Leveraging Artificial Intelligence to Bolster the Energy Sector in Smart Cities: A Literature Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- Learning: This aspect of AI relies on data collection and analysis to create algorithms that facilitate the development of efficiency-promoting processes. By processing large data sets, AI systems can identify patterns, trends, and correlations, enabling them to learn from past experiences and make informed decisions.
- Cognition: The cognitive capabilities of AI help to recognize similarities and patterns in previous processes. Drawing on past experience and knowledge, AI can interpret complex data, recognize trends, and generate valuable insights, improving decision-making processes.
- Actions: AI is capable of making automatic decisions within specified time frames. This involves the real-time processing of data to generate responses and take actions based on predetermined rules or learned behaviors. Such automation can streamline various tasks, leading to increased efficiency and precision. These fundamental AI functionalities play a crucial role in a wide array of industries, including energy management in Smart Cities, predictive analytics, natural language processing, robotics, and more. As AI continues to advance, its potential for transformative impact across diverse fields remains substantial [8].
- How can the implementation of AI methods address crucial challenges in the energy sector?
- What AI methodologies are currently being employed in Smart Cities to address challenges in the energy sector?
- What advantages does the application of AI in the energy sector offer that conventional methods cannot achieve?
- What are the latest trends in applying AI in Smart Cities to improve the energy sector?
2. Methodology
3. Results
3.1. Literature Review and Content Analysis
3.1.1. Energy Generation
3.1.2. Renewable Energy Sources within Smart Cities
3.1.3. Energy Transmission
3.1.4. Energy Distribution
3.1.5. Energy Consumption
4. Discussion
4.1. Energy Generation
4.2. Energy Transmission
4.3. Energy Distribution
4.4. Energy Consumption
4.5. Research Gaps
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| ACO | Ant Colony Optimization |
| ADM | Automatic Decision Making |
| AIA | Artificial Intelligence Analytics |
| AIMS-SB | Artificial Intelligence Technique for Monitoring Systems in Smart Buildings |
| ANN | Artificial Neural Network |
| AVWC | Automated Vacuum Waste Collection |
| BCT | Blockchain Technology |
| BiKSTM | Bidirectional Long Short-Term Memory |
| CNN | Convolutional Neural Network |
| DaaS | Device as a Service |
| DAI | Distributed Artificial Intelligence |
| DCESN | Deep-Chain Echo State Network |
| DCNN | Dilated Convolutional Neural Network |
| DERMS | Distributed Energy Management System |
| DNN | Deep Neural Network |
| DRL | Deep Reinforcement Learning |
| DSM | Demand Side Management |
| FCA | Fairness Cooperation Algorithm |
| FFTA | Finite-Time Terminal Attractor |
| GA | Genetic Algorithm |
| GHG | Greenhouse gas |
| GPSO | Gradient Particle Swarm Optimization |
| IGWO | Improved Gray Wolf Optimization |
| IOT | Internet of Things |
| IPTO | Improved Phase Timing Optimization |
| LSTM | Long Short-Term Memory |
| MAS | Multi Agent Systems |
| MCDA | Multiple Criteria Decision Analysis |
| MKL | Machine Kernel Learning |
| ML | Machine Learning |
| MPPT | Maximum Power Point Tracking |
| PV | Photovoltaic |
| QRL | Quantum-Inspired Reinforcement Learning |
| RNN | Recurrent Neural Network |
| SAE | Stacked Autoencoder |
| SM | Smart Metering |
| SMART | Simple Multi-Attribute Rating |
| SVM | Support Vector Machine |
| XELF | Explainable Electrical Load Forecasting |
References
- Llanez-Caballero, I.; Ibarra, L.; Peña-Quintal, A.; Catzín-Contreras, G.; Ponce, P.; Molina, A.; Ramirez-Mendoza, R. The “Smart” concept from an electrical sustainability viewpoint. Energies 2023, 16, 3072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Zhao, Y.; Gangadhari, R.K.; Li, Z. Analyzing the adoption challenges of the Internet of things (Iot) and artificial intelligence (ai) for smart cities in china. Sustainability 2021, 13, 10983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, Z.; Al-Turjman, F.; Mostarda, L.; Gagliardi, R. Applications of artificial intelligence and machine learning in smart cities. Comput. Commun. 2020, 154, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, W. Digital systems in smart city and infrastructure: Digital as a service. Smart Cities 2018, 1, 134–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghaddam, S.M.S.H.; Dashtdar, M.; Jafari, H. AI applications in smart cities’ energy systems automation. Repa Proc. Ser. 2022, 3, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehmood, M.U.; Chun, D.; Han, H.; Jeon, G.; Chen, K. A review of the applications of artificial intelligence and big data to buildings for energy-efficiency and a comfortable indoor living environment. Energy Build. 2019, 202, 109383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, T.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, D.; Tariq, R.; Bassam, A.; Ullah, F.; AlGhamdi, A.S.; Alshamrani, S.S. Energetics Systems and artificial intelligence: Applications of industry 4.0. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 334–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Jin, Y.; Akram, M.; Chen, X.; Ji, J. Application of bio-inspired algorithms in maximum power point tracking for PV systems under partial shading conditions—A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 81, 840–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. Declaración PRISMA 2020: Una guía actualizada para la publicación de revisiones sistemáticas. Rev. Española Cardiol. 2021, 74, 790–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghadami, N.; Gheibi, M.; Kian, Z.; Faramarz, M.G.; Naghedi, R.; Eftekhari, M.; Fathollahi-Fard, A.M.; Dulebenets, M.A.; Tian, G. Implementation of solar energy in smart cities using an integration of artificial neural network, photovoltaic system and classical Delphi methods. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 74, 103149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serban, A.C.; Lytras, M.D. Artificial intelligence for smart renewable energy sector in europe—Smart energy infrastructures for next generation smart cities. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 77364–77377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzaoui, A.E.; Singh, S.K.; Pan, Y.; Park, J.H. Block5GIntell: Blockchain for AI-Enabled 5G Networks. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 145918–145935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.L.; Qin, D.; Wang, L.C.; Sim, G.H. 6G Massive Radio Access Networks: Key Applications, Requirements and Challenges. IEEE Open J. Veh. Technol. 2021, 2, 54–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Chen, H.; Chen, X.; Chen, J. Semantic framework of internet of things for smart cities: Case studies. Sensors 2016, 16, 1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramli, M.A.; Bouchekara, H.; Alghamdi, A.S. Optimal sizing of PV/wind/diesel hybrid microgrid system using multi-objective self-adaptive differential evolution algorithm. Renew. Energy 2018, 121, 400–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Gu, C.; Dong, Z.; Jirutitijaroen, P.; Chen, N.; Walsh, W.M. Solar irradiance forecasting using spatial-temporal covariance structures and time-forward kriging. Renew. Energy 2013, 60, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldenbroek, V.; Verhoef, L.A.; van Wijk, A.J. Fuel cell electric vehicle as a power plant: Fully renewable integrated transport and energy system design and analysis for smart city areas. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 8166–8196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luca, G.; Fabozzi, S.; Massarotti, N.; Vanoli, L. A renewable energy system for a nearly zero greenhouse city: Case study of a small city in southern Italy. Energy 2018, 143, 347–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar, J.; Garces-Jimenez, A.; R-moreno, M.; García, R. A systematic literature review on the use of artificial intelligence in energy self-management in smart buildings. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 151, 111530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, H.; Haque, A.; Blaabjerg, F. Machine learning in wireless sensor networks for smart cities: A survey. Electronics 2021, 10, 1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.; Haq, I.U.; Khan, S.U.; Rho, S.; Lee, M.Y.; Baik, S.W. DB-Net: A novel dilated CNN based multi-step forecasting model for power consumption in integrated local energy systems. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2021, 133, 107023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, L.T.; Nguyen, H.; Dou, J.; Zhou, J. A comparative study of PSO-ANN, GA-ANN, ICA-ANN, and ABC-ANN in estimating the heating load of buildings’ energy efficiency for smart city planning. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idowu, S.; Saguna, S.; Åhlund, C.; Schelén, O. Applied machine learning: Forecasting heat load in district heating system. Energy Build. 2016, 133, 478–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Wang, B.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, Y. Blockchain and computational intelligence inspired incentive-compatible demand response in internet of electric vehicles. IEEE Trans. Emerg. Top. Comput. Intell. 2019, 3, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, L.T.; Nguyen, H.; Zhou, J.; Dou, J.; Moayedi, H. Estimating the heating load of buildings for smart city planning using a novel artificial intelligence technique PSO-XGBoost. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingwersen, P.; Serrano-López, A.E. Smart city research 1990–2016. Scientometrics 2018, 117, 1205–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, A.; Srikumar, V.; Smith, A.D. Predicting electricity consumption for commercial and residential buildings using deep recurrent neural networks. Appl. Energy 2018, 212, 372–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, A.; Haydarov, K.; Haq, I.U.; Muhammad, K.; Rho, S.; Lee, M.; Baik, S.W. Deep learning assisted buildings energy consumption profiling using smart meter data. Sensors 2020, 20, 873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsamhi, S.H.; Ma, O.; Ansari, M.S.; Almalki, F.A. Survey on collaborative smart drones and internet of things for improving smartness of smart cities. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 128125–128152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez-Canteli, J.R.; Ulyanin, S.; Kämpf, J.; Nagy, Z. Fusing TensorFlow with building energy simulation for intelligent energy management in smart cities. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2019, 45, 243–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyasawa, A.; Akira, S.; Fujimoto, Y.; Hayashi, Y. Forecast of area-scale behaviours of behind-the-metre solar power and load based on smart-metering net demand data. IET Smart Cities 2023, 5, 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiullah, M.; Rahman, S.; Imteyaz, B.; Aroua, M.K.; Hossain, M.I.; Rahman, S.M. Review of Smart City Energy Modeling in Southeast Asia. Smart Cities 2023, 6, 72–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Sun, B.; Feng, Q.; Wang, Z.; Pan, J. Physics-Informed AI Surrogates for Day-Ahead Wind Power Probabilistic Forecasting with Incomplete Data for Smart Grid in Smart Cities. CMES Comput. Model. Eng. Sci. 2023, 137, 527–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhar, A.; Haidar, A.M.; Abdullah, M.; Das, N. Smart grid mechanism for green energy management: A comprehensive review. Int. J. Green Energy 2023, 20, 284–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayer, D.; Pruckner, M. A digital twin of a local energy system based on real smart meter data. Energy Inform. 2023, 6, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alymani, M.; Mengash, H.A.; Aljebreen, M.; Alasmari, N.; Allafi, R.; Alshahrani, H.; Elfaki, M.A.; Hamza, M.A.; Abdelmageed, A.A. Sustainable residential building energy consumption forecasting for smart cities using optimal weighted voting ensemble learning. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2023, 57, 103271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Habaibeh, A.; Yaseen, S.; Nweke, B. A comparative study of low and high resolution infrared cameras for IoT smart city applications: A comparative study of low and high resolution infrared cameras. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2023, 14, 102108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvaraj, R.; Kuthadi, V.M.; Baskar, S. Smart building energy management and monitoring system based on artificial intelligence in smart city. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2023, 56, 103271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Huang, Y.; Li, B.; Peng, H.; Wang, J.; Zhou, W. Connectivity Enhancement of E-VANET Based on QL-mRSU Self-Learning Energy-Saving Algorithm. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 3810–3825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, R.; Zeng, S.; Song, Q.; Wu, Z. Deep-Chain Echo State Network With Explainable Temporal Dependence for Complex Building Energy Prediction. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2023, 19, 426–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlHajri, I.; Ahmadian, A.; Alazmi, R. A comprehensive technical, economic, and environmental evaluation for optimal planning of renewable energy resources to supply water desalination units: Kuwait case study. Energy 2023, 275, 127416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantin Irudaya Raj, E.; Appadurai, M.; Lurthu Pushparaj, T.; Chithambara Thanu, M. Wind turbines with aramid fiber composite wind blades for smart cities like urban environments: Numerical simulation study. MRS Energy Sustain. 2023, 10, 139–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.; Khan, S.U.; Ullah, F.U.M.; Lee, M.Y.; Baik, S.W. AI-Assisted Hybrid Appr Approach for Energy Management in IoT-based Smart Microgrid. IEEE Internet Things J. 2023, 10, 18861–18875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulpiani, G.; Vetters, N.; Shtjefni, D.; Kakoulaki, G.; Taylor, N. Let’s hear it from the cities: On the role of renewable energy in reaching climate neutrality in urban Europe. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2023, 183, 113444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kedir, N.; Nguyen, P.H.; Pérez, C.; Ponce, P.; Fayek, A.R. Systematic Literature Review on Fuzzy Hybrid Methods in Photovoltaic Solar Energy: Opportunities, Challenges, and Guidance for Implementation. Energies 2023, 16, 3795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Icaza-Alvarez, D.; Jurado, F.; Tostado-Véliz, M. Long-term planning for the integration of electric mobility with 100renewable energy generation under various degrees of decentralization: Case study Cuenca, Ecuador. Energy Rep. 2023, 9, 4816–4829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, J.; Rho, S.; Baik, S.W. Toward explainable electrical load forecasting of buildings: A comparative study of tree-based ensemble methods with Shapley values. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2022, 54, 102888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, D. A Survey on Information Communication Technologies in Modern Demand-Side Management for Smart Grids: Challenges, Solutions, and Opportunities. IEEE Eng. Manag. Rev. 2023, 51, 76–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidari, A.; Navimipour, N.J.; Unal, M. Applications of ML/DL in the management of smart cities and societies based on new trends in information technologies: A systematic literature review. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 85, 104089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, E.C.; Cheng, C.A.; Wu, R.C. Artificial Intelligence of Things-Based Optimal Finite-Time Terminal Attractor and Its Application to Maximum Power Point Tracking of Photovoltaic Arrays in Smart Cities. Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2022, 2022, 4213217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Gao, Y.; Liu, B. An artificial intelligence-based electric multiple units using a smart power grid system. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 13376–13388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosrojerdi, F.; Akhigbe, O.; Gagnon, S.; Ramirez, A.; Richards, G. Integrating artificial intelligence and analytics in smart grids: A systematic literature review. Int. J. Energy Sect. Manag. 2021, 16, 318–338. [Google Scholar]
- Chavhan, S.; Gupta, D.; Gochhayat, S.P.; Chandana, B.; Khanna, A.; Shankar, K.; Rodrigues, J.J.P.C. Edge Computing AI-IoT Integrated Energy-efficient Intelligent Transportation System for Smart Cities. ACM Trans. Internet Technol. 2022, 22, 4213217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hawawreh, M.; Elgendi, I.; Munasinghe, K. An Online Model to Minimize Energy Consumption of IoT Sensors in Smart Cities. IEEE Sens. J. 2022, 22, 19524–19532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Nikolovski, S.; Chakrabarti, P. GWLBC: Gray Wolf Optimization Based Load Balanced Clustering for Sustainable WSNs in Smart City Environment. Sensors 2022, 22, 7113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Algahtani, M.; Kaewunruen, S. Energy Forecasting in a Public Building: A Benchmarking Analysis on Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM), Support Vector Regression (SVR), and Extreme Gradient Boosting (XGBoost) Networks. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 9788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, H.; Al-Masri, E.; Kotevska, O.; Souri, A. A Multi-Objective Approach for Optimizing Edge-Based Resource Allocation Using TOPSIS. Electronics 2022, 11, 2888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Xie, R.; Yu, F.R.; Huang, T.; Liu, Y. Green Intelligence Networking for Connected and Autonomous Vehicles in Smart Cities. IEEE Trans. Green Commun. Netw. 2022, 6, 1591–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murthy Nimmagadda, S.; Harish, K.S. Review paper on technology adoption and sustainability in India towards smart cities. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2022, 81, 27217–27245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, N.; Haseeb, K.; Ali, M.; Jeon, G. Secured Protocol with Collaborative IoT-Enabled Sustainable Communication Using Artificial Intelligence Technique. Sustainability 2022, 14, 8919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamponi, M.E.; Barbierato, E. The Dual Role of Artificial Intelligence in Developing Smart Cities. Smart Cities 2022, 5, 728–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naveed, Q.N.; Alqahtani, H.; Khan, R.U.; Almakdi, S.; Alshehri, M.; Rasheed, M.A.A. An Intelligent Traffic Surveillance System Using Integrated Wireless Sensor Network and Improved Phase Timing Optimization. Sensors 2022, 22, 3333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akkad, M.Z.; Haidar, S.; Bányai, T. Design of Cyber-Physical Waste Management Systems Focusing on Energy Efficiency and Sustainability. Designs 2022, 6, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garlik, B. Energy Centers in a Smart City as a Platform for the Application of Artificial Intelligence and the Internet of Things. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 3386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saba, D.; Cheikhrouhou, O.; Alhakami, W.; Sahli, Y.; Hadidi, A.; Hamam, H. Intelligent Reasoning Rules for Home Energy Management (IRRHEM): Algeria Case Study. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaimen, K.; Brahmia, M.E.A.; Moalic, L.; Abouaissa, A.; Idoumghar, L. A Survey of Artificial Intelligence Based WSNs Deployment Techniques and Related Objectives Modeling. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 113294–113329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, W. iBuilding: Artificial intelligence in intelligent buildings. Neural Comput. Appl. 2022, 34, 875–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chen, J.; Yuan, Z.; Xu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Al-Bahrani, M. Multi-objective risk-constrained optimal performance of hydrogen-based multi energy systems for future sustainable societies. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 87, 104176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doosti, R.; Sedighizadeh, M.; Sedighizadeh, D.; Sheikhi Fini, A. Robust stochastic optimal operation of an industrial building including plug in electric vehicle, solar-powered compressed air energy storage and ice storage conditioner: A case study in the city of Kaveh, Iran. IET Smart Cities 2022, 4, 56–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vyas, M.; Chowdhury, S.; Verma, A.; Jain, V. Solar Photovoltaic Tree: Urban PV power plants to increase power to land occupancy ratio. Renew. Energy 2022, 190, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlHammadi, A.; Al-Saif, N.; Al-Sumaiti, A.S.; Marzband, M.; Alsumaiti, T.; Heydarian-Forushani, E. Techno-Economic Analysis of Hybrid Renewable Energy Systems Designed for Electric Vehicle Charging: A Case Study from the United Arab Emirates. Energies 2022, 15, 6621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balabel, A.; Alwetaishi, M.; Abdelhafiz, A.; Issa, U.; Sharaky, I.; Shamseldin, A.; Al-Surf, M.; Al-Harthi, M. Potential of Solatube technology as passive daylight systems for sustainable buildings in Saudi Arabia. Alex. Eng. J. 2022, 61, 339–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuvvula, R.S.; Devaraj, E.; Madurai Elavarasan, R.; Iman Taheri, S.; Irfan, M.; Teegala, K.S. Multi-objective mutation-enabled adaptive local attractor quantum behaved particle swarm optimisation based optimal sizing of hybrid renewable energy system for smart cities in India. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2022, 49, 101689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponce, P.; Pérez, C.; Fayek, A.R.; Molina, A. Solar energy implementation in manufacturing industry using multi-criteria decision-making fuzzy TOPSIS and S4 framework. Energies 2022, 15, 8838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konhäuser, W. Digitalization in Buildings and Smart Cities on the Way to 6G. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2021, 121, 1289–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Romero, A.; Mateo-Romero, H.F.; Gallardo-Saavedra, S.; Alonso-Gómez, V.; Alonso-García, M.D.C.; Hernández-Callejo, L. Evaluation of artificial intelligence-based models for classifying defective photovoltaic cells. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 4226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Liu, Q.; Yan, K.; Du, Y. Deep Learning Enhanced Solar Energy Forecasting with AI-Driven IoT. Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2021, 2021, 9249387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, G.S.; Dubey, S.K.; Bharti, S.K. Tracard: A tool for smart city resource management based on novel framework algorithm. Recent Adv. Comput. Sci. Commun. 2021, 14, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonopoulos, I.; Robu, V.; Couraud, B.; Flynn, D. Data-driven modelling of energy demand response behaviour based on a large-scale residential trial. Energy AI 2021, 4, 100071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calamaro, N.; Beck, Y.; Ben Melech, R.; Shmilovitz, D. An Energy-Fraud Detection-System Capable of Distinguishing Frauds from Other Energy Flow Anomalies in an Urban Environment. Sustainability 2021, 13, 10696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manman, L.; Goswami, P.; Mukherjee, P.; Mukherjee, A.; Yang, L.; Ghosh, U.; Menon, V.G.; Nkenyereye, L. Distributed Artificial Intelligence Empowered Sustainable Cognitive Radio Sensor Networks: A Smart City on-demand Perspective. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 75, 103265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Dai, J.; Issakhov, A.; Almojil, S.F.; Souri, A. Towards decision support systems for energy management in the smart industry and Internet of Things. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2021, 161, 107671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirella, G.T.; Russo, A.; Benassi, F.; Czermański, E.; Goncharuk, A.G.; Oniszczuk-Jastrzabek, A. Energy re-shift for an urbanizing world. Energies 2021, 14, 5516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.C.; Lin, Y.H.; Gururaj, H.L. Partitional clustering-hybridized neuro-fuzzy classification evolved through parallel evolutionary computing and applied to energy decomposition for demand-side management in a smart home. Processes 2021, 9, 1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, D.; Latif, S.; Anwar, A.; Hussain, S.J.; Jhanjhi, N.; Sama, N.U.; Humayun, M. Utilization of ICT and AI techniques in harnessing residential energy consumption for an energy-aware smart city: A review. Int. J. Adv. Appl. Sci. 2021, 8, 50–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chen, Q.; Wang, J. Fuzzy rough set based sustainable methods for energy efficient smart city development. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2021, 40, 8173–8183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanase-Patil, A.B.; Kaldate, A.P.; Lokhande, S.D.; Panchal, H.; Suresh, M.; Priya, V. A review of artificial intelligence-based optimization techniques for the sizing of integrated renewable energy systems in smart cities. Environ. Technol. Rev. 2020, 9, 111–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Lu, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Jia, W. Advances in smart sensing and medical electronics by self-powered sensors based on triboelectric nanogenerators. Micromachines 2021, 12, 698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Xu, C.; Mashima, D.; Biswas, P.P.; Chipurupalli, G.; Zhou, B.; Wu, Y. PowerNet: A smart energy forecasting architecture based on neural networks. IET Smart Cities 2020, 2, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loose, N.; Thommessen, C.; Mehlich, J.; Derksen, C.; Eicker, S. Unified energy agents for combined district heating and electrical network simulation. Sustainability 2020, 12, 9301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattahi, J.; Wright, D.; Schriemer, H. An energy internet DERMS platform using a multi-level Stackelberg game. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 60, 102262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S. Analysis of intelligent versus smart infrastructure. Int. J. Adv. Res. Eng. Technol. 2020, 11, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinakis, V.; Doukas, H.; Koasidis, K.; Albuflasa, H. From intelligent energy management to value economy through a digital energy currency: Bahrain city case study. Sensors 2020, 20, 1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, A.S.; Nasir, H.; Fayaz, M.; Lajis, A.; Ullah, I.; Shah, A. Dynamic user preference parameters selection and energy consumption optimization for smart homes using deep extreme learning machine and bat algorithm. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 204744–204762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Zhao, R.; Lai, S.; Dan, Z.; Xia, J.; Fan, L. Intelligent Offloading Strategy Design for Relaying Mobile Edge Computing Networks. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 35127–35135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, H.; Zhang, J.; Sivaparthipan, C.; Muthu, B.A. Sustainable smart city building construction methods. Sustainability 2020, 12, 4947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algieri, A.; Morrone, P.; Bova, S. Techno-economic analysis of biofuel, solar and wind multi-source small-scale CHP systems. Energies 2020, 13, 3002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D. Urban energy system management for enhanced energy potential for upcoming smart cities. Energy Explor. Exploit. 2020, 38, 1968–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghajani, D.; Abbaspour, M.; Radfar, R.; Mohammadi, A. Using Web-GIS technology as a smart tool for resiliency management to monitor wind farms performances (Ganjeh site, Iran). Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 16, 5011–5022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oun, A.; Benabdallah, I.; Cherif, A. Improved industrial modeling and harmonic mitigation of a grid connected steel plant in Libya. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 2019, 10, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, H.; Das, S.; Biswas, S.; Burgueño, R. Data mining methodology employing artificial intelligence and a probabilistic approach for energy-efficient structural health monitoring with noisy and delayed signals. Expert Syst. Appl. 2019, 135, 259–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Guo, S.; Liu, J.; Yang, Y. Energy-Efficient Fair Cooperation Fog Computing in Mobile Edge Networks for Smart City. IEEE Internet Things J. 2019, 6, 7543–7554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krayem, A.; Al Bitar, A.; Ahmad, A.; Faour, G.; Gastellu-Etchegorry, J.P.; Lakkis, I.; Gerard, J.; Zaraket, H.; Yeretzian, A.; Najem, S. Urban energy modeling and calibration of a coastal Mediterranean city: The case of Beirut. Energy Build. 2019, 199, 223–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin-Perez, R.; Michailidis, I.T.; Garcia-Carrillo, D.; Korkas, C.D.; Kosmatopoulos, E.B.; Skarmeta, A. PLUG-N-HARVEST Architecture for secure and intelligent management of near-zero energy buildings. Sensors 2019, 19, 843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aymen, F.; Mahmoudi, C. A novel energy optimization approach for electrical vehicles in a smart city. Energies 2019, 12, 929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoury, D.; Keyrouz, F. A predictive convolutional neural network model for source-load forecasting in smart grids. WSEAS Trans. Power Syst. 2019, 14, 181–189. [Google Scholar]
- Alhussein, M.; Haider, S.I.; Aurangzeb, K. Microgrid-level energy management approach based on short-term forecasting ofwind speed and solar irradiance. Energies 2019, 12, 1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risso, C. Benefits of demands control in a smart-grid to compensate the volatility of non-conventional energies. Rev. Fac. Ing. 2019, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Njuguna Matheri, A.; Mbohwa, C.; Ntuli, F.; Belaid, M.; Seodigeng, T.; Catherine Ngila, J.; Kinuthia Njenga, C. Waste to energy bio-digester selection and design model for the organic fraction of municipal solid waste. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 82, 1113–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chui, K.T.; Lytras, M.D.; Visvizi, A. Energy sustainability in smart cities: Artificial intelligence, smart monitoring, and optimization of energy consumption. Energies 2018, 11, 2869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashfaq, A.; Ianakiev, A. Cost-minimised design of a highly renewable heating network for fossil-free future. Energy 2018, 152, 613–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laiola, E.; Giungato, P. Wind characterization in Taranto city as a basis for innovative sustainable urban development. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 172, 3535–3545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rekik, M.; Chtourou, Z.; Mitton, N.; Atieh, A. Geographic routing protocol for the deployment of virtual power plant within the smart grid. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2016, 25, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Paz, J.F.; Bajo, J.; Rodríguez, S.; Villarrubia, G.; Corchado, J.M. Intelligent system for lighting control in smart cities. Inf. Sci. 2016, 372, 241–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peña, M.; Biscarri, F.; Guerrero, J.I.; Monedero, I.; León, C. Rule-based system to detect energy efficiency anomalies in smart buildings, a data mining approach. Expert Syst. Appl. 2016, 56, 242–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Deng, Y.; Yang, Q.; Sun, J. An Energy-Efficient Train Control Framework for Smart Railway Transportation. IEEE Trans. Comput. 2016, 65, 1407–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sȩdziwy, A.; Kotulski, L. Towards highly energy-efficient roadway lighting. Energies 2016, 9, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lützenberger, M.; Masuch, N.; Küster, T.; Freund, D.; Voß, M.; Hrabia, C.E.; Pozo, D.; Fähndrich, J.; Trollmann, F.; Keiser, J.; et al. A common approach to intelligent energy and mobility services in a smart city environment. J. Ambient Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 2015, 6, 337–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, C.; Manyà, F.; Mateu, C.; Sole-Mauri, F. Modeling energy consumption in automated vacuum waste collection systems. Environ. Model. Softw. 2014, 56, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.J.; Lee, J.; Kim, S.B.; Hyun, J.S.; Park, G.L. Spatio-temporal correlation analysis of wind speed and sunlight for predicting power generation in Jeju. Int. J. Multimed. Ubiquitous Eng. 2013, 8, 273–282. [Google Scholar]
- Riaz, M.; Farid, H.M.A.; Jana, C.; Pal, M.; Sarkar, B. Efficient city supply chain management through spherical fuzzy dynamic multistage decision analysis. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2023, 126, 106712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guchhait, R.; Sarkar, B. Increasing Growth of Renewable Energy: A State of Art. Energies 2023, 16, 2665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












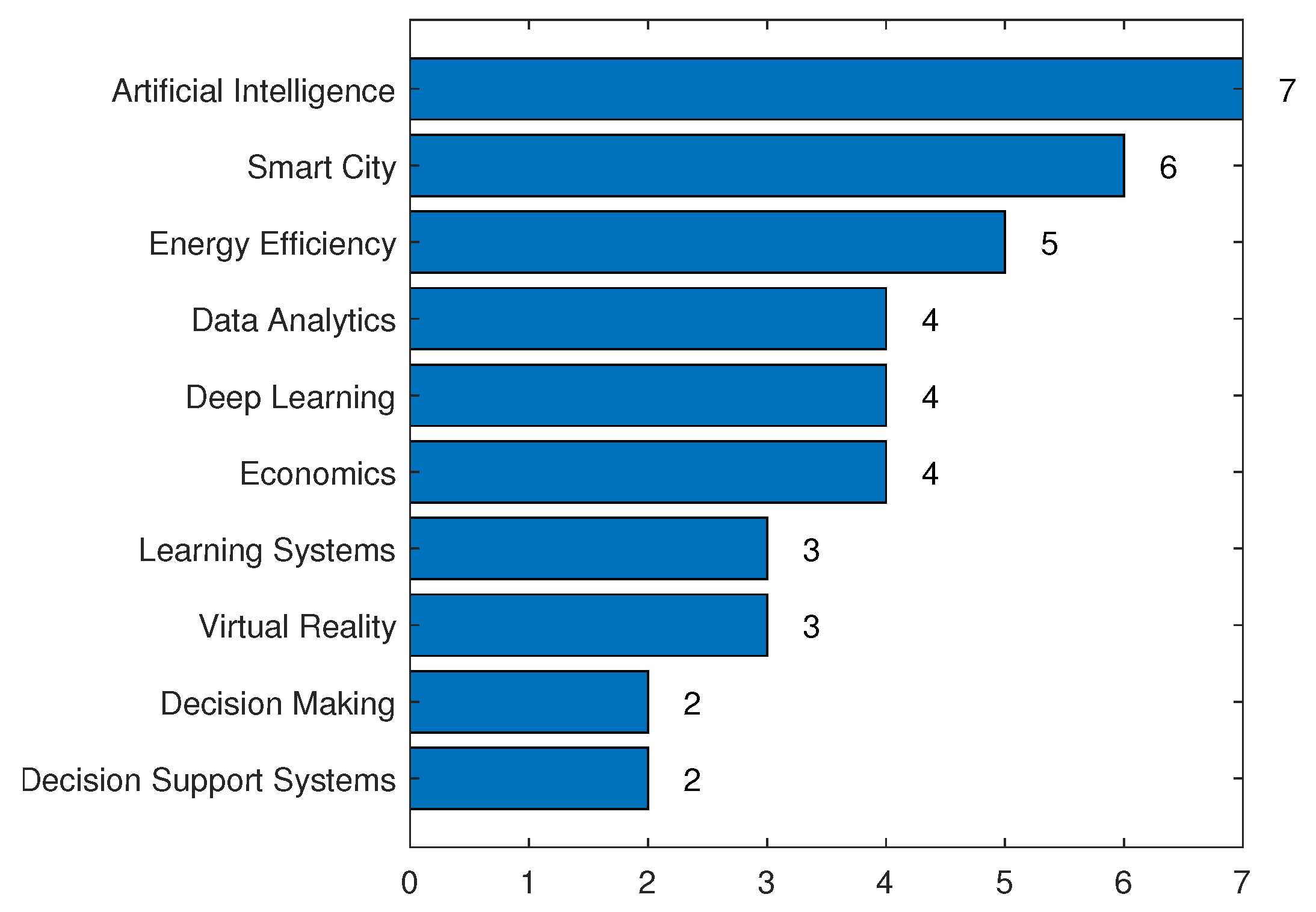




| Rank | Publisher | No. of Articles |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Sustainable Cities and Society | 4 |
| 2 | IEEE Access | 3 |
| 3 | Sensors | 3 |
| 4 | Applied Sciences | 2 |
| 5 | IET Smart Cities | 2 |
| Authors, Year | Title | Citations | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ghadami N. et al. [2021] [10] | Implementation of solar energy in Smart Cities using an integration of artificial neural network, photovoltaic system, and classical Delphi methods | 75 | Sustainable Cities and Society |
| Serban AC. et al. [2020] [11] | Artificial Intelligence for smart renewable energy sector in Europe—smart energy infrastructures for next-generation Smart Cities | 66 | IEEE Access |
| Azzaoui AE, [2020] [12] | Block5GIntell: Blockchain for AI-enabled 5G networks | 55 | IEEE Access |
| Lee YL, [2021] [13] | 6G massive radio access networks: Key applications, requirements and challenges | 52 | IEEE Open Journal of Vehicular Technology |
| Zhang, N., [2016] [14] | Semantic framework of Internet of Things for Smart Cities: Case studies | 47 | Sensors |
| Rank | Publisher | No. of Articles |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Energy | 6 |
| 2 | Renewable Energy | 4 |
| 3 | Energies | 3 |
| 4 | Energy Reports | 3 |
| 5 | Applied Energy | 2 |
| Authors, Year | Title | Citations | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ramli Mam et al. [2018] [15] | Optimal sizing of PV/wind/diesel hybrid microgrid system using multi-objective self-adaptive differential evolution algorithm | 345 | Renewable Energy |
| Yang D. et al. [2013] [16] | Solar irradiance forecasting using spatial–temporal covariance structures and time-forward kriging | 121 | Renewable Energy |
| Oldenbroek V, et al. [2017] [17] | Fuel cell electric vehicle as a power plant: Fully renewable integrated transport and energy system design and analysis for Smart City areas | 76 | International Journal of Hydrogen Energy |
| De Luca G. et al. [2018] [18] | A renewable energy system for a nearly zero greenhouse city: Case study of a small city in southern Italy | 51 | Energy |
| Soliman Ms et al. [2021] [11] | Supervisory energy management of a hybrid battery/PV/tidal/wind sources integrated into a DC-microgrid energy storage system | 42 | Energy Reports |
| Rank | Publisher | No. of Articles |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | IEEE Access | 3 |
| 2 | Sustainable Cities and Society | 3 |
| 3 | Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing | 3 |
| 4 | Sustainability | 2 |
| 5 | Computer Communications | 1 |
| Authors, Year | Title | Citations | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ullah N. et al. [2020] [3] | Applications of Artificial Intelligence and Machine learning in Smart Cities | 258 | Computer Communications |
| Serrano W. et al. [2018] [4] | Digital systems in Smart Cities and infrastructure | 66 | Smart Cities |
| Aguilar J. et al. [2021] [19] | A systematic literature review on the use of Artificial Intelligence in energy self-management in smart buildings. | 53 | Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews |
| Sharma H, [2021] [20] | Machine learning in wireless sensor networks for Smart Cities: a survey. | 52 | Electronics |
| Khan N., [2021] [21] | DB-Net: A novel dilated CNN-based multi-step forecasting model for power consumption in integrated local energy systems. | 50 | International Journal of Electrical Power |
| Rank | Publisher | No. of Articles |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Sustainability | 4 |
| 2 | Applied Sciences | 3 |
| 3 | Energy and Buildings | 2 |
| 4 | Energy | 1 |
| 5 | Future Generation Computer Systems | 1 |
| Authors, Year | Title | Citations | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Le L.T. et al. [2019] [22] | A comparative study of PSO-ANN, GA-ANN, ICA-ANN, and ABC-ANN in estimating the heating load of buildings’ energy efficiency for Smart City planning | 182 | Applied Sciences |
| Idowu S. et al. [2016] [23] | Applied machine learning: Forecasting heat load in district heating system | 152 | Energy and Buildings |
| Zhou Z. et al. [2019] [24] | Blockchain and computational intelligence inspired incentive-compatible demand response in internet of electric vehicles | 91 | IEEE Transactions on Emerging Topics in Computational Intelligence |
| Le L.T, [2019] [25] | Estimating the heating load of buildings for Smart City planning using a novel Artificial Intelligence technique PSO-XGBoost. | 71 | Applied Sciences |
| Ingwersen, P., [2018] [26] | Smart City research 1990–2016. | 36 | Scientometrics |
| Rank | Publisher | No. of Articles |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | IEEE Access | 9 |
| 2 | Sustainable Cities and Society | 9 |
| 3 | Sustainability | 6 |
| 4 | Energies | 5 |
| 5 | Sensors | 5 |
| Authors, Year | Title | Citations | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rahman A., [2018] [27] * | Predicting electricity consumption for commercial and residential buildings using deep Recurrent Neural Networks | 423 | Applied Energies |
| Ullah, Z., [2020] [28] | Applications of Artificial Intelligence and machine learning in Smart Cities | 258 | Computer Communications |
| Alsamhi, S. [2019] [29] | Survey on collaborative smart drones and Internet of Things for improving smartness of Smart Cities | 195 | IEEE Access |
| Vázquez-Canteli, J. R., [2019] [30] | Fusing TensorFlow with building energy simulation for intelligent energy management in Smart Cities | 113 | Sustainable Cities and Society |
| Area of Application | Author(s) | Year | Category | Method | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Generation | Miyasawa A. et al. [31] | 2023 | Demand forecasting | Smart metering, nonparametric regression models. | IET Smart Cities |
| Generation | Shafiullah M. et al. [32] | 2023 | Energy Systems | Artificial Intelligence, IoT | Smart Cities |
| Generation | Wu Z. et al. [33] | 2023 | Wind power forecasting | Probabilistic Physics-informed AI for completing dataset caused by ocassional shutdwon | CMES—Computer Modeling in Engineering and Sciences |
| Transmission | Fakhar A. et al. [34] | 2023 | Smart Grids with Renewable Energy | Cloud Computing, IoT, Blockchain | International Journal of Green Energy |
| Consumption | Bayer D. and Pruckner M. [35] | 2023 | Energy Systems in Buildings | Digital Twin | Energy Informatics |
| Consumption | Alymani M. et al. [36] | 2023 | Forecasting energy consumption | Stacked Autoencoder (SAE), Deep Neural Network (DNN), Bidirectional Long Short-Term Memory (BiLSTM) | Sustainable Energy Technologies and Assessments |
| Consumption | Al-Habaibeh A. et al. [37] | 2023 | Estimate crowds in cities | Internet of Things (IoT) | Ain Shams Engineering Journal |
| Consumption | Selvaraj R. et al. [38] | 2023 | Energy consumption management | Artifitial Intelligence Technique for Monitoring Systems in Smart Buildings (AIMS-SB) | Sustainable Energy Technologies and Assessments |
| Consumption | Feng Y. et al. [39] | 2023 | Energy Saving | Reinforcement Learning | IEEE Access |
| Consumption | Jiang R. et al. [40] | 2023 | Demand Prediction | Deep-chain echo state network (DCESN) | IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics |
| Consumption | AlHajri I. et al. [41] | 2023 | Urban Planning | Long-Short Term memory networks | Energy |
| Renewables | Fantin Irudaya Raj E. et al. [42] | 2023 | Wind turbines in smart cities | Structural, modal, and harmonic analyses performed using ANSYS | MRS Energy and Sustainability |
| Generation | Khan N. et al. [43] | 2023 | Power Generation Forecasting | Multi-Head Attention (MHA)-based deep Autoencoder(AE) with Extreme Gradient Boosting (XBG) algorithm | IEEE Internet of Things Journal |
| Renewables | Ulpiani G. et al. [44] | 2023 | Renewable energy in high GHG’s emitting sectors in cities | Social and Political analysis | Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews |
| Renewables | Kedir N. et al. [45] | 2023 | Solar/PV Systems | Fuzzy Hybrid Methods | Energies |
| Consumption | Icaza-Alvarez D. et al. [46] | 2023 | Estimation on the power demand | Energy Plan tool | Energy Reports |
| Generation | Moon J. et al. [47] | 2022 | Electrical load forecasting | Explainable Electrical Load Forecasting (XELF) Methodology | Sustainable Energy Technologies and Assessments |
| Transmission | Said D. [48] | 2022 | Demand-Side Management | Big data, Blockchain, Machine learning (ML), IoT | IEEE Engineering Management Review |
| Generation | Heidari A. et al. [49] | 2022 | Smart cities power and energy management | Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) | Sustainable Cities and Society |
| Generation | Chang E.-C. et al. [50] | 2022 | PV tracking and control | Finite Time Terminal Attractor (FFTA) | Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing |
| Transmission | Liu Z. et al. [51] | 2022 | Smart Power Grids, Power Systems | Machine learning (ML) | Energy Reports |
| Transmission | Khosrojerdi F. et al. [52] | 2022 | Smart Grid | Artificial Intelligence Analytics (AIA) | International Journal of Energy Sector Management |
| Consumption | Chavhan S. et al. [53] | 2022 | Energy-efficient transport | AI-IoT System | ACM Transactions on Internet Technology |
| Consumption | Al-Hawawreh M. et al. [54] | 2022 | Smart decision making | Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) | IEEE Sensors Journal |
| Consumption | Singh S. et al. [55] | 2022 | Clustering for Wireless Sensors Networks | Improved gray wolf optimization (IGWO) | Sensors |
| Consumption | Huang J. et al. [56] | 2022 | Building energy forecast | Three ML algorithms (SVR, XGBoost, and LSTM) | Applied Sciences |
| Consumption | Mohamed H. et al. [57] | 2022 | Reduce energy consumption | TOPSIS fuzzy | Electronics |
| Consumption | Ren Y. et al. [58] | 2022 | Data management in energy consumption | Quantum-inspired Reinforcement Learning (QRL) | IEEE Transactions on Green Communications and Networking |
| Consumption | Murthy Nimmagadda S. and Harish K.S. [59] | 2022 | Building smart cities | Internet of Things (IoT), Connectivity, Cloud computing and AI | Multimedia Tools and Applications |
| Consumption | Islam N. et al. [60] | 2022 | Data management | Secured protocol with collaborative learning for IoT using AI techniques | Sustainability |
| Consumption | Zamponi M.E. and Barbierato E. [61] | 2022 | Forecast energy consumption | Different AI algorithms | Smart Cities |
| Consumption | Naveed Q.N. et al. [62] | 2022 | Transportation data management | Improved phase timing optimization (IPTO) | Sensors |
| Consumption | Akkad M.Z. et al. [63] | 2022 | Energy consumption and emissions | IoT, Smart bins, multi-percentage sensors | Designs |
| Consumption | Garlik B. [64] | 2022 | Energy consumption reduction in buildings | Artificial Intelligence with IoT | Applied Sciences |
| Consumption | Saba D. et al. [65] | 2022 | Smart home electricity management | Decision-making tool (IRRHEM) | Applied Sciences |
| Consumption | Zaimen K. et al. [66] | 2022 | Wireless Sensor Networks | Generic algorithm, particle swarm optimization, flower pollination, and ant colony optimization | IEEE Access |
| Consumption | Serrano W. [67] | 2022 | Smart Buildings | Neural networks with deep learning structure | Neural Computing and Applications |
| Renewables | Li J. et al. [68] | 2022 | Hydrogen production and conversion | Fuzzy Methods | Sustainable Cities and Society |
| Renewables | Doosti R. et al. [69] | 2022 | Industrial Building renewable energy | CPLEX Solver | IET Smart Cities |
| Renewables | Vyas M. et al. [70] | 2022 | Urban Space Utilization | Use of PV Trees on urban areas | Renewable Energy |
| Renewables | AlHammadi A. et al. [71] | 2022 | Hybrid renewable systems for vehicle charging | Hybrid Optimization of Multiple Energy Resources | Energies |
| Renewables | Balabel A. et al. [72] | 2022 | Solar energy in building sectors | Solatube technology analysis | Alexandria Engineering Journal |
| Renewables | Nuvvula R.S.S. et al. [73] | 2022 | Optimal configuration of PV and wind conversion system | Particle Swarm Optimization | Sustainable Energy Technologies and Assessments |
| Renewables | Ponce P. et al. [74] | 2022 | Solar/PV Systems | Fuzzy TOPSIS | Energies |
| Generation | Konhäuser W. [75] | 2021 | Local energy generation | Blockchain Technology (BCT) | Wireless Personal Communications |
| Generation | Pérez-Romero Á. et al. [76] | 2021 | Operation and Maintenance of PV plants | Five AI-based models | Applied Sciences |
| Generation | Zhou H. et al. [77] | 2021 | PV energy generation forecasting | Hybrid Deep Learning | Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing |
| Generation | Saini G.S. et al. [78] | 2021 | Resource Management | Fuzzy Logic | Recent Advances in Computer Science and Communications |
| Transmission | Antonopoulos I. et al. [79] | 2021 | Smart Grid Smart City (SGSC) project | Energy Demand Response Modeling | Energy and AI |
| Distribution | Wang K. et al. [2] | 2021 | Decision making in Smart Cities | IoT and Artificial Intelligence | Sustainability |
| Distribution | Calamaro N. et al. [80] | 2021 | Energy losses detection | Energy fraud detection algorithm | Sustainability |
| Consumption | Manman L. et al. [81] | 2021 | Energy efficiency | Distributed Artificial Intelligence (DAI) | Sustainable Cities and Society |
| Consumption | Li J. et al. [82] | 2021 | Decision Support Systems | Internet of Things (IoT) | Computers and Industrial Engineering |
| Consumption | Ghadami N. et al. [10] | 2021 | Forecast energy consumption | Artificial Neural Network (ANN) | Sustainable Cities and Society |
| Consumption | Cirella G.T. et al. [83] | 2021 | Smart Electricity | Different AI algorithms | Energies |
| Consumption | Hu Y.-C. et al. [84] | 2021 | Energy decomposition in smart meter | Neuro-fuzzy classifier | Processes |
| Consumption | Mahmood D. et al. [85] | 2021 | Energy Management | Demand Side Management (DSM) | International Journal of Advanced and Applied Sciences |
| Consumption | Wang X. et al. [86] | 2021 | Energy consumption of ac-grid system | Fuzzy Logic | Journal of Intelligent and Fuzzy Systems |
| Generation | Kanase-Patil A.B. et al. [87] | 2020 | Power generation in Smart City | Different AI algorithms | Environmental Technology Reviews |
| Generation | Serban A.C. and Lytras M.D. [11] | 2020 | Renewable Energy in Smart Cities | Different AI algorithms | IEEE Access |
| Generation | Jiang Y. et al. [88] | 2020 | Improvement of Urban Development | IoT | IEEE Access |
| Transmission | Cheng Y. et al. [89] | 2020 | Demand Forecasting | Neural Network | IET Smart Cities |
| Transmission | Ullah Z. et al. [3] | 2020 | Energy Efficiency of Smart Grids | Machine learning (ML), Deep Reinforcement Learning | Computer Communications |
| Distribution | Loose N. et al. [90] | 2020 | Smart grids, energy networks | Unified energy agent | Sustainability |
| Distribution | Fattahi J. et al. [91] | 2020 | Financial Resources | Distributed Energy Management System (DERMS) | Sustainable Cities and Society |
| Consumption | Sharma S. [92] | 2020 | Infrastructure | Smart vs Intelligent comparison | International Journal of Advanced Research in Engineering and Technology |
| Consumption | Marinakis V. et al. [93] | 2020 | Energy consumption reduction | Novel framework with reward schemes | Sensors |
| Consumption | Ullah A. et al. [28] | 2020 | Energy consumption prediction | Clustering based analysis | Sensors |
| Consumption | Shah A.S. et al. [94] | 2020 | Energy consumption in smart buildings | Bat algorithm, fuzzy logic | IEEE Access |
| Consumption | Azzaoui A.E. et al. [12] | 2020 | Energy saving | Blockchain and AI | IEEE Access |
| Consumption | Guo Y. et al. [95] | 2020 | Minimizing cost of energy consumption | Ant colony optimization (ACO) | IEEE Access |
| Consumption | Zhuang H. et al. [96] | 2020 | Building energy management | ANN and Fuzzy Logic Controller | Environmental Modeling and Software |
| Renewables | Algieri A. et. al. [97] | 2020 | Biofuel Rankine Cycle combined with Renewable sources | Multivariable optimization | Energies |
| Renewables | Kumar D. [98] | 2020 | Urban energy system | Simulation of hybrid urban renewable energy systems | Energy Exploration and Exploitation |
| Generation | Aghajani D. et al. [99] | 2019 | Wind Turbines Monitoring | Geographic information system and RETSCREEN software | International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology |
| Generation | Oun A. et al. [100] | 2019 | Energy rationalization of a steel plant | AI, Smart Metering (SM), Automated Decision Making (ADM) | International Journal of Advanced Computer Science and Applications |
| Consumption | Salehi H. et al. [101] | 2019 | Structural Health Monitoring Energy Consumption | Data mining with pattern recognition, an innovative probabilistic approach, and machine learning | Expert Systems with Applications |
| Consumption | Dong Y. et al. [102] | 2019 | Energy consumption management | Fairness cooperation algorithm (FCA) | IEEE Internet of Things Journal |
| Consumption | Krayem A. et al. [103] | 2019 | Energy consumption prediction | Archetypal classification | Energy and Buildings |
| Consumption | Marin-Perez R. et al. [104] | 2019 | Energy consumption improvement | PLUG-N-HARVEST architecture | Sensors |
| Consumption | Vázquez-Canteli J.R. et al. [30] | 2019 | Energy saving and demand response | Advanced machine learning algorithms | Sustainable Cities and Society |
| Consumption | Aymen F. and Mahmoudi‘ C. [105] | 2019 | Electric Vehicles energy | Support vector classification | Energies |
| Renewables | Khoury D. and Keyrouz F. [106] | 2019 | Wind and Solar power forecasting | Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) | WSEAS Transactions on Power Systems |
| Consumption | Alhussein M. et al. [107] | 2019 | Microgrid energy management | Deep learning model | Energies |
| Consumption | Risso C. [108] | 2019 | Energy demand control | Combinatorial optimization dispatch models | Revista Facultad de Ingeniería |
| Generation | Njuguna Matheri A. et al. [109] | 2018 | Waste quantification for biofuel | Simple Multi Attribute Rating (SMART) of Multiple Criteria Decision Analysis (MCDA) | Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews |
| Transmission | Serrano W. [4] | 2018 | Digital Systems, Transmission Networks | Digital as a Service (DaaS), IoT, Blockchain, Virtual Reality | Smart Cities |
| Consumption | Chui K.T. et al. [110] | 2018 | Electricity consumption | Hybrid genetic algorithm support vector machine kernel learning approach (GA-SVM-MKL) | Energies |
| Consumption | Rahman A. et al. [27] | 2018 | Medium-long term energy predictions | Recurrent Neural Network (RNN) | Applied Energy |
| Renewables | Ramli M.A.M. et al. [27] | 2018 | Microgrid Systems | Multi-Objective Self-Adaptive Different Evolution (MOSaDE) algorithm | Renewable Energy |
| Renewables | Ashfaq A. and Ianakiev A. [111] | 2018 | Technical and cost design to decarbonize the heating network | Large Scale heat pump and thermal heat storage | Energy |
| Generation | Laiola E. and Giungato P. [112] | 2018 | Wind characterization | Statistical methods used for meteorological and economic data | Journal of Cleaner Production |
| Renewables | Oldebroek V. et al. [17] | 2017 | Fully Renewable integrated transport | An energy balance and cost analysis | International Journal of Hydrogen Energy |
| Transmission | Rekik M. et al. [113] | 2016 | Smart Grid | Ant Colony Optimization (ACO) | Sustainable Cities and Society |
| Consumption | De Paz J.F. et al. [114] | 2016 | Optimization of energy consumption and cost | Artificial neural networks (ANN), multi-agent systems (MAS) | Information Sciences |
| Consumption | Peña M. et al. [115] | 2016 | Energy inefficiencies detection in smart buildings. | Data mining | Expert Systems with Applications |
| Consumption | Huang J. et al. [116] | 2016 | Energy consumption of train | Decision tree, data mining | IEEE Transactions on Computers |
| Consumption | Sȩdziwy A. and Kotulski L. [117] | 2016 | Lighting system energy consumption | Dynamic street lighting control | Energies |
| Transmission | Lützenberger M. et al. [118] | 2015 | Energy in Smart Cities | Distributed Artificial Intelligence Laboratory | Journal of Ambient Intelligence and Humanized Computing |
| Consumption | Fernández C. et al. [119] | 2014 | Energy consumption modeling | Automated vacuum waste collection (AVWC) | Sustainability |
| Consumption | Yang D. et al. [16] | 2013 | Solar irradiance forecasting | Time-Forward kriging | Renewable Energy |
| Generation | Park C.J. et al. [120] | 2013 | Forecasting of renewable energy | Spatio-Temporal correlation | International Journal of Multimedia and Ubiquitous Engineering |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Camacho, J.d.J.; Aguirre, B.; Ponce, P.; Anthony, B.; Molina, A. Leveraging Artificial Intelligence to Bolster the Energy Sector in Smart Cities: A Literature Review. Energies 2024, 17, 353. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17020353
Camacho JdJ, Aguirre B, Ponce P, Anthony B, Molina A. Leveraging Artificial Intelligence to Bolster the Energy Sector in Smart Cities: A Literature Review. Energies. 2024; 17(2):353. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17020353
Chicago/Turabian StyleCamacho, José de Jesús, Bernabé Aguirre, Pedro Ponce, Brian Anthony, and Arturo Molina. 2024. "Leveraging Artificial Intelligence to Bolster the Energy Sector in Smart Cities: A Literature Review" Energies 17, no. 2: 353. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17020353
APA StyleCamacho, J. d. J., Aguirre, B., Ponce, P., Anthony, B., & Molina, A. (2024). Leveraging Artificial Intelligence to Bolster the Energy Sector in Smart Cities: A Literature Review. Energies, 17(2), 353. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17020353








