Low-Wind-Speed Galloping Wind Energy Harvester Based on a W-Shaped Bluff Body
Abstract
1. Introduction
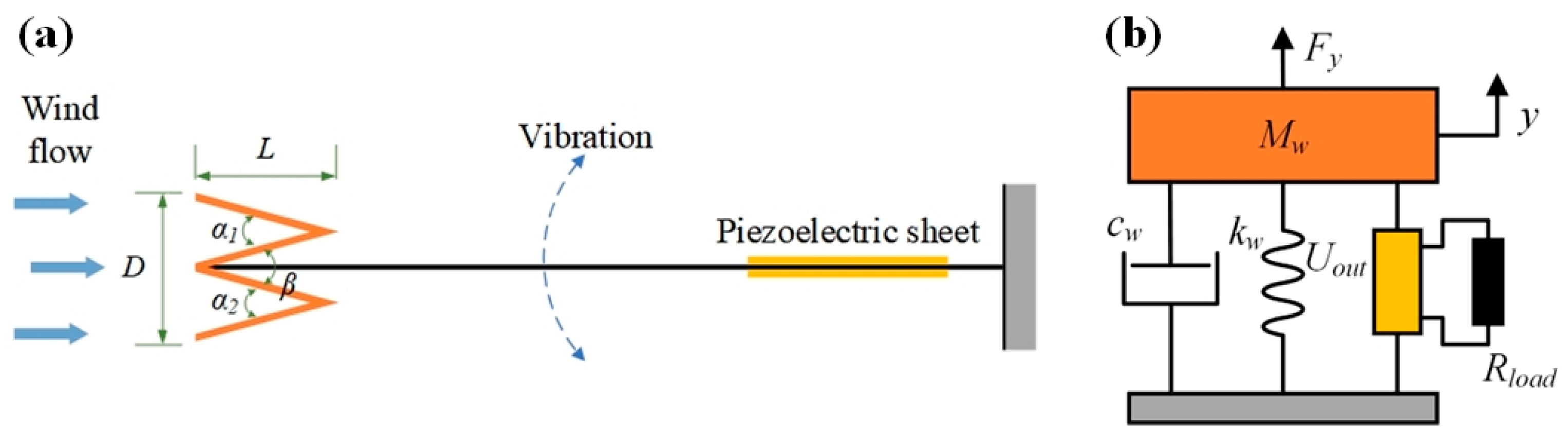
2. Theoretical Modeling and Analysis
3. Finite Element Simulation Analysis
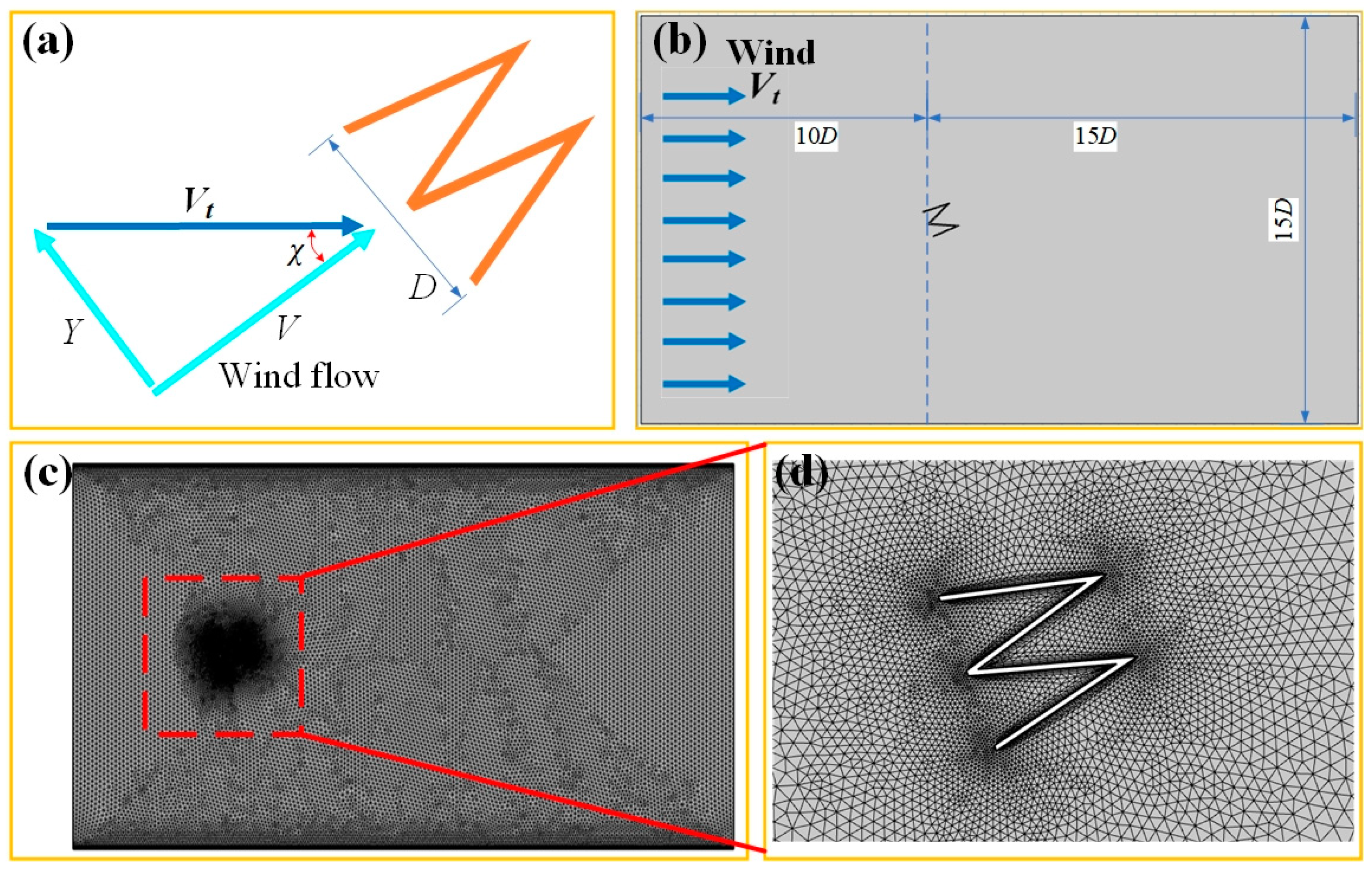
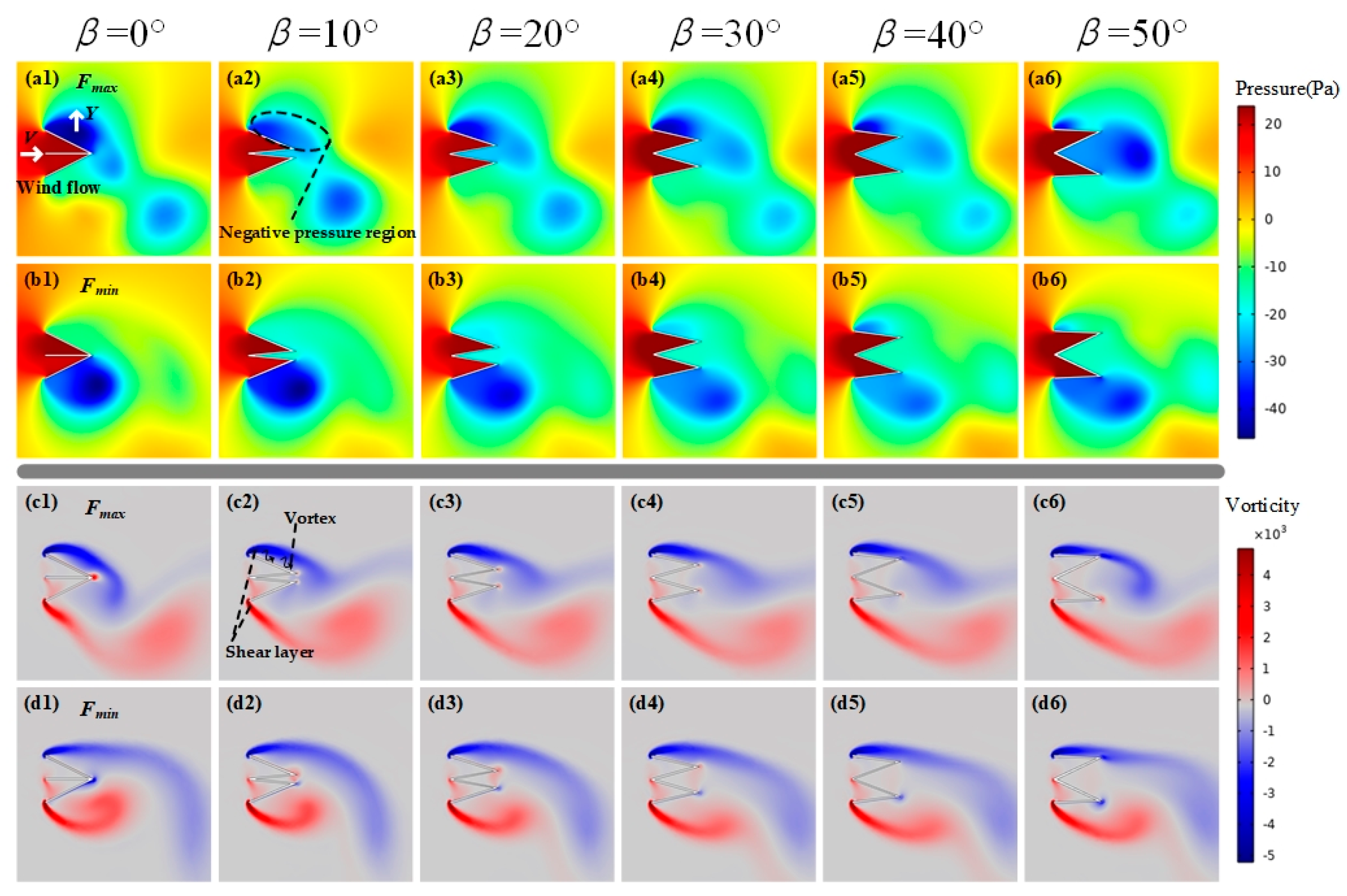
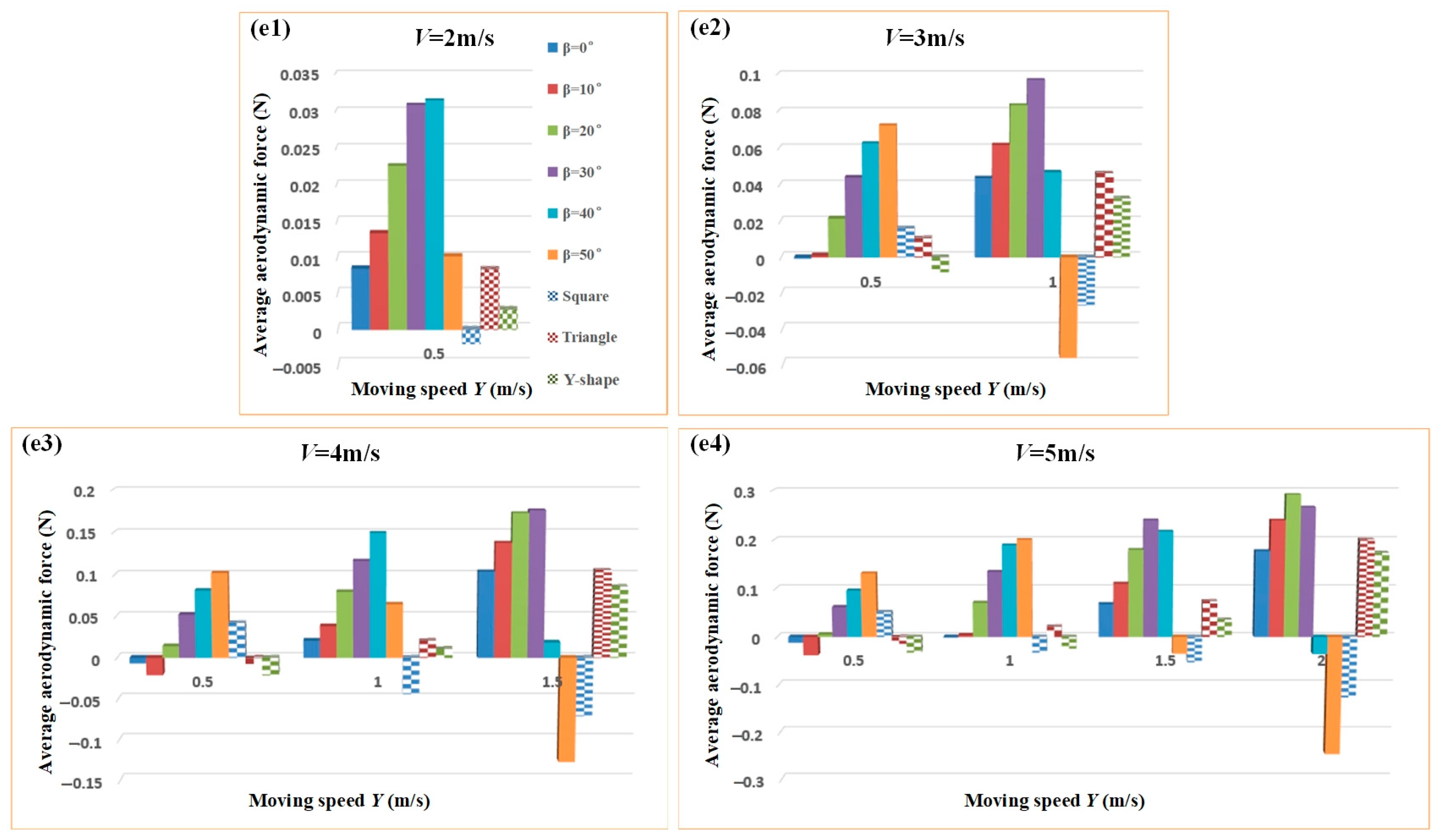
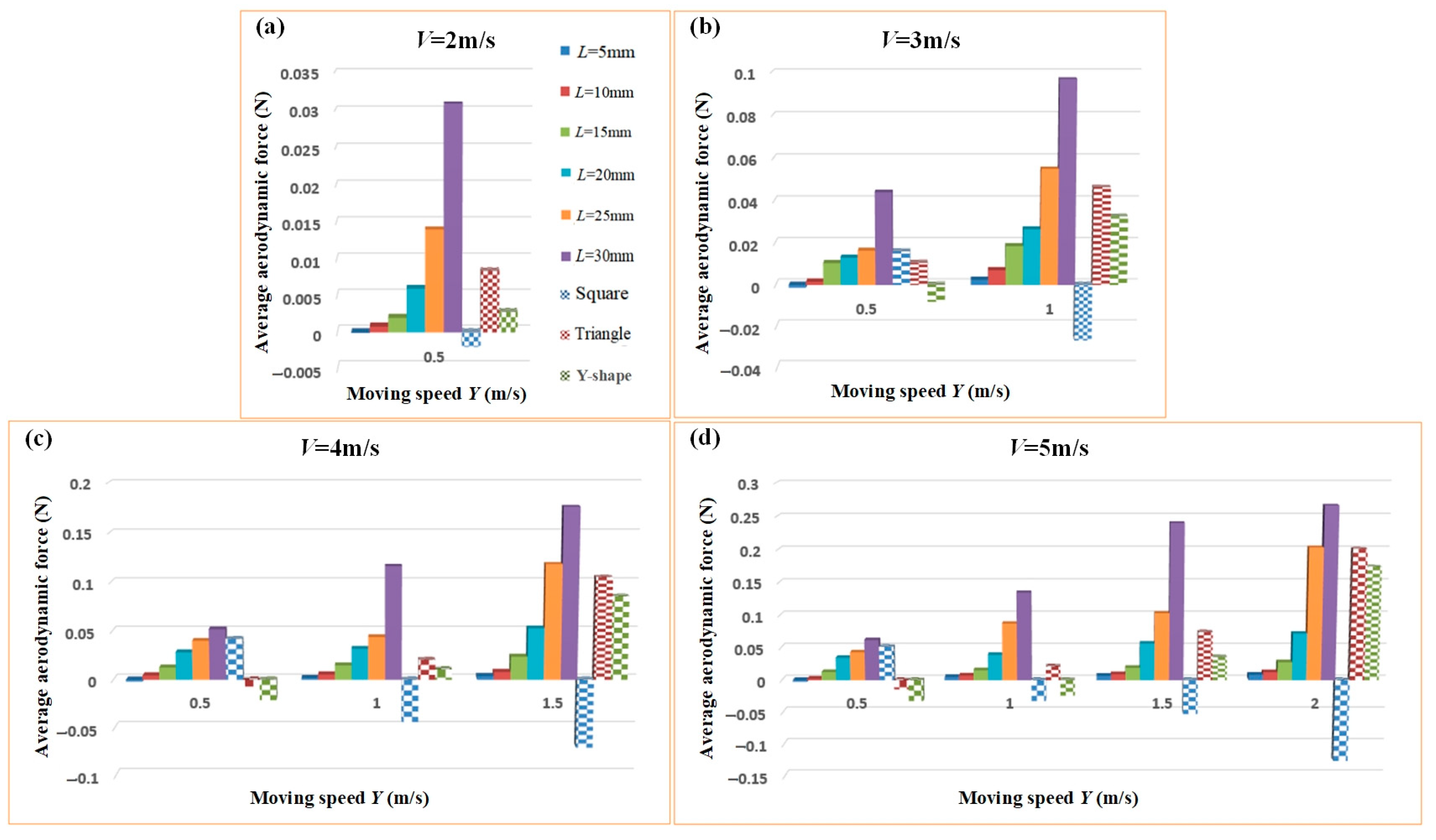
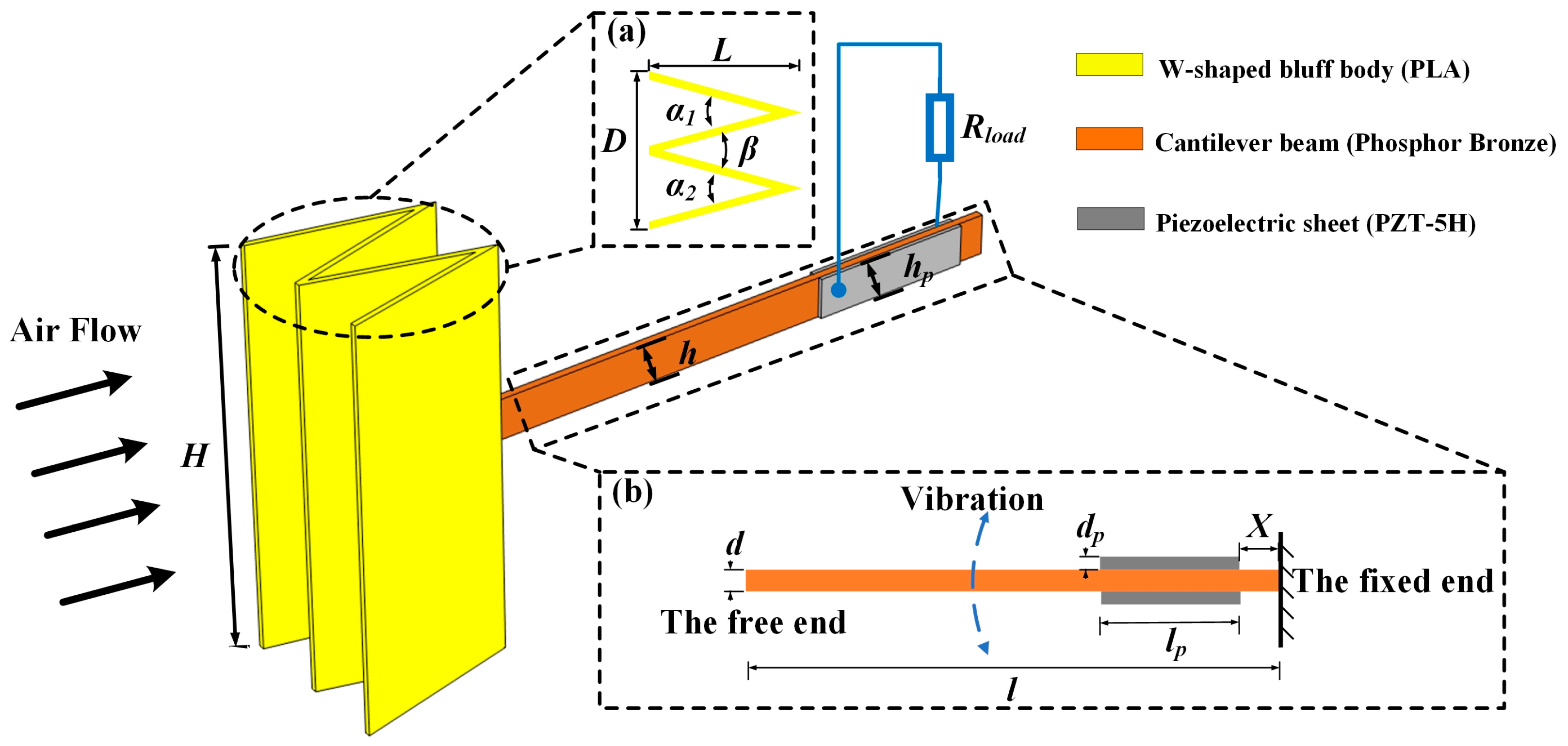
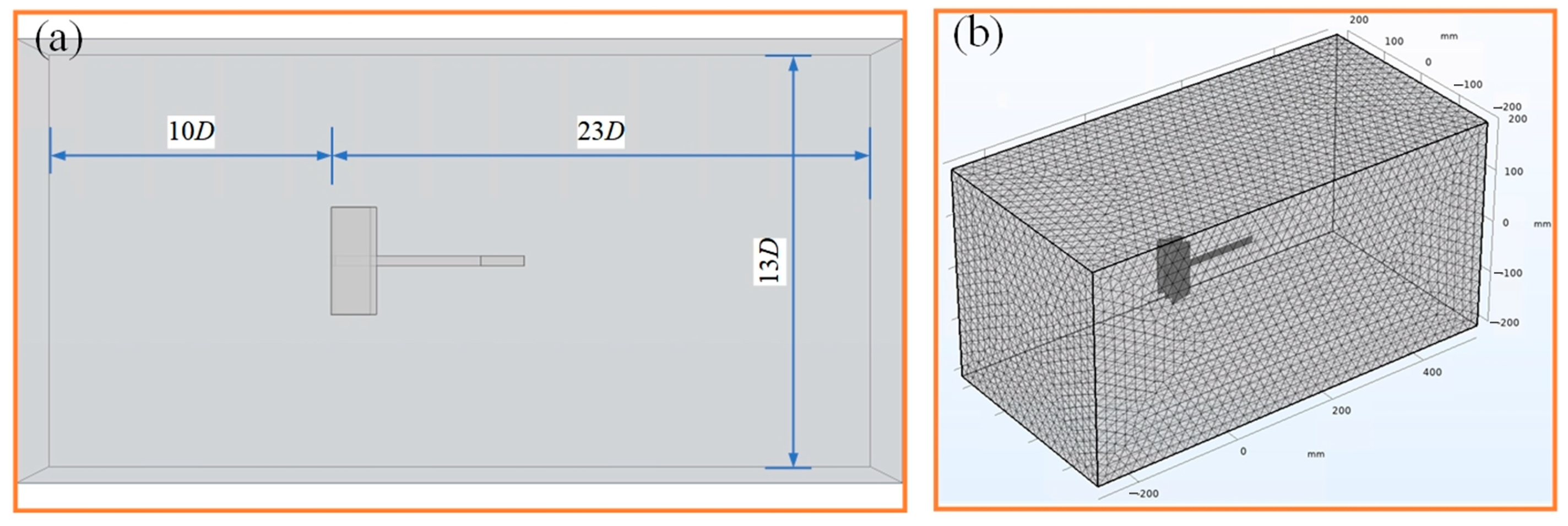
3.1. Bluff Body Modeling and Simulation Analysis
3.2. Modeling and Simulation of Wind Energy Harvesters
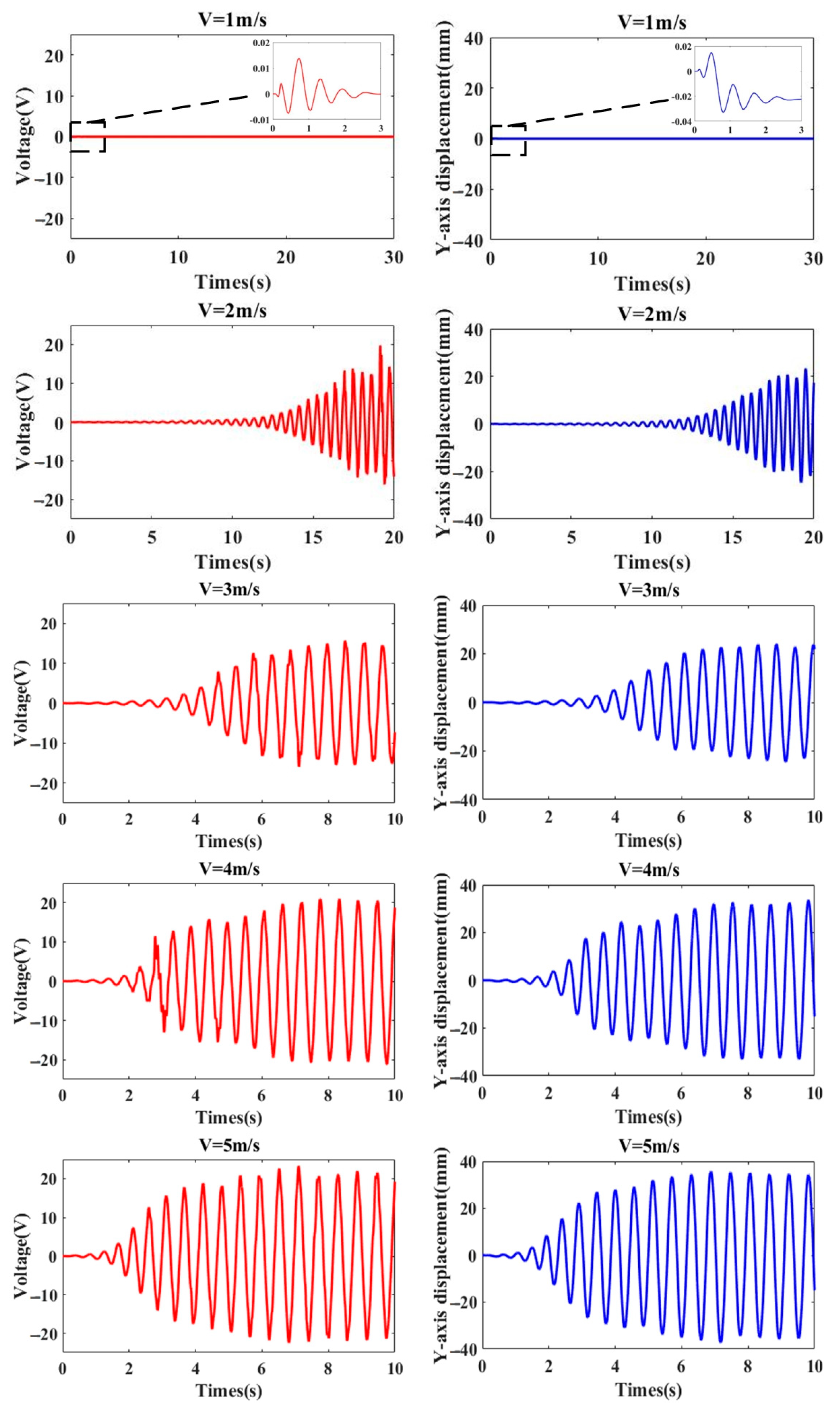
3.2.1. Analysis of Output Voltage
3.2.2. Analysis of Cut-in Speed
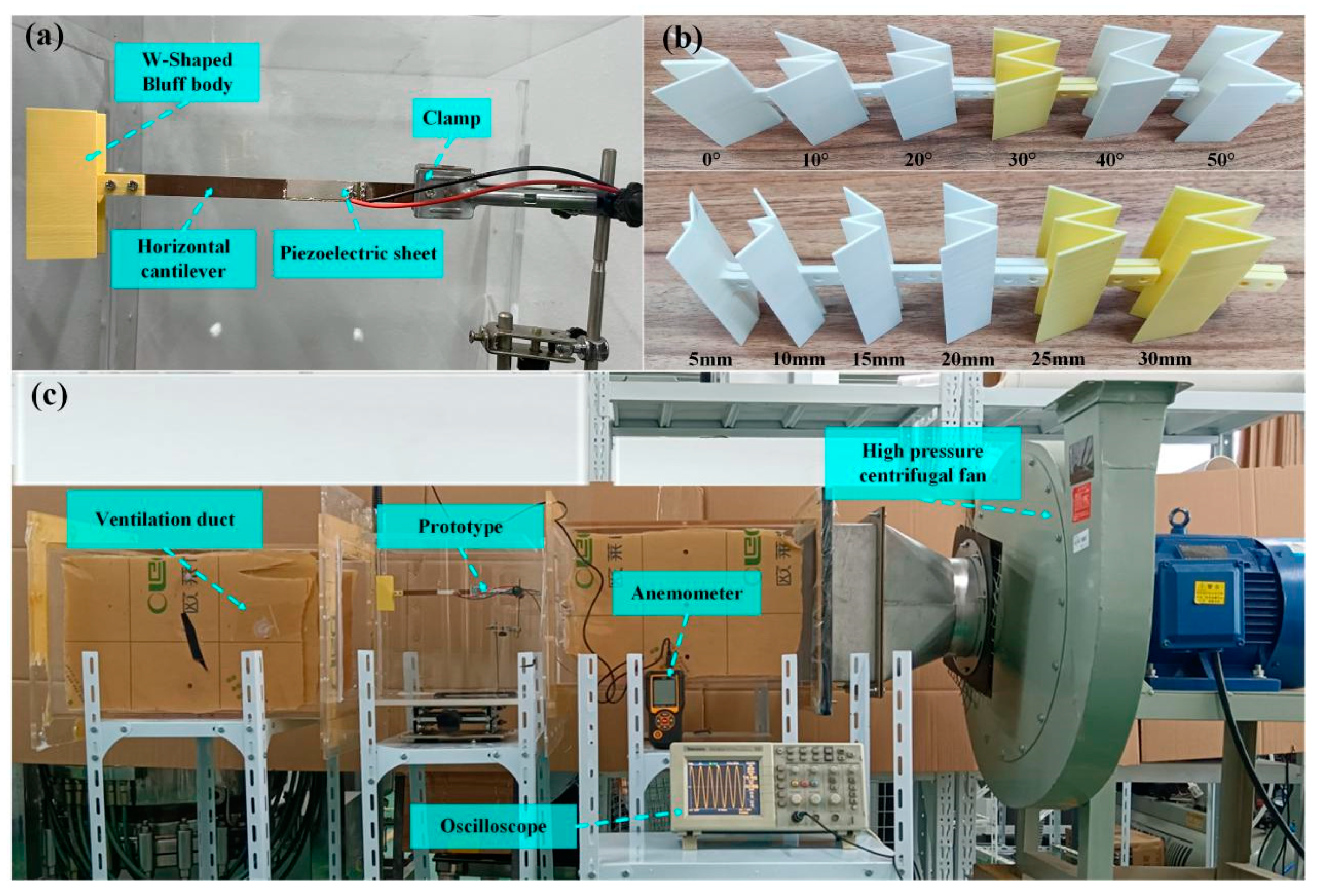
4. Experimental Verification
4.1. Experimental Setup
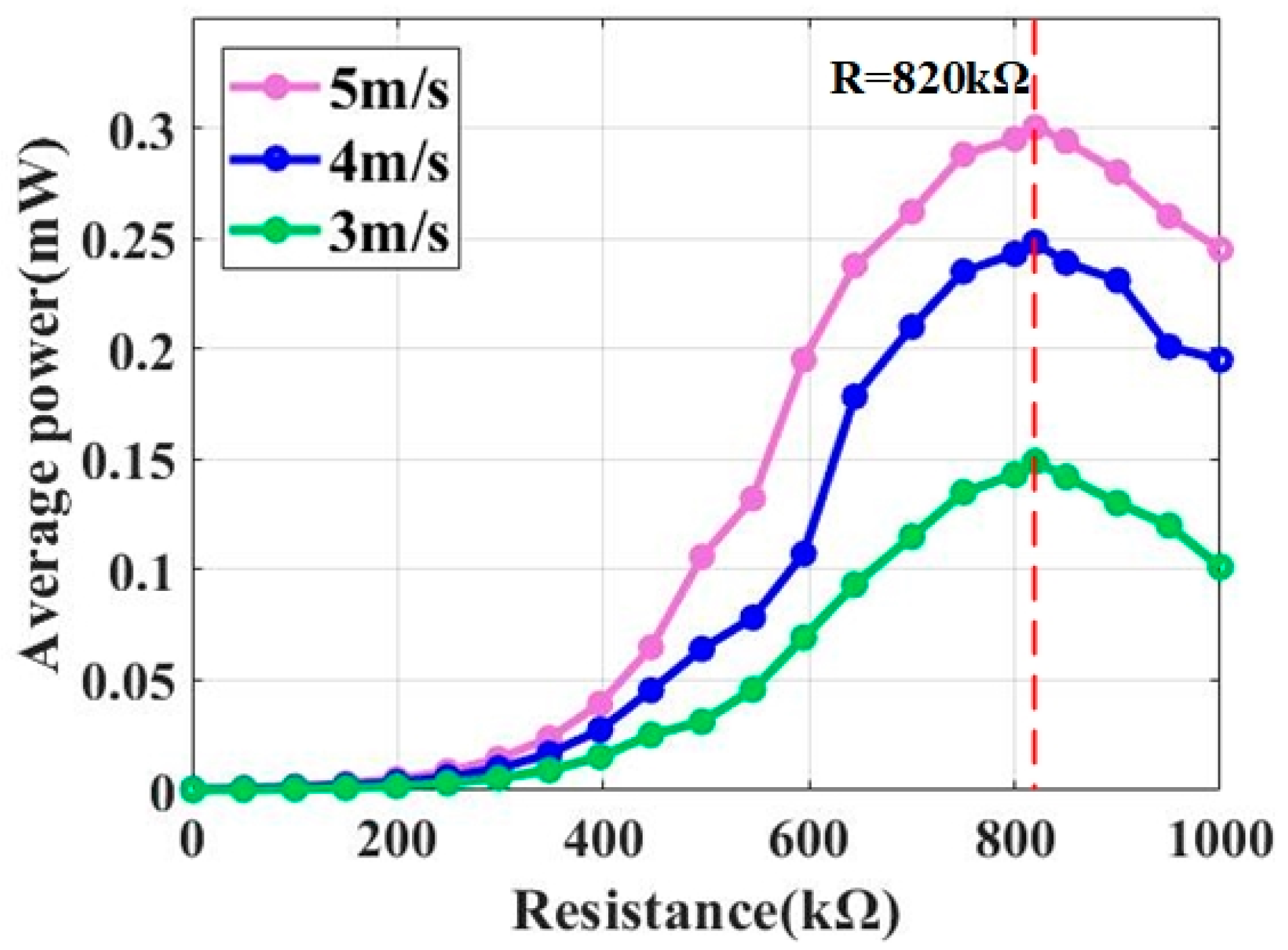
4.2. Impedance Matching
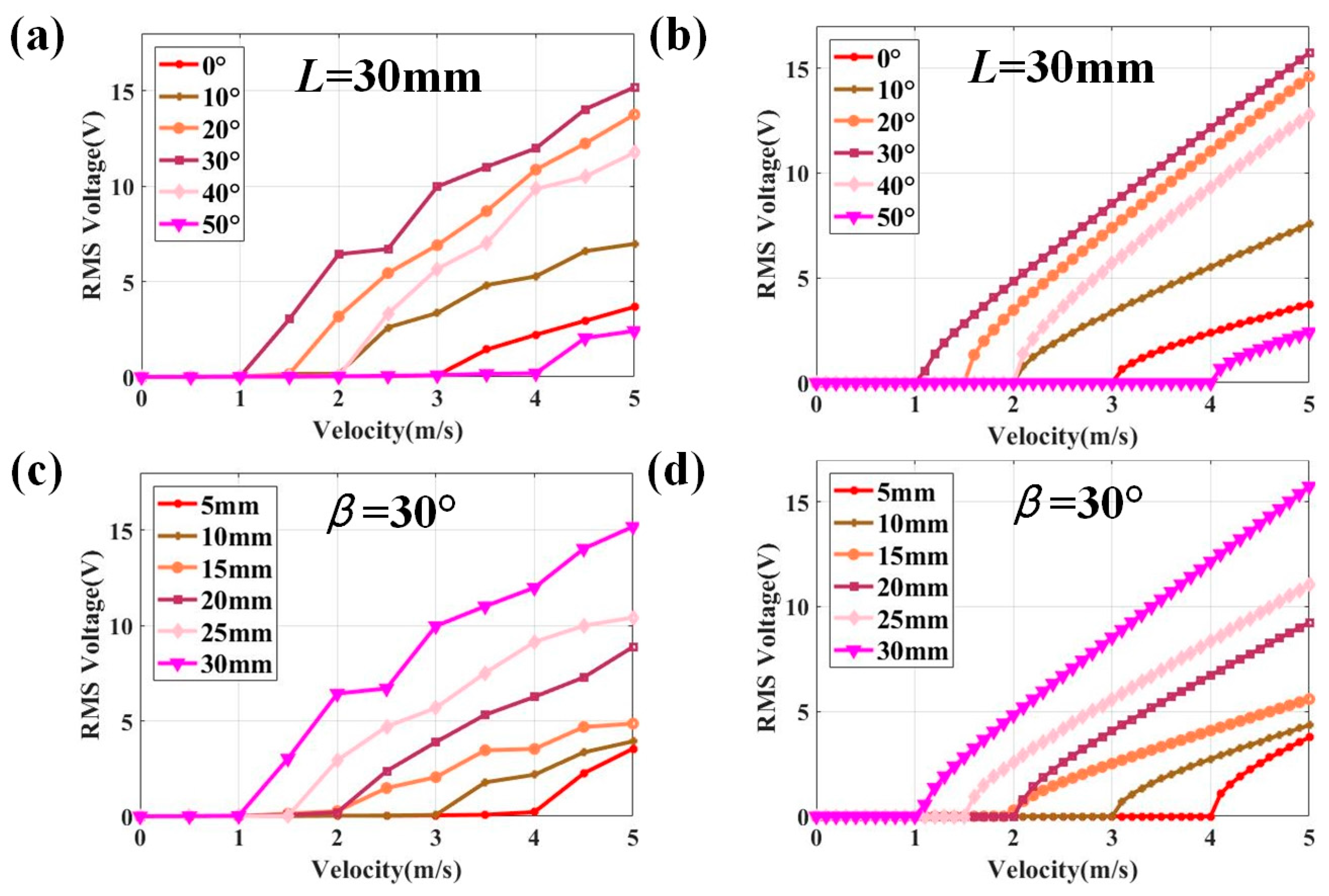
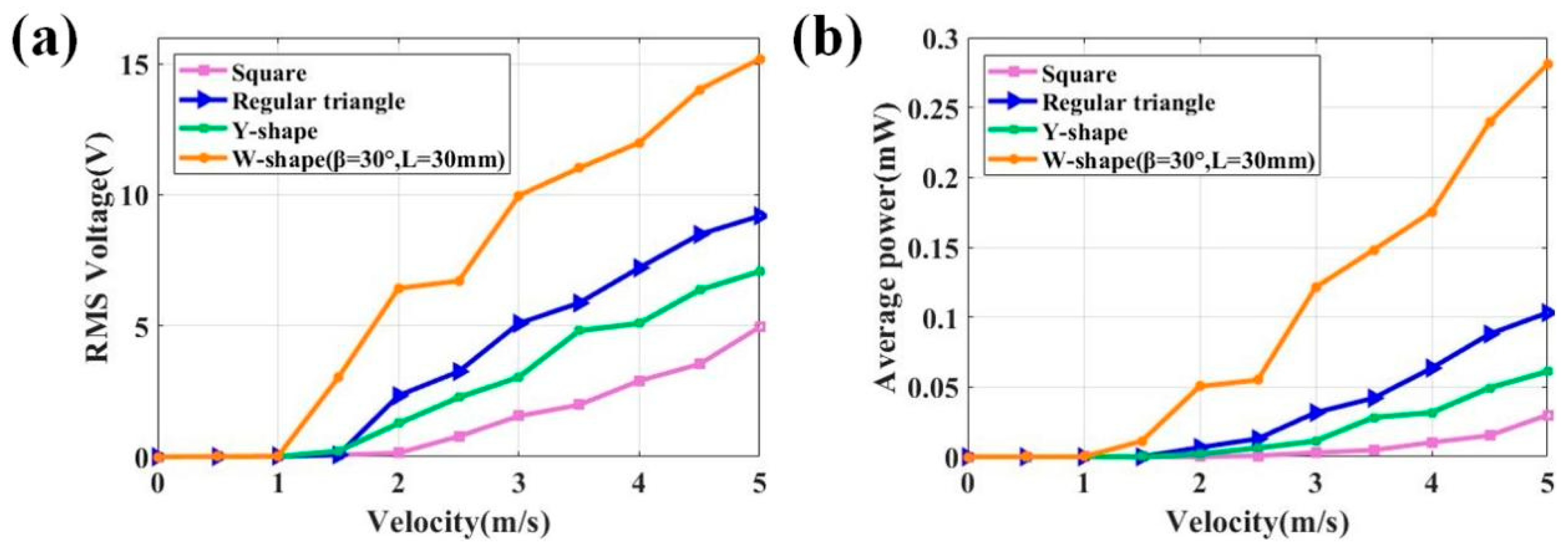
4.3. Analysis of Harvesting Performance
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fadel, E.; Gungor, V.; Nassef, L.; Akkari, N.; Malik, M.A.; Almasri, S.; Akyildiz, I.F. A survey on wireless sensor networks for smart grid. Comput. Commun. 2015, 71, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Shen, W.; Wang, X. Applications of Wireless Sensor Networks in Marine Environment Monitoring: A Survey. Sensors 2014, 14, 16932–16954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, B.; Rehmani, M.H. Applications of wireless sensor networks for urban areas: A survey. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2016, 60, 192–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Shi, D.; Xing, W.; Sun, J.; Zhu, Z. Study on the spectroscopic parameters and transition probabilities of 25 low-lying states of the AlC+ cation. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2017, 202, 265–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muralt, P. Ferroelectric thin films for micro-sensors and actuators: A review. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2000, 10, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibo, A.; Daqaq, M.F. On the optimal performance and universal design curves of galloping energy harvesters. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 104, 023901. Available online: https://pubs.aip.org/aip/apl/article-pdf/doi/10.1063/1.4861599/13545242/023901_1_online.pdf (accessed on 12 July 2022). [CrossRef]
- Fang, S.; Wang, S.; Zhou, S.; Yang, Z.; Liao, W.H. Analytical and experimental investigation of the centrifugal softening and stiffening effects in rotational energy harvesting. J. Sound Vib. 2020, 488, 115643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foong, F.M.; Thein, C.K.; Yurchenko, D. Important considerations in optimising the structural aspect of a SDOF electromagnetic vibration energy harvester. J. Sound Vib. 2020, 482, 115470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erturun, U.; Eisape, A.; West, J.E. Design and analysis of a vibration energy harvester using push-pull electrostatic conversion. Smart Mater. Struct. 2020, 29, 105018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamid, H.M.A.; Çelik Butler, Z. A novel MEMS triboelectric energy harvester and sensor with a high vibrational operating frequency and wide bandwidth fabricated using UV-LIGA technique. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2020, 313, 112175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddique, A.R.M.; Mahmud, S.; Heyst, B.V. A comprehensive review on vibration based micro power generators using electromagnetic and piezoelectric transducer mechanisms. Energy Convers. Manag. 2015, 106, 728–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zu, J. Comparison of PZN-PT, PMN-PT single crystals and PZT ceramic for vibration energy harvesting. Energy Convers. Manag. 2016, 122, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Jasim, A.; Chen, X. Energy harvesting technologies in roadway and bridge for different applications—A comprehensive review. Appl. Energy 2018, 212, 1083–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelkefi, A. Aeroelastic energy harvesting: A review. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 2016, 100, 112–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naqvi, A.; Ali, A.; Altabey, W.A.; Kouritem, S.A. Energy Harvesting from Fluid Flow Using Piezoelectric Materials: A Review. Energies 2022, 15, 7424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostami, A.B.; Armandei, M. Renewable energy harvesting by vortex-induced motions: Review and benchmarking of technologies. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 70, 193–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Meng, B.; Xia, Y.; Deng, Z.; Dai, H.; Hagedorn, P.; Peng, Z.; Wang, L. Galloping triboelectric nanogenerator for energy harvesting under low wind speed. Nano Energy 2020, 70, 104477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Yang, Z.; Zhou, S. Performance enhancement for a magnetic-coupled bi-stable flutter-based energy harvester. Smart Mater. Struct. 2020, 29, 085045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armandei, M.; Fernandes, A.C. Marine current energy extraction through buffeting. Int. J. Mar. Energy 2016, 14, 52–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, Y.Y.; Padilla, R.V.; Unger, A.; Barraza, R.; Thabet, A.M.; Izadgoshasb, I. A self-tunable wind energy harvester utilising a piezoelectric cantilever beam with bluff body under transverse galloping for field deployment. Energy Convers. Manag. 2021, 245, 114559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, L.; Gao, S.; Jin, L.; Guo, S.; Sun, Y.; Liu, F. The Design and Experiment of a Spring-Coupling Electromagnetic Galloping Energy Harvester. Micromachines 2023, 14, 968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, C.; Gu, S.; Yang, K.; Li, H.; Lai, Y.; Yurchenko, D. Enhancement of low-speed piezoelectric wind energy harvesting by bluff body shapes: Spindle-like and butterfly-like cross-sections. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2020, 103, 105898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.F.; Zou, H.X.; Wei, K.X.; Liu, J.G. Enhanced performance of piezoelectric wind energy harvester by a curved plate. Smart Mater. Struct. 2019, 28, 125022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.R.; Zou, H.X.; Zhang, W.M.; Peng, Z.K.; Meng, G. Y-type three-blade bluff body for wind energy harvesting. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2018, 112, 233903. Available online: https://pubs.aip.org/aip/apl/article-pdf/doi/10.1063/1.5029415/14514013/233903_1_online.pdf (accessed on 12 July 2022). [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Bao, B.; Chen, J.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Q. Passively adaptive wind energy harvester featuring a double-airfoil bluff body with adjustable attack angles. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2023, 185, 109814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Tse, K.T.; Kwok, K.C.S.; Song, J.; Lyu, Y. Aerodynamic modification to a circular cylinder to enhance the piezoelectric wind energy harvesting. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2016, 109, 193902. Available online: https://pubs.aip.org/aip/apl/article-pdf/doi/10.1063/1.4967497/8672168/193902_1_online.pdf (accessed on 12 July 2022). [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhou, S.; Zhang, Z.; Yurchenko, D. High-performance piezoelectric wind energy harvester with Y-shaped attachments. Energy Convers. Manag. 2019, 181, 645–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini, Y.; Emdad, H.; Farid, M. An accurate model for numerical prediction of piezoelectric energy harvesting from fluid structure interaction problems. Smart Mater. Struct. 2014, 23, 095034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akaydin, H.D.; Elvin, N.; Andreopoulos, Y. Energy Harvesting from Highly Unsteady Fluid Flows using Piezoelectric Materials. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2010, 21, 1263–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, T.; Yan, Z. Analytical solution and optimal design for galloping-based piezoelectric energy harvesters. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2016, 109, 253902. Available online: https://pubs.aip.org/aip/apl/article-pdf/doi/10.1063/1.4972556/14491139/253902_1_online.pdf (accessed on 12 July 2022). [CrossRef]
- Barrero-Gil, A.; Alonso, G.; Sanz-Andres, A. Energy harvesting from transverse galloping. J. Sound Vib. 2010, 329, 2873–2883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.R.; Zhang, W.M.; Peng, Z.K.; Meng, G. Fork-shaped bluff body for enhancing the performance of galloping-based wind energy harvester. Energy 2019, 183, 92–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Qin, W.; Zhu, P.; Shang, S. Scavenging wind energy by a Y-shaped bi-stable energy harvester with curved wings. Energy 2018, 153, 400–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Tang, L. Comparative study of tip cross-sections for efficient galloping energy harvesting. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 102, 064105. Available online: https://pubs.aip.org/aip/apl/article-pdf/doi/10.1063/1.4792737/14280753/064105_1_online.pdf (accessed on 15 July 2022). [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Abdelkefi, A.; Dai, H.; Naseer, R.; Wang, L. Design and experimental analysis of broadband energy harvesting from vortex-induced vibrations. J. Sound Vib. 2017, 408, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Yang, Y. An impact-based broadband aeroelastic energy harvester for concurrent wind and base vibration energy harvesting. Appl. Energy 2018, 212, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Zhang, L.; Wu, C.; Mao, X.; Jiang, D. Flow induced motion and energy harvesting of bluff bodies with different cross sections. Energy Convers. Manag. 2015, 91, 416–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Wu, G.; Xu, C.; Jiang, X.; Tian, F.; Liu, J.; Wang, T.; Wang, X.; Fu, G. Multidirectional galloping-based wind energy harvester based on a cylindrical cantilever beam and multi-tooth blunt body. Phys. Scr. 2023, 98, 055207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Geometric Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Bluff body height H (mm) | 70 |
| Bluff body cross-section width D (mm) | 30 |
| Bluff body cross-section length L (mm) | 30 |
| Cantilever beam length l (mm) | 180 |
| Cantilever beam height h (mm) | 10 |
| Cantilever beam width d (mm) | 1 |
| Piezoelectric sheet length lp (mm) | 40 |
| Piezoelectric sheet height hp (mm) | 10 |
| Piezoelectric sheet width dp (mm) | 0.2 |
| Material Parameter | Phosphor Bronze | PLA |
|---|---|---|
| Density ρ [kg/m3] | 8800 | 1250 |
| Young’s modulus E [GPa] | 113 | 2.3 |
| Poisson’s ratio μ | 0.33 | 0.35 |
| Parameter | Symbol | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Equivalent mass | m | 0.012 | Kg |
| Damping ratio | ζ | 0.017 | |
| Natural frequency | ωn | 49.45 | Hz |
| Equivalent damping | C | 0.0202 | N·s/m |
| Equivalent stiffness | K | 29.34 | N/m |
| Air density | ρ | 1.29 | Kg/m3 |
| Electromechanical coupling coefficient | θ | 0.15 | mN/V |
| Piezoelectric capacitance | Cp | 0.73 | nF |
| β (deg) | 0 | 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a1 | 3.06 | 4.55 | 6.10 | 8.55 | 4.56 | 2.30 |
| a3 | 7500 | 4100 | 1730 | 2350 | 1440 | 6840 |
| L (mm) | 5 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 25 | 30 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a1 | 2.30 | 3.05 | 4.65 | 4.50 | 6.06 | 8.55 |
| a3 | 2800 | 5550 | 7800 | 2700 | 3000 | 2350 |
| L = 30 mm | Wind speed (m/s) | 0.0 | 0.5 | 1.0 | 1.5 | 2.0 | 2.5 | 3.0 | 3.5 | 4.0 | 4.5 | 5.0 | |
| β = 0° | Average value (V) | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 1.4 | 2.2 | 2.9 | 3.7 | |
| Standard deviation (V) | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.1 | ||
| Theoretical value (V) | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.6 | 2.4 | 3.6 | 3.8 | ||
| Percentage difference | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | \ | 8.98% | 7.58% | 19.44% | 2.31% | ||
| β = 10° | Average value (V) | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 2.6 | 3.4 | 4.8 | 5.3 | 6.6 | 7.0 | |
| Standard deviation (V) | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.3 | ||
| Theoretical value (V) | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 2.1 | 3.4 | 4.5 | 5.5 | 7.4 | 7.6 | ||
| Percentage difference | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | \ | \ | 19.28% | 0.00% | 6.14% | 3.26% | 10.38% | 7.13% | ||
| β = 20° | Average value (V) | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.2 | 3.2 | 5.4 | 6.9 | 8.7 | 10.9 | 12.2 | 13.8 | |
| Standard deviation (V) | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.6 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.7 | 0.6 | ||
| Theoretical value (V) | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 3.5 | 5.5 | 7.4 | 9.2 | 11.0 | 14.3 | 14.6 | ||
| Percentage difference | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | \ | 8.51% | 1.14% | 6.63% | 5.87% | 1.58% | 14.15% | 5.86% | ||
| β = 30° | Average value (V) | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 3.0 | 6.4 | 6.7 | 10.0 | 11.0 | 12.0 | 14.0 | 15.2 | |
| Standard deviation (V) | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.3 | 0.8 | 0.7 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 0.6 | 0.3 | 0.7 | ||
| Theoretical value (V) | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 2.8 | 4.8 | 6.7 | 8.5 | 10.3 | 12.1 | 13.9 | 15.7 | ||
| Percentage difference | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 6.99% | 33.23% | 0.00% | 16.67% | 6.52% | 0.81% | 0.55% | 3.49% | ||
| β = 40° | Average value (V) | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 3.3 | 5.7 | 7.0 | 9.9 | 10.5 | 11.8 | |
| Standard deviation (V) | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 0.7 | 0.6 | 0.7 | ||
| Theoretical value (V) | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 3.6 | 5.7 | 7.5 | 9.3 | 12.4 | 12.8 | ||
| Percentage difference | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 8.11% | 0.00% | 7.61% | 5.74% | 15.32% | 7.74% | ||
| β = 50° | Average value (V) | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 2.0 | 2.4 | |
| Standard deviation (V) | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.3 | 0.2 | ||
| Theoretical value (V) | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 2.3 | 2.4 | ||
| Percentage difference | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | \ | \ | \ | \ | 11.56% | 0.00% | ||
| β = 30° | Wind speed (m/s) | 0.0 | 0.5 | 1.0 | 1.5 | 2.0 | 2.5 | 3.0 | 3.5 | 4.0 | 4.5 | 5.0 | |
| L = 5 mm | Average value (V) | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 2.3 | 3.5 | |
| Standard deviation (V) | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.4 | 0.6 | ||
| Theoretical value (V) | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 2.5 | 3.8 | ||
| Percentage difference | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | \ | \ | \ | 8.35% | 7.19% | ||
| L = 10 mm | Average value (V) | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 1.8 | 2.2 | 3.4 | 3.9 | |
| Standard deviation (V) | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.4 | ||
| Theoretical value (V) | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.8 | 2.7 | 3.6 | 4.3 | ||
| Percentage difference | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | \ | 0.00% | 16.88% | 5.58% | 10.71% | ||
| L = 15 mm | Average value (V) | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 1.5 | 2.1 | 3.5 | 3.5 | 4.7 | 4.9 | |
| Standard deviation (V) | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.6 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.3 | ||
| Theoretical value (V) | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.3 | 1.6 | 2.5 | 3.3 | 4.1 | 4.8 | 5.6 | ||
| Percentage difference | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | \ | 0.00% | 6.25% | 16.00% | 6.06% | 14.63% | 2.08% | 12.28% | ||
| L = 20 mm | Average value (V) | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.2 | 2.4 | 3.9 | 5.3 | 6.3 | 7.3 | 8.9 | |
| Standard deviation (V) | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 0.5 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 0.6 | ||
| Theoretical value (V) | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 2.6 | 4.1 | 5.4 | 6.7 | 8.0 | 9.2 | ||
| Percentage difference | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | \ | 5.45% | 4.10% | 1.70% | 5.70% | 8.01% | 3.58% | ||
| L = 25 mm | Average value (V) | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 2.9 | 4.7 | 5.7 | 7.5 | 9.1 | 10.0 | 10.4 | |
| Standard deviation (V) | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.3 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.5 | 0.8 | 0.4 | 0.3 | ||
| Theoretical value (V) | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 2.6 | 4.1 | 5.6 | 7.0 | 8.3 | 9.7 | 11.0 | ||
| Percentage difference | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 11.54% | 13.41% | 2.95% | 7.76% | 9.58% | 3.35% | 5.52% | ||
| L = 30 mm | Average value (V) | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 3.0 | 6.4 | 6.7 | 10.0 | 11.0 | 12.0 | 14.0 | 15.2 | |
| Standard deviation (V) | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.3 | 0.8 | 0.7 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 0.6 | 0.3 | 0.7 | ||
| Theoretical value (V) | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 2.8 | 4.8 | 6.7 | 8.5 | 10.3 | 12.1 | 13.9 | 15.7 | ||
| Percentage difference | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 6.99% | 33.23% | 0.00% | 16.67% | 6.52% | 0.81% | 0.55% | 3.49% | ||
| Bluff Body | Resistance (kΩ) | Wind Speed (m/s) | Power Density (μW/cm3) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | Author | Shape | Windward Width (cm) | Height (cm) | |||
| 1 | Zhou [22] | Curved-plate | 3.5 | 10.0 | 900 | 5.5 | 0.81 |
| 2 | Hu [26] | Square (with leading-edge fins) | 2.4 | 24.0 | 5000 | 5.0 | 0.24 |
| 3 | Yang [34] | Square | 4.0 | 15.0 | 105 | 5.0 | 17 |
| 4 | Zhang [35] | Square (with stiffener) | 4.0 | 15.0 | 100 | 5.0 | 20 |
| 5 | Zhao [36] | D-shape | 3.0 | 23.5 | 700 | 4.7 | 13 |
| 6 | Ding [37] | Cylinder (with rods) | 4.8 | 24.0 | 5000 | 5.5 | 0.09 |
| 7 | Lu [38] | Hexagram | 3.0 | 5.0 | 2200 | 8.0 | 9.8 |
| 8 | Our work | Square | 3.0 | 7.0 | 820 | 5.0 | 0.3 |
| Regular triangle | 3.0 | 7.0 | 820 | 5.0 | 3.4 | ||
| Y-shape | 3.0 | 7.0 | 820 | 5.0 | 13.9 | ||
| W-shape | 3.0 | 7.0 | 820 | 5.0 | 31 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, J.; Li, Z.; Zhang, H. Low-Wind-Speed Galloping Wind Energy Harvester Based on a W-Shaped Bluff Body. Energies 2024, 17, 958. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17040958
Zheng J, Li Z, Zhang H. Low-Wind-Speed Galloping Wind Energy Harvester Based on a W-Shaped Bluff Body. Energies. 2024; 17(4):958. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17040958
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Jianfeng, Zichang Li, and Han Zhang. 2024. "Low-Wind-Speed Galloping Wind Energy Harvester Based on a W-Shaped Bluff Body" Energies 17, no. 4: 958. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17040958
APA StyleZheng, J., Li, Z., & Zhang, H. (2024). Low-Wind-Speed Galloping Wind Energy Harvester Based on a W-Shaped Bluff Body. Energies, 17(4), 958. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17040958







