Novel Burst-Mode Control for Medium-to-Light Load Operation of Dual-Active-Bridge Converters, Achieving Minimum Backflow Power, Zero-Voltage-Switching, and DC Bias Suppression
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- No additional components are needed for efficiency improvement under light-load conditions.
- Complete ZVS condition is considered for optimal operation of burst-mode and ZVS is achieved for entire load range.
- Backflow power is minimized at the light-load condition.
- DC bias current elimination is applied for the burst-mode.
- A mode switching algorithm between the burst-mode and normal-mode is proposed.
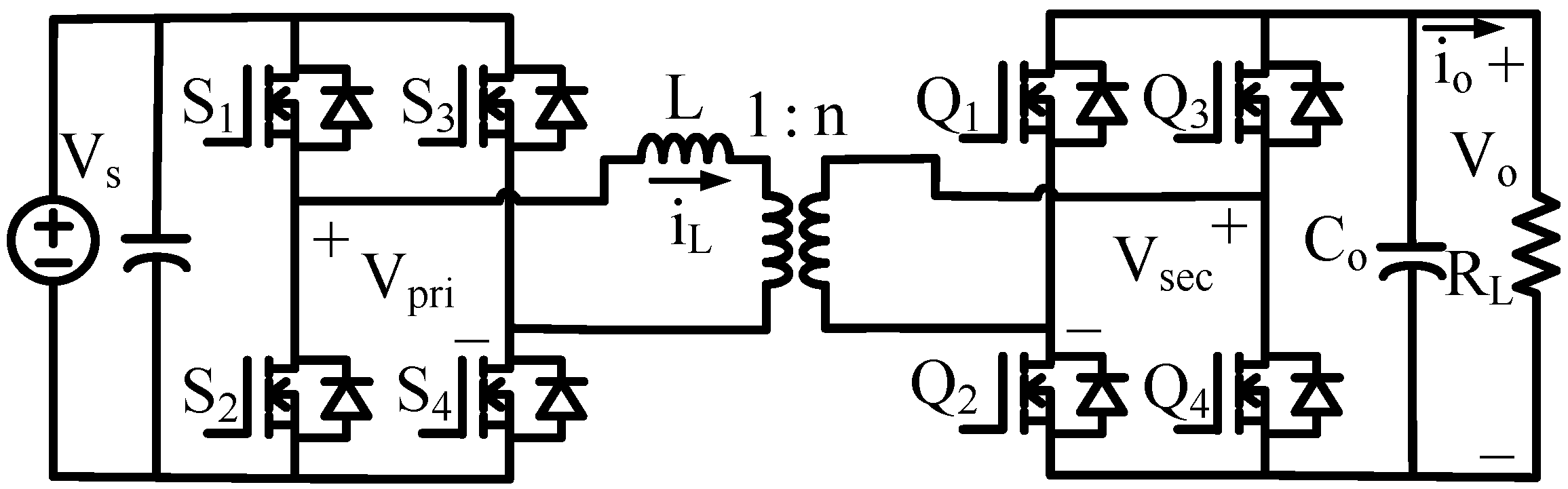
2. Operation of the Isolated DAB Converter
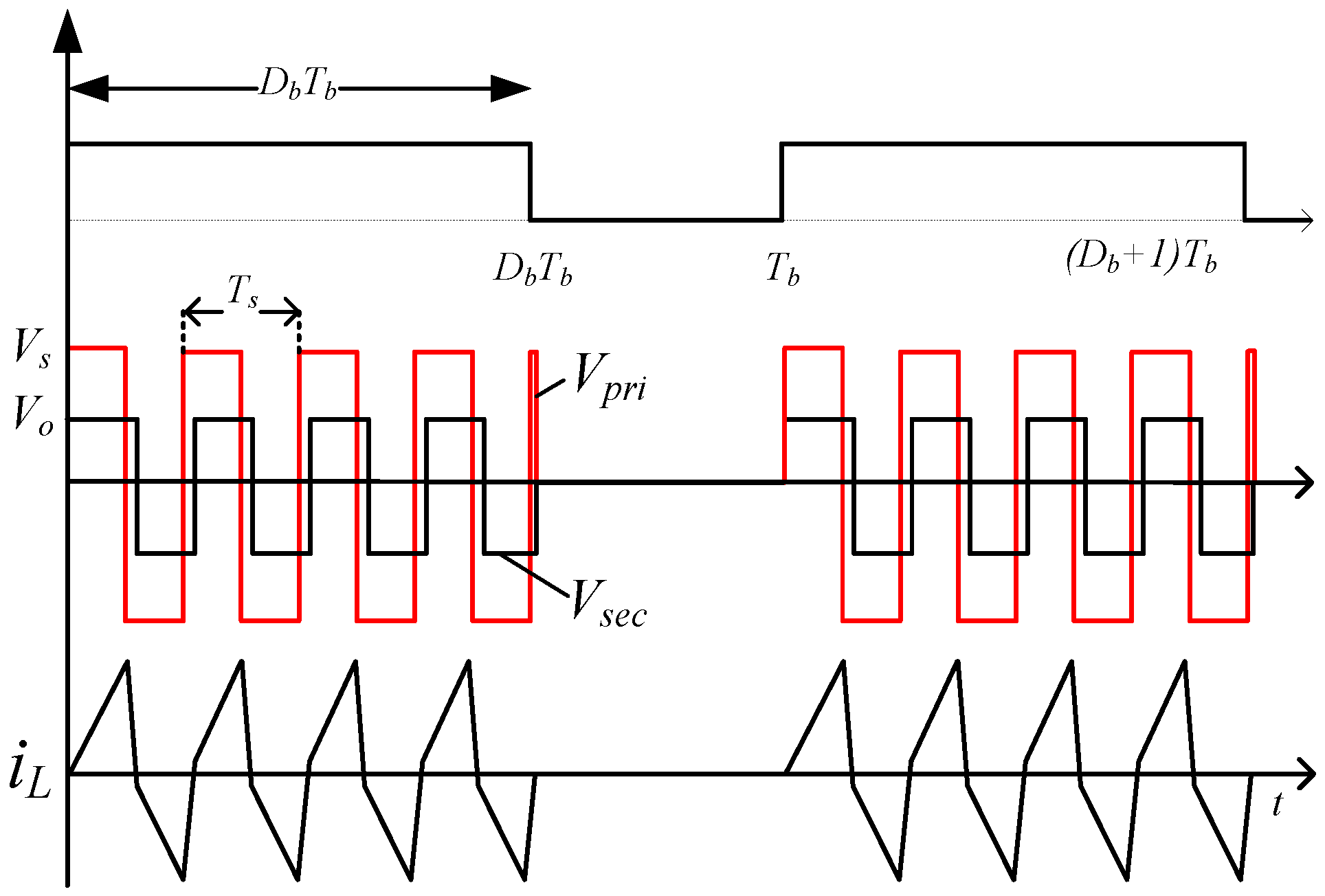
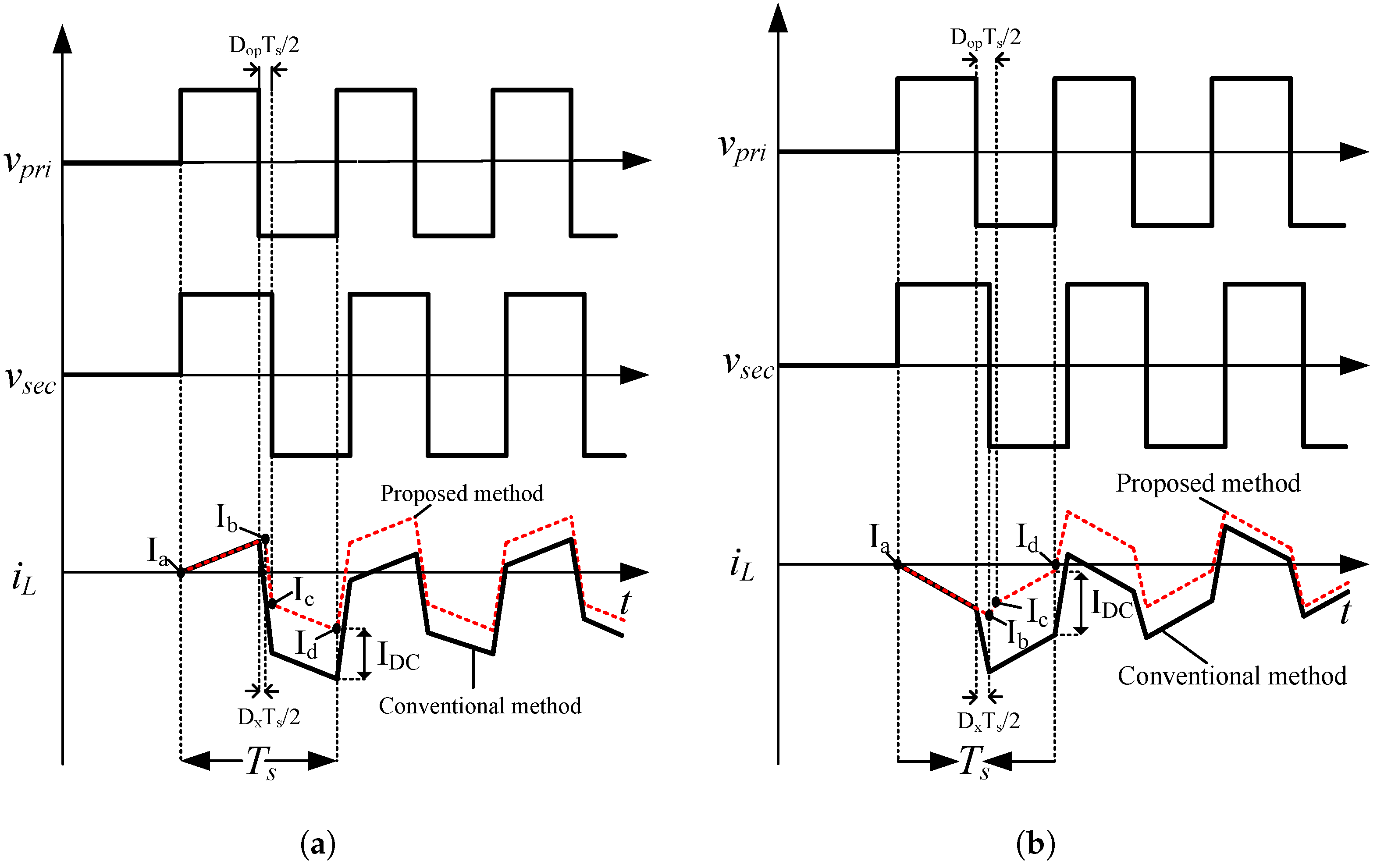
3. Proposed Burst-Mode
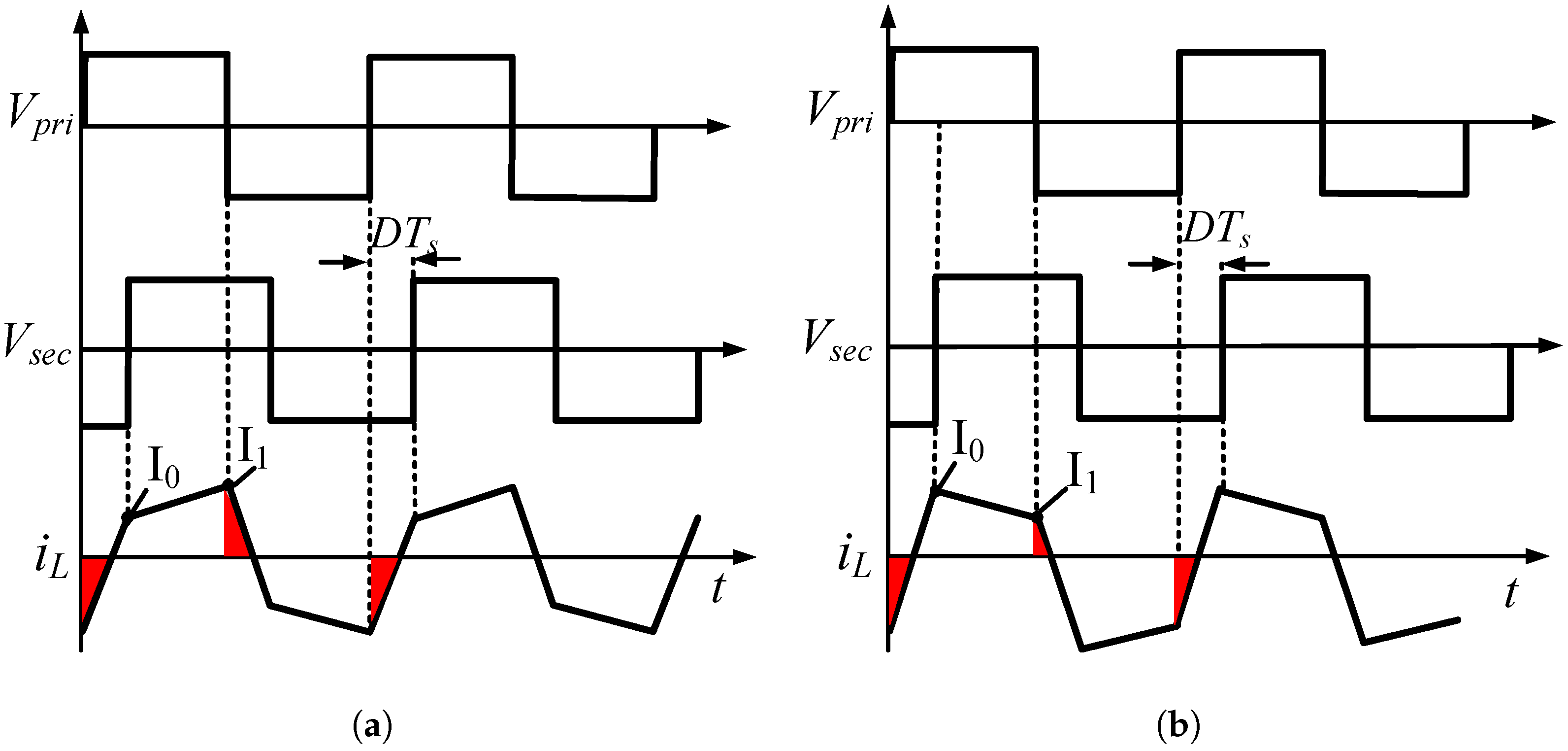
3.1. Burst-Mode Operation
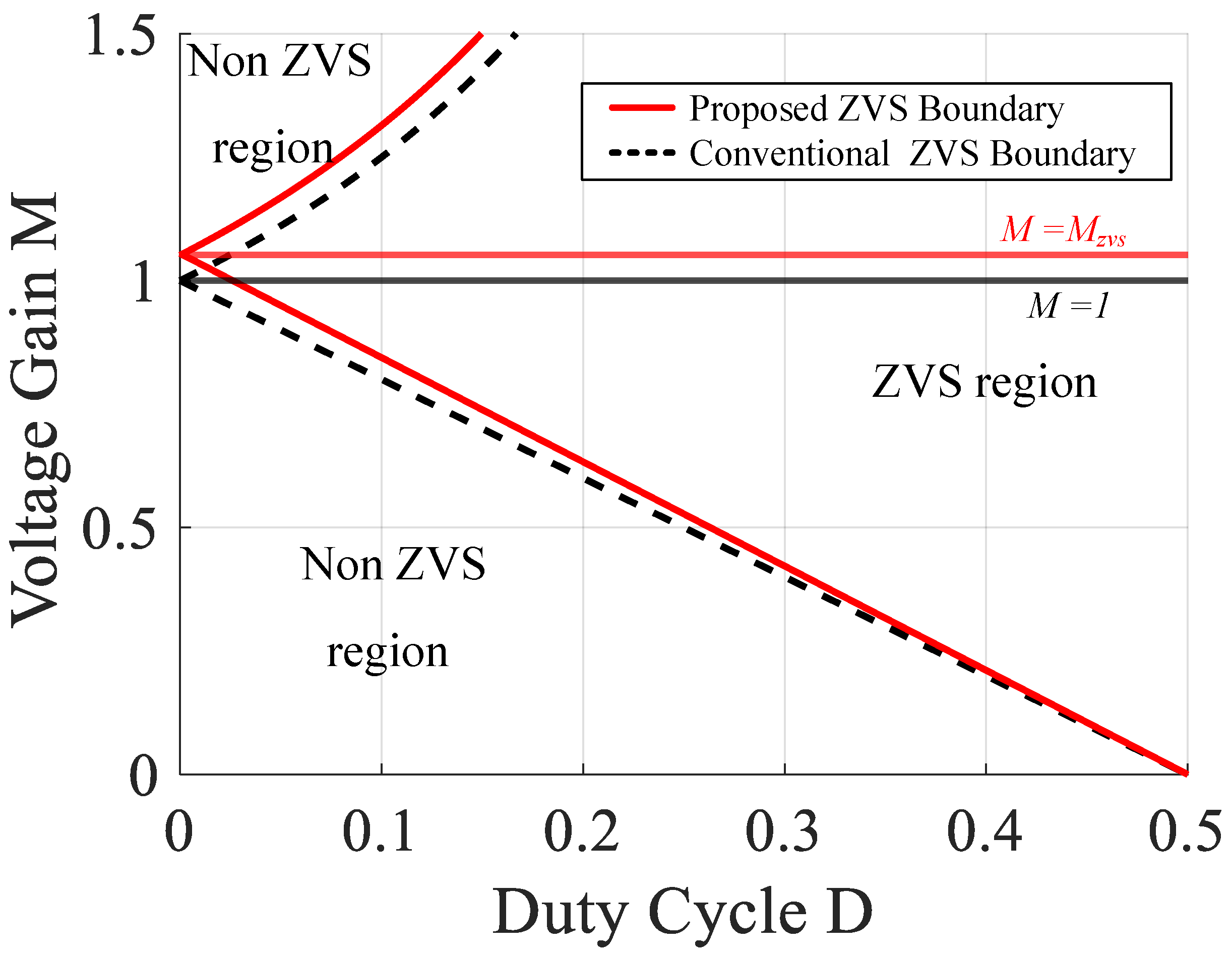
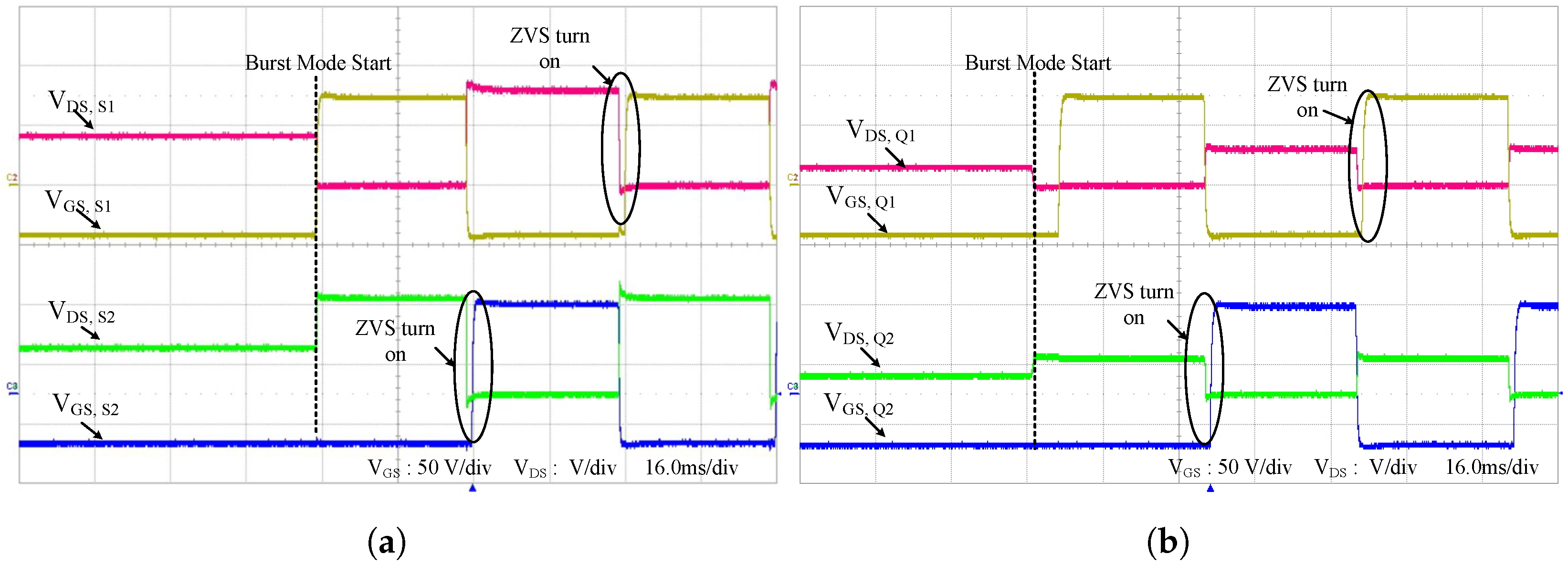
3.2. ZVS Condition
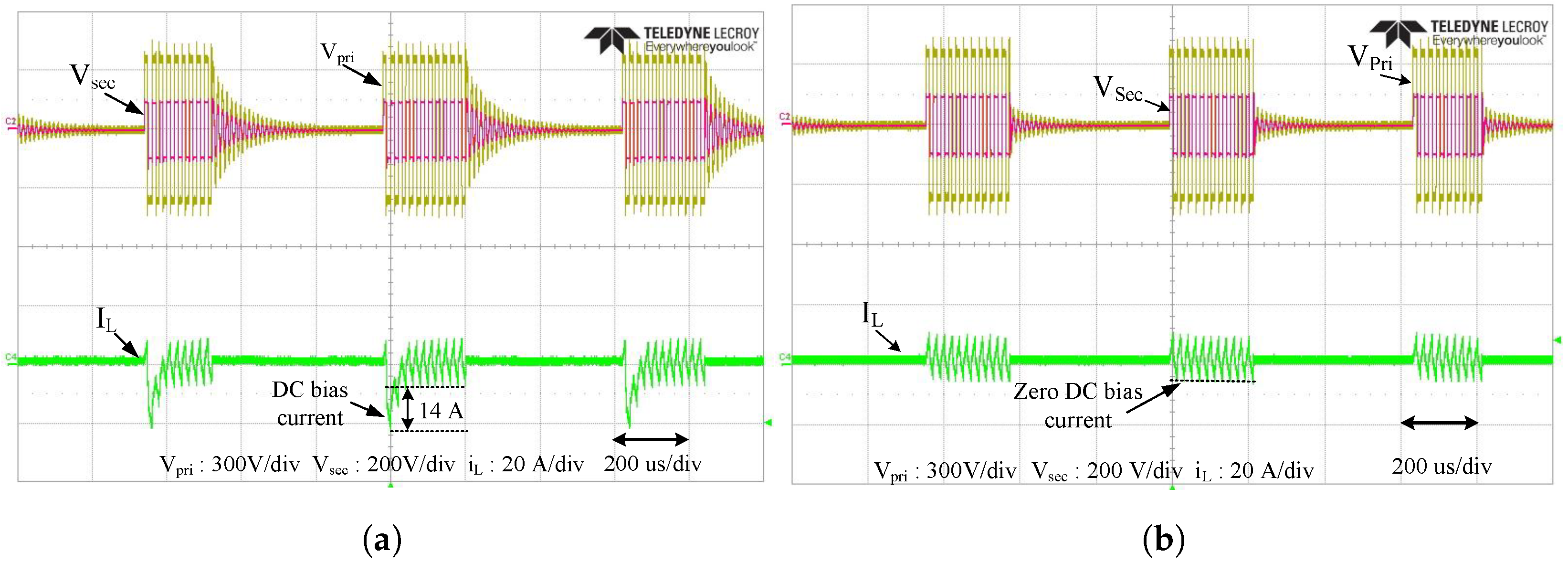
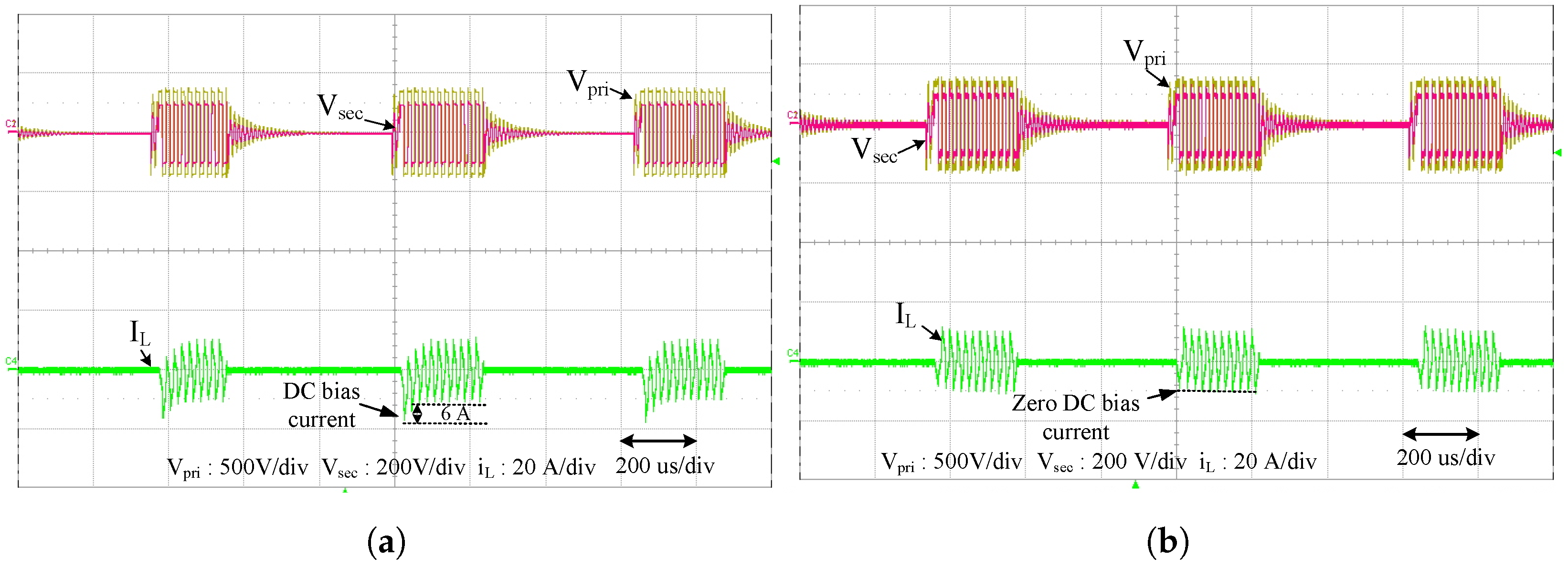
3.3. DC Bias Elimination
4. Design Procedure
- Step 1:
- The initial system parameters such as , , , , and are given by the system requirement.
- Step 2:
- The value of inductance L can be calculated by (3).
- Step 3:
- Step 4:
- The critical load resistance value is calculated by (25).
- Step 5:
- Output capacitor value is calculated by (26).
- Step 6:
- The value of series inductance L should be satisfied by (23). If it is not satisfied, then the design procedure is repeated from Step 3. If the condition is met, the design procedure is finished.
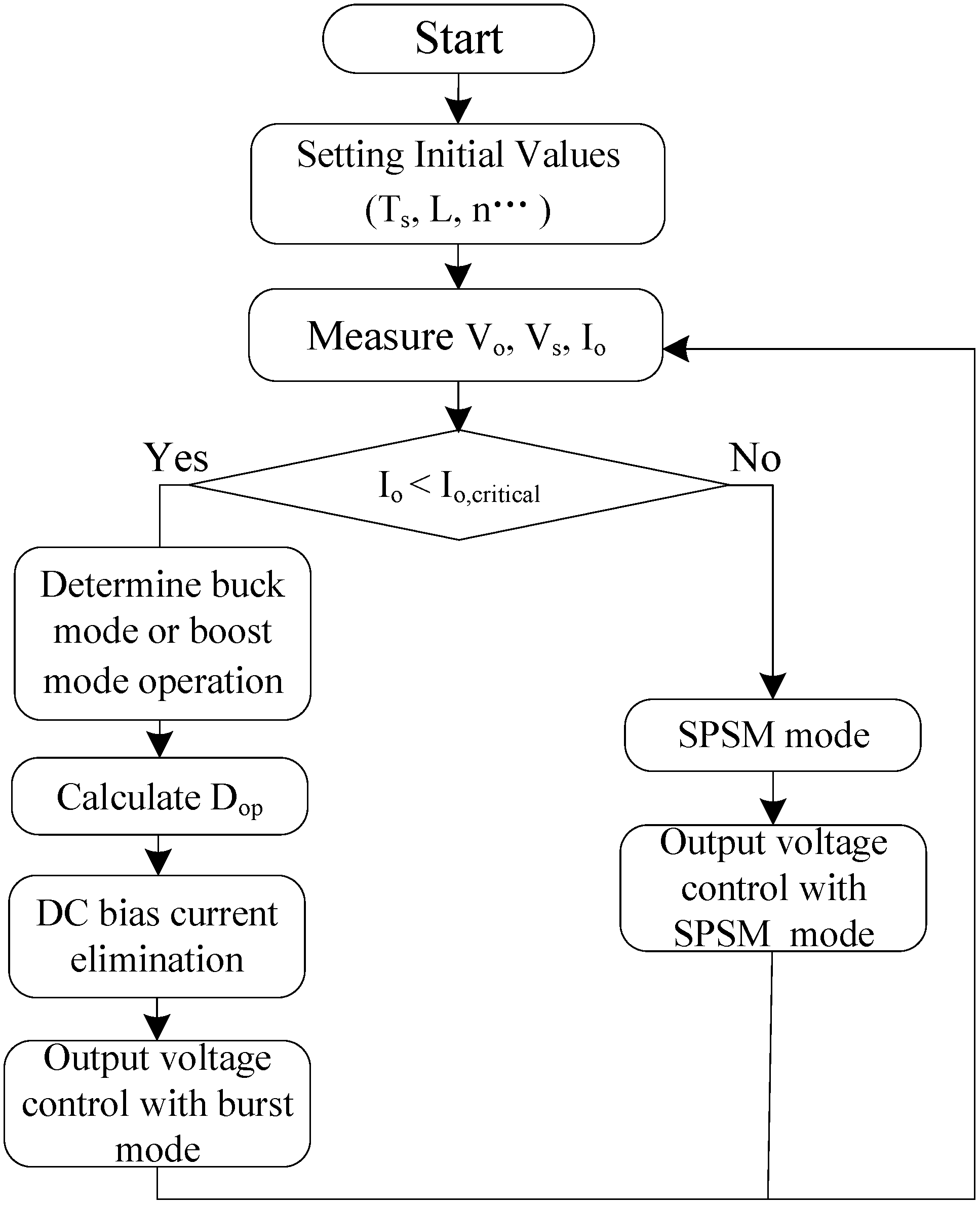
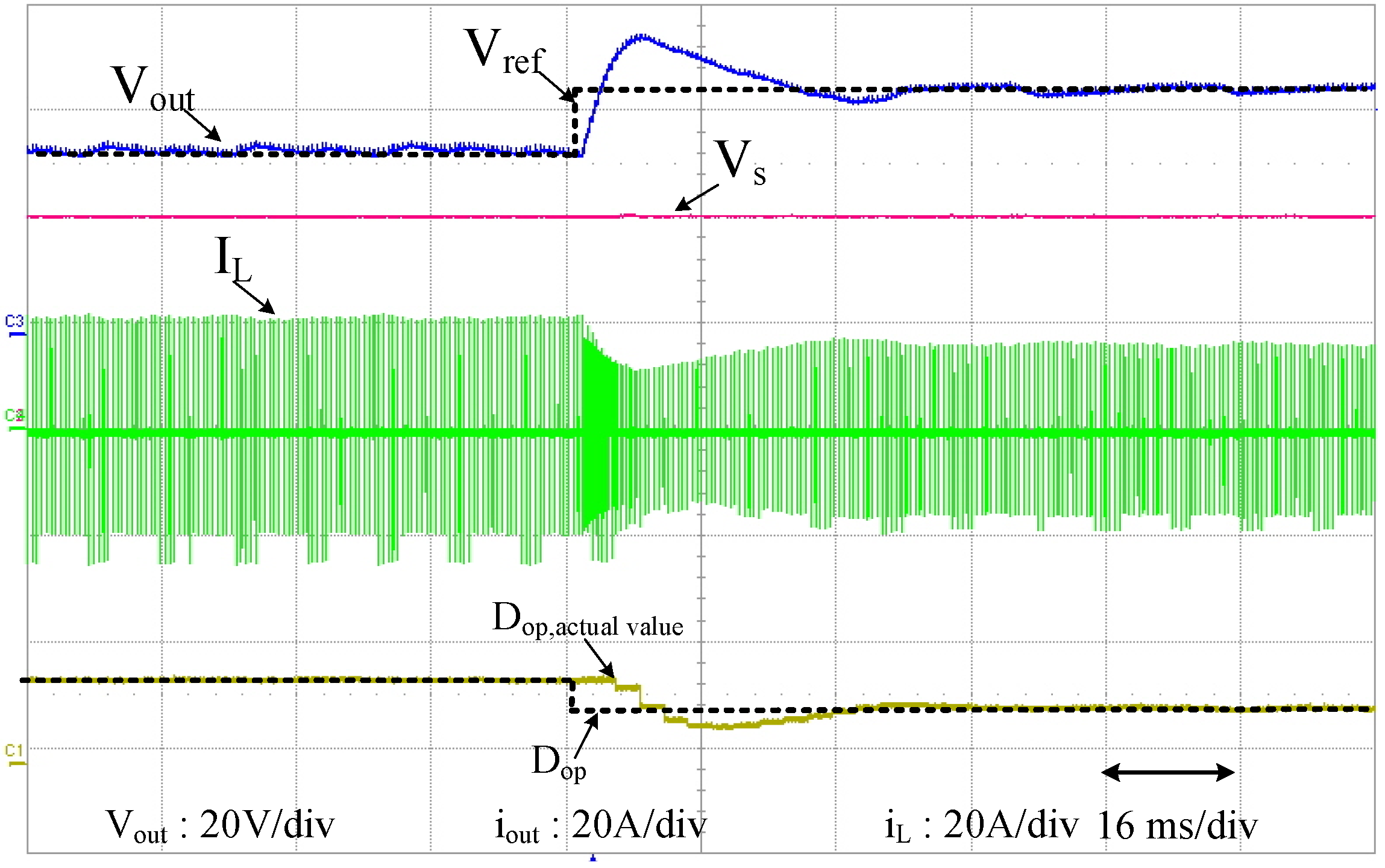
5. Control Mode Switching
6. Experimental Verification
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kheraluwala, M.; Gascoigne, R.; Divan, D.; Baumann, E. Performance characterization of a high-power dual active bridge DC-to-DC converter. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 1992, 28, 1294–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Song, Q.; Liu, W.; Sun, Y. Overview of Dual-Active-Bridge Isolated Bidirectional DC–DC Converter for High-Frequency-Link Power-Conversion System. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2014, 29, 4091–4106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Doncker, R.; Divan, D.; Kheraluwala, M. A three-phase soft-switched high-power-density DC/DC converter for high-power applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 1991, 27, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Xu, G.; Han, H.; Liu, D.; Sun, Y.; Su, M. Light-Load Efficiency Enhancement of High-Frequency Dual-Active-Bridge Converter Under SPS Control. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2021, 68, 12941–12946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, H.; Mi, C. Eliminate Reactive Power and Increase System Efficiency of Isolated Bidirectional Dual-Active-Bridge DC–DC Converters Using Novel Dual-Phase-Shift Control. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2008, 23, 2905–2914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Wen, H.; Chen, J.; Hu, Y.; Jiang, L.; Chen, G.; Ma, J. Minimum-Backflow-Power Scheme of DAB-Based Solid-State Transformer With Extended-Phase-Shift Control. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2018, 54, 3483–3496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Kim, B.K.; Kim, S. Single pulse width modulation for dual-active-bridge converters considering parasitic capacitance of MOSFETs. J. Power Electron. 2023, 23, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, K.W.; Yun, C.W.; Jung, G.G.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, H.S.; Jung, J.H. Enhanced four-port dual-active-bridge converter employing power decoupling capability for DC microgrid islanding mode operation. J. Power Electron. 2024, 24, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Yu, Q.; Sun, W. Extended-Phase-Shift Control of Isolated Bidirectional DC–DC Converter for Power Distribution in Microgrid. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2012, 27, 4667–4680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, H.; Nie, Z.; Mi, C.C. Experimental Comparison of Traditional Phase-Shift, Dual-Phase-Shift, and Model-Based Control of Isolated Bidirectional DC–DC Converters. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2010, 25, 1444–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Lei, W. Unified Triple-Phase-Shift Control to Minimize Current Stress and Achieve Full Soft-Switching of Isolated Bidirectional DC–DC Converter. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 4169–4179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhou, Y.; Yu, D. Self-Adapting Voltage Balancing Method for IPOS DAB Converter with TPS Control. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 2024, 34, 5702706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Song, C.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, H.; Wang, M.; Li, G.; Guo, H.; Hou, N. Direct Phase-Shift-Angle Optimization Strategy for DAB Converters’ Efficiency Enhancement Based on Fundamental Extended Phase-Shift Modulation. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2024, 12, 4678–4690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, S.; Chen, L.; Shan, Z.; Gao, F.; Chen, H.; Sha, D.; Dragičević, T. Modeling and Advanced Control of Dual-Active-Bridge DC–DC Converters: A Review. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2022, 37, 1524–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez Alonso, A.R.; Sebastian, J.; Lamar, D.G.; Hernando, M.M.; Vazquez, A. An overall study of a Dual Active Bridge for bidirectional DC/DC conversion. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition, Atlanta, GA, USA, 12–16 September 2010; pp. 1129–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Cui, X.; Zhuo, F.; Tian, J.; Zheng, Z.; Xu, R. Novel asymmetric duty modulation for DAB converters to improve light load efficiency. J. Power Electron. 2023, 23, 592–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, Y.P.; Loo, K.H.; Yaqoob, M.; Lai, Y.M. A Structurally Reconfigurable Resonant Dual-Active-Bridge Converter and Modulation Method to Achieve Full-Range Soft-Switching and Enhanced Light-Load Efficiency. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2019, 34, 4195–4207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Xu, G.; Sha, D.; Liu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Su, M. Review of Dual-Active-Bridge Converters with Topological Modifications. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2023, 38, 9046–9076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong, C.T.; Choi, S.J. Analysis of Capacitor Parasitic Effects on Output Voltage Ripple and Load Transient of DAB Converters. In Proceedings of the 2023 11th International Conference on Power Electronics and ECCE Asia (ICPE 2023—ECCE Asia), Jeju, Republic of Korea, 22–25 May 2023; pp. 2885–2891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W.; Lee, F.C.; Mattavelli, P. Optimal Trajectory Control of Burst Mode for LLC Resonant Converter. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2013, 28, 457–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes, D.; Hernandez-Gonzalez, L.; Ramirez-Hernandez, J.; Vargas, M. Modeling and Control of an Inductive Power Transmitter Based on Buck–Half Bridge–Resonant Tank. Electronics 2024, 13, 1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbajal-Retana, M.; Hernandez-Gonzalez, L.; Ramirez-Hernandez, J.; Avalos-Ochoa, J.G.; Guevara-Lopez, P.; Loboda, I.; Sotres-Jara, L.A. Interleaved buck converter for inductive wireless power transfer in DC–DC converters. Electronics 2020, 9, 949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Liu, B.; Duan, S. Burst-mode and phase-shift hybrid control method of LLC converters for wide output range applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 67, 1013–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Mannen, T.; Isobe, T. Improved Burst Mode Operation for DAB Converters to Achieve ZVS in Full-Load-Range by Considering Device Voltage Oscillation. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE 24th Workshop on Control and Modeling for Power Electronics (COMPEL), Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 25–28 June 2023; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Kulothungan, G.S.; Krishnamoorthy, H.S. Improved Circuit Design and Adaptive Burst Mode Control in PSFB Converters for Higher Efficiency Over a Wide Power Range. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 9152–9163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyer, V.M.; Gulur, S.; Bhattacharya, S. Hybrid control strategy to extend the ZVS range of a dual active bridge converter. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition (APEC), Tampa, FL, USA, 26–30 March 2017; pp. 2035–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, Q.; Wen, H.; Shi, H.; Zhu, Y. A Comparative Review of High-Frequency Transient DC Bias Current Mitigation Strategies in Dual-Active-Bridge DC–DC Converters Under Phase-Shift Modulations. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2022, 58, 2166–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Song, Q.; Liu, W.; Zhao, Y. Transient DC Bias and Current Impact Effects of High-Frequency-Isolated Bidirectional DC–DC Converter in Practice. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2016, 31, 3203–3216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, Y.F. An Optimized Phase-Shift Modulation For Fast Transient Response in a Dual-Active-Bridge Converter. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2014, 29, 2661–2665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Gui, H.; Bai, H. Complete ZVS Analysis in Dual Active Bridge. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2021, 36, 1247–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong, C.T.; Choi, S.J. Improved ZVS Criterion for Series Resonant Converters. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 5333–5344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, B.R.; Park, J.S.; Truong, C.T.; Choi, S.J. Novel Burst-mode Control Strategy for Enhanced Light-load Efficiency of DAB Converters. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition (ECCE), Phoenix, AZ, USA, 20–24 October 2024; pp. 2691–2697. [Google Scholar]
- Oggier, G.G.; Ordonez, M. High-Efficiency DAB Converter Using Switching Sequences and Burst Mode. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2016, 31, 2069–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Ref. | Type of Control | Soft-Switching Range | Minimum Backflow Power | Implementation Complexity | DC Bias Elimination |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [4] | SPS | Partial | No | Low | No |
| [9] | EPS | Partial | Yes | Medium | No |
| [10] | DPS | Partial | Yes | Medium | No |
| [11] | TPS | Full | Yes | High | No |
| [33] | SPS + burst-mode | Partial | No | Low | No |
| This paper | SPS + burst-mode | Full | Yes | Low | Yes |
| Symbol | Parameters | Values | Calculated | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DC input voltage | 400 | V | ||
| DC output voltage | 100–180 | V | ||
| Switching frequency | 50 | kHz | ||
| Output power | 0–4 | kW | ||
| Transformer turn ratio | 2:1 | |||
| Output filter capacitance | 500 | 450 | F | |
| Series inductance | 50 | 44 | H | |
| Burst frequency | 2.5 | kHz | ||
| Critical value of load resistance | 50 | 50.16 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Truong, C.-T.; Na, B.-R.; Park, J.-S.; Choi, S.-J. Novel Burst-Mode Control for Medium-to-Light Load Operation of Dual-Active-Bridge Converters, Achieving Minimum Backflow Power, Zero-Voltage-Switching, and DC Bias Suppression. Energies 2024, 17, 5748. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17225748
Truong C-T, Na B-R, Park J-S, Choi S-J. Novel Burst-Mode Control for Medium-to-Light Load Operation of Dual-Active-Bridge Converters, Achieving Minimum Backflow Power, Zero-Voltage-Switching, and DC Bias Suppression. Energies. 2024; 17(22):5748. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17225748
Chicago/Turabian StyleTruong, Chanh-Tin, Byeong-Ryeol Na, Jeong-Soo Park, and Sung-Jin Choi. 2024. "Novel Burst-Mode Control for Medium-to-Light Load Operation of Dual-Active-Bridge Converters, Achieving Minimum Backflow Power, Zero-Voltage-Switching, and DC Bias Suppression" Energies 17, no. 22: 5748. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17225748
APA StyleTruong, C.-T., Na, B.-R., Park, J.-S., & Choi, S.-J. (2024). Novel Burst-Mode Control for Medium-to-Light Load Operation of Dual-Active-Bridge Converters, Achieving Minimum Backflow Power, Zero-Voltage-Switching, and DC Bias Suppression. Energies, 17(22), 5748. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17225748







