A Three-Phase Multilevel Inverter Synthesized with 31 Levels and Optimal Gating Angles Based on the GA and GWO to Supply a Three-Phase Induction Motor
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Multilevel Inverter Topologies
3. Artificial Intelligence Algorithms
4. Results
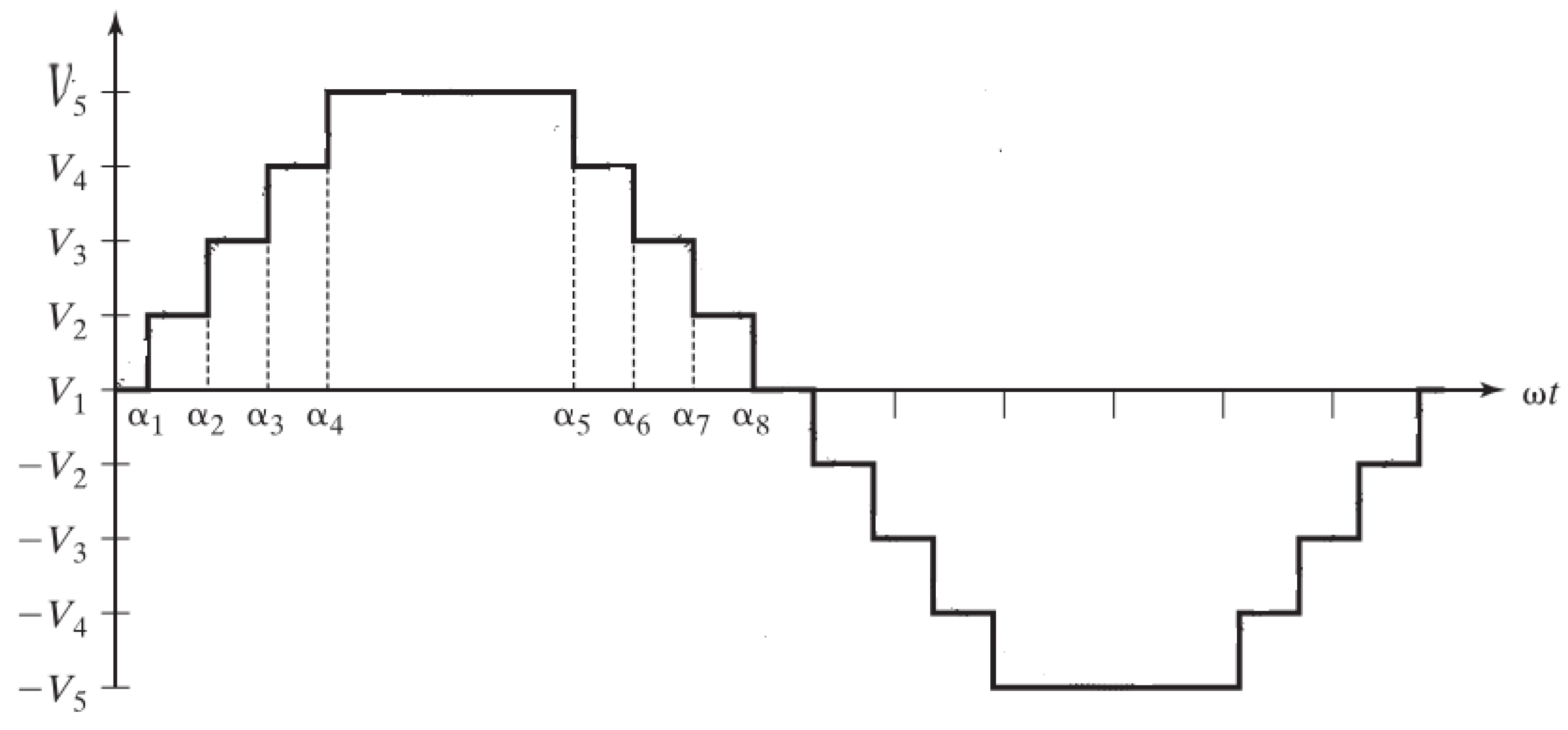
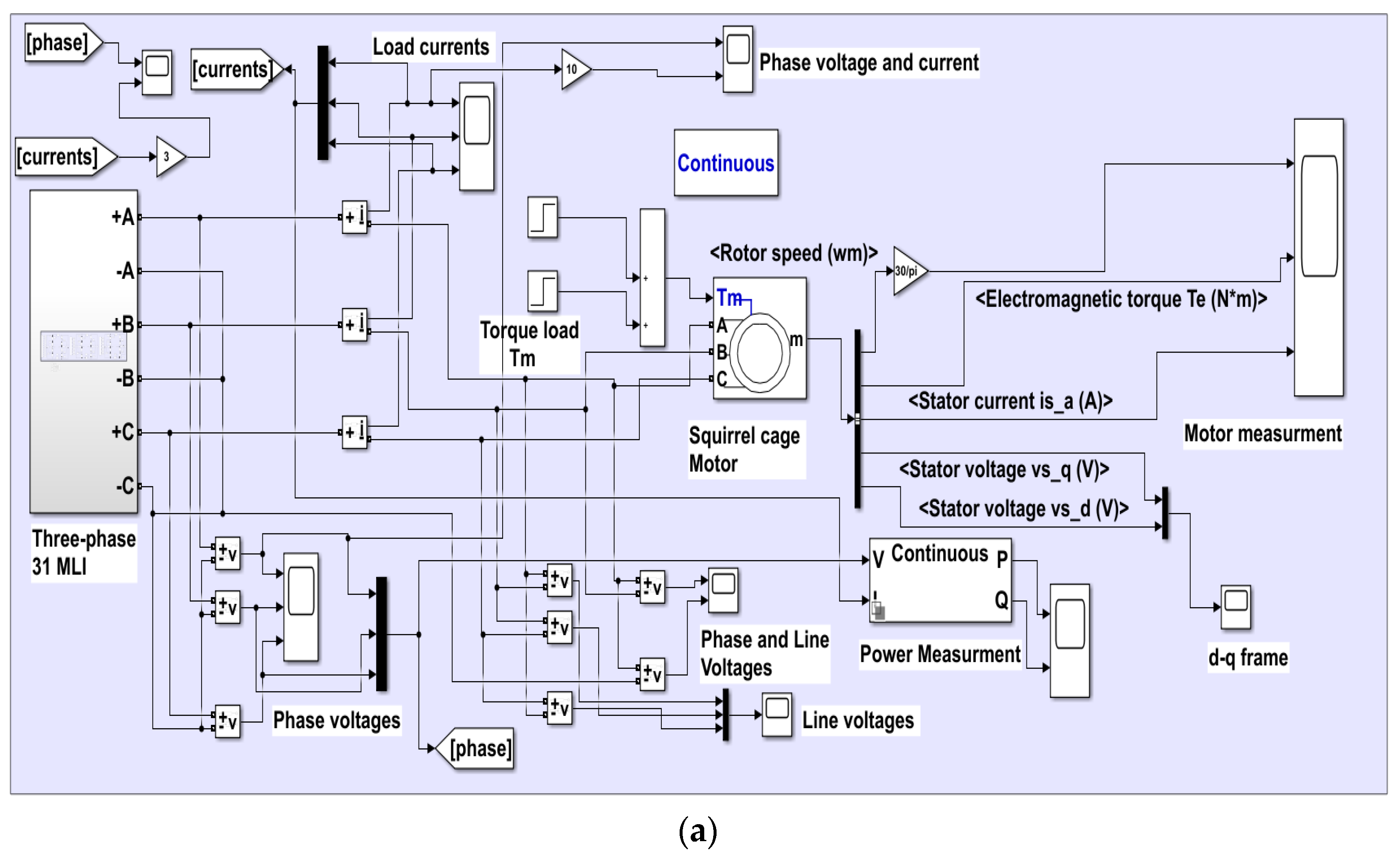
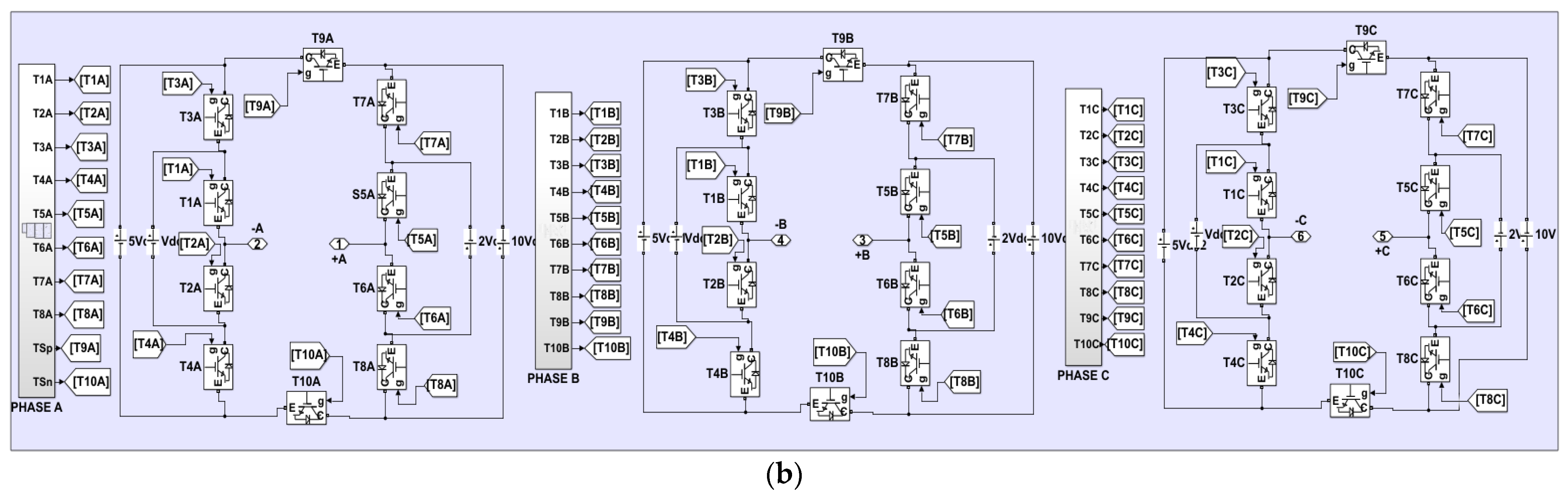
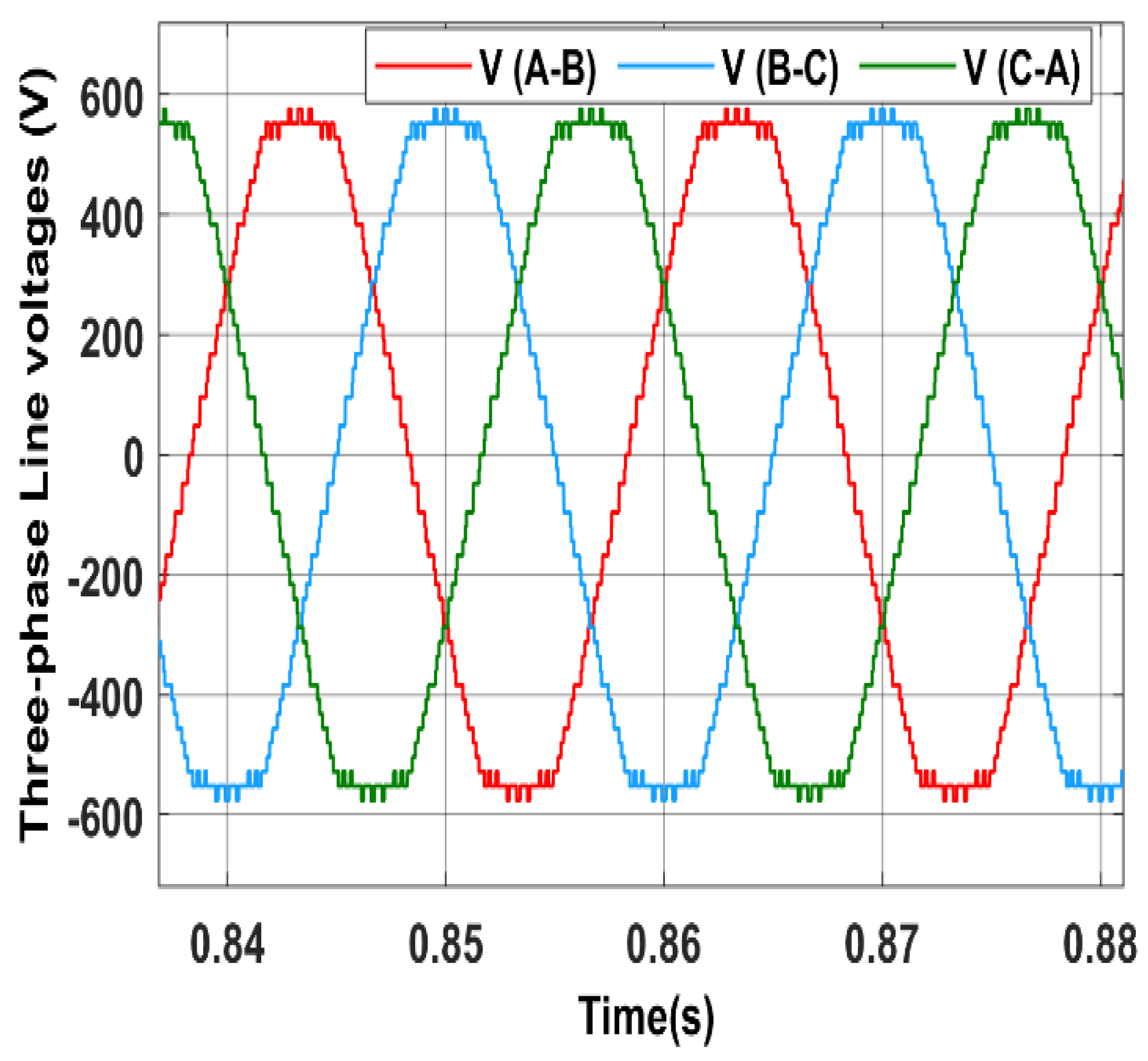
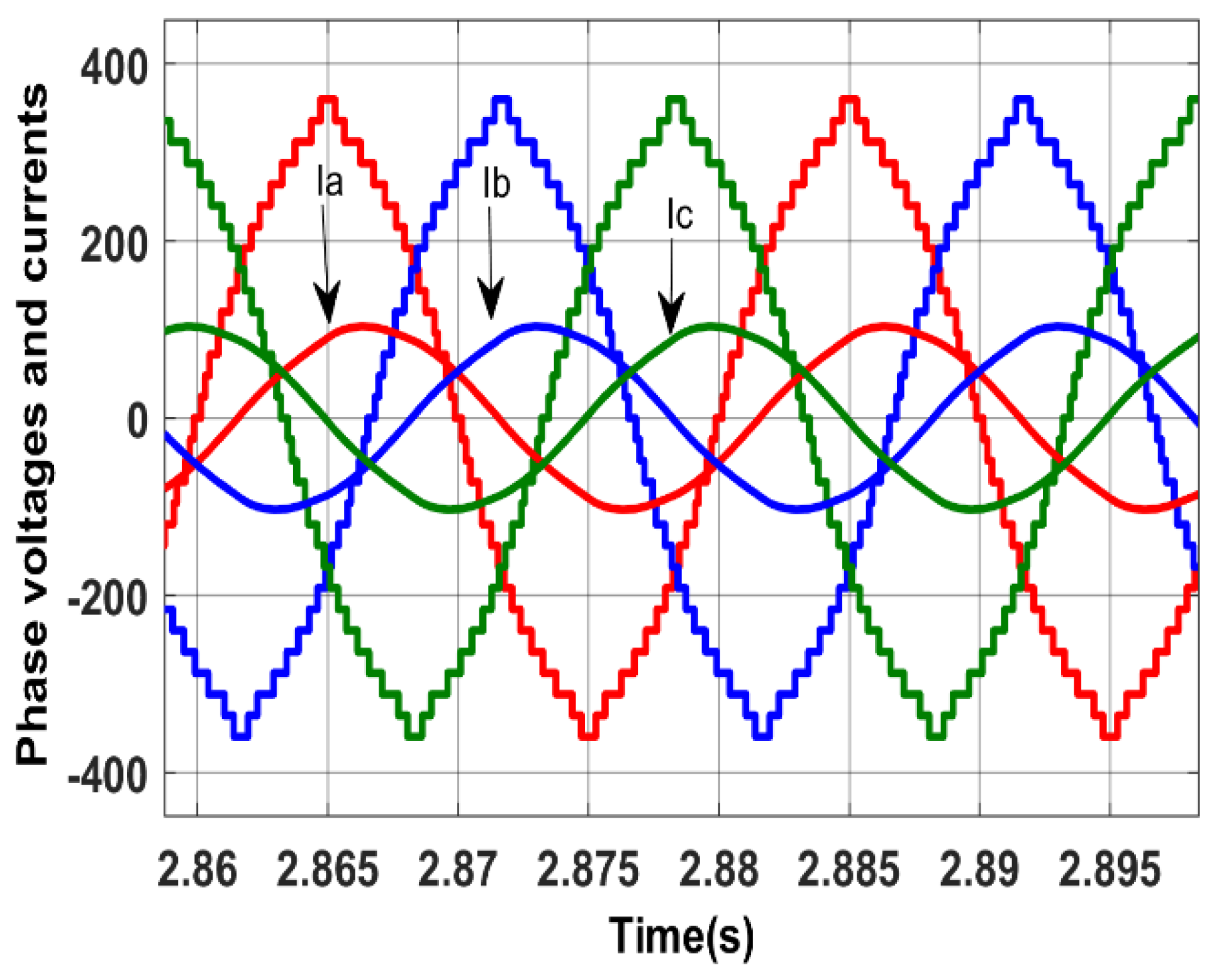
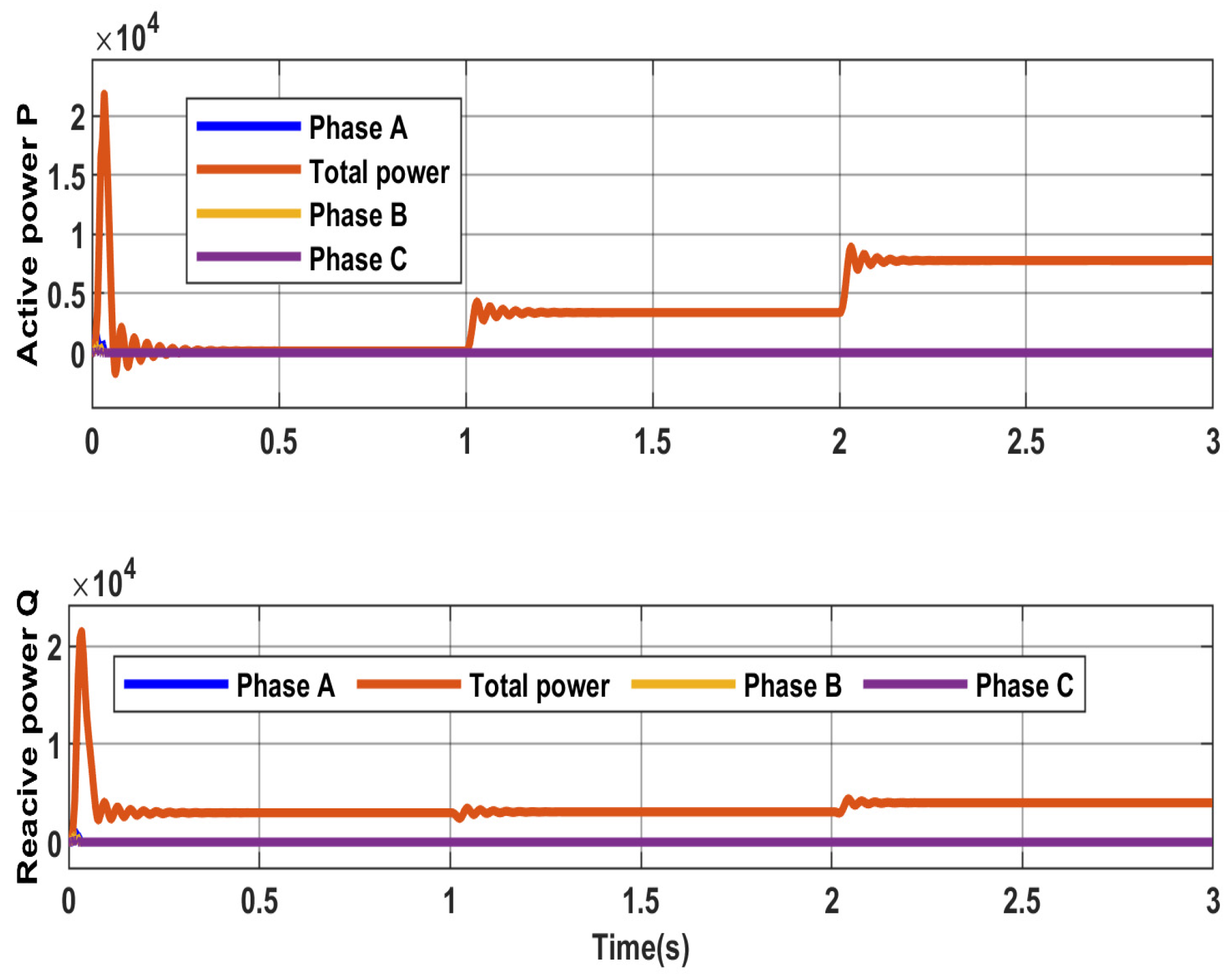
4.1. Simulation Results
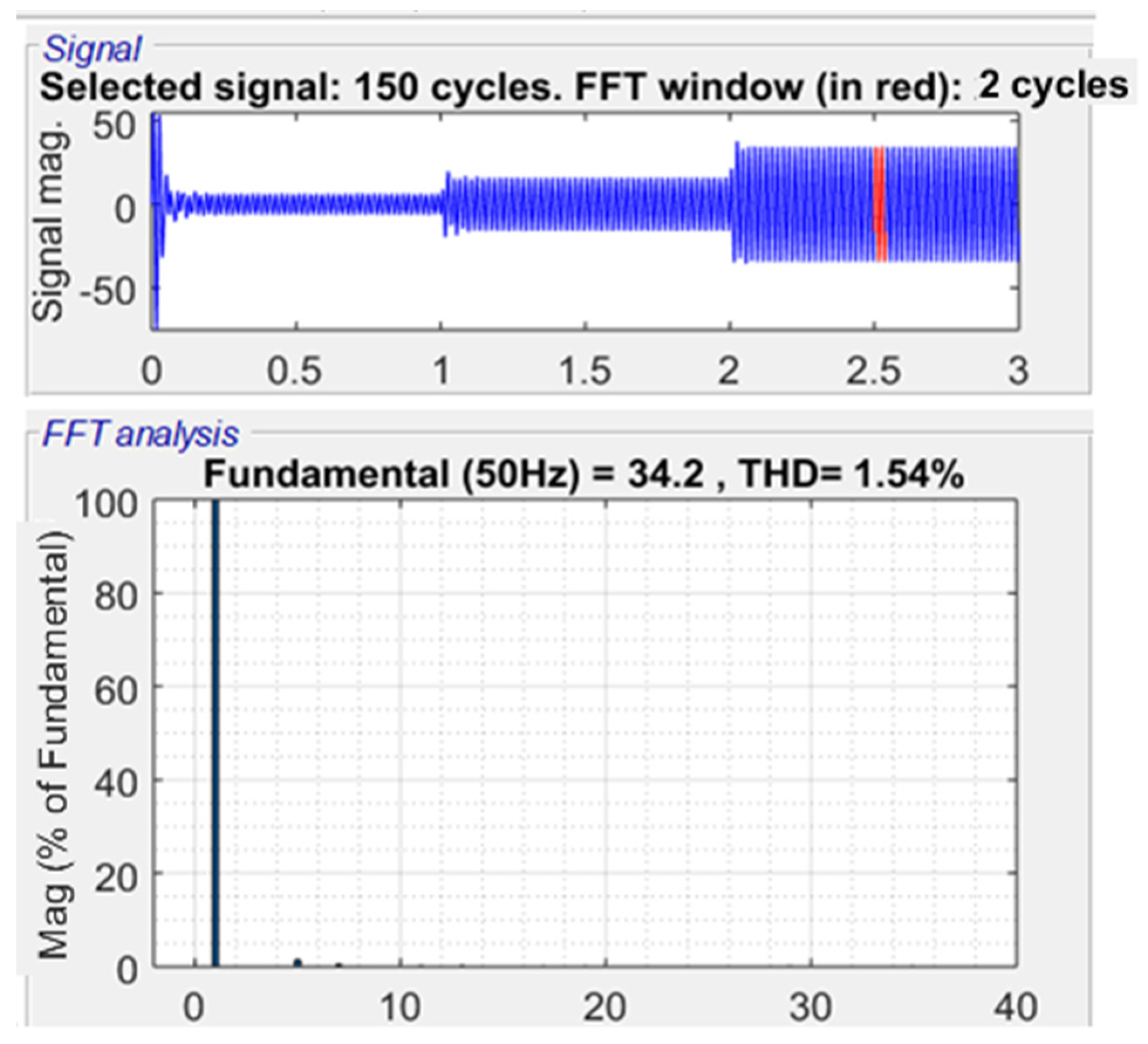
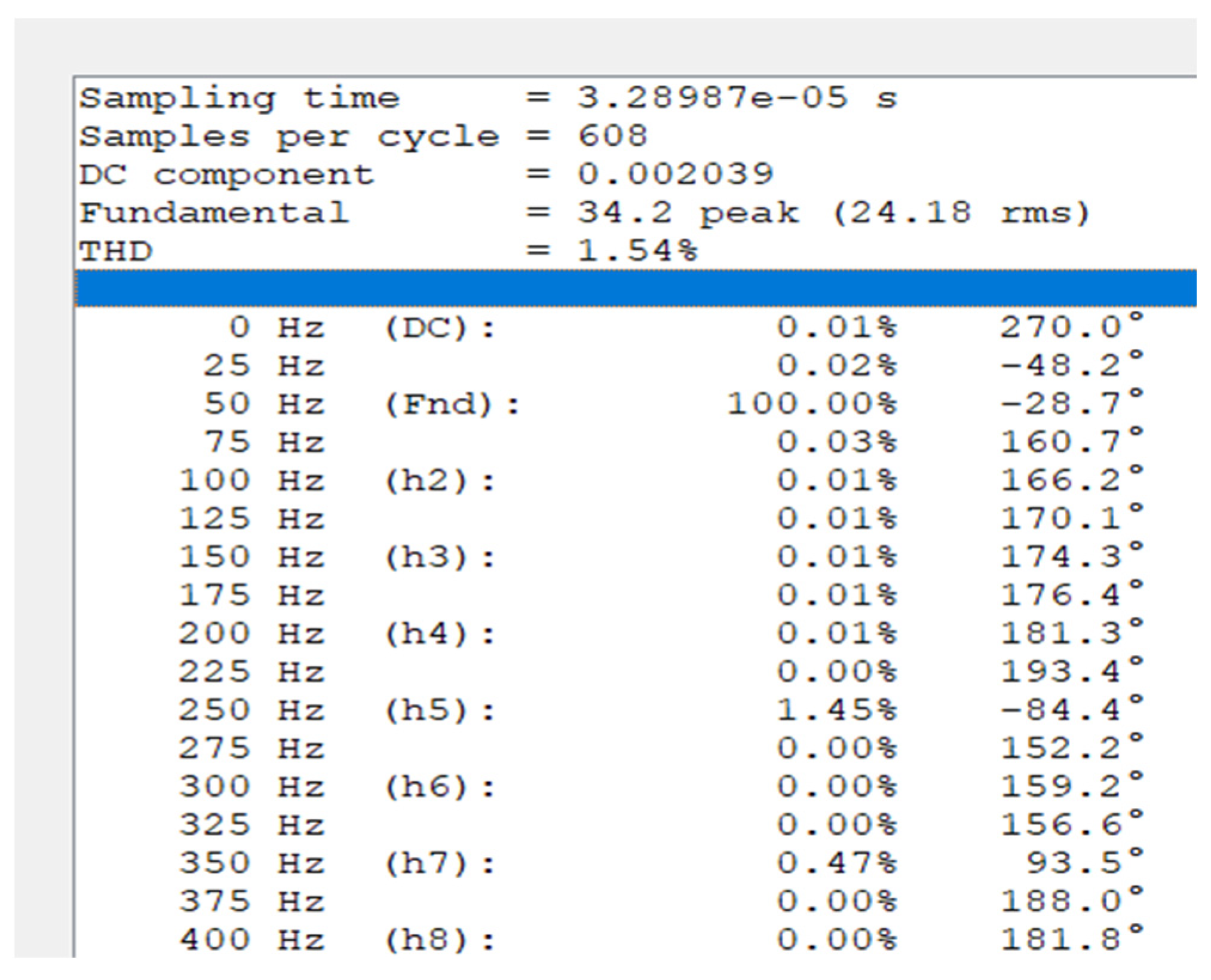
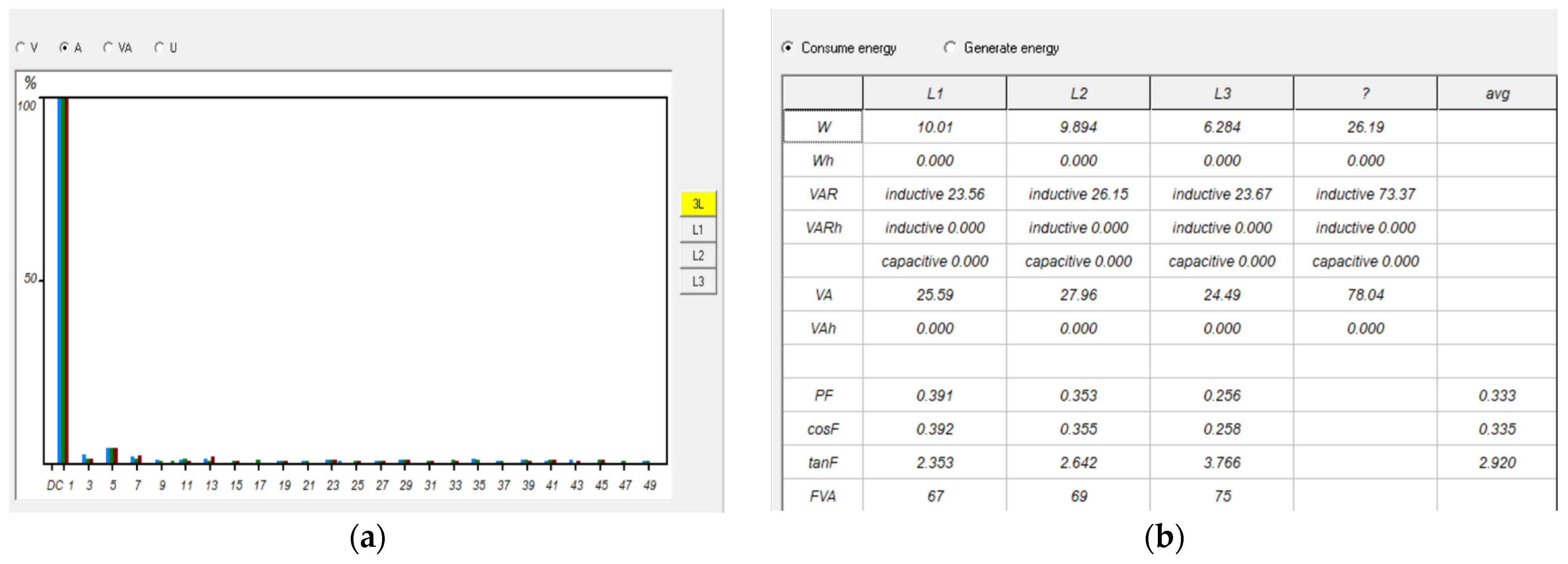
4.2. Practical Results
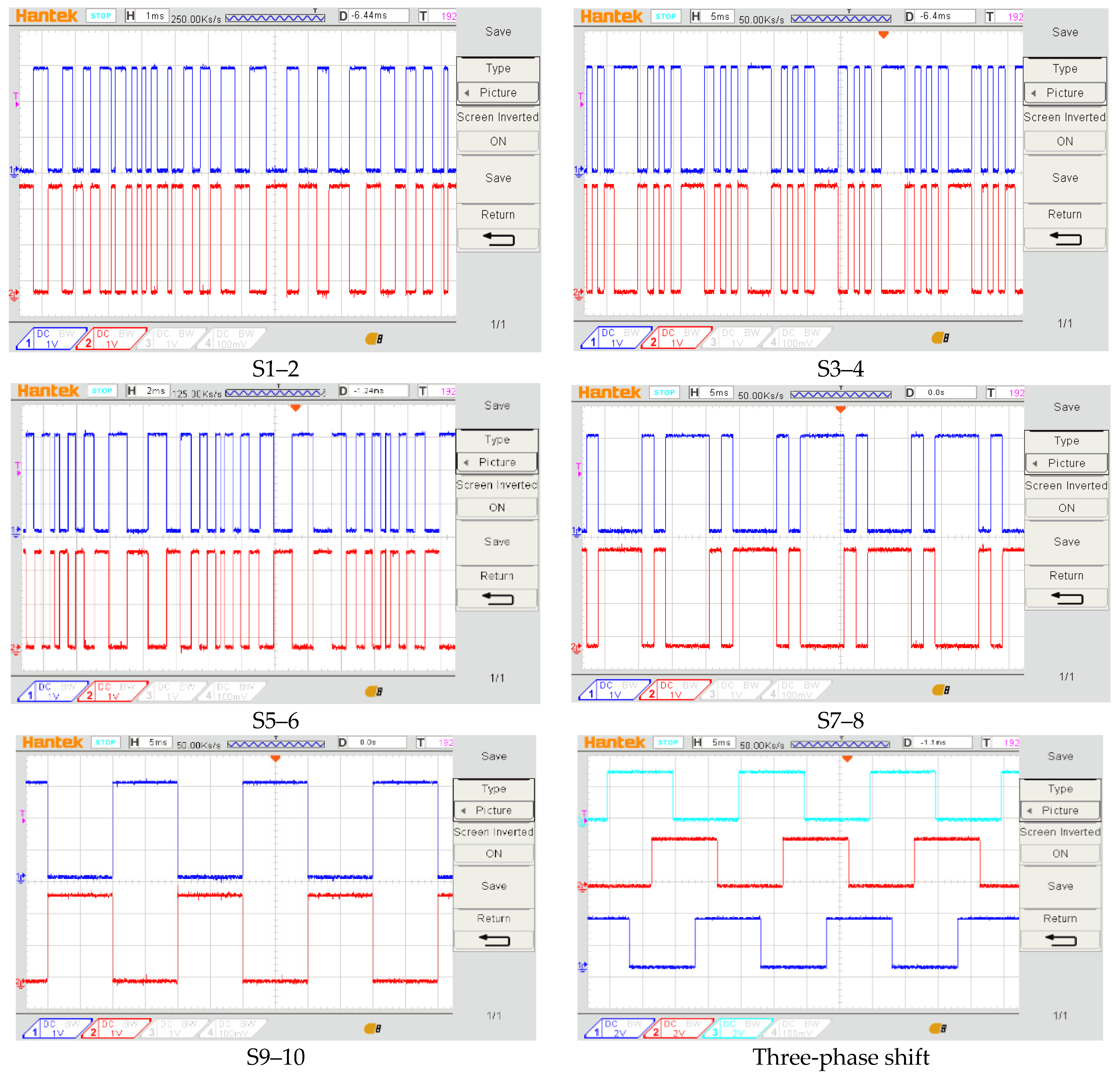
4.2.1. Generating Gating Pulses
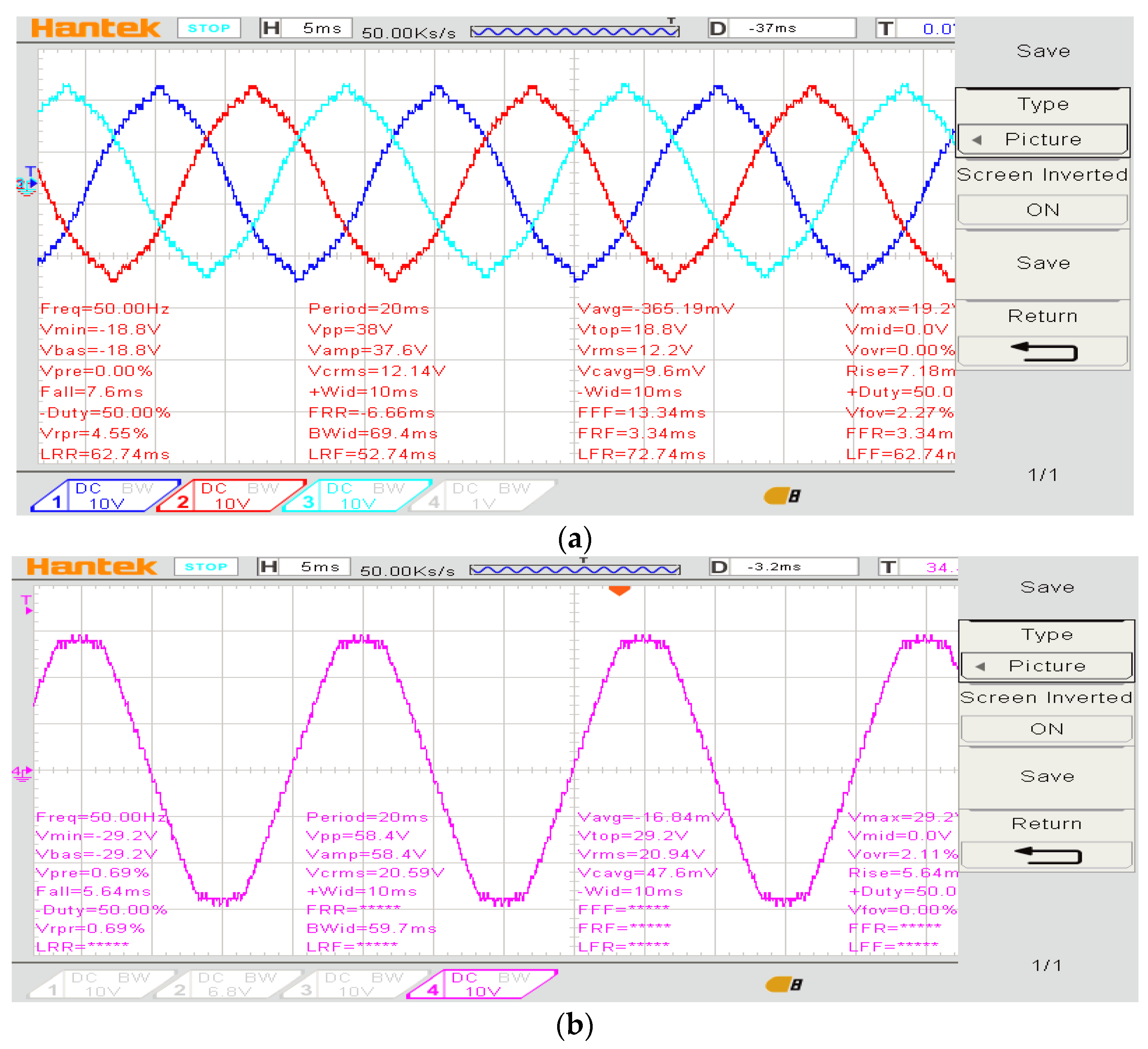
4.2.2. The Proposed 31-Level MLI Operating at No Load
4.2.3. Load Test
5. Conclusions
6. Future Suggestions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Maheswari, K.; Bharanikumar, R.; Arjun, V.; Amrish, R.; Bhuvanesh, M. A comprehensive review on cascaded H-bridge multilevel inverter for medium voltage high power applications. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 45, 2666–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, L.; Wei, Q.; Li, Y. A Practical Current Source Inverter-Based High-Power Medium-Voltage PV System. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2023, 38, 2617–2625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, A.; Sekhar, O.C.; Kumar, M.S. A Novel Three Phase Multilevel Inverter with Single DC Link for Induction Motor Drive Applications. Int. J. Electr. Comput. Eng. (IJECE) 2018, 8, 763–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengamalai, U.; Anbazhagan, G.; Thentral, T.M.T.; Vishnuram, P.; Khurshaid, T.; Kamel, S. Three Phase Induction Motor Drive: A Systematic Review on Dynamic Modeling, Parameter Estimation, and Control Schemes. Energies 2022, 15, 8260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durgalakshmi, K.; Anbarasu, P.; Karpagam, V.; Venkatesh, A.; Kannapiran, B.; Sharma, V. Utilization of Reduced Switch Components with Different Topologies in Multi-Level Inverter for Renewable Energy Applications-A Detailed Review. In Proceedings of the 2022 5th International Conference on Contemporary Computing and Informatics (IC3I), Uttar Pradesh, India, 14–16 December 2022; pp. 913–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bughneda, A.; Salem, M.; Richelli, A.; Ishak, D.; Alatai, S. Review of Multilevel Inverters for PV Energy System Applications. Energies 2021, 14, 1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kala, P.; Arora, S. A comprehensive study of classical and hybrid multilevel inverter topologies for renewable energy applications. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 76, 905–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poorfakhraei, A.; Narimani, M.; Emadi, A. A Review of Multilevel Inverter Topologies in Electric Vehicles: Current Status and Future Trends. IEEE Open J. Power Electron. 2021, 2, 155–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, G.K.; Rivera, M.; Loganathan, V.; Ravikumar, D.; Mohan, B. Trends and Challenges in Multi-Level Inverter with Reduced Switches. Electronics 2021, 10, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vemuganti, H.P.; Sreenivasarao, D.; Ganjikunta, S.K.; Suryawanshi, H.M.; Abu-Rub, H. A Survey on Reduced Switch Count Multilevel Inverters. IEEE Open J. Ind. Electron. Soc. 2021, 2, 80–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddique, M.D.; Iqbal, A.; Memon, M.A.; Mekhilef, S. A New Configurable Topology for Multilevel Inverter With Reduced Switching Components. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 188726–188741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antar, R.K.; Hussein, T.A.; Abdullah, A.M. Design and implementation of reduced number of switches for new multilevel inverter topology without zero-level state. Int. J. Power Electron. Drive Syst. (IJPEDS) 2022, 13, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, T.A.; Ishak, D. Three-phase MLI with Reduced Number of Switches and Hybrid Optimized Switching. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Energy, Power, Environment, Control, and Computing (ICEPECC), Gujrat, Pakistan, 8–9 March 2023; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardar, M.U.; Vaimann, T.; Kütt, L.; Kallaste, A.; Asad, B.; Akbar, S.; Kudelina, K. Inverter-Fed Motor Drive System: A Systematic Analysis of Condition Monitoring and Practical Diagnostic Techniques. Energies 2023, 16, 5628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoch, S.; Chauhan, S.S.; Kumar, V. A review on genetic algorithm: Past, present, and future. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2021, 80, 8091–8126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambora, A.; Gupta, K.; Chopra, K. Genetic Algorithm-A Literature Review. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Machine Learning, Big Data, Cloud and Parallel Computing (COMITCon), Faridabad, India, 14–16 February 2019; pp. 380–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadimi-Shahraki, M.H.; Taghian, S.; Mirjalili, S. An improved grey wolf optimizer for solving engineering problems. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 166, 113917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, J.C.; Singh, S. A better exploration strategy in Grey Wolf Optimizer. J. Ambient Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 2021, 12, 1099–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaei, E.; Laali, S.; Alilu, S. Cascaded Multilevel Inverter with Series Connection of Novel H-Bridge Basic Units. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 61, 6664–6671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhanamjayulu, C.; Arunkumar, G.; Pandian, B.J.; Kumar, C.V.R.; Kumar, M.P.; Jerin, A.R.A.; Venugopal, P. Real-Time Implementation of a 31-Level Asymmetrical Cascaded Multilevel Inverter for Dynamic Loads. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 51254–51266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaei, E.; Laali, S.; Bayat, Z. A Single-Phase Cascaded Multilevel Inverter Based on a New Basic Unit with Reduced Number of Power Switches. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 62, 922–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alishah, R.S.; Hosseini, S.H.; Babaei, E.; Sabahi, M. A New General Multilevel Converter Topology Based on Cascaded Connection of Submultilevel Units with Reduced Switching Components, DC Sources, and Blocked Voltage by Switches. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 7157–7164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alishah, R.S.; Hosseini, S.H.; Babaei, E.; Sabahi, M. Optimization Assessment of a New Extended Multilevel Converter Topology. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 4530–4538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, M.H. Power Electronics, Devices, Circuits and Applications; Pearson Education Limited: London, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Almomani, O. A Feature Selection Model for Network Intrusion Detection System Based on PSO, GWO, FFA and GA Algorithms. Symmetry 2020, 12, 1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
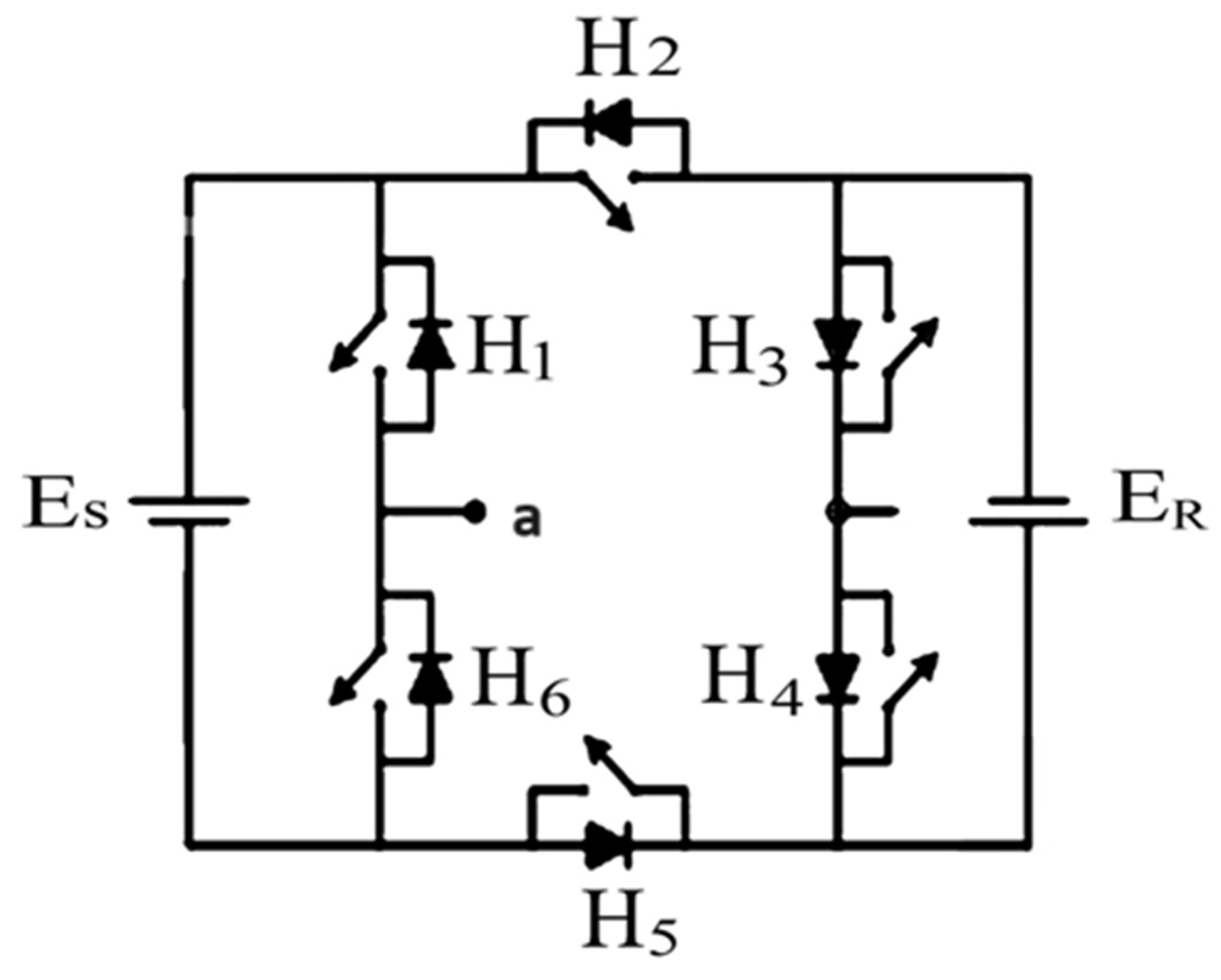

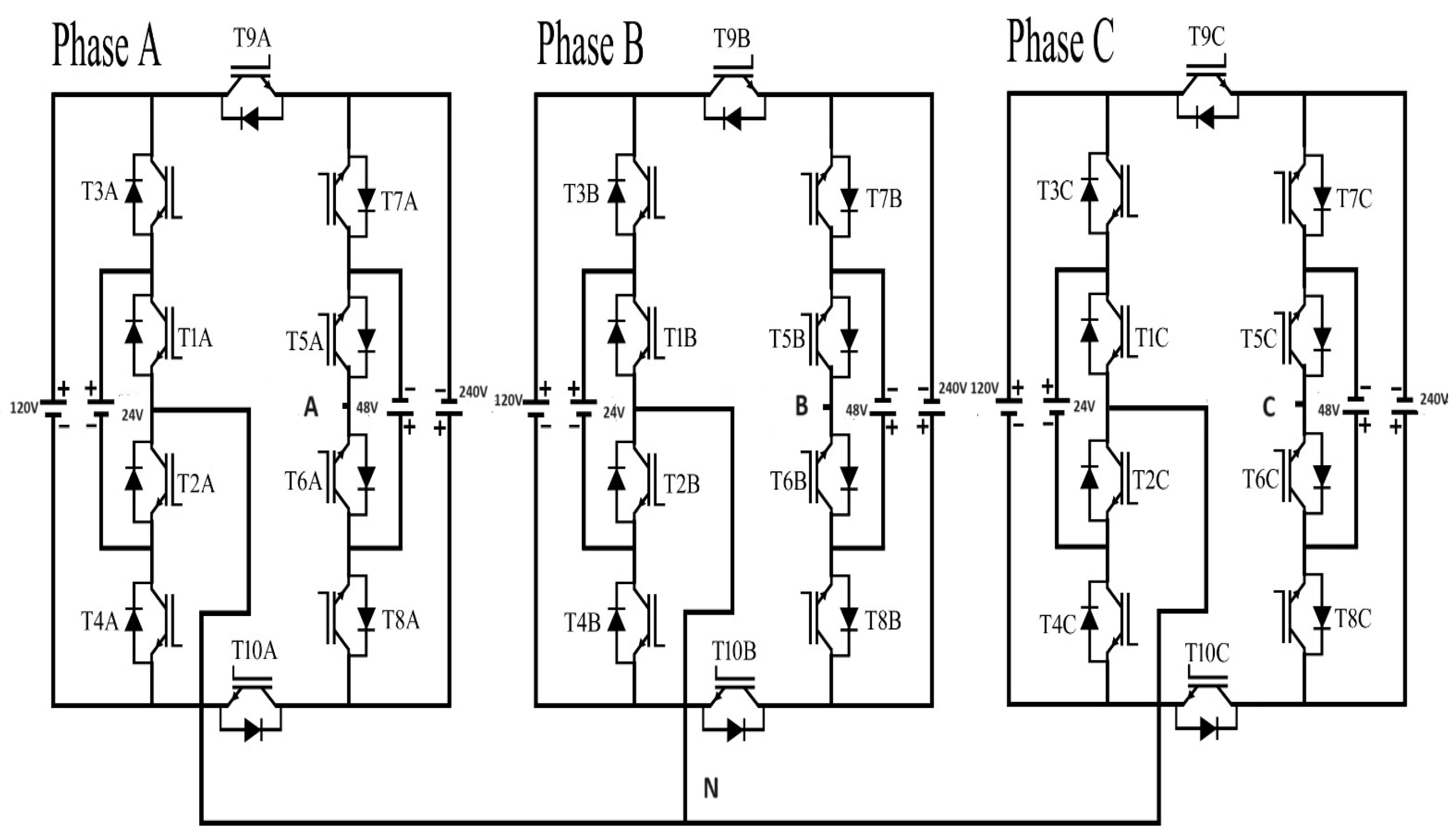










| Topology | No. of Levels | No. of Switches | No. of DC Sources | No. of Phases | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [19] | 7 | 6 | 2 | 1 phase | Simple structure | Isolated DC sources |
| [21] | 9 | 11 | 4 | 1 phase | Cells share power equally | Switches withstand different voltage ratings |
| [22] | 17 | 12 | 4 | 1 phase | Symmetric and asymmetric topology | Complex control |
| [23] | 17 | 10 | 4 | 1 phase | Modular structure | Lower number of switches increases power rating |
| Proposed/ phase | 31 | 10 | 4 | 3 phase | Simple and modular structure suitable for cascaded topologies; requires switches with unidirectional operation | Switches exposed to various voltage ratings |
| Angle | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GA | 3.3 | 6.1 | 13.1 | 16.7 | 23.1 | 27.2 | 33.5 | 38.7 | 45.5 | 52.2 | 58.5 | 66.2 | 74.7 | 83.8 | 85 |
| GWO | 1.2 | 11.8 | 23.3 | 32.2 | 42.2 | 50.6 | 58.9 | 67.4 | 71.2 | 79.6 | 80.4 | 85.1 | 85.9 | 86 | 86 |
| Optimum | 2.4 | 5.21 | 8.42 | 14.2 | 16.3 | 22.6 | 27.4 | 31.6 | 37.1 | 42.9 | 50.5 | 58.4 | 67.4 | 78.6 | 85 |
| T1 T2 * | T3 T4 * | T5 T6 * | T7 T8 * | T9 T10 * | Level | Duration | Shift |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 2 | ||
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 3 | ||
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 4 | ||
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 5 | ||
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 6 | ||
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 7 | ||
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 8 | ||
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 9 | ||
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 10 | ||
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 11 | ||
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 12 | ||
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 13 | ||
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 14 | ||
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 15 | ||
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 14 | ||
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 13 | ||
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 12 | ||
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 11 | ||
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 10 | ||
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 9 | ||
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 8 | ||
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 7 | ||
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 6 | ||
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 5 | ||
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 4 | ||
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 3 | ||
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 2 | ||
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| = 6778 | = 14,472 | = 23,389 | = 39,472 | = 45,445 | = 62,889 | = 76,278 | = 87,917 |
| = 103,056 | = 119,222 | = 140,361 | = 162,278 | = 187,389 | = 218,445 | = 236,111 | |
| T1 | T3 | T5 | T7 | T9 | Duration | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T2 * | T4 * | T6 * | T8 * | T10 * | PHASE A | ||
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 → 6778 | |
| 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 6779 → 14,472 | |
| 3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 14,473→ 23,389 | |
| 4 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 23,390 → 39,472 | |
| 5 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 39,473 → 45,445 | |
| 6 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 45,446 → 62,889 | |
| 7 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 62,890 → 76,278 | |
| 8 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 76,279 → 87,917 | |
| 9 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 87,918 → 103,056 | |
| 10 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 103,057 → 119,222 | |
| 11 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 119,223 → 140,361 | |
| 12 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 140,362 → 162,278 | |
| 13 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 162,279 → 187,389 | |
| 14 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 187,390 → 218,445 | |
| 15 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 218,446 → 236,111 | |
| 16 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 236,112 → 263,890 | |
| 17 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 263,891 → 281,557 | |
| 18 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 281,558 → 312,613 | |
| 19 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 312,614 →337,725 | |
| 20 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 337,726 → 359,643 | |
| 21 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 359,644 → 380,783 | |
| 22 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 380,784 → 396,950 | |
| 23 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 396,951 → 412,089 | |
| 24 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 412,090 → 423,729 | |
| 25 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 423,730 → 437,120 | |
| 26 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 437,121 → 454,564 | |
| 27 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 454,565 → 460,538 | |
| 28 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 460,539 → 476,622 | |
| 29 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 476,623 → 485,540 | |
| 30 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 485,541 → 493,235 | |
| 31 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 493,236 → 500,000 |
| Phase Voltage | Line Voltage | Current | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMS (V) | THD % | Phase Shift Unbalance% | RMS (V) | THD % | Phase Shift Unbalance% | RMS (mA) | THD % | |
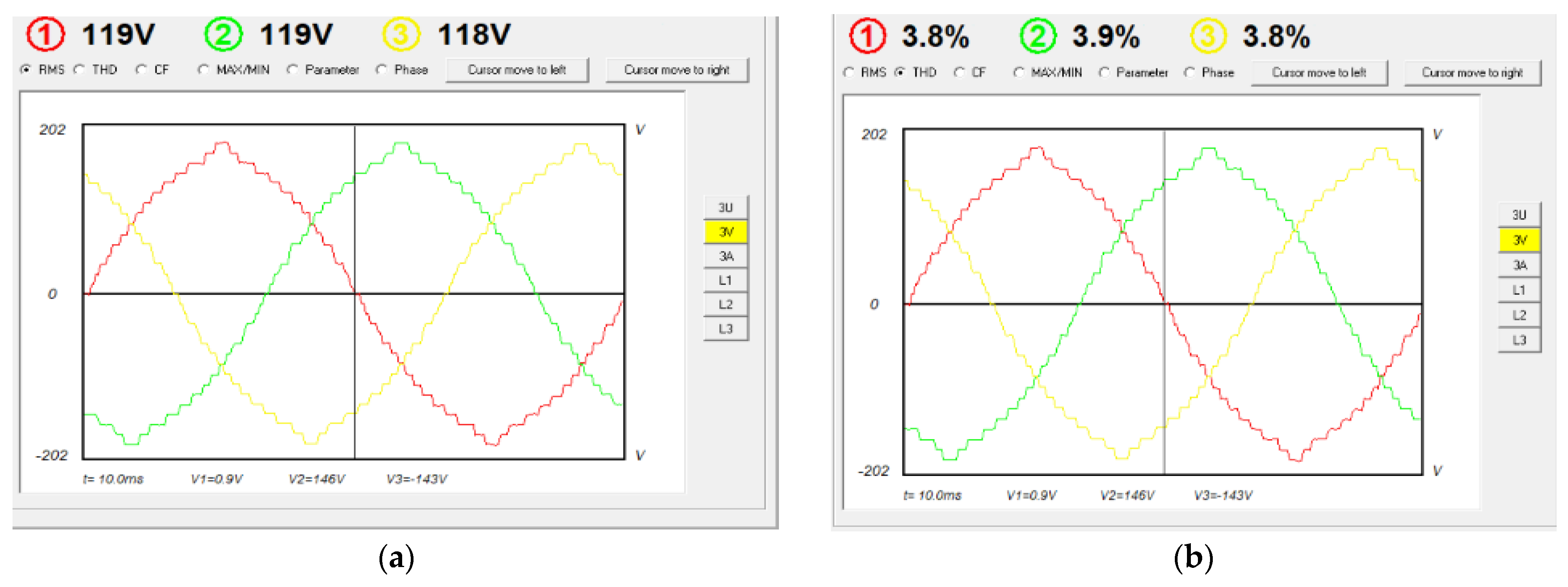
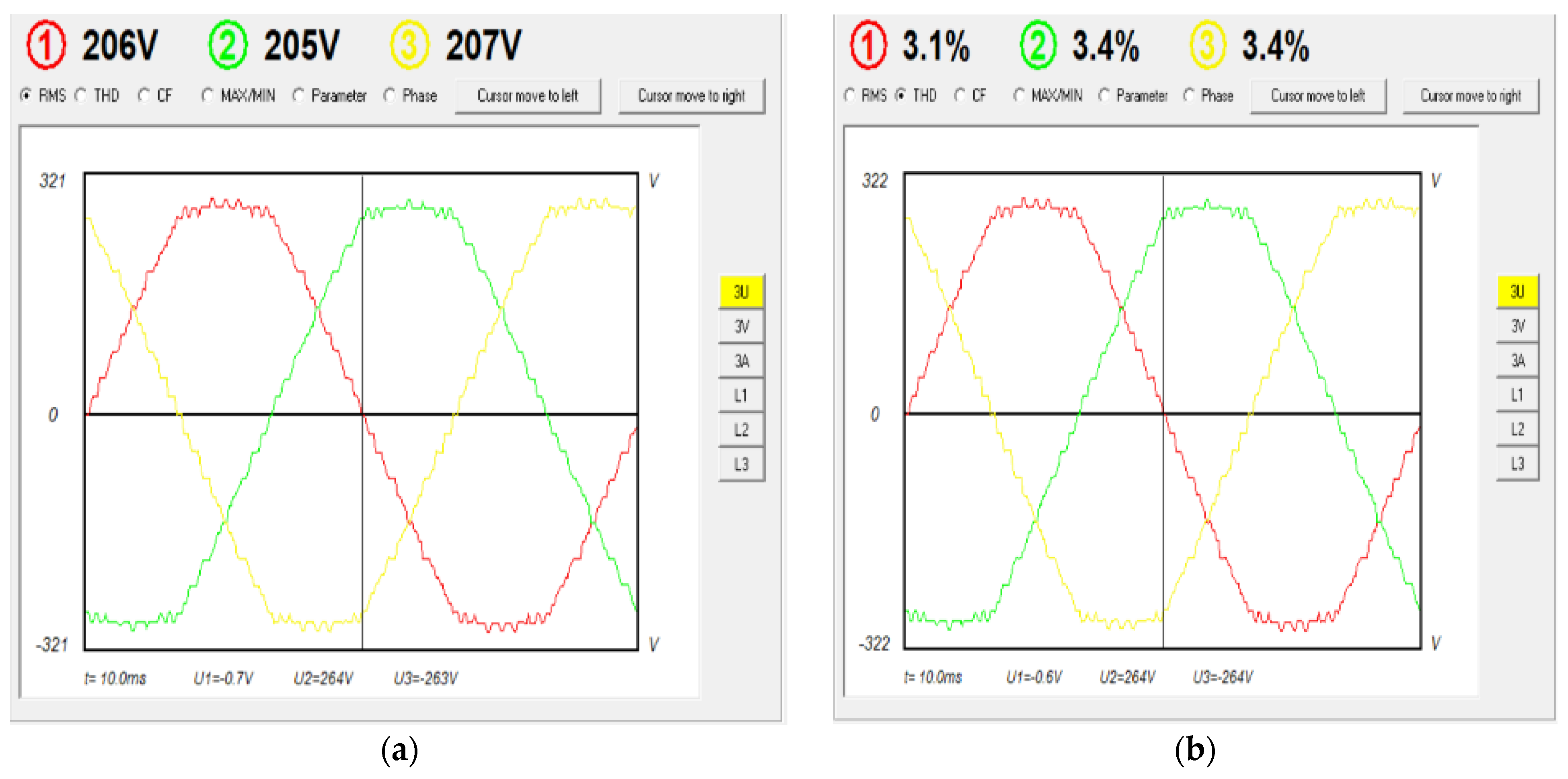
| No load | 119 | 3.8 | 0.4 | 207 | 3.1 | 0.4 | — | — |
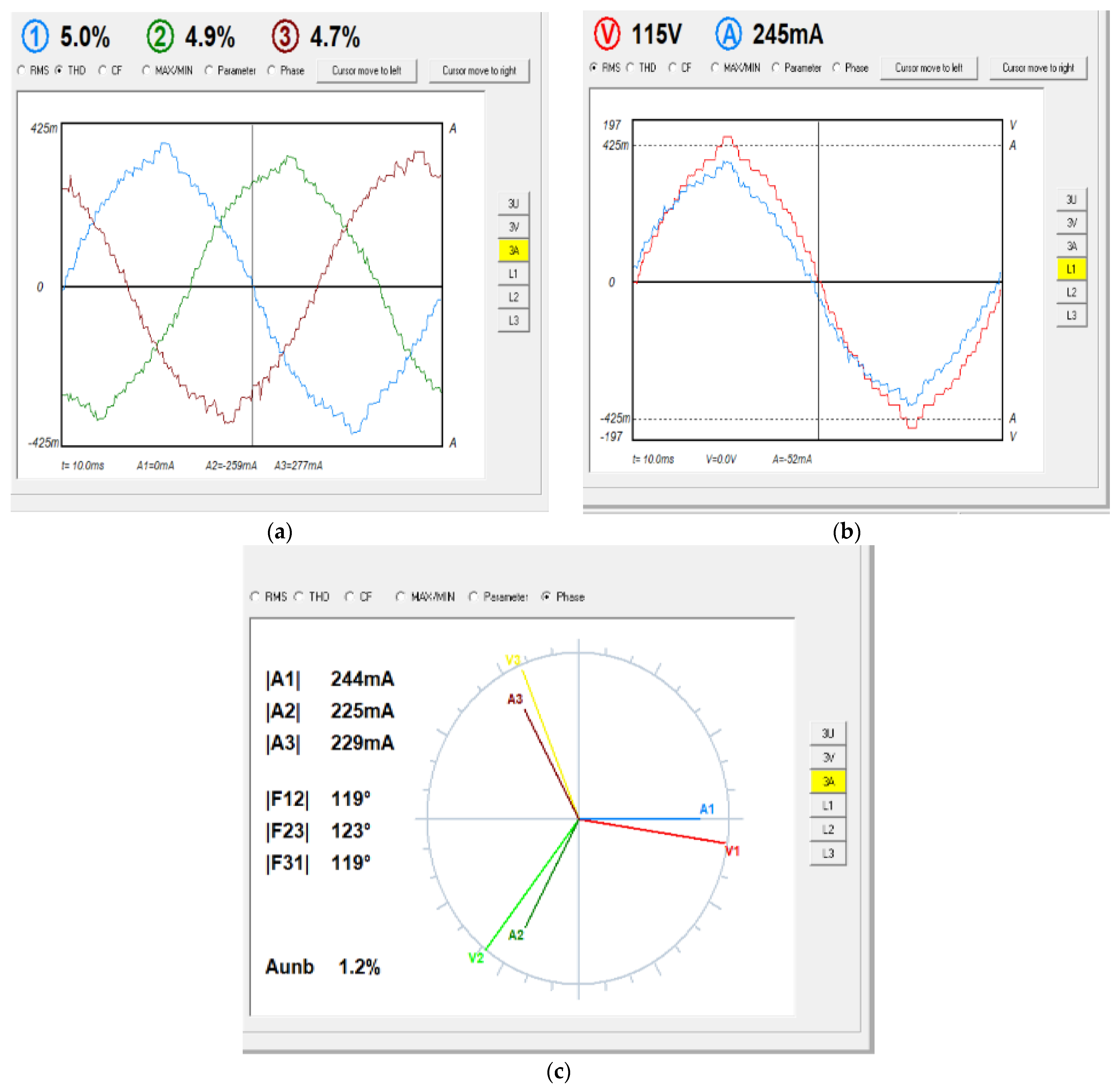
| Resistance | 119 | 4.6 | 0.4 | 207 | 4.0 | 0.4 | 245 | 4.7 |
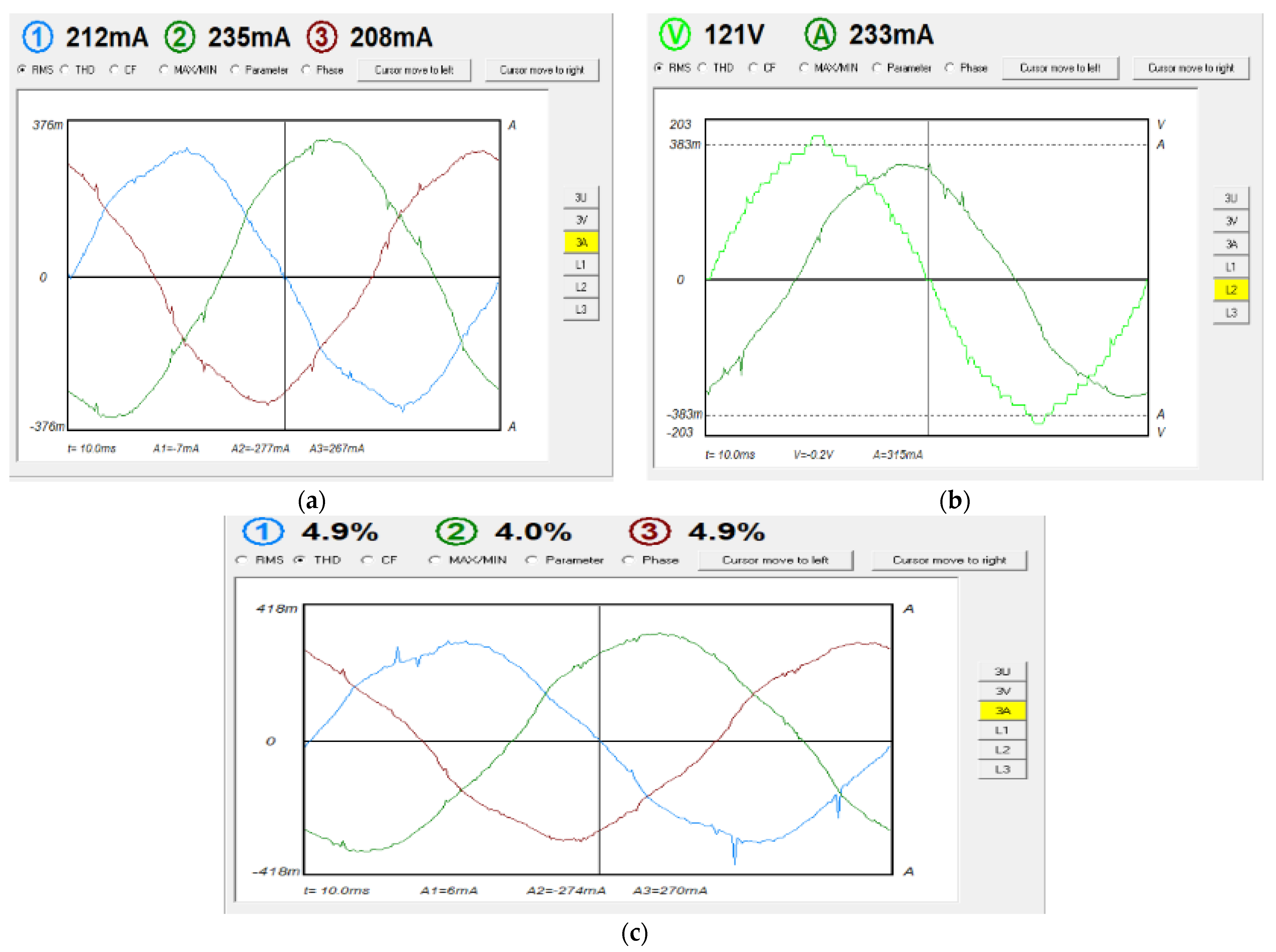
| Motor/No load | 121 | 4.6 | 0.4 | 210 | 4.0 | 0.4 | 235 | 4.0 |
| Motor/Load | 121 | 4.6 | 0.4 | 210 | 4.0 | 0.4 | 831 | 3.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hussein, T.A.; Ishak, D.; Tarnini, M. A Three-Phase Multilevel Inverter Synthesized with 31 Levels and Optimal Gating Angles Based on the GA and GWO to Supply a Three-Phase Induction Motor. Energies 2024, 17, 1267. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17051267
Hussein TA, Ishak D, Tarnini M. A Three-Phase Multilevel Inverter Synthesized with 31 Levels and Optimal Gating Angles Based on the GA and GWO to Supply a Three-Phase Induction Motor. Energies. 2024; 17(5):1267. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17051267
Chicago/Turabian StyleHussein, Taha Ahmad, Dahaman Ishak, and Mohamad Tarnini. 2024. "A Three-Phase Multilevel Inverter Synthesized with 31 Levels and Optimal Gating Angles Based on the GA and GWO to Supply a Three-Phase Induction Motor" Energies 17, no. 5: 1267. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17051267
APA StyleHussein, T. A., Ishak, D., & Tarnini, M. (2024). A Three-Phase Multilevel Inverter Synthesized with 31 Levels and Optimal Gating Angles Based on the GA and GWO to Supply a Three-Phase Induction Motor. Energies, 17(5), 1267. https://doi.org/10.3390/en17051267






