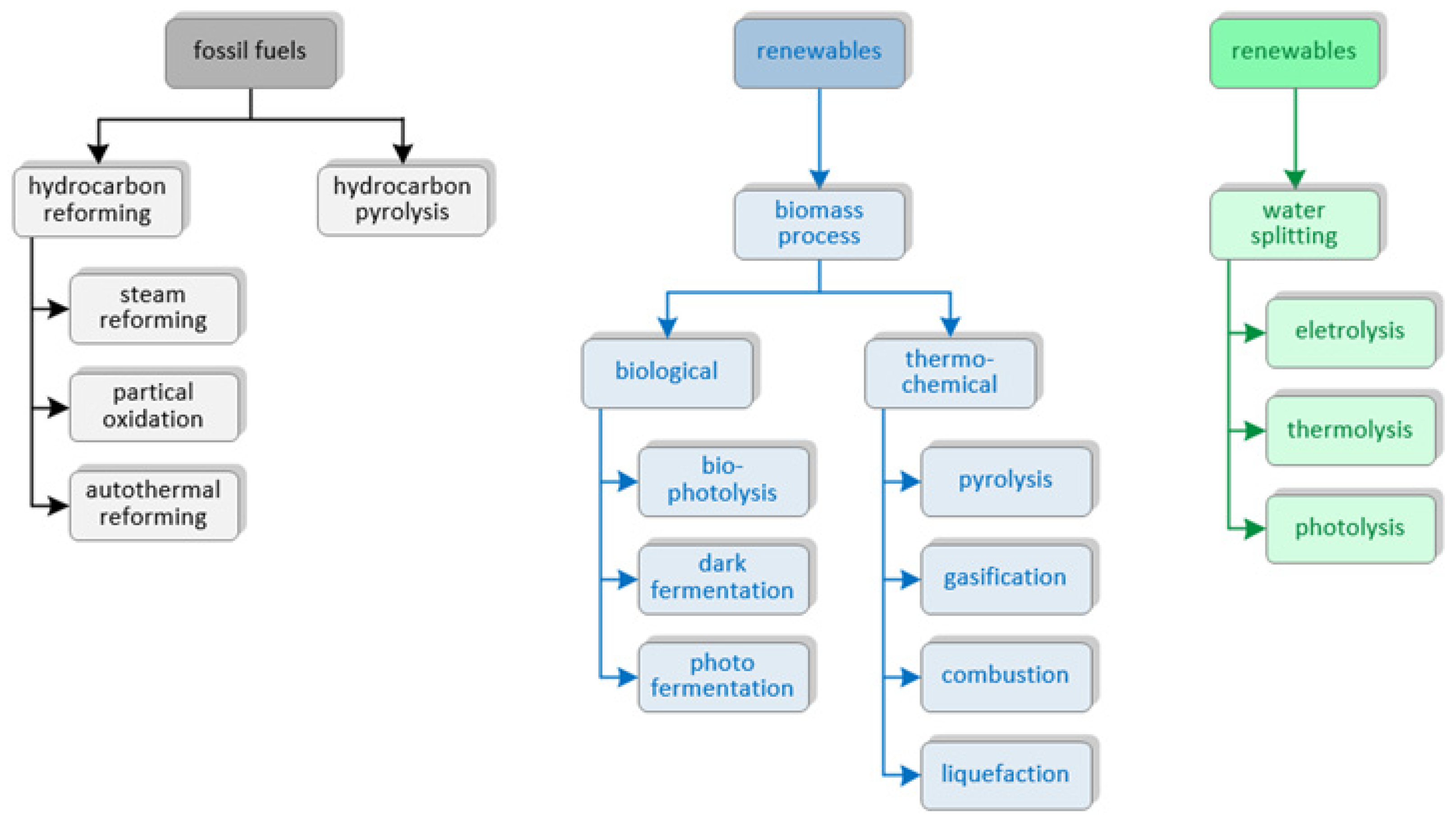
3. Hydrogen Production in a Hydrogen Refueling Station
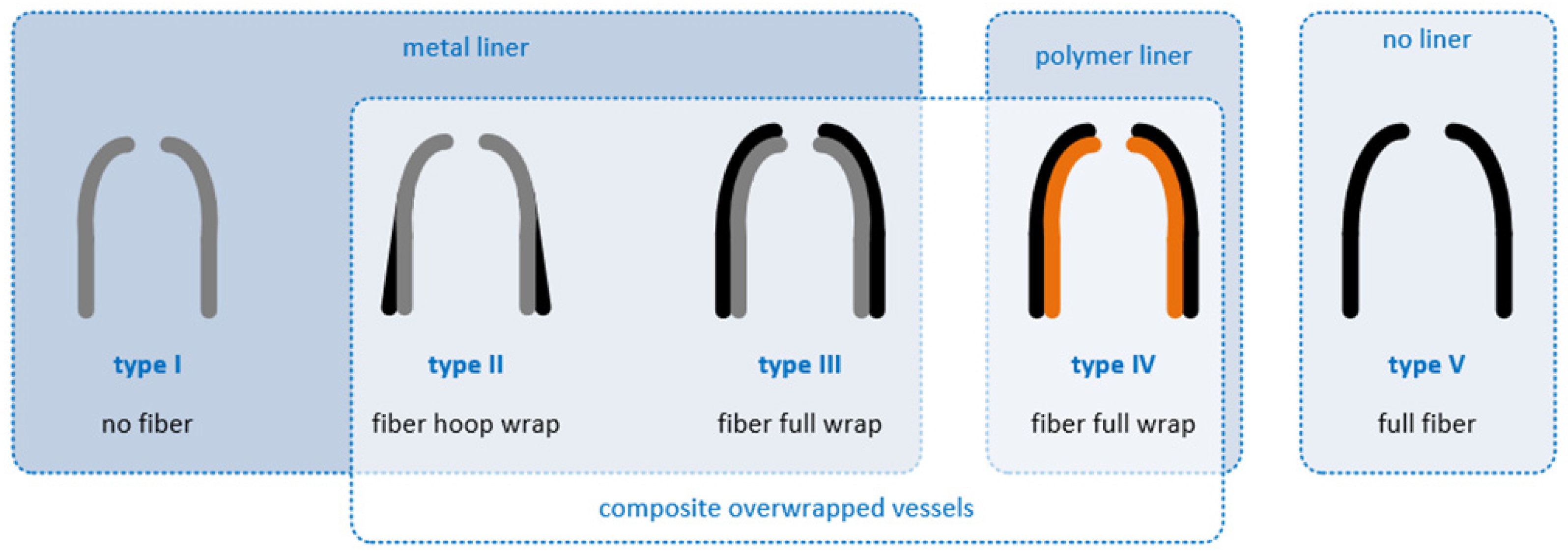
4. Types of Hydrogen Storage in Hydrogen Refueling Stations
5. Compression in Hydrogen Refueling Stations
5.1. Types of Compressors
5.2. Compression and Storage Systems
6. Refueling Process Specifications
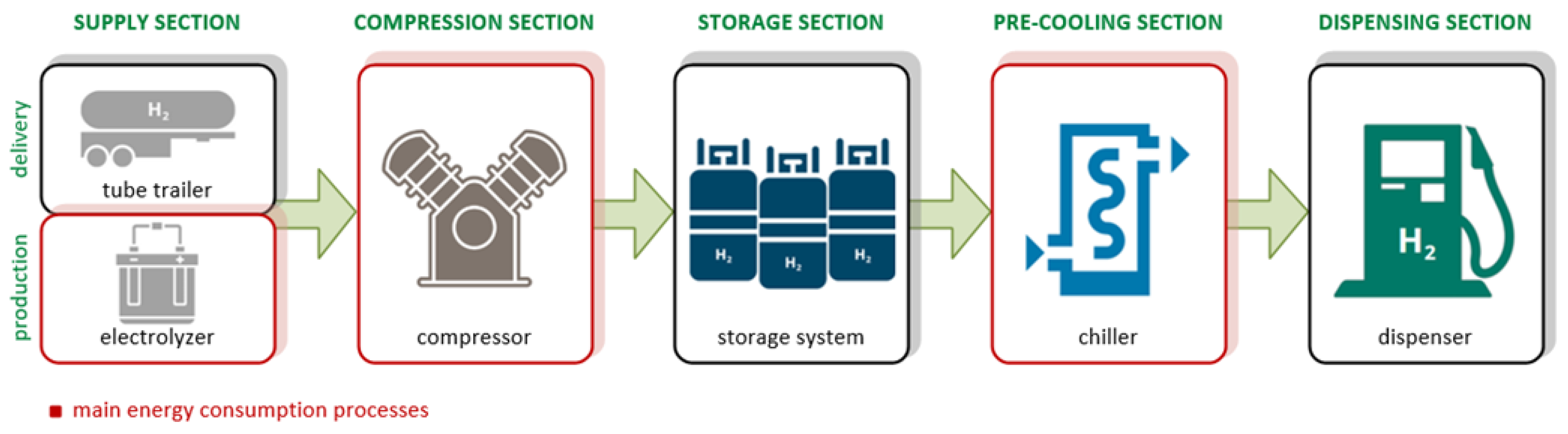
7. Energy Consumption in Hydrogen Refueling Stations
Energy Management Strategies
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Williams, I.D.; Blyth, M. Autogeddon or Autoheaven: Environmental and Social Effects of the Automotive Industry from Launch to Present. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 858, 159987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pramuanjaroenkij, A.; Kakaç, S. The Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles: The Highlight Review. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2023, 48, 9401–9425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Transportation Emissions Worldwide—Statistics & Facts. Available online: https://www.statista.com/topics/7476/transportation-emissions-worldwide/#topicOverview (accessed on 24 November 2023).
- Tiseo, I. Annual Global Emissions of Carbon Dioxide 1940–2023. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/276629/global-co2-emissions/ (accessed on 8 December 2023).
- Kinsella, L.; Stefaniec, A.; Foley, A.; Caulfield, B. Pathways to Decarbonising the Transport Sector: The Impacts of Electrifying Taxi Fleets. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2023, 174, 113160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albatayneh, A.; Juaidi, A.; Jaradat, M.; Manzano-Agugliaro, F. Future of Electric and Hydrogen Cars and Trucks: An Overview. Energy 2023, 16, 3230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F. Hydrogen Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles: State of Art and Outlooks. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 9th International Conference on Power Electronics Systems and Applications (PESA), Hong Kong, 20–22 September 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Silvestri, L.; Di Micco, S.; Forcina, A.; Minutillo, M.; Perna, A. Power-to-Hydrogen Pathway in the Transport Sector: How to Assure the Economic Sustainability of Solar Powered Refueling Stations. Energy Convers. Manag. 2022, 252, 115067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hydrogen Insights 2023 December Update. Available online: https://hydrogencouncil.com/en/hydrogen-insights-2023-december-update/ (accessed on 13 December 2023).
- Aravindan, M.; Hariharan, V.S.; Narahari, T.; Kumar, A.; Madhesh, K.; Kumar, P.; Prabakaran, R. Fuelling the Future: A Review of Non-Renewable Hydrogen Production and Storage Techniques. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2023, 188, 113791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishaq, H.; Dincer, I.; Crawford, C. A Review on Hydrogen Production and Utilization: Challenges and Opportunities. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47, 26238–26264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smitkova, M.F.; Janicek, F.; Martins, F. Hydrogen Economy: Brief Sumarization of Hydrogen Economy. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Electrical, Computer and Energy Technologies (ICECET), Prague, Czech Republic, 20–22 July 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Camões, M.F.; Anes, B. Hydrated Protons. In Reference Module in Chemistry, Molecular Sciences and Chemical Engineering; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Momirlan, M.; Veziroglu, T. The Properties of Hydrogen as Fuel Tomorrow in Sustainable Energy System for a Cleaner Planet. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2005, 30, 795–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, I. Physical and Chemical Properties of Hydrogen. In Energy Carriers and Conversion Systems with Emphasis on Hydrogen; EOLSS Publications: Chiba, Japan, 2009; pp. 50–55. [Google Scholar]
- Sobre o Hidrogénio. Available online: https://www.ap2h2.pt/sobre-h2.php (accessed on 11 December 2023).
- Makridis, S.S. Hydrogen Storage and Compression. Methane Hydrog. Energy Storage 2016, 1, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souto, H.; Nogueira, T. O Hidrogénio Como Vetor Energético Do Futuro. Neutro À Terra 2024, 32, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, Q.; Sameen, A.Z.; Salman, H.M.; Jaszczur, M.; Al-Jiboory, A.K. Hydrogen Energy Future: Advancements in Storage Technologies and Implications for Sustainability. J. Energy Storage 2023, 72, 108404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farias, C.B.B.; Barreiros, R.C.S.; da Silva, M.F.; Casazza, A.A.; Converti, A.; Sarubbo, L.A. Use of Hydrogen as Fuel: A Trend of the 21st Century. Energies 2022, 15, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ahmed, A.; Hossain, S.; Mukhtar, B.; Rahman, S.U.; Abualhamayel, H.; Zaidi, J. Hydrogen Highway: An Overview. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Energy Conference, Manama, Bahrain, 18–22 December 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Alazemi, J.; Andrews, J. Automotive Hydrogen Fuelling Stations: An International Review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 48, 483–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Liu, Z. Investment of Hydrogen Refueling Station Based on Compound Real Options. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 57, 198–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escamilla, A.; Sánchez, D.; García-Rodríguez, L. Assessment of Power-to-Power Renewable Energy Storage Based on the Smart Integration of Hydrogen and Micro Gas Turbine Technologies. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47, 17505–17525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mio, A.; Barbera, E.; Massi Pavan, A.; Bertucco, A.; Fermeglia, M. Sustainability Analysis of Hydrogen Production Processes. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 54, 540–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hren, R.; Vujanović, A.; Van Fan, Y.; Klemeš, J.J.; Krajnc, D.; Čuček, L. Hydrogen Production, Storage and Transport for Renewable Energy and Chemicals: An Environmental Footprint Assessment. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2023, 173, 113113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, Q.; Algburi, S.; Sameen, A.Z.; Salman, H.M.; Jaszczur, M. Green Hydrogen: A Pathway to a Sustainable Energy Future. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 50, 310–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junior, O.; Laurindo, D. O HIDROGÊNIO COMO VETOR ENERGÉTICO. In Estudos Interdisciplinares: Ciências Exatas e da Terra e Engenharias; Atena Editora: Ponta Grossa, Brasil, 2018; pp. 150–166. [Google Scholar]
- Arsad, A.Z.; Hannan, M.A.; Al-Shetwi, A.Q.; Begum, R.A.; Hossain, M.J.; Ker, P.J.; Mahlia, T.I. Hydrogen Electrolyser Technologies and Their Modelling for Sustainable Energy Production: A Comprehensive Review and Suggestions. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2023, 48, 27841–27871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zainal, B.S.; Ker, P.J.; Mohamed, H.; Ong, H.C.; Fattah, I.M.R.; Rahman, S.M.A.; Nghiem, L.D.; Mahlia, T.M.I. Recent Advancement and Assessment of Green Hydrogen Production Technologies. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2024, 189, 113941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Shafie, M. Hydrogen Production by Water Electrolysis Technologies: A Review. Results Eng. 2023, 20, 101426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, D.; Tan, G.-L.; Li, G.-W.; Liang, J.-G.; Ahmad, S.M.; Bahadur, A.; Humayun, M.; Ullah, H.; Khan, A.; Bououdina, M. State-of-the-Art Hydrogen Generation Techniques and Storage Methods: A Critical Review. J. Energy Storage 2023, 64, 107196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiva Kumar, S.; Lim, H. An Overview of Water Electrolysis Technologies for Green Hydrogen Production. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 13793–13813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benghanem, M.; Mellit, A.; Almohamadi, H.; Haddad, S.; Chettibi, N.; Alanazi, A.M.; Dasalla, D.; Alzahrani, A. Hydrogen Production Methods Based on Solar and Wind Energy: A Review. Energy 2023, 16, 757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebbahi, S.; Nabil, N.; Alaoui-Belghiti, A.; Laasri, S.; Rachidi, S.; Hajjaji, A. Assessment of the Three Most Developed Water Electrolysis Technologies: Alkaline Water Electrolysis, Proton Exchange Membrane and Solid-Oxide Electrolysis. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 66, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.H.; Rajuli, M.F. An Overview of Pure Hydrogen Production via Electrolysis and Hydrolysis. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 84, 521–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, H.; Murawski, J.; Shinde, D.V.; Stephens, I.E.L.; Hinds, G.; Smith, G. Impact of Impurities on Water Electrolysis: A Review. Sustain. Energy Fuels 2023, 7, 1565–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindquist, G.A.; Xu, Q.; Oener, S.Z.; Boettcher, S.W. Membrane Electrolyzers for Impure-Water Splitting. Joule 2020, 4, 2549–2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarhan, C.; Çil, M.A. A Study on Hydrogen, the Clean Energy of the Future: Hydrogen Storage Methods. J. Energy Storage 2021, 40, 102676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caponi, R.; Bocci, E.; Del Zotto, L. Techno-Economic Model for Scaling Up of Hydrogen Refueling Stations. Energy 2022, 15, 7518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genovese, M.; Fragiacomo, P. Hydrogen Refueling Station: Overview of the Technological Status and Research Enhancement. J. Energy Storage 2023, 61, 106758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Lv, H.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, C.; He, P. Review on Equipment Configuration and Operation Process Optimization of Hydrogen Refueling Station. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47, 3033–3053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, D.; Lee, S.; Kim, S. A Thermodynamic Model for Cryogenic Liquid Hydrogen Fuel Tanks. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 3786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Uratani, J.; Huang, Y.; Xu, L.; Griffiths, S.; Ding, Y. Hydrogen Liquefaction and Storage: Recent Progress and Perspectives. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2023, 176, 113204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, Y.; Chen, S.; Li, C.; Chen, X.; Xie, L.; Chen, J.; Long, R. Techno-Economic Analysis of Hydrogen Storage and Transportation from Hydrogen Plant to Terminal Refueling Station. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 52, 547–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Jiang, Z. Overview of Hydrogen Storage and Transportation Technology in China. Unconv. Resour. 2023, 3, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosu, S.; Rajamohan, N. Recent Advancements in Hydrogen Storage—Comparative Review on Methods, Operating Conditions and Challenges. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 52, 352–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalkiadakis, N.; Stubos, A.; Stamatakis, E.; Zoulias, E.; Tsoutsos, T. A Review on Hydrogen Compression Methods for Hydrogen Refuelling Stations. In Hydrogen Electrical Vehicles; Scrivener Publishing: Beverly, MA, USA, 2023; pp. 47–73. [Google Scholar]
- Okonkwo, P.C.; Barhoumi, E.M.; Ben Belgacem, I.; Mansir, I.B.; Aliyu, M.; Emori, W.; Uzoma, P.C.; Beitelmal, W.H.; Akyüz, E.; Radwan, A.B.; et al. A Focused Review of the Hydrogen Storage Tank Embrittlement Mechanism Process. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2023, 48, 12935–12948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.K.; Ha, S.K. A Review on the Cost Analysis of Hydrogen Gas Storage Tanks for Fuel Cell Vehicles. Energies 2023, 16, 5233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.; Zhang, R.; Shi, Z.; Lin, J. Review of Common Hydrogen Storage Tanks and Current Manufacturing Methods for Aluminium Alloy Tank Liners. Int. J. Lightweight Mater. Manuf. 2023, 7, 269–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Su, Y.; Lv, H.; Liu, M.; Li, W.; Zhang, C. Review of Decompression Damage of the Polymer Liner of the Type IV Hydrogen Storage Tank. Polymers 2023, 15, 2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Air, A.; Shamsuddoha, M.; Gangadhara Prusty, B. A Review of Type V Composite Pressure Vessels and Automated Fibre Placement Based Manufacturing. Compos. B Eng. 2023, 253, 110573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.; Han, N.; Yan, J.; Feng, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Fan, J.; Zeng, L.; Li, H.; Wang, H. Electrochemical Compression Technologies for High-Pressure Hydrogen: Current Status, Challenges and Perspective. Electrochem. Energy Rev. 2020, 3, 690–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlova, S.; Mezeckis, N.; Vasudev, V.P.K. Compression of Hydrogen Gas for Energy Storage: A Review. Latv. J. Phys. Tech. Sci. 2023, 60, 4–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sdanghi, G.; Maranzana, G.; Celzard, A.; Fierro, V. Towards Non-Mechanical Hybrid Hydrogen Compression for Decentralized Hydrogen Facilities. Energy 2020, 13, 3145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sdanghi, G.; Maranzana, G.; Celzard, A.; Fierro, V. Review of the Current Technologies and Performances of Hydrogen Compression for Stationary and Automotive Applications. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 102, 150–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Ooi, K.T.; Dong, P.; Yang, Z.; Zhou, S.; Zhao, S. Dynamic and Energy Analysis of a Liquid Piston Hydrogen Compressor. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2023, 48, 20694–20704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caponi, R.; Ferrario, A.M.; Bocci, E.; Bødker, S.; del Zotto, L. Single-Tank Storage versus Multi-Tank Cascade System in Hydrogen Refueling Stations for Fuel Cell Buses. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47, 27633–27645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartolucci, L.; Cordiner, S.; Mulone, V.; Tatangelo, C.; Antonelli, M.; Romagnuolo, S. Multi-Hub Hydrogen Refueling Station with on-Site and Centralized Production. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2023, 48, 20861–20874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, B.H.; Joe, C.H. Investigation of Configuration on Multi-Tank Cascade System at Hydrogen Refueling Stations with Mass Flow Rate. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 49, 1140–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Su, S.; Xu, Q.; Lv, H.; Zhao, Y.; Xia, L.; Zhang, G.; Hu, K. Optimization of Hydrogen Refueling Strategy: Based on Energy Consumption and Refueling Demand. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 71, 625–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadi, M.; Deymi-Dashtebayaz, M. Hydrogen Refueling Process from the Buffer and the Cascade Storage Banks to HV Cylinder. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 18496–18504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothuizen, E.; Rokni, M. Optimization of the Overall Energy Consumption in Cascade Fueling Stations for Hydrogen Vehicles. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 582–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genovese, M.; Cigolotti, V.; Jannelli, E.; Fragiacomo, P. Current Standards and Configurations for the Permitting and Operation of Hydrogen Refueling Stations. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2023, 48, 19357–19371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Fu, J.; Liu, Z.; Liu, J. Review of Researches on Important Components of Hydrogen Supply Systems and Rapid Hydrogen Refueling Processes. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2023, 48, 1904–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chochlidakis, C.-G.; Rothuizen, E.D. Overall Efficiency Comparison between the Fueling Methods of SAEJ2601 Using Dynamic Simulations. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 11842–11854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fueling Protocols for Light Duty Gaseous Hydrogen Surface Vehicles. Available online: https://www.sae.org/standards/content/j2601_202005/ (accessed on 4 January 2024).
- Luo, H.; Xiao, J.; Bénard, P.; Yang, T.; Tong, L.; Chahine, R.; Yuan, Y.; Yuan, C.; Yao, C. Improvement of MC Method in SAE J2601 Hydrogen Refuelling Protocol Using Dual-Zone Dual-Temperature Model. J. Energy Storage 2024, 81, 110416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddi, K.; Elgowainy, A.; Rustagi, N.; Gupta, E. Impact of Hydrogen SAE J2601 Fueling Methods on Fueling Time of Light-Duty Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 16675–16685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, A.; Mayer, T.; Semmel, M.; Guerrero Morales, M.A.; Wind, J. Energetic Evaluation of Hydrogen Refueling Stations with Liquid or Gaseous Stored Hydrogen. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 6795–6812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.-Q.; Chen, Y.; Ma, Y.B.; Kwon, J.-T.; Xu, H.; Li, J.-C. A Study on the Joule-Thomson Effect of during Filling Hydrogen in High Pressure Tank. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2023, 41, 102678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Lu, C.; Ye, S.; Hua, Z.; Gu, C. Optimization on Volume Ratio of Three-Stage Cascade Storage System in Hydrogen Refueling Stations. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47, 13430–13441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greene, D.L.; Ogden, J.M.; Lin, Z. Challenges in the Designing, Planning and Deployment of Hydrogen Refueling Infrastructure for Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles. eTransportation 2020, 6, 100086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Zhu, Z.; Feng, Y.; Tan, W. Economic Analysis of Hydrogen Refueling Station Considering Different Operation Modes. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2023, 52, 1577–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagano, A.; Gabbar, H. Techno-Economic Analysis of a Hydrogen Refueling Station Located in Turin. In Proceedings of the IEEE 11th International Conference on Smart Energy Grid Engineering (SEGE), Oshawa, ON, Canada, 13–15 August 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Fragiacomo, P.; Genovese, M. Numerical Simulations of the Energy Performance of a PEM Water Electrolysis Based High-Pressure Hydrogen Refueling Station. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 27457–27470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caponi, R.; Monforti Ferrario, A.; Del Zotto, L.; Bocci, E. Hydrogen Refueling Station Cost Model Applied to Five Real Case Studies for Fuel Cell Buses. E3S Web Conf. 2021, 312, 07010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zun, M.T.; McLellan, B.C. Cost Projection of Global Green Hydrogen Production Scenarios. Hydrogen 2023, 4, 932–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poudineh, R.; Patonia, A. Cost-Competitive Green Hydrogen: How to Lower the Cost of Electrolysers? Available online: https://www.oxfordenergy.org/publications/cost-competitive-green-hydrogen-how-to-lower-the-cost-of-electrolysers/ (accessed on 6 December 2023).
- Blazquez-Diaz, C. Techno-Economic Modelling and Analysis of Hydrogen Fuelling Stations. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 495–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Chen, J.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Ye, J.; Shao, S.; Xie, J. Effects of Pressure Levels in Three-Cascade Storage System on the Overall Energy Consumption in the Hydrogen Refueling Station. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 31334–31345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgowainy, A.; Reddi, K.; Lee, D.-Y.; Rustagi, N.; Gupta, E. Techno-Economic and Thermodynamic Analysis of Pre-Cooling Systems at Gaseous Hydrogen Refueling Stations. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 29067–29079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talpacci, E.; Reuβ, M.; Grube, T.; Cilibrizzi, P.; Gunnella, R.; Robinius, M.; Stolten, D. Effect of Cascade Storage System Topology on the Cooling Energy Consumption in Fueling Stations for Hydrogen Vehicles. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 6256–6265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genovese, M.; Blekhman, D.; Dray, M.; Fragiacomo, P. Improving Chiller Performance and Energy Efficiency in Hydrogen Station Operation by Tuning the Auxiliary Cooling. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47, 2532–2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurer, W.; Justl, M.; Keuschnigg, R. Improving Hydrogen Refueling Stations to Achieve Minimum Refueling Costs for Small Bus Fleets. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2023, 48, 29821–29834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genovese, M.; Blekhman, D.; Dray, M.; Piraino, F.; Fragiacomo, P. Experimental Comparison of Hydrogen Refueling with Directly Pressurized vs. Cascade Method. Energy 2023, 16, 5749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barhoumi, E.M.; Okonkwo, P.C.; Ben Belgacem, I.; Zghaibeh, M.; Tlili, I. Optimal Sizing of Photovoltaic Systems Based Green Hydrogen Refueling Stations Case Study Oman. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47, 31964–31973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Gao, W.; Zhang, L.; Li, Q.; Ren, H. Economic Analysis of a Photovoltaic Hydrogen Refueling Station Based on Hydrogen Load. Energy 2023, 16, 6406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minutillo, M.; Perna, A.; Forcina, A.; Di Micco, S.; Jannelli, E. Analyzing the Levelized Cost of Hydrogen in Refueling Stations with On-Site Hydrogen Production via Water Electrolysis in the Italian Scenario. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 13667–13677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, O.; Rehme, J.; Cerin, P. Levelized Cost of Hydrogen for Refueling Stations with Solar PV and Wind in Sweden: On-Grid or off-Grid? Energy 2022, 241, 122906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Micco, S.; Minutillo, M.; Perna, A.; Jannelli, E. On-Site Solar Powered Refueling Stations for Green Hydrogen Production and Distribution: Performances and Costs. E3S Web Conf. 2022, 334, 01005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, S.; Yonggang, P.; Jia, X. A Photovoltaic-Assisted in-Situ Hydrogen Refueling Station System and Its Capacity Optimization Method. In Proceedings of the 2023 5th Asia Energy and Electrical Engineering Symposium (AEEES), Chengdu, China, 23–26 March 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Maurer, W.; Rechberger, P.; Justl, M.; Keuschnigg, R. Parameter Study for Dimensioning of a PV Optimized Hydrogen Supply Plant. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47, 40815–40825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shams, M.H.; Niaz, H.; Liu, J.J. Energy Management of Hydrogen Refueling Stations in a Distribution System: A Bilevel Chance-Constrained Approach. J. Power Sources 2022, 533, 231400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Sun, J.; Peng, Y.; Chen, X. Optimized Operation Plan for Hydrogen Refueling Station with On-Site Electrolytic Production. Sustainability 2022, 15, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Technology | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| AWE | Mature technology Low capital cost High stability Longer lifetime | Low hydrogen purity Low operational pressure Lower current density Corrosivity of electrolyte Slow startup Gas permeation |
| PEM | High hydrogen purity High current density Compact and simple design Quick response time High dynamic operation | High membrane cost Acidic environment Lower durability |
| AAEM | High hydrogen purity Simple design Low cost Low concentrated liquid electrolyte | Low lifetime Low ionic conductivity Low membrane stability |
| SOE | High efficiency Low capital cost Requires low energy | Safety and sealing problems Uses brittle material Unstable electrodes |
| Type | Material Characteristic |
|---|---|
| I | All-metal gas tank |
| II | Metal-lined gas tank hoop-wound with fiber |
| III | Metal-lined gas tank fully wound with fiber |
| IV | Polymer-lined gas tank fully wound with fiber |
| V | All-composite liner-less gas tank |
| Types of Compressors | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Piston compressor | Mature technology Adaptability to a large range of flow rates High discharge pressures | Embrittlement phenomena Several moving parts Manufacturing and maintenance complexity Difficulty in managing heat transfer Presence of vibrations and noise Not suitable for high compression ratios |
| Diaphragm compressor | Mature technology Low cooling requirement Ideal for handling pure gases and explosives | Diaphragm failure Complex design Limited throughput |
| Ionic liquid compressor | High efficiency High compression ratio Low energy consumption Low noise emissions No gas contamination Reduced wear and long service Quite isothermal compression Small number of moving parts | Liquid leaks Cavitation phenomena Corrosion |
| Metal hydride compressor | Thermally driven compressor Absence of moving parts Compact design Safety Absence of noise High-purity hydrogen production | High desorption temperature High heat of absorption Limited heat transfer Necessity of using appropriate alloys Low efficiency High weight Low compression rates |
| Electrochemical compressor | Low cost of operation Absence of moving parts High-purity hydrogen production Very high compression efficiency Use as a purifier | Difficulty in manufacturing the cell assembly Difficulty in realizing a perfect sealing High cell resistance Not suitable for very high discharge pressures Low compression rates |
| Article | Electricity Prices Analysis | Use of Renewable Sources Analysis | Strategy Based on Electricity Prices | Strategy Based on Renewable Production |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [76] | No | Yes | No | Yes |
| [88] | No | Yes | No | Yes |
| [89] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| [90] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| [91] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| [92] | No | Yes | No | Yes |
| [93] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| [94] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| [95] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| [96] | Yes | No | Yes | No |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pereira, R.; Monteiro, V.; Afonso, J.L.; Teixeira, J. Hydrogen Refueling Stations: A Review of the Technology Involved from Key Energy Consumption Processes to Related Energy Management Strategies. Energies 2024, 17, 4906. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17194906
Pereira R, Monteiro V, Afonso JL, Teixeira J. Hydrogen Refueling Stations: A Review of the Technology Involved from Key Energy Consumption Processes to Related Energy Management Strategies. Energies. 2024; 17(19):4906. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17194906
Chicago/Turabian StylePereira, Rafael, Vitor Monteiro, Joao L. Afonso, and Joni Teixeira. 2024. "Hydrogen Refueling Stations: A Review of the Technology Involved from Key Energy Consumption Processes to Related Energy Management Strategies" Energies 17, no. 19: 4906. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17194906
APA StylePereira, R., Monteiro, V., Afonso, J. L., & Teixeira, J. (2024). Hydrogen Refueling Stations: A Review of the Technology Involved from Key Energy Consumption Processes to Related Energy Management Strategies. Energies, 17(19), 4906. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17194906








