Electrical Tortuosities of Porous Structures Based on Triply Periodic Minimal Surfaces and Honeycombs for Power-to-Heat Systems
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Geometric Structures
2.1. TPMS-Based Structures
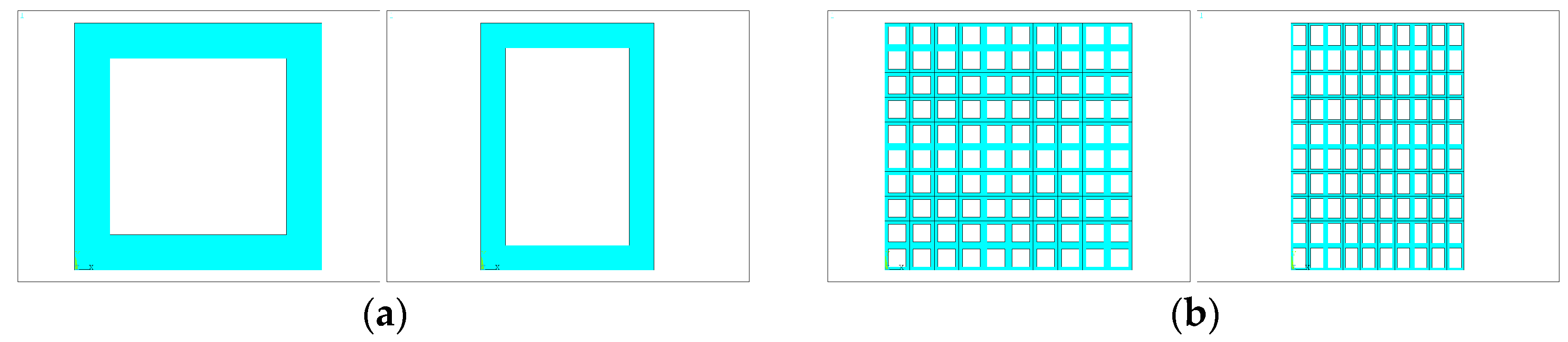
2.2. Honeycomb Structures
3. Methodology and Modeling
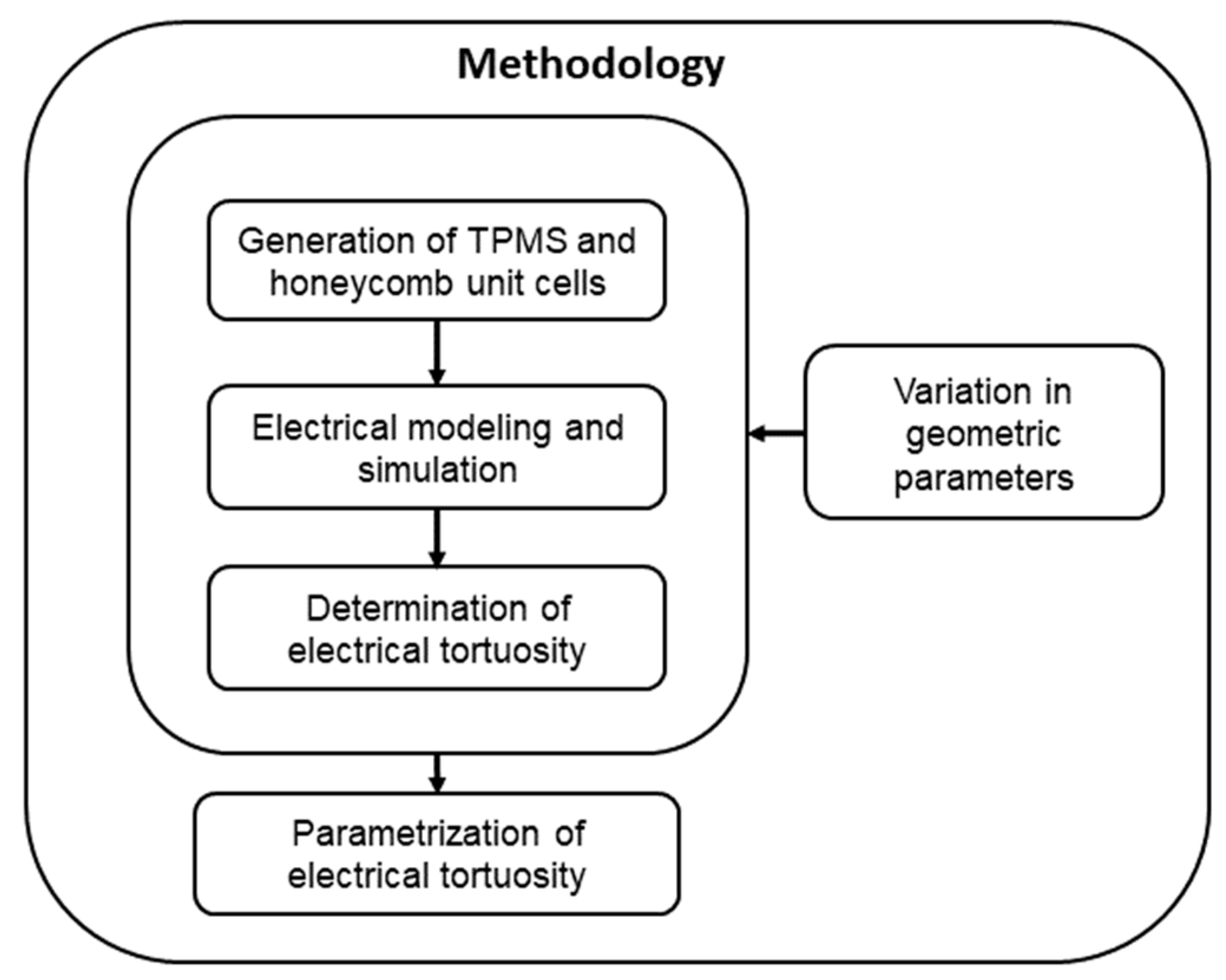
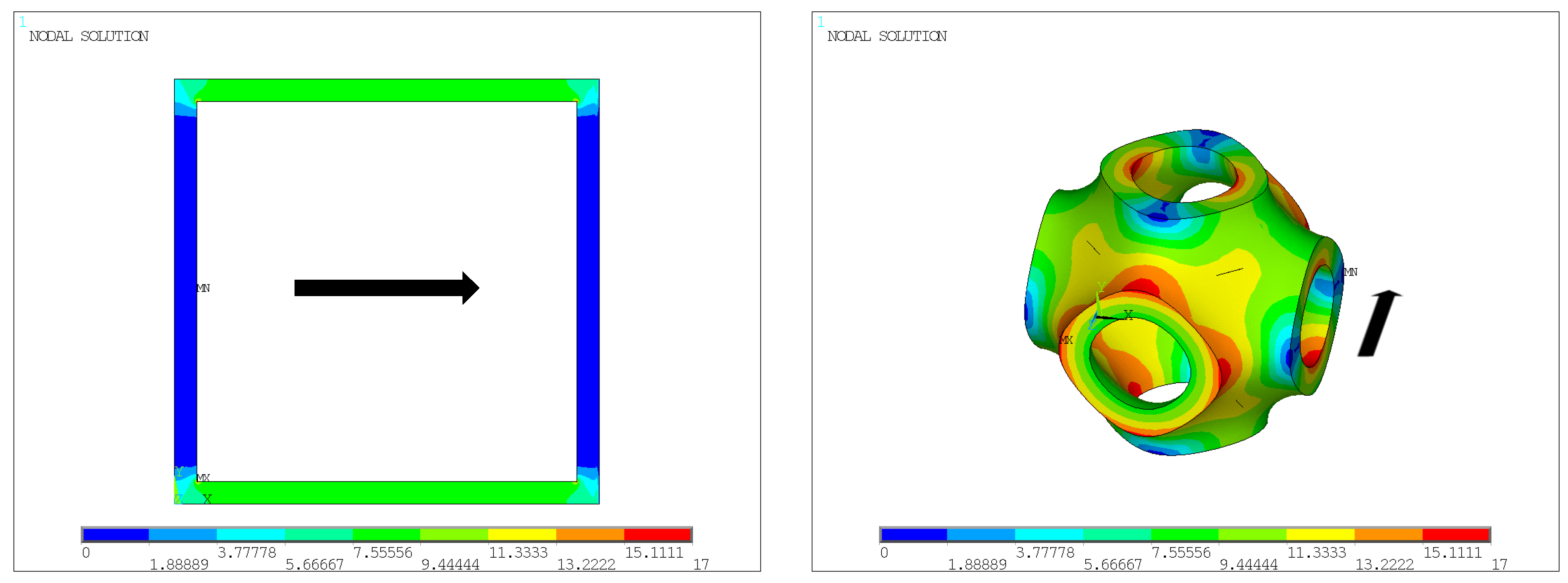
3.1. Methodology
3.2. Electrical Modeling
4. Results and Discussions
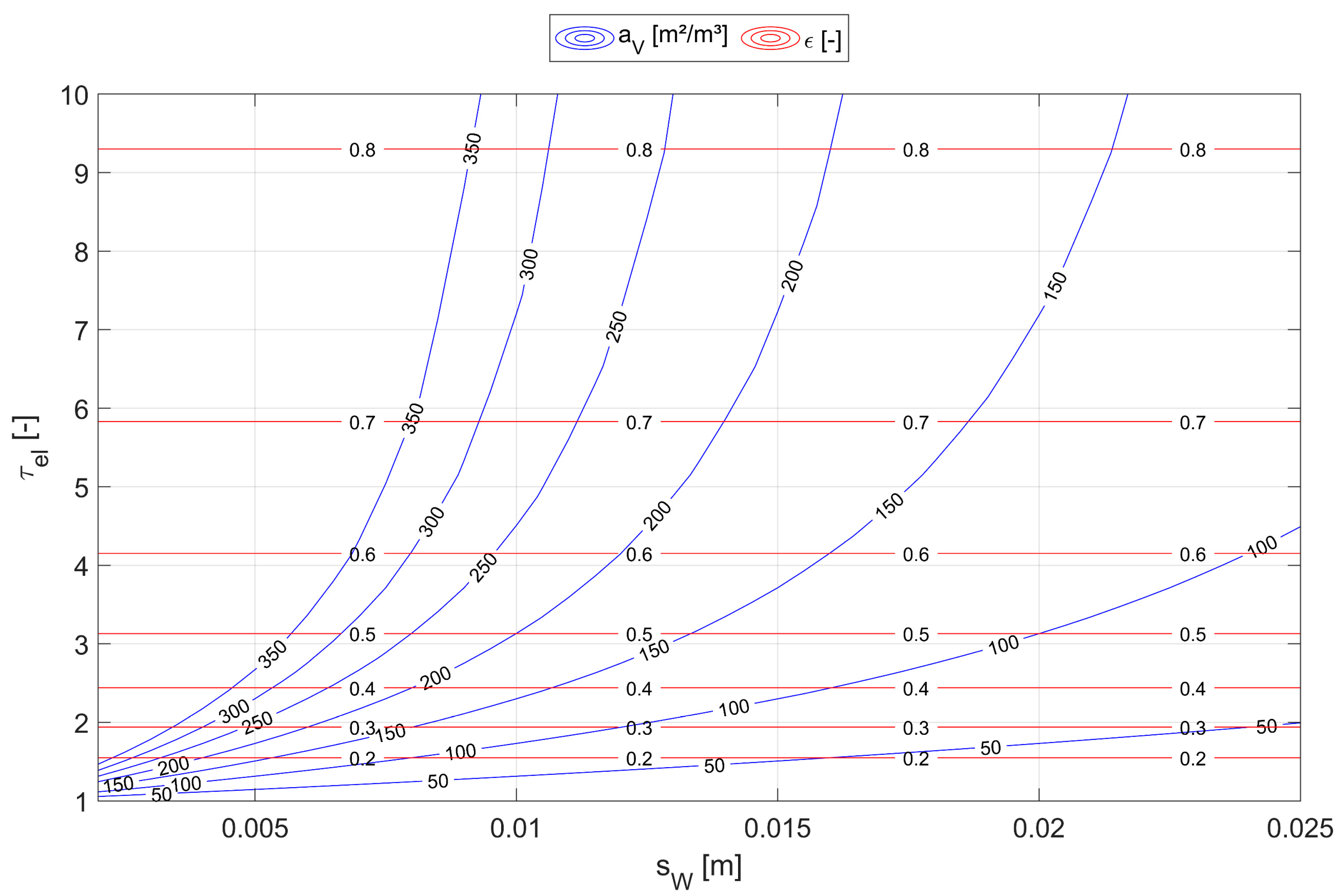
4.1. Effect of Specific Surface on Electrical Tortuosity for TPMS and Honeycomb Structures
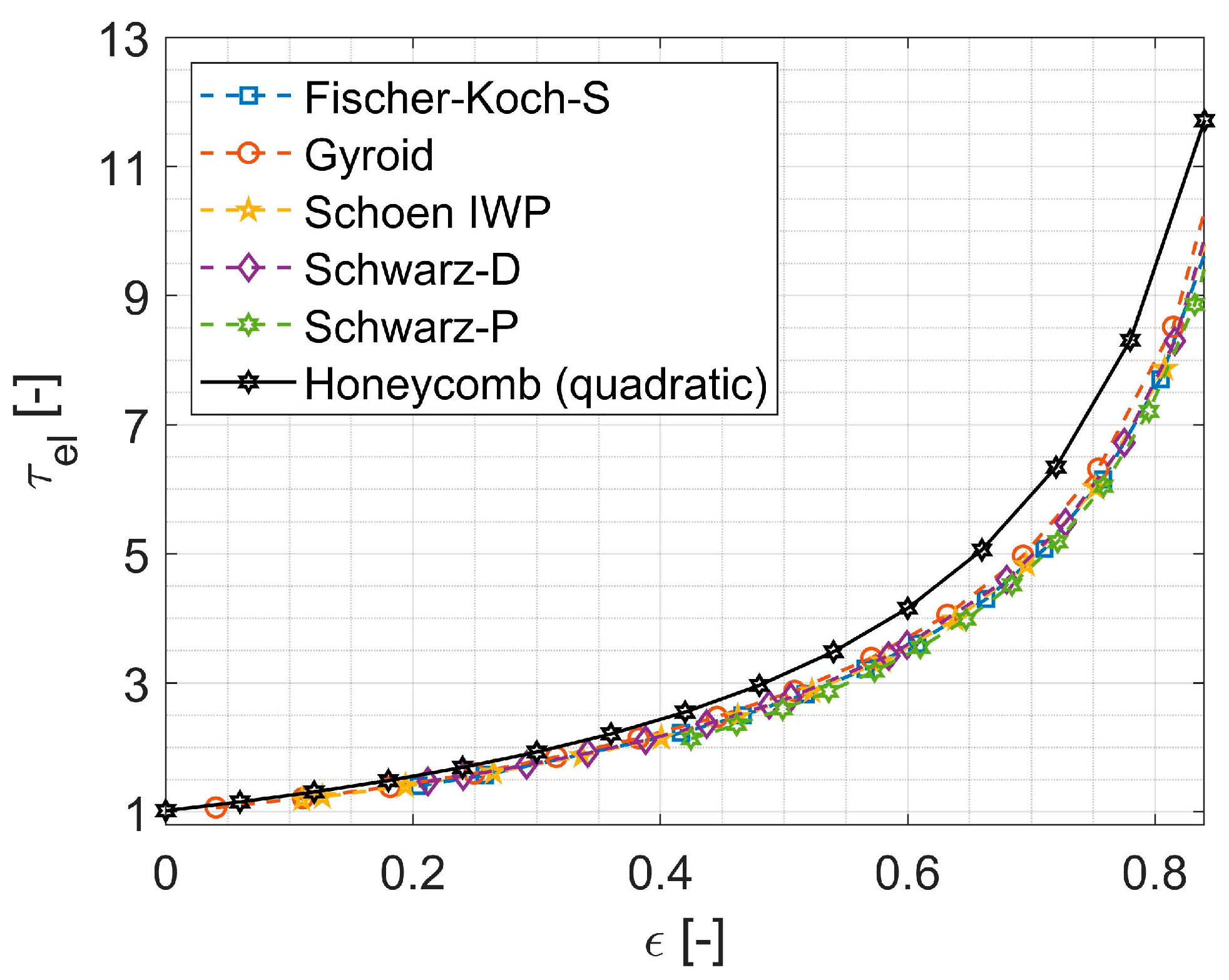
4.2. Effect of Void Fraction on Electrical Tortuosity for Isotropic TPMS and Honeycomb Structures
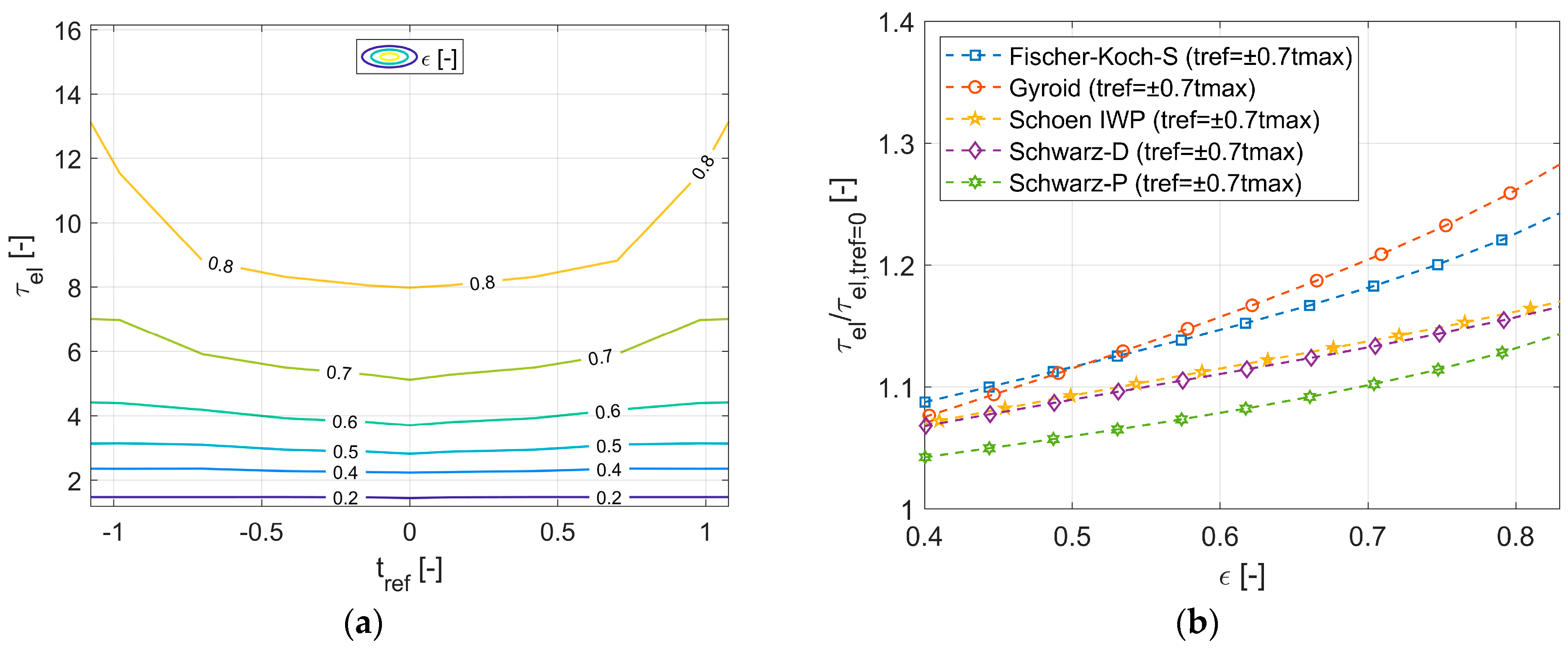
4.3. Effect of Level-Set Parameter on Electrical Tortuosity for Isotropic TPMS Structures
| Geometric Structure | Mean Error | Maximum Error | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fischer-Koch-S | 3.0% | 6.6% | |
| Gyroid | 3.3% | 8.2% | |
| Schoen IWP | 3.3% | 11.0% | |
| Schwarz-D | 2.8% | 8.8% | |
| Schwarz-P | 2.0% | 5.5% | |
| Honeycomb (quadratic) | 0.5% | 1.2% |
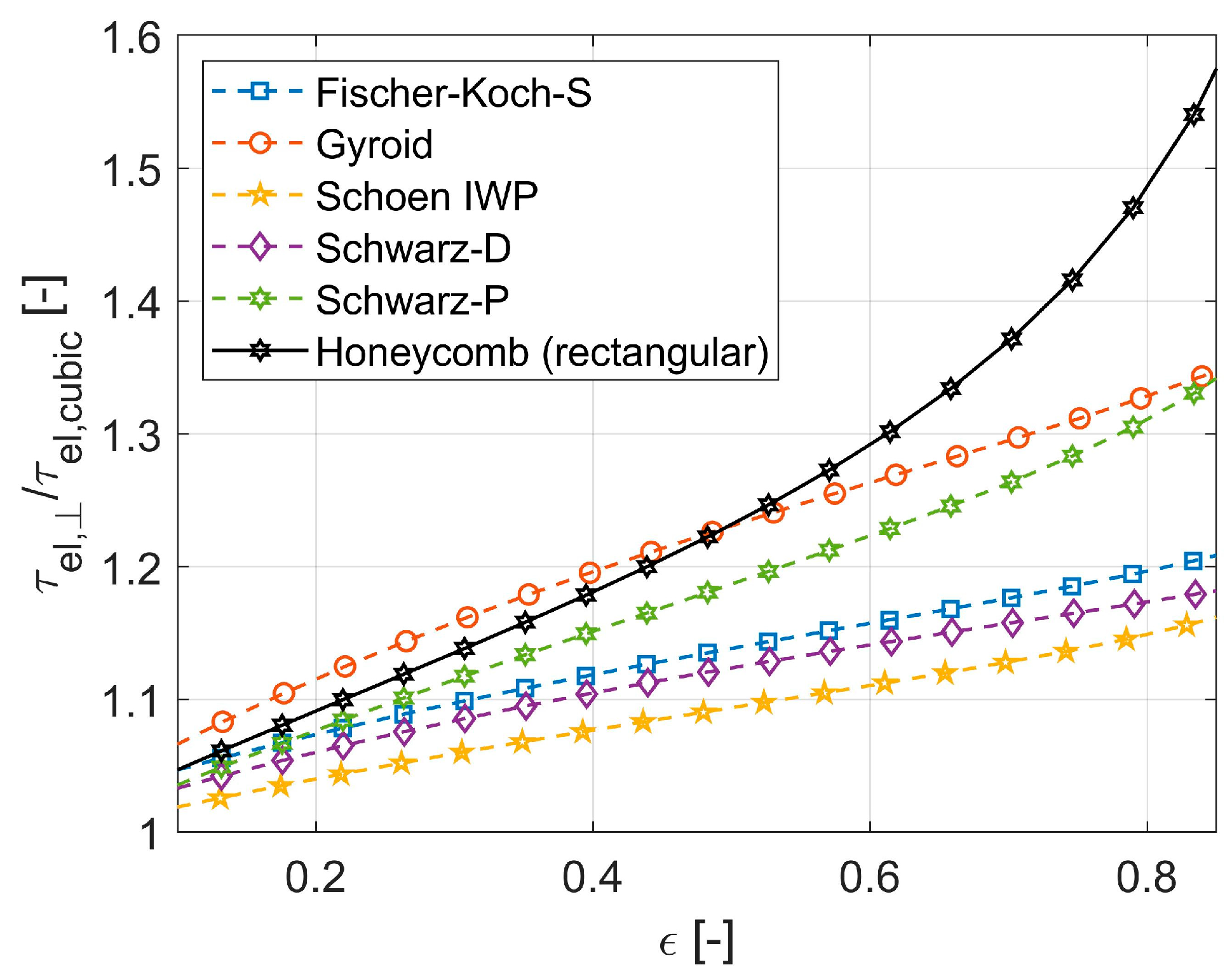
4.4. Effect of Anisotropy on Electrical Tortuosity for TPMS and Honeycomb Structures
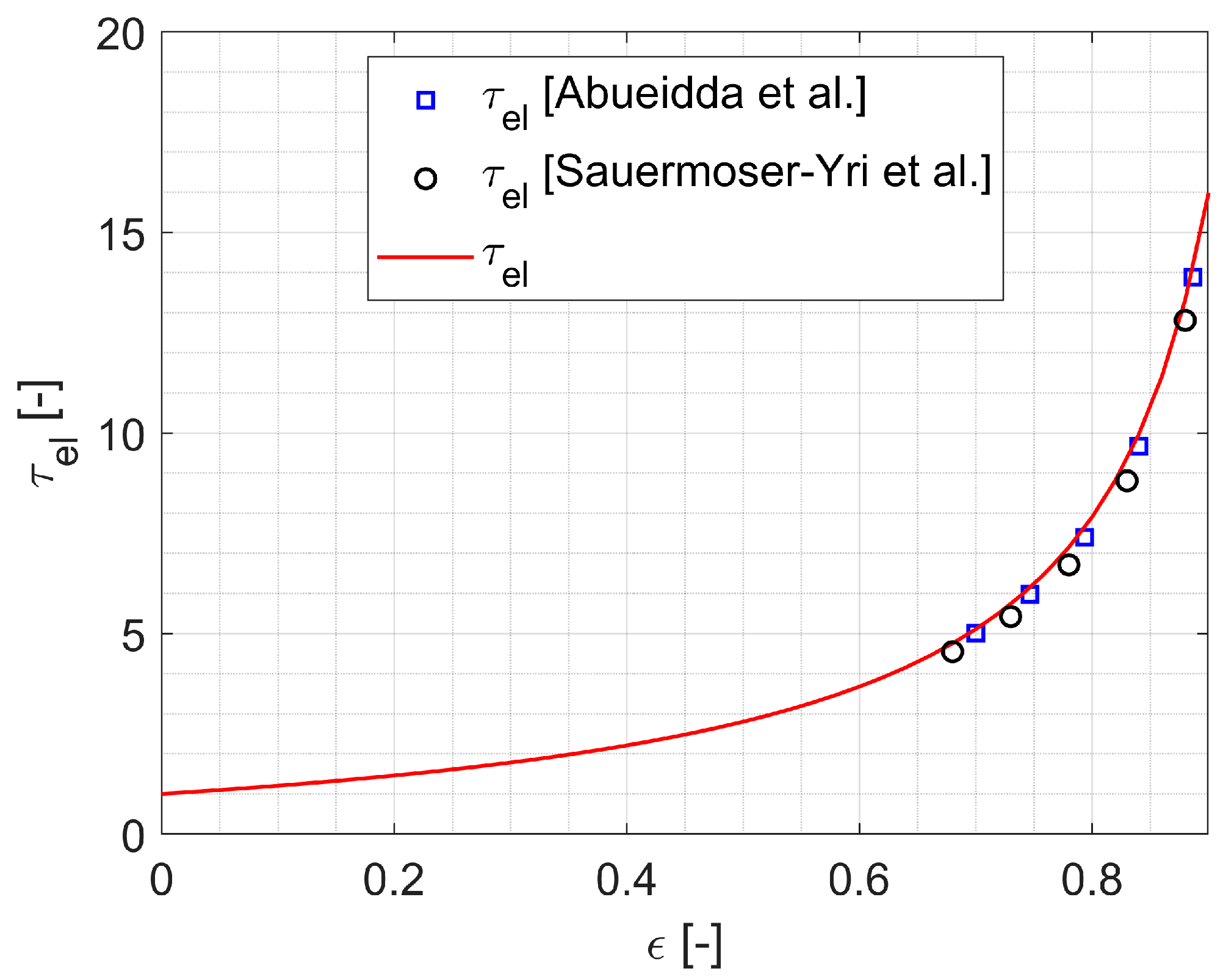
4.5. Comparison to the Literature and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lupi, S. Fundamentals of Electroheat: Electrical Technologies for Process Heating, 1st ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Belik, S. Techno-economic evaluation of a Brayton battery configuration with power-to-heat extension. J. Energy Storage 2023, 68, 107416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreißigacker, V. Power-to-heat in adiabatic compressed air energy storage power plants for cost reduction and increased flexibility. Heat Mass Transf. 2017, 54, 955–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benato, A. Performance and cost evaluation of an innovative Pumped Thermal Electricity Storage power system. Energy 2017, 138, 419–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knote, T. E-Bus-Standard: “Ansätze zur Standardisierung und Zielkosten für Elektrobusse”; Fraunhofer-Institut für Verkehrs- und Infrastruktursysteme (IVI): Dresden, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreißigacker, V.; Hofer, L. High-Performance Solid Medium Thermal Energy Storage System for Heat Supply in Battery Electric Vehicles: Proof of Concept and Experimental Testing. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 10943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreißigacker, V. Solid Media Thermal Energy Storage System for Heating Electric Vehicles: Advanced Concept for Highest Thermal Storage Densities. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 8027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanbarian, B.; Hunt, A.G.; Ewing, R.P.; Sahimi, M. Tortuosity in Porous Media: A Critical Review. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2013, 77, 1461–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clennell, M.B. Tortuosity: A guide through the maze. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 1997, 122, 299–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Cheng, D.; Oo, K.; Pan, W.; McCrimmon, T.-L.; Bai, S. Optimization of Triply Periodic Minimal Surface Heat Exchanger to Achieve Compactness, High Efficiency, and Low-Pressure Drop. Energies 2024, 17, 5141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeranee, K.; Rao, Y. A Review of Recent Investigations on Flow and Heat Transfer Enhancement in Cooling Channels Embedded with Triply Periodic Minimal Surfaces (TPMS). Energies 2022, 15, 8994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Gao, F.; Hu, W. Design, Modeling and Characterization of Triply Periodic Minimal Surface Heat Exchangers with Additive Manufacturing. In Proceedings of the Solid Freeform Fabrication, Austin, TX, USA, 12–14 August 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Yu, G.; Yu, Z. Bioinspired heat exchangers based on triply periodic minimal surfaces for supercritical CO2 cycles. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2020, 179, 115686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyer, J.; Moore, T.; Nguyen, D.; Roy, P.; Stolaroff, J. Heat transfer and pressure drop characteristics of heat exchangers based on triply periodic minimal and periodic nodal surfaces. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2022, 209, 118192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Fu, J.; Yao, X.; He, Y. Triply periodic minimal surface (TPMS) porous structures: From multi-scale design, precise additive manufacturing to multidisciplinary applications. Int. J. Extrem. Manuf. 2022, 4, 022001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kladovasilakis, N.; Tsongas, K.; Tzetzis, D. Mechanical and FEA-Assisted Characterization of Fused Filament Fabricated Triply Periodic Minimal Surface Structures. J. Compos. Sci. 2021, 5, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Marzocca, P.; Tran, P. Triply periodic minimal surfaces based honeycomb structures with tuneable mechanical responses. Virtual Phys. Prototyp. 2022, 18, e2125879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.; Han, Y.; Lu, J. Design and Optimization of Lattice Structures: A Review. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 6374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.-C.; Lin, X.-C.; Xiong, J.-Y.; Wu, H.-H.; Zhao, G.-W.; Fang, D. Electrical properties of 3D printed graphite cellular lattice structures with triply periodic minimal surface architectures. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 125609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abueidda, D.W.; Abu Al-Rub, R.K.; Dalaq, A.S.; Lee, D.-W.; Khan, K.A.; Jasiuk, I. Effective conductivities and elastic moduli of novel foams with triply periodic minimal surfaces. Mech. Mater. 2016, 95, 102–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauermoser-Yri, M.; Veldurthi, N.; Wölfle, C.H.; Svartvatn, P.J.; Flo Hoem, S.O.; Lid, M.J.; Bock, R.; Palko, J.W.; Torgersen, J. On the porosity-dependent permeability and conductivity of triply periodic minimal surface based porous media. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 27, 585–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catchpole-Smith, S.; Sélo, R.R.J.; Davis, A.W.; Ashcroft, I.A.; Tuck, C.J.; Clare, A. Thermal conductivity of TPMS lattice structures manufactured via laser powder bed fusion. Addit Manuf 2019, 30, 100846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pichler, M.; Haddadi, B.; Jordan, C.; Harasek, M. Modeling the effective thermal conductivity of hollow bricks at high temperatures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 309, 125066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, E.; Shi, Z.; Chen, M.; Tang, S.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, W. Investigation of effective thermal conductivity of SiC foam ceramics with various pore densities. Open Phys. 2022, 20, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, C.A.; Radzilowski, L.H.; Thomas, E.L. Triply periodic level surfaces as models for cubic tricontinuous block copolymer morphologies. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. London. Ser. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 1996, 354, 2009–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ketan, O.; Abu Al-Rub, R.K. MSLattice: A free software for generating uniform and graded lattices based on triply periodic minimal surfaces. Mater. Des. Process. Commun. 2020, 3, e205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ketan, O.; Abu Al-Rub, R.K. Multifunctional Mechanical Metamaterials Based on Triply Periodic Minimal Surface Lattices. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2019, 21, 1900524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Kong, H.; Zhou, X.; Li, G.; Du, J. Design and Characterization of Sheet-Based Gyroid Porous Structures with Bioinspired Functional Gradients. Materials 2020, 13, 3844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
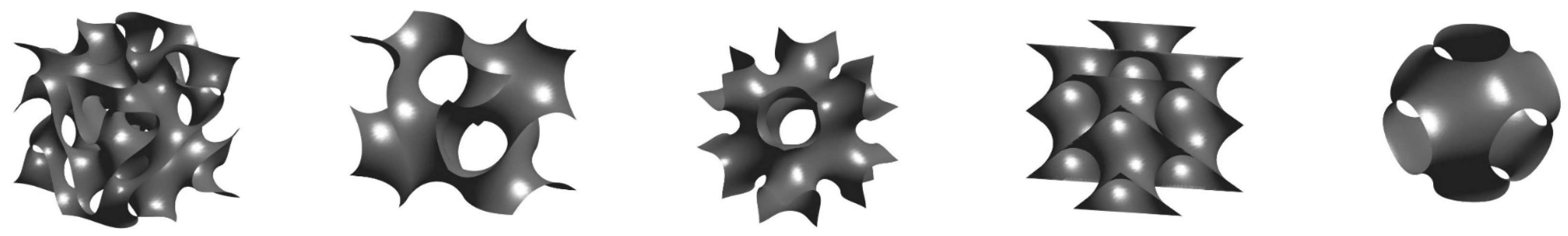
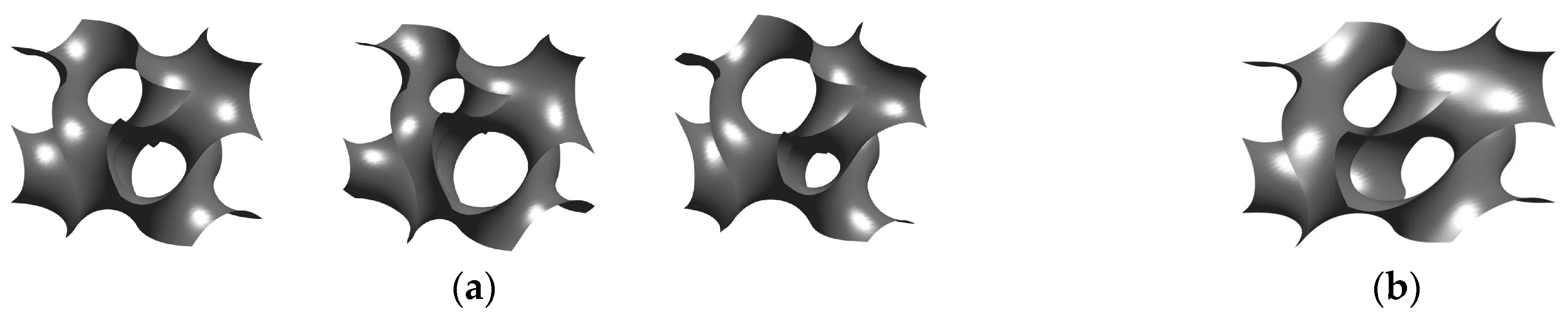


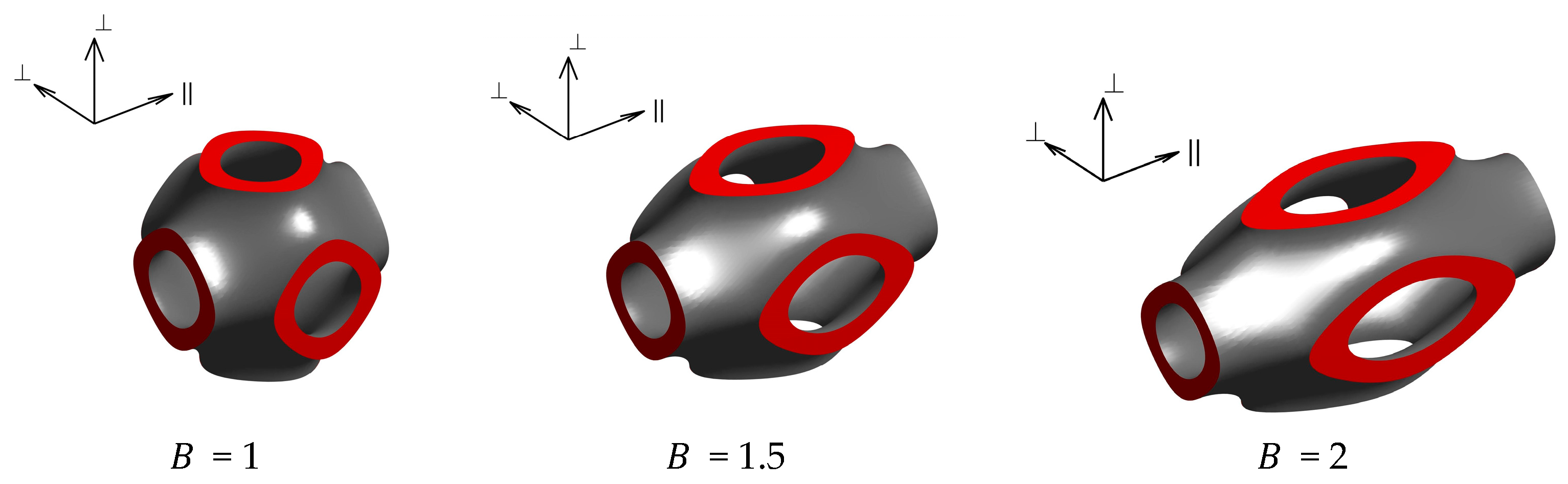

| TPMS Structure | [-] | [-] |
|---|---|---|
| Fischer-Koch-S | −0.75 | 0.75 |
| Gyroid | −1.4 | 1.4 |
| Schoen IWP | −2.99 | 2.99 |
| Schwarz-D | −0.99 | 0.99 |
| Schwarz-P | −1.0 | 1.0 |
| Geometric Structure | Mean Error | Maximum Error | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fischer-Koch-S | 2.6% | 5.6% | |
| Gyroid | 4.7% | 9.6% | |
| Schoen IWP | 3.2% | 4.5% | |
| Schwarz-D | 2.6% | 4.2% | |
| Schwarz-P | 3.7% | 8.2% | |
| Honeycomb (rectangular) | 3.7% | 10.8% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ott, T.; Dreißigacker, V. Electrical Tortuosities of Porous Structures Based on Triply Periodic Minimal Surfaces and Honeycombs for Power-to-Heat Systems. Energies 2024, 17, 5781. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17225781
Ott T, Dreißigacker V. Electrical Tortuosities of Porous Structures Based on Triply Periodic Minimal Surfaces and Honeycombs for Power-to-Heat Systems. Energies. 2024; 17(22):5781. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17225781
Chicago/Turabian StyleOtt, Thorsten, and Volker Dreißigacker. 2024. "Electrical Tortuosities of Porous Structures Based on Triply Periodic Minimal Surfaces and Honeycombs for Power-to-Heat Systems" Energies 17, no. 22: 5781. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17225781
APA StyleOtt, T., & Dreißigacker, V. (2024). Electrical Tortuosities of Porous Structures Based on Triply Periodic Minimal Surfaces and Honeycombs for Power-to-Heat Systems. Energies, 17(22), 5781. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17225781




